The Impact of Metabolic Syndrome on Heart Failure in Young Korean Population: A Nationwide Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Database Source
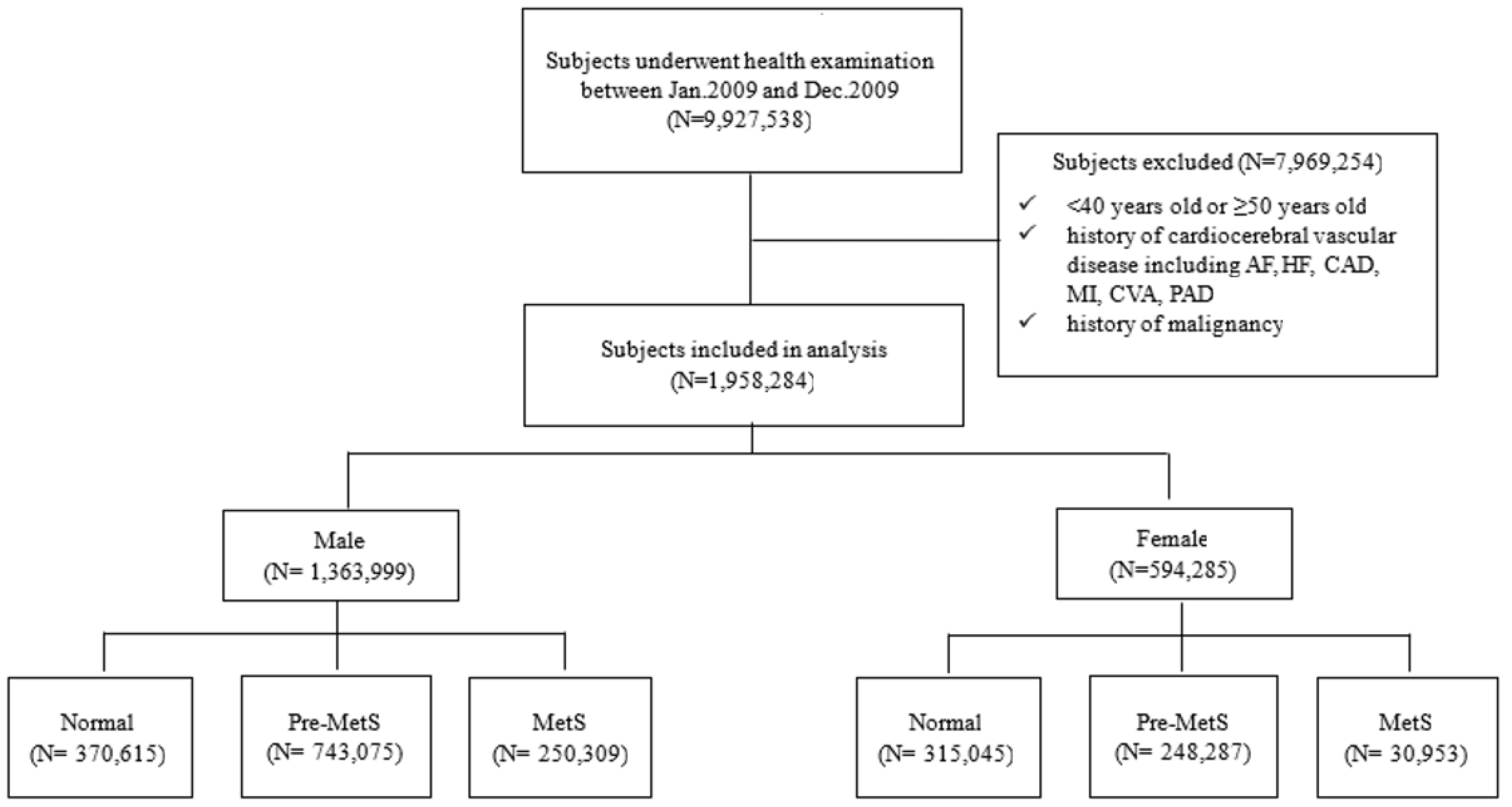
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Definitions of Variables
2.4. Primary Outcome and Follow-Up
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics and Prevalence of Metablic Syndrome (MetS)
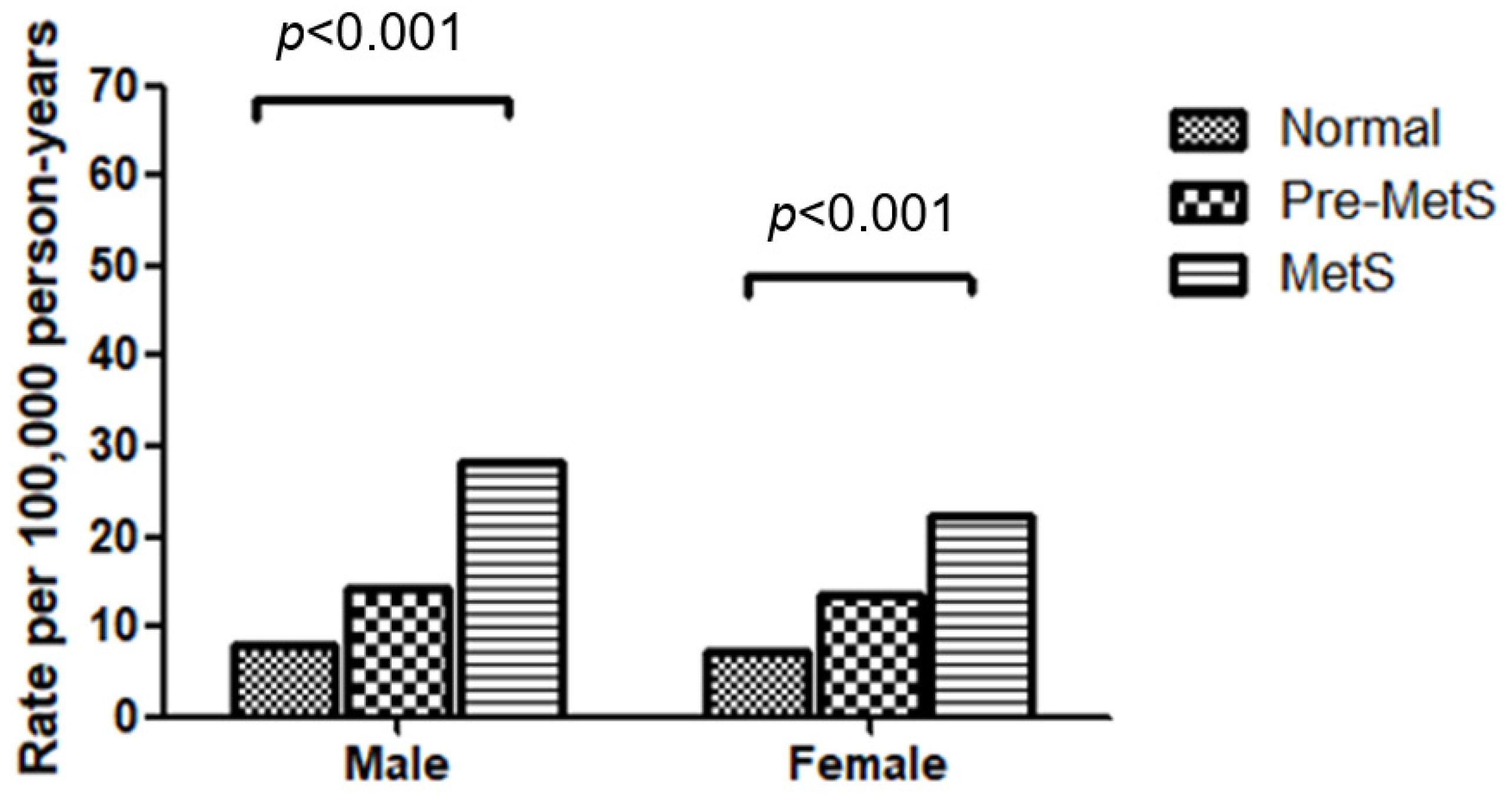
3.2. Incidence Rates of Heart Failure by Metabolic Syndrome Status and Demographic Factors
3.3. Effect of Metabolic Syndrome and Pre-Metabolic Syndrome on Heart Failure
3.4. Additional Risk Factors for Heart Failure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bozkurt, B.; Coats, A.J.; Tsutsui, H.; Abdelhamid, M.; Adamopoulos, S.; Albert, N.; Anker, S.D.; Atherton, J.; Bohm, M.; Butler, J.; et al. Universal Definition and Classification of Heart Failure: A Report of the Heart Failure Society of America, Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology, Japanese Heart Failure Society and Writing Committee of the Universal Definition of Heart Failure. J. Card. Fail. 2021, 23, 352–380. [Google Scholar]
- Ponikowski, P.; Anker, S.D.; AlHabib, K.F.; Cowie, M.R.; Force, T.L.; Hu, S.; Jaarsma, T.; Krum, H.; Rastogi, V.; Rohde, L.E.; et al. Heart failure: Preventing disease and death worldwide. ESC Heart Fail. 2014, 1, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komanduri, S.; Jadhao, Y.; Guduru, S.S.; Cheriyath, P.; Wert, Y. Prevalence and risk factors of heart failure in the USA: NHANES 2013–2014 epidemiological follow-up study. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect. 2017, 7, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Lip, G.Y.; Banerjee, A. Heart failure in East Asia. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2013, 9, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shamiri, M.Q. Heart failure in the Middle East. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2013, 9, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Park, J.J.; Lee, C.J.; Park, S.J.; Choi, J.O.; Choi, S.; Park, S.M.; Choi, E.Y.; Kim, E.J.; Yoo, B.S.; Kang, S.M.; et al. Heart Failure Statistics in Korea, 2020: A Report from the Korean Society of Heart Failure. Int. J. Heart Fail. 2021, 3, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarese, G.; Lund, L.H. Global Public Health Burden of Heart Failure. Card. Fail. Rev. 2017, 3, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Virani, S.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Delling, F.N.; Deo, R.