Tracking Metabolite Variations during the Degradation of Vegetables in Rice Bran Bed with Intact-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Degradation Experiments
2.3. Sample Preparation for NMR Measurements
2.4. NMR Measurements
2.5. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results
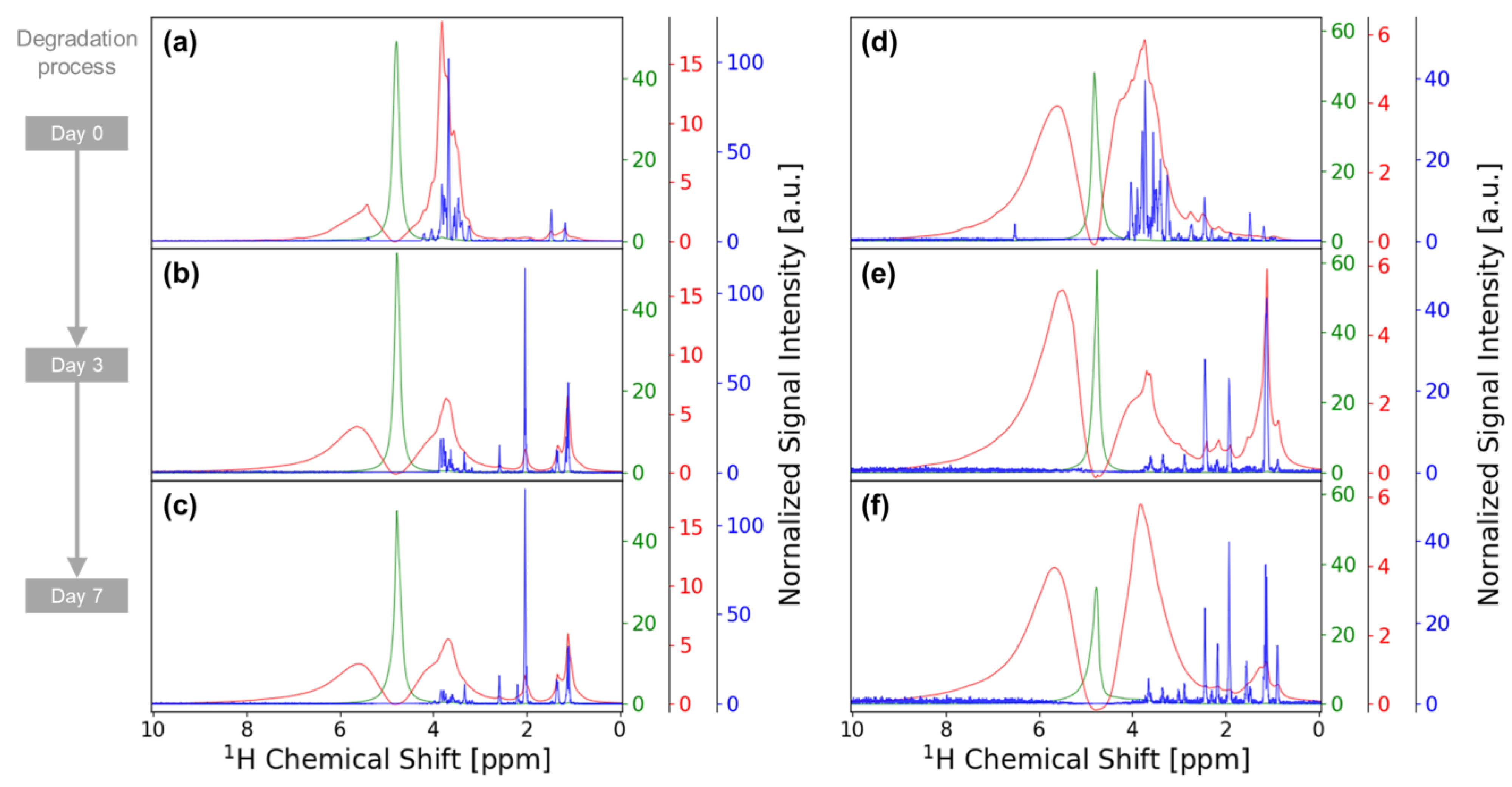
3.1. Performance of iSQC Experiment for Intact Samples
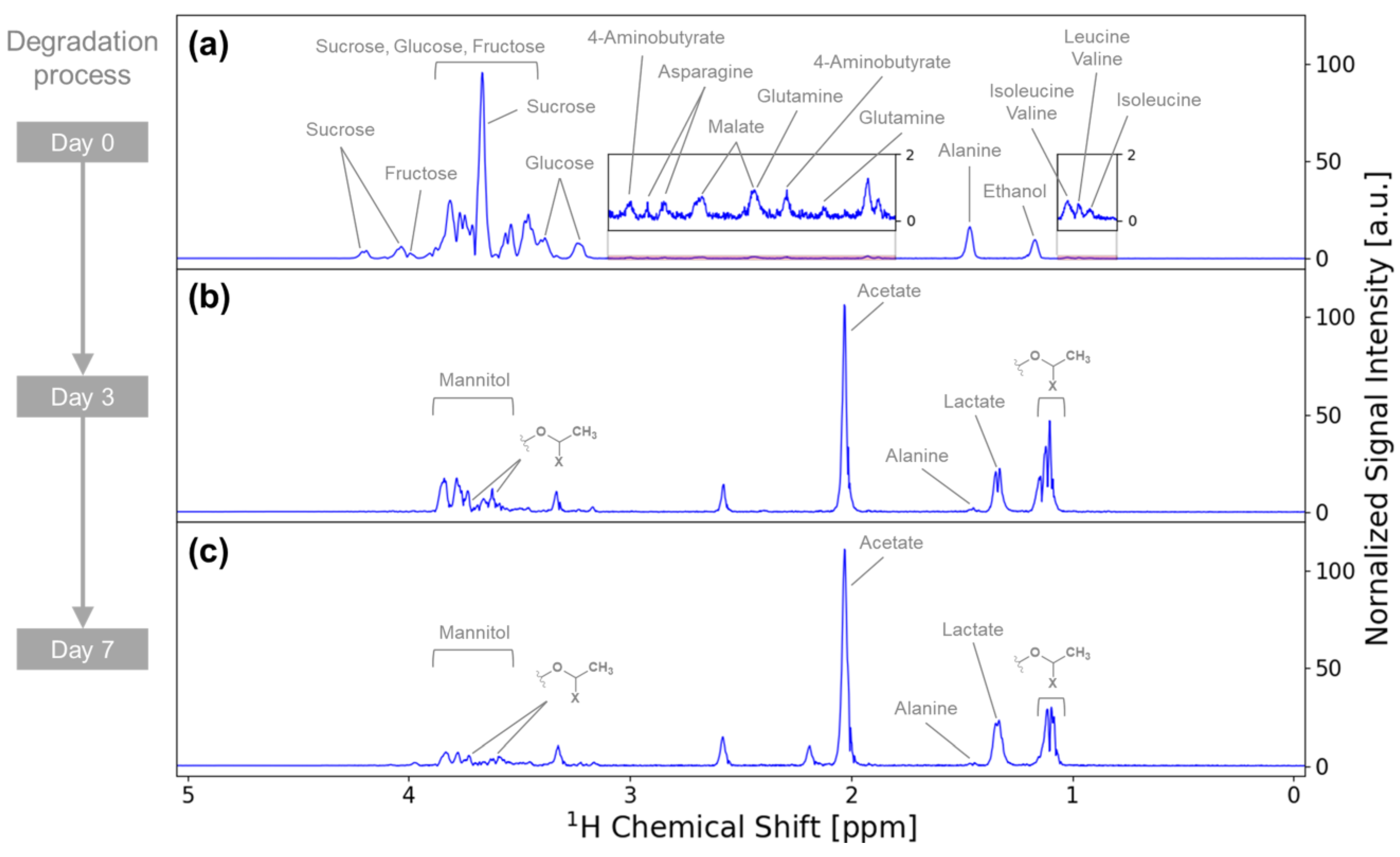
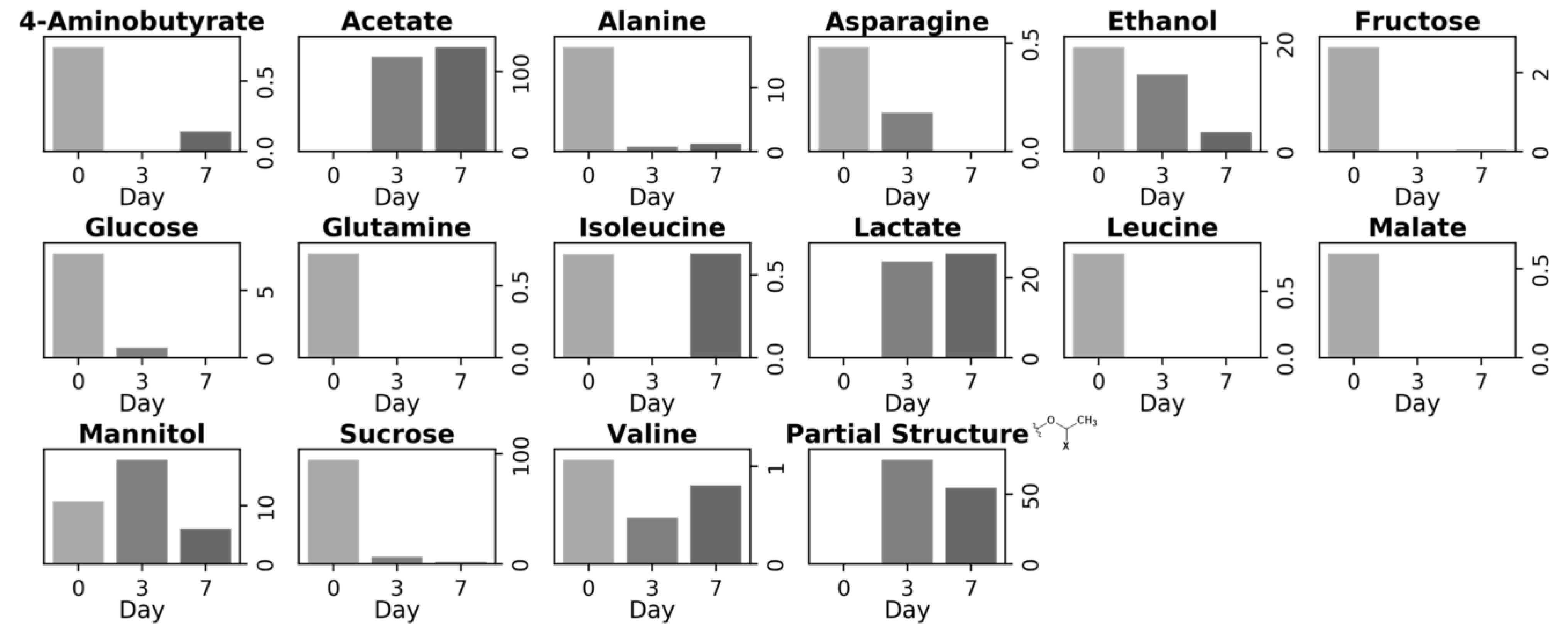
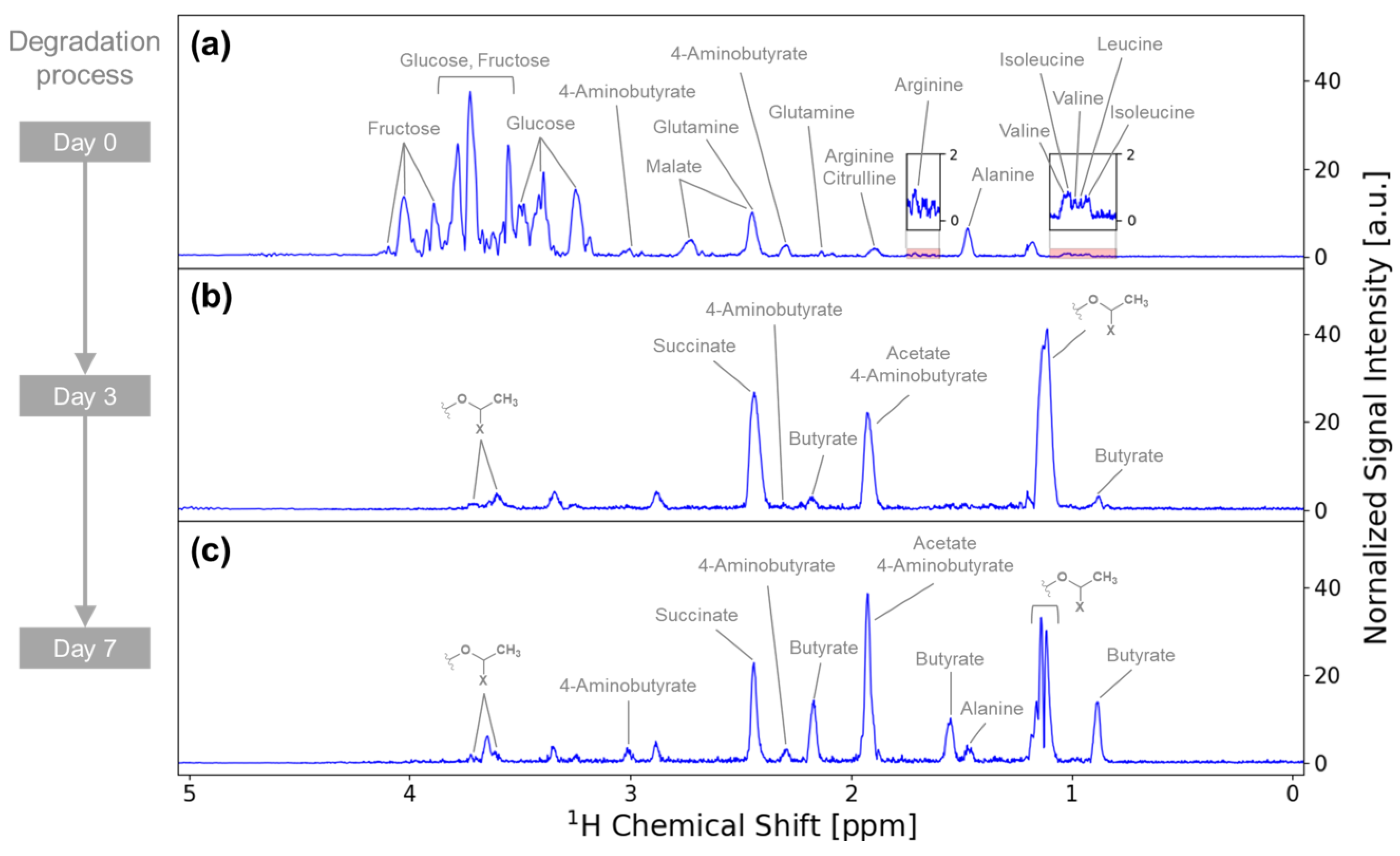
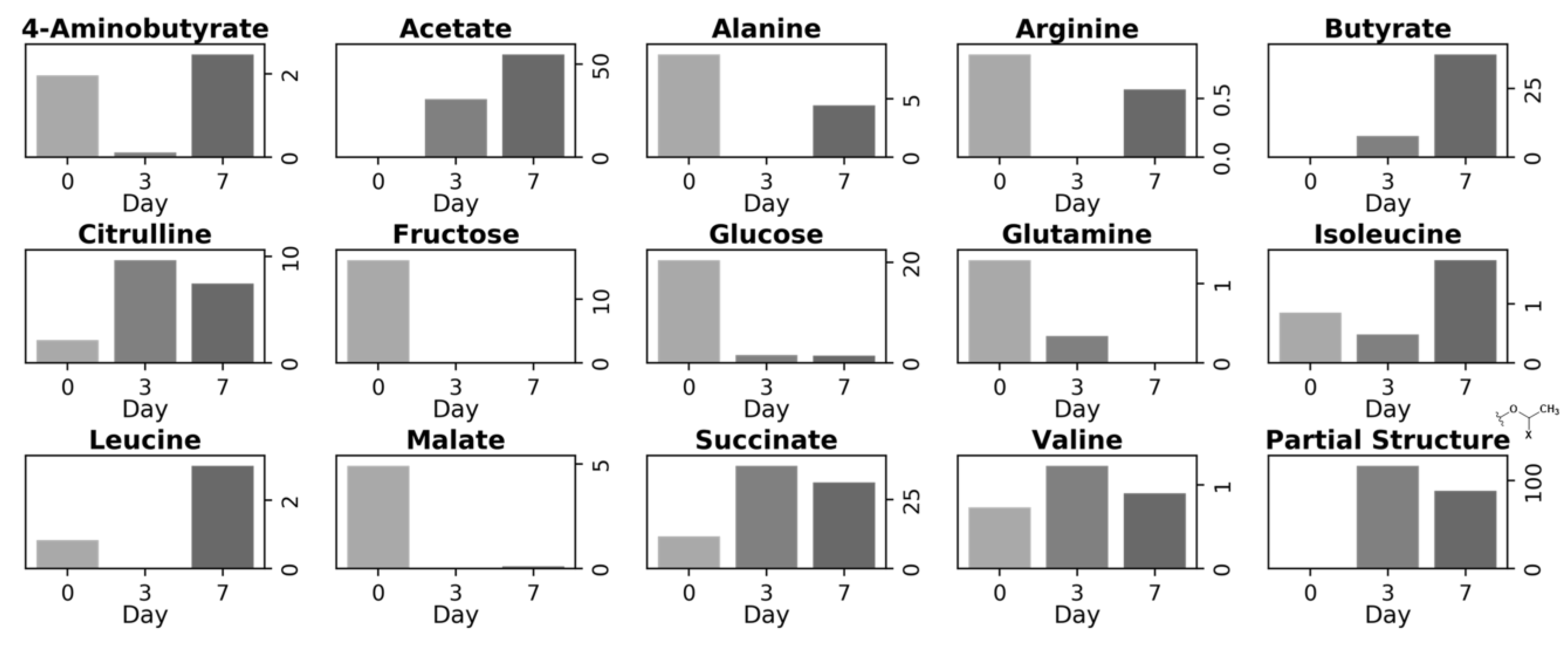
3.2. Metabolite Variation during Vegetable Degradation
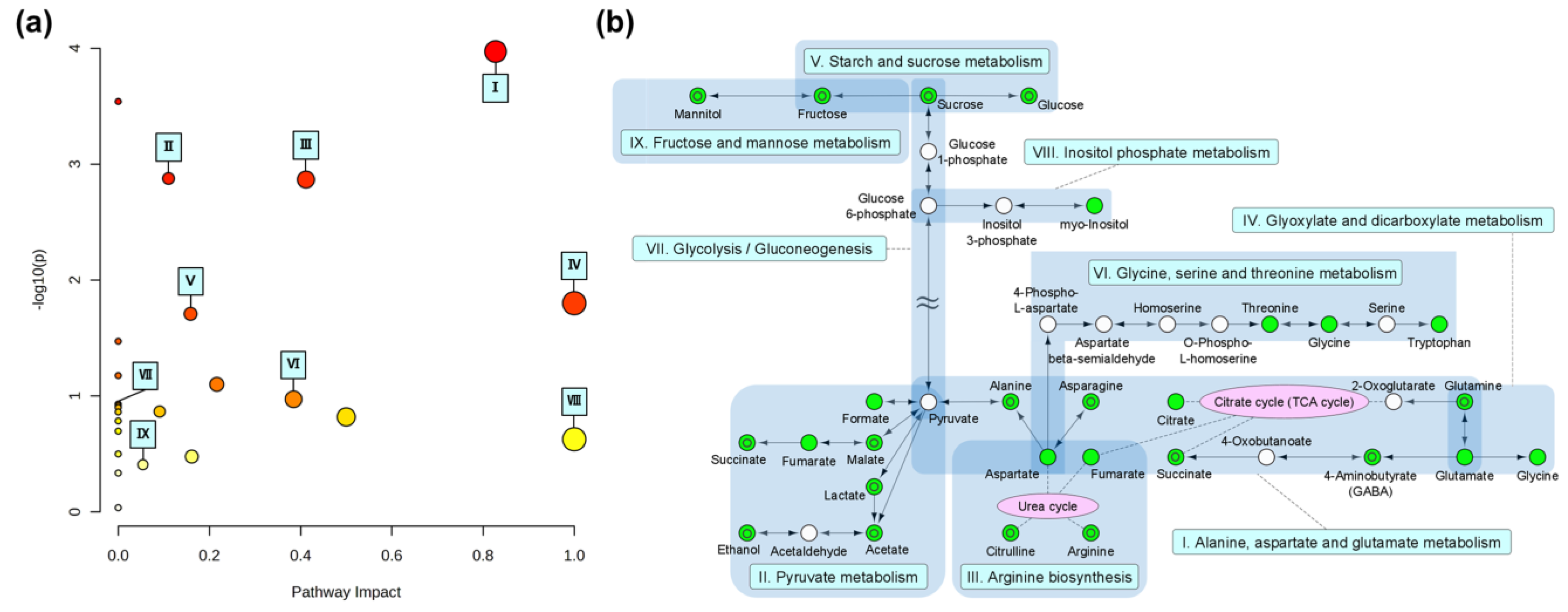
3.3. Investigation of the Metabolic Pathways Related to Degradation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dimidi, E.; Cox, S.; Rossi, M.; Whelan, K. Fermented Foods: Definitions and Characteristics, Impact on the Gut Microbiota and Effects on Gastrointestinal Health and Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, J.B.; Nair, B.M. The History of Fermented Foods. In Handbook of Fermented Functional Foods; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Paul Ross, R.P.; Morgan, S.; Hill, C. Preservation and Fermentation: Past, Present and Future. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 79, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanbury, P.F.; Whitaker, A.; Hall, S.J. Principles of