Application of the Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography (HILIC-MS) Novel Protocol to Study the Metabolic Heterogeneity of Glioblastoma Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of External Standards Spiked with Internal Standard
2.2. Collection of Cell Culture Media and Lysates
2.3. Media and Lysates Preparation for LC-MS Analysis
2.4. LC-MS Analysis
2.5. Processing of Spectra
2.6. Quantification of Metabolites
2.7. Protein Quantification
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Design and Testing of LC-MS
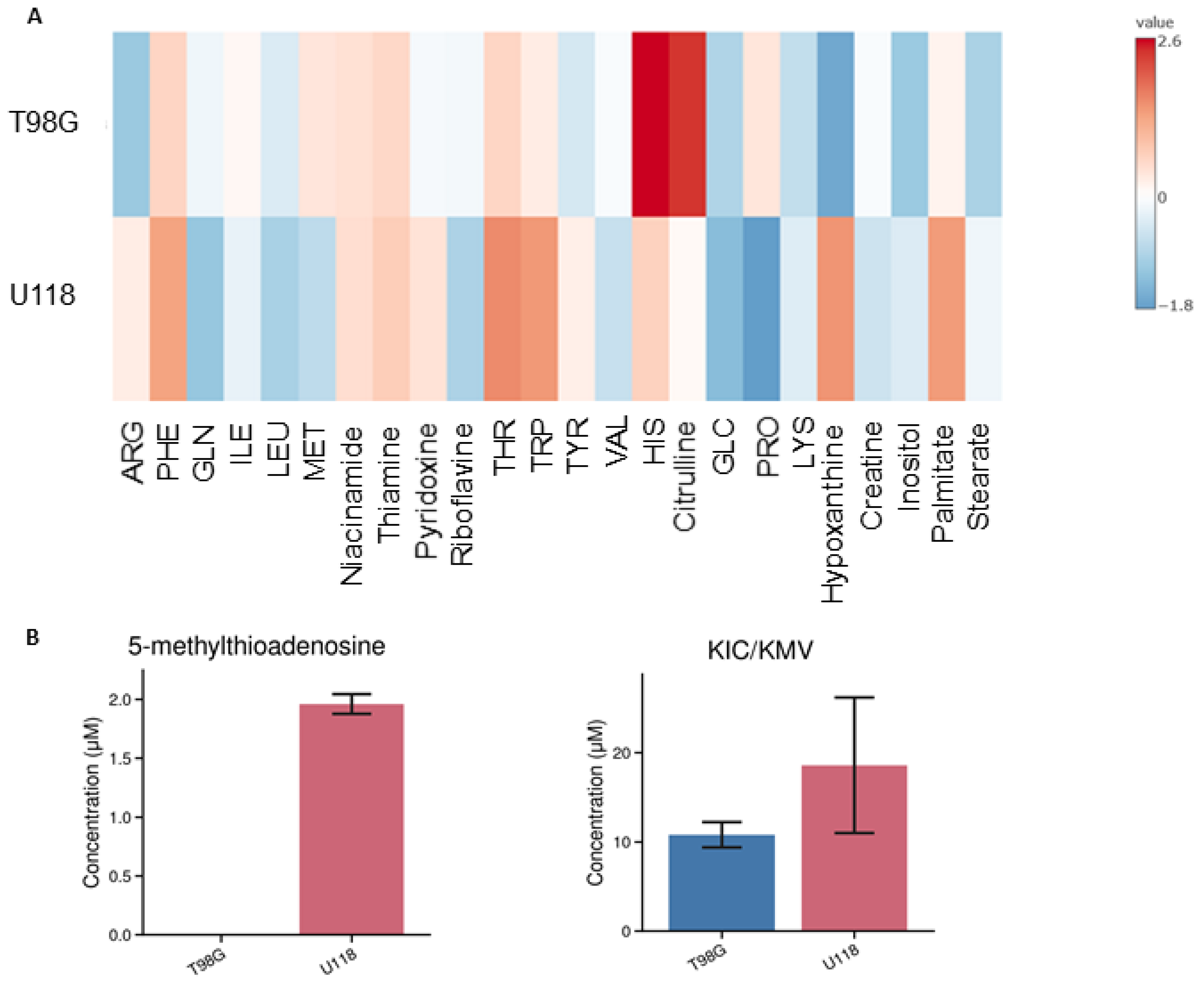
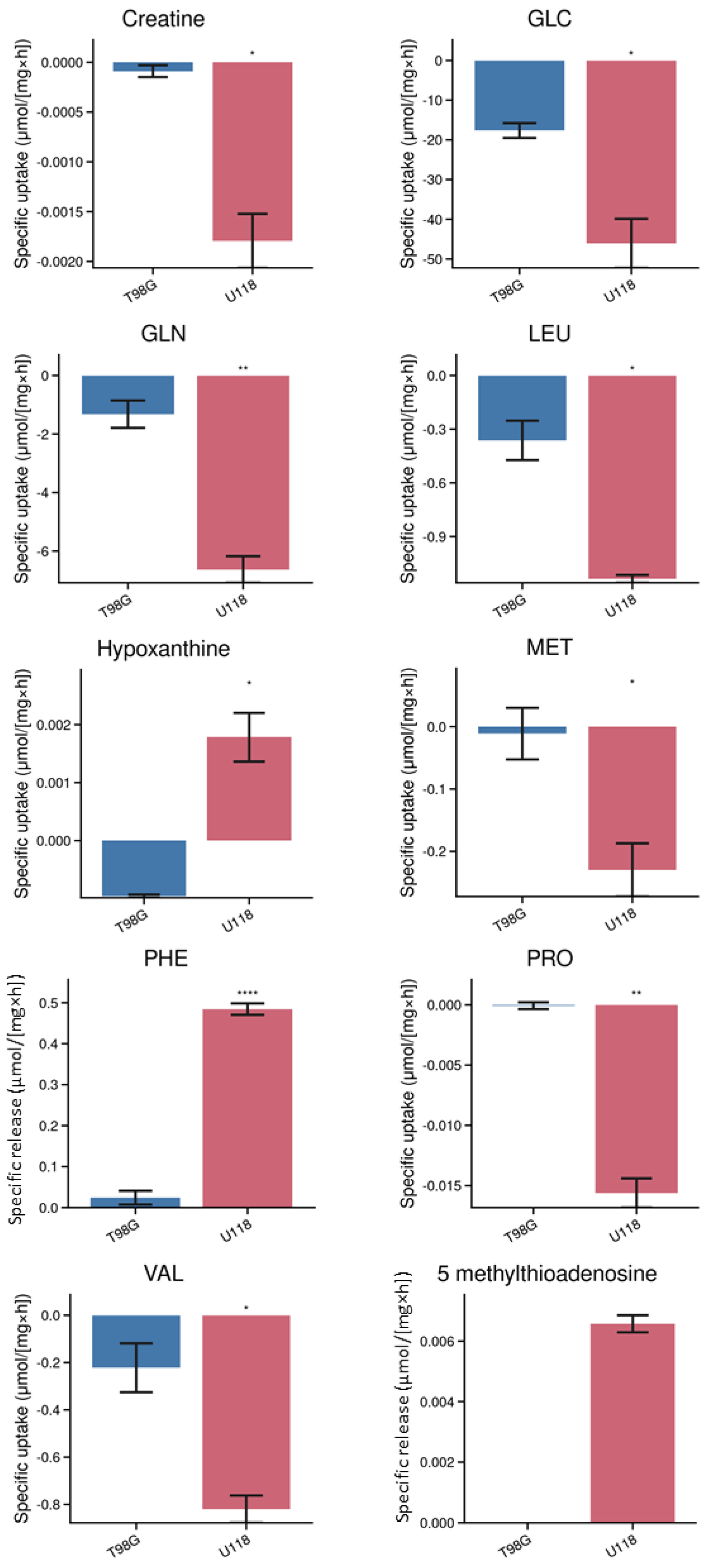
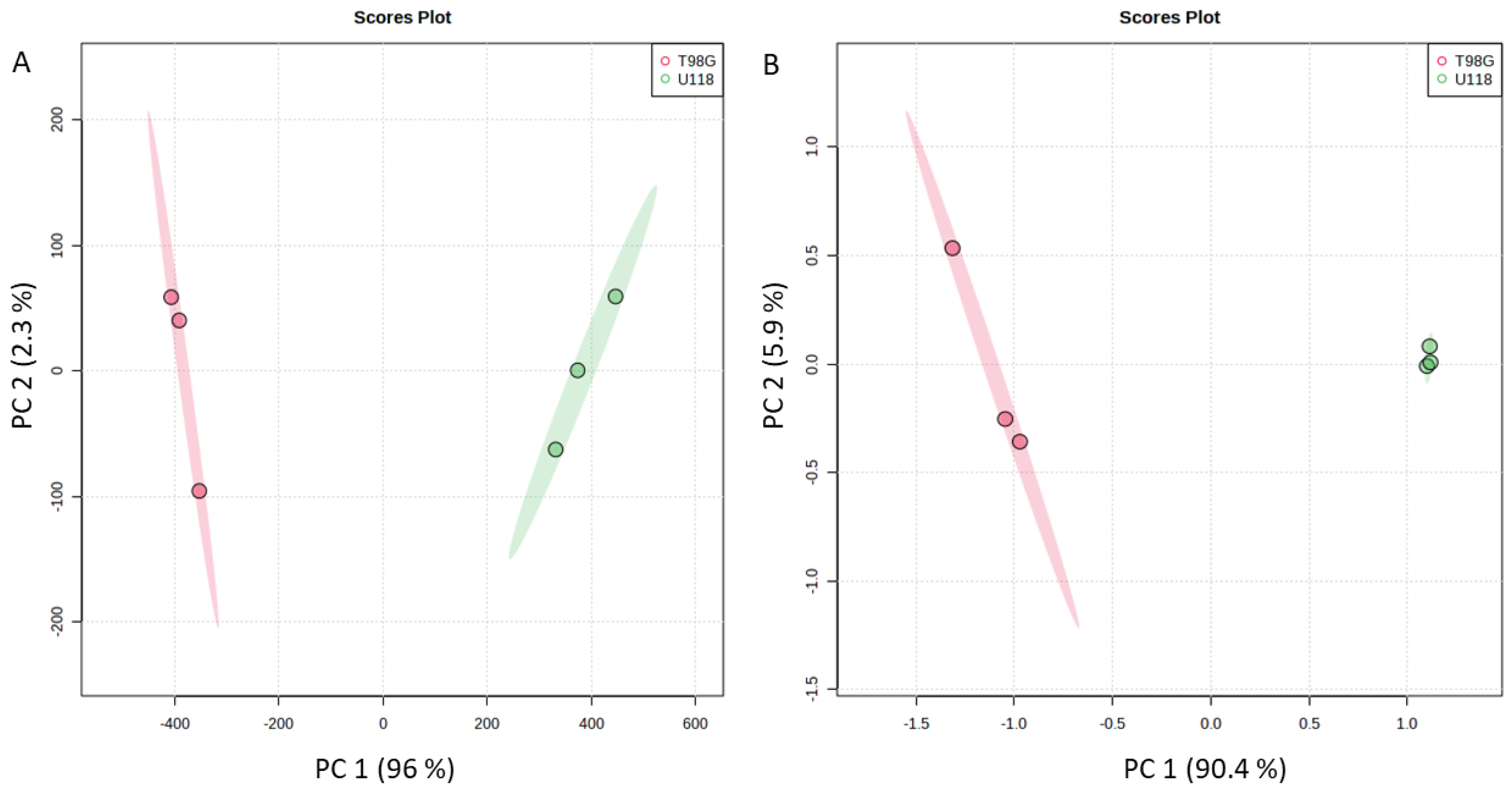
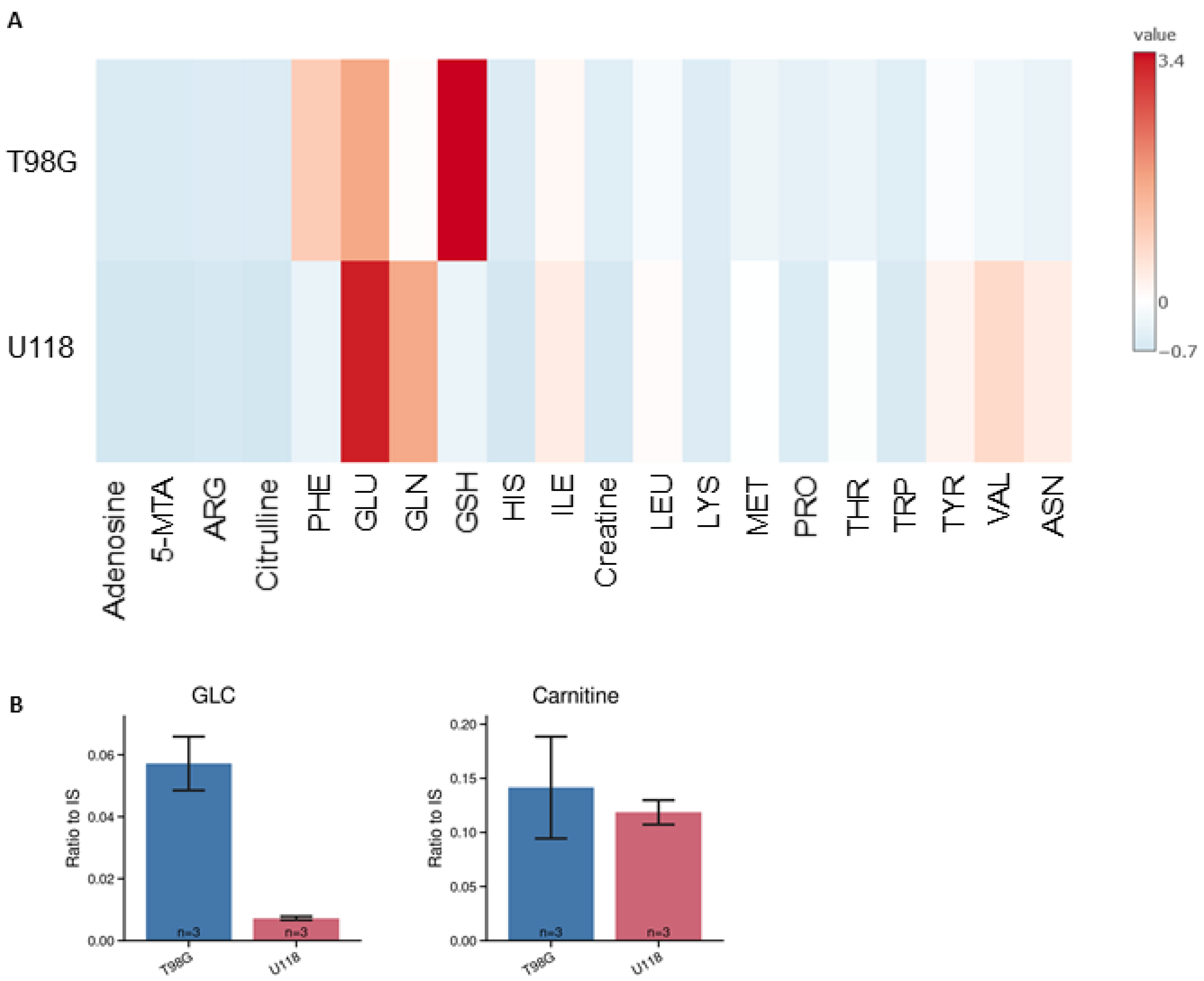
3.1. Identification and Quantification of Metabolites in Media
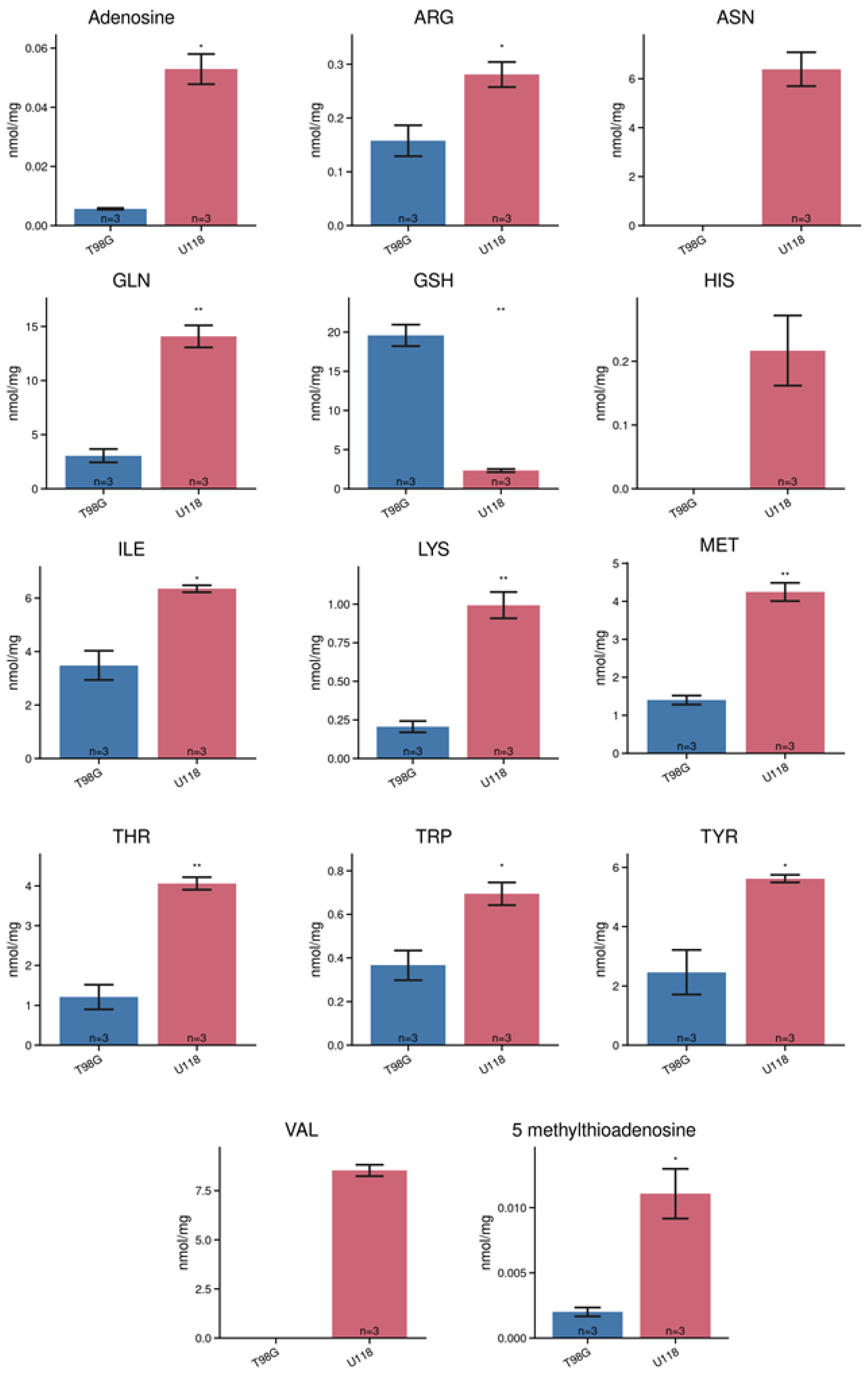
3.2. Identification and Quantification of Metabolites in Lysates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanif, F.; Muzaffar, K.; Perveen, K.; Malhi, S.; Simjee, S. Glioblastoma Multiforme: A Review of Its Epidemiology and Pathogenesis through Clinical Presentation and Treatment. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2017, 18, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapointe, S.; Perry, A.; Butowski, N.A. Primary Brain Tumours in Adults. Lancet 2018, 392, 432–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhard, C.; Reita, D.; Martin, S.; Entz-Werle, N.; Dontenwill, M. Glioblastoma Metabolism: Insights and Therapeutic Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarzuela, L.; Durán, R.V.; Tomé, M. Metabolism and Signaling Crosstalk in Glioblastoma Progression and Therapy Resistance. Mol. Oncol. 2023; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, N.N.; Thompson, C.B. The Emerging Hallmarks of Cancer Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; DeBerardinis, R.J. Mechanisms and Implications of Metabolic Heterogeneity in Cancer. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.; Gao, W.-Q.; Liu, Y. Metabolic Heterogeneity in Cancer: An Overview and Therapeutic Implications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2020, 1874, 188421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demicco, M.; Liu, X.-Z.; Leithner, K.; Fendt, S.-M. Metabolic Heterogeneity in Cancer. Nat. Metab. 2024, 6, 18–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, E.; Ji, B.; Jin, K.; Chen, Y. Branched-Chain Amino Acids Catabolism and Cancer Progression: Focus on Therapeutic Interventions. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1220638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondáš, E.; Kráľová Trančíková, A.; Baranovičová, E.; Šofranko, J.; Hatok, J.; Kowtharapu, B.S.; Galanda, T.; Dobrota, D.; Kubatka, P.; Busselberg, D.; et al. Expression of 3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA Carboxylase in Brain Tumors and Capability to Catabolize Leucine by Human Neural Cancer Cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieu, E.L.; Nguyen, T.; Rhyne, S.; Kim, J. Amino Acids in Cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cui, L.; Lu, S.; Xu, S. Amino Acid Metabolism in Tumor Biology and Therapy. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jiang, J.; Shen, A.; Miao, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cong, P.; Gao, P. Rewired Metabolism of Amino Acids and Its Roles in Glioma Pathology. Metabolites 2022, 12, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Liu, X.; Cheng, C.; Yu, W.; Yi, P. Metabolism of Amino Acids in Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 603837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Geng, F.; Cheng, X.; Guo, D. Lipid Metabolism Reprogramming and Its Potential Targets in Cancer. Cancer Commun. 2018, 38, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, Y.; Geng, F.; Guo, D. Lipid Metabolism in Glioblastoma: From De Novo Synthesis to Storage. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vettore, L.; Westbrook, R.L.; Tennant, D.A. New Aspects of Amino Acid Metabolism in Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, C.E.; Silver, D.J.; Siebzehnrubl, F.A.; Deleyrolle, L.P. Metabolic Heterogeneity and Adaptability in Brain Tumors. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 5101–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griguer, C.E.; Oliva, C.R.; Gillespie, G.Y. Glucose Metabolism Heterogeneity in Human and Mouse Malignant Glioma Cell Lines. J. Neurooncol. 2005, 74, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hensley, C.T.; Faubert, B.; Yuan, Q.; Lev-Cohain, N.; Jin, E.; Kim, J.; Jiang, L.; Ko, B.; Skelton, R.; Loudat, L.; et al. Metabolic Heterogeneity in Human Lung Tumors. Cell 2016, 164, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, O. Separation Tecniques: Chromatography. N. Clin. Istanb. 2016, 3, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holčapek, M.; Byrdwell, W.C. (Eds.) Handbook of Advanced Chromatography—Mass Spectrometry Techniques; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; AOCS Press: London, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-0-12-811732-3. [Google Scholar]
- Moldoveanu, S.; David, V. Other HPLC Separations Performed on Hydrophobic Stationary Phases. In Essentials in Modern HPLC Separations; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 421–446. ISBN 978-0-323-91177-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.-Y.; Li, S.; Zhu, Q.-F.; Wang, Q.; Hussain, D.; Feng, Y.-Q. Derivatization for Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Small-Molecular Weight Compounds. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 119, 115608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lioupi, A.; Marinaki, M.; Virgiliou, C.; Begou, O.; Gika, H.; Wilson, I.; Theodoridis, G. Probing the Polar Metabolome by UHPLC-MS. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 161, 117014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Velde, B.; Guillarme, D.; Kohler, I. Supercritical Fluid Chromatography—Mass Spectrometry in Metabolomics: Past, Present, and Future Perspectives. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1161, 122444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca, M.; Alcoriza, M.I.; Garcia-Cañaveras, J.C.; Lahoz, A. Reviewing the Metabolome Coverage Provided by LC-MS: Focus on Sample Preparation and Chromatography-A Tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1147, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spagou, K.; Tsoukali, H.; Raikos, N.; Gika, H.; Wilson, I.D.; Theodoridis, G. Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography Coupled to MS for Metabonomic/Metabolomic Studies. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Zou, L.; Yin, X.; Ong, C.N. HILIC-MS for Metabolomics: An Attractive and Complementary Approach to RPLC-MS. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2016, 35, 574–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondáš, E.; Kráľová Trančíková, A.; Dibdiaková, K.; Galanda, T.; Hatok, J.; Račay, P.; Dobrota, D.; Murín, R. Immunodetection of Pyruvate Carboxylase Expression in Human Astrocytomas, Glioblastomas, Oligodendrogliomas, and Meningiomas. Neurochem. Res. 2023, 48, 1728–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondáš, E.; Kráľová Trančíková, A.; Majerčíková, Z.; Pokusa, M.; Baranovičová, E.; Bystrický, P.; Dobrota, D.; Murín, R. Expression of Pyruvate Carboxylase in Cultured Human Astrocytoma, Glioblastoma and Neuroblastoma Cells. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2021, 40, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šofranko, J.; Mitro, P.; Lazúrová, Z.; Péč, M.J.; Bolek, T.; Péčová, R.; Samoš, M.; Murín, R. Application of Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Mass Spectrometry for Direct Estimation of the Total Levels of Adenosine and Its Catabolites in Human Blood. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, K.J.; Pratt, B.; Bose, N.; Dubois, L.G.; St. John-Williams, L.; Perrott, K.M.; Ky, K.; Kapahi, P.; Sharma, V.; MacCoss, M.J.; et al. Skyline for Small Molecules: A Unifying Software Package for Quantitative Metabolomics. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 1447–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.J. Principles and Applications of Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry in Clinical Biochemistry. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2009, 30, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein Measurement with the Folin Phenol Reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietzke, M.; Vazquez, A. Metabolite AutoPlotter—An Application to Process and Visualise Metabolite Data in the Web Browser. Cancer Metab. 2020, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Z.; Zhou, G.; Ewald, J.; Chang, L.; Hacariz, O.; Basu, N.; Xia, J. Using MetaboAnalyst 5.0 for LC–HRMS Spectra Processing, Multi-Omics Integration and Covariate Adjustment of Global Metabolomics Data. Nat. Protoc. 2022, 17, 1735–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saigusa, D.; Okamura, Y.; Motoike, I.N.; Katoh, Y.; Kurosawa, Y.; Saijyo, R.; Koshiba, S.; Yasuda, J.; Motohashi, H.; Sugawara, J.; et al. Establishment of Protocols for Global Metabolomics by LC-MS for Biomarker Discovery. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Illana, Á.; Piñeiro-Ramos, J.D.; Sanjuan-Herráez, J.D.; Vento, M.; Quintás, G.; Kuligowski, J. Evaluation of Batch Effect Elimination Using Quality Control Replicates in LC-MS Metabolite Profiling. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1019, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeckling, C.D.; Beger, R.D.; Cheng, L.L.; Cumeras, R.; Cuthbertson, D.J.; Dasari, S.; Davis, W.C.; Dunn, W.B.; Evans, A.M.; Fernández-Ochoa, A.; et al. Current Practices in LC-MS Untargeted Metabolomics: A Scoping Review on the Use of Pooled Quality Control Samples. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 18645–18654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrieder, E.-M.; Kretschmer, F.; Böcker, S.; Witting, M. Current State-of-the-Art of Separation Methods Used in LC-MS Based Metabolomics and Lipidomics. J. Chromatogr. B 2022, 1188, 123069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siuzdak, G. Activity Metabolomics and Mass Spectrometry; MCC Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Bai, J.; An, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, R.; He, J.; Bi, X.; Song, Y.; Abliz, Z. Plasma Metabolome Analysis by Integrated Ionization Rapid-Resolution Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 27, 2071–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondyli, A.; Schrader, W. Evaluation of the Combination of Different Atmospheric Pressure Ionization Sources for the Analysis of Extremely Complex Mixtures. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 34, e8676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez de Souza, L.; Alseekh, S.; Scossa, F.; Fernie, A.R. Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry Variants for Metabolomics Research. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sindelar, M.; Patti, G.J. Chemical Discovery in the Era of Metabolomics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 9097–9105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, J.; Chowdhry, S.; Wu, S.; Zhang, W.; Masui, K.; Mischel, P.S. Altered Cellular Metabolism in Gliomas—An Emerging Landscape of Actionable Co-Dependency Targets. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elia, I.; Broekaert, D.; Christen, S.; Boon, R.; Radaelli, E.; Orth, M.F.; Verfaillie, C.; Grünewald, T.G.P.; Fendt, S.-M. Proline Metabolism Supports Metastasis Formation and Could Be Inhibited to Selectively Target Metastasizing Cancer Cells. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harders, A.R.; Spellerberg, P.; Dringen, R. Exogenous Substrates Prevent the Decline in the Cellular ATP Content of Primary Rat Astrocytes During Glucose Deprivation. Neurochem. Res. 2024, 49, 1188–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, P. 5′-Methylthioadenosine and Cancer: Old Molecules, New Understanding. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaroch, K.; Modrakowska, P.; Bojko, B. Glioblastoma Metabolomics—In Vitro Studies. Metabolites 2021, 11, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Gu, J.; Huang, C.; Liu, D.; Huang, H.; Huang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Yang, W.; Liu, K.; Lin, D.; et al. Malignancy-Associated Metabolic Profiling of Human Glioma Cell Lines Using 1H NMR Spectroscopy. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidoni, L.; Ricci-Vitiani, L.; Rosi, A.; Palma, A.; Grande, S.; Luciani, A.M.; Pelacchi, F.; di Martino, S.; Colosimo, C.; Biffoni, M.; et al. 1H NMR Detects Different Metabolic Profiles in Glioblastoma Stem-like Cells. NMR Biomed. 2014, 27, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niechi, I.; Uribe-Ojeda, A.; Erices, J.I.; Torres, Á.; Uribe, D.; Rocha, J.D.; Silva, P.; Richter, H.G.; San Martín, R.; Quezada, C. Adenosine Depletion as A New Strategy to Decrease Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cells Aggressiveness. Cells 2019, 8, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamphorst, J.J.; Nofal, M.; Commisso, C.; Hackett, S.R.; Lu, W.; Grabocka, E.; Vander Heiden, M.G.; Miller, G.; Drebin, J.A.; Bar-Sagi, D.; et al. Human Pancreatic Cancer Tumors Are Nutrient Poor and Tumor Cells Actively Scavenge Extracellular Protein. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commisso, C.; Davidson, S.M.; Soydaner-Azeloglu, R.G.; Parker, S.J.; Kamphorst, J.J.; Hackett, S.; Grabocka, E.; Nofal, M.; Drebin, J.A.; Thompson, C.B.; et al. Macropinocytosis of Protein Is an Amino Acid Supply Route in Ras-Transformed Cells. Nature 2013, 497, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakya, S.; Gromovsky, A.D.; Hale, J.S.; Knudsen, A.M.; Prager, B.; Wallace, L.C.; Penalva, L.O.F.; Brown, H.A.; Kristensen, B.W.; Rich, J.N.; et al. Altered Lipid Metabolism Marks Glioblastoma Stem and Non-Stem Cells in Separate Tumor Niches. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parik, S.; Fernández-García, J.; Lodi, F.; De Vlaminck, K.; Derweduwe, M.; De Vleeschouwer, S.; Sciot, R.; Geens, W.; Weng, L.; Bosisio, F.M.; et al. GBM Tumors Are Heterogeneous in Their Fatty Acid Metabolism and Modulating Fatty Acid Metabolism Sensitizes Cancer Cells Derived from Recurring GBM Tumors to Temozolomide. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 988872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kant, S.; Kesarwani, P.; Prabhu, A.; Graham, S.F.; Buelow, K.L.; Nakano, I.; Chinnaiyan, P. Enhanced Fatty Acid Oxidation Provides Glioblastoma Cells Metabolic Plasticity to Accommodate to Its Dynamic Nutrient Microenvironment. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, P.; Kim, S.-H.; Ito, S.; Yang, C.; Wang, P.; Xiao, M.-T.; et al. Oncometabolite 2-Hydroxyglutarate Is a Competitive Inhibitor of α-Ketoglutarate-Dependent Dioxygenases. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanders, R.J.A.; Mooyer, P. D-2-Hydroxyglutaric Acidaemia: Identification of a New Enzyme,d-2-Hydroxyglutarate Dehydrogenase, Localized in Mitochondria. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1995, 18, 194–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Hu, H. The Roles of 2-Hydroxyglutarate. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 651317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonneau, M.; Gagné, L.M.; Lalonde, M.-E.; Germain, M.-A.; Motorina, A.; Guiot, M.-C.; Secco, B.; Vincent, E.E.; Tumber, A.; Hulea, L.; et al. The Oncometabolite 2-Hydroxyglutarate Activates the mTOR Signalling Pathway. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondáš, E.; Baranovičová, E.; Bystrický, P.; Šofránko, J.; Evinová, A.; Dohál, M.; Hatoková, Z.; Murín, R. Both Enantiomers of 2-Hydroxyglutarate Modulate the Metabolism of Cultured Human Neuroblastoma Cells. Neurochem. Res. 2024. in review. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Soga, T.; Pollard, P.J. Oncometabolites: Linking Altered Metabolism with Cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3652–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Common Name | IUPAC Name | m/z | tR (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acetoacetate | 3-Oxobutanoic acid | 101.0258 | 5.5 |
