Abstract
Exposure to cadmium (Cd) can affect neurodevelopment and results in increased potential of developing neurodegenerative diseases during the early developmental stage of organisms, but the mechanisms through which exposure to environmentally relevant concentrations of Cd lead to developmental neurotoxicity remain unclear. Although we know that microbial community fixations overlap with the neurodevelopmental window during early development and that Cd-induced neurodevelopmental toxicity may be related to the disruption of microorganisms during early development, information on the effects of exposure to environmentally relevant Cd concentrations on gut microbiota disruption and neurodevelopment is scarce. Therefore, we established a model of zebrafish exposed to Cd (5 µg/L) to observe the changes in the gut microbiota, SCFAs, and free fatty acid receptor 2 (FFAR2) in zebrafish larvae exposed to Cd for 7 days. Our results indicated that there were significant changes in the gut microbial composition due to the exposure to Cd in zebrafish larvae. At the genus level, there were decreases in the relative abundances of Phascolarctobacterium, Candidatus Saccharimonas, and Blautia in the Cd group. Our analysis revealed that the acetic acid concentration was decreased (p > 0.05) while the isobutyric acid concentration was increased (p < 0.05). Further correlation analysis indicated a positive correlation between the content of acetic acid and the relative abundances of Phascolarctobacterium and Candidatus Saccharimonas (R = 0.842, p < 0.01; R = 0.767, p < 0.01), and a negative correlation between that of isobutyric acid and the relative abundance of Blautia glucerasea (R = −0.673, p < 0.05). FFAR2 needs to be activated by SCFAs to exert physiological effects, and acetic acid is its main ligand. The FFAR2 expression and the acetic acid concentration were decreased in the Cd group. We speculate that FFAR2 may be implicated in the regulatory mechanism of the gut–brain axis in Cd-induced neurodevelopmental toxicity.
1. Introduction
Cadmium (Cd), a highly toxic heavy metal pollutant, is widely available in the environment. Because of its long half-life (about 20–40 years) and slow excretion rate, Cd tends to accumulate in the human body, leading to various toxic effects, the most concerning of which is developmental neurotoxicity, which includes the induction of neuronal apoptosis, glial cell activation and neuroinflammatory factor release in the brain nervous system. China is among the countries with serious Cd pollution, and there have been several cases of Cd pollution in Chinese river basins. For example, the concentration of Cd in freshwater is usually between 10 and 500 ng/L, while the Cd concentration in the Luan River basin in northeastern China is 1.120–4.474 µg/L (the national drinking water standard (GB/T5750-2006) is 5 µg/L) and in the Longjiang River is 45.01 µg/L [1]. Most existing related studies explored Cd toxicity caused by high concentrations (100 mg/kg) in humans [2]. However, these concentrations are much higher than the Cd concentrations that the normal population is typically exposed to. According to Feng et al., low doses of Cd exposure can also cause various adverse effects [3,4]. However, the concentrations of Cd exposure used in existing studies (2.5 mg/L a week) are still much higher than the actual environmental exposure doses [5,6], and research related to environmental low-dose Cd exposure remains scarce. Our previous studies found that environmental low-concentration Cd exposure caused developmental neurotoxicity and changes in the gut microbiota of zebrafish [7], but the mechanisms involved were not explored in depth. It is hypothesized that the gut–brain axis may be involved in the regulation of Cd-induced neurodevelopmental toxicity.
The microbiota has a crucial influence in maintaining normal physiological functions; notably, the gut–brain axis is a channel of interconnection between the gut and the brain [8]. The homeostasis of the brain environment and its downstream regulatory effects are more sensitive to the gut microbiota, and when the composition of gut microbiota changes significantly, metabolic processes in the brain are altered, leading to cognitive and behavioral dysfunction. The changing composition of the gut microbiota during homeostasis allows the release of metabolites synthesized by the microbiota into the gut lumen with effects on metabolism, immune system function and behavior. Heavy metal exposure leads to changes in the composition of the gut flora and metabolites, which in turn affect the integrity of the gut barrier, and the destruction of the gut barrier leads to an increased intake of heavy metals in the body, thus further enhancing their toxicity; at the same time, changes in intestinal metabolites can affect the function of the central nervous system through the gut–brain axis. Exposure to chemicals during the window of embryonic and early larval development, even at low concentrations considered safe, can disrupt the intestinal flora [9]. The animal colon contains large numbers of undigested complex carbohydrates (oligosaccharides, non-starch polysaccharides, resistant starch, etc.), which are able to serve as substrates for anaerobic fermentation by intestinal bacteria, and the main metabolic end products produced are short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which are the most important metabolites of the intestinal microbiota, especially acetate, propionate and butyrate, while increased levels of intestinal SCFAs can regulate intestinal flora balance and mitigate cognitive dysfunction and are now recognized as the link between the gut flora and the host cells; these molecules are made up of components of gut bacteria. Not only are they important energy sources that can be directly used by intestinal bacteria, but they are also one of the energy sources required by the intestinal epithelial cells. Of course, in addition to being a substrate for energy synthesis, the regulatory functions of SCFAs in host physiological activities and the immune response are beginning to be known. It is noteworthy that the physiological regulation of neurodevelopmental toxicity that SCFAs participate in requires the activation of the FFAR2-signaling pathway [10]. FFAR2 can be activated by a variety of SCFAs, but it is the most sensitive to acetic acid. Acetic acid is the major ligand of FFAR2 [11]; FFAR2 binding to acetic acid plays a crucial role in humans.
