The Metabolic Footprint of Systemic Effects in the Blood Caused by Radiotherapy and Inflammatory Conditions: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction and Preparation
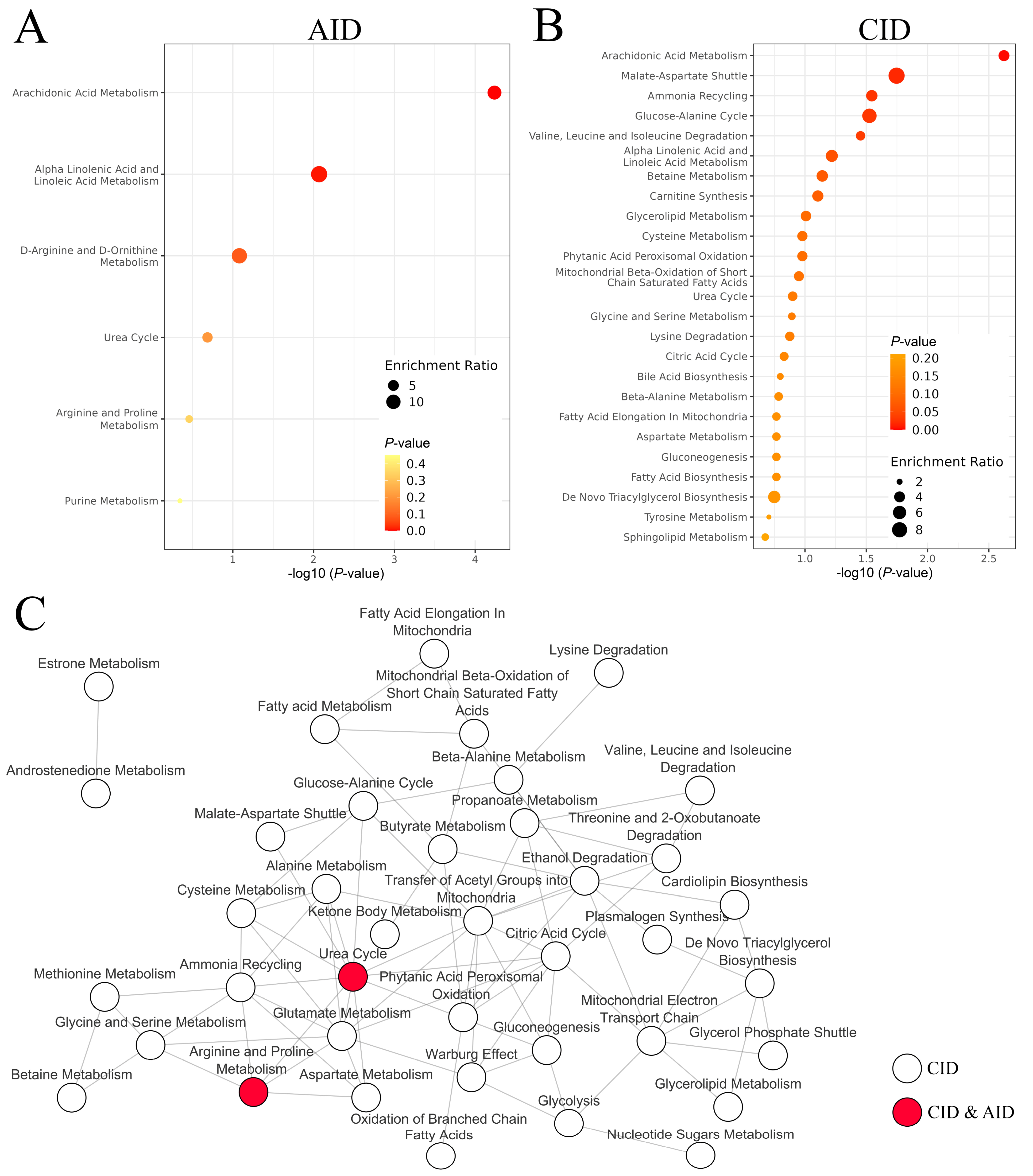
2.4. Pathway Analysis
3. Results
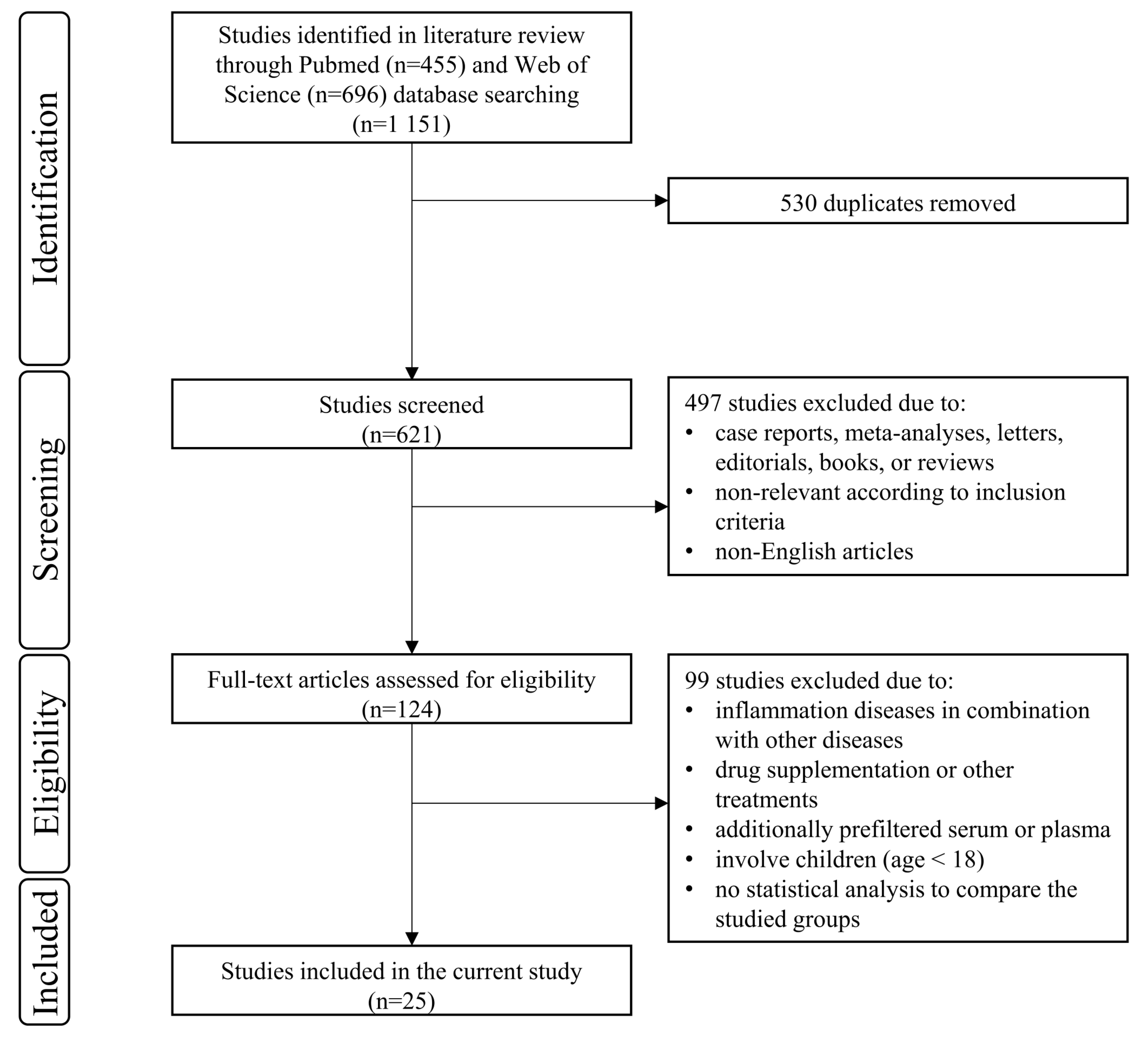
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Systemic Effects Caused by Acute Inflammatory Diseases
3.4. Systemic Effects Caused by Chronic Inflammatory Diseases
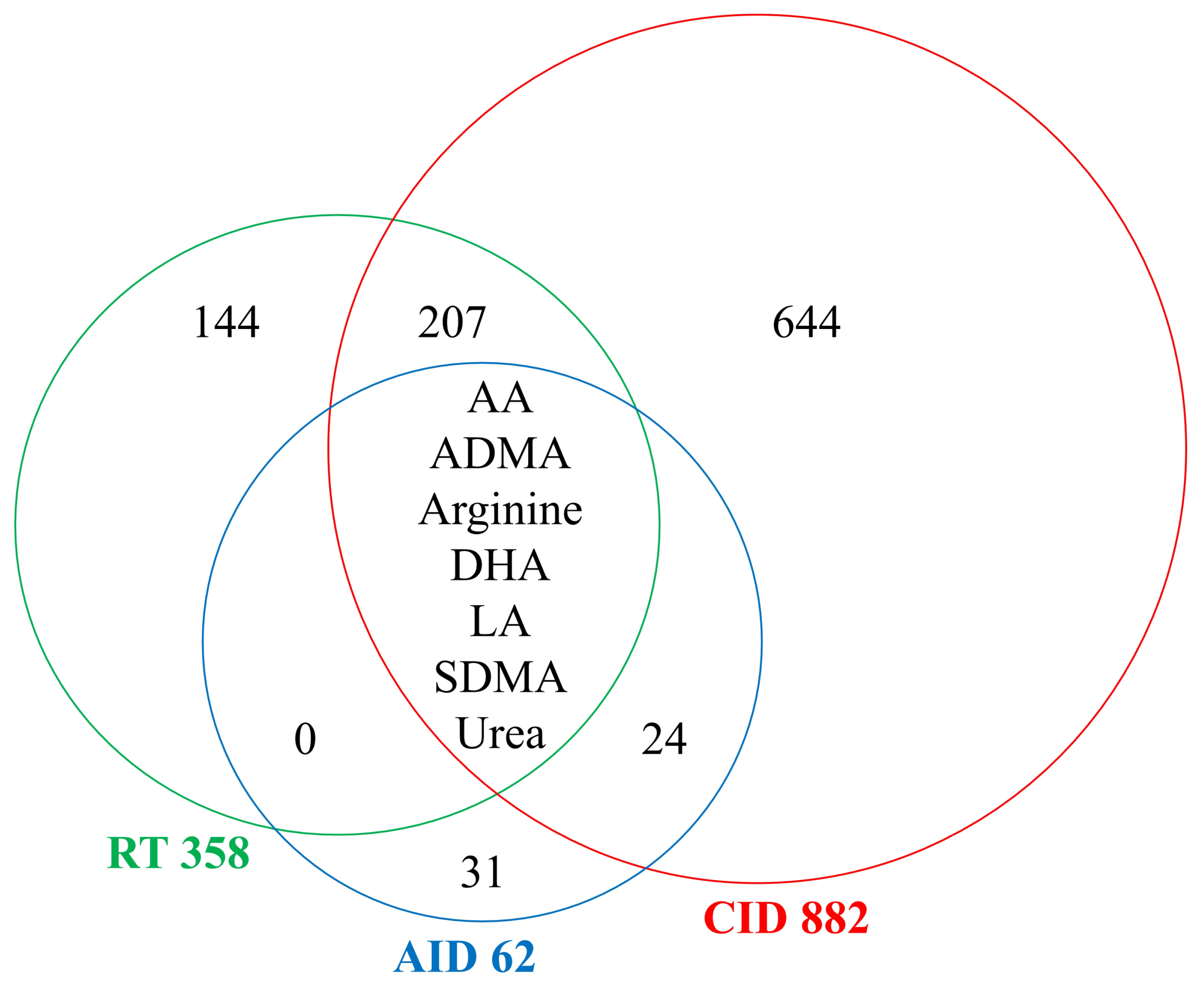
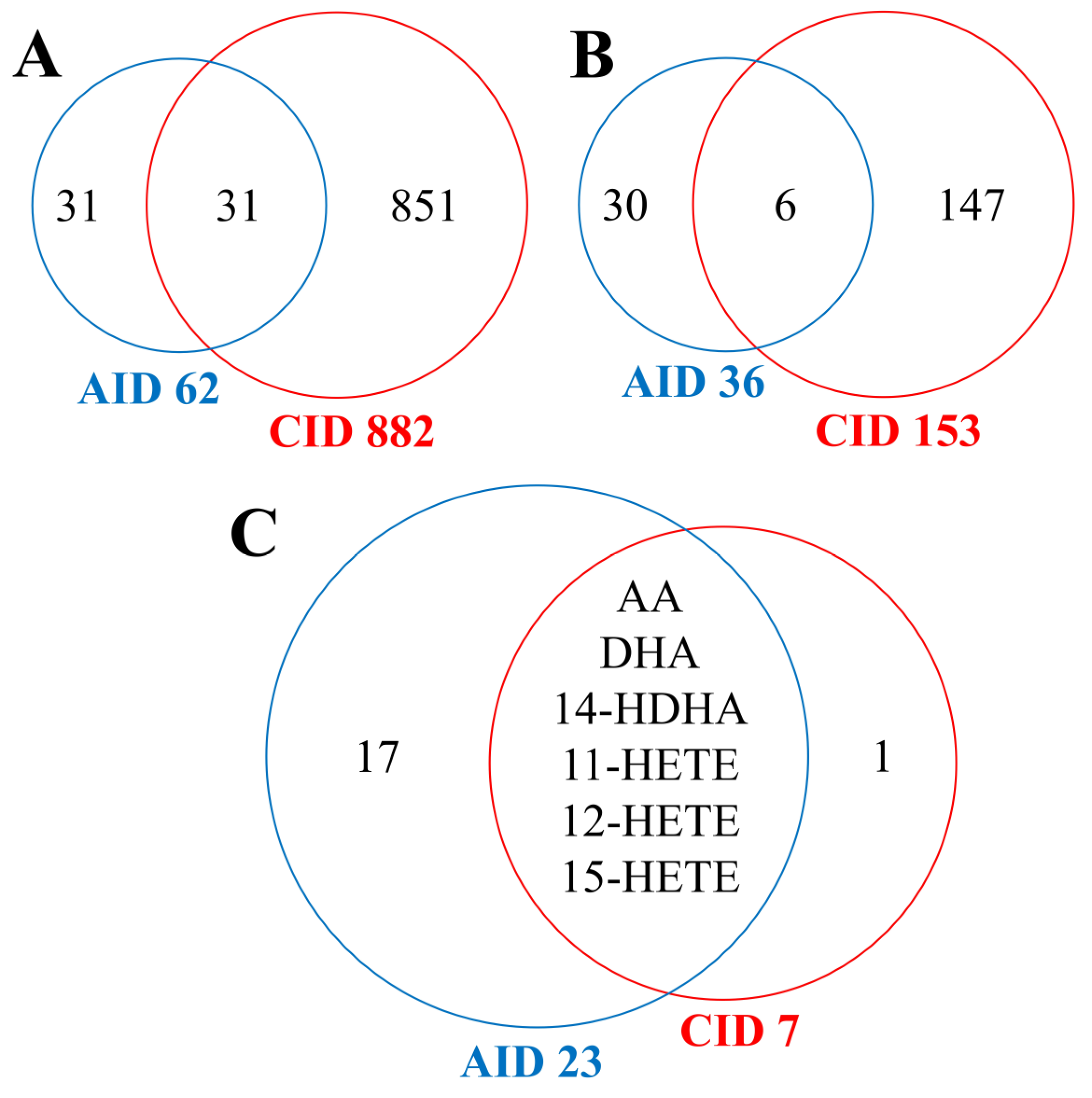
3.5. Comparison of Systemic Effects Caused by Acute and Chronic Inflammatory Diseases
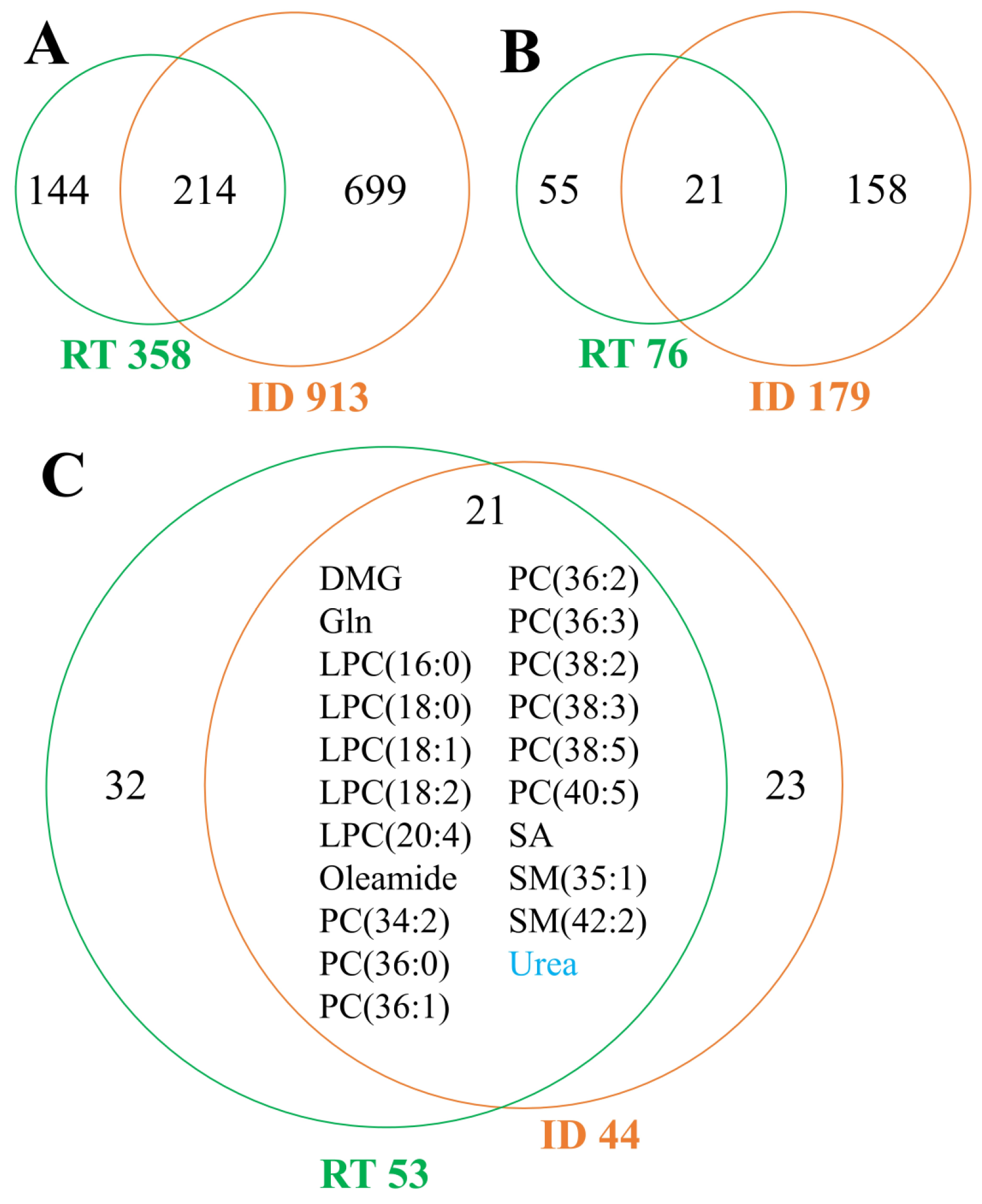
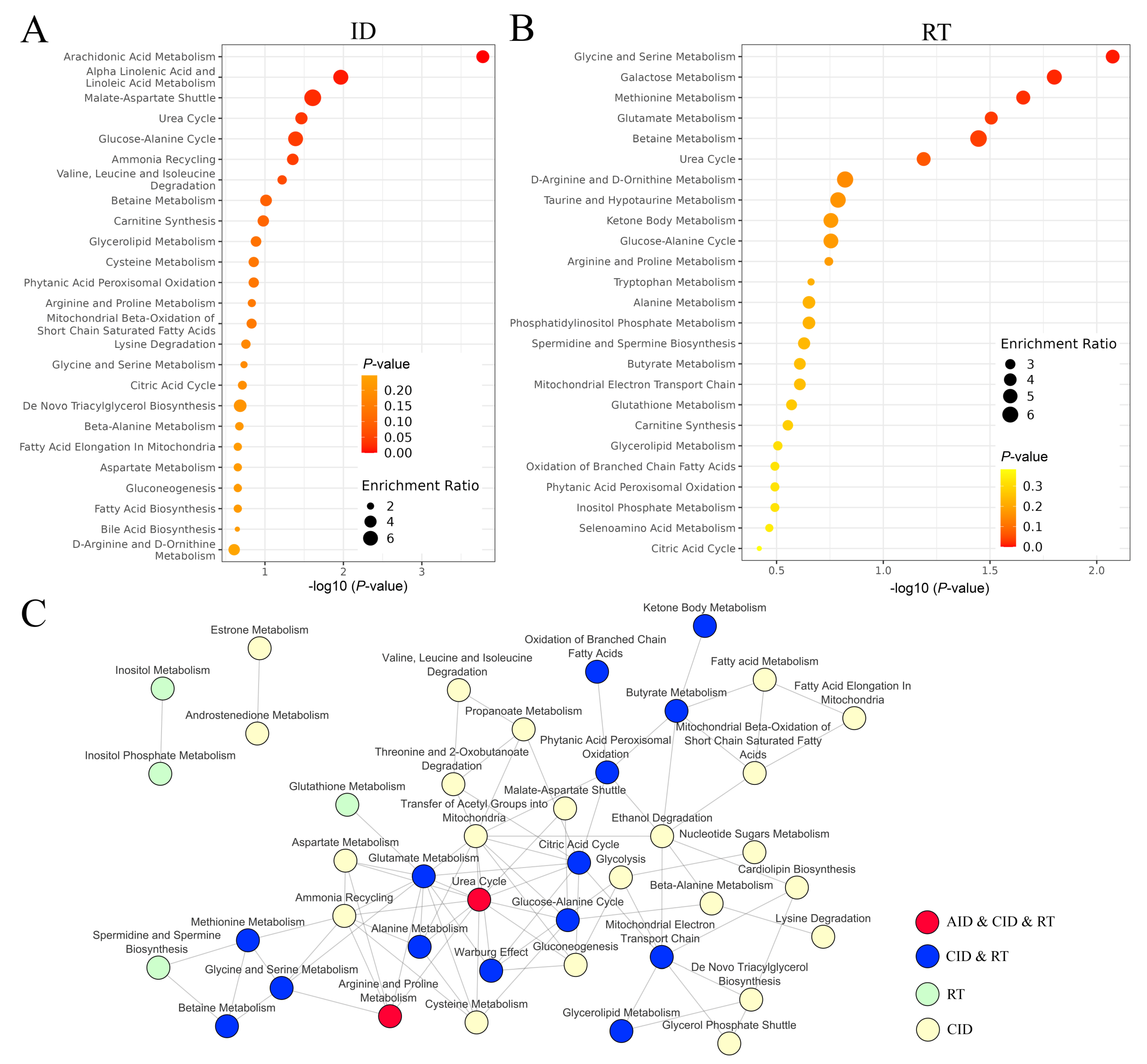
3.6. Systemic Effects Caused by Radiotherapy
3.7. Comparison of Systemic Effects Caused by Radiotherapy and Inflammation-Related Diseases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.S.; Wang, H.J.; Qian, H.L. Biological effects of radiation on cancer cells. Mil. Med. Res. 2018, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, S.J.; Butterworth, K.T.; Trainor, C.; McGarry, C.K.; O’Sullivan, J.M.; Schettino, G.; Hounsell, A.R.; Prise, K.M. A kinetic-based model of radiation-induced intercellular signalling. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, S.; Chandna, S. Radiation-induced inflammatory cascade and its reverberating crosstalks as potential cause of post-radiotherapy second malignancies. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017, 36, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, H.A.; Villar, R.C. Radiotherapy and immune response: The systemic effects of a local treatment. Clinics 2018, 73, e557s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, W.H.; Schaue, D. Radiation-induced tissue damage and response. J. Pathol. 2020, 250, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonati, L.; Barbieri, S.; Guardamagna, I.; Ottolenghi, A.; Baiocco, G. Radiation-induced cell cycle perturbations: A computational tool validated with flow-cytometry data. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, F.J.; Riley, J.S. When cell death goes wrong: Inflammatory outcomes of failed apoptosis and mitotic cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2023, 30, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, G.C.; West, C.M.; Dunning, A.M.; Elliott, R.M.; Coles, C.E.; Pharoah, P.D.; Burnet, N.G. Normal tissue reactions to radiotherapy: Towards tailoring treatment dose by genotype. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wygoda, A.; Maciejewski, B.; Skladowski, K.; Hutnik, M.; Pilecki, B.; Golen, M.; Rutkowski, T. Pattern analysis of acute mucosal reactions in patients with head and neck cancer treated with conventional and accelerated irradiation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2009, 73, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maggio, F.M.; Minafra, L.; Forte, G.I.; Cammarata, F.P.; Lio, D.; Messa, C.; Gilardi, M.C.; Bravata, V. Portrait of inflammatory response to ionizing radiation treatment. J. Inflamm. 2015, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.H.; Marmagkiolis, K.; Balanescu, D.V.; Hakeem, A.; Donisan, T.; Finch, W.; Virmani, R.; Herrman, J.; Cilingiroglu, M.; Grines, C.L.; et al. Radiation-Induced Vascular Disease–A State-of-the-Art Review. