Early Metabolomic and Immunologic Biomarkers as Prognostic Indicators for COVID-19
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subject Recruitment
2.2. Sampling and Investigations
2.3. Analysis
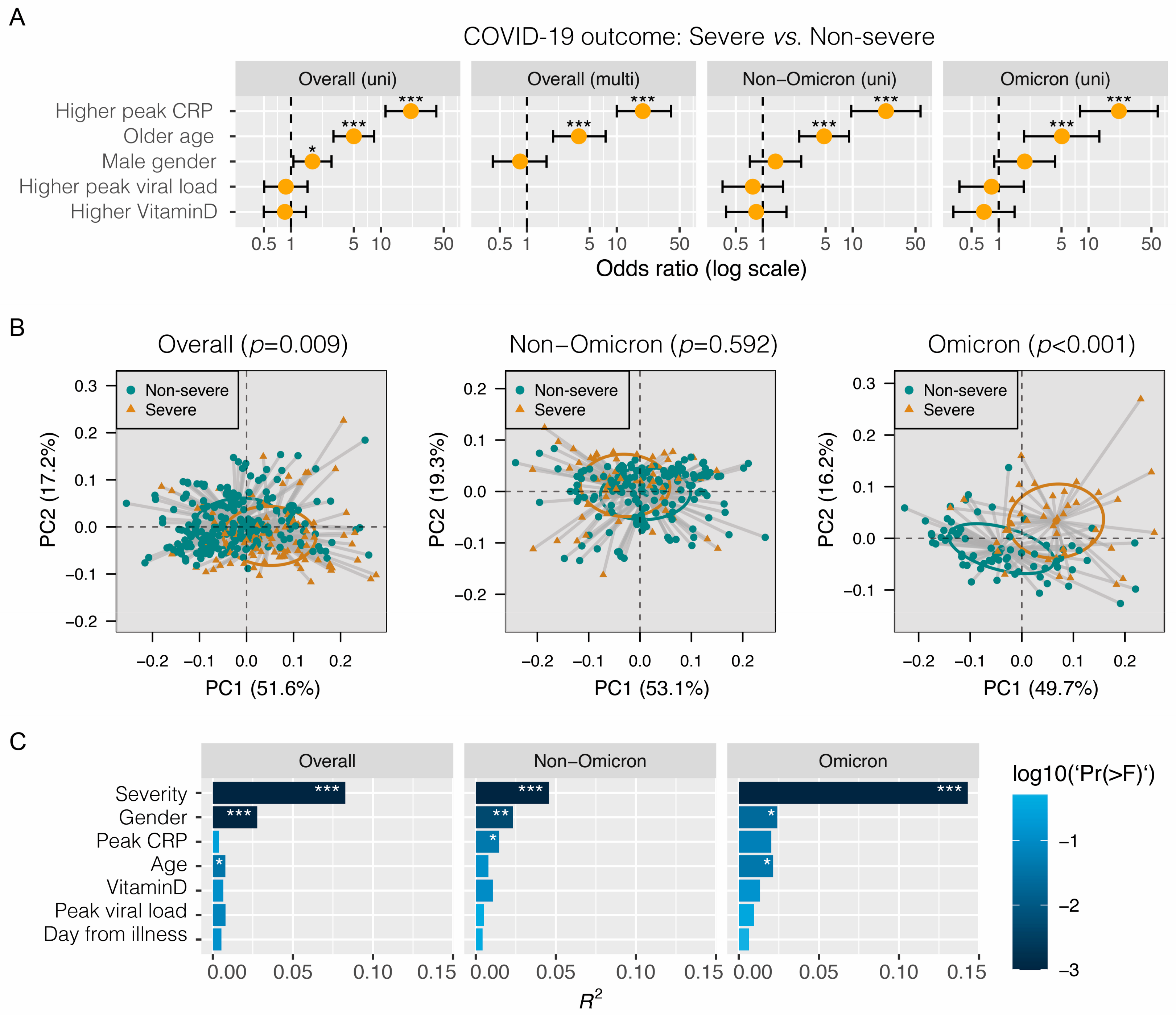
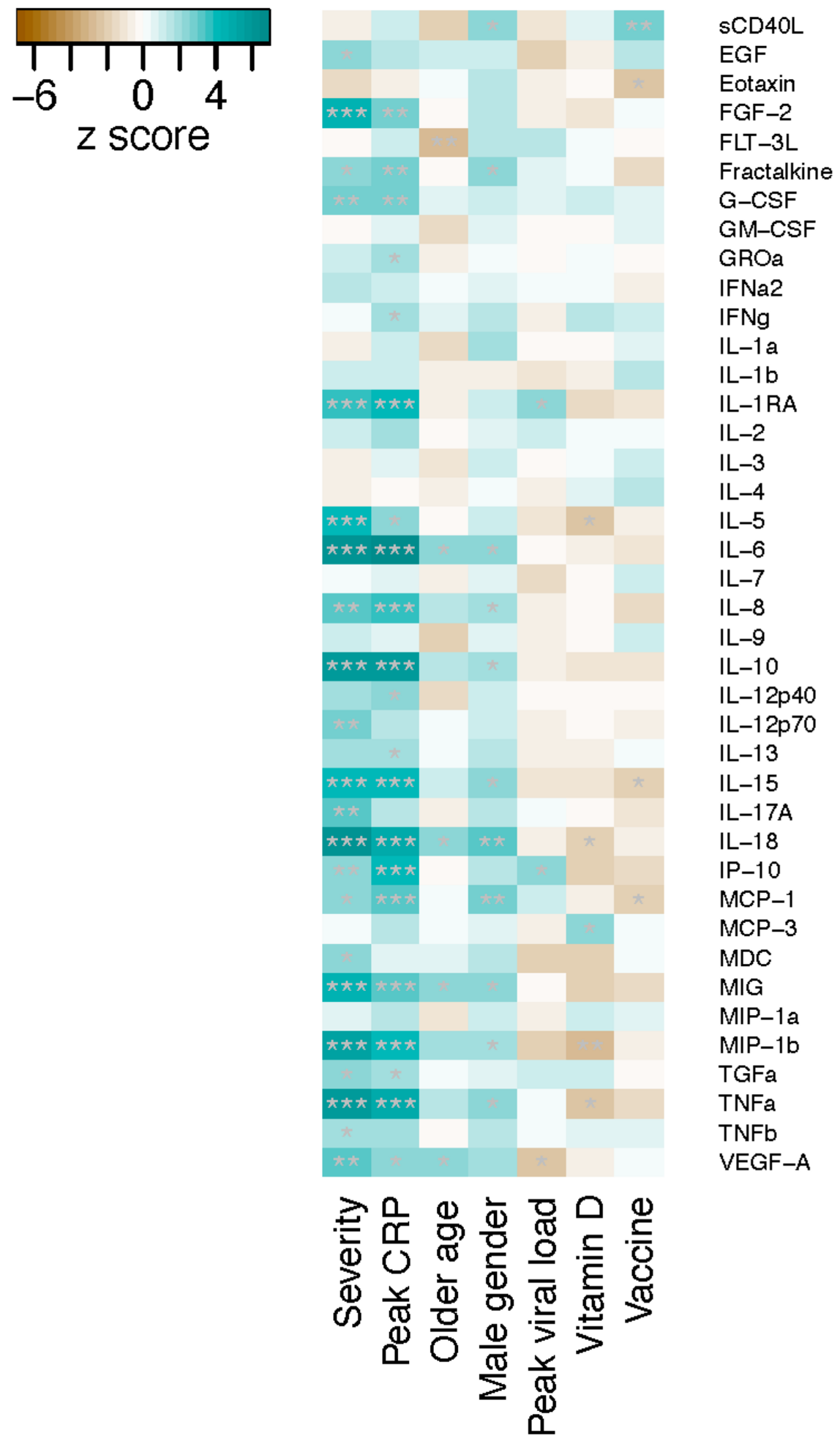