We examined the effects of Cd at 0.1, 1.25, 2.5, and 5 μg/L on zebrafish in our previous study [7] and found that the effects of Cd at 5 μg/L on neurodevelopmental toxicity and gut microbiota of zebrafish were significant. Therefore, in order to further explore the regulatory processes of the gut–brain axis in Cd neurodevelopmental toxicity, an experiment was conducted to examine the changes in the gut microbiota structure, SCFAs, and FFAR2 expression through exposing zebrafish embryos and larvae to Cd concentrations (5 µg/L) for 7 days and performing correlation analysis. Our results contribute to the neurodevelopmental toxicity mechanism of Cd and provide a new direction and reference basis for evaluating the environmental ecotoxicity of Cd.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Embryo Breeding
Wild-type AB-strain zebrafish were used in this experiment, which were purchased from the laboratory of the College of Public Health, Southern Medical University. Adult zebrafish were housed in tanks in a 14 h light and 10 h dark cycle at 28 ± 1 °C and a pH of 6.5–7.5. The zebrafish were fed twice a day, and the impurities in the fish tank were regularly cleaned during the experiment. Sexually mature male and female zebrafish were selected in a 1:1 ratio and placed in a tank with a partition for ovulation and fertilization. The next morning, the spacer was withdrawn, the embryos were collected within 30 min, using the zebrafish embryo growth medium used by Bahuguna et al. [12], and normal embryo was selected and maintained in Danieau’s embryo medium (17.4 mmol/L NaCl, 0.21 mmol/L KCl, 0.12 mmol/L MgSO4, 0.15 mmol/L, Ca(NO3)2, and 1.5 mmol/L HEPES; pH = 7.2), incubated in a constant temperature incubator at 28.5 °C. The fish were observed under a somatic microscope 2 h post-fertilization (hpf). After each group of zebrafish larvae had developed up until 5 days post-fertilization (dpf), they were placed in transparent water tanks and continued to be cultured, with 7 dpf as the observation endpoint to observe and record the developmental changes in zebrafish larvae.
2.2. Embryo Treatment
The concentration of heavy metals was calculated by the following equation. An amount of 0.07332 g of cadmium chloride was weighed and placed in a 50 mL centrifuge tube, while 40 mL of double distilled water (ddH2O) was measured with a measuring cylinder, added into the centrifuge tube, shaken well and allowed to stand to obtain 10 mmol/L of the CdCl2 transparent stock solution. The desired concentration (5 μg/L for Cd) was then obtained by adding 5 mL of the stock solution to 107 mL of ddH2O. The experiment included a control group and a Cd group, with 5 samples in each group and 40 zebrafish embryos in each sample. The collected embryos were maintained in Danieau’s embryo medium. Zebrafish embryos were exposed with Cd by adding 30 mL of 5 μg/L CdCl2 to Danieau’s embryo medium; after 12 h, impurities and dead embryos were removed. The control group was maintained without any Cd treatment.
2.3. Microbiota Analysis
Each group had 5 replicates with 40 larvae per replicate. Genomic DNA was extracted according to the instructions of DNA extraction kits corresponding to various samples. Then, the integrity and purity were tested by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis and NanoDropOne. Genomic DNA was used as a template for PCR amplification and the electrophoresis detection of products. Barcode primers and PremixTaq (TaKaRa) were used for PCR amplification according to the V3/V4 region. Illumina MiSeq sequencing was conducted at Magigene Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China). The QIIME data analysis package was used to perform 16S rRNA data analysis. The correlation matrix between bacterial microbiota composition and locomotor activity (activity counts and distance) was generated using Pearson’s correlation coefficient. A heat map of this correlation matrix was created using the pheatmap package in R software.
