Personalized Nutrition in Pediatric Chronic Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
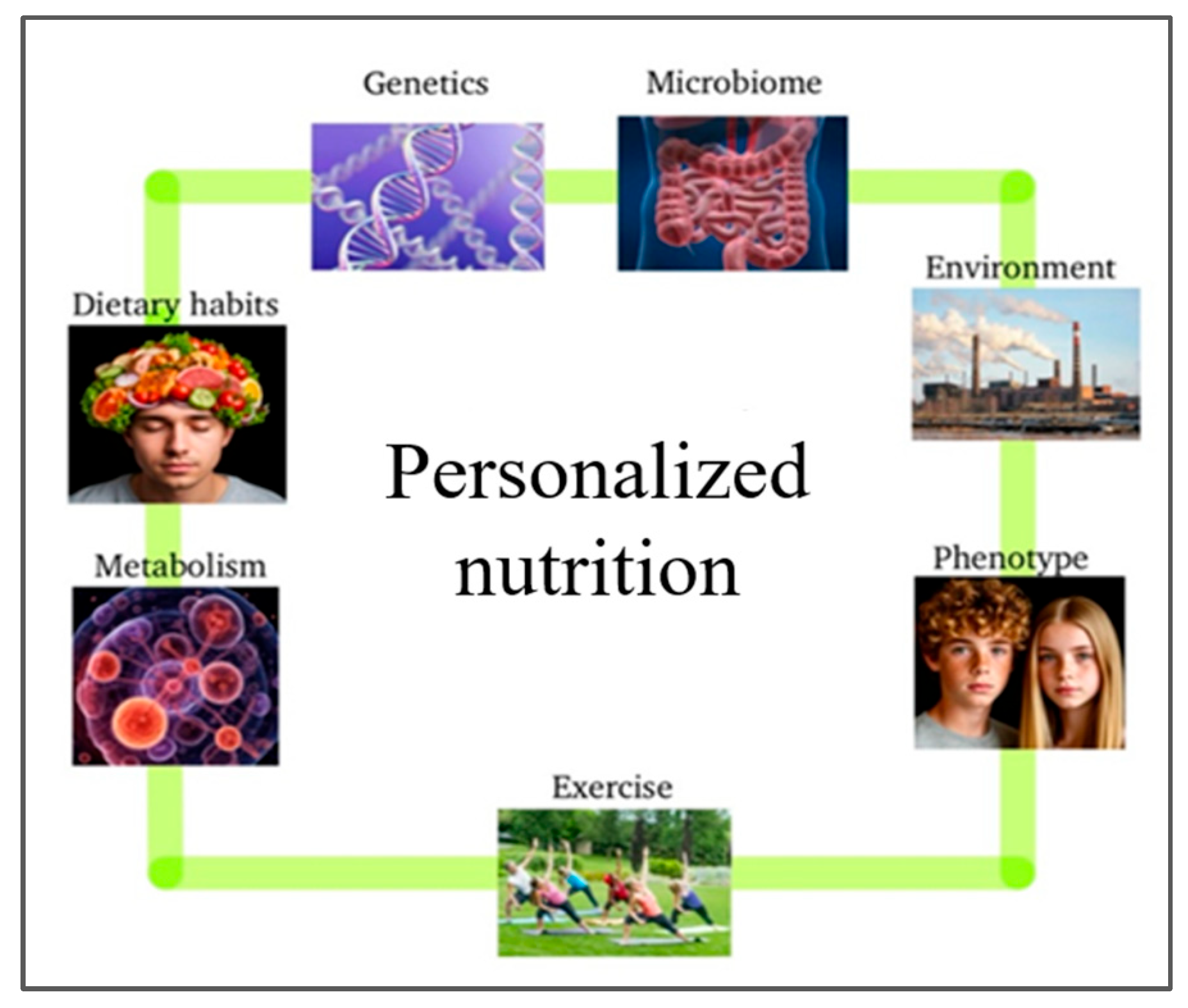
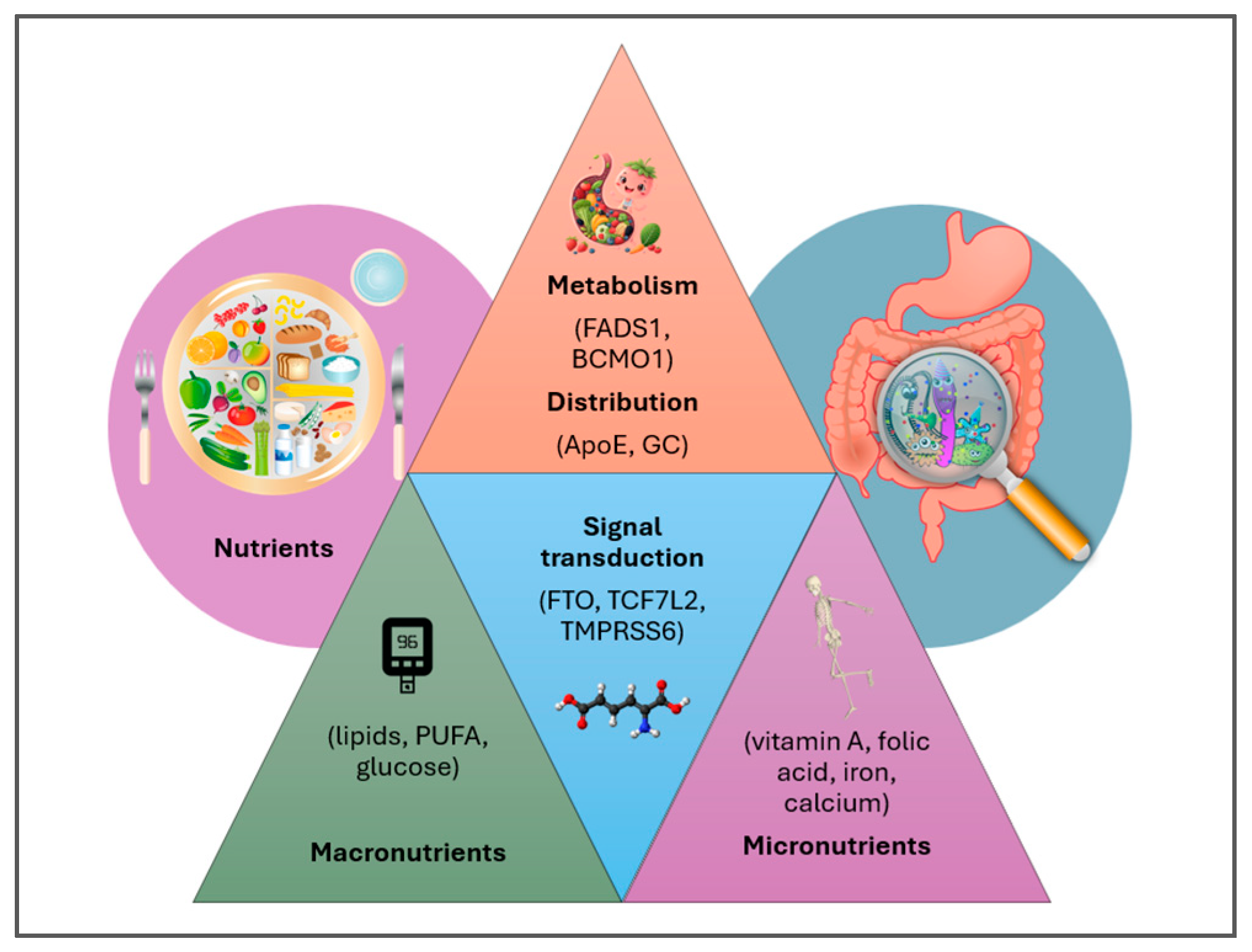
3. Personalized Nutrition in Pediatric Populations
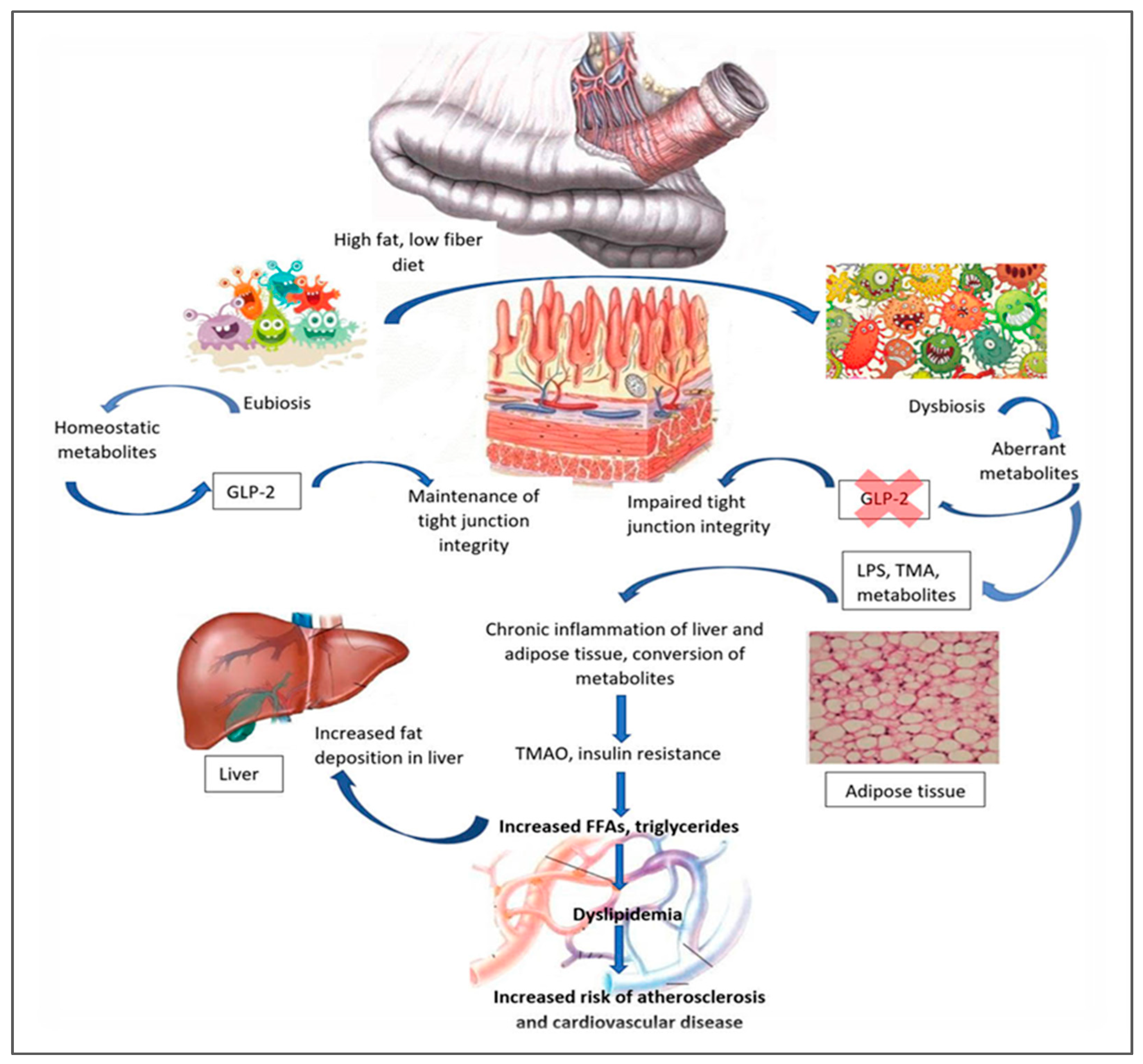
3.1. The Human Microbiome in Pediatric Chronic Conditions
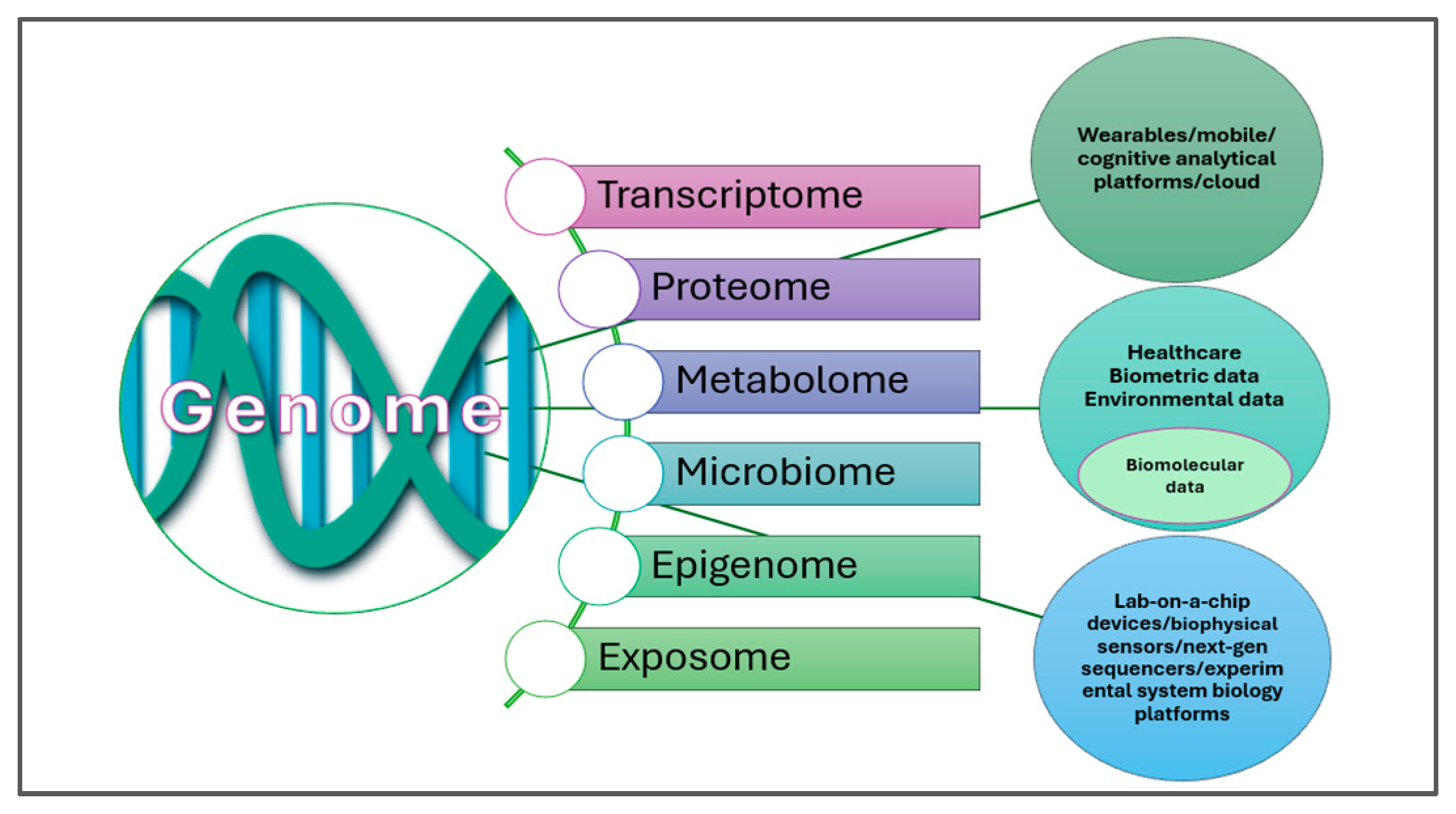
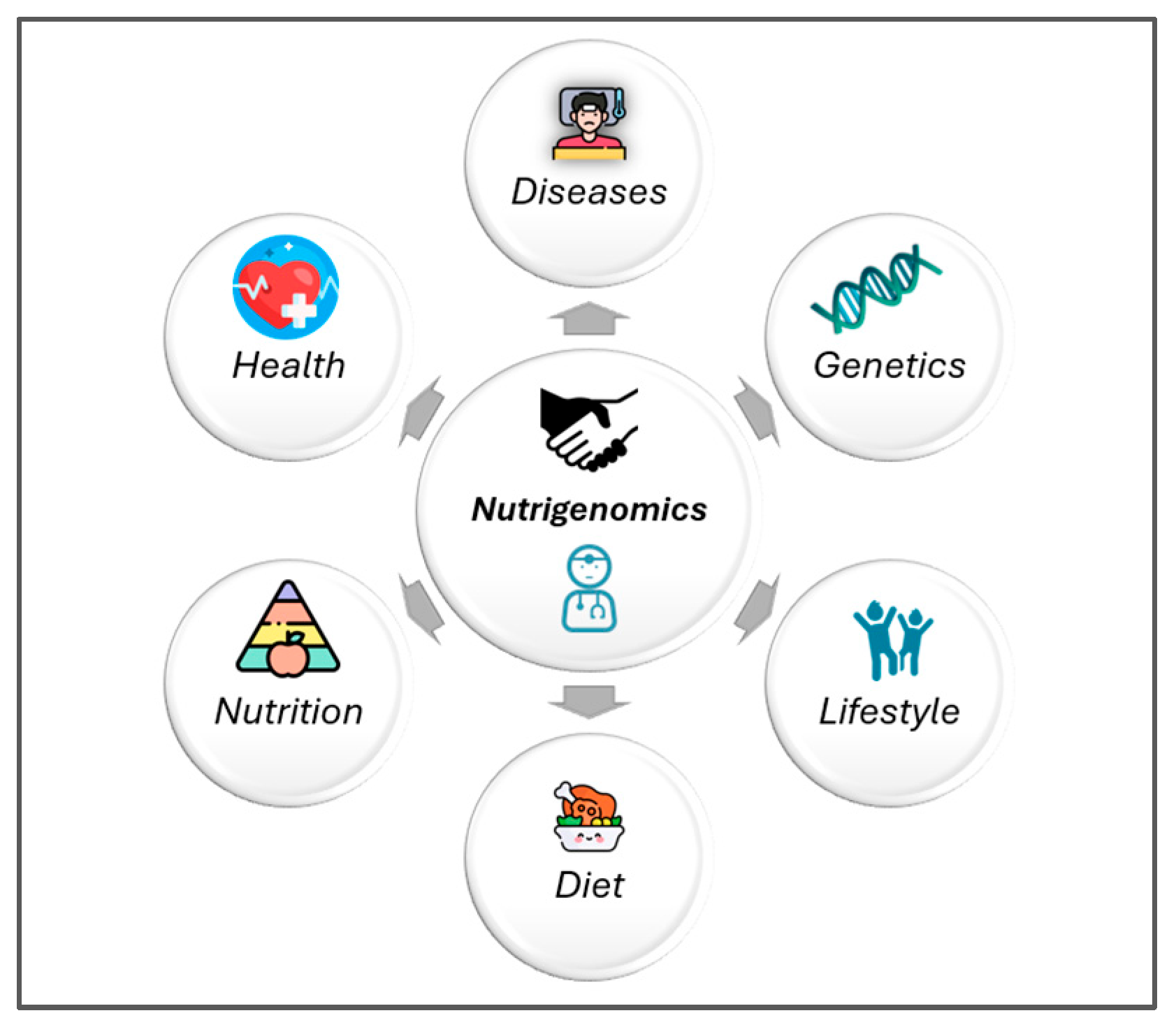
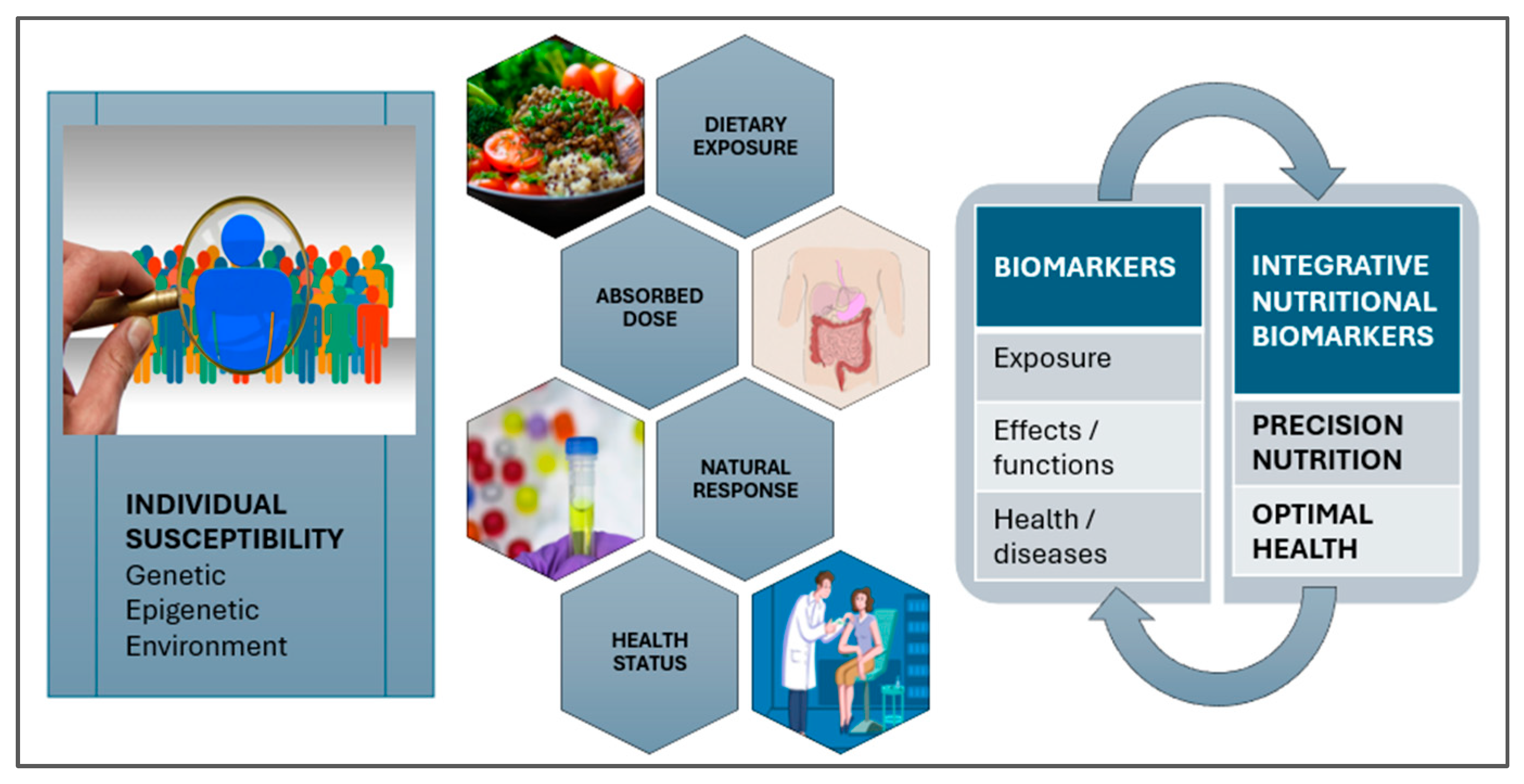
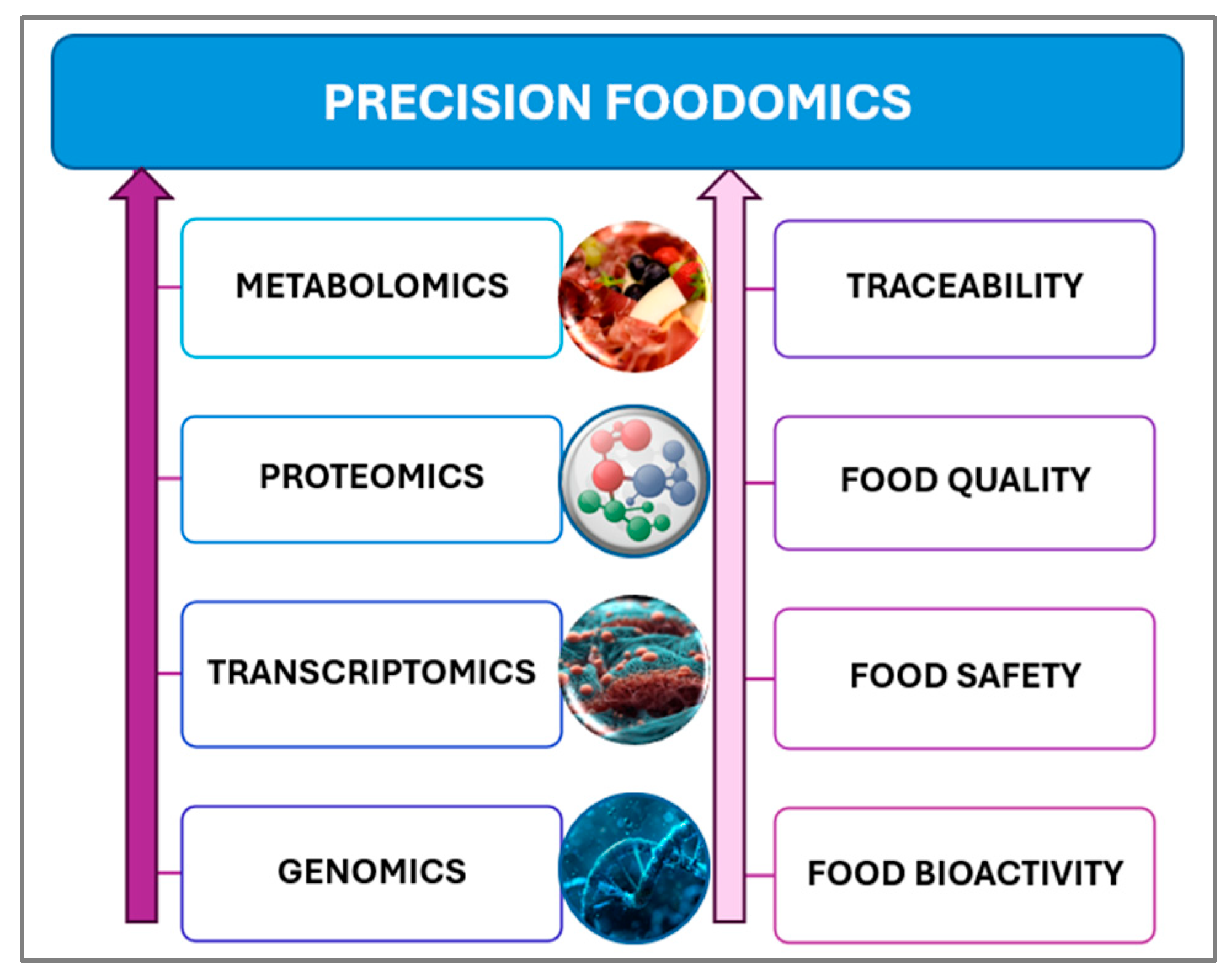
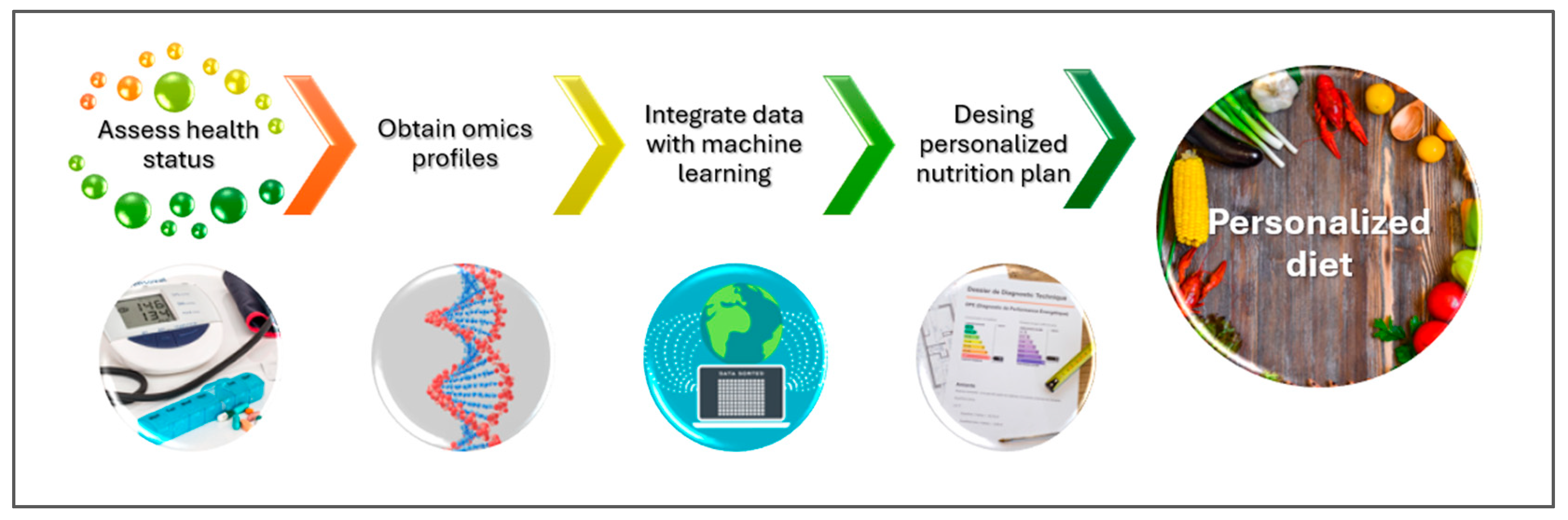
3.2. Personalized Nutrition via the Resources of Precision Foodomics
4. Personalized Nutrition in Chronic Diseases
4.1. Obesity
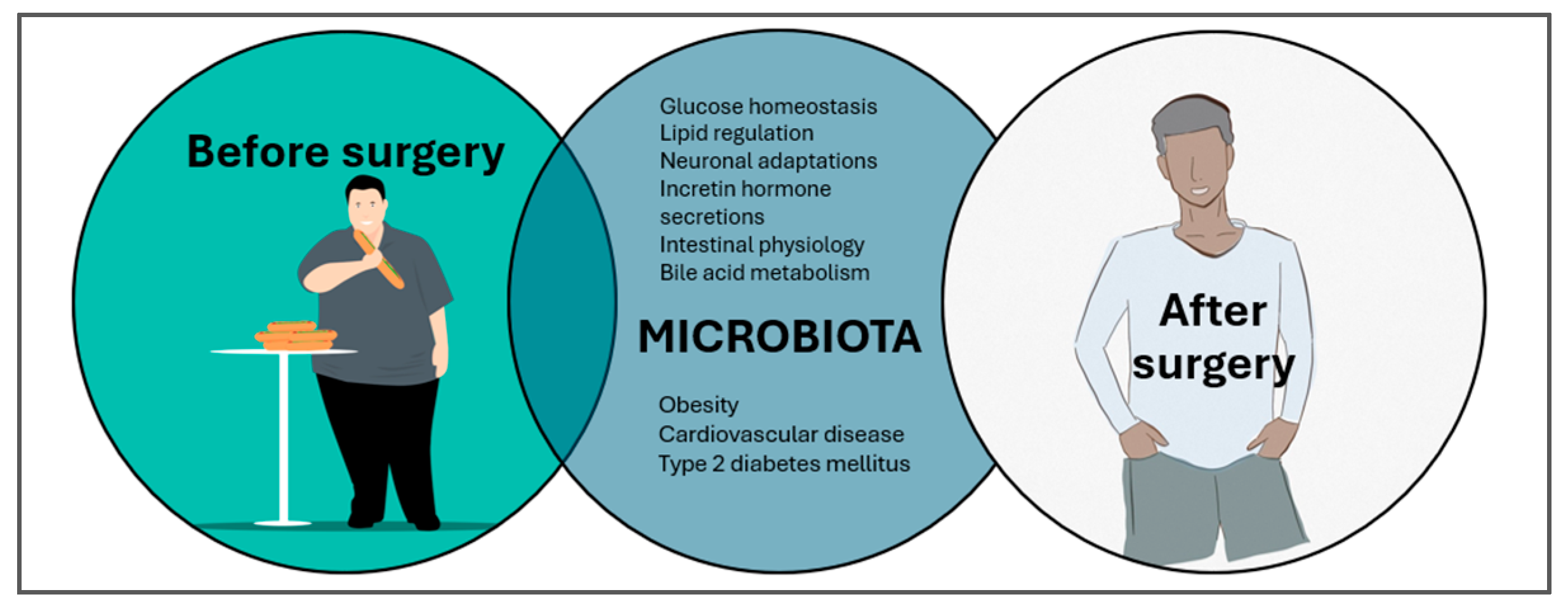
4.2. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
4.3. Type 1 Diabetes
4.4. Celiac Disease
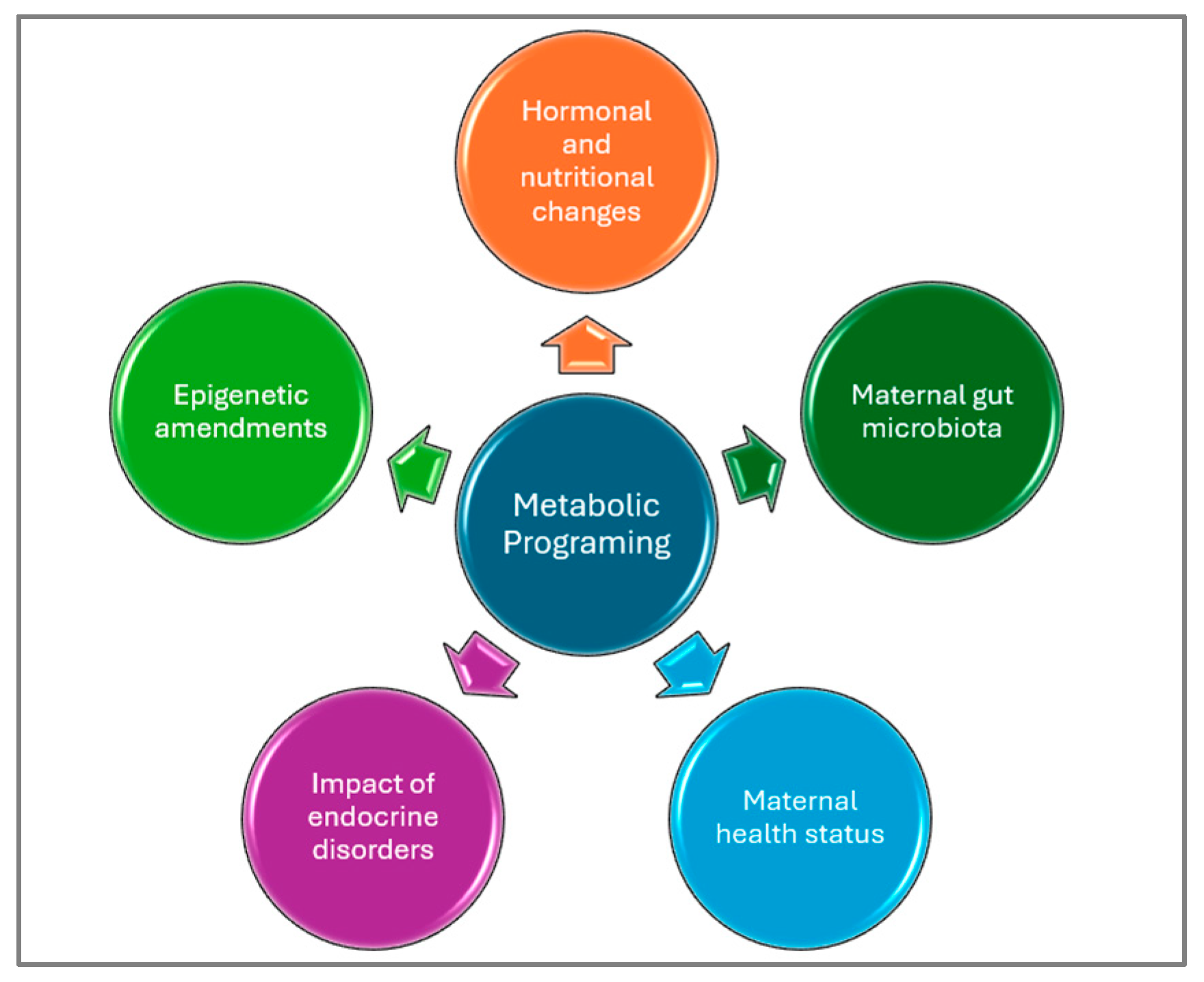
5. New Perspectives
5.1. Childhood Obesity
5.2. Childhood Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
5.3. Childhood Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
5.4. Childhood Celiac Disease
6. Discussion