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2018 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2018, 137, e67–e492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, M.N.; Kober, L.; Weeke, P.; Vasan, R.S.; Jeppesen, J.L.; Smith, J.G.; Gislason, G.H.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Andersson, C. Age-Specific Trends in Incidence, Mortality, and Comorbidities of Heart Failure in Denmark, 1995 to 2012. Circulation 2017, 135, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barasa, A.; Schaufelberger, M.; Lappas, G.; Swedberg, K.; Dellborg, M.; Rosengren, A. Heart failure in young adults: 20-year trends in hospitalization, aetiology, and case fatality in Sweden. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tromp, J.; Paniagua, S.M.A.; Lau, E.S.; Allen, N.B.; Blaha, M.J.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Hillege, H.L.; Lee, D.E.; Levy, D.; Vasan, R.S.; et al. Age dependent associations of risk factors with heart failure: Pooled population based cohort study. BMJ 2021, 372, n461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone-Filardi, P.; Savarese, G.; Scarano, M.; Cavazzina, R.; Trimarco, B.; Minneci, S.; Maggioni, A.P.; Tavazzi, L.; Tognoni, G.; Marchioli, R. Prognostic impact of metabolic syndrome in patients with chronic heart failure: Data from GISSI-HF trial. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 178, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, J.; Rodondi, N.; Zhu, Y.; Figaro, K.; Fazio, S.; Vaughan, D.E.; Satterfield, S.; Newman, A.B.; Goodpaster, B.; Bauer, D.C.; et al. Metabolic syndrome and the risk of cardiovascular disease in older adults. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sarnola, K.; Ruotsalainen, S.; Moilanen, L.; Lepisto, P.; Laakso, M.; Kuusisto, J. The metabolic syndrome predicts incident congestive heart failure: A 20-year follow-up study of elderly Finns. Atherosclerosis 2010, 210, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.E.; Gona, P.; Pencina, M.J.; Tu, J.V.; Austin, P.C.; Vasan, R.S.; Kannel, W.B.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Lee, D.S.; Levy, D. Discriminating clinical features of heart failure with preserved vs. reduced ejection fraction in the community. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 1734–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.E.; Kim, H.; Sung, J.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, M.S.; Han, S.W.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Ryu, K.H. The association between metabolic syndrome and heart failure in middle-aged men and women: Population-based study of 2 million individuals. Epidemiol. Health 2022, 44, e2022078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingelsson, E.; Arnlov, J.; Lind, L.; Sundstrom, J. Metabolic syndrome and risk for heart failure in middle-aged men. Heart 2006, 92, 1409–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regitz-Zagrosek, V. Sex and Gender Differences in Heart Failure. Int. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 2, 157–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.E.; Lyass, A.; Lee, D.S.; Vasan, R.S.; Kannel, W.B.; Larson, M.G.; Levy, D. Predictors of new-onset heart failure: Differences in preserved versus reduced ejection fraction. Circ. Heart Fail. 2013, 6, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regitz-Zagrosek, V.; Brokat, S.; Tschope, C. Role of gender in heart failure with normal left ventricular ejection fraction. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2007, 49, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, S.J.; Cuijpers, I.; Heymans, S.; Jones, E.A.V. Cellular and Molecular Differences between HFpEF and HFrEF: A Step Ahead in an Improved Pathological Understanding. Cells 2020, 9, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Shah, A.M.; Blaha, M.J.; Chang, P.P.; Rosamond, W.D.; Matsushita, K. Cigarettes smoking, cessation, and risk of heart failure with preserved and reduced ejection fraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 2298–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagiakrishnan, K.; Banach, M.; Ahmed, A.; Aronow, W.S. Complex relationship of obesity and obesity paradox in heart failure—Higher risk of developing heart failure and better outcomes in established heart failure. Ann. Med. 2016, 48, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzai, S.; Persits, I.; Martens, P.; Chen, P.H.; Estep, J.D.; Tang, W.H.W. Significance of adipose tissue quantity and distribution on obesity paradox in heart failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2023, 207, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, M.C.; Pizzolanti, G.; Torregrossa, V.; Misiano, G.; Milano, S.; Giordano, C. Visceral adiposity index (VAI) is predictive of an altered adipokine profile in patients with type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone-Filardi, P.; Paolillo, S.; Costanzo, P.; Savarese, G.; Trimarco, B.; Bonow, R.O. The role of metabolic syndrome in heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 2630–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witteles, R.M.; Fowler, M.B. Insulin-resistant cardiomyopathy clinical evidence, mechanisms, and treatment options. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putnam, K.; Shoemaker, R.; Yiannikouris, F.; Cassis, L.A. The renin-angiotensin system: A target of and contributor to dyslipidemias, altered glucose homeostasis, and hypertension of the metabolic syndrome. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 302, H1219–H1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterlin, A.; Počivavšek, K.; Petrovič, D.; Peterlin, B. The Role of microRNAs in Heart Failure: A Systematic Review. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 15, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candia, P.; Spinetti, G.; Specchia, C.; Sangalli, E.; Sala, L.; Uccellatore, A.; Lupini, S.; Genovese, S.; Matarese, G.; Ceriello, A. A unique plasma microRNA profile defines type 2 diabetes progression. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askin, L.; Tanriverdi, O. Is the microRNA-221/222 Cluster Ushering in a New Age of Cardiovascular Diseases? Cor Vasa 2023, 65, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verjans, R.; Peters, T.; Beaumont, F.J.; Leeuwen, R.; Herwaarden, T.; Verhesen, W.; Munts, C.; Bijnen, M.; Henkens, M.; Diez, J.; et al. MicroRNA-221/222 Family Counteracts Myocardial Fibrosis in Pressure Overload-Induced Heart Failure. Hypertension 2018, 71, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Males | Females | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal N = 370,615 (27.17) | Pre-MetS N = 743,075 (54.48) | MetS N = 250,309 (18.35) | p-Value | Normal N = 315,045 (53.01) | Pre-MetS N = 248,287 (41.78) | MetS N = 30,953 (5.21) | p-Value | |
| Smoking status | ||||||||
| Non-smoker | 108,206 (31.06) | 186,630 (53.57) | 53,559 (15.37) | <0.0001 | 292,085 (53.1) | 229,944 (41.8) | 28,067 (5.1) | <0.0001 |
| Ex-smoker | 72,032 (27.36) | 144,365 (54.83) | 46,911 (17.82) | 8790 (54.2) | 6502 (40.09) | 926 (5.71) | ||
| Current smoker | 187,975 (25.25) | 408,046 (54.8) | 148,575 (19.95) | 11,876 (49.43) | 10,383 (43.21) | 1769 (7.36) | ||
| Alcohol consumption | ||||||||
| No drink | 108,150 (30.88) | 185,583 (52.99) | 56,469 (16.12) | <0.0001 | 193,963 (52.16) | 157,877 (42.45) | 20,039 (5.39) | <0.0001 |
| 2–3 per month | 208,989 (27.17) | 419,430 (54.53) | 140,730 (18.3) | 103,714 (54.97) | 75,983 (40.27) | 8979 (4.76) | ||
| 1–4 per week | 40,330 (21.22) | 107,484 (56.54) | 42,287 (22.24) | 10,575 (50.06) | 9292 (43.99) | 1257 (5.95) | ||
| ≥5 per week | 8098 (21.03) | 22,170 (57.56) | 8247 (21.41) | 2046 (48.16) | 1918 (45.15) | 284 (6.69) | ||
| Exercise | ||||||||
| No exercise | 154,017 (26.61) | 316,334 (54.66) | 108,365 (18.73) | <0.0001 | 175,092 (52.96) | 138,610 (41.93) | 16,881 (5.11) | <0.0001 |
| 1–4 per week | 82,087 (26.98) | 165,111 (54.27) | 57,034 (18.75) | 62,212 (53.23) | 48,634 (41.61) | 6022 (5.15) | ||
| ≥5 per week | 130,735 (27.92) | 254,721 (54.41) | 82,736 (17.67) | 75,261 (52.8) | 59,411 (41.68) | 7868 (5.52) | ||
| Family history of hypertension | ||||||||
