Advancing Personalized Medicine by Analytical Means: Selection of Three Metabolites That Allows Discrimination between Glaucoma, Diabetes, and Controls
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Metabolomics
2.3. Data Compilation and Computational Analyses
3. Results
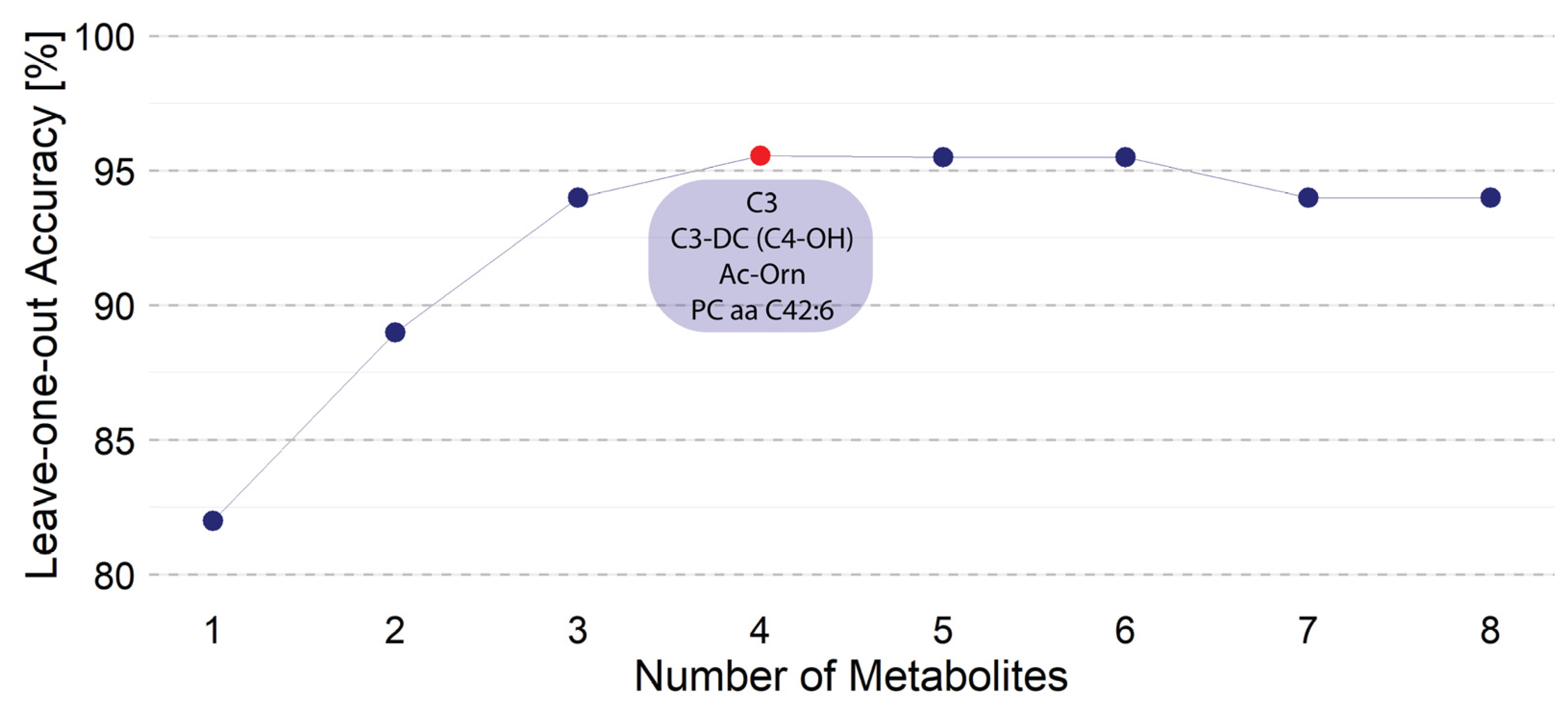
3.1. Linear Discrimination Analysis (LDA) Considering All Metabolites
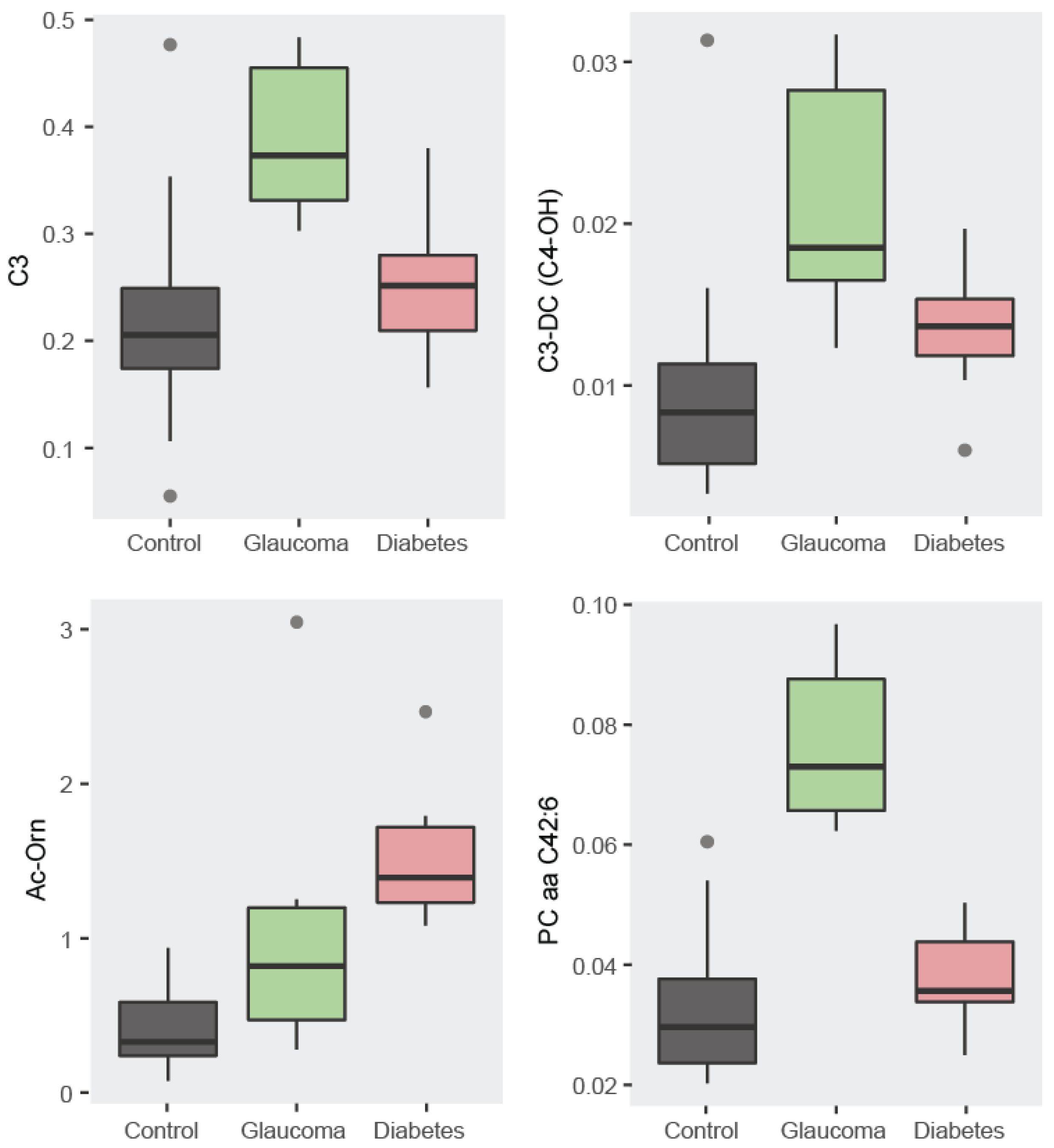
3.1.1. Descriptive Statistics: Boxplots
3.1.2. Correlation Analysis
3.2. Linear Discrimination Analysis (LDA) Considering the Most Discriminative Metabolites and Selecting an Optimal Non-Linear Combination
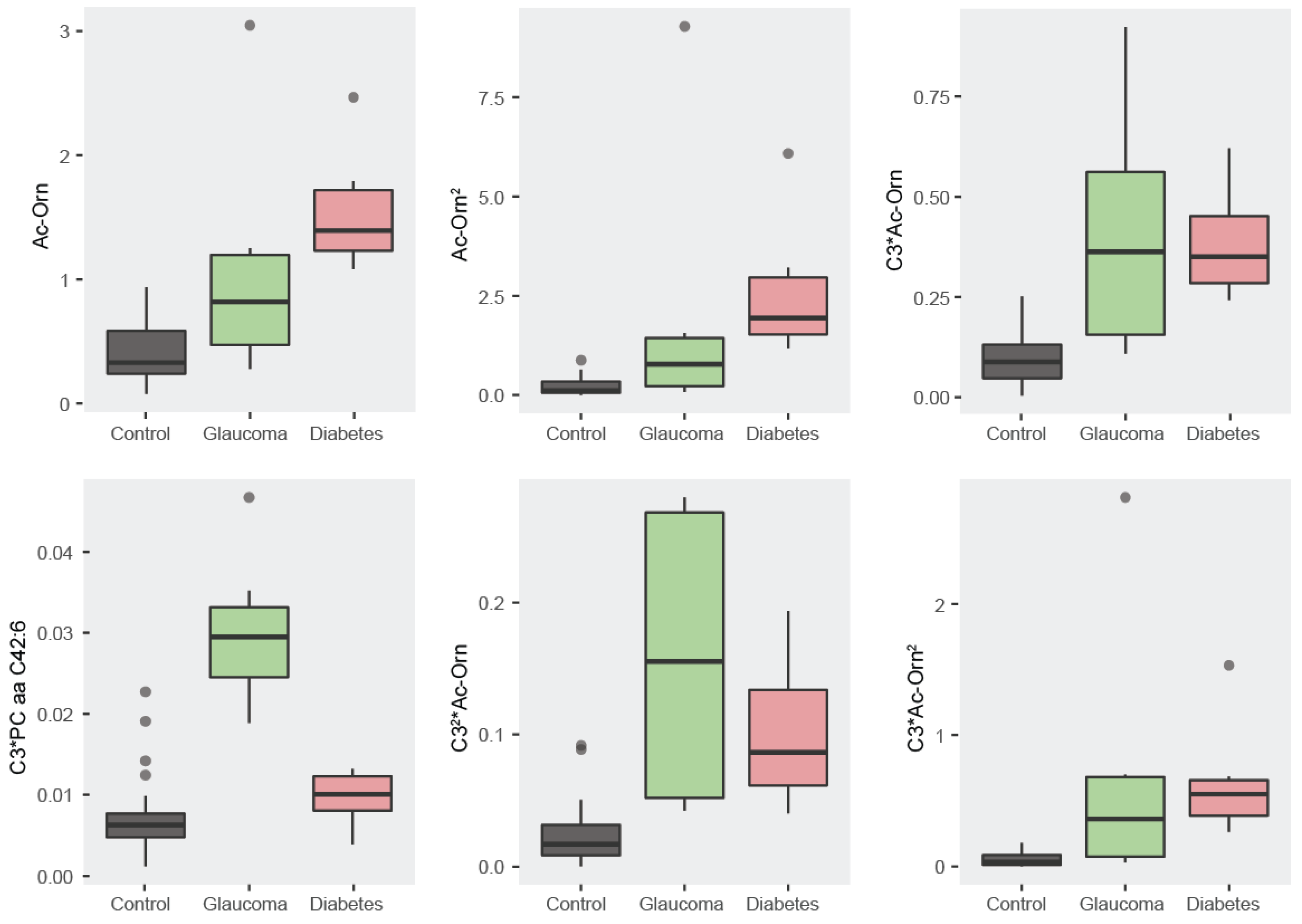
3.2.1. Descriptive Statistics: Boxplots
