Vertical Metabolome Transfer from Mother to Child: An Explainable Machine Learning Method for Detecting Metabolomic Heritability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
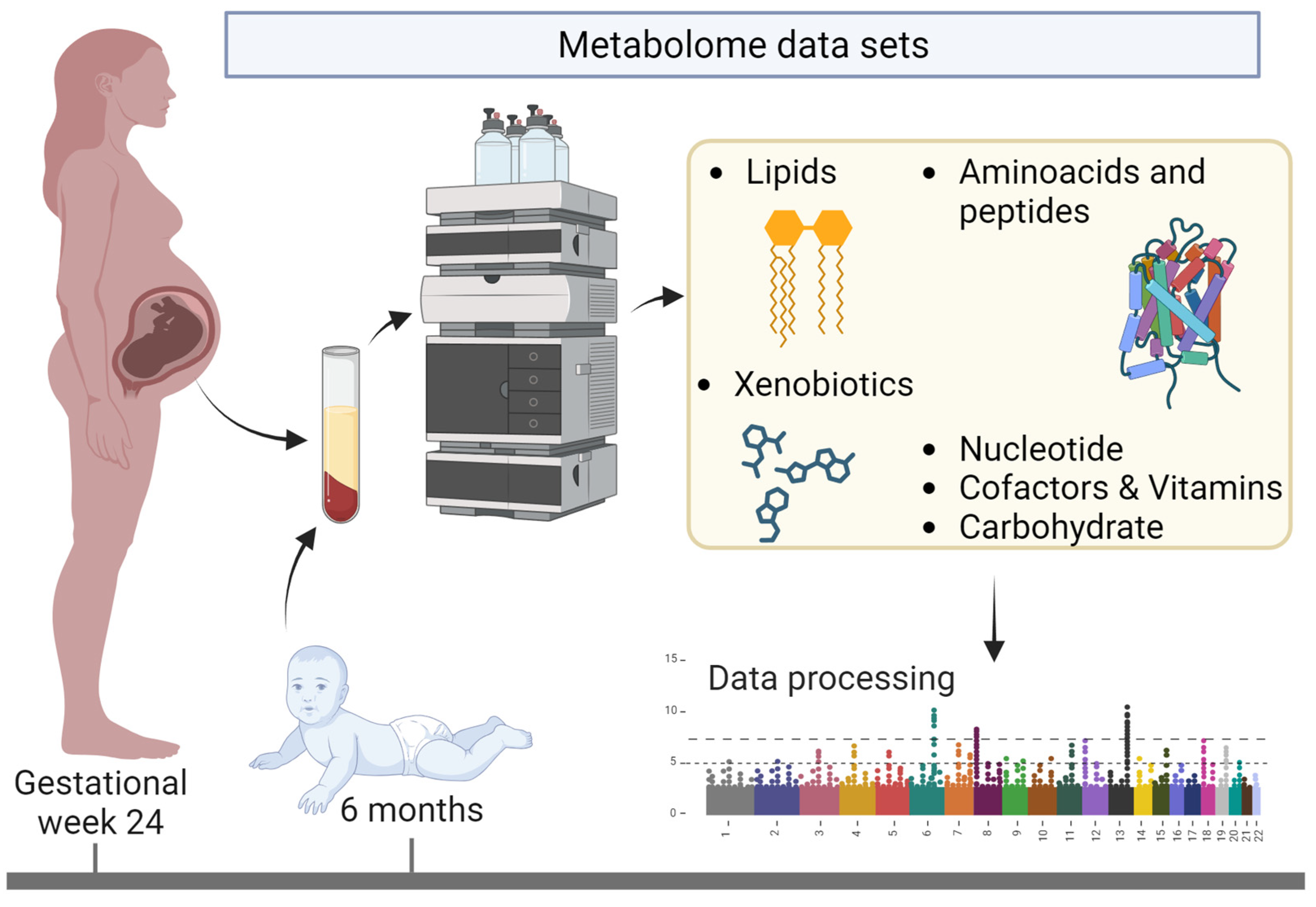
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Metabolites as Features in the Models
2.3. Machine Learning Methods, Statistics, and Model Scoring
2.4. Feature Selection and Model Explainability
3. Results
3.1. Machine Learning Results
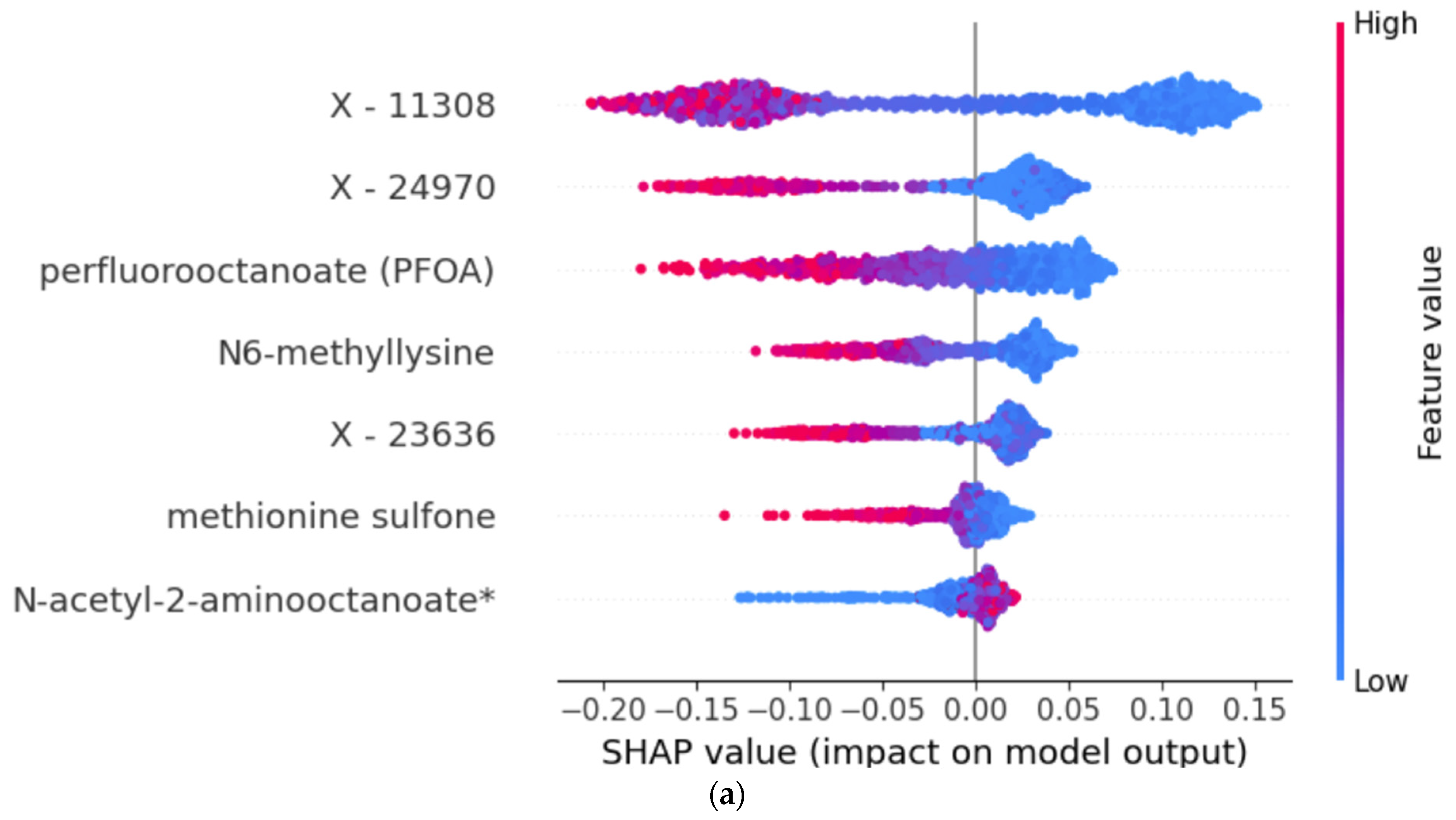
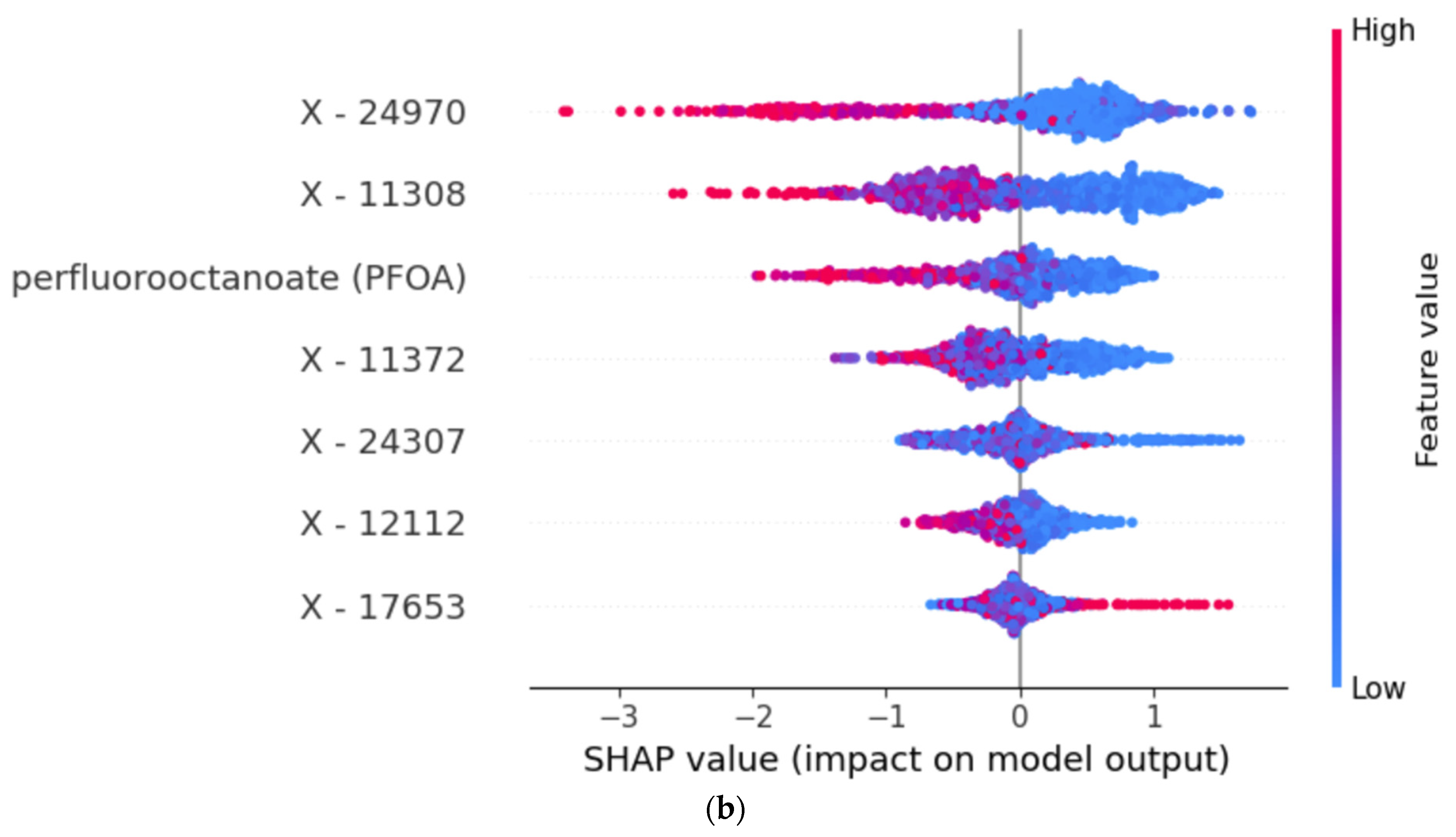
3.2. Model Explanations and Important Features
3.3. Model Results after Exclusion of Xenobiotics
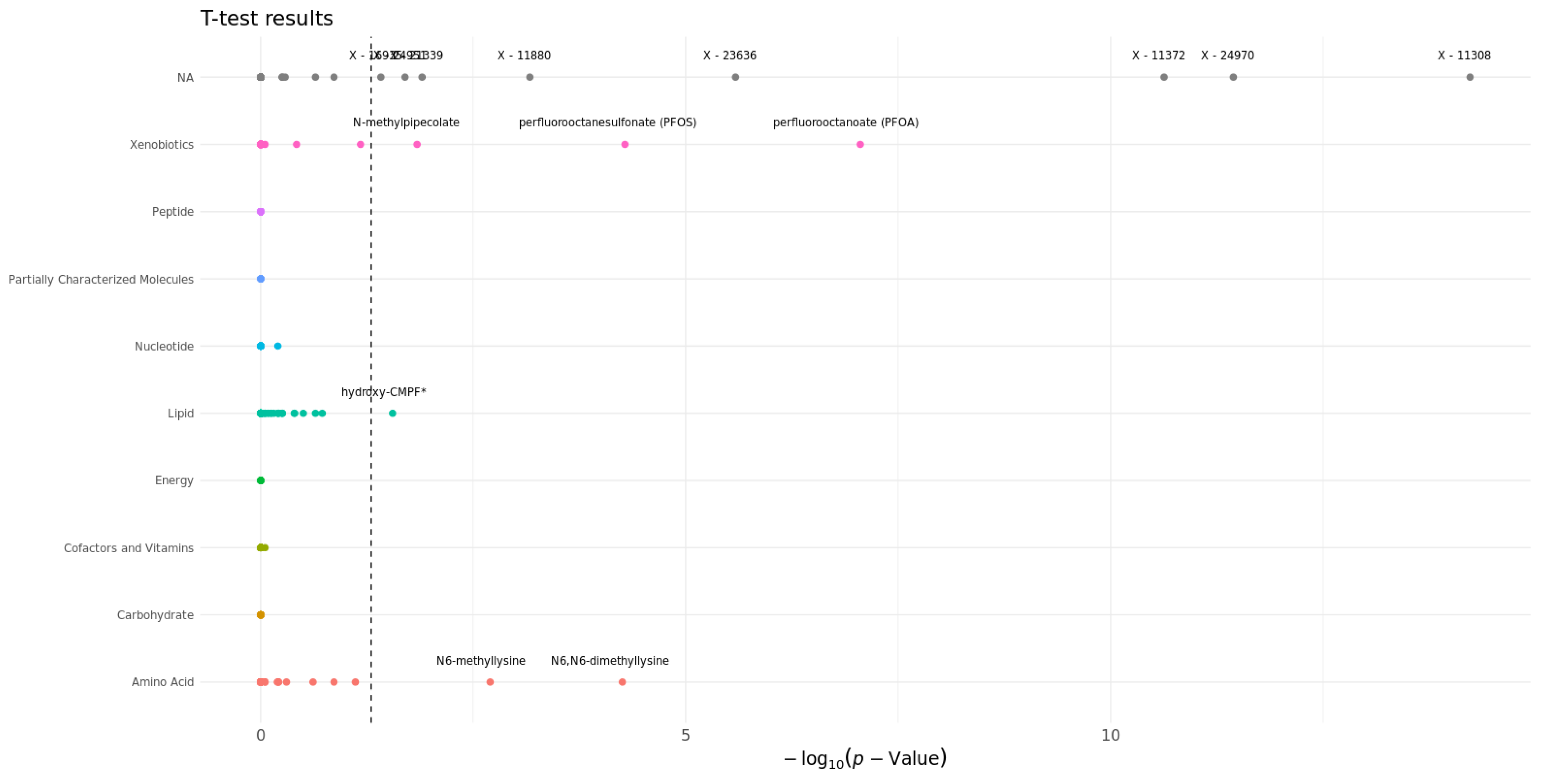
3.4. Statistical Analysis
3.5. Association to Infections and Breastfeeding
4. Discussion
Limitations and Future Research
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Model Hyperparameter Space
- (1)
- Random Forest
- (2)
- Logistic Regression
- (3)
- LightGBM (LGBM)
Appendix B. Final Model Hyperparameters
- (1)
- Random Forest
- (2)
- Logistic Regression
- (3)
- LightGBM (LGBM)
References
- Rago, D.; Rasmussen, M.A.; Lee-Sarwar, K.A.; Weiss, S.T.; Lasky-Su, J.; Stokholm, J.; Bønnelykke, K.; Chawes, B.L.; Bisgaard, H. Fish-Oil Supplementation in Pregnancy, Child Metabolomics and Asthma Risk. EBioMedicine 2019, 46, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevelsted, A.; Gürdeniz, G.; Rago, D.; Pedersen, C.-E.T.; Lasky-Su, J.A.; Checa, A.; Zhang, P.; Wheelock, C.E.; Normann, S.S.; Kristensen, D.M.; et al. Effect of Perfluoroalkyl Exposure in Pregnancy and Infancy on Intrauterine and Childhood Growth and Anthropometry. Sub Study from COPSAC2010 Birth Cohort. EBioMedicine 2022, 83, 104236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortensen, M.S.; Rasmussen, M.A.; Stokholm, J.; Brejnrod, A.D.; Balle, C.; Thorsen, J.