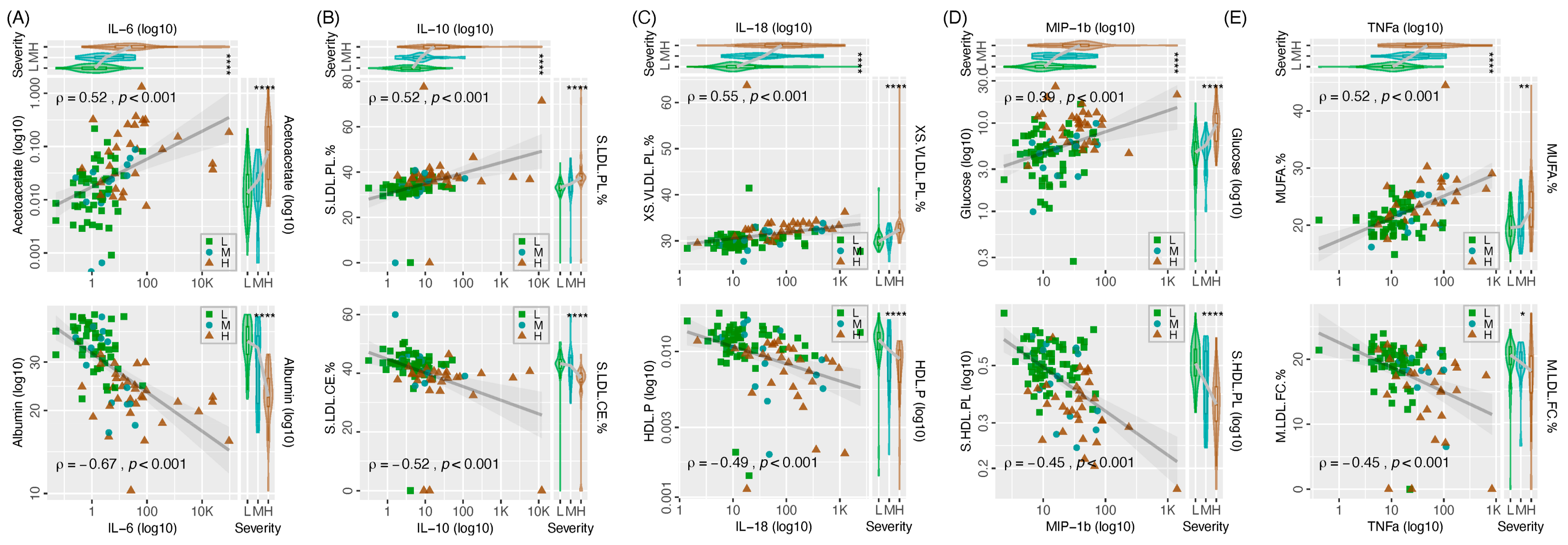
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases?n=c (accessed on 30 April 2024).