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 652761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, A.R.; Maity, A.; Sanzari, J.K. A Review of Radiation-Induced Coagulopathy and New Findings to Support Potential Prevention Strategies and Treatments. Radiat. Res. 2016, 186, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Story, M.D.; Durante, M. Radiogenomics. Med. Phys. 2018, 45, e1111–e1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yu, J.; Kong, D.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shui, J.; Li, Z.; Luo, H.; Wang, K. Population and single-cell transcriptome analyses reveal diverse transcriptional changes associated with radioresistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 55, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelonek, K.; Pietrowska, M.; Widlak, P. Systemic effects of ionizing radiation at the proteome and metabolome levels in the blood of cancer patients treated with radiotherapy: The influence of inflammation and radiation toxicity. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2017, 93, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widłak, P.; Pietrowska, M.; Polańska, J.; Rutkowski, T.; Jelonek, K.; Kalinowska-Herok, M.; Gdowicz-Kłosok, A.; Wygoda, A.; Tarnawski, R.; Składowski, K. Radiotherapy-related changes in serum proteome patterns of head and neck cancer patients; The effect of low and medium doses of radiation delivered to large volumes of normal tissue. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widlak, P.; Jelonek, K.; Wojakowska, A.; Pietrowska, M.; Polanska, J.; Marczak, Ł.; Miszczyk, L.; Składowski, K. Serum proteome signature of radiation response: Upregulation of inflammation-related factors, and downregulation of apolipoproteins and coagulation factors in cancer patients subjected to radiotherapy—A pilot study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 92, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelonek, K.; Krzywon, A.; Jablonska, P.; Slominska, E.M.; Smolenski, R.T.; Polanska, J.; Rutkowski, T.; Mrochem-Kwarciak, J.; Skladowski, K.; Widlak, P. Systemic Effects of Radiotherapy and Concurrent Chemo-Radiotherapy in Head and Neck Cancer Patients-Comparison of Serum Metabolome Profiles. Metabolites 2020, 10, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelonek, K.; Krzywon, A.; Papaj, K.; Polanowski, P.; Szczepanik, K.; Skladowski, K.; Widlak, P. Dose-dependence of radiotherapy-induced changes in serum levels of choline-containing phospholipids; The importance of lower doses delivered to large volumes of normal tissues. Strahlenther. Und Onkol. 2021, 197, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spratlin, J.L.; Serkova, N.J.; Eckhardt, S.G. Clinical applications of metabolomics in oncology: A review. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsahafi, E.; Begg, K.; Amelio, I.; Raulf, N.; Lucarelli, P.; Sauter, T.; Tavassoli, M. Clinical update on head and neck cancer: Molecular biology and ongoing challenges. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Xi, X.P.; Wang, H.; Han, Y.Q.; Xiao, F.; Hu, Y.; He, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, L.; et al. PET/CT-guided dose-painting versus CT-based intensity modulated radiation therapy in locoregional advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Ghoshal, S.; Patil, V.M.; Oinam, A.S.; Sharma, S.C. Preliminary results of SIB-IMRT in head and neck cancers: Report from a regional cancer center in northern India. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2009, 5, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gujral, D.M.; Miah, A.B.; Bodla, S.; Richards, T.M.; Welsh, L.; Schick, U.; Powell, C.J.; Clark, C.H.; Bidmead, M.A.; Grove, L.; et al. Final long-term results of a phase I/II study of dose-escalated intensity-modulated radiotherapy for locally advanced laryngo-hypopharyngeal cancers. Oral Oncol. 2014, 50, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studer, G.; Peponi, E.; Kloeck, S.; Dossenbach, T.; Huber, G.; Glanzmann, C. Surviving hypopharynx-larynx carcinoma in the era of IMRT. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 77, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berwouts, D.; Madani, I.; Duprez, F.; Olteanu, A.L.; Vercauteren, T.; Boterberg, T.; Deron, P.; Bonte, K.; Huvenne, W.; De Neve, W.; et al. Long-term outcome of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography-guided dose painting for head and neck cancer: Matched case-control study. Head Neck 2017, 39, 2264–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschuymer, S.; Nevens, D.; Duprez, F.; Daisne, J.-F.; Dok, R.; Laenen, A.; Voordeckers, M.; De Neve, W.; Nuyts, S. Randomized clinical trial on reduction of radiotherapy dose to the elective neck in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; update of the long-term tumor outcome. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 143, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevens, D.; Duprez, F.; Daisne, J.-F.; Schatteman, J.; Van der Vorst, A.; De Neve, W.; Nuyts, S. Recurrence patterns after a decreased dose of 40 Gy to the elective treated neck in head and neck cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 123, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, P.D.; Neal, C.R.; Hardy, S.M.; Schreiber, A.M. Single-Arm Phase 2 Trial of Elective Nodal Dose Reduction for Patients With Locoregionally Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 100, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.K.; Oh, D.; Lee, E.; Kim, T.G.; Lee, H.; Nam, H.; Noh, J.M.; Ahn, Y.C. Feasibility of Selective Neck Irradiation with Lower Elective Radiation Dose in Treating Nasopharynx Cancer Patients. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 51, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, D.J.; Pham, N.-L.; Shah, J.L.; Sen, N.; Williams, K.A.; Subramaniam, R.M.; Moore, W.; Chorley, R.; Ahn, C.; Khan, S.M. Prospective Phase 2 Study of Radiation Therapy Dose and Volume De-escalation for Elective Neck Treatment of Oropharyngeal and Laryngeal Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 109, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zukauskaite, R.; Hansen, C.R.; Grau, C.; Samsøe, E.; Johansen, J.; Petersen, J.B.B.; Andersen, E.; Brink, C.; Overgaard, J.; Eriksen, J.G. Local recurrences after curative IMRT for HNSCC: Effect of different GTV to high-dose CTV margins. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 126, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burr, A.R.; Harari, P.M.; Ko, H.C.; Bruce, J.Y.; Kimple, R.J.; Witek, M.E. Reducing radiotherapy target volume expansion for patients with HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 2019, 92, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Herk, M. Errors and margins in radiotherapy. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2004, 14, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wygoda, A.; Rutkowski, T.; Hutnik, M.; Skladowski, K.; Golen, M.; Pilecki, B. Acute mucosal reactions in patients with head and neck cancer. Three patterns of mucositis observed during radiotherapy. Strahlenther. Und Onkol. 