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Bisgaard, H.; Sørensen, S.J. Modeling Transfer of Vaginal Microbiota from Mother to Infant in Early Life. eLife 2021, 10, e57051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aderemi, A.V.; Ayeleso, A.O.; Oyedapo, O.O.; Mukwevho, E. Metabolomics: A Scoping Review of Its Role as a Tool for Disease Biomarker Discovery in Selected Non-Communicable Diseases. Metabolites 2021, 11, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanisevic, J.; Thomas, A. Metabolomics as a Tool to Understand Pathophysiological Processes. In Clinical Metabolomics: Methods and Protocols; Giera, M., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 3–28. ISBN 978-1-4939-7592-1. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, C.H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: Beyond Biomarkers and towards Mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rago, D.; Pedersen, C.E.T.; Huang, M.; Kelly, R.S.; Gürdeniz, G.; Brustad, N.; Knihtilä, H.; Lee-Sarwar, K.A.; Morin, A.; Rasmussen, M.A.; et al. Characteristics and Mechanisms of a Sphingolipid-Associated Childhood Asthma Endotype. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brustad, N.; Olarini, A.; Kim, M.; Chen, L.; Ali, M.; Wang, T.; Cohen, A.S.; Ernst, M.; Hougaard, D.; Schoos, A.-M.; et al. Diet-Associated Vertically Transferred Metabolites and Risk of Asthma, Allergy, Eczema, and Infections in Early Childhood. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 34, e13917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, S.; Härkönen, T.; Vatanen, T.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Knip, M.; Orešič, M. Impact of Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances on Fecal Microbiota Composition in Mother-Infant Dyads. Environ. Int. 2023, 176, 107965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyötyläinen, T.; Ghaffarzadegan, T.; Karthikeyan, B.S.; Triplett, E.; Orešič, M.; Ludvigsson, J. Impact of Environmental Exposures on Human Breast Milk Lipidome in Future Immune-Mediated Diseases. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 2214–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, A.K.; Eckel, S.P.; Habre, R.; Yang, T.; Faham, D.; Farzan, S.F.; Grubbs, B.H.; Kannan, K.; Robinson, M.; Lerner, D.; et al. Prenatal Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) Exposure Is Associated With Lower Infant Birthweight Within the MADRES Pregnancy Cohort. Front. Epidemiol. 