| Yes | 27,906 (21.25) | 71,696 (54.6) | 31,707 (24.15) | <0.0001 | 39,661 (48.91) | 35,768 (44.11) | 5662 (6.98) | <0.0001 |
| No | 237,651 (27.94) | 462,524 (54.38) | 150,405 (17.68) | 173,966 (54.23) | 131,137 (40.88) | 15,667 (4.88) | ||
| Family history of diabetes mellitus | ||||||||
| Yes | 29,463 (22.45) | 70,197 (53.49) | 31,570 (24.06) | <0.0001 | 33,355 (48.17) | 30,572 (44.15) | 5317 (7.68) | <0.0001 |
| No | 236,013 (27.76) | 463,762 (54.54) | 150,480 (17.7) | 180,136 (54.2) | 136,232 (40.99) | 16,003 (4.81) | ||
| Family history of stroke | ||||||||
| Yes | 14,615 (24.86) | 32,194 (54.77) | 11,975 (20.37) | 13,702 (49.64) | 12,125 (43.93) | 1776 (6.43) | <0.0001 | |
| No | 250,698 (27.19) | 501,498 (54.39) | 169,836 (18.42) | 199,573 (53.42) | 154,493 (41.35) | 19,519 (5.22) | ||
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | ||||||||
| <200 | 261,932 (33.5) | 411,862 (52.68) | 108,007 (13.82) | <0.0001 | 238,476 (55.15) | 177,102 (40.96) | 16,810 (3.89) | <0.0001 |
| 200–239 | 91,537 (20.99) | 248,664 (57.03) | 95,841 (21.98) | 66,388 (49.98) | 56,378 (42.44) | 10,070 (7.58) | ||
| >239 | 17,146 (11.73) | 82,549 (56.48) | 46,461 (31.79) | 10,181 (35.03) | 14,807 (50.95) | 4073 (14.02) | ||
| ALT (IU/L) | ||||||||
| <40 | 336,406 (32.08) | 577,298 (55.05) | 134,932 (12.87) | <0.0001 | 309,388 (53.86) | 239,051 (41.61) | 26,032 (4.53) | <0.0001 |
| 40–99 | 31,471 (11.08) | 151,745 (53.44) | 100,737 (35.48) | 4992 (28.5) | 8255 (47.13) | 4267 (24.36) | ||
| >100 | 2738 (8.72) | 14,032 (44.67) | 14,640 (46.61) | 665 (28.91) | 981 (42.65) | 654 (28.43) | ||
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | ||||||||
| <13.5(Male), <12(Female) | 23,528 (34.25) | 36,674 (53.38) | 8498 (12.37) | <0.0001 | 69,722 (52.48) | 57,487 (43.27) | 5639 (4.24) | <0.0001 |
| 13.5–17.5(Male), 12–15.5 (Female) | 344,900 (27.02) | 696,717 (54.58) | 234,973 (18.41) | 244,407 (53.23) | 189,793 (41.34) | 24,940 (5.43) | ||
| >17.5(Male), >15.5(Female) | 2187 (11.69) | 9684 (51.76) | 6838 (36.55) | 888 (39.68) | 980 (43.79) | 370 (16.53) | ||
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | ||||||||
| ≤1.5 | 359,495 (27.29) | 717,074 (54.44) | 240,626 (18.27) | <0.0001 | 309,009 (53.02) | 243,392 (41.76) | 30,403 (5.22) | 0.0387 |
| >1.5 | 11,103 (23.75) | 25,977 (55.56) | 9671 (20.69) | 6014 (52.54) | 4884 (42.67) | 549 (4.8) | ||
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | ||||||||
| <18.5 | 15,245 (58.26) | 10,561 (40.36) | 363 (1.39) | <0.0001 | 33,371 (71.33) | 13,244 (28.31) | 170 (0.36) | <0.0001 |
| 18.5–22.9 | 195,445 (44.13) | 228,356 (51.56) | 19,056 (4.3) | 215,994 (61.73) | 129,301 (36.96) | 4587 (1.31) | ||