2.4. SCFAs Quantification by GC-MS
The larvae (7 dpf, n = 200 per group, five replicates) were transferred into the tube and washed at least three times with purified water. Then, the larvae were pooled and esterification using PBS and a ribitol internal standard was carried out. Afterward, the mixture was centrifuged at 4000 r/min for 10 min. The supernatant was aspirated and analyzed via GC-MS, and the concentration of SCFAs in zebrafish larvae was calculated.
2.5. FFAR2 Expression Examination via qPCR
The reagent trizol was added to the samples to extract the total RNA, followed by the addition of chloroform and then centrifugation. The isolated RNA was then precipitated using isopropyl alcohol, rinsed with ethanol, and detected using qPCR. The PCR conditions were as follows: 30 s incubation at 95 °C, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s, 55 °C for 20 s, and 72 °C for 20 s. Primers for FFAR2 and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (gapdh) were generated using Primer3 software, as listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
List of primers used for gene expression.
2.6. Preparation of Graphics and Statistical Analysis
The results of quantitative resources were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation; graphics and statistical analysis were processed using SPSS16.0 software. Significant difference were distinguished at probability (p) value of <0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Alterations in the Structure of the Gut Microbiota in Zebrafish Larvae
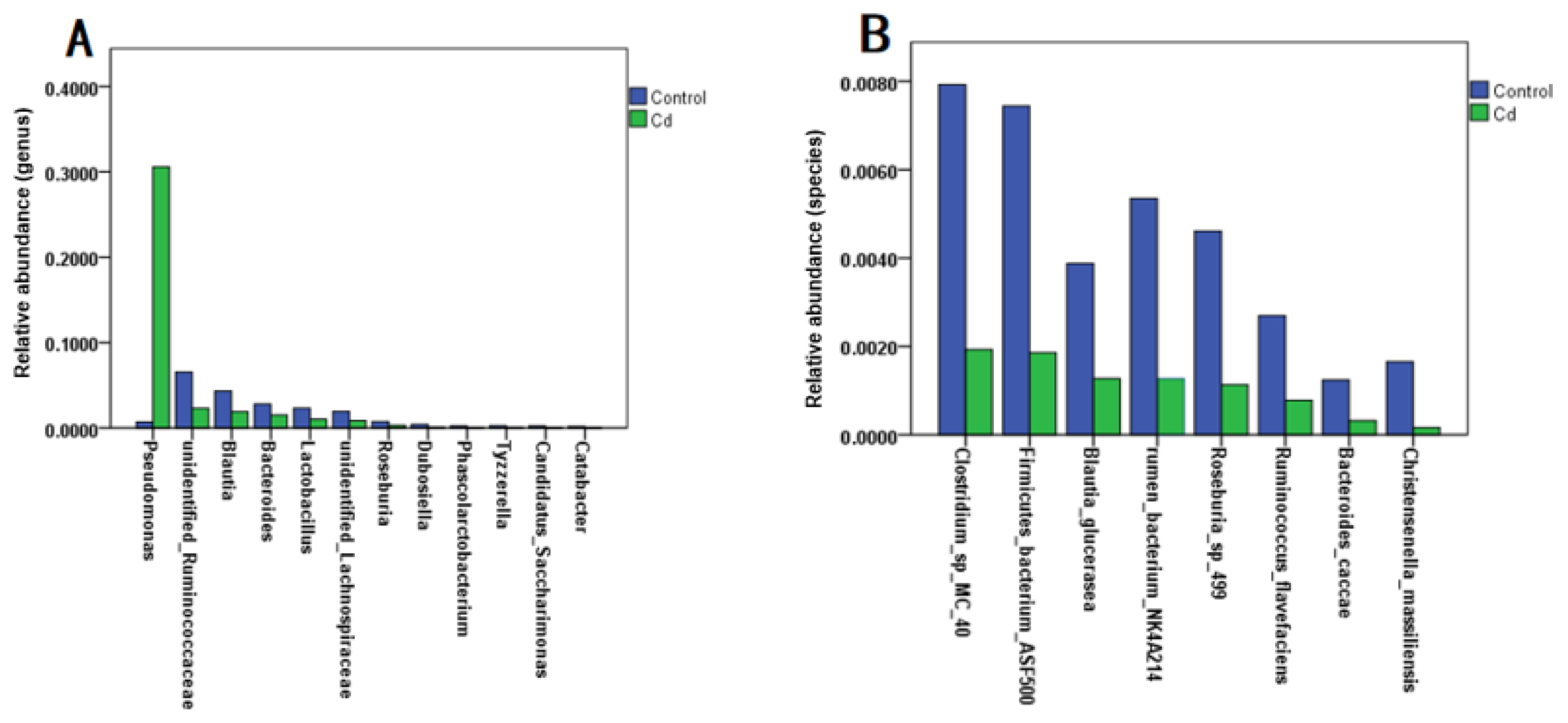
Evidence shows that heavy metal exposure can disrupt the intestinal flora, affecting heavy metal absorption and ultimately enhancing or mitigating heavy metal toxicity [13]. To explored the effect of Cd exposure on the relative abundance of gut microbiota, we analyzed zebrafish larvae and found that Cd exposure caused a significant increase in the relative abundance of Pseudomonas at the genus level compared with the control group (p < 0.05). At the genus level, the relative abundances of gut microbiota in unidentified Ruminococcaceae, Blauti, Bacteroides, Lactobacillus, unidentified Lachnospiraceae, Roseburia, and Dubosiella, and Phascolarctobacterium were significantly decreased (p < 0.05) (Figure 1A). At the species level, Cd exposure caused a significant decrease in the relative abundances of Clostridium sp. MC 40, Firmicutes bacterium ASF500, Blautia glucerasea, rumen bacterium NK4A214, Roseburia sp. 499, Ruminococcus flavefaciens, Bacteroides caccae, and Christensenella massiliensis (p < 0.05) (Figure 1B). This was consistent with the results of the previous experiment [7].