2022, 2, 934715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taibl, K.R.; Dunlop, A.L.; Barr, D.B.; Li, Y.-Y.; Eick, S.M.; Kannan, K.; Ryan, P.B.; Schroder, M.; Rushing, B.; Fennell, T.; et al. Newborn Metabolomic Signatures of Maternal Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Exposure and Reduced Length of Gestation. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olarini, A.; Ernst, M.; Gürdeniz, G.; Kim, M.; Brustad, N.; Bønnelykke, K.; Cohen, A.; Hougaard, D.; Lasky-Su, J.; Bisgaard, H.; et al. Vertical Transfer of Metabolites Detectable from Newborn’s Dried Blood Spot Samples Using UPLC-MS: A Chemometric Study. Metabolites 2022, 12, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B.; Tang, R.M.Y.; Cheah, I.K. Diet-Derived Antioxidants: The Special Case of Ergothioneine. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 14, 323–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, G.; Rantalainen, M.; Maher, A.D.; Li, J.V.; Malmodin, D.; Ahmadi, K.R.; Faber, J.H.; Hallgrímsdóttir, I.B.; Barrett, A.; Toft, H.; et al. Human Metabolic Profiles Are Stably Controlled by Genetic and Environmental Variation. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckman, K.K.; Smith, C.J.; Jelliffe-Pawlowski, L.L.; Momany, A.M.; Berberich, S.L.; Murray, J.C. Metabolic Heritability at Birth: Implications for Chronic Disease Research. Hum. Genet. 2014, 133, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illig, T.; Gieger, C.; Zhai, G.; Römisch-Margl, W.; Wang-Sattler, R.; Prehn, C.; Altmaier, E.; Kastenmüller, G.; Kato, B.S.; Mewes, H.-W.; et al. A Genome-Wide Perspective of Genetic Variation in Human Metabolism. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Akanno, E.C.; Valente, T.S.; Abo-Ismail, M.; Karisa, B.K.; Wang, Z.; Plastow, G.S. Genomic Heritability and Genome-Wide Association Studies of Plasma Metabolites in Crossbred Beef Cattle. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 538600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmermann, A.; Avenbuan, O.N.; Romano, M.E.; Braun, J.M.; Tolstrup, J.S.; Vandenberg, L.N.; Fenton, S.E. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Breastfeeding as a Vulnerable Function: A Systematic Review of Epidemiological Studies. Toxics 2023, 11, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgenrud, B.; Stene, L.C.; Tapia, G.; Bøås, H.; Pepaj, M.; Berg, J.P.; Thorsby, P.M.; Orešič, M.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Rønningen, K.S. Longitudinal Plasma Metabolic Profiles, Infant Feeding, and Islet Autoimmunity in the MIDIA Study. Pediatr. Diabetes 2017, 18, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guixeres-Esteve, T.; Ponce-Zanón, F.; Morales, J.M.; Lurbe, E.; Alvarez-Pitti, J.; Monleón, D. Impact of Maternal Weight Gain on the Newborn Metabolome. Metabolites 2023, 13, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, C.; Hu, Y.; Song, X.; Jia, Y.; Shi, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; et al. Vertical Transmission of the Gut Microbiota Influences Glucose Metabolism in Offspring of Mice with Hyperglycaemia in Pregnancy. Microbiome 2022, 10, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, R.; Lee, A.; Lu, Z.; Liu, A.; Troendle, J.F.; Mills, J.L. Association Analysis of Complex Diseases Using Triads, Parent-Child Dyads and Singleton Monads. BMC Genet. 2013, 14, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisgaard, H.; Stokholm, J.; Chawes, B.L.; Vissing, N.H.; Bjarnadóttir, E.; Schoos, A.-M.M.; Wolsk, H.M.; Pedersen, T.M.; Vinding, R.K.; Thorsteinsdóttir, S.; et al. Fish Oil–Derived Fatty Acids in Pregnancy and Wheeze and Asthma in Offspring. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2530–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawes, B.L.; Bønnelykke, K.; Stokholm, J.; Vissing, N.H.; Bjarnadóttir, E.; Schoos, A.