Machine Learning-Based Plasma Metabolomics in Liraglutide-Treated Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients and Diet-Induced Obese Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
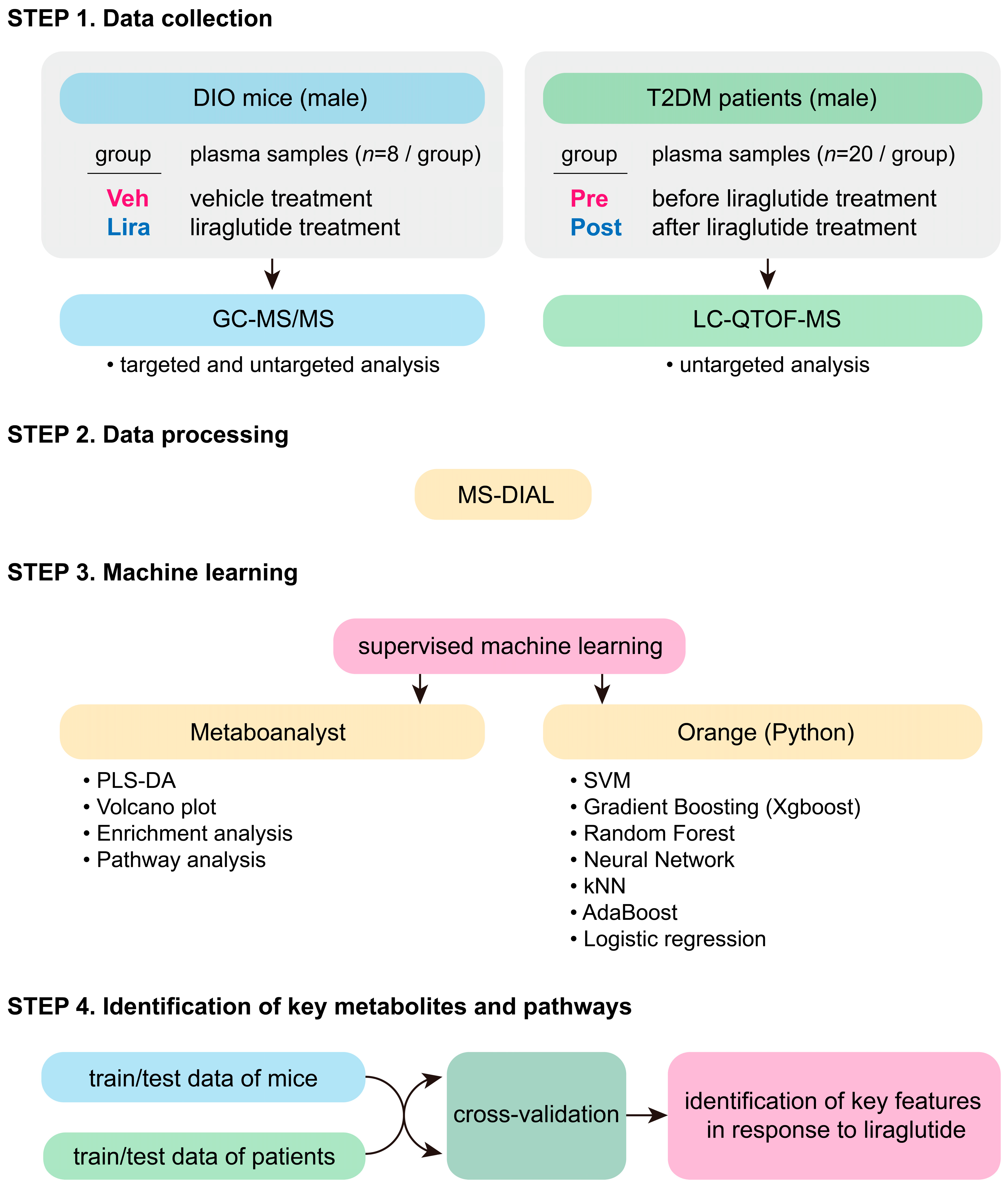
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Processing
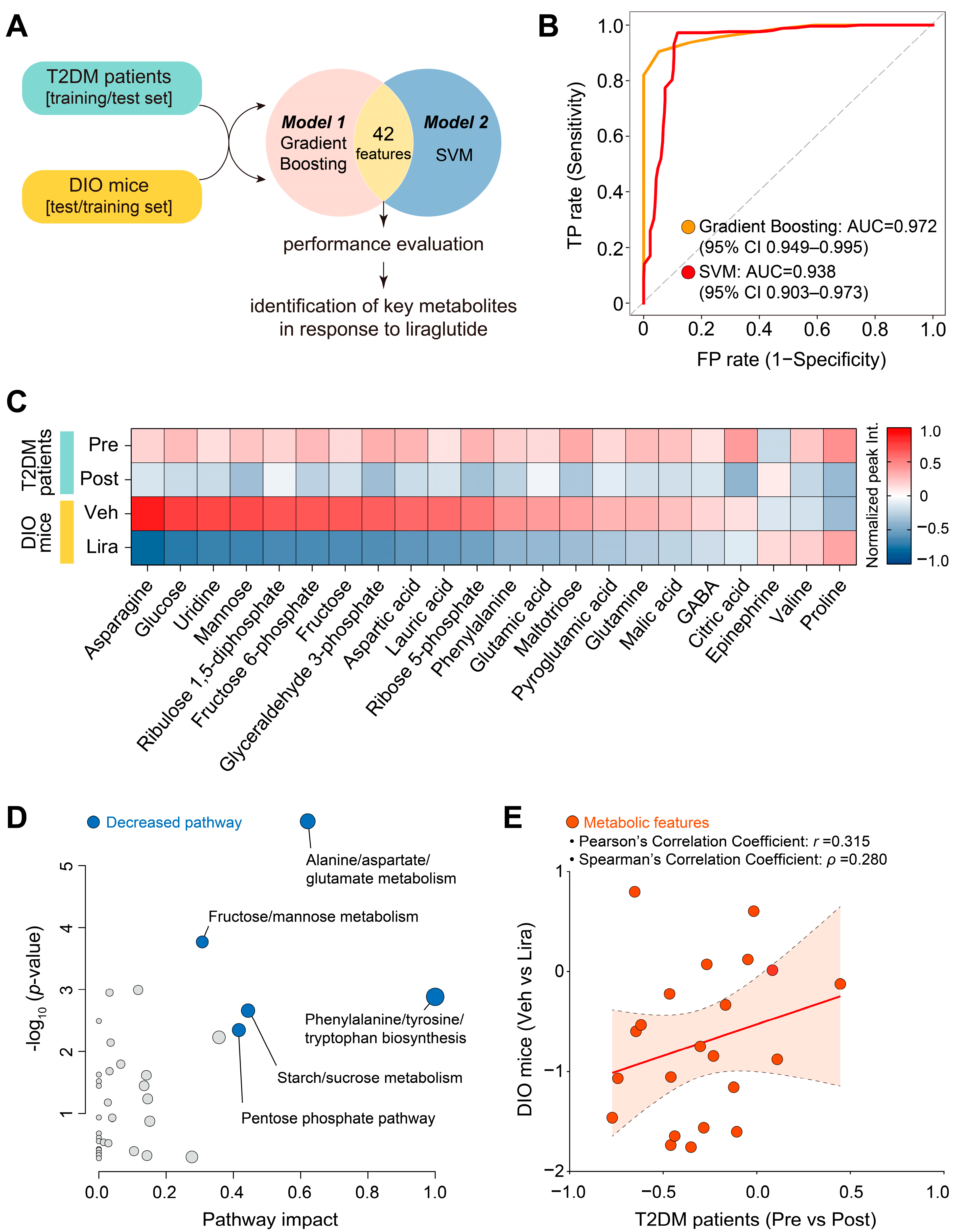
2.3. Machine Learning Processing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Design
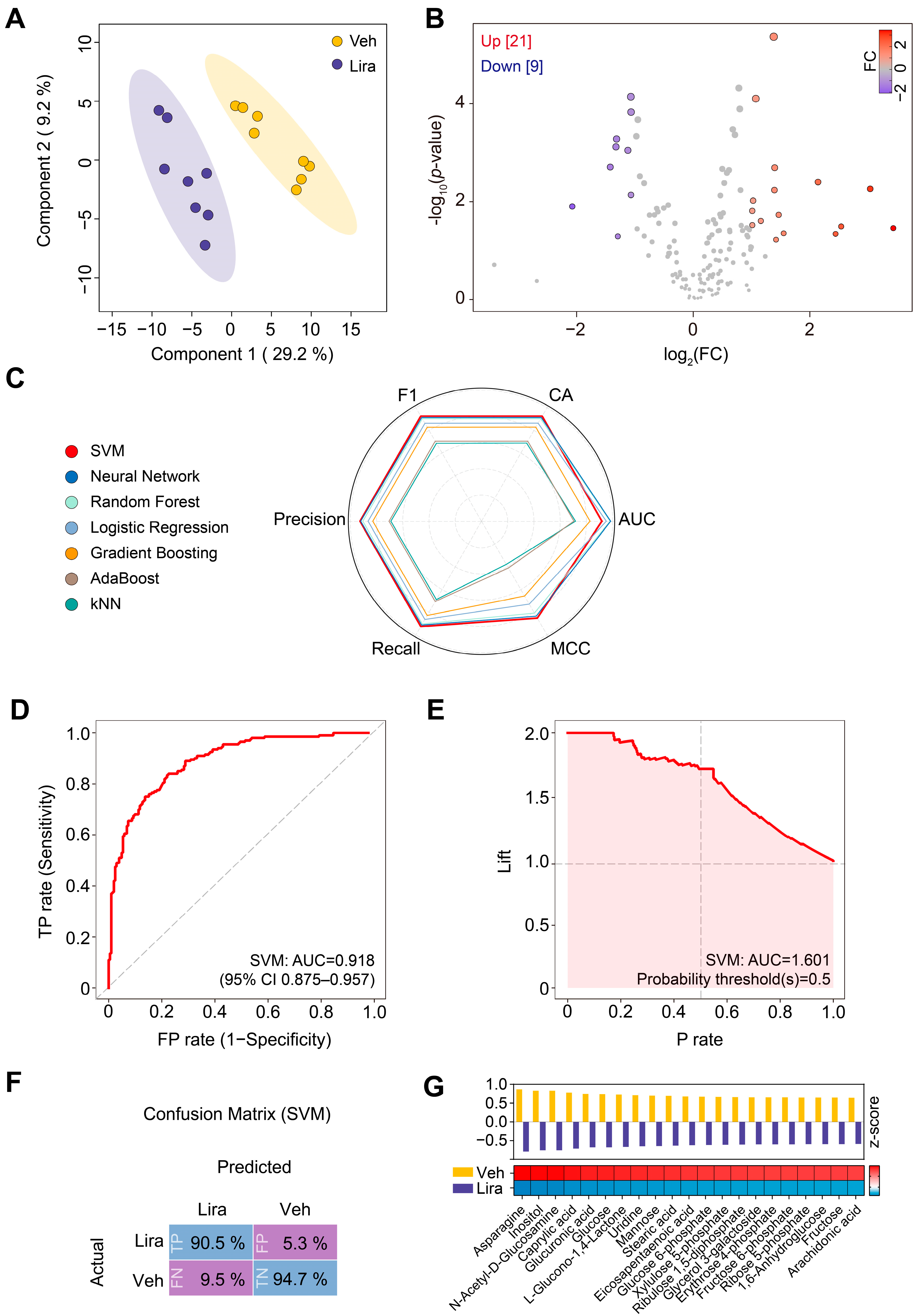
3.2. Changes in Plasma Metabolome in DIO Mice in Response to Liraglutide
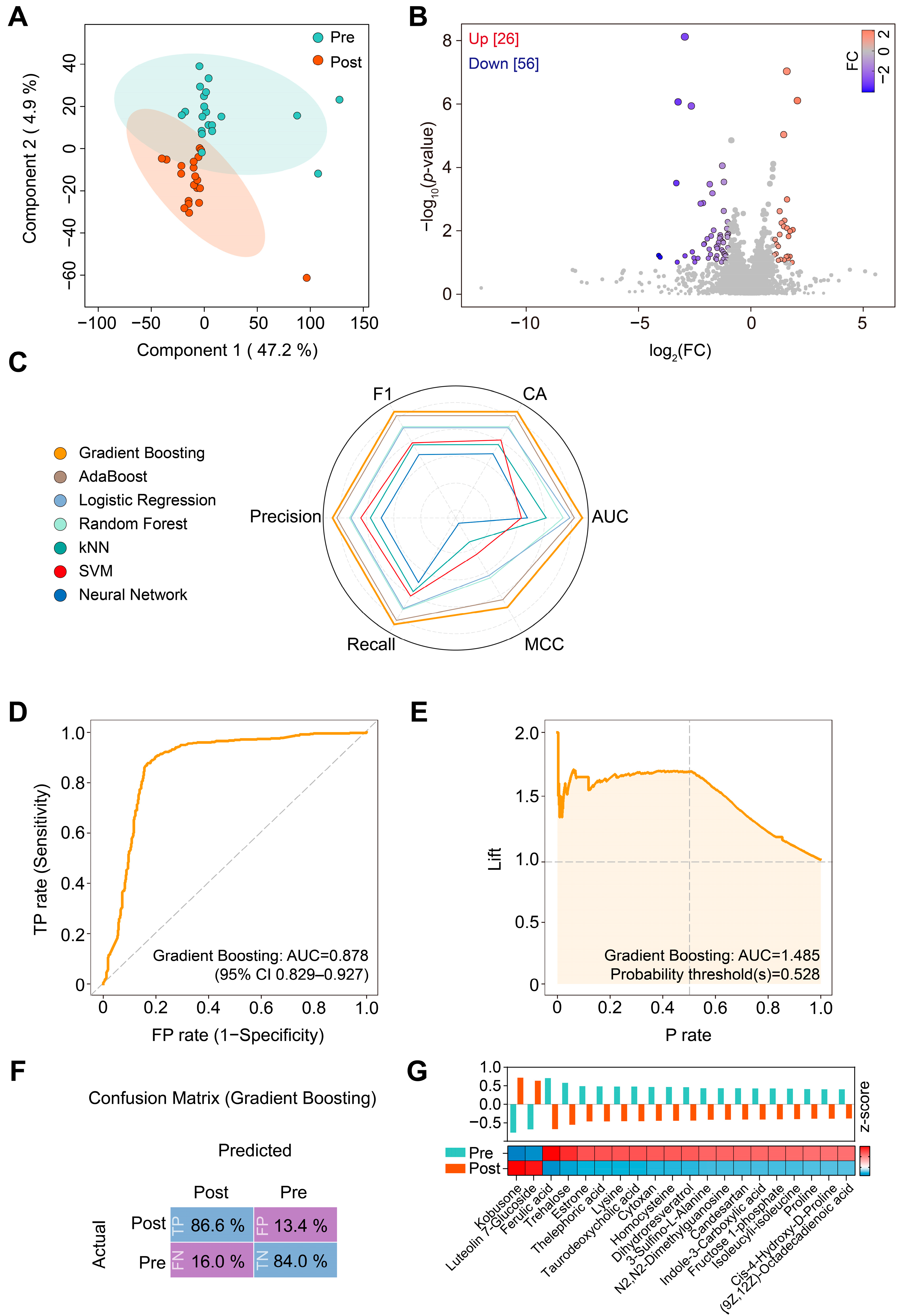
3.3. Changes in Plasma Metabolome in Patients with T2DM in Response to Liraglutide
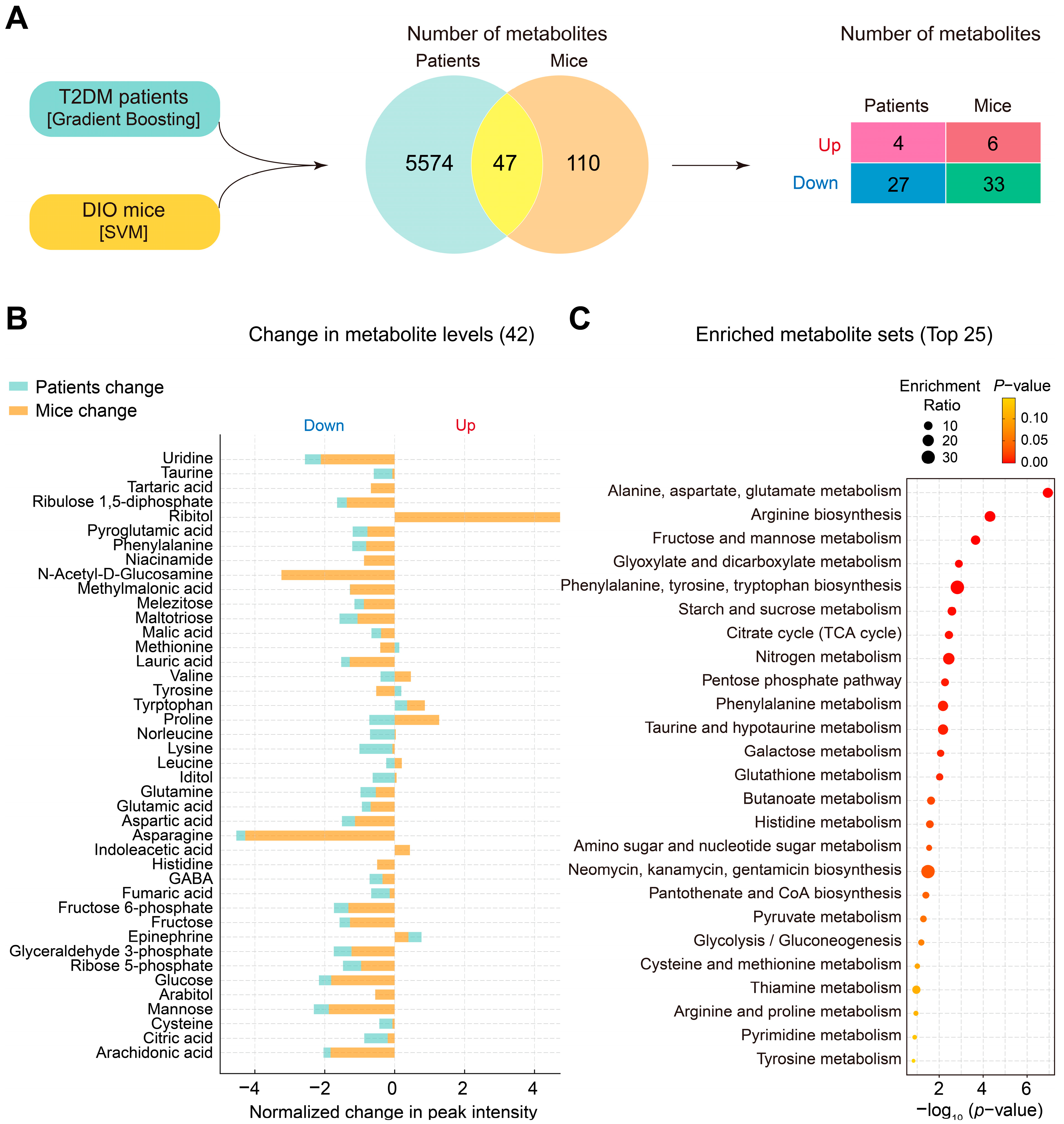
3.4. Changes in Plasma Metabolites and Metabolic Pathways Following Liraglutide Treatment in DIO Mice and Patients with T2DM
3.5. Identification of Key Plasma Metabolites and Metabolic Pathways Changed by Liraglutide in Both DIO Mice and Patients with T2DM
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Ferrannini, E.; Groop, L.; Henry, R.R.; Herman, W.H.; Holst, J.J.; Hu, F.B.; Kahn, C.R.; Raz, I.; Shulman, G.I.; et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, S.; Khoo, B.; Tan, T. Targeting the incretin system in obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2024, 20, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenkilde, M.M. Advances in incretin-based therapeutics for obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2024, 20, 67–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F. Metabolic messengers: Glucagon-like peptide 1. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, P.J.; Fledelius, C.; Knudsen, L.B.; Tang-Christensen, M. Systemic administration of the long-acting GLP-1 derivative NN2211 induces lasting and reversible weight loss in both normal and obese rats. Diabetes 2001, 50, 