| Acetylcarnitine | 3-Acetyloxy-4-trimethylammonio-butanoate | 204.1230 | 13.3 |
| Acetyl-CoA | O1-{(3R)-4-[(3-{[2-(Acetylsulfanyl)ethyl]amino}-3-oxopropyl)amino]-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-4-oxobutyl} O3-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)oxolan-2-yl]methyl} dihydrogen diphosphate | 404.0488 | 12.3 |
| N-Acetylcysteine | 2-Acetamido-3-sulfanylpropanoic aci | 164.0914 | 6.3 |
| Adenosine | 2-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol | 268.1022 | 3.7 |
| ADP | [(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Aminopurin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl phosphono hydrogen phosphate | 426.0137 | 11.2 |
| AICA Riboside-5-phosphate | 1-(5-Amino-4-carbamoyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)-1,4-anhydro-D-ribitol 5-(dihydrogen phosphate) | 339.0685 | 10.8 |
| Alanine | 2-Aminopropanoic acid | 90.055 | 7.3 |
| Alanyl-Glutamine | 5-Amino-2-[[(2S)-2-aminopropanoyl]amino]-5-oxopentanoic acid | 218.1508 | 5.7 |
| γ-Aminobutyric acid | 4-Aminobutanoic acid | 104.0706 | 4.6 |
| Arachidonic acid | Icosa-5,8,11,14-tetraenoic acid | 303.2324 | 1.7 |
| Arachidonic acid methyl ester | Methyl-icosa-5,8,11,14-tetraenoic acid | 319.2225 | 1.7 |
| Arginine | 2-Amino-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoic acid | 175.119 | 15.9 |
| Ascorbic acid | 3,4-Dihydroxy-5-((S)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl)furan-2(5H)-one | 175.0238 | 12.7 |
| Asparagine | 2,4-Diamino-4-oxobutanoic acid | 133.0596 | 10.4 |
| Aspartic acid | 2-Aminobutanedioic acid | 134.0476 | 10.9 |
| ATP | [[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Aminopurin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl] phosphono hydrogen phosphate | (−) 505.9805 | 14.0 |
| ATP Betaine | [[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Aminopurin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl] phosphono hydrogen phosphate 2-(Trimethylazaniumyl)acetate | 507.9996 | 14.0 |
| 118.0863 | 1.6 | ||
| Biopterin | 2-Amino-6-(1,2-dihydroxypropyl)-1H-pteridin-4-one | (−) 236.0804 | 7.2 |
| Biopterin Biotin | 2-Amino-6-(1,2-dihydroxypropyl)-1H-pteridin-4-one 2-Oxohexahydro-1H-thieno [3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl]pentanoic acid | 238.1131 | 7.2 |
| 245.0954 | 8.8 | ||
| Butyrylcarnitine | 3-Butanoyloxy-4-(trimethylazaniumyl)butanoate | 232.1543 | 10.8 |
| Caffeine | 1,3,7-Trimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dion | 195.0937 | 1.8 |
| cAMP | (4aR,6R,7R,7aS)-6-(6-Aminopurin-9-yl)-2-hydroxy-2-oxo-4a,6,7,7a-tetrahydro-4H-furo [3,2-d][1,3,2]dioxaphosphinin-7-ol | (−) 328.0414 | 9.7 |
| cAMP Carnitine | (4aR,6R,7R,7aS)-6-(6-Aminopurin-9-yl)-2-hydroxy-2-oxo-4a,6,7,7a-tetrahydro-4H-furo [3,2-d][1,3,2]dioxaphosphinin-7-ol 3-Hydroxy-4-(trimethylazaniumyl)butanoate | 330.0603 | 9.7 |
| 227.1125 | 12.1 | ||
| Carnitine Carnosine | 3-Hydroxy-4-(trimethylazaniumyl)butanoate 2-(3-Aminopropanamido)-3-(3H-imidazol-4-yl)propanoic acid | 162.1125 | 15.6 |
| 227.1125 | 12.1 | ||
| Cervonic acid | Docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoic acid | 327.2330 | 2.2 |
| Citric acid | 2-Hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid | 191.0197 | 21.6 |
| Citrulline | 2-Amino-5-(carbamoylamino)pentanoic acid[ | 176.1029 | 10.3 |
| Coenzyme A | [[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Aminopurin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-phosphonooxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl] [(3R)-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-4-oxo-4-[[3-oxo-3-(2-sulfanylethylamino)propyl]amino]butyl] hydrogen phosphate | 357.0813 | 5.3 |
| Creatine | 2-[Carbamimidoyl(methyl)amino]acetic acid | 132.0768 | 2.4 |
| Creatinine | 2-Amino-1-methyl-5H-imidazol-4-one | 114.0662 | 8.5 |
| Cystathionine | S-((R)-2-Amino-2-carboxyethyl)-L-homocysteine | 223.0742 | 13.1 |
| Cytosine | 4-Aminopyrimidin-2(1H)-one | 112.0497 | 6.4 |
| Decanoylcarnitine | 3-Decanoyloxy-4-(trimethylazaniumyl)butanoate | 316.2482 | 7.6 |
| 7,8-Dihydrobiopterin | 2-Amino-6-(1,2-dihydroxypropyl)-7,8-dihydro-1H-pteridin-4-one | 240.1149 | 7.5 |