-M.M.; Wolsk, H.M.; Pedersen, T.M.; Vinding, R.K.; Thorsteinsdóttir, S.; et al. Effect of Vitamin D3 Supplementation During Pregnancy on Risk of Persistent Wheeze in the Offspring: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 315, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression Shrinkage and Selection Via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Hastie, T. Regularization and Variable Selection via the Elastic Net. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2005, 67, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.Y. LightGBM: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 3147–3155. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, R.L.M.; Palczewska, A.; Palczewski, J.; Kidley, N. Comparison of the Predictive Performance and Interpretability of Random Forest and Linear Models on Benchmark Data Sets. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 1773–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Mucs, D.; Norinder, U.; Svensson, F. LightGBM: An Effective and Scalable Algorithm for Prediction of Chemical Toxicity-Application to the Tox21 and Mutagenicity Data Sets. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59, 4150–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovrić, M.; Đuričić, T.; Hussain, H.; Lučić, B.; Kern, R. PyChemFlow: An Automated Pre-Processing Pipeline in Python for Reproducible Machine Learning on Chemical Data 2023. preprint. [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, F. Bayesian Optimization: Open Source Constrained Global Optimization Tool for Python. Available online: https://github.com/fmfn/BayesianOptimization (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Snoek, J.; Larochelle, H.; Adams, R.P. Practical Bayesian Optimization of Machine Learning Algorithms. In Proceedings of the NIPS 2012, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 13 June 2012; Volume 4, pp. 2951–2959. [Google Scholar]