2530–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, M.; Rosebraugh, C. Weighing risks and benefits of liraglutide-the FDA’s review of a new antidiabetic therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 774–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J.; Dritselis, A.; Kirkpatrick, P. Liraglutide. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2010, 9, 267–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrup, A.; Rossner, S.; Van Gaal, L.; Rissanen, A.; Niskanen, L.; Al Hakim, M.; Madsen, J.; Rasmussen, M.F.; Lean, M.E.; Group, N.N.S. Effects of liraglutide in the treatment of obesity: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Lancet 2009, 374, 1606–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.J.; Bergenstal, R.; Bode, B.; Kushner, R.F.; Lewin, A.; Skjoth, T.V.; Andreasen, A.H.; Jensen, C.B.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Grp, N.-S. Efficacy of liraglutide for weight loss among patients with type 2 diabetes: The SCALE diabetes randomized clinical trial. Jama-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2015, 314, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi-Sunyer, X.; Astrup, A.; Fujioka, K.; Greenway, F.; Halpern, A.; Krempf, M.; Lau, D.C.W.; le Roux, C.W.; Ortiz, R.V.; Jensen, C.B.; et al. A randomized, controlled trial of 3.0 mg of liraglutide in weight management. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Oh, S.; Kim, E.K. Glucagon-like peptide-1 analog liraglutide leads to multiple metabolic alterations in diet-induced obese mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buganova, M.; Pelantova, H.; Holubova, M.; Sediva, B.; Maletinska, L.; Zelezna, B.; Kunes, J.; Kacer, P.; Kuzma, M.; Haluzik, M. The effects of liraglutide in mice with diet-induced obesity studied by metabolomics. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 233, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Xi, L.Q.; Zhang, Z.X.; Ge, X.X.; Li, W.Y.; Peng, W.F.; Jiang, X.H.; Liu, W.; Zhao, N.; Wang, X.Y.; et al. Metabolic remodeling of glycerophospholipids acts as a signature of dulaglutide and liraglutide treatment in recent-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 13, 1097612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelidi, A.M.; Kokkinos, A.; Sanoudou, D.; Connelly, M.A.; Alexandrou, A.; Mingrone, G.; Mantzoros, C.S. Early metabolomic, lipid and lipoprotein changes in response to medical and surgical therapeutic approaches to obesity. Metabolism 2023, 138, 155346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.Y.; Xu, Y.S.; Li, J.; An, W.R.; Luo, D.; Huang, C.C.; Huang, Y.Q. Explore the effect and target of liraglutide on islet function in type 2 diabetic rats by miRNA omics technology. Diabetes Metab. Synd. Ob. 2021, 14, 3795–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekhzaimy, A.A.; Masood, A.; Benabdelkamel, H.; Elhassan, T.; Musambil, M.; Alfadda, A.A. Plasma proteomics reveals an improved cardio-metabolic profile in patients with type 2 diabetes post-liraglutide treatment. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Re. 2022, 19, 14791641221094322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiullah, M.; Benabdelkamel, H.; Masood, A.; Ekhzaimy, A.A.; Musambil, M.; Joy, S.S.; Alfadda, A.A. Urinary proteome differences in patients with type 2 diabetes pre and post liraglutide treatment. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 1407–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: Beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Bio. 2016, 17, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S. Emerging applications of metabolomics in drug discovery and precision