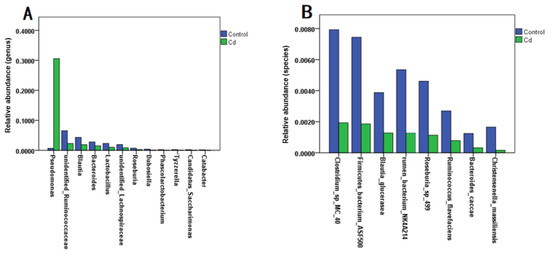
Figure 1.
Effect of Cd exposure on the relative abundance of zebrafish gut microbiota. (A) Genus level; (B) species level.
3.2. Changes in the Concentrations of SCFAs in Zebrafish Larvae
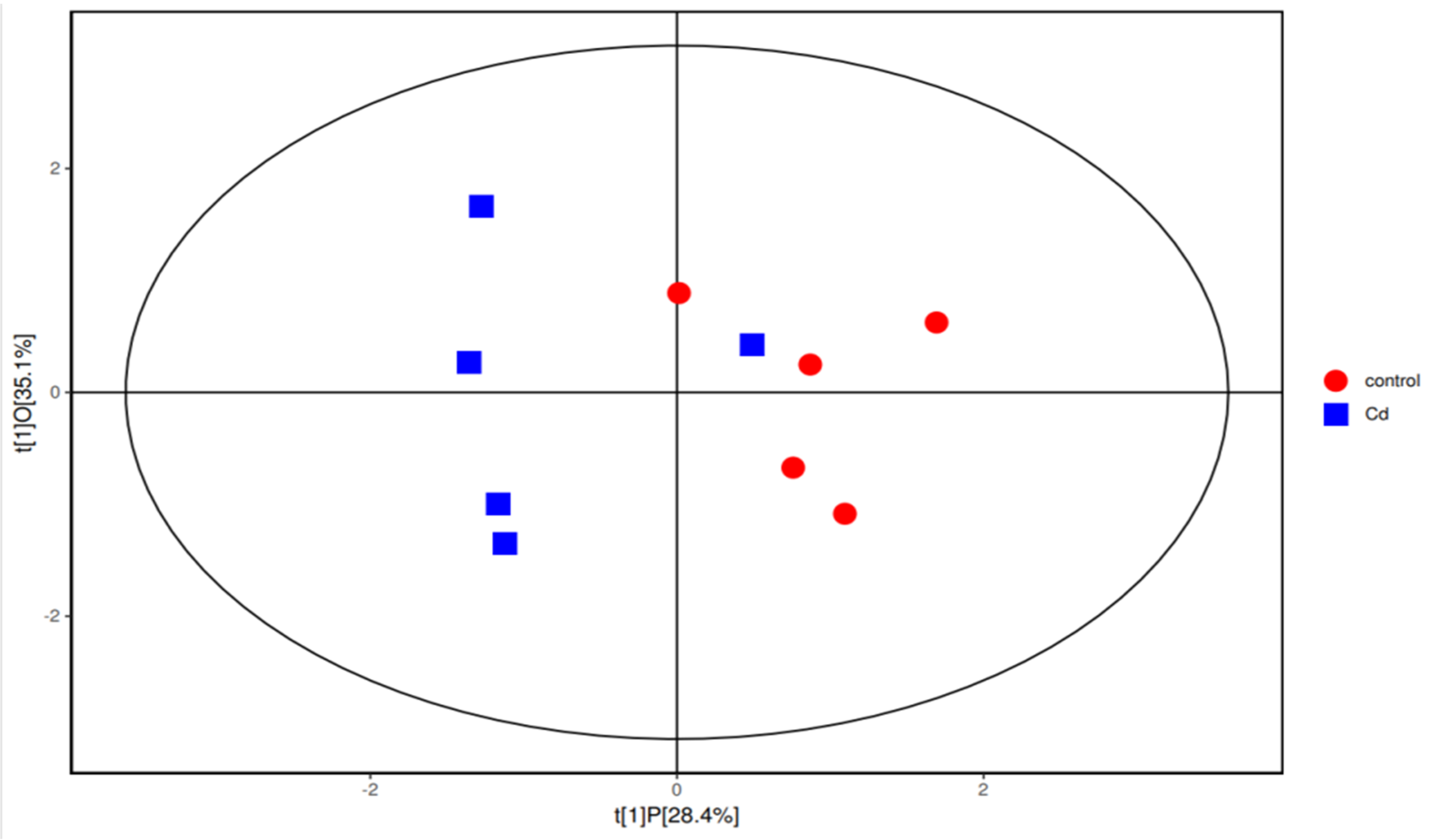
Gut flora-producing SCFAs include Bacteroides, Lactobacillus, and unidentified Lachnospiraceae [14]. Interestingly, the abundances of all these bacteria decreased in the Cd group in this study. To explore the mechanism of Cd-induced changes in the concentrations of SCFAs, the SCFAs were analyzed. The analysis showed that the average concentration of isobutyric acid in the Cd group was significantly increased (p < 0.05) (Table 2). The average concentrations of acetic acid between the control group and the Cd group showed no significant difference (p > 0.05). In addition, the mean concentrations of isovalerate, valerate, and caproic acid in SCFAs between the two groups showed no