- Lovrić, M.; Malev, O.; Klobučar, G.; Kern, R.; Liu, J.J.; Lučić, B. Predictive Capability of QSAR Models Based on the CompTox Zebrafish Embryo Assays: An Imbalanced Classification Problem. Molecules 2021, 26, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D.; Jurman, G. The Advantages of the Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC) over F1 Score and Accuracy in Binary Classification Evaluation. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovrić, M.; Pavlović, K.; Žuvela, P.; Spataru, A.; Lučić, B.; Kern, R.; Wong, M.W. Machine Learning in Prediction of Intrinsic Aqueous Solubility of Drug-like Compounds: Generalization, Complexity, or Predictive Ability? J. Chemom. 2021, 35, e3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, A.; Toloşi, L.; Sander, O.; Lengauer, T. Permutation Importance: A Corrected Feature Importance Measure. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicodemus, K.K.; Malley, J.D.; Strobl, C.; Ziegler, A. The Behaviour of Random Forest Permutation-Based Variable Importance Measures under Predictor Correlation. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.-I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 4768–4777. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Pérez, R.; Bajorath, J. Interpretation of Machine Learning Models Using Shapley Values: Application to Compound Potency and Multi-Target Activity Predictions. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2020, 34, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. [Google Scholar]
- Galal, A.; Talal, M.; Moustafa, A. Applications of Machine Learning in Metabolomics: Disease Modeling and Classification. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1017340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcos-Zambrano, L.J.; Karaduzovic-Hadziabdic, K.; Loncar Turukalo, T.; Przymus, P.; Trajkovik, V.; Aasmets, O.; Berland, M.; Gruca, A.; Hasic, J.; Hron, K.; et al. Applications of Machine Learning in Human Microbiome Studies: A Review on Feature Selection, Biomarker Identification, Disease Prediction and Treatment. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, D.; Dharmanshu Mahajan, K.; Khanna, R.; Chugh, G. Gene Family Classification Using Machine Learning: A Comparative Analysis. In Data Analytics and Management; Swaroop, A., Polkowski, Z., Correia, S.D., Virdee, B., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 343–360. [Google Scholar]