| 23–24.9 | 100,361 (28.51) | 213,364 (60.6) | 38,353 (10.89) | 44,400 (45.05) | 49,312 (50.03) | 4848 (4.92) | ||
| 25–29.9 | 59,083 (12.41) | 269,099 (56.53) | 147,815 (31.05) | 20,766 (24.83) | 48,734 (58.27) | 14,129 (16.89) | ||
| ≥30 | 481 (0.72) | 21,695 (32.43) | 44,722 (66.85) | 514 (3.33) | 7696 (49.88) | 7219 (46.79) | ||
| Males | Females | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-HF | HF | p-Value | Non-HF | HF | p-Value | |
| Metabolic status | ||||||
| Normal | 370,441 (99.95) | 174 (0.05) | <0.0001 | 314,919 (99.96) | 126 (0.04) | <0.0001 |
| Pre-MetS | 742,431 (99.91) | 643 (0.09) | 248,080 (99.92) | 207 (0.08) | ||
| MetS | 249,865 (99.82) | 444 (0.18) | 30,907 (99.85) | 46 (0.15) | ||
| Smoking status | ||||||
| Non-smoker | 348,148 (99.93) | 247 (0.07) | <0.0001 | 549,764 (99.94) | 332 (0.06) | 0.0001 |
| Ex-smoker | 263,133 (99.93) | 175 (0.07) | 16,205 (99.92) | 13 (0.08) | ||
| Current smoker | 743,762 (99.89) | 833 (0.11) | 23,997 (99.87) | 31 (0.13) | ||
| Alcohol consumption | ||||||
| No drink | 349,854 (99.9) | 348 (0.1) | <0.0001 | 371,642 (99.94) | 237 (0.06) | 0.9930 |
| 2–3 per month | 768,511 (99.92) | 637 (0.08) | 188,558 (99.94) | 118 (0.06) | ||
| 1–4 per week | 189,897 (99.89) | 204 (0.11) | 21,110 (99.93) | 14 (0.07) | ||
| ≥5 per week | 38,457 (99.85) | 58 (0.15) | 4245 (99.93) | 3 (0.07) | ||
| Exercise | ||||||
| No exercise | 578,189 (99.91) | 527 (0.09) | 0.8200 | 330,371 (99.94) | 212 (0.06) | 0.7400 |
| 1–4 per week | 303,949 (99.91) | 282 (0.09) | 116,799 (99.94) | 69 (0.06) | ||
| ≥5 per week | 467,748 (99.91) | 444 (0.09) | 142,445 (99.93) | 95 (0.07) | ||
| Family history of hypertension | ||||||
| Yes | 131,163 (99.89) | 145 (0.11) | 0.0124 | 81,037 (99.93) | 54 (0.07) | 0.8864 |
| No | 849,831 (99.91) | 749 (0.09) | 320,561 (99.93) | 209 (0.07) | ||
| Family history of diabetes mellitus | ||||||
| Yes | 131,085 (99.89) | 145 (0.11) | 0.0104 | 69,187 (99.92) | 57 (0.08) | 0.0492 |
| No | 849,509 (99.91) | 745 (0.09) | 332,167 (99.94) | 204 (0.06) | ||
| Family history of stroke | ||||||
| Yes | 58,703 (99.86) | 81 (0.14) | <0.0001 | 27,578 (99.91) | 25 (0.09) | 0.0886 |
| No | 921,222 (99.91) | 809 (0.09) | 373,348 (99.94) | 237 (0.06) | ||
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | ||||||
| <200 | 781,244 (99.93) | 557 (0.07) | <0.0001 | 432,127 (99.94) | 261 (0.06) | 0.1453 |
| 200–239 | 435,622 (99.9) | 419 (0.1) | 132,743 (99.93) | 93 (0.07) | ||
| >239 | 145,871 (99.81) | 285 (0.19) | 29,036 (99.91) | 25 (0.09) | ||
| ALT (IU/L) | ||||||
| <40 | 1047,786 (99.92) | 850 (0.08) | <0.0001 | 574,118 (99.94) | 353 (0.06) | 0.0001 |
| 40–99 | 283,598 (99.88) | 354 (0.12) | 17,489 (99.86) | 25 (0.14) | ||