significant differences (p > 0.05). To further explore the relationship between Cd and SCFAs, we used orthogonal partial least-squares discrimination analysis (OPLS-DA) and found that the concentrations of SCFAs in the Cd group and the control group were different (Figure 2).

Table 2.
Comparison of the short-chain fatty acid concentrations in zebrafish in the control group and Cd group.
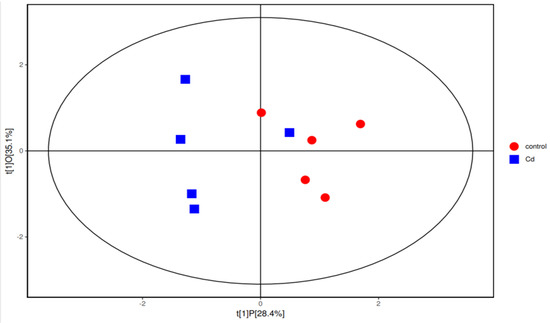
Figure 2.
Orthogonal partial least-squares discrimination analysis (OPLS−DA) in the Cd group and the control group.
3.3. Correlation Analysis between SCFAs and Gut Flora
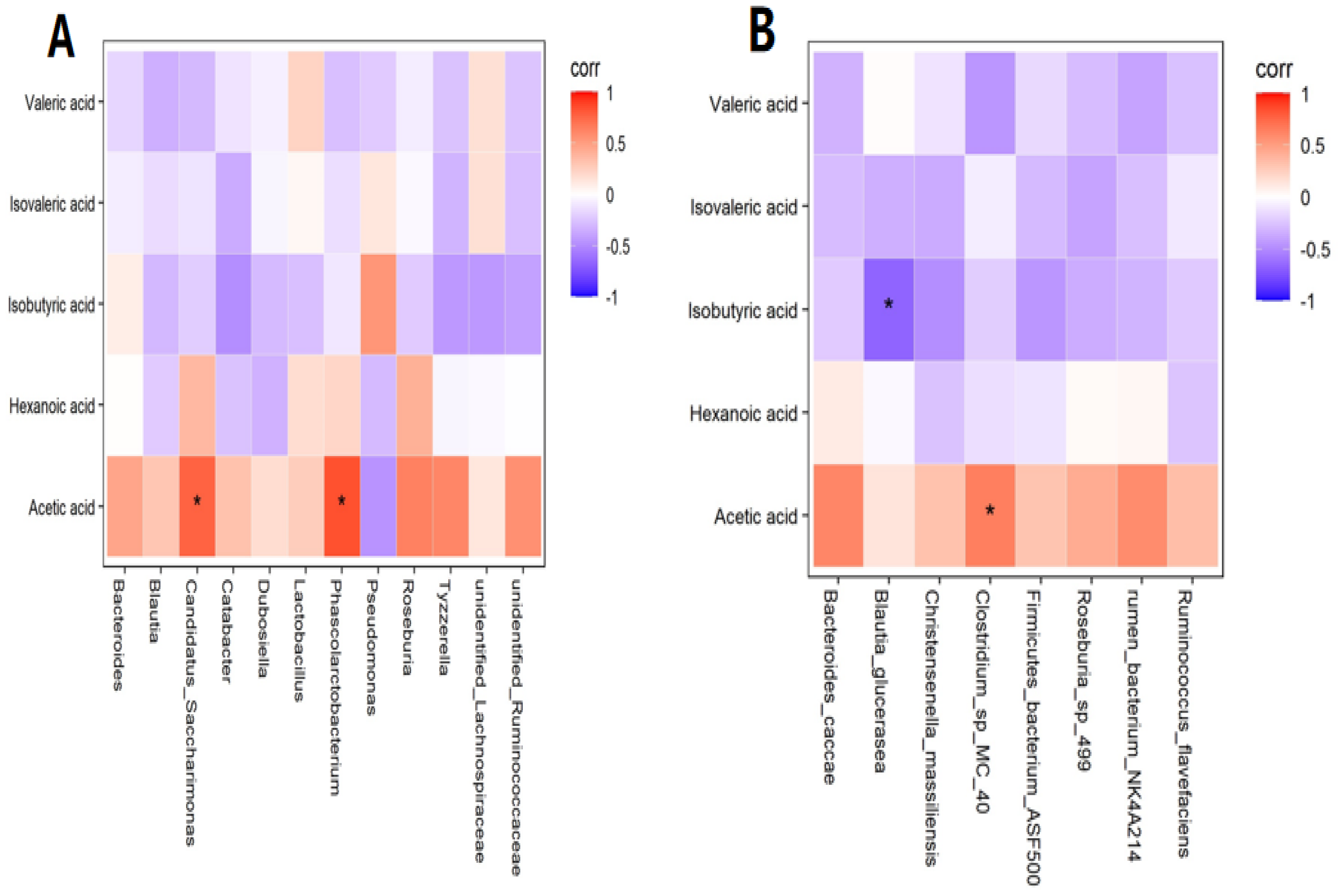
In preliminary experiments, we found some interesting phenomena. Although there was no statistical significance in the average concentrations of acetic acid in zebrafish larvae in the control group and Cd group (p > 0.05), the average concentration of acetic acid in the Cd group was 39.953 nmol/g, while that in