Application of Eight Machine Learning Algorithms in the Establishment of Infertility and Pregnancy Diagnostic Models: A Comprehensive Analysis of Amino Acid and Carnitine Metabolism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
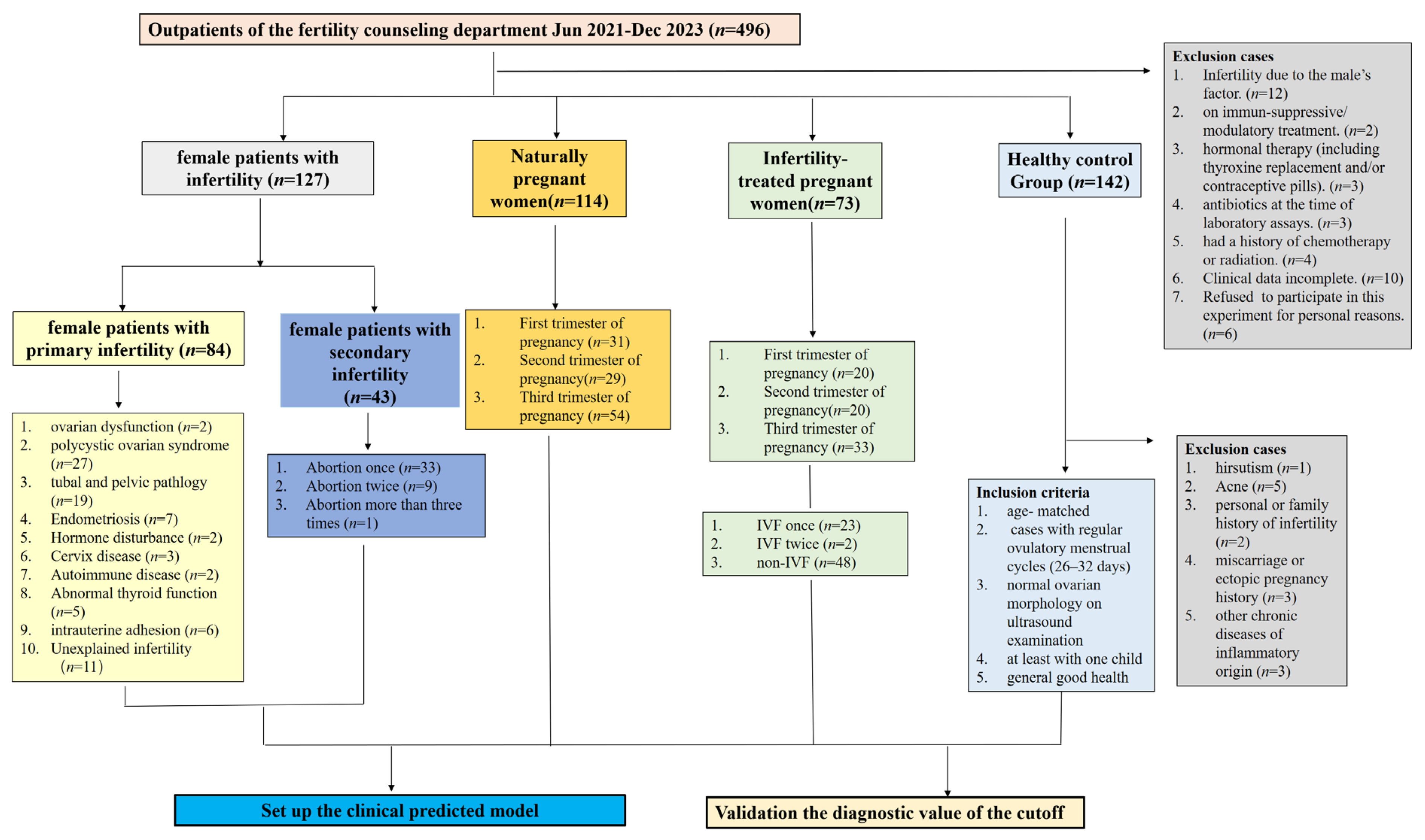
2.1. Participants
2.2. Sera Preparation
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. MS Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analyses
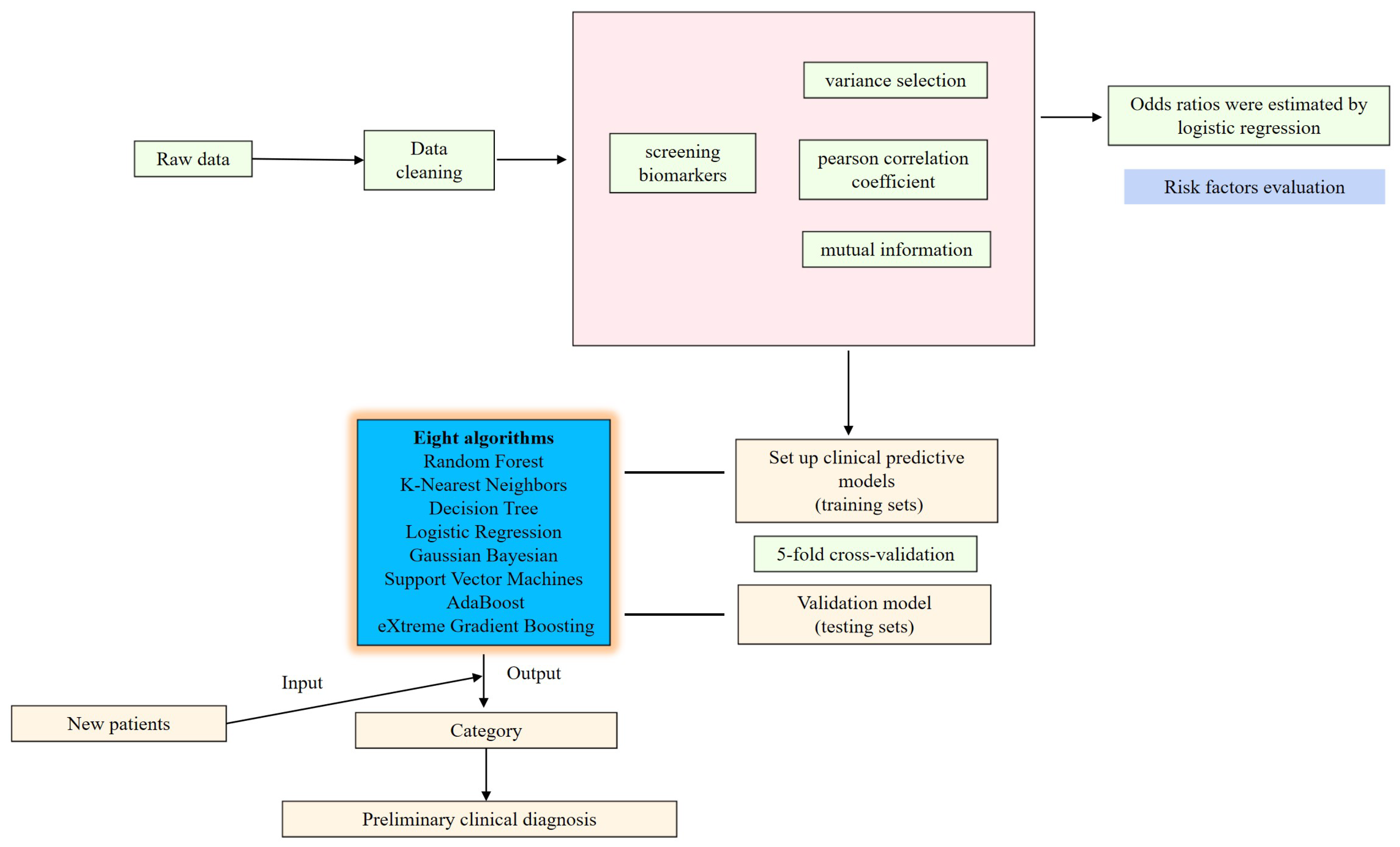
2.6. Establishment of Diagnostic Models
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
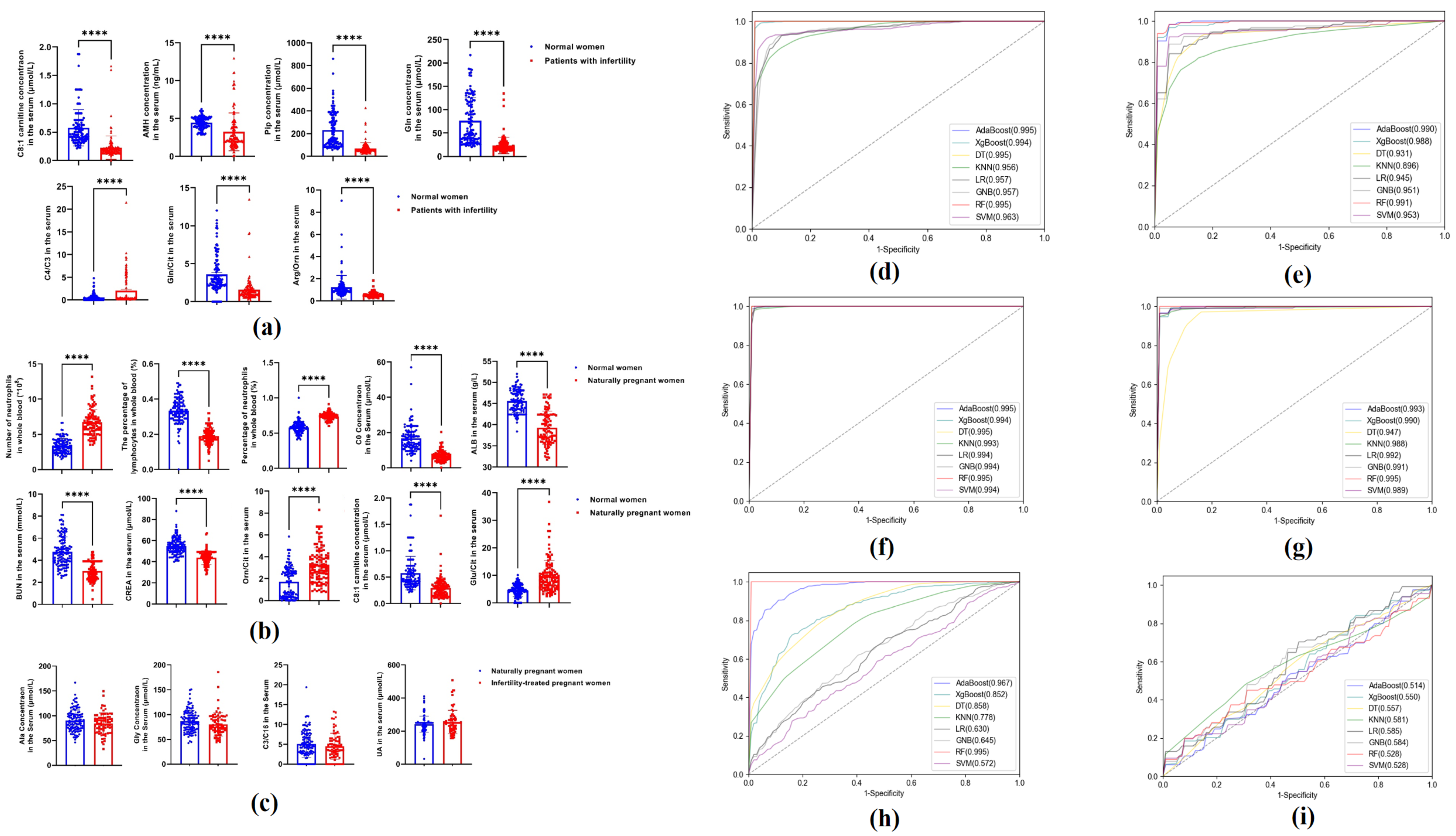
3.2. Distribution of the Measured Indicators in Each Group
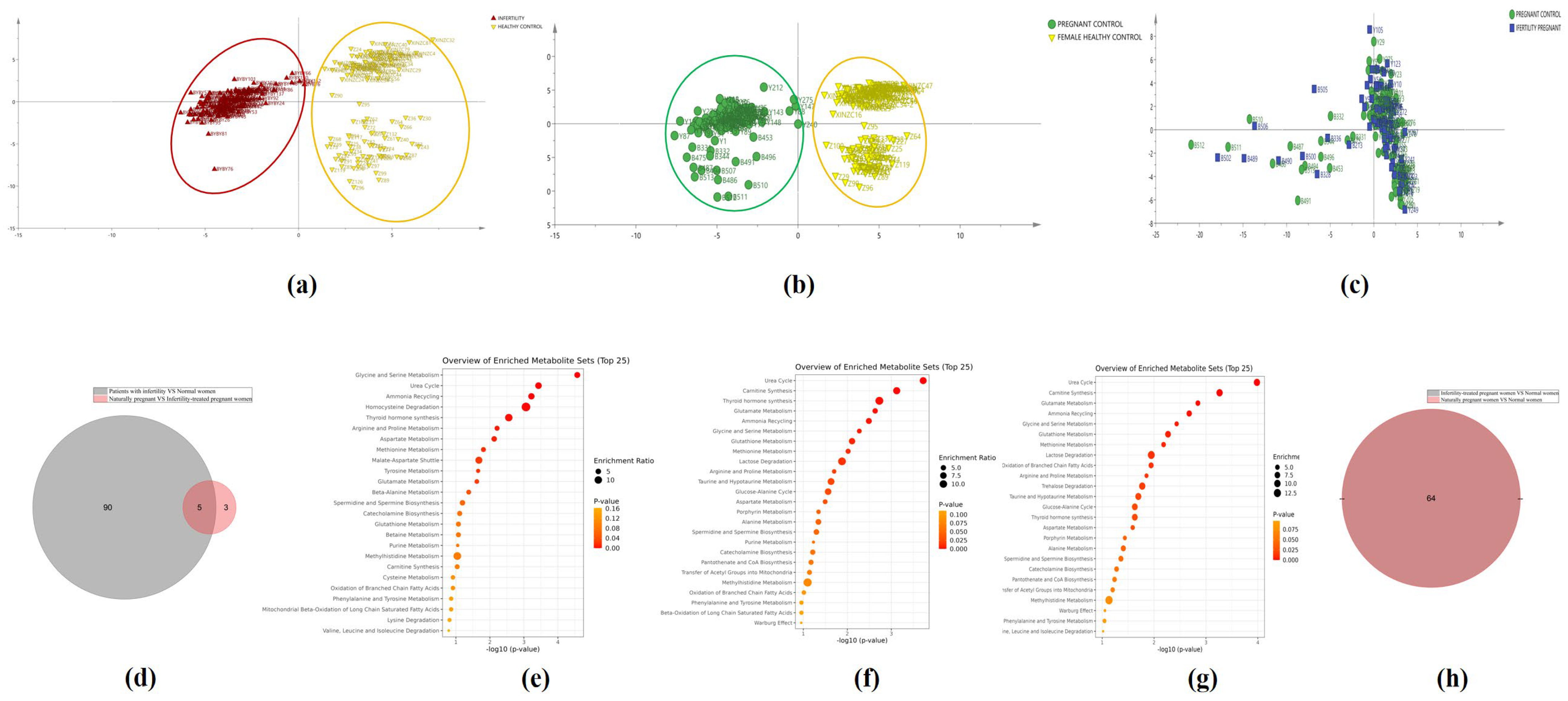
3.3. Metabolic Pathways
3.4. Performance Evaluation of Candidate Indices Using Classification Algorithm
3.5. Selected Indices as Independent Predictors of Infertility in Women
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bozhedomov, V.A.; Shomarufov, A.B.; Bozhedomova, G.E.; Okhobotov, D.A.; Kamalov, D.M.; Kamalov, A.A. Varicocele and reproductive function: Epidemiology and infertility risk (the eamination of 3632 patients). Urologiia 2021, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.D.; Fantus, R.J.; Cohen, A.J.; Wan, V.; Hudnall, M.T.; Pham, M.; Brannigan, R.E.; Halpern, J.A. Unmet financial burden of infertility care and the impact of state insurance mandates in the United States: Analysis from a popular crowdfunding platform. Fertil. Steril. 2021, 116, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farquhar, C.M.; Bhattacharya, S.; Repping, S.; Mastenbroek, S.; Kamath, M.S.; Marjoribanks, J.; Boivin, J. Female subfertility. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Jiang, Q.; Yin, Y. Increased risk of ovarian and breast malignancies in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A review article. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2023, 69, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Yang, L.; Guo, Z.; Yao, N.; Zhang, S.; Pu, P. Obesity and its impact on female reproductive health: Unraveling the connections. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1326546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salhi, S.; Rahim, A.; Chentouf, M.; Harrak, H.; Bister, J.L.; Hamidallah, N.; El Amiri, B. Reproductive Enhancement through Phytochemical Characteristics and Biological Activities of Date Palm Pollen: A Comprehensive Review on Potential Mechanism Pathways. Metabolites 2024, 14, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikulkova, M.; Abdrabou, W.; Carlton, J.M.; Idaghdour, Y. Exploiting integrative metabolomics to study host-parasite interactions in Plasmodium infections. Trends Parasitol. 2024, 40, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäntyselkä, S.; Kolari, K.; Baumert, P.; Ylä-Outinen, L.; Kuikka, L.; Lahtonen, S.; Permi, P.; Wackerhage, H.; Kalenius, E.; Kivelä, R.; et al. Serine synthesis pathway enzyme PHGDH is critical for muscle cell biomass, anabolic metabolism, and mTORC1 signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 326, E73–E91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameni, M.; Musaigwa, F.; Kamguia, L.M.; Kamdem, S.D.; Mbanya, G.; Lamberton, P.H.L.; Komguep Nono, J. Harnessing Schistosoma-associated metabolite changes in the human host to identify biomarkers of infection and morbidity: Where are we and what should we do next? PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lindheim, S.R.; Qi, J.; Li, X.; Ding, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wei, D.; et al. Influence of metabolic syndrome on female fertility and in vitro fertilization outcomes in PCOS women. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 221, 138.e1–138.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salliss, M.E.; Farland, L.V.; Mahnert, N.D.; Herbst-Kralovetz, M.M. The role of gut and genital microbiota and the estrobolome in endometriosis, infertility and chronic pelvic pain. Hum. Reprod. Update 2021, 28, 92–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnavard, A.; Chatterjee, R.; Wen, H.; Gaylord, C.; Mugusi, S.; Klatt, K.C.; Smith, E.R. Molecular epidemiology of pregnancy using omics data: Advances, success stories, and challenges. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskind, N.E.; McRae, C.; Sharma, V.; Fisher, J. Understanding subfertility at a molecular level in the female through the application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. Hum. Reprod. Update 2011, 17, 228–241. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Ren, J.; Ren, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, X. Using metabolomics and proteomics to identify the potential urine biomarkers for prediction and diagnosis of gestational diabetes. EBioMedicine 2024, 101, 105008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, L.; Testa, L.; Crovetto, F.; Crispi, F. 10. Role of high dimensional technology in preeclampsia (omics in preeclampsia). Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2024, 92, 102427. [Google Scholar]
- Toadere, T.M.; Ţichindeleanu, A.; Bondor, D.A.; Topor, I.; Trella, Ş.E.; Nenu, I. Bridging the divide: Unveiling mutual immunological pathways of cancer and pregnancy. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 73, 793–807. [Google Scholar]
- Au, L.S.; Feng, Q.; Shingshetty, L.; Maheshwari, A.; Mol, B.W. Evaluating prognosis in unexplained infertility. Fertil. Steril. 2024, 121, 717–729. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, R.S.; Khan, Z.; Zhao, Y. Fertility Preservation in Women: Indications and Options for Therapy. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020, 95, 770–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirguis, M.S.; Arribas, E.M.; Kapoor, M.M.; Patel, M.M.; Perez, F.; Nia, E.S.; Ding, Q.; Moseley, T.W.; Adrada, B.E. Multimodality Imaging of Benign and Malignant Diseases of the Nipple-Areolar Complex. RadioGraphics 2024, 44, e230113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedars, M.I. Evaluation of Female Fertility-AMH and Ovarian Reserve Testing. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greener, J.G.; Kandathil, S.M.; Moffat, L.; Jones, D.T. A guide to machine learning for biologists. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, R.C. Machine Learning in Medicine. Circulation 2015, 132, 1920–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handelman, G.S.; Kok, H.K.; Chandra, R.V.; Razavi, A.H.; Lee, M.J.; Asadi, H. eDoctor: Machine learning and the future of medicine. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.W.; Choi, J.W.; Shin, E.H. Machine learning model for predicting malaria using clinical information. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 129, 104151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, M.K.; Adeli, K. Physiological and metabolic adaptations in pregnancy: Importance of trimester-specific reference intervals to investigate maternal health and complications. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2022, 59, 76–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hya, K.M.; Huang, Z.; Chua, C.M.S.; Shorey, S. Experiences of men undergoing assisted reproductive technology: A qualitative systematic review. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2024, 165, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Singh, A.K. Reactive oxygen species in seminal plasma as a cause of male infertility. J. Gynecol. Obstet. Hum. Reprod. 2018, 47, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, S.A.; Kallen, A.N. Diagnosis and Management of Infertility: A Review. JAMA 2021, 326, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Chen, S.R. Molecular genetics of infertility: Loss-of-function mutations in humans and corresponding knockout/mutated mice. Hum. Reprod. Update 2021, 27, 154–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.O.; Turk, A.; Kunej, T. Towards a Multi-Omics of Male Infertility. World J. Men’s Health 2023, 41, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennewein, M.F.; Abu-Raya, B.; Jiang, Y.; Alter, G.; Marchant, A. Transfer of maternal immunity and programming of the newborn immune system. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwatani, Y.; Amino, N.; Kabutomori, O.; Kaneda, T.; Tanizawa, O.; Miyai, K. Peripheral large granular lymphocytes in normal pregnant and postpartum women: Decrease in late pregnancy and dynamic change in the puerperium. J. Reprod. Immunol. 1989, 16, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okosieme, O.E.; Agrawal, M.; Usman, D.; Evans, C. Method-dependent variation in TSH and FT4 reference intervals in pregnancy: A systematic review. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2021, 58, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.; Compagno, M.; Pihl, S.; Strevens, H.; Persson, B.; Wetterö, J.; Nilsson, B.; Sjöwall, C. Variation of Complement Protein Levels in Maternal Plasma and Umbilical Cord Blood during Normal Pregnancy: An Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalew, M.; Adane, B.; Damtie, Y.; Kefale, B.; Arefaynie, M.; Yasin, T. Trend and determinants of anemia change among pregnant and/or lactating women in Ethiopia: A multivariate decomposition analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, R.; Sun, J.; Yoo, H.; Kim, S.; Cho, Y.