Fermentation Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Anraku, K.; Nonaka, K.; Yamaga, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Shin, M.C.; Wakita, M.; Hamamoto, A.; Akaike, N. Removal of Toxin (Tetrodotoxin) from Puffer Ovary by Traditional Fermentation. Toxins 2013, 5, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; Ferranti, P. The Evolution of Analytical Chemistry Methods in Foodomics. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1428, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubert, J.; Zachariasova, M.; Hajslova, J. Advances in High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry Based on Metabolomics Studies for Food—A Review. Food Addit. Contam. A 2015, 32, 1685–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, B.K.; Ahn, H.J.; van den Berg, F.; Lee, C.H.; Hong, Y.S. Metabolomic Insight into Soy Sauce through 1H NMR Spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6862–6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Rituerto, E.L.; Cabredo, S.; López, M.; Avenoza, A.; Busto, J.H.; Peregrina, J.M.; Peregrina, J.M. A Thorough Study on the Use of Quantitative 1H-NMR in Rioja Red Wine Fermentation Processes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 2112–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Graaf, R.A. Vivo NMR Spectroscopy: Principles and Techniques; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, M.; Davies, N.P.; Grundy, R.G.; Peet, A.C. A Quantitative Comparison of Metabolite Signals as Detected by In Vivo MRS with Ex Vivo 1H HR-MAS for Childhood Brain Tumours. NMR Biomed. 