2013, 189, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewski, B.; Withers, H.R.; Taylor, J.M.G.; Hliniak, A. Dose fractionation and regeneration in radiotherapy for cancer of the oral cavity and oropharynx. Part 2. Normal tissue responses: Acute and late effects. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1990, 18, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottosson, S.; Zackrisson, B.; Kjellén, E.; Nilsson, P.; Laurell, G. Weight loss in patients with head and neck cancer during and after conventional and accelerated radiotherapy. Acta Oncol. 2013, 52, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzetti, F.; Cotogni, P. Nutritional Issues in Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Healthcare 2020, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Zaid, Z.; Kay Neoh, M.; Mat Daud, Z.A.; Md Yusop, N.B.; Ibrahim, Z.; Abdul Rahman, Z.; Jamhuri, N.; Abdul Azim, A.Z. Weight Loss in Post-Chemoradiotherapy Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Nutrients 2022, 14, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacicedo, J.; Casquero, F.; Martinez-Indart, L.; del Hoyo, O.; Gomez de Iturriaga, A.; Navarro, A.; Bilbao, P. A prospective analysis of factors that influence weight loss in patients undergoing radiotherapy. Chin. J. Cancer 2014, 33, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ghadjar, P.; Hayoz, S.; Zimmermann, F.; Bodis, S.; Kaul, D.; Badakhshi, H.; Bernier, J.; Studer, G.; Plasswilm, L.; Budach, V.; et al. Impact of weight loss on survival after chemoradiation for locally advanced head and neck cancer: Secondary results of a randomized phase III trial (SAKK 10/94). Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, A.; Valdes, A.M. The Metabolomic Signatures of Weight Change. Metabolites 2019, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, C.N.; Chiang, N.; Dalli, J.; Levy, B.D. Lipid mediators in the resolution of inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 7, a016311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciotti, E.; FitzGerald, G.A. Prostaglandins and inflammation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 986–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, D.; Campisi, J.; Verdin, E.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Targ, S.; Franceschi, C.; Ferrucci, L.; Gilroy, D.W.; Fasano, A.; Miller, G.W.; et al. Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. Bmj 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goenawan, I.H.; Bryan, K.; Lynn, D.J. DyNet: Visualization and analysis of dynamic molecular interaction networks. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2713–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elabdeen, H.R.; Mustafa, M.; Szklenar, M.; Rühl, R.; Ali, R.; Bolstad, A.I. Ratio of pro-resolving and pro-inflammatory lipid mediator precursors as potential markers for aggressive periodontitis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.W.; Zhou, W.; Liao, Y.; Hu, S.C.; Chen, T.L.; Song, Z.C. Analysis of metabolic profiles of generalized aggressive periodontitis. J. Periodontal. Res. 2018, 53, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şengül, V.; Güney, Z.; Kurgan, Ş.; Önder, C.; Serdar, M.A.; Günhan, M. Evaluation of salivary and serum methylated arginine metabolites and nitric oxide synthase in advanced periodontitis patients. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 5061–5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M.; Yay, E.; Atalay, N.; Balci, N.; Kurgan, Ş.; Toygar, H.; Serdar, M.A. Do arginine metabolites have a role in periodontitis due to smoking? A new perspective. Oral Dis. 2022, 00, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Wu, J.; Johnson, M.A.; Grapov, D.; Azizi, B.; Dhillon, J.; Fiehn, O. Metabolomics in psoriatic disease: Pilot study reveals metabolite differences in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. F1000Res 2014, 3, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Chuan-Jian, L.; Ling, H.; Jing-Wen, D.; Ze-Hui, H.; Yu-Hong, Y.; Zhong-Zhao, Z. Untargeted serum metabonomics study of psoriasis vulgaris based on ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 95931–95944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myśliwiec, H.; Baran, A.; Harasim-Symbor, E.; Myśliwiec, P.; Milewska, A.J.; Chabowski, A.; Flisiak, I. Serum fatty acid profile in psoriasis and its comorbidity. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2017, 309, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, C.; Wen, B.; Hou, G.; Lei, L.; Mei, Z.; Jia, X.; Chen, X.; Zhu, W.; Li, J.; Kuang, Y.; et al. Lipidomics profiling reveals the role of glycerophospholipid metabolism in psoriasis. Gigascience 2017, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorokin, A.V.; Norris, P.C.; English, J.T.; Dey, A.K.; Chaturvedi, A.; Baumer, Y.; Silverman, J.; Playford, M.P.; Serhan, C.N.; Mehta, N.N. Identification of proresolving and inflammatory lipid mediators in human psoriasis. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2018, 12, 1047–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, A.V.; Domenichiello, A.F.; Dey, A.K.; Yuan, Z.X.; Goyal, A.; Rose, S.M.; Playford, M.P.; Ramsden, C.E.; Mehta, N.N. Bioactive Lipid Mediator Profiles in Human Psoriasis Skin and Blood. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1518–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, L.P.; Xue, L.F.; Yin, G.S.; Wu, X.S. Identification of psoriasis vulgaris biomarkers in human plasma by non-targeted metabolomics based on UPLC-Q-TOF/MS. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 3940–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yao, D.N.; Lu, Y.; Deng, J.W.; Wei, J.A.; Yan, Y.H.; Deng, H.; Han, L.; Lu, C.J. Metabonomics Study on Serum Characteristic Metabolites of Psoriasis Vulgaris Patients With Blood-Stasis Syndrome. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 558731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Su, S.; Yang, Q.; Le, Y.; Chen, L.; Hu, M.; Guo, X.; Zheng, J.; Li, X.; Yu, Y. Metabolic profiling reveals interleukin-17A monoclonal antibody treatment ameliorate lipids metabolism with the potentiality to reduce cardiovascular risk in psoriasis patients. Lipids Health Dis. 2021, 20, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarentini, E.; Odorici, G.; Righi, V.; Paganelli, A.; Giacomelli, L.; Mirisola, V.; Mucci, A.; Benassi, L.; D’Aversa, E.; Lasagni, C.; et al. Integrated metabolomic analysis and cytokine profiling define clusters of immuno-metabolic correlation in new-onset psoriasis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottas, A.; Fishman, D.; Okas, T.L.; Püssa, T.; Toomik, P.; Märtson, A.; Kingo, K.; Soomets, U. Blood serum metabolome of atopic dermatitis: Altered energy cycle and the markers of systemic