3.2.2. Correlation Analysis
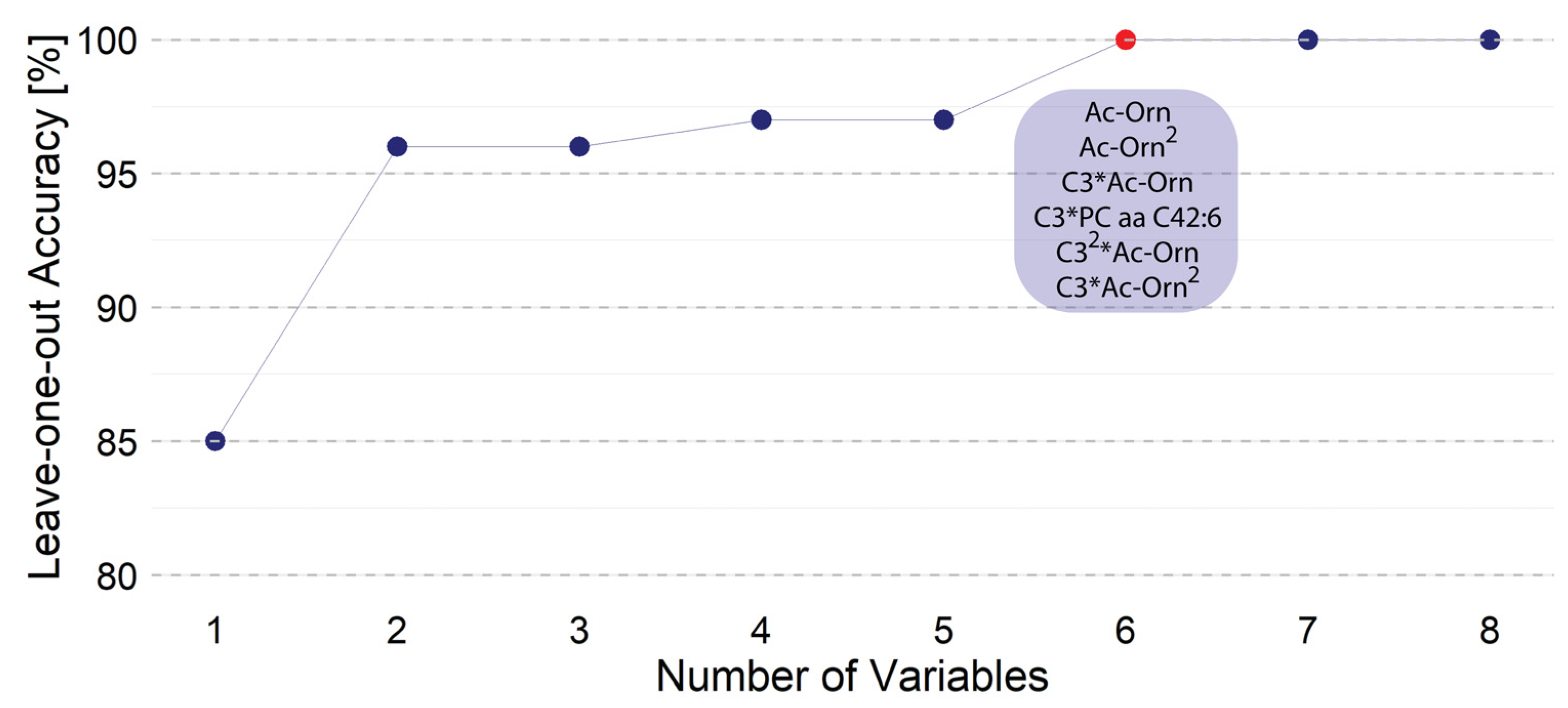
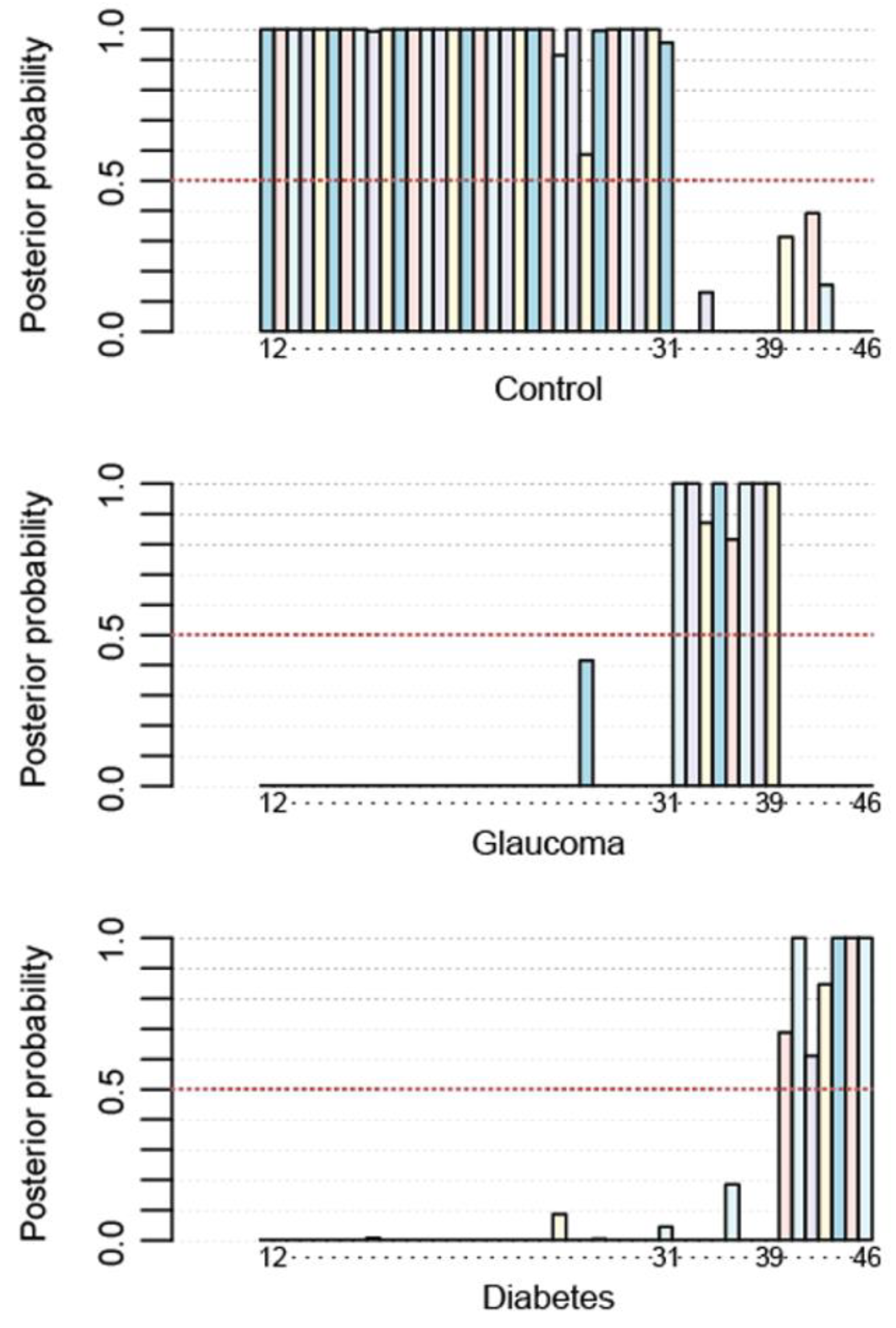
3.2.3. Non-Linear Method to Achieve 100% Accuracy
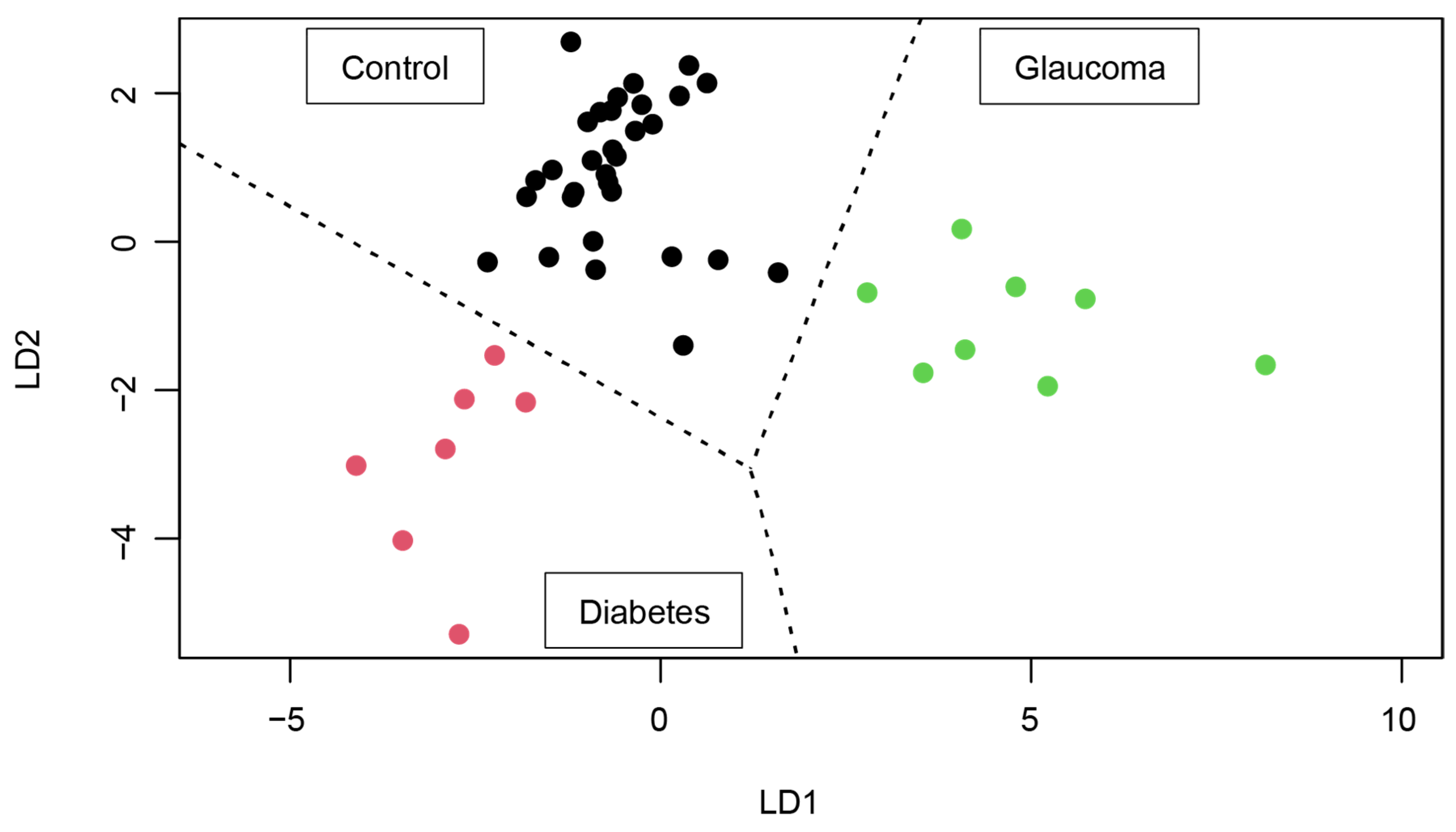
3.2.4. 2D Map Space Reflecting Position of Controls, Glaucoma Patients, and Type 2 Diabetes Patients
C3*PC aa C42:6 + 30.440 × C32*Ac-Orn + 27.188 × C3*Ac-Orn2.