- Tailored dietary guidance aligned with individual growth patterns and metabolic profiles.
- Provision of nutrient-adequate meals that support immune function and healthy development.
- Expert oversight from PN specialists to optimize pediatric interventions.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Escobedo-Monge, M.F.; Barrado, E.; Parodi-Román, J.; Escobedo-Monge, M.A.; Torres-Hinojal, M.C.; Marugán-Miguelsanz, J.M. Copper/Zinc Ratio in Childhood and Adolescence: A Review. Metabolites 2023, 13, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisk, L.E.; Sharma, N. Prevalence and Trends in Pediatric-Onset Chronic Conditions in the United States, 1999-2018. Acad. Pediatr. 2025, 25, 102810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zheng, J.; Cheng, J.; Zou, H.; Li, M.; Deng, B.; Luo, R.; Wang, F.; Huang, D.; Li, G.; et al. Personalized nutrition: A review of genotype-based nutritional supplementation. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 992986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S. Editorial: Precision nutrition and nutrients: Making the promise a reality. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1553149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, N.; Tovar, A.R. The Present and Future of Personalized Nutrition. Rev. Investig. Clin. 2021, 73, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.; Kaur, J.; Singh, J.; Rasane, P.; Sharma, K.; Bhadariya, V.; Kaur, S.; Kumar, V. Genetics, Nutrition, and Health: A New Frontier in Disease Prevention. J. Am. Nutr. Assoc. 2024, 43, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drabsch, T.; Holzapfel, C.A. Scientific Perspective of Personalised Gene-Based Dietary Recommendations for Weight Management. Nutrients 2019, 11, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendoline, A.-M. Biannual Publication: OMICS in nutrition (Las ómicas en la nutrición). Mex. J. Med. Res. ICSa 2022, 10, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson, M.D.; Stout, R.; Dysinger, W. Lifestyle Medicine: Prevention, Treatment, and Reversal of Disease. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 107, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.; Singh, D.K.; Kumar, A. Microbial, environmental and anthropogenic factors influencing the indoor microbiome of the built environment. J. Basic Microbiol. 2021, 61, 267–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laiho, J.E.; Laitinen, O.H.; Malkamäki, J.; Puustinen, L.; Sinkkonen, A.; Pärkkä, J.; Hyöty, H. Exposomic determinants of immune-mediated diseases: Special focus on type 1 diabetes, celiac disease, asthma, and allergies: The HEDIMED project approach. Environ. Epidemiol. 2022, 6, e212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, K.H.; Hall, L.J. Improving causality in microbiome research: Can human genetic epidemiology help? Welcome Open Res. 2020, 4, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanen, T.; Franzosa, E.A.; Schwager, R.; Tripathi, S.; Arthur, T.D.; Vehik, K.; Lernmark, Å.; Hagopian, W.A.; Rewers, M.J.; She, J.X.; et al. The human gut microbiome in early-onset type 1 diabetes from the TEDDY study. Nature 2018, 562, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIABIMMUNE. Available online: https://diabimmune.broadinstitute.org/diabimmune/ (accessed on 3 August 2025).