| Dimethylarginine | (2S)-5-(Diaminomethylideneamino)-2-(dimethylamino)pentanoic acid | 203.1491 | 10.3 |
| Dimethyllysine | 2-Amino-6-(dimethylamino)hexanoic acid | 175.1428 | 17.7 |
| Dodecanoylcarnitine | 3-Decanoyloxy-4-(trimethylazaniumyl)butanoate | 344.2795 | 7.4 |
| Dopamine | 4-(2-Aminoethyl)benzene-1,2-diol | 154.0863 | 2.3 |
| EDTA | 2-[2-[Bis(carboxymethyl)amino]ethyl-(carboxymethyl)amino]acetic acid | (−) 291.0769 | 12.1 |
| EDTA EGTA | 2-[2-[Bis(carboxymethyl)amino]ethyl-(carboxymethyl)amino]acetic acid 2-[2-[2-[2-[Bis(carboxymethyl)amino]ethoxy]ethoxy]ethyl-(carboxymethyl)amino]acetic acid | 293.0982 | 12.1 |
| 381.1511 | 10.0 | ||
| Folic acid | 2-[[4-[(2-Amino-4-oxo-1H-pteridin-6-yl)methylamino]benzoyl]amino]pentanedioic acid | 440.1324 | 8.7 |
| Fructose-6-phosphate | 6-O-Phosphono-α-D-fructofuranose | 259.0217 | 11.7 |
| Fumaric acid | (E)-But-2-enedioic acid | 115.0037 | 17.6 |
| Gabapentin | 2-[1-(Aminomethyl)cyclohexyl]acetic acid | 172.1332 | 1.7 |
| Glucose | (3R,4S,5S,6R)-6-(Hydroxymethyl)oxane-2,3,4,5-tetrol | 179.0561 | 7.8 |
| Glucose-6-phosphate | Glucopyranose 6-phosphate | 259.0224 | 19.4 |
| L-Glutamic acid | (2S)-2-Aminopentanedioic acid | 148.0604 | 10.2 |
| L-Glutamine | (2S)-2,5-Diamino-5-oxopentanoic acid | 147.0764 | 9.8 |
| Glutaric acid | Pentanedioic acid | 131.0346 | 12.1 |
| Glutathione | (2S)-2-Amino-5-[[(2R)-1-(carboxymethylamino)-1-oxo-3-sulfanylpropan-2-yl]amino]-5-oxopentanoic acid | 308.0906 | 11.4 |
| Glycerol 1-phosphate | 2,3-Dihydroxyprop yl dihydrogen phosphate | 171.008 | 10.9 |
| Guanine | 2-Amino-1,9-dihydro-6H-purin-6-one | 152.0563 | 7.1 |
| GMP | [(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(2-Amino-6-oxo-1H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl dihydrogen phosphate | 362.0501 | 11.2 |
| Hexanoylcarnitine | 3-Hexanoyloxy-4-(trimethylazaniumyl)butanoate | 260.1856 | 8.9 |
| Histamine | 2-(1H-Imidazol-4-yl)ethanamine | 112.0869 | 11.4 |
| Histidine | 2-Amino-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)propanoic acid | 156.0768 | 14.1 |
| Homocarnosine | 2-(4-Aminobutanoylamino)-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)propanoic acid | 241.1278 | 12.2 |
| Homocysteine | 2-Amino-4-sulfanylbutanoic acid | 136.0427 | 9.8 |
| α-Hydroxyglutaric acid | 2-Hydroxypentanedioic acid | 147.0293 | 12.0 |
| 3-Hydroxybutyric acid | 3- Hydroxypentanedioic acid | 103.0401 | 2.4 |
| D-2-Hydroxyglutaric acid | (2R)-2-Hydroxypentanedioic acid | 147.0314 | 11.4 |
| L-2-Hydroxyglutaric acid | (2S)-2-Hydroxypentanedioic acid | 147.0314 | 11.4 |
| 3-Hydroxyisobutyric acid | 3-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanoic acid | 103.0401 | 2.4 |
| Hydroxyproline | 4-Hydroxypyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid | 132.0998 | 10.0 |
| Hypoxanthine | 1,9-Dihydro-6H-purin-6-one | 135.0375 | 5.7 |
| Inosine | 3,4-Dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-6,9-dihydro-3H-purin-6-one | 269.0858 | 6.9 |
| Inosine 5′-monophosphate | [3,4-bis(trimethylsilyloxy)-5-(6-trimethylsilyloxypurin-9-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methyl bis(trimethylsilyl) phosphate | (−) 347.041 | 10.7 |
| Inosine 5′-monophosphate Inositol | [3,4-bis(trimethylsilyloxy)-5-(6-trimethylsilyloxypurin-9-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methyl bis(trimethylsilyl) phosphate Cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol | 349.1287 | 10.7 |
| 179.0521 | 8.9 | ||
| Isocitrate | 1-Hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid | 191.0197 | 21.6 |
| Isoleucine | 2-Amino-3-methylpentanoic acid | 132.1019 | 7.3 |
| Isovaleryl-CoA | S-{(9R)-1-[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydro-2-furanyl]-3,5,9-trihydroxy-8,8-dimethyl-3,5-dioxido-10,14-dioxo-2,4,6-trioxa-11,15-diaza-3λ5,5λ5- diphosphaheptadecan-17-yl} 2-methylpropanethioate | 850.1486 | 11.1 |
| Itaconic acid | Methylidenebutanedioic acid | 129.0219 | 10.2 |
| α-Ketoisocaproic acid | 4-Methyl-2-oxopentanoic acid | (−) 129.0582 | 2.9 |
| α-Ketoisovaleric acid | 3-Methyl-2-oxobutanoic acid | (−) 115.0428 | 3.3 |