C3*PC aa C42:6 + 45.883054 × C32*Ac-Orn + 16.104838 × C3*Ac-Orn2.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Pan, D.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Yan, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Yang, M.; Liu, G. Applications of multi-omics analysis in human diseases. MedComm 2023, 4, e315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, R.; Serrano-Marín, J. Can chronic therapeutic drug use by the elderly affect Alzheimers disease risk and rate of progression? Explor. Neuroprot. Ther. 2023, 3, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Shardell, M.D.; Kuo, P.L.; Tanaka, T.; Simonsick, E.M.; Moaddel, R.; Resnick, S.M.; Ferrucci, L. Plasma metabolomic signatures of dual decline in memory and gait in older adults. GeroScience 2023, 45, 2659–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Huang, L.; Jin, E.; Liang, Z.; Zhao, M. Plasma metabolomic profiling of central serous chorioretinopathy. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 203, 108401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillo, A.; Marin, S.; Serrano-Marín, J.; Bernal-Casas, D.; Binetti, N.; Navarro, G.; Cascante, M.; Sánchez-Navés, J.; Franco, R. Biogenic Amine Levels Markedly Increase in the Aqueous Humor of Individuals with Controlled Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Minno, A.; Gelzo, M.; Caterino, M.; Costanzo, M.; Ruoppolo, M.; Castaldo, G. Challenges in Metabolomics-Based Tests, Biomarkers Revealed by Metabolomic Analysis, and the Promise of the Application of Metabolomics in Precision Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, P.; Ho, A.M.C.; Tufvesson-Alm, M.; Lindberg, D.R.; Grant, C.W.; Orhan, F.; Eren, F.; Bhat, M.; Engberg, G.; Schwieler, L.; et al. Identification of cerebrospinal fluid and serum metabolomic biomarkers in first episode psychosis patients. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buergel, T.; Steinfeldt, J.; Ruyoga, G.; Pietzner, M.; Bizzarri, D.; Vojinovic, D.; Upmeier zu Belzen, J.; Loock, L.; Kittner, P.; Christmann, L.; et al. Metabolomic profiles predict individual multidisease outcomes. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2309–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Cai, Y.; Yao, H.; Lin, C.; Xie, Y.; Tang, S.; Zhang, A. Small molecule metabolites: Discovery of biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, A.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Dennis, S.; Hutch, M.; Xu, Z.; Wang, F.; Cheng, F.; Luo, Y. Multimodal machine learning in precision health: A scoping review. NPJ Digit. Med. 2022, 5, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pammi, M.; Aghaeepour, N.; Neu, J. Multiomics, artificial intelligence, and precision medicine in perinatology. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 93, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, C.A.; Rajpurkar, P.; Sowrirajan, H.; Phillips, N.A.; Le, A.T.; Wu, M.; Garamani, N.; Sahoo, M.K.; Wood, M.L.; Huang, C.H.; et al. Nasopharyngeal metabolomics and machine learning approach for the diagnosis of influenza. EBioMedicine 2021, 71, 103546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedi, V.; Khan, A.; Chaudhary, D.; Misra, D.; Avula, V.; Mathrawala, D.; Kraus, C.; Marshall, K.A.; Chaudhary, N.; Li, X.; et al. Using artificial intelligence for improving stroke diagnosis in emergency departments: A practical framework. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2020, 13, 1756286420938962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillo, A.; Marin, S.; Serrano-Marín, J.; Binetti, N.; Navarro, G.; Cascante, M.; Sánchez-Navés, J.; Franco, R. Targeted Metabolomics Shows That the Level of Glutamine, Kynurenine, Acyl-Carnitines and Lysophosphatidylcholines Is Significantly Increased in the Aqueous Humor of Glaucoma Patients. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, Y.; Koul, A.; Singla, R.; Ijaz, M.F. Artificial intelligence in disease diagnosis: A systematic literature review, synthesizing framework and future research agenda. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2023, 14, 8459–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonomo, R.; Cavaletti, G.; Skene, D.J. Metabolomics markers in Neurology: Current knowledge and future perspectives for therapeutic targeting. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2020, 20, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan-Smith, G.; Wallace, G.R.; Douglas, M.R.; Sinclair, A.J. The role of metabolomics in neurological disease. J. Neuroimmunol. 