inflammation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raouf, J.; Idborg, H.; Englund, P.; Alexanderson, H.; Dastmalchi, M.; Jakobsson, P.J.; Lundberg, I.E.; Korotkova, M. Targeted lipidomics analysis identified altered serum lipid profiles in patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.; Mir, S.A.; Ji, S.; Ooi, X.T.; Chua, E.W.L.; Yi Wei, Y.; Wenk, M.R.; Bendt, A.K.; Chandran, N.S. Understanding the systemic burden of disease in hidradenitis suppurativa from plasma lipidomic analysis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2022, 107, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, T.; Herrmann, N.; Maintz, L.; Nümm, T.J.; Welchowski, T.; Claus, R.A.; Gräler, M.H.; Bieber, T. Altered Serum Phospholipids in Atopic Dermatitis and Association with Clinical Status. JID Innov. 2022, 2, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelonek, K.; Pietrowska, M.; Ros, M.; Zagdanski, A.; Suchwalko, A.; Polanska, J.; Marczyk, M.; Rutkowski, T.; Skladowski, K.; Clench, M.R.; et al. Radiation-induced changes in serum lipidome of head and neck cancer patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6609–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ros-Mazurczyk, M.; Wojakowska, A.; Marczak, L.; Polanski, K.; Pietrowska, M.; Jelonek, K.; Dominczyk, I.; Hajduk, A.; Rutkowski, T.; Skladowski, K.; et al. Ionizing radiation affects profile of serum metabolites: Increased level of 3-hydroxybutyric acid in serum of cancer patients treated with radiotherapy. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2017, 64, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojakowska, A.; Zebrowska, A.; Skowronek, A.; Rutkowski, T.; Polanski, K.; Widlak, P.; Marczak, L.; Pietrowska, M. Metabolic Profiles of Whole Serum and Serum-Derived Exosomes Are Different in Head and Neck Cancer Patients Treated by Radiotherapy. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Tomàs, E.; Arguís, M.; Arenas, M.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Murcia, M.; Sabater, S.; Torres, L.; Baiges-Gayà, G.; Hernández-Aguilera, A.; Camps, J.; et al. Alterations in plasma concentrations of energy-balance-related metabolites in patients with lung, or head & neck, cancers: Effects of radiotherapy. J. Proteom. 2020, 213, 103605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boguszewicz, Ł.; Bieleń, A.; Ciszek, M.; Wendykier, J.; Szczepanik, K.; Skorupa, A.; Mrochem-Kwarciak, J.; Składowski, K.; Sokół, M. NMR-Based Metabolomics in Investigation of the Radiation Induced Changes in Blood Serum of Head and Neck Cancer Patients and Its Correlation with the Tissue Volumes Exposed to the Particulate Doses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, M.; Hirano, T. The molecular mechanisms of chronic inflammation development. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepak, P.; Axelrad, J.E.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N. The Role of the Radiologist in Determining Disease Severity in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 29, 447–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousuf, A.; Ibrahim, W.; Greening, N.J.; Brightling, C.E. T2 Biologics for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milenkovic, V.M.; Stanton, E.H.; Nothdurfter, C.; Rupprecht, R.; Wetzel, C.H. The Role of Chemokines in the Pathophysiology of Major Depressive Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutolo, M.; Soldano, S.; Smith, V. Pathophysiology of systemic sclerosis: Current understanding and new insights. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Hu, W.; Wang, R.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, M.; Li, M.; Cai, J.; Rose, P.; Mao, J.; Zhu, Y.Z. Signaling pathways in rheumatoid arthritis: Implications for targeted therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Ghosh, N.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Roy Chowdhury, S.; Chaudhury, K. Metabolomics of asthma, COPD, and asthma-COPD overlap: An overview. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2023, 60, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, C.C.; Ushakova, A.; Skogseth, R.E.; Alves, G.; Tysnes, O.B.; Aarsland, D.; Lange, J.; Maple-Grødem, J. Inflammatory Biomarkers in Newly Diagnosed Patients with Parkinson Disease and Related Neurodegenerative Disorders. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflammation 2023, 10, e200132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Gao, M.Q.; Jiang, X.C.; Pan, X.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Pang, B. Research progress and value of albumin-related inflammatory markers in the prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer: A review of clinical evidence. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 1294–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frego, N.; Contieri, R.; Diana, P.; Mancon, S.; Colombo, P.; Lazzeri, M.; Buffi, N.M.; Casale, P.; Hurle, R. Inflammatory markers and Type 2 diabetes mellitus as prognostic risk factors in low-risk bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2023, 132, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudukelimu, A.; Barberis, M.; Redegeld, F.A.; Sahin, N.; Westerhoff, H.V. Predictable Irreversible Switching Between Acute and Chronic Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laiakis, E.C.; Canadell, M.P.; Grilj, V.; Harken, A.D.; Garty, G.Y.; Astarita, G.; Brenner, D.J.; Smilenov, L.; Fornace, A.J., Jr. Serum lipidomic analysis from mixed neutron/X-ray radiation fields reveals a hyperlipidemic and pro-inflammatory phenotype. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, B.; Mika, J.; Jelonek, K.; Cruz-Garcia, L.; Roelants, C.; Testard, I.; Cherradi, N.; Lumniczky, K.; Polozov, S.; Napieralska, A.; et al. Systemic modulation of stress and immune parameters in patients treated for prostate adenocarcinoma by intensity-modulated radiation therapy or stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy. Strahlenther. Und Onkol. 2020, 196, 1018–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| AND | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | - metabolite | - radiotherapy | - serum | - human | - mass spectrometry |
| - metabolites | - radiation | - sera | - humans | - MS | |
| - metabolome | - dermatitis | - plasma | - patient | - gas chromatography | |
| - metabonome | - mucositis | - plasmas | - patients | - GC | |
| - metabolic | - laryngitis | - blood | - liquid chromatography | ||
| - metabolomic | - odynophagia | - LC | |||
| - metabolomics | - esophagitis | - capillary electrophoresis | |||
| - lipid | - pharyngitis | - CE | |||
| - lipids - lipidome - lipidomics | - tonsillitis - aphtha - otitis | - matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight | |||
| - lipidomic | - epiglottitis - sinusitis - pulpitis | - matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight | |||
| - periodontitis | - MALDI-TOF | ||||
| - gingivitis | - triple quadrupole | ||||
| - xerostomia | - QQQ | ||||
| - shingles | - ion trap | ||||