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.W.; Chung, J.H.; Oh, S.Y.; Lee, S.Y. A Prospective Study of Serum Trace Elements in Healthy Korean Pregnant Women. Nutrients 2016, 8, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, K.L.; Hellmuth, C.; Uhl, O.; Buss, C.; Wadhwa, P.D.; Koletzko, B.; Entringer, S. Longitudinal Metabolomic Profiling of Amino Acids and Lipids across Healthy Pregnancy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manta-Vogli, P.D.; Schulpis, K.H.; Dotsikas, Y.; Loukas, Y.L. The significant role of carnitine and fatty acids during pregnancy, lactation and perinatal period. Nutritional support in specific groups of pregnant women. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 2337–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manousopoulou, A.; Al-Daghri, N.M.; Sabico, S.; Garay-Baquero, D.J.; Teng, J.; Alenad, A.; Alokail, M.S.; Athanasopoulos, N.; Deligeoroglou, E.; Chrousos, G.P.; et al. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and Insulin Physiology: An Observational Quantitative Serum Proteomics Study in Adolescent, Normal-Weight Females. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2019, 13, e1800184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arffman, R.K.; Saraswat, M.; Joenväärä, S.; Khatun, M.; Agarwal, R.; Tohmola, T.; Sundström-Poromaa, I.; Renkonen, R.; Piltonen, T.T. Thromboinflammatory changes in plasma proteome of pregnant women with PCOS detected by quantitative label-free proteomics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumford, S.L.; Chavarro, J.E.; Zhang, C.; Perkins, N.J.; Sjaarda, L.A.; Pollack, A.Z.; Schliep, K.C.; Michels, K.A.; Zarek, S.M.; Plowden, T.C.; et al. Dietary fat intake and reproductive hormone concentrations and ovulation in regularly menstruating women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somigliana, E.; Paffoni, A.; Busnelli, A.; Filippi, F.; Pagliardini, L.; Vigano, P.; Vercellini, P. Age-related infertility and unexplained infertility: An intricate clinical dilemma. Hum. Reprod. 2016, 31, 1390–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junovich, G.; Azpiroz, A.; Incera, E.; Ferrer, C.; Pasqualini, A.; Gutierrez, G. Endometrial CD16+ and CD16− NK cell count in fertility and unexplained infertility. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2013, 70, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Mao, X.; Lei, H.; Dong, B.; Guo, D.; Zheng, B.; Sun, P. Peripheral Blood Inflammatory-Immune Cells as a Predictor of Infertility in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. J. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 13, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Algorithms | Sensitivity | Specificity | Accuracy | PPV | NPV | MCC | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AdaBoost | Training set | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 0.995 (0.986–1.000) |
| Test set | 97.60% | 97.45% | 97.51% | 97.58% | 97.45% | 95.03% | 0.990 (0.978–1.000) | |
| XGBoost | Training set | 97.24% | 99.33% | 98.24% | 99.41% | 97.02% | 96.50% | 0.994 (0.984–1.000) |
| Test set | 92.16% | 95.78% | 93.76% | 95.87% | 91.82% | 87.81% | 0.988 (0.974–1.000) | |
| DT | Training set | 99.80% | 99.77% | 99.79% | 99.81% | 99.79% | 99.58% | 0.995 (0.986–1.000) |
| Test set | 91.61% | 94.26% | 92.52% | 94.53% | 91.14% | 85.76% | 0.931 (0.898–0.964) | |
| KNN | Training set | 82.89% | 93.85% | 88.07% | 93.79% | 83.10% | 76.81% | 0.956 (0.930–0.982) |
| Test set | 77.67% | 90.23% | 83.43% | 90.27% | 78.16% | 68.16% | 0.896 (0.856–0.936) | |
| LR | Training set | 92.31% | 89.67% | 91.08% | 90.90% | 91.32% | 82.10% | 0.957 (0.931–0.983) |
| Test set | 90.31% | 86.24% | 87.97% | 87.99% | 88.50% | 76.51% | 0.945 (0.916–0.974) | |
| GNB | Training set | 96.86% | 66.64% | 82.57% | 76.44% | 94.95% | 67.32% | 0.957 (0.931–0.983) |
| Test set | 96.17% | 69.72% | 83.38% | 77.79% | 94.26% | 68.87% | 0.951 (0.923–0.979) | |
| RF | Training set | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 0.995 (0.986–1.000) |
| Test set | 96.89% | 94.93% | 95.84% | 95.27% | 96.52% | 91.80% | 0.991 (0.979–1.000) | |
| SVM | Training set | 92.33% | 94.29% | 93.26% | 94.78% | 91.69% | 86.54% | 0.963 (0.939–0.987) |
| Test set | 90.21% | 94.94% | 92.13% | 95.02% | 89.36% | 84.76% | 0.953 (0.926–0.980) |
| Algorithms | Sensitivity | Specificity | Accuracy | PPV | NPV | MCC | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AdaBoost | Training set | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 0.995 (0.986–1.000) |