- Fu, L.; Wang, B.; Yuan, T.; Chen, X.; Ao, Y.; Fitzpatrick, T.; Li, P.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, Y.F.; Duan, Q.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Infect. 2020, 80, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, S.D.; Oommen, A.M. Epidemiology of COVID-19. J. Dig. Endosc. 2020, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Z.L. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. 2021, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Chen, D.; Yuan, D.; Lausted, C.; Choi, J.; Dai, C.L.; Voillet, V.; Duvvuri, V.R.; Scherler, K.; Troisch, P.; et al. Multi-Omics Resolves a Sharp Disease-State Shift between Mild and Moderate COVID-19. Cell 2020, 183, 1479–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Chen, Y.; Xia, H.; Wang, C.; Tan, C.Y.; Cai, X.; Liu, Y.; Ji, F.; Xiong, P.; Liu, R.; et al. Transcriptional and Proteomic Insights into the Host Response in Fatal COVID-19 Cases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 28336–28343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demichev, V.; Tober-Lau, P.; Lemke, O.; Nazarenko, T.; Thibeault, C.; Whitwell, H.; Röhl, A.; Freiwald, A.; Szyrwiel, L.; Ludwig, D.; et al. A Time-Resolved Proteomic and Prognostic Map of COVID-19. Cell Syst. 2021, 12, 780–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yao, X.; Ma, S.; Ping, Y.; Fan, Y.; Sun, S.; He, Z.; Shi, Y.; Sun, L.; Xiao, S.; et al. A Single-Cell Transcriptomic Landscape of the Lungs of Patients with COVID-19. Nat. Cell Biol. 2021, 23, 1314–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, C.; de Prost, N.; Fourati, S.; Lamoureux, C.; Gricourt, G.; N’debi, M.; Canoui-Poitrine, F.; Désveaux, I.; Picard, O.; Demontant, V.; et al. Viral Genomic, Metagenomic and Human Transcriptomic Characterization and Prediction of the Clinical Forms of COVID-19. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moraes Pontes, J.G.; dos Santos, R.V.; Tasic, L. NMR-Metabolomics in COVID-19 Research. In Application of Omic Techniques to Identify New Biomarkers and Drug Targets for COVID-19; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Guest, P.C., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 1412, pp. 197–209. [Google Scholar]
- Würtz, P.; Havulinna, A.S.; Soininen, P.; Tynkkynen, T.; Prieto-Merino, D.; Tillin, T.; Ghorbani, A.; Artati, A.; Wang, Q.; Tiainen, M.; et al. Metabolite profiling and cardiovascular event risk: A prospective study of 3 population-based cohorts. Circulation 2015, 131, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holmes, M.V.; Millwood, I.Y.; Kartsonaki, C.; Hill, M.R.; Bennett, D.A.; Boxall, R.; Guo, Y.; Xu, X.; Bian, Z.; Hu, R.; et al. Lipids, Lipoproteins, and Metabolites and Risk of Myocardial Infarction and Stroke. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Würtz, P.; Kangas, A.J.; Soininen, P.; Lawlor, D.A.; Davey Smith, G.; Ala-Korpela, M. Quantitative serum nuclear magnetic resonance metabolomics in large-scale epidemiology: A primer on -omic technologies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 186, 1084–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soininen, P.; Kangas, A.J.; Würtz, P.; Suna, T.; Ala-Korpela, M. Quantitative serum nuclear magnetic resonance metabolomics in cardiovascular epidemiology and genetics. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2015, 8, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, M.O.; Pamukçu, E.; Yakar, B. The role of vitamin D deficiency on COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Epidemiol. Health 2021, 43, e2021074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lui, G.; Ling, L.; Lai, C.K.; Tso, E.Y.; Fung, K.S.; Chan, V.; Ho, T.H.; Luk, F.; Chen, Z.; Ng, J.K.; et al. Viral Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Across a Spectrum of Disease Severity in COVID-19. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 318–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Living Guidance for Clinical Management of COVID-19, 2021, by World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-clinical-2021-2 (accessed on 18 April 2024).