| α-Keto-β-methylvaleric acid | 2-formylpentanoic acid | (−) 129.0582 | 2.9 |
| Kynurenine | 2-Amino-4-(2-aminophenyl)-4-oxo-butanoic acid | 209.0921 | 11.2 |
| Lactic acid | 2-Hydroxypropanoic acid | 89.0244 | 2.0 |
| Leucine | 2-Amino-4-methylpentanoic acid | 132.1019 | 7.5 |
| γ-Linolenic acid | Octadeca-6,9,12-trienoic acid | 277.2173 | 2.2 |
| Linoleic acid | Octadeca-9,12-dienoate | 279.233 | 2.3 |
| Lysine | 2,6-Diaminohexanoic acid | 147.1128 | 15.8 |
| Malic acid | 2-Hydroxybutanedioic acid | 133.0142 | 17.5 |
| Methionine | 2-Amino-4-(methylthio)butanoic acid | 150.0583 | 8.8 |
| 3-Methyladenine | 3-Methyl-7H-purin-6-imine | 157.0774 | 2.4 |
| Methylcrotonyl-CoA | 3′-O-Phosphonoadenosine 5′-[(3R)-3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4-{[3-({2-[(3-methylbut-2-enoyl)sulfanyl]ethyl}amino)-3-oxopropyl]amino}-4-oxobutyl dihydrogen diphosphate] | 850.1654 | 11.3 |
| Methylcrotonyl-CoA 5-Methylcytosine | 3′-O-Phosphonoadenosine 5′-[(3R)-3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4-{[3-({2-[(3-methylbut-2-enoyl)sulfanyl]ethyl}amino)-3-oxopropyl]amino}-4-oxobutyl dihydrogen diphosphate] 4-Amino-5-methylpyrimidin-2(1H)-one | (−) 848.1336 | 11.3 |
| 126.0617 | 4.2 | ||
| 6-O-Methylguanine | 6-Methoxy-9H-purin-2-amine | 166.0703 | 3.6 |
| 7-Methylguanine | 2-Amino-7-methyl-1,7-dihydro-6H-purin-6-one | 166.071 | 5.5 |
| 5-Methylthioadenosine | 5′-S-Methyl-5′-thioadenosine | 298.0958 | 1.9 |
| Trimethyllysine | (5-Amino-5-carboxypentyl)-trimethylazanium | 189.1598 | 8.5 |
| NAD+ | 5-(6-Aminopurin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl] [(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(3-carbamoylpyridin-1-ium-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl hydrogen phosphate | 665.1215 | 16.8 |
| NADH | 5-(6-Aminopurin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-oxidophosphoryl] [(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(3-carbamoylpyridin-1-ium-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl phosphate | 666.1337 | 16.4 |
| Neopterin | 2-Amino-6-(1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl)pteridin-4(1H)-one | 252.0678 | 8.9 |
| Neopterin | 2-Amino-6-(1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl)pteridin-4(1H)-one | 254.1203 | 8.9 |
| Niacinamide | Pyridine-3-carboxamide | 123.057 | 1.8 |
| N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid | 2-(Methylamino)butanedioic acid | (−) 146.0484 | 7.1 |
| N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid N-Methyllysine | 2-(Methylamino)butanedioic acid [(5S)-5-Carboxy-5-(methylamino)pentyl]azanium | 148.0605 | 7.1 |
| 161.1273 | 16.2 | ||
| N-Methyl phenylalanine | 2-(Methylamino)-3-phenylpropanoic acid | 180.1015 | 7.2 |
| Octanoylcarnitine | 3-Octanoyloxy-4-(trimethylazaniumyl)butanoate | 288.2169 | 8.0 |
| Ornithine | 2,5-Diaminopentanoic acid | 133.0972 | 15.5 |
| 2-Oxoglutaric acid | 2-Oxopentanedioic acid | 145.0142 | 16.0 |
| Palmitic acid | Hexadecanoic acid | 255.2330 | 2.3 |
| Palmitoylcarnitine | 3-hexadecanoyloxy-4-(trimethylazaniumyl)butanoate | 400.3421 | 7.0 |
| Pantothenic acid | 2,4-Dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanamido]propanoic acid | (−) 218.0983 | 7.4 |
| Pantothenic acid Phenylalanine | 2,4-Dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanamido]propanoic acid 2-Amino-3-phenylpropanoic acid | 220.1334 | 7.4 |
| 166.9863 | 7.2 | ||
| Phenylbutyric acid | 4-Phenylbutanoic acid | 163.076 | 2.2 |
| Phosphocreatine | N-Methyl-N-(phosphonocarbamimidoyl)glycine | 210.0258 | 12.2 |
| Phosphoenolpyruvic acid | 2-(Phosphonooxy)prop-2-enoic acid | 169.1011 | 1.4 |
| Proline | Pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid | 116.0706 | 8.5 |
| Pyridoxine | 4,5-Bis(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpyridin-3-ol | 170.0941 | 2.7 |
| Pyroglutamic acid | 5-Oxopyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid | 130.0449 | 10.2 |
| Retinol | 3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraen-1-ol | 285.2224 | 3.9 |