| Test set | 99.13% | 97.21% | 98.23% | 97.62% | 99.13% | 96.54% | 0.993 (0.982–1.000) | |
| XGBoost | Training set | 98.88% | 99.14% | 99.01% | 99.10% | 98.92% | 98.02% | 0.994 (0.984–1.000) |
| Test set | 96.44% | 95.50% | 96.02% | 95.71% | 96.73% | 92.19% | 0.990 (0.977–1.000) | |
| DT | Training set | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 0.995 (0.986–1.000) |
| Test set | 96.65% | 93.03% | 94.71% | 93.46% | 96.49% | 89.81% | 0.947 (0.917–0.977) | |
| KNN | Training set | 96.23% | 99.12% | 97.69% | 99.09% | 96.39% | 95.41% | 0.993 (0.982–1.000) |
| Test set | 94.44% | 98.22% | 96.44% | 98.14% | 95.11% | 92.96% | 0.988 (0.974–1.000) | |
| LR | Training set | 99.12% | 97.79% | 98.46% | 97.83% | 99.11% | 96.92% | 0.994 (0.984–1.000) |
| Test set | 99.13% | 97.21% | 98.23% | 97.62% | 99.13% | 96.54% | 0.992 (0.980–1.000) | |
| GNB | Training set | 98.24% | 98.45% | 98.35% | 98.46% | 98.25% | 96.70% | 0.994 (0.984–1.000) |
| Test set | 96.39% | 98.08% | 97.34% | 98.42% | 96.83% | 94.86% | 0.991 (0.979–1.000) | |
| RF | Training set | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 0.995 (0.986–1.000) |
| Test set | 96.44% | 97.21% | 96.91% | 97.62% | 96.83% | 94.05% | 0.995 (0.986–1.000) | |
| SVM | Training set | 99.77% | 99.34% | 99.56% | 99.34% | 99.79% | 99.12% | 0.994 (0.984–1.000) |
| Test set | 98.26% | 96.55% | 97.33% | 96.47% | 98.26% | 98.26% | 0.989 (0.975–1.000) |
| Algorithms | Sensitivity | Specificity | Accuracy | PPV | NPV | MCC | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AdaBoost | Training set | 94.02% | 84.26% | 90.19% | 90.23% | 90.11% | 79.30% | 0.967 (0.943–0.991) |
| Test set | 64.87% | 33.02% | 52.15% | 60.10% | 37.78% | −2.12% | 0.514 (0.429–0.599) | |
| XGBoost | Training set | 90.69% | 56.89% | 77.43% | 76.52% | 79.83% | 51.76% | 0.852 (0.799–0.905) |
| Test set | 77.04% | 33.52% | 59.72% | 64.34% | 47.89% | 11.36% | 0.550 (0.466–0.634) | |
| DT | Training set | 87.88% | 67.64% | 79.84% | 81.84% | 81.86% | 59.15% | 0.858 (0.806–0.910) |
| Test set | 75.69% | 31.84% | 31.84% | 62.97% | 49.81% | 9.68% | 0.557 (0.473–0.641) | |
| KNN | Training set | 82.28% | 57.56% | 72.58% | 75.02% | 67.89% | 41.34% | 0.778 (0.713–0.843) |
| Test set | 71.89% | 37.88% | 58.07% | 64.63% | 45.40% | 9.83% | 0.581 (0.498–0.664) | |