| - erysipelas | - IT | ||||
| - sialadenitis | - quadrupole ion trap | ||||
| - angina | - QIT | ||||
| - orbitrap | |||||
| - Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance | |||||
| - FTICR | |||||
| - nuclear magnetic resonance | |||||
| - NMR | |||||
| - magnetic resonance spectroscopy | |||||
| - MRS | |||||
| Clinical Model | Controls 1 (n) | Cases 2 (n) | Type of Material | Method of Analysis | Analyzed Metabolites | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Inflammatory Disease | ||||||
| AgP | 19 | 19 | serum | LC-MS/MS | n3 and n6 PUFAs | [49] |
| AgP | 20 | 20 | serum | GC-MS | global profile | [50] |
| periodontitis | 24 | 21 | serum | LC-MS/MS | arginine and derivatives | [51] |
| periodontitis | 20 | 20 | serum | LC-MS/MS | arginine and derivatives | [52] |
| Chronic Inflammatory Disease | ||||||
| psoriasis | 10 | 10 | serum | GC-MS | global profile | [53] |
| psoriasis | 75 | 75 | serum | LC-MS | global profile | [54] |
| psoriasis | 32 | 85 | serum | GC-MS | fatty acid profile | [55] |
| psoriasis | 45 | 45 | plasma | LC-MS/MS | global profile | [56] |
| psoriasis | 7 | 7 | serum and plasma | LC-MS/MS | BLMs | [57] |
| psoriasis | 30 | 60 | serum and plasma | LC-MS/MS; GC-MS | BLMs | [58] |
| psoriasis | 12 | 12 | plasma | LC-MS | global profile | [59] |
| psoriasis | 45 | 50 | serum | LC-MS | global profile | [60] |
| psoriasis | 28 | 28 | serum | LC-MS | lipid profile | [61] |
| psoriasis | 7 | 7 | serum | NMR | global profile | [62] |
| AD | 24 | 25 | serum | LC-MS/MS | global profile 3 | [63] |
| PM or DM | 12 | 13 | serum | LC-MS/MS; GC-FID | global profile | [64] |
| HS | 73 | 60 | plasma | LC-MS/MS | global profile | [65] |
| AD | 47 | 30 | serum | LC-MS/MS | Cer, Sph, LPC, PC, SM, and LPE | [66] |
| Radiotherapy 4 | ||||||
| CAIR (1.8; 72) | 66 | 66 | serum | MALDI-MS | global profile | [67] |
| CAIR (1.8; 72) | 20 | 20 | serum | GC-MS | global profile | [68] |
| CAIR; CFRT; (1.8–2.5; 62.5–72) | 18 | 18 | serum | LC-MS/MS | global profile 3 | [18] |
| CAIR (1.8; 72) | 10 | 10 | serum | GC-MS | global profile | [69] |
| CFRT (2; 70) | 28 | 28 | plasma | GC-MS | amino acids | [70] |
| CAIR; CFRT; MAN (1.8–3; 51–72) | 106 | 106 | serum | NMR | global profile | [71] |
| CAIR; CFRT; MAN (1.8–3; 51–72) | 45 | 45 | serum | LC-MS/MS | global profile | [19] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jelonek, K.; Mrowiec, K.; Gabryś, D.; Widłak, P. The Metabolic Footprint of Systemic Effects in the Blood Caused by Radiotherapy and Inflammatory Conditions: A Systematic Review. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13091000
Jelonek K, Mrowiec K, Gabryś D, Widłak P. The Metabolic Footprint of Systemic Effects in the Blood Caused by Radiotherapy and Inflammatory Conditions: A Systematic Review. Metabolites. 2023; 13(9):1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13091000
Chicago/Turabian StyleJelonek, Karol, Katarzyna Mrowiec, Dorota Gabryś, and Piotr Widłak. 2023. "The Metabolic Footprint of Systemic Effects in the Blood Caused by Radiotherapy and Inflammatory Conditions: A Systematic Review" Metabolites 13, no. 9: 1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13091000
APA StyleJelonek, K., Mrowiec, K., Gabryś, D., & Widłak, P. (2023). The Metabolic Footprint of Systemic Effects in the Blood Caused by Radiotherapy and Inflammatory Conditions: A Systematic Review. Metabolites, 13(9), 1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13091000