| >100 | 31,353 (99.82) | 57 (0.18) | 2299 (99.96) | 1 (0.04) | ||
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | ||||||
| <13.5(Male), <12(Female) | 68,616 (99.88) | 84 (0.12) | <0.0001 | 132,742 (99.92) | 106 (0.08) | 0.0119 |
| 13.5–17.5(Male), 12–15.5 (Female) | 1,275,446 (99.91) | 1143 (0.09) | 458,870 (99.94) | 270 (0.06) | ||
| >17.5(Male), >15.5(Female) | 18,675 (99.82) | 34 (0.18) | 2235 (99.87) | 3 (0.13) | ||
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | ||||||
| ≤1.5 | 1,315,989 (99.91) | 1205 (0.09) | 0.0673 | 582,435 (99.94) | 369 (0.06) | 0.3129 |
| >1.5 | 46,696 (99.88) | 55 (0.12) | 11,437 (99.91) | 10 (0.09) | ||
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | ||||||
| <18.5 | 2,6144 (99.9) | 25 (0.1) | <0.0001 | 46,761 (99.95) | 24 (0.05) | <0.0001 |
| 18.5–22.9 | 442,552 (99.93) | 305 (0.07) | 349,695 (99.95) | 187 (0.05) | ||
| 23–24.9 | 35,1822 (99.93) | 256 (0.07) | 98,488 (99.93) | 72 (0.07) | ||
| 25–29.9 | 475,453 (99.89) | 543 (0.11) | 83,554 (99.91) | 75 (0.09) | ||
| ≥30 | 66,766 (99.8) | 132 (0.2) | 15,408 (99.86) | 21 (0.14) | ||
| Males | Females | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolic Status | Non-Adjusted HR (95% CI) | Adjusted HR (95% CI) | Non-Adjusted HR (95% CI) | Adjusted HR (95% CI) |
| Normal | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Pre-metabolic synd. | 2.057 (1.669–2.536) | 1.607 (1.293–1.997) | 2.084 (1.591–2.73) | 1.893 (1.43–2.505) |
| Metabolic synd. | 4.134 (3.322–5.144) | 1.968 (1.526–2.539) | 3.421 (2.245–5.215) | 2.398 (1.466–3.923) |
| Age, per year | NA | 1.067 (1.042–1.094) | NA | 1.021 (0.98–1.064) |
| Smoking status | ||||
| Non-smoker | NA | 1 | NA | 1 |
| Ex-smoker | NA | 0.924 (0.732–1.167) | NA | 1.336 (0.683–2.611) |
| Current smoker | NA | 1.139 (0.951–1.364) | NA | 2.355 (1.503–3.69) |
| Alcohol consumption | ||||
| No drink | NA | 1 | NA | 1 |
| 2–3 per month | NA | 0.898 (0.764–1.055) | NA | 0.995 (0.76–1.302) |
| 1–4 per week | NA | 1.134 (0.915–1.405) | NA | 0.735 (0.368–1.47) |
| ≥5 per week | NA | 1.367 (0.967–1.932) | NA | 0.283 (0.039–2.069) |
| Exercise | ||||
| No exercise | NA | 1 | NA | 1 |
| 1–4 per week | NA | 1.085 (0.913–1.29) | NA | 0.850 (0.606–1.192) |
| ≥5 per week | NA | 1.059 (0.907–1.236) | NA | 0.962 (0.715–1.295) |
| Family history of heart disease | ||||
| No | NA | 1 | NA | 1 |
| Yes | NA | 0.925 (0.705–1.214) | NA | 1.154 (0.709–1.877) |
| Family history of hypertension | ||||
| No | NA | 1 | NA | 1 |
| Yes | NA | 0.975 (0.805–1.181) | NA | 0.884 (0.644–1.212) |
| Family history of diabetes mellitus | ||||
| No | NA | 1 | NA | 1 |
| Yes | NA | 1.100 (0.912–1.328) | NA | 1.301 (0.958–1.768) |
| Family history of stroke | ||||
| No | NA | 1 | NA | 1 |