- Vatanen, T.; Kostic, A.D.; d’Hennezel, E.; Siljander, H.; Franzosa, E.A.; Yassour, M.; Kolde, R.; Vlamakis, H.; Arthur, T.D.; Hämäläinen, A.M.; et al. Variation in Microbiome LPS Immunogenicity Contributes to Autoimmunity in Humans. Cell 2016, 165, 842–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, E.Y.; McBride, S.W.; Hsien, S.; Sharon, G.; Hyde, E.R.; McCue, T.; Codelli, J.A.; Chow, J.; Reisman, S.E.; Petrosino, J.F.; et al. Microbiota modulate behavioral and physiological abnormalities associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. Cell 2013, 155, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.W.; Adams, J.B.; Gregory, A.C.; Borody, T.; Chittick, L.; Fasano, A.; Khoruts, A.; Geis, E.; Maldonado, J.; McDonough-Means, S.; et al. Microbiota Transfer Therapy alters gut ecosystem and improves gastrointestinal and autism symptoms: An open-label study. Microbiome 2017, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunde, R.B.; Thorsen, J.; Kim, M.; Schoos, A.M.; Stokholm, J.; Bønnelykke, K.; Bisgaard, H.; Chawes, B. Bacterial colonisation of the airway in neonates and risk of asthma and allergy until age 18 years. Eur. Respir. J. 2024, 63, 2300471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, A.B.; Yassour, M.; Sauk, J.; Garner, A.; Jiang, X.; Arthur, T.; Lagoudas, G.K.; Vatanen, T.; Fornelos, N.; Wilson, R.; et al. A novel Ruminococcus gnavus clade enriched in inflammatory bowel disease patients. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gevers, D.; Kugathasan, S.; Denson, L.A.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Van Treuren, W.; Ren, B.; Schwager, E.; Knights, D.; Song, S.J.; Yassour, M.; et al. The treatment-naive microbiome in new-onset Crohn’s disease. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanton, L.V.; Charbonneau, M.R.; Salih, T.; Barratt, M.J.; Venkatesh, S.; Ilkaveya, O.; Subramanian, S.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Jorgensen, J.M.; et al. Gut bacteria that prevent growth impairments transmitted by microbiota from malnourished children. Science 2016, 351, aad3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantazi, A.C.; Balasa, A.L.; Mihai, C.M.; Chisnoiu, T.; Lupu, V.V.; Kassim, M.A.K.; Mihai, L.; Frecus, C.E.; Chirila, S.I.; Lupu, A.; et al. Development of Gut Microbiota in the First 1000 Days after Birth and Potential Interventions. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Serna, D.; Villanueva-Martin, G.; Acosta-Herrera, M.; Márquez, A.; Martín, J. Approaching Shared Pathophysiology in Immune-Mediated Diseases through Functional Genomics. Genes 2020, 11, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardinoglu, A.; Turkez, H.; Shong, M.; Srinivasulu, V.P.; Nielsen, J.; Palsson, B.O.; Hood, L.; Uhlen, M. Longitudinal big biological data in the AI era. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2025, 21, 1147–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Rönn, T. Epigenetics in Human Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1028–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Hu, J.; Lyu, X.; Huang, H.; Cheng, X. Exploring the Interdisciplinary Nature of Precision Medicine: Network Analysis and Visualization. JMIR Med. Inform. 2021, 9, e23562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Jellinger, K.A. Advances in Molecular Medicine: Unravelling Disease Complexity and Pioneering Precision Healthcare. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zuo, T.; Frey, N.; Rangrez, A.Y. A systematic framework for understanding the microbiome in human health and disease: From basic principles to clinical translation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donald, K.; Finlay, B.B. Early-life interactions between the microbiota and immune system: Impact on immune system development and atopic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 735–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singar, S.; Nagpal, R.; Arjmandi, B.H.; Akhavan, N.S. Personalized Nutrition: Tailoring Dietary Recommendations through Genetic Insights. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keathley, J.; Garneau, V.; Zavala-Mora, D.; Heister, R.R.; Gauthier, E.; Morin-Bernier, J.; Green, R.; Vohl, M.C. A Systematic Review and Recommendations Around Frameworks for Evaluating Scientific Validity in Nutritional Genomics. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 789215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcum, J.A. Nutrigenetics/Nutrigenomics, Personalized Nutrition, and Precision Healthcare. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2020, 9, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, G.P.; Silano, M.; Mazzocchi, A.; Bettocchi, S.; De Cosmi, V.; Agostoni, C. Personalized nutrition approach in pediatrics: A narrative review. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 89, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Pérez, L.; Escoté, X.; Companys, J.; Alcaide-Hidalgo, J.M.; Bosch, M.; Rabassa, M.; Crescenti, A.; Valls, R.M.; Pedret, A.; Solà, R.; et al. A single-blinded, randomized, parallel intervention to evaluate genetics and omics-based personalized nutrition in general population via an e-commerce tool: The PREVENTOMICS e-commerce study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 120, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Song, C.; Shi, M.; Chen, R.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, W.; Hu, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Effect of Customized Nutritious Breakfast and Nutrition Education on Nutritional Status of Preschool Children in Economically Underdeveloped Multi-Ethnic Areas: A Cluster Randomized Clinical Trial in Linxia, China. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancheva, R.; Fitneva, S.A.; Chamova, R.; Marinov, D.; Toneva, A.; Hadzhieva, S.; Braykova, R.; Yoncheva, N.; Tsvetanova, S.; Nikolova, S.; et al. A randomized controlled trial protocol for the introduction of a multidisciplinary individualized nutritional intervention in children with cerebral palsy. Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 2024, 41, 101343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motevalli, M.; Drenowatz, C.; Tanous, D.R.; Khan, N.A.; Wirnitzer, K. Management of Childhood Obesity-Time to Shift from Generalized to Personalized Intervention Strategies. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NUTRIGENOMIX. Available online: https://nutrigenomix.com/about (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- Rajasekaran, A.; Davison, K. Genomics and Gene-Based Personalized Nutrition. In Nutritional Health: Strategies for Disease Prevention; Temple, N.J., Wilson, T., Jacobs, D.R., Jr., Bray, G.A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; p. 297. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, Z.C.; Silverman, J.D.; Dressman, H.K.; Wei, Z.; Dallow, E.P.; Armstrong, S.C.; Seed, P.C.; Rawls, J.F.; David, L.A. Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production by Gut Microbiota from Children with Obesity Differs According to Prebiotic Choice and Bacterial Community Composition. mBio 2020, 11, e00914-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Kurilshikov, A.; Yang, S.; van Oortmerssen, J.A.E.; van Hilten, A.; Ahmadizar, F.; Roshchupkin, G.; Kraaij, R.; Duijts, L.; Fu, J.; et al. Association between gut microbiome profiles and host metabolic health across the life course: A population-based study. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2024, 50, 101195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, S.; Drew, D.; Linenberg, I.; Wolf, J.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.; Davies, R.; Al Khatib, H.; Hart, D.; Surdurlescu, G.; Yarand, D.; et al. Personalised REsponses to DIetary Composition Trial (PREDICT): An Intervention Study to Determine Inter-Individual Differences in Postprandial Response to Foods, PROTOCOL (Version 1) Available at Protocol Exchange. Available online: https://www.protocols.io/view/personalised-responses-to-dietary-composition-tria-261gerw3dl47/v1 (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Picó, C.; Serra, F.; Rodríguez, A.M.; Keijer, J.; Palou, A. Biomarkers of Nutrition and Health: New Tools for New Approaches. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagoumintzis, G.; Patrinos, G.P. Triangulating nutrigenomics, metabolomics and microbiomics toward personalized nutrition and healthy living. Hum. Genom. 2023, 8, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, J.; Ni, J.; Xue, K.; Wang, F.; Zheng, J.; Cheng, J.; Wu, P.; Runyon, M.K.; Guo, H.; Du, J.; et al. Personalized Nutrition Intervention Improves Health Status in Overweight/Obese Chinese Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 919882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahato, D.K.; Kamle, M.; Pandhi, S.; Pandey, S.; Gupta, A.; Paul, V.; Kalsi, R.; Agrawal, S.; Islam, D.; Khare, S.; et al. Foodomics: A sustainable approach for the specific nutrition and diets for human health. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Pozo, A.; Das, S.; Hyman, B.T. APOE and Alzheimer’s disease: Advances in genetics, pathophysiology, and therapeutic approaches. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltell, O.; Sorlí, J.V.; Asensio, E.M.; Barragán, R.; González, J.I.; Giménez-Alba, I.M.; Zanón-Moreno, V.; Estruch, R.; Ramírez-Sabio, J.B.; Pascual, E.C.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study for Serum Omega-3 and Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: Exploratory Analysis of the Sex-Specific Effects and Dietary Modulation in Mediterranean Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2020, 12, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinkler, L.; Abdulkadir, M.; Herle, M.; Mulder, R.; Harris, H.; Jansen, P.; Qi, B.; Munn-Chernoff, M.; Thornton, L.; Pisetsky, E.; et al. 11. Genome-Wide association studies of childhood fussy eating and avoidant restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID). Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2023, 75 (Suppl. S1), S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silao, C.L.T. A Child’s Nutrition and Epigenetics. Nestle Nutr. Inst. Workshop Ser. 2023, 97, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Gkiouleka, M.; Karalexi, M.; Sergentanis, T.N.; Nouvakis, D.; Proikaki, S.; Kornarou, E.; Vassilakou, T. The Epigenetic Role of Nutrition Among Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Literature Review. Children 2025, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, K.K.; Craig, J.M.; Dawson, S.L. Relationships between the maternal prenatal diet and epigenetic state in infants: A systematic review of human studies. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2023, 14, 540–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiomar de Almeida Brasiel, P.; Cristina Potente Dutra Luquetti, S. Metabolic Programming and Nutrition. In New Insights into Metabolic Syndrome; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Sun, Y.; Nie, L.; Cui, A.; Zhao, P.; Leung, W.K.; Wang, Q. Metabolic memory: Mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.D.; Fu, E.; Kobayashi, M.A. Prevention and Management of Childhood Obesity and Its Psychological and Health Comorbidities. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2020, 16, 351–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobedo-Monge, M.F.; Torres-Hinojal, M.C.; Barrado, E.; Escobedo-Monge, M.A.; Marugán-Miguelsanz, J.M. Zinc Nutritional Status in a Series of Children with Chronic Diseases: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo-Monge, M.F.; Barrado, E.; Parodi-Román, J.; Escobedo-Monge, M.A.; Torres-Hinojal, M.C.; Marugán-Miguelsanz, J.M. Copper and Copper/Zn Ratio in a Series of Children with Chronic Diseases: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo-Monge, M.F.; Barrado, E.; Parodi-Román, J.; Escobedo-Monge, M.A.; Torres-Hinojal, M.C.; Marugán-Miguelsanz, J.M. Magnesium Status and Ca/Mg Ratios in a Series of Children and Adolescents with Chronic Diseases. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo-Monge, M.F.; Bahillo-Curieses, P.; Parodi-Román, J.; Escobedo-Monge, M.A.; Alonso-López, P.; Marugán-Miguelsanz, J.M. Calcium, Phosphate, and Vitamin D in Children and Adolescents with Chronic Diseases: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Noncommunicable Diseases: Childhood Overweight and Obesity. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/noncommunicable-diseases-childhood-overweight-and-obesity (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Calcaterra, V.; Verduci, E.; Milanta, C.; Agostinelli, M.; Todisco, C.F.; Bona, F.; Dolor, J.; La Mendola, A.; Tosi, M.; Zuccotti, G. Micronutrient Deficiency in Children and Adolescents with Obesity-A Narrative Review. Children 2023, 10, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobstein, T.; Jackson-Leach, R.; Moodie, M.L.; Hall, K.D.; Gortmaker, S.L.; Swinburn, B.A.; James, W.P.; Wang, Y.; McPherson, K. Child and adolescent obesity: Part of a bigger picture. Lancet 2019, 385, 2510–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratakis, N.; Anguita-Ruiz, A.; Fabbri, L.; Maitre, L.; González, J.R.; Andrusaityte, S.; Basagaña, X.; Borràs, E.; Keun, H.C.; Chatzi, L.; et al. Multi-omics architecture of childhood obesity and metabolic dysfunction uncovers biological pathways and prenatal determinants. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes-Servín, J.; Avila-Nava, A.; González-Salazar, L.E.; Pérez-González, O.A.; Servín-Rodas, M.D.C.; Serralde-Zuñiga, A.E.; Medina-Vera, I.; Guevara-Cruz, M. Resting Energy Expenditure Prediction Equations in the Pediatric Population: A Systematic Review. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 795364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Huhulea, E.N.; Abraham, E.; Bienenstock, R.; Aifuwa, E.; Hirani, R.; Schulhof, A.; Tiwari, R.K.; Etienne, M. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Obesity Risk Prediction and Management: Approaches, Insights, and Recommendations. Medicina 2025, 61, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganatra, H.A. Machine Learning in Pediatric Healthcare: Current Trends, Challenges, and Future Directions. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllidis, A.; Alexiadis, A.; Elmas, D.; Gerovasilis, G.; Votis, K.; Tzovaras, D. A social robot-based platform for health behavior change toward prevention of childhood obesity. Univers. Access Inf. Soc. 2023, 22, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larizza, C.; Bosoni, P.; Quaglini, S.; Chasseur, M.; Bevolo, V.; Zuccotti, G.; Calcaterra, V. V-care: An application to support lifestyle improvement in children with obesity. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2023, 177, 105140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, D.; Kok, E.; Tufano, M.; Tekinerdogan, B.; Feskens, E.J.M.; Camps, G. Machine Learning in Nutrition Research. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 22, 2573–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Song, C.; Cui, J.; Lin, X.; Li, N.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Chong, F.; Wang, C.; et al. A fusion decision system to identify and grade malnutrition in cancer patients: Machine learning reveals feasible workflow from representative real-world data. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4958–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormond, K.E.; Blasimme, A.; Vayena, E. Ethical Aspects of Pediatric Genetic Care: Testing and Treatment. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 70, 1029–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, S.M.; Abrahams, M.; Anthony, J.C.; Bao, Y.; Barragan, M.; Bermingham, K.M.; Blander, G.; Keck, A.S.; Lee, B.Y.; Nieman, K.; et al. Personalized nutrition: Perspectives on challenges, opportunities, and guiding principles for data use and fusion. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, Y.; Wong, S.H.; Chee, D.G.H.; Ng, B.S.P.; Ang, W.W.; Han, C.Y.; Cheng, L.J. Technology-delivered personalized nutrition intervention on dietary outcomes among adults with overweight and obesity: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Obes. Rev. 2024, 25, e13699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Dai, Y.; Ma, X.; Peng, H.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y. Personalized optimal nutrition lifestyle for self-obesity management using metaalgorithms. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Holwerda, A.; Park, O.H.; Albracht-Schulte, K.; Niraula, S.; Thompson, L.; Oldewage-Theron, W. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Nutrition Research: A Scoping Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porri, D.; Wasniewska, M.; Luppino, G.; Morabito, L.A.; La Rosa, E.; Pepe, G.; Corica, D.; Valenzise, M.; Messina, M.F.; Zirilli, G.; et al. The Rising Burden of Childhood Obesity: Prevention Should Start in Primary School. Nutrients 2025, 17, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannou, G.; Petrou, I.; Manou, M.; Tragomalou, A.; Ramouzi, E.; Vourdoumpa, A.; Genitsaridi, S.-M.; Kyrkili, A.; Diou, C.; Papadopoulou, M.; et al. Dietary and Physical Activity Habits of Children and Adolescents before and after the Implementation of a Personalized, Intervention Program for the Management of Obesity. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouvari, M.; Karipidou, M.; Tsiampalis, T.; Mamalaki, E.; Poulimeneas, D.; Bathrellou, E.; Panagiotakos, D.; Yannakoulia, M. Digital Health Interventions for Weight Management in Children and Adolescents: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2022, 24, e30675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramanik, S.; Mondal, S.; Palui, R.; Ray, S. Type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents: Exploring the disease heterogeneity and research gaps to optimum management. World J. Clin. Pediatr. 2024, 13, 91587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valaiyapathi, B.; Gower, B.; Ashraf, A.P. Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes in Children and Adolescents. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2020, 16, 220–229. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, N.; Verma, N.; Dungan, K. Monitoring Technologies—Continuous Glucose Monitoring, Mobile Technology, Biomarkers of Glycemic Control. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Ahmed, S.F., Anawalt, B., Blackman, M.R., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Hofland, J.K., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279046/ (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Xu, H.; Chen, R.; Hou, X.; Li, N.; Han, Y.; Ji, S. The clinical potential of 1,5-anhydroglucitol as biomarker in diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1471577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 14. Children and Adolescents: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47 (Suppl. S1), S258–S281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeev, A.M.; Malisetty, H.; Baidya, O.P.; Vamshy, J.K.; Siddhanta, S.; Dharan, B.G. Pediatric Nutrition and Its Role in Preventing Non-communicable Diseases: A Review. Cureus 2025, 17, e87431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niechciał, E.; Wais, P.; Bajtek, J.; Kędzia, A. Current Perspectives for Treating Adolescents with Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes: A Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, B.C.E.; Seeley, R.J. How does “metabolic surgery” work its magic? New evidence for gut microbiota. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2018, 25, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Heo, J.S.; Baek, K.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Baek, K.H.; Kim, K.E.; Sheen, Y.H. Zonulin level, a marker of intestinal permeability, is increased in association with liver enzymes in young adolescents. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 481, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küme, T.; Acar, S.; Tuhan, H.; Çatlı, G.; Anık, A.; Gürsoy Çalan, Ö.; Böber, E.; Abacı, A. The Relationship between Serum Zonulin Level and Clinical and Laboratory Parameters of Childhood Obesity. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2017, 9, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamamah, S.; Hajnal, A.; Covasa, M. Influence of Bariatric Surgery on Gut Microbiota Composition and Its Implication on Brain and Peripheral Targets. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, D.A.; Patti, M.E. Glucose metabolism after bariatric surgery: Implications for T2DM remission and hypoglycaemia. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsso, C.E.; Peng, Y.; Deehan, E.C.; Tan, Q.; Field, C.J.; Madsen, K.L.; Walter, J.; Prado, C.M.; Tun, H.M.; Haqq, A.M. Composition and Functions of the Gut Microbiome in Pediatric Obesity: Relationships with Markers of Insulin Resistance. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, P.C.; Kohn, B. Use of the microbiome in the management of children with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2019, 31, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwaly, A.; Kriaa, A.; Hassani, Z.; Carraturo, F.; Druart, C.; IHMCSAConsortium; Arnauts, K.; Wilmes, P.; Walter, J.; Rosshart, S.; et al. A Consensus Statement on establishing causality, therapeutic applications and the use of preclinical models in microbiome research. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 22, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, E.; Haller, D. Intestinal epithelial cell metabolism at the interface of microbial dysbiosis and tissue injury. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, Y.; Olivares, M.; Moya-Pérez, Á.; Agostoni, C. Understanding the role of gut microbiome in metabolic disease risk. Pediatr. Res. 2015, 77, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malnick, S.D.H.; Ohayon Michael, S. The Intestinal Microbiome and the Metabolic Syndrome-How Its Manipulation May Affect Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD). Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 7197–7211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.X.; Guo, Y. Gut microbiome: New perspectives for type 2 diabetes prevention and treatment. World J. Clin. Cases 2023, 11, 7508–7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Feng, R.; Li, M.; Liu, L.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yin, C. Causal relationship between gut microbiota and childhood obesity: A Mendelian randomization study and case-control study. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2024, 63, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magne, F.; Gotteland, M.; Gauthier, L.; Zazueta, A.; Pesoa, S.; Navarrete, P.; Balamurugan, R. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio: A Relevant Marker of Gut Dysbiosis in Obese Patients? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Qi, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Meng, X.; Aikepaer, A.; Lin, Y.; Su, C.; Liu, Y.; Feng, X.; et al. When short-chain fatty acids meet type 2 diabetes mellitus: Revealing mechanisms, envisioning therapies. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2025, 233, 116791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crudele, L.; Gadaleta, R.M.; Cariello, M.; Moschetta, A. Gut microbiota in the pathogenesis and therapeutic approaches of diabetes. EBioMedicine 2023, 97, 104821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.N.; Liu, X.T.; Liang, Z.H.; Wang, J.H. Gut microbiota in obesity. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 3837–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Li, M.; Luo, D.; Tang, B. Gut Microbiota: An Important Participant in Childhood Obesity. Adv. Nutr. 2025, 16, 100362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitch, T.C.A.; Hall, L.J.; Walsh, S.K.; Leventhal, G.E.; Slack, E.; de Wouters, T.; Walter, J.; Clavel, T. Microbiome-based interventions to modulate gut ecology and the immune system. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 1095–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinalian, R.; Ahmadikhatir, S.; Esfahani, E.N.; Namazi, N.; Larijani, B. The roles of personalized nutrition in obesity and diabetes management: A review. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2022, 21, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, M.A.; Mirmira, R.G. The pathogenic “symphony” in type 1 diabetes: A disorder of the immune system, β cells, and exocrine pancreas. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 1500–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Chierico, F.; Conta, G.; Matteoli, M.C.; Fierabracci, A.; Reddel, S.; Macari, G.; Gardini, S.; Guarrasi, V.; Levi Mortera, S.; Marzano, V.; et al. Gut Microbiota Functional Traits, Blood pH, and Anti-GAD Antibodies Concur in the Clinical Characterization of T1D at Onset. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veres-Székely, A.; Szász, C.; Pap, D.; Szebeni, B.; Bokrossy, P.; Vannay, Á. Zonulin as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis Disorders: Encouraging Results Emerging Questions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oram, R.A.; Sims, E.K.; Evans-Molina, C. Beta cells in type 1 diabetes: Mass and function; sleeping or dead? Diabetologia 2019, 62, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Chierico, F.; Rapini, N.; Deodati, A.; Matteoli, M.C.; Cianfarani, S.; Putignani, L. Pathophysiology of Type 1 Diabetes and Gut Microbiota Role. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, P.; Flint, H.J. Formation of propionate and butyrate by the human colonic microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parada Venegas, D.; De la Fuente, M.K.; Landskron, G.; González, M.J.; Quera, R.; Dijkstra, G.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Faber, K.N.; Hermoso, M.A. Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)-Mediated Gut Epithelial and Immune Regulation and Its Relevance for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 277. [Google Scholar]
- Verduci, E.; Mameli, C.; Amatruda, M.; Petitti, A.; Vizzuso, S.; El Assadi, F.; Zuccotti, G.; Alabduljabbar, S.; Terranegra, A. Early Nutrition and Risk of Type 1 Diabetes: The Role of Gut Microbiota. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 612377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, C.M.; Valentini, A.; Calabrese, G. Gut Microbiota and Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: The Effect of Mediterranean Diet. Front. Nutr. 2021, 7, 612773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Chen, G. Personalized nutrition for people with diabetes and at risk of diabetes has begun. J. Future Foods 2022, 2, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakleas, K.; Soldatou, A.; Karachaliou, F.; Karavanaki, K. Associated autoimmune diseases in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 781–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volta, U.; Tovoli, F.; Caio, G. Clinical and immunological features of celiac disease in patients with Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Expert. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 5, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitella, E.; Cozzolino, D.; Ginaldi, L.; Romano, C. Celiac Disease: A Transitional Point of View. Nutrients 2025, 17, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Houmich, T.; Admou, B. Celiac disease: Understandings in diagnostic, nutritional, and medicinal aspects. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2021, 35, 20587384211008709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyoud, S.H.; Shakhshir, M.; Abushanab, A.S.; Koni, A.; Hamdallah, M.; Al-Jabi, S.W. Mapping the knowledge structure of a gluten-free diet: A global perspective. Transl. Med. Commun. 2023, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, H.; Reeves, S.; Jeanes, Y.M. Identifying and improving adherence to the gluten-free diet in people with coeliac disease. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2019, 78, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasret, A.C. Effect of adherence to a gluten-free diet on vitamin and micronutrient deficiencies in celiac disease patients. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 300–304. [Google Scholar]
- Kreutz, J.M.; Adriaanse, M.P.M.; van der Ploeg, E.M.C.; Vreugdenhil, A.C.E. Narrative Review: Nutrient Deficiencies in Adults and Children with Treated and Untreated Celiac Disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caio, G.; Volta, U.; Sapone, A.; Leffler, D.A.; De Giorgio, R.; Catassi, C.; Fasano, A. Celiac disease: A comprehensive current review. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrunka, M.; Janda, L.; Šťastná, M.; Pinkasová, T.; Pecl, J.; Kunovský, L.; Dítě, P.; Jabandžiev, P. Celiac Disease: Promising Biomarkers for Follow-Up. J. Gastrointestin. Liver Dis. 2023, 32, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valitutti, F.; Cucchiara, S.; Fasano, A. Celiac Disease and the Microbiome. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caio, G.; Lungaro, L.; Segata, N.; Guarino, M.; Zoli, G.; Volta, U.; De Giorgio, R. Effect of Gluten-Free Diet on Gut Microbiota Composition in Patients with Celiac Disease and Non-Celiac Gluten/Wheat Sensitivity. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akobeng, A.K.; Singh, P.; Kumar, M.; Al Khodor, S. Role of the gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of coeliac disease and potential therapeutic implications. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 3369–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, K.; Dogru, D.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Palm, N.W.; Altindis, E.; Ludvigsson, J. Children who develop celiac disease are predicted to exhibit distinct metabolic pathways among their gut microbiota years before diagnosis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2025, 13, e0146824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, O.; Castellana, S.; Bevilacqua, A.; Latiano, A.; Latiano, T.; Panza, A.; Fontana, R.; Ippolito, A.M.; Biscaglia, G.; Gentile, A.; et al. Adherence to Gluten-Free Diet Restores Alpha Diversity in Celiac People but the Microbiome Composition Is Different to Healthy People. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliciak, I.; Drogowski, K.; Garczyk, A.; Kopeć, S.; Horwat, P.; Bogdański, P.; Stelmach-Mardas, M.; Mardas, M. Influence of Gluten-Free Diet on Gut Microbiota Composition in Patients with Coeliac Disease: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavarian, P.N.; Mosher, T.L.; Abu El Haija, M. Use of glucagon-like-peptide 1 receptor agonist in the treatment of childhood obesity. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2024, 36, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vondikakis, I.; Politi, E.; Goulis, D.; Dimitrakopoulos, G.; Georgoulis, M.; Saltaouras, G.; Kontogianni, M.; Brisimi, T.; Logothetis, M.; Kakoulidis, H.; et al. Integrated Framework for Managing Childhood Obesity Based on Biobanks, AI Tools and Methods, and Serious Games. Electronics 2025, 14, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, M.; ElGibreen, H.; Alafif, N.; Joumaa, C. Reducing Children’s Obesity in the Age of Telehealth and AI/IoT Technologies in Gulf Countries. Systems 2022, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIHR Imperial Biomedical Research Centre. Type 2 Diabetes Can Be Predicted 10 Years Ahead Using AI. 2024. Available online: https://imperialbrc.nihr.ac.uk/2024/11/18/type-2-diabetes-can-be-predicted-10-years-ahead-using-ai/ (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- Kovatchev, B.P.; Colmegna, P.; Pavan, J.; Diaz Castañeda, J.L.; Villa-Tamayo, M.F.; Koravi, C.L.K.; Santini, G.; Alix, C.; Stumpf, M.; Brown, S.A. Human-machine co-adaptation to automated insulin delivery: A randomised clinical trial using digital twin technology. NPJ Digit. Med. 2025, 8, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagiotou, M.; Strømmen, K.; Brigato, L.; de Galan, B.E.; Mougiakakou, S. Role of artificial intelligence in enhancing insulin recommendations and therapy outcomes. Diabetologie 2025, 21, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Diabetes Federation. Kids and Diabetes in Schools. Promoting Diabetes Education for a Healthy Tomorrow. Available online: https://kids.idf.org/ (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- Alves Abrantes, J.J.P.; Veríssimo de Azevedo, J.C.; Fernandes, F.L.; Duarte Almeida, V.; Custódio De Oliveira, L.A.; Ferreira de Oliveira, M.T.; Ferreira de Oliveira, M.T.; Galvão De Araújo, J.M.; Lanza, D.C.F.; Bezerra, F.L.; et al. Viruses as a potential environmental trigger of type 1 diabetes mellitus (Review). Biomed. Rep. 2024, 20, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, E.L.; Dayan, C.M.; Chatenoud, L.; Sumnik, Z.; Simmons, K.M.; Szypowska, A.; Gitelman, S.E.; Knecht, L.A.; Niemoeller, E.; Tian, W.; et al. Teplizumab and β-Cell Function in Newly Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2151–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritschel, T.K.S.; Reenberg, A.T.; Lindkvist, E.B.; Laugesen, C.; Svensson, J.; Ranjan, A.G.; Nørgaard, K.; Dammann, B.; Jørgensen, J.B. A one-size-fits-all artificial pancreas for people with type 1 diabetes based on physiological insight and feedback control. In Proceedings of the 2023 European Control Conference (ECC), Bucharest, Romania, 13–16 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kioulaphides, S.; García, A.J. Encapsulation and immune protection for type 1 diabetes cell therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2024, 207, 115205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Masot, R.; Jiménez-Muñoz, M.; Herrador-López, M.; Navas-López, V.M.; Obis, E.; Jové, M.; Pamplona, R.; Nestares, T. Metabolomic Profiling in Children with Celiac Disease: Beyond the Gluten-Free Diet. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saviano, A.; Petruzziello, C.; Brigida, M.; Morabito Loprete, M.R.; Savioli, G.; Migneco, A.; Ojetti, V. Gut Microbiota Alteration and Its Modulation with Probiotics in Celiac Disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirtaş Güner, D.; Baskın, K. Allergic and immunologic evaluation of children with celiac disease. Front. Pediatr. 2025, 13, 1568174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipasquale, V.; Romano, C. New Therapeutic Challenges in Pediatric Gastroenterology: A Narrative Review. Healthcare 2025, 13, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huey, S.L.; Mehta, N.H.; Steinhouse, R.S.; Jin, Y.; Kibbee, M.; Kuriyan, R.; Finkelstein, J.L.; Mehta, S. Precision nutrition-based interventions for the management of obesity in children and adolescents up to the age of 19 years. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2025, 1, CD015877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fachal, C.V.; Fernández-González, S.M.; Moreno-Álvarez, A.; Solar-Boga, A. Nutritional Screening Tools in the Pediatric Population: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spriggs, M. (Children and bioethics: Clarifying consent and assent in medical and research settings. Br. Med. Bull. 2023, 145, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Lázaro, D.; Seco-Calvo, J. Nutrition, Nutritional Status and Functionality. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelms, C.L.; Shaw, V.; Greenbaum, L.A.; Anderson, C.; Desloovere, A.; Haffner, D.; Oosterveld, M.J.S.; Paglialonga, F.; Polderman, N.; Qizalbash, L.; et al. Assessment of nutritional status in children with kidney diseases-clinical practice recommendations from the Pediatric Renal Nutrition Taskforce. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2021, 36, 995–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Matonti, L.; Blasetti, A.; Chiarelli, F. Nutrition and growth in children. Minerva Pediatr. 2020, 72, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dable-Tupas, G.; Talampas-Abundo, M.D.; Abundo, I.C.; Derecho, C.M. Nutrigenomics in the management and prevention of malnutrition, stunting, and other nutritional disorders. In Drug Discovery Update, Role of Nutrigenomics in Modern-Day Healthcare and Drug Discovery; Dable-Tupas, G., Egbuna, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 147–175. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, A.; Sherman, J.; Fewtrell, M. Postdischarge Nutrition in Preterm Infants. Neoreviews 2022, 23, e541–e557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo, N.; Alashkar Alhamwe, B.; Caraballo, L.; Ding, M.; Ferrante, A.; Garn, H.; Garssen, J.; Hii, C.S.; Irvine, J.; Llinás-Caballero, K.; et al. Perinatal and Early-Life Nutrition, Epigenetics, and Allergy. Nutrients 2021, 13, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchkov, S.; Lustig, R.H.; Escobedo-Monge, M.F.; Blokh, S.; Andronova, N.; Goryacheva, O.; Moyseyak, M.B.; Vlasov, T.; Polyakova, V.; Antonova, E.; et al. Personalized and precision medicine as a health-care model of the next step generation through translational applications of individualized nutrition- and food design-driven resources. Glob. Transl. Med. 2025, 4, 60–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.H.; Anthony, J.C.; Carvajal, R.; Chae, L.; Khoo, C.S.H.; Latulippe, M.E.; Matusheski, N.V.; McClung, H.L.; Rozga, M.; Schmid, C.H.; et al. Perspective: Guiding Principles for the Implementation of Personalized Nutrition Approaches That Benefit Health and Function. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agne, I.; Gedrich, K. Personalized dietary recommendations for obese individuals—A comparison of ChatGPT and the Food4Me algorithm. Clin. Nutr. Open Sci. 2024, 56, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Food Programme. Available online: https://www.wfp.org/news/unicef-wfp-and-who-join-forces-global-efforts-improve-nutrition-children-and-women (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Martínez-González, M.A.; Kim, H.S.; Prakash, V.; Ramos-Lopez, O.; Zotor, F.; Martinez, J.A. Personalised, population and planetary nutrition for precision health. BMJ Nutr. Prev. Health 2021, 4, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostoni, C.; Boccia, S.; Banni, S.; Mannucci, P.M.; Astrup, A. Sustainable and personalized nutrition: From earth health to public health. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 86, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo-Monge, M.F.; Parodi-Román, J.; Escobedo-Monge, M.A.; Marugán-Miguelsanz, J.M. The Biological Value of Proteins for Pediatric Growth and Development: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röttger-Wirtz, S.; De Boer, A. Personalised Nutrition: The EU’s Fragmented Legal Landscape and the Overlooked Implications of EU Food Law. Eur. J. Risk Regul. 2021, 12, 212–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CORDIS European Comission. Personalized Nutrition. Available online: https://cordis.europa.eu/programme/id/H2020_DT-SFS-14-2018 (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- Rogus, S.; Lurie, P. Personalized nutrition: Aligning science, regulation, and marketing. Health Aff. Sch. 2024, 2, qxae107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study/Taxa | Disease/ Outcome | Type of Evidence | Population | Key Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEDDY Study (The Environmental Determinants of Diabetes in the Young) | Type 1 Diabetes (T1DM) | Longitudinal; microbiome sampling from birth in genetically at-risk children | 8676 children (United States, European Union) | Microbiome changes (e.g., reduction in Bifidobacteria) precede autoantibody appearance | [13] |
| DIABIMMUNEStudy | Autoimmunity, allergies | Prospective birth cohort; detailed microbiome profiling in high vs. low disease incidence regions | Finland, Estonia, Russia | Early microbial diversity and specific strains (e.g., Bacteroides dorei) associated with T1DM risk | [14,15] |
| Bacteroides fragilis and Bifidobacterium spp. | Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), depression | Experimental: Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT) and probiotic administration from ASD children into mice | ASD vs. neurotypical children | FMT from ASD children induces behavioral changes in mice; probiotic strains reverse some effects | [16,17] |
| COPSAC (Copenhagen Prospective Study on Asthma in Childhood) | Asthma, allergies | Longitudinal cohort; microbiome profiling and early-life exposures | 700+ infants | Early Streptococcus colonization linked to wheezing and asthma risk; diversity protective | [18] |
| Ruminococcus gnavus, Escherichia coli | Crohn’s disease (early onset) | Longitudinal microbiome tracking and flare-up correlation | Pediatric Crohn’s cohorts | R. gnavus bloom precedes flare-ups; E. coli expansion seen during inflammation | [19,20] |
| Gut bacteria | Malnutrition, stunting | Gnotobiotic mouse models colonized with microbiota from malnourished vs. healthy infants | Malnourished Bangladeshi children | Transfer of dysbiotic microbiota causes growth impairment in mice; supplementation with defined strains rescues growth | [21] |
| Study | Benefits | Drawbacks | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| TEDDY (The Environmental Determinants of Diabetes in the Young) |
|
| [13] |
| DIABIMMUNE (Hygiene Hypothesis and Autoimmunity Study) |
|
| [14,15] |
| COPSAC (Copenhagen Prospective Studies on Asthma in Childhood) |
|
| [18] |
| Intervention | TEDDY Insight | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Exclusive breastfeeding ≥ 6 months | Enhances microbial diversity, delays autoimmunity | Risk of islet autoimmunity |
| Introduce solids at 4–6 months | Supports balanced microbiome maturation | Risk of T1DM |
| Avoid early antibiotics | Preserves protective gut bacteria | Autoantibody risk |
| High-fiber, SCFA-promoting foods | Enhances immune-regulatory metabolites | T1DM marker development |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Escobedo-Monge, M.; Lustig, R.H.; Suchkov, S.; Blokh, S.; Andronova, N.; Goryacheva, O.; Moyseyak, M.B.; Vlasov, T.; Solís Herrera, A.; Polyakova, V.; et al. Personalized Nutrition in Pediatric Chronic Diseases. Metabolites 2025, 15, 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15100653
Escobedo-Monge M, Lustig RH, Suchkov S, Blokh S, Andronova N, Goryacheva O, Moyseyak MB, Vlasov T, Solís Herrera A, Polyakova V, et al. Personalized Nutrition in Pediatric Chronic Diseases. Metabolites. 2025; 15(10):653. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15100653
Chicago/Turabian StyleEscobedo-Monge, Marlene, Robert H. Lustig, Sergey Suchkov, Sofia Blokh, Natalya Andronova, Olga Goryacheva, Marina Borisovna Moyseyak, Timur Vlasov, Arturo Solís Herrera, Veronika Polyakova, and et al. 2025. "Personalized Nutrition in Pediatric Chronic Diseases" Metabolites 15, no. 10: 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15100653
APA StyleEscobedo-Monge, M., Lustig, R. H., Suchkov, S., Blokh, S., Andronova, N., Goryacheva, O., Moyseyak, M. B., Vlasov, T., Solís Herrera, A., Polyakova, V., Antonova, E., & Tuykavin, A. (2025). Personalized Nutrition in Pediatric Chronic Diseases. Metabolites, 15(10), 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15100653







