Widely Targeted Metabolomics Revealed the Metabolic Basis of Physiological Function and Flavor of Natto
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fermentation of Soybeans
2.2. Sample Preparation and Metabolite Extraction
2.3. Quality Control and UHPLC-MS Analysis
2.4. MS Data and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Widely Targeted Metabolic Analysis of Natto
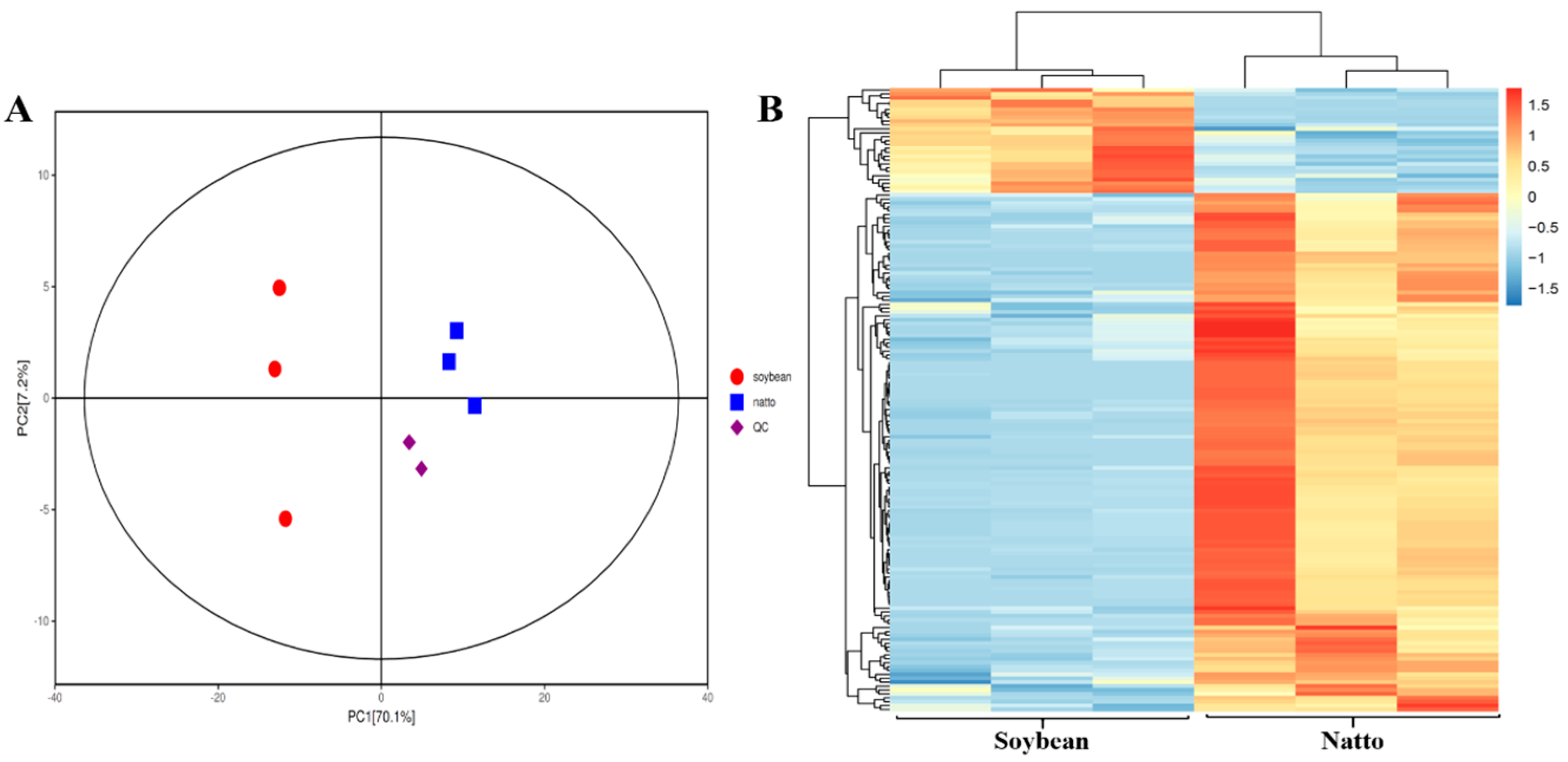
3.2. Multivariate Analysis of Identified Metabolites
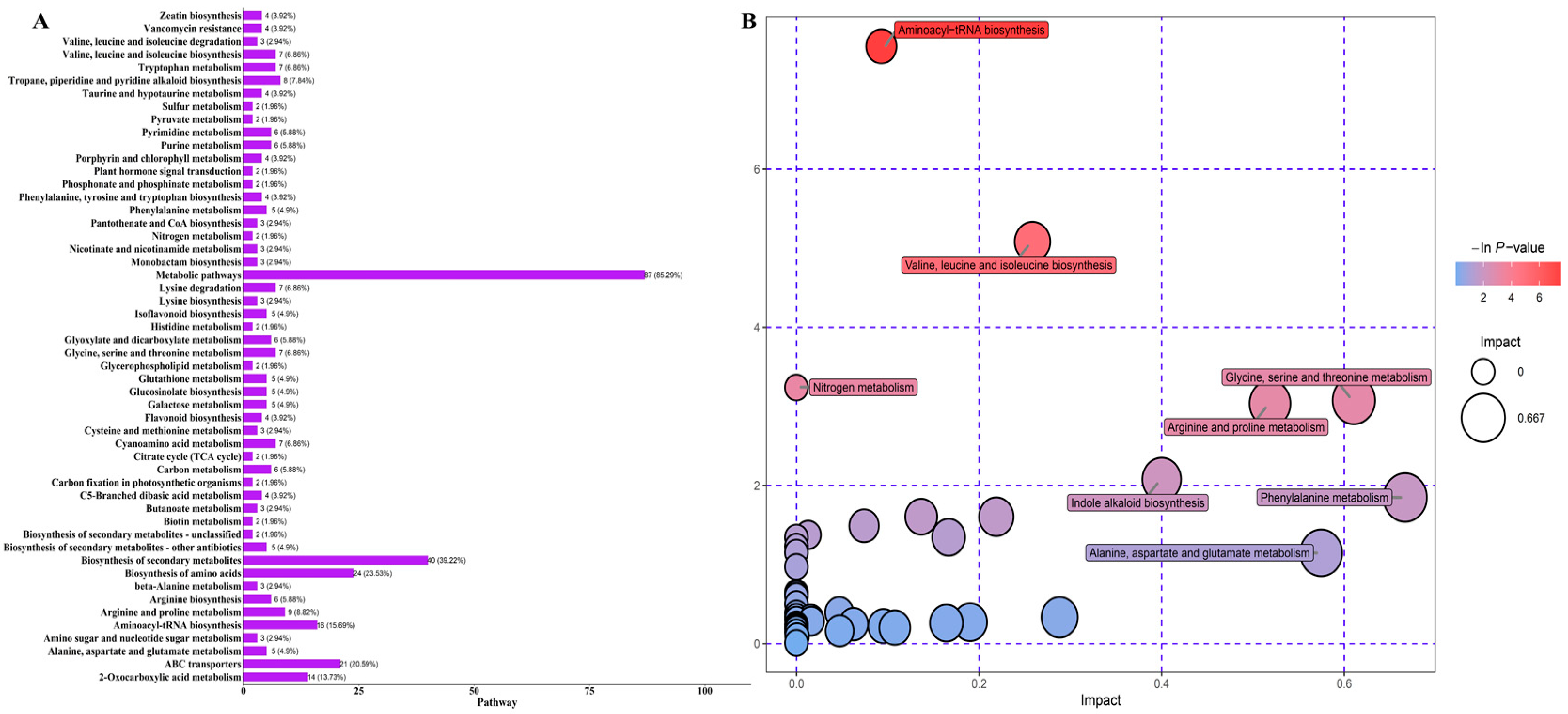
3.3. KEGG Classification and Enrichment Analysis of Differential Metabolites
3.4. Differences in the Contents of Isoflavones, Purines, Saccharides, and Alkaloids in Natto and Soybean
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kurzer, M.S. Soy consumption for reduction of menopausal symptoms. Inflammopharmacology 2008, 16, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.H.; Green-Johnson, J.M.; Buckley, N.D.; Lin, Q.Y. Bioactivity of soy-based fermented foods: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. An. Int. Rev. J. 2019, 37, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, C.S.; Kai, T.Y.; Sue, T.K. Optimization process of black soybean natto using response surface methodology. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, 294–301. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Ge, C.; Yuan, W.; Zhu, R.Y.; Zhang, W.J.; Xue, J. Characterization of fermented black soybean natto inoculated with Bacillus natto during fermentation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lawrence, P.; Worobo, R.W. High levels of branched chain fatty acids in natto and other Asian fermented foods. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, C.; Wada, K.; Tamura, T.; Konishi, K.; Goto, Y.; Koda, S.; Kawachi, T.; Tsuji, M.; Nakamura, K. Dietary soy and natto intake and cardiovascular disease mortality in japanese adults: The takayama study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.; Nomura, K.; Hong, K.; Ito, A.; Asada, A.; Nishimuro, S. Purification and characterization of a strong fibrinolytic enzyme (Nattokinase) in the vegetable cheese natto, a popular soybean fermented food in Japan. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 197, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.F.; Mo, S.Y.; Liu, X.X.; Chen, J.F.