2009, 22, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarou-Kanian, V.; Joudiou, N.; Louat, F.; Yon, M.; Szeremeta, F.; Même, S.; Massiot, D.; Decoville, M.; Fayon, F.; Beloeil, J.C. Metabolite Localization in Living Drosophila Using High Resolution Magic Angle Spinning NMR. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Tsuboi, Y.; Kikuchi, J. Spatial Molecular-Dynamically Ordered NMR Spectroscopy of Intact Bodies and Heterogeneous Systems. Commun. Chem. 2020, 3, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Cai, S.; Huang, Y.; Lin, Y. High-Resolution NMR Spectroscopy in Inhomogeneous Fields. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2015, 90–91, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Huang, Y.; Cai, S.; Chen, Z. Intermolecular Zero Quantum Coherence in NMR Spectroscopy. Annu. Rep. NMR Spectrosc. 2013, 78, 209–257. [Google Scholar]
- Tomita, S.; Ikeda, S.; Tsuda, S.; Someya, N.; Asano, K.; Kikuchi, J.; Chikayama, E.; Ono, H.; Sekiyama, Y. A Survey of Metabolic Changes in Potato Leaves by NMR-Based Metabolic Profiling in Relation to Resistance to Late Blight Disease under Field Conditions. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2017, 55, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fugariu, I.; Bermel, W.; Lane, D.; Soong, R.; Simpson, A.J. In-Phase Ultra High-Resolution in Vivo NMR. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 6324–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmus, J.J.; Jaroniec, C.P. Nmrglue: An Open Source Python Package for the Analysis of Multidimensional Nmr Data. J. Biomol. NMR 2013, 55, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercier, P.; Lewis, M.J.; Chang, D.; Baker, D.; Wishart, D.S. Towards Automatic Metabolomic Profiling of High-Resolution One-Dimensional Proton NMR Spectra. J. Biomol. NMR 2011, 49, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewald, J.; Zhou, G.; Lu, Y.; Kolic, J.; Ellis, C.; Johnson, J.D.; Macdonald, P.E.; Xia, J. Web-Based Multi-omics Integration Using the Analyst Software Suite. Nat. Protoc. 2024, 19, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.W.; Park, S.E.; Kim, E.J.; Seo, S.H.; Cho, K.M.; Kwon, S.J.; Lee, M.H.; Son, H.S. Effects of Garlic on Kimchi Metabolites Exerted through Selective Growth Control of Lactobacillus and Leuconostoc. LWT 2024, 198, 116053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, M.; Lopes, C.T.; Fong, D.; Kucera, M.; Cheung, M.; Siper, M.C.; Huck, G.; Dong, Y.; Sumer, O.; Bader, G.D. Cytoscape. Js 2023 Update: A Graph Theory Library for Visualization and Analysis. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, K.; Ono, K.; Kanaya, S.; Takahashi, K. Keggscape: A Cytoscape App for Pathway Data Integration. F1000Research 2014, 3, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bax, A.; Freeman, R. Investigation of Complex Networks of Spin-Spin Coupling by Two-Dimensional NMR. J. Magn. Reson. 