medicine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamathevan, J.; Clark, D.; Czodrowski, P.; Dunham, I.; Ferran, E.; Lee, G.; Li, B.; Madabhushi, A.; Shah, P.; Spitzer, M.; et al. Applications of machine learning in drug discovery and development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greener, J.G.; Kandathil, S.M.; Moffat, L.; Jones, D.T. A guide to machine learning for biologists. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shilo, S.; Segal, E. Endocrinology in the multi-omics era. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2024, 20, 73–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topol, E.J. High-performance medicine: The convergence of human and artificial intelligence. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebal, U.W.; Phan, A.N.T.; Sudhakar, M.; Raman, K.; Blank, L.M. Machine learning applications for mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. Metabolites 2020, 10, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galal, A.; Talal, M.; Moustafa, A. Applications of machine learning in metabolomics: Disease modeling and classification. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1017340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.D.; Xue, C.; Kolachalama, V.B.; Donald, W.A. Interpretable machine learning on metabolomics data reveals biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. ACS Cent. Sci. 2023, 9, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Shao, X.; Wang, M.; Ma, F.; Yang, L.; Nie, M.; Jin, P.; Yao, K.; et al. Metabolomic machine learning predictor for diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsugawa, H.; Cajka, T.; Kind, T.; Ma, Y.; Higgins, B.; Ikeda, K.; Kanazawa, M.; VanderGheynst, J.; Fiehn, O.; Arita, M. MS-DIAL: Data-independent MS/MS deconvolution for comprehensive metabolome analysis. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, G.; Hui, F.; Xu, L.; Viau, C.; Spigelman, A.F.; MacDonald, P.E.; Wishart, D.S.; Li, S.; et al. MetaboAnalyst 6.0: Towards a unified platform for metabolomics data processing, analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W398–W406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, E.M.; Xu, L.Y. Guide to metabolomics analysis: A bioinformatics workflow. Metabolites 2022, 12, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demsar, J.; Curk, T.; Erjavec, A.; Gorup, C.; Hocevar, T.; Milutinovic, M.; Mozina, M.; Polajnar, M.; Toplak, M.; Staric, A.; et al. Orange: Data mining toolbox in python. J. Mach. Learn Res. 2013, 14, 2349–2353. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, I.H. Machine learning: Algorithms, real-world applications and research directions. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainio, O.; Teuho, J.; Klen, R. Evaluation metrics and statistical tests for machine learning. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jendle, J.; Hyotylainen, T.; Oresic, M.; Nystrom, T. Pharmacometabolomic profiles in type 2 diabetic subjects treated with liraglutide or glimepiride. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tochikubo, O.; Nakamura, H.; Jinzu, H.; Nagao, K.; Yoshida, H.; Kageyama, N.; Miyano, H. Weight loss is associated with plasma free amino acid alterations in subjects with metabolic syndrome. Nutr. Diabetes 2016, 6, e197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirniö, P.; Väyrynen, J.P.; Klintrup, K.; Mäkelä, J.; Karhu, T.; Herzig, K.H.; Minkkinen, I.; Mäkinen, M.J.; Karttunen, T.J.; Tuomisto, A. Alterations in serum amino-acid profile in the progression of colorectal cancer: Associations with systemic inflammation, tumour stage and patient survival. Brit. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanatidou, A.I.; Mikropoulou, E.V.; Amerikanou, C.; Milanovic, M.; Stojanoski, S.; Bjelan, M.; Cesarini, L.; Campolo, J.; Thanopoulou, A.; Banerjee, R.; et al. Plasma amino acids in NAFLD patients with obesity are associated with steatosis and fibrosis: Results from the MAST4HEALTH study. Metabolites 2023, 13, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Sun, W.W.; Chen, J.C.; Zhang, H.L.; Liu, J.; Lin, Y.; Lin, P.C.; Wu, B.X.; An, Y.P.; Huang, L.; et al. Phenylalanine impairs insulin signaling and inhibits glucose uptake through modification of IRβ. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satapati, S.; Sunny, N.E.; Kucejova, B.; Fu, X.; He, T.T.; Mendez-Lucas, A.; Shelton, J.M.; Perales, J.C.; Browning, J.D.; Burgess, S.C. Elevated TCA cycle function in the pathology of diet-induced hepatic insulin resistance and fatty liver. J. Lipid. Res. 2012, 53, 1080–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Kido, J.; Matsumoto, S.; Shimizu, K.; Nakamura, K. Associations among amino acid, lipid, and glucose metabolic profiles in childhood obesity. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libert, D.M.; Nowacki, A.S.; Natowicz, M.R. Metabolomic analysis of obesity, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes: Amino acid and acylcarnitine levels change along a spectrum of metabolic wellness. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratheiser, K.M.; Brillon, D.J.; Campbell, R.G.; Matthews, D.E. Epinephrine produces a prolonged elevation in metabolic rate in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 68, 1046–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staten, M.A.; Matthews, D.E.; Cryer, P.E.; Bier, D.M. Physiological increments in epinephrine stimulate metabolic-rate in humans. Am. J. Physiol. 1987, 253, E322–E330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, F.C.B.; Bauer, E.J.; Ribeiro, C.M.; Pereira, S.A.; Beserra, B.T.S.; Wajner, S.M.; Maia, A.L.; Neves, F.A.R.; Coelho, M.S.; Amato, A.A. Liraglutide activates type 2 deiodinase and enhances β3-adrenergic-induced thermogenesis in mouse adipose tissue. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 12, 803363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beiroa, D.; Imbernon, M.; Gallego, R.; Senra, A.; Herranz, D.; Villarroya, F.; Serrano, M.; Ferno, J.; Salvador, J.; Escalada, J.; et al. GLP-1 agonism stimulates brown adipose tissue thermogenesis and browning through hypothalamic AMPK. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3346–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessen, L.; Smith, E.P.; Ulrich-Lai, Y.; Herman, J.P.; Seeley, R.J.; Sandoval, D.; D’Alessio, D. Central nervous system GLP-1 receptors regulate islet hormone secretion and glucose homeostasis in male rats. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 2124–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lontchi-Yimagou, E.; Aleksic, S.; Hulkower, R.; Gospin, R.; Goyal, A.; Kuo, B.; Mitchell, W.G.; You, J.Y.; Upadhyay, L.; Carey, M.; et al. Plasma epinephrine contributes to the development of experimental hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure. J. Clin. Endocr. Metab. 2020, 105, 3416–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryer, P.E.; Davis, S.N.; Shamoon, H. Hypoglycemia in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2003, 26, 1902–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, T.X.; Yang, J.W.; Zhou, S.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Li, Y.K.; Tong, X.M. The role of the pentose phosphate pathway in diabetes and cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britt, E.C.; Lika, J.; Giese, M.A.; Schoen, T.J.; Seim, G.L.; Huang, Z.P.; Lee, P.Y.; Huttenlocher, A.; Fan, J. Switching to the cyclic pentose phosphate pathway powers the oxidative burst in activated neutrophils. Nat. Metab. 