the control group was 51.844 nmol/g. The concentration difference reached 11.981 nmol/g, which was a great difference. Therefore, further correlation analysis was conducted. At the genus level, a positive correlation was found between acetic acid and Phascolarctobacterium and Candidatus Saccharimonas (R = 0.842, p < 0.01; R = 0.767, p < 0.01) (Figure 3A). At the species level, a positive correlation was observed between acetic acid and Clostridium sp. MC 40 in the Cd group (R = 0.648, p < 0.05), while a negative correlation was observed between isobutyric acid and Blautia glucerasea (R = −0.673, p < 0.05) (Figure 3B). Collectively, the changes in the concentrations of SCFAs were caused by changes in the gut flora.
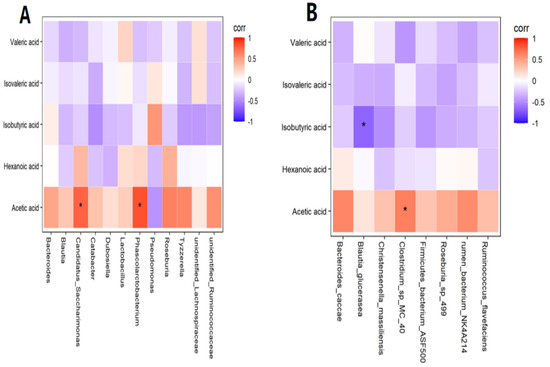
Figure 3.
(A) Correlation analysis with short−chain fatty acids (SCFAs) at the genus level. (B) Correlation analysis with SCFAs at the species level. Note: * means significance at p < 0.05.