| LR | Training set | 87.80% | 22.93% | 62.37% | 63.81% | 55.33% | 14.30% | 0.630 (0.550–0.710) |
| Test set | 87.56% | 20.51% | 61.34% | 62.90% | 58.74% | 13.17% | 0.585 (0.502–0.668) | |
| GNB | Training set | 88.06% | 28.44% | 64.65% | 65.61% | 60.33% | 20.65% | 0.645 (0.566–0.724) |
| Test set | 87.39% | 25.69% | 63.49% | 64.76% | 55.16% | 16.07% | 0.584 (0.501–0.667) | |
| RF | Training set | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 0.995 (0.986–1.000) |
| Test set | 72.01% | 23.84% | 52.67% | 58.97% | 38.51% | −3.44% | 0.528 (0.443–0.613) | |
| SVM | Training set | 99.10% | 7.41% | 63.17% | 62.42% | 0.572 (0.489–0.655) | ||
| Test set | 96.59% | 4.03% | 60.23% | 60.97% | 0.528 (0.443–0.613) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Zhou, L.; Hao, X.; Yang, L.; Ding, L.; Xing, R.; Hu, J.; Wang, F.; Zhai, X.; Guo, Y.; et al. Application of Eight Machine Learning Algorithms in the Establishment of Infertility and Pregnancy Diagnostic Models: A Comprehensive Analysis of Amino Acid and Carnitine Metabolism. Metabolites 2024, 14, 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14090492
Zhang R, Zhou L, Hao X, Yang L, Ding L, Xing R, Hu J, Wang F, Zhai X, Guo Y, et al. Application of Eight Machine Learning Algorithms in the Establishment of Infertility and Pregnancy Diagnostic Models: A Comprehensive Analysis of Amino Acid and Carnitine Metabolism. Metabolites. 2024; 14(9):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14090492
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Rui, Lei Zhou, Xiaoyan Hao, Liu Yang, Li Ding, Ruiqing Xing, Juanjuan Hu, Fengjuan Wang, Xiaonan Zhai, Yuanbing Guo, and et al. 2024. "Application of Eight Machine Learning Algorithms in the Establishment of Infertility and Pregnancy Diagnostic Models: A Comprehensive Analysis of Amino Acid and Carnitine Metabolism" Metabolites 14, no. 9: 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14090492
APA StyleZhang, R., Zhou, L., Hao, X., Yang, L., Ding, L., Xing, R., Hu, J., Wang, F., Zhai, X., Guo, Y., Cai, Z., Gao, J., Yang, J., & Liu, J. (2024). Application of Eight Machine Learning Algorithms in the Establishment of Infertility and Pregnancy Diagnostic Models: A Comprehensive Analysis of Amino Acid and Carnitine Metabolism. Metabolites, 14(9), 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14090492