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Chen, X.L.; Chen, J.M.; Dai, S.M. Soy foods might weaken the sensitivity of tamoxifen in premenopausal patients with lumina a subtype of breast cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2018, 19, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianluca, R.; Luciana, B. Soy, soy foods and their role in vegetarian diets. Nutrients 2018, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark, M. Soy foods, isoflavones, and the health of postmenopausal women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 423–430. [Google Scholar]
- Araki, R.; Fujie, K.; Yuine, N.; Watabe, Y.; Maruo, K.; Suzuki, H.; Hashimoto, K. The possibility of suppression of increased postprandial blood glucose levels by Gamma-Polyglutamic Acid-Rich Natto in the early phase after eating: A randomized crossover pilot study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, J.; Wen, R.; Nishikawa, T.; Nunomura, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Sejima, Y.; Gokan, T.; Furukawa, M.; Yokota, T.; Osawa, N.; et al. Natto extract inhibits infection caused by the Aujeszky’s disease virus in mice. Microbiol. Immunol. 2023, 67, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; McGowan, E.M.; Ren, N.; Lal, S.; Nassif, N.; Shad-Kaneez, F.; Qu, X.; Lin, Y. Nattokinase: A Promising Alternative in Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. Biomark. Insights 2018, 13, 117727191878513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimidi, E.; Cox, S.R.; Rossi, M.; Whelan, K. Fermented Foods: Definitions and Characteristics, Impact on the Gut Microbiota and Effects on Gastrointestinal Health and Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kada, S.; Yabusaki, M.; Kaga, T.; Ashida, H.; Yoshida, K. Identification of two major ammonia-releasing reactions involved in secondary natto fermentation. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 1869–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, Y.; Iki, M.; Tamaki, J.; Kouda, K.; Yura, A.; Kadowaki, E.; Sato, Y.; Moon, J.S.; Tomioka, K.; Okamoto, N.; et al. Association between vitamin K intake from fermented soybeans, natto, and bone mineral density in elderly Japanese men: The Fujiwara-kyo Osteoporosis Risk in Men (FORMEN) study. Osteoporos. Int. 2012, 23, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Hara, Y.; Raboy, V.; Saneoka, H. Characteristics and Quality of Japanese Traditional Fermented Soybean (Natto) from a Low-phytate Line. Plant Foods Human. Nutr. 2020, 75, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, G.; Li, C.; He, L.; Zeng, X.; Zhu, Q. Effects of different strains and fermentation method on nattokinase activity, biogenic amines, and sensory characteristics of natto. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 4414–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranowska, I.; Bajkacz, S. A new UHPLC-MS/MS method for the determination of flavonoids in supplements and DPPH -UHPLC-UV method for the evaluation of the radical scavenging activity of flavonoids. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Gong, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.Q.; Yu, S.B.; Xiong, L.Z.; Luo, J. A novel integrated method for large-scale detection, identification, and quantification of widely targeted metabolites: Application in the study of rice metabolomics. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Xu, T.; Liu, X.W.; Wang, X.H.; Xia, T. The expression of beta-glucosidase during natto fermentation increased the active isoflavone content. Food Biosci. 2021, 43, 101286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, R.C.D.; Moco, S.; Lommen, A.; Keurentjes, J.J.B.; Bino, R.J.; Hall, R.D. Untargeted large-scale plant metabolomics using liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 778–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doppler, M.; Kluger, B.; Bueschl, C.; Schneider, C.; Krska, R.; Delcambre, S.; Hiller, K.; Lemmens, M.; Schuhmacher, R. Stable isotope-assisted evaluation of different extraction solvents for untargeted metabolomics of plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS: Processing mass spectrometry data for metabolite profiling using nonlinear peak alignment, matching, and identification. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 779–787. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhl, C.; Tautenhahn, R.; Böttcher, C.; Larson, T.R.; Steffen, N. CAMERA: An integrated strategy for compound spectra extraction and annotation of liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry data sets. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Tong, X.; Peng, Y.; Ma, P.; Zhang, M.Z.; Liu, H.M.; Chen, X.Q.; Liang, Y.Z. Multiscale peak detection in wavelet space. Anal. Anal. J. R. Soc. Chem. 2015, 140, 7955–7964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.W.; Li, K.; Shi, Y.X.; Li, Y.F.; Dong, L.; Liu, L.; Li, M.Y.; Ren, H.; Liu, X.Q.; Fang, C.Y.; et al. Cross-species comparison of metabolomics to decipher the metabolic diversity in ten fruits. Metabolites 2021, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanaka, K.; Takebayashi, J.; Matsumoto, T.; Ishimi, Y. Determination of 15 isoflavone isomers in soy foods and supplements by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 4012–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, R.; Liu, X.; Bolling, B. Flavonoids and gut health. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2020, 61, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaya, P.; Angala, P.; Jose, M.L. Expression of a β-glucosidase in bacteria with biotechnological interest confers them the ability to deglycosylate lignans and flavonoids in vegetal foods. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 4903–4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmood, T.; Muanprasat, C. Deoxyelephantopin and Its Isomer Isodeoxyelephantopin: Anti-Cancer Natural Products with Multiple Modes of Action. Molecules 2022, 27, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavo, L.; Favrè, G.; Pilone, V.; Rossetti, G.; Sena, G.D.; Iannelli, A.; Barbarisi, A. Low-Purine Diet Is More Effective Than Normal-Purine Diet in Reducing the Risk of Gouty Attacks After Sleeve Gastrectomy in Patients Suffering of Gout Before Surgery: A Retrospective Study. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, S.; Wu, J.; Shahid, M.Q.; He, Y.H.; Lin, S.Q.; Liu, Z.H.; Yang, X.H. Identification of key taste components in loquat using widely targeted metabolomics. Food Chem. 2020, 18, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, C.; Lin, J. Widely Targeted Metabolomics Revealed the Metabolic Basis of Physiological Function and Flavor of Natto. Metabolites 2024, 14, 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14120663
Yin X, Wang X, Xu L, Zhao J, Li C, Lin J. Widely Targeted Metabolomics Revealed the Metabolic Basis of Physiological Function and Flavor of Natto. Metabolites. 2024; 14(12):663. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14120663
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Xiaolong, Xiaona Wang, Lili Xu, Jianzhi Zhao, Can Li, and Jianqiang Lin. 2024. "Widely Targeted Metabolomics Revealed the Metabolic Basis of Physiological Function and Flavor of Natto" Metabolites 14, no. 12: 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14120663
APA StyleYin, X., Wang, X., Xu, L., Zhao, J., Li, C., & Lin, J. (2024). Widely Targeted Metabolomics Revealed the Metabolic Basis of Physiological Function and Flavor of Natto. Metabolites, 14(12), 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14120663