3.4. Effects of Cd Exposure on Host Gene Expression
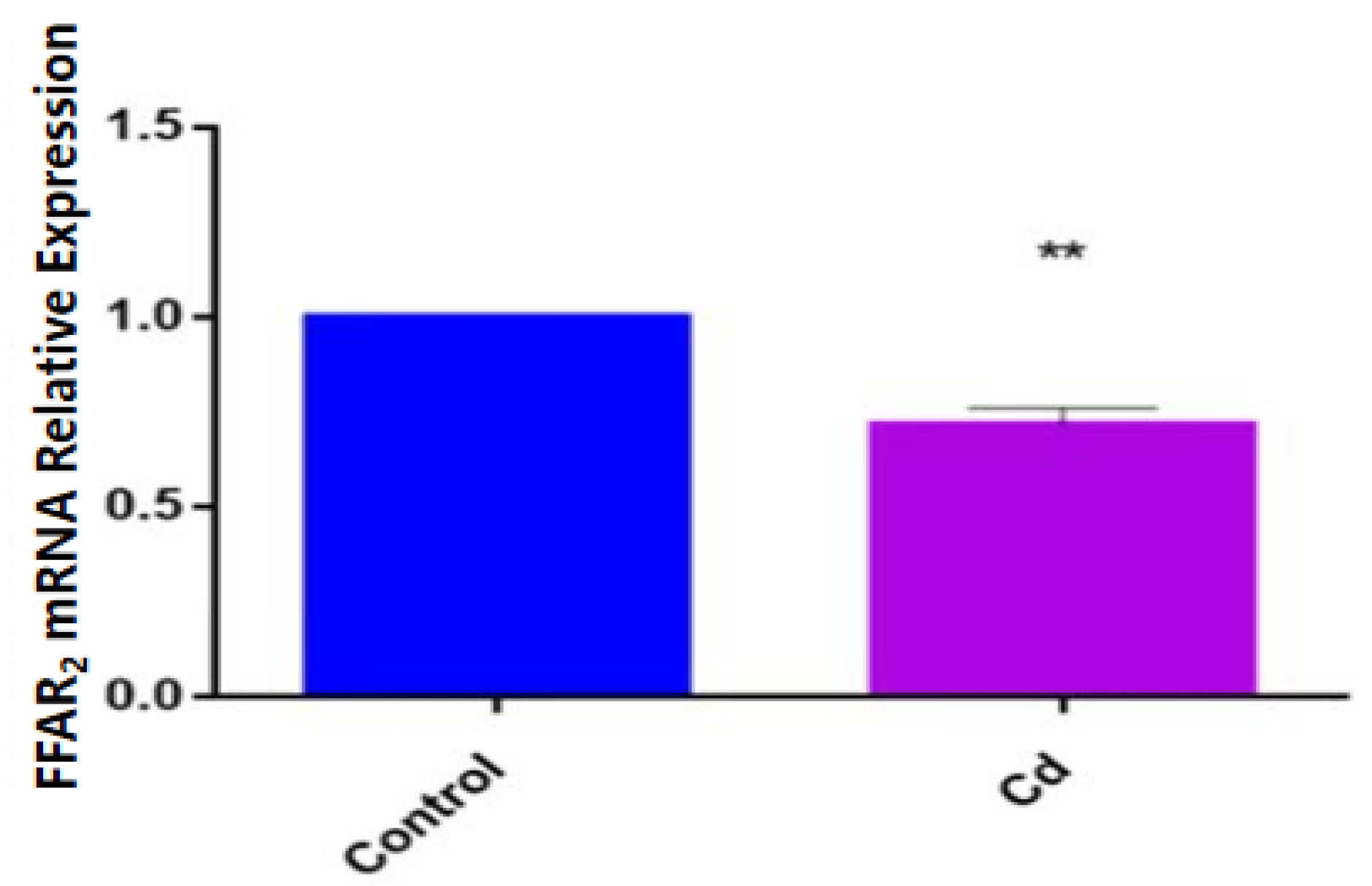
To determine how the expression of FFAR2 changed under Cd exposure, we detected the expression of FFAR2 in zebrafish larvae via qPCR and found that the expression of FFAR2 mRNA in the Cd group was significantly decreased compared with that in the control group (p < 0.01) (Figure 4).
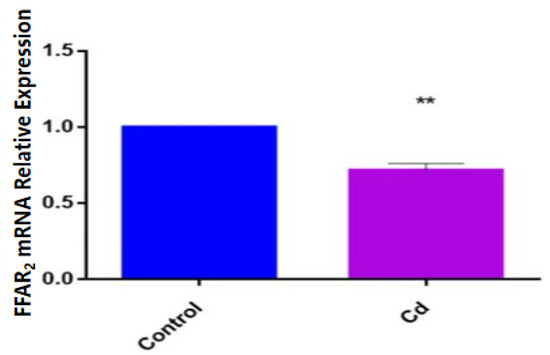
Figure 4.
Relative expression of FFAR2 mRNA in zebrafish in the Cd group and control group. Note: ** means significance at p < 0.01.