- Starnes, H.M.; Rock, K.D.; Jackson, T.W.; Belcher, S.M. A Critical Review and Meta-Analysis of Impacts of Per- and Polyfluorinated Substances on the Brain and Behavior. Front. Toxicol. 2022, 4, 881584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panyard, D.J.; Kim, K.M.; Darst, B.F.; Deming, Y.K.; Zhong, X.; Wu, Y.; Kang, H.; Carlsson, C.M.; Johnson, S.C.; Asthana, S.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Metabolomics Identifies 19 Brain-Related Phenotype Associations. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeleznik, O.A.; Wittenbecher, C.; Deik, A.; Jeanfavre, S.; Avila-Pacheco, J.; Rosner, B.; Rexrode, K.M.; Clish, C.B.; Hu, F.B.; Eliassen, A.H. Intrapersonal Stability of Plasma Metabolomic Profiles over 10 Years among Women. Metabolites 2022, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasić, S.Z.; Kesić, S. Editorial: Nonlinearity in Living Systems: Theoretical and Practical Perspectives on Metrics of Physiological Signal Complexity. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcobal, A.; Kashyap, P.C.; Nelson, T.A.; Aronov, P.A.; Donia, M.S.; Spormann, A.; Fischbach, M.A.; Sonnenburg, J.L. A Metabolomic View of How the Human Gut Microbiota Impacts the Host Metabolome Using Humanized and Gnotobiotic Mice. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1933–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlinchey, A.; Sinioja, T.; Lamichhane, S.; Sen, P.; Bodin, J.; Siljander, H.; Dickens, A.M.; Geng, D.; Carlsson, C.; Duberg, D.; et al. Prenatal Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances Modulates Neonatal Serum Phospholipids, Increasing Risk of Type 1 Diabetes. Environ. Int. 2020, 143, 105935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| RF | LGBM | LR | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy Test set | 0.72 | 0.66 | 0.45 |