2012, 248, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, J.L.; Atherton, H.; Shockcor, J.; Atzori, L. Metabolomics as a tool for cardiac research. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2011, 8, 630–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarrah, R.W.; Crown, S.B.; Zhang, G.F.; Shah, S.H.; Newgard, C.B. Cardiovascular Metabolomics. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 1238–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Marín, J.; Marin, S.; Bernal-Casas, D.; Lillo, A.; González-Subías, M.; Navarro, G.; Cascante, M.; Sánchez-Navés, J.; Franco, R. A metabolomics study in aqueous humor discloses altered arginine metabolism in Parkinson’s disease. Fluids Barriers CNS 2023, 20, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Kong, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Tang, G.; Wu, J.; Sun, X. Metabolomic Profiling of Aqueous Humor and Plasma in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Patients Points Towards Novel Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 621146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeleznik, O.A.; Kang, J.H.; Lasky-Su, J.; Eliassen, A.H.; Frueh, L.; Clish, C.B.; Rosner, B.A.; Elze, T.; Hysi, P.; Khawaja, A.; et al. Plasma metabolite profile for primary open-angle glaucoma in three US cohorts and the UK Biobank. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, S.; Faheem, S.M.; Nawaz, S.S.; Siddiqui, K. The role of metabolomics in personalized medicine for diabetes. Pers. Med. 2021, 18, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelleni, M.T. Mini Review Integrative Obesity and Diabetes Together towards an early global detection of type 2 diabetes using a simplified metabolomics’ test. Integr Obes. Diabetes 2015, 1, 96–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reynier, P.; Leruez, S.; Procaccio, V.; Chao de la Marca, J.M.; Lenaers, G.; Bonneau, D.; Gohier, P. Metabolic Signature and Use Thereof for the Diagnosis of Glaucoma. World Intellectual Property Organization Patent WO2019185918A1, 29 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Bisbal, M.; Pinazo Durán, M.; Martínez Máñez, R.; Botello Marabotto, M.; Sanz González, S. Method for Detecting Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma Using Metabolomic Techniques 2023. World Intellectual Property Organization Patent PCT/ES2022/070703. WO/2023/079202, 11 May 2023. [Google Scholar]

| C3 | 0.4921 * | 0.3685 * | 0.5109 * |
| C3-DC (C4-OH) | 0.3018 * | 0.4539 * | |
| Ac-Orn | 0.3703 * | ||
| PC aa C42:6 |
| Ac-Orn | 0.8575 * | 0.3760 * | 0.2715 | 0.1843 | 0.1986 |
| Ac-Orn2 | 0.3719 * | 0.1813 | 0.1710 | 0.3177 * | |
| C3*Ac-Orn | 0.7258 * | 0.8972 * | 0.7186 * | ||
| C3*PC aa C42:6 | 0.7808 * | 0.4784 * | |||
| C32*Ac-Orn | 0.7293 * | ||||
| C3*Ac-Orn2 |
| Real | Control | Glaucoma | Diabetes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test | ||||
| Control | 31 | 0 | 0 | |
| Glaucoma | 0 | 8 | 0 | |
| Diabetes | 0 | 0 | 7 | |
| Real | Control | Glaucoma | Diabetes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test | ||||
| Control | 19 | 0 | 1 | |
| Glaucoma | 0 | 8 | 0 | |
| Diabetes | 0 | 0 | 7 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernal-Casas, D.; Serrano-Marín, J.; Sánchez-Navés, J.; Oller, J.M.; Franco, R. Advancing Personalized Medicine by Analytical Means: Selection of Three Metabolites That Allows Discrimination between Glaucoma, Diabetes, and Controls. Metabolites 2024, 14, 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14030149
Bernal-Casas D, Serrano-Marín J, Sánchez-Navés J, Oller JM, Franco R. Advancing Personalized Medicine by Analytical Means: Selection of Three Metabolites That Allows Discrimination between Glaucoma, Diabetes, and Controls. Metabolites. 2024; 14(3):149. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14030149
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernal-Casas, David, Joan Serrano-Marín, Juan Sánchez-Navés, Josep M. Oller, and Rafael Franco. 2024. "Advancing Personalized Medicine by Analytical Means: Selection of Three Metabolites That Allows Discrimination between Glaucoma, Diabetes, and Controls" Metabolites 14, no. 3: 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14030149
APA StyleBernal-Casas, D., Serrano-Marín, J., Sánchez-Navés, J., Oller, J. M., & Franco, R. (2024). Advancing Personalized Medicine by Analytical Means: Selection of Three Metabolites That Allows Discrimination between Glaucoma, Diabetes, and Controls. Metabolites, 14(3), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14030149