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, A.H.; Miao, J.H.; Sun, H.; Han, Y.; Yan, G.L.; Wu, F.F.; Wang, X.J. Metabolomics biotechnology, applications, and future trends: A systematic review. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 37245–37257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, E.; Chan, E.Y.S.; Ng, K.H.; Yu, K.M.; Li, H.; Wang, Y. Towards clinical application of GlycA and GlycB for early detection of inflammation associated with (pre)diabetes and cardiovascular disease: Recent evidence and updates. J. Inflamm. 2023, 20, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourgin, M.; Durand, S.; Kroemer, G. Diagnostic, Prognostic and Mechanistic Biomarkers of COVID-19 Identified by Mass Spectrometric Metabolomics. Metabolites 2023, 13, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Shu, T.; Yang, X.; Song, J.X.; Zhang, M.; Yao, C.; Liu, W.; Huang, M.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Q.; et al. Plasma metabolomic and lipidomic alterations associated with COVID-19. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, H.M.; Liu, Y.; Frampas, C.F.; Longman, K.; Spick, M.; Stewart, A.; Sinclair, E.; Kasar, N.; Greener, D.; Whetton, A.D.; et al. Metabolomics Markers of COVID-19 Are Dependent on Collection Wave. Metabolites 2022, 12, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Yi, X.; Sun, Y.; Bi, X.; Du, J.; Zhang, C.; Quan, S.; Zhang, F.; Sun, R.; Qian, L.; et al. Proteomic and Metabolomic Characterization of COVID-19 Patient Sera. Cell 2020, 182, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Nie, M.; Pang, H.; Wang, B.; Hu, J.; Meng, X.; Li, K.; Ran, X.; Long, Q.; Deng, H.; et al. Integrated cytokine and metabolite analysis reveals immunometabolic reprogramming in COVID-19 patients with therapeutic implications. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Liu, C.; Li, D.; Huang, Q.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, C.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Y.; et al. Metabolomic analyses reveal new stage-specific features of COVID-19. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 59, 2100284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, I.; Wright Muelas, M.; Taylor, J.M.; Davison, A.S.; Xu, Y.; Grixti, J.M.; Gotts, N.; Sorokin, A.; Goodacre, R.; Kell, D.B. Untargeted metabolomics of COVID-19 patient serum reveals potential prognostic markers of both severity and outcome. Metabolomics 2021, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Gomez, A.; Rodríguez-Morató, J.; Haro, N.; Marín-Corral, J.; Masclans, J.R.; Pozo, O.J. Untargeted detection of the carbonyl metabolome by chemical derivatization and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in precursor ion scan mode: Elucidation of COVID-19 severity biomarkers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1196, 339405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, B.S.B.; Ferreira, V.G.; Piagge, P.M.F.D.; Almeida, M.B.; Assunção, N.A.; Raimundo, J.R.S.; Fonseca, F.L.A.; Carrilho, E.; Cardoso, D.R. 1H qNMR-Based Metabolomics Discrimination of COVID-19 Severity. J. Proteome Res. 2022, 21, 1640–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amora, P.; Silva, I.D.C.G.; Budib, M.A.; Ayache, R.; Silva, R.M.S.; Silva, F.C.; Appel, R.M.; Júnior, S.S.; Pontes, H.B.D.; Alvarenga, A.C.; et al. Towards risk stratification and prediction of disease severity and mortality in COVID-19: Next generation metabolomics for the measurement of host response to COVID-19 infection. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- More, T.H.; Mozafari, B.; Märtens, A.; Herr, C.; Lepper, P.M.; Danziger, G.; Volk, T.; Hoersch, S.; Krawczyk, M.; Guenther, K.; et al. Plasma Metabolome Alterations Discriminate between COVID-19 and Non-COVID-19 Pneumonia. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, K.H.; McCullagh, J.S.O. A lipidomic view of SARS-CoV-2. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20210953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzone, C.; Conde, R.; Embade, N.; Mato, J.M.; Millet, O. Metabolomics as a powerful tool for diagnostic, pronostic and drug intervention analysis in COVID-19. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1111482. [Google Scholar]