| AUC Test set | 0.71 | 0.68 | 0.63 |
| MCC CV | 0.40 | 0.37 | 0.12 |
| MCC Test set | 0.42 | 0.36 | 0.11 |
| LGBM Feature | LGBM PI | RF Feature | RF PI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | X-11308 | 0.202 | X-11308 | 0.106 |
| 2. | X-24970 | 0.191 | perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) | 0.036 |
| 3. | perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) | 0.119 | N6-methyllysine | 0.035 |
| 4. | X-24307 | 0.104 | X-24970 | 0.030 |
| 5. | X-12112 | 0.090 | N-acetyl-2-aminooctanoate | 0.021 |
| 6. | X-11372 | 0.081 | methionine sulfone | 0.013 |
| 7. | X-17653 | 0.062 | X-23636 | 0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lovrić, M.; Horner, D.; Chen, L.; Brustad, N.; Schoos, A.-M.M.; Lasky-Su, J.; Chawes, B.; Rasmussen, M.A. Vertical Metabolome Transfer from Mother to Child: An Explainable Machine Learning Method for Detecting Metabolomic Heritability. Metabolites 2024, 14, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14030136
Lovrić M, Horner D, Chen L, Brustad N, Schoos A-MM, Lasky-Su J, Chawes B, Rasmussen MA. Vertical Metabolome Transfer from Mother to Child: An Explainable Machine Learning Method for Detecting Metabolomic Heritability. Metabolites. 2024; 14(3):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14030136
Chicago/Turabian StyleLovrić, Mario, David Horner, Liang Chen, Nicklas Brustad, Ann-Marie Malby Schoos, Jessica Lasky-Su, Bo Chawes, and Morten Arendt Rasmussen. 2024. "Vertical Metabolome Transfer from Mother to Child: An Explainable Machine Learning Method for Detecting Metabolomic Heritability" Metabolites 14, no. 3: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14030136
APA StyleLovrić, M., Horner, D., Chen, L., Brustad, N., Schoos, A.-M. M., Lasky-Su, J., Chawes, B., & Rasmussen, M. A. (2024). Vertical Metabolome Transfer from Mother to Child: An Explainable Machine Learning Method for Detecting Metabolomic Heritability. Metabolites, 14(3), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14030136