| Riboflavin | 7,8-Dimethyl-10-[(2S,3S,4R)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxypentyl]benzo[g]pteridine-2,4-dione | 377.1488 | 4.0 |
| Ribose | 5-(Hydroxymethyl)oxolane-2,3,4-triol | 149.047 | 9.9 |
| Serotonin | 3-(2-Aminoethyl)-1H-indol-5-ol | 177.1002 | 3.2 |
| Stearic acid | Octadecanoic acid | 283.2643 | 2.3 |
| Succinyl-CoA | 4-{[1,3-Dihydroxy-1,3-dioxo-3-(3′-O-phosphonoadenosin-5′-O-yl)-1λ5,3λ5-diphosphoxan-1-yl]oxy}-3,3-dimethylbutanamido]propanamido}ethyl)sulfanyl]-4-oxobutanoic acid | 117.0198 | 11.8 |
| Taurine | 2-Aminoethanesulfonic acid | 126.0231 | 10.0 |
| Tetradecanoylcarnitine | 3-Tetradecanoyloxy-4-(trimethylazaniumyl)butanoate | 372.3108 | 7.2 |
| Tetrahydrobiopterin | 2-Amino-6-[(1R,2S)-1,2-dihydroxypropyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropteridin-4(1H)-one | 242.1244 | 7.9 |
| Thiamine | 2-[3-[(4-Amino-2-methylpyrimidin-5-yl)methyl]-4-methyl-1,3-thiazol-3-ium-5-yl]ethanol | 265.1181 | 12.8 |
| Threonine | 2-Amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid | 120.0655 | 7.7 |
| Tocopherol | 2,5,7,8-Tetramethyl-2-[(4R,8R)-4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl]-3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzopyran-6-ol | 429.3738 | 2.2 |
| Tryptophan | 2-Amino-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)propanoic acid | 205.0972 | 7.8 |
| Tyrosine | 2-Amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid | 182.0812 | 20.1 |
| Valine | 2-Amino-3-methylbutanoic acid | 118.0863 | 7.7 |
| Vitamin D | 9,10-Secocholesta-5,7,10(19)-trien-3-ol | 383.3319 | 3.0 |
| Vitamin K | 3,7,11,15-Tetramethylhexadec-2-enyl]naphthalene-1,4-dione | 449.3425 | 4.3 |
| Xanthine | 3,7-Dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione | 151.0285 | 5.8 |
| Column | tR(ILE) (min) | tR(LEU) (min) | Peak Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sequant® ZIC®-cHILIC | 7.3 | 7.5 | 1.28 |
| Sequant® ZIC® pHILIC | 6.7 | 7.0 | 1.08 |
| Raptor Polar X | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.25 |
| YMC-Triart-Diol-HILIC | 7.4 | 7.5 | 0.55 |
| Analyte | Concentration Range (nM) | Linearity | Precision (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adenosine | 3.7–375 | 0.9920 | 5.4 |
| Arginine | 27.7–574 | 0.9664 | 19.2 |
| Asparagine | 7.5–751 | 0.9615 | 13.8 |
| Glutamate | 34–680 | 0.9734 | 13.5 |
| Glutamine | 68.4–685 | 0.9824 | 8.6 |
| Glutathione—reduced | 3.3–325 | 0.9820 | 15.9 |
| Histidine | 64.4–644 | 0.9923 | 30.5 |
| Hypoxanthine | 7.3–735 | 0.9857 | 8.4 |
| Isoleucine | 76.2–762 | 0.9690 | 8.7 |
| Leucine | 76.2–762 | 0.9637 | 8.2 |
| Methionine | 6.7–670 | 0.9718 | 29.7 |
| 5-Methylcytosine | 40–800 | 0.9922 | 7.6 |
| 5-Methylthioadenosine | 3.4–335 | 0.9978 | 10.2 |
| Phenylalanine | 6.1–605 | 0.9768 | 8.2 |
| Threonine | 8.4–840 | 0.9735 | 15.0 |
| Tryptophan | 4.9–490 | 0.9905 | 13.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šofranko, J.; Gondáš, E.; Murín, R. Application of the Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography (HILIC-MS) Novel Protocol to Study the Metabolic Heterogeneity of Glioblastoma Cells. Metabolites 2024, 14, 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14060297
Šofranko J, Gondáš E, Murín R. Application of the Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography (HILIC-MS) Novel Protocol to Study the Metabolic Heterogeneity of Glioblastoma Cells. Metabolites. 2024; 14(6):297. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14060297
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠofranko, Jakub, Eduard Gondáš, and Radovan Murín. 2024. "Application of the Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography (HILIC-MS) Novel Protocol to Study the Metabolic Heterogeneity of Glioblastoma Cells" Metabolites 14, no. 6: 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14060297
APA StyleŠofranko, J., Gondáš, E., & Murín, R. (2024). Application of the Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography (HILIC-MS) Novel Protocol to Study the Metabolic Heterogeneity of Glioblastoma Cells. Metabolites, 14(6), 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14060297