- Sotelo-Orozco, J.; Chen, S.Y.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Slupsky, C.M. A Comparison of Serum and Plasma Blood Collection Tubes for the Integration of Epidemiological and Metabolomics Data. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 682134. [Google Scholar]
- Vignoli, A.; Tenori, L.; Morsiani, C.; Turano, P.; Capri, M.; Luchinat, C. Serum or Plasma (and Which Plasma), That Is the Question. J. Proteome Res. 2022, 21, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics | Total (n = 327) | Non-Omicron # (n = 217) | Omicron * (n = 110) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| Female | 217 | 160 | 57 |
| Male | 110 | 57 | 53 |
| Age, mean ± SD (range), years | 55 ± 17 (19–89) | 52 ± 16 (21–85) | 61 ± 19 (19–89) |
| 19–60 | 172 | 134 | 38 |
| 61–65 | 39 | 32 | 7 |
| 66–89 | 116 | 51 | 65 |
| Sampling from onset, mean ± SD (range), days | 7 ± 5 (1–33) | 7 ± 5 (1–24) | 6 ± 5 (1–33) |
| ≤7 | 212 | 128 | 84 |
| >7 | 115 | 89 | 26 |
| COVID-19 severity | |||
| Asymptomatic | 14 | 10 | 4 |
| Mild | 123 | 66 | 57 |
| Moderate | 91 | 83 | 8 |
| Severe | 35 | 28 | 7 |
| Critical | 55 | 27 | 28 |
| Fatal | 9 | 3 | 6 |
| Peak viral load, mean ± SD (range), Ct | 23.54 ± 6.57 (11.10–38.97) | 24.75 ± 6.76 (11.10–38.65) | 21.46 ± 5.67 (11.32–38.97) |
| ≤20 | 92 | 50 | 42 |
| >20 | 171 | 116 | 55 |
| NA | 64 | 51 | 13 |
| Peak C-reactive protein, mean ± SD (range), mg/L | 47.85 ± 76.55 (0.06–487.03) | 39.52 ± 64.96 (0.06–487.03) | 62.25 ± 91.79 (0.13–466.74) |
| ≤30 | 188 | 122 | 66 |
| >30 | 112 | 68 | 44 |
| NA | 27 | 27 | 0 |
| 25-OH vitamin D, mean ± SD (range), ng/mL | 17.69 ± 9.37 (1.44–79.47) | 17.01 ± 10.11 (2.78–79.47) | 18.74 ± 8.02 (1.44–43.18) |
| ≤12 | 85 | 61 | 24 |
| 13–20 | 97 | 62 | 35 |
| 21–30 | 71 | 31 | 40 |
| >30 | 27 | 17 | 10 |
| NA | 47 | 46 | 1 |
| Day from illness onset | 7 ± 5 (1–33) | 7 ± 5 (1–24) | 6 ± 5 (1–33) |
| ≤7 days | 212 | 128 | 84 |
| >7 days | 115 | 89 | 26 |
| SARS-CoV-2 mRNA or inactivated vaccine | |||
| No | 254 | 217 | 37 |
| 1 dose | 22 | 0 | 22 |
| 2 doses | 45 | 0 | 45 |
| 3 doses | 6 | 0 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Fung, E.; Wong, C.-K.; Ling, L.; Lui, G.; Lai, C.K.C.; Ng, R.W.Y.; Sze, R.K.H.; Ho, W.C.S.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Early Metabolomic and Immunologic Biomarkers as Prognostic Indicators for COVID-19. Metabolites 2024, 14, 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14070380
Chen Z, Fung E, Wong C-K, Ling L, Lui G, Lai CKC, Ng RWY, Sze RKH, Ho WCS, Hui DSC, et al. Early Metabolomic and Immunologic Biomarkers as Prognostic Indicators for COVID-19. Metabolites. 2024; 14(7):380. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14070380
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zigui, Erik Fung, Chun-Kwok Wong, Lowell Ling, Grace Lui, Christopher K. C. Lai, Rita W. Y. Ng, Ryan K. H. Sze, Wendy C. S. Ho, David S. C. Hui, and et al. 2024. "Early Metabolomic and Immunologic Biomarkers as Prognostic Indicators for COVID-19" Metabolites 14, no. 7: 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14070380
APA StyleChen, Z., Fung, E., Wong, C.-K., Ling, L., Lui, G., Lai, C. K. C., Ng, R. W. Y., Sze, R. K. H., Ho, W. C. S., Hui, D. S. C., & Chan, P. K. S. (2024). Early Metabolomic and Immunologic Biomarkers as Prognostic Indicators for COVID-19. Metabolites, 14(7), 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14070380