1981, 44, 542–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhong, J. High-Resolution NMR Spectra in Inhomogeneous Fields via IDEAL (Intermolecular Dipolar-Interaction Enhanced All Lines) Method. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 446–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Cai, C.; Cai, S.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z. Intermolecular Double-Quantum Coherence NMR Spectroscopy in Moderate Inhomogeneous Fields. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009, 74, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cai, S.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z. Intermolecular Single-Quantum Coherence Sequences for High-Resolution NMR Spectra in Inhomogeneous Fields. J. Magn. Reson. 2010, 203, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Chen, H.; Xiang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Z. GC-TOF-MS-Based Non-targeted Metabolomic Analysis of Differential Metabolites in Chinese Ultra-Long-Term Industrially Fermented Kohlrabi and Their Associated Metabolic Pathways. Metabolites 2022, 12, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.; Huang, T.; Xu, Y.; Peng, Z.; Liu, Z.; Guan, Q.; Xie, M.; Xiong, T. Metatranscriptomics Reveals the Gene Functions and Metabolic Properties of the Major Microbial Community during Chinese Sichuan Paocai Fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2021, 98, 103573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Lu, H.; Zhang, T.; Zeng, W. Characterization of Genomic, Physiological, and Probiotic Features of Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum JS21 Strain Isolated from Traditional Fermented Jiangshui. Foods 2024, 13, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yetiman, A.E.; Keskin, A.; Darendeli, B.N.; Kotil, S.E.; Ortakci, F.; Dogan, M. Characterization of Genomic, Physiological, and Probiotic Features Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum DY46 Strain Isolated from Traditional Lactic Acid Fermented Shalgam Beverage. Food Biosci. 2022, 46, 101499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.J.; Lee, H.; Na, G.; Jung, H.; Kim, D.G.; Shin, S.I.; Jung, S.E.; Choi, I.D.; Lee, J.H.; Sim, J.H.; et al. Metabolic and Lipidomic Profiling of Vegetable Juices Fermented with Various Probiotics. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cao, S.; Yang, Y.; Cai, S.; Zhan, H.; Tan, C.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z. Ultrahigh-Resolution NMR Spectroscopy for Rapid Chemical and Biological Applications in Inhomogeneous Magnetic Fields. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 7115–7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Cai, H.; Lin, Y.; Cui, X.; Chen, Z. Usage of the Ultrafast Intermolecular Single-Quantum Coherence (UF iSQC) Sequence for NMR Spectroscopy of Ex Vivo Tissue. Int. Food Res. J. 2015, 77, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Obuchi, Y.; Chikayama, E.; Date, Y.; Kikuchi, J. Exploratory Machine-Learned Theoretical Chemical Shifts Can Closely Predict Metabolic Mixture Signals. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 8213–8220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gänzle, M.G. Lactic Metabolism Revisited: Metabolism of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Food Fermentations and Food Spoilage. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 2, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuy, N.M.; Ha, H.T.N.; Tai, N.V. Lactic Acid Fermentation of Radish and Cucumber in Rice Bran Bed. Agric. Conspec Sci. 2022, 87, 245–252. [Google Scholar]
- Doi, K.; Phuong, O.T.A.; Kawatou, F.; Nagayoshi, Y.; Fujino, Y.; Ohshima, T. Identification and Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Fermented Rice Bran Product. AiM 2013, 3, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ooshima, M.; Yamaguchi, N.; Nakanishi, Y.; Hitomi, Y.; Hiradate, S. Changes in Chemical Form of Phosphorus in Rice Bran during Fermentation Process as Determined by 31P Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 68, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, N.S. Glycolysis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2021, 13, a040535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, R.; Varacallo, M. Biochemistry, Glycolysis; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Taillefer, M.; Sparling, R. Glycolysis as the Central Core of Fermentation. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2016, 156, 55–77. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Lv, M.; Shao, Z.; Hungwe, M.; Wang, J.; Bai, X.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; Geng, W. Metabolism Characteristics of Lactic Acid Bacteria and the Expanding Applications in Food Industry. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 612285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ito, K.; Yamamoto, R.; Sekiyama, Y. Tracking Metabolite Variations during the Degradation of Vegetables in Rice Bran Bed with Intact-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Metabolites 2024, 14, 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14070391
Ito K, Yamamoto R, Sekiyama Y. Tracking Metabolite Variations during the Degradation of Vegetables in Rice Bran Bed with Intact-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Metabolites. 2024; 14(7):391. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14070391
Chicago/Turabian StyleIto, Kengo, Ryusei Yamamoto, and Yasuyo Sekiyama. 2024. "Tracking Metabolite Variations during the Degradation of Vegetables in Rice Bran Bed with Intact-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy" Metabolites 14, no. 7: 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14070391
APA StyleIto, K., Yamamoto, R., & Sekiyama, Y. (2024). Tracking Metabolite Variations during the Degradation of Vegetables in Rice Bran Bed with Intact-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Metabolites, 14(7), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14070391