2022, 4, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Poudel, A.; Welchko, R.; Mekala, N.; Chandramani-Shivalingappa, P.; Rosca, M.G.; Li, L.X. Liraglutide improves insulin sensitivity in high fat diet induced diabetic mice through multiple pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 861, 172594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiraki, A.; Oyama, J.; Komoda, H.; Asaka, M.; Komatsu, A.; Sakuma, M.; Kodama, K.; Sakamoto, Y.; Kotooka, N.; Hirase, T.; et al. The glucagon-like peptide 1 analog liraglutide reduces TNF-α-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 2012, 221, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Kim, E.-K. Machine Learning-Based Plasma Metabolomics in Liraglutide-Treated Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients and Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Metabolites 2024, 14, 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14090483
Park S, Kim E-K. Machine Learning-Based Plasma Metabolomics in Liraglutide-Treated Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients and Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Metabolites. 2024; 14(9):483. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14090483
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Seokjae, and Eun-Kyoung Kim. 2024. "Machine Learning-Based Plasma Metabolomics in Liraglutide-Treated Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients and Diet-Induced Obese Mice" Metabolites 14, no. 9: 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14090483
APA StylePark, S., & Kim, E.-K. (2024). Machine Learning-Based Plasma Metabolomics in Liraglutide-Treated Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients and Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Metabolites, 14(9), 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14090483