| Yes | NA | 1.287 (1.018–1.628) | NA | 1.431 (0.941–2.176) |
| Body mass index | ||||
| <18.5 | NA | 1.400 (0.814–2.409) | NA | 1.278 (0.785–2.079) |
| 18.5–22.9 | NA | 1 | NA | 1 |
| 23–24.9 | NA | 0.879 (0.718–1.077) | NA | 1.177 (0.839–1.652) |
| 25–29.9 | NA | 0.955 (0.789–1.157) | NA | 1.136 (0.794–1.624) |
| ≥30 | NA | 1.246 (0.943–1.647) | NA | 1.308 (0.71–2.411) |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | ||||
| <13.5(Male), <12(Female) | NA | 1.695 (1.28–2.244) | NA | 1.426 (1.072–1.898) |
| 13.5–17.5(Male), 12–15.5 (Female) | NA | 1 | NA | 1 |
| >17.5(Male), >15.5(Female) | NA | 1.039 (0.694–1.556) | NA | 1.401 (0.345–5.684) |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | ||||
| ≤1.5 | NA | 1 | NA | 1 |
| >1.5 | NA | 1.235 (0.921–1.654) | NA | 1.288 (0.635–2.611) |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | ||||
| <200 | NA | 1 | NA | 1 |
| 200–239 | NA | 1.052 (0.898–1.231) | NA | 0.980 (0.728–1.318) |
| >239 | NA | 1.281 (1.062–1.545) | NA | 1.155 (0.702–1.9) |
| ALT (IU/L) | ||||
| <40 | NA | 1 | NA | 1 |
| 40–99 | NA | 0.964 (0.819–1.136) | NA | 2.078 (1.287–3.357) |
| >100 | NA | 1.318 (0.94–1.849) | NA | 0.804 (0.112–5.783) |
| Acute myocardial infarction | ||||
| No | NA | 1 | NA | 1 |
| Yes | NA | 238.245 (203.671–278.688) | NA | 214.404 (118.231–388.806) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, T.-E.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, H.; Sung, J.; Kim, D.-K.; Lee, M.-S.; Han, S.W.; Kim, H.-J.; Ki, H.K.; Kim, S.H.; et al. The Impact of Metabolic Syndrome on Heart Failure in Young Korean Population: A Nationwide Study. Metabolites 2024, 14, 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14090485
Kim T-E, Kim DY, Kim H, Sung J, Kim D-K, Lee M-S, Han SW, Kim H-J, Ki HK, Kim SH, et al. The Impact of Metabolic Syndrome on Heart Failure in Young Korean Population: A Nationwide Study. Metabolites. 2024; 14(9):485. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14090485
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Tae-Eun, Do Young Kim, Hyeongsu Kim, Jidong Sung, Duk-Kyung Kim, Myoung-Soon Lee, Seong Woo Han, Hyun-Joong Kim, Hyun Kyun Ki, Sung Hea Kim, and et al. 2024. "The Impact of Metabolic Syndrome on Heart Failure in Young Korean Population: A Nationwide Study" Metabolites 14, no. 9: 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14090485
APA StyleKim, T.-E., Kim, D. Y., Kim, H., Sung, J., Kim, D.-K., Lee, M.-S., Han, S. W., Kim, H.-J., Ki, H. K., Kim, S. H., & Ryu, K.-H. (2024). The Impact of Metabolic Syndrome on Heart Failure in Young Korean Population: A Nationwide Study. Metabolites, 14(9), 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14090485