4. Discussion
Cd is one of the most toxic heavy metals, as well as a global pollutant and widely found in plastic manufacturing, metal smelting, battery, paint and other industries. Cd can damage human neurons and affect the construction of the neural network system and the development of synapses, thus causing cognitive impairment of neurological functions; the impact on children is especially of great concern. Long-term exposure to Cd can cause memory loss, inattention and even affect psychological behavior in children. Low-dose Cd exposure can cause neural-tube malformations and developmental delays in the early developmental stage. There is increasing evidence emphasizing the role of the gut’s flora and its metabolites in neurodevelopmental toxicity. The effects on the central nervous system could pass through the gut–brain axis [15,16]. Dysbiosis of the gut microflora can cause changes in the concentrations of metabolites, which can induce various diseases [17,18,19,20,21,22]. In this study, we established a zebrafish model, exposed it to environmentally relevant concentrations of Cd (5 µg/L), and examined the relevant indicators. In addition, we analyzed whether or not environmentally relevant Cd exposure altered the gut microbiota’s composition and the concentrations of SCFAs and subsequently investigated the effects of changes in the concentration of SCFAs on the expression of FFAR2 at the genetic level. Our results indicated that environmentally relevant concentrations of Cd had adverse effects on the gut flora and neuromotor behavior of zebrafish, resulting in the disruption of the intestinal flora, decreased concentration of SCFAs and reduced motility. In addition, our results indicated the changes in FFAR2 expression. It is worth focusing on the fact that the gut microbiota’s composition in zebrafish larvae was disturbed even when exposed to low concentrations of Cd (Figure 1A,B). The dominant groups in the zebrafish gut flora included Firmicutes and Proteobacteria, and the results indicated that the proportion of Firmicutes decreased while the proportion of Proteobacteria increased in zebrafish larvae after 7 days of Cd exposure. The above results were consistent with those of some existing studies [7,22].
To investigate the effect of gut microbial disruption on metabolites, this work examined the SCFAs in zebrafish larvae using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. The results indicated that the disruption of the gut microbiota led to an increase in the concentrations of isobutyric acid (p < 0.05) and decrease in the concentrations of acetic acid (p > 0.05) in zebrafish. The concentrations of isobutyric acid are associated with some bacteria involved in mood regulation [23]. In the present study, further analysis revealed that the concentrations of isobutyric acid were negatively correlated with Blautia glucerasea (R = −0.673, p < 0.05). Petrov et al. indicated that the relative abundance of Blautia glucerasea in both patients with major depression disorders and Parkinson’s disease was decreased [24,25], suggesting that Blautia glucerasea is associated with psychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases. A related study from Belgium in 2016 [23] reported elevated isobutyric acid in the stools of 113 children with affective disorders, suggesting that changes in isobutyric acid concentrations may be related to children’s emotions. Three clinical studies showed significant differences in the composition of oropharyngeal [26,27] and intestinal flora [28] between patients with schizophrenia and control patients, and similar changes in intestinal bacterial profiles in children with autism were observed. Notably, the experimental results in this study showed a great difference in the mean concentration of acetic acid in the control group and the Cd group, with a decrease in the concentration of acetic acid in zebrafish from the Cd group compared with that in the control group. Acetic acid, as one of the most abundant SCFAs in the colon, is involved in many physiological modulations through regulating the levels of hypothalamic neurotransmitters, glutamate, and glutamine [29]. The difference in acetic acid concentrations was not statistically significant (p > 0.05) between the control group and Cd group, but the results are still important. In a study of depressed patients that found acetic acid concentrations to be significantly lower in depressed patients, the levels of SCFAs were also reduced in mice with Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The oral administration of acetate reduced cognitive dysfunction and improved neurological impairment in mice [29]. To further investigate the mechanisms involved, this study analyzed the correlation between intestinal flora and acetic acid. The test results indicated that the concentrations of acetic acid in the Cd group were highly significantly and positively correlated with the levels of both Phascolarctobacterium and Candidatus Saccharimonas. (R = 0.842, p < 0.01; R = 0.767, p < 0.01). Phascolarctobacterium belongs to Firmicutes and produces large amounts of acetic acid/propionic acid [30]. It is positively correlated with positive emotions in humans [31]. A large amount of evidence showed that Phascolarctobacterium has beneficial neuroprotective effects on the host [32], assists in improving the cognitive level, and reduces the prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease [33,34,35]. Saccharimonas was found to be abundant in the gut of patients with nonviolent schizophrenia, which provides new insights into violent behavior in schizophrenia from the perspective of gut microbes [36]. There is growing evidence that changes in gut microbial composition are associated with various neuropsychiatric disorders. From Figure 1, we can observe that, at the genus level, the relative abundances of eight gut microbes that may be connected with neurodevelopment were significantly lower in the Cd group than in the control group. This result suggests that Cd may affect neurodevelopment through the gut–brain axis channel.
FFAR2 acts mainly by sensing SCFAs in the intestine and being activated by three major SCFAs: acetic acid, propionic acid, and butyric acid, with acetic acid being the primary ligand for FFAR2. The activation of FFAR2 by SCFAs is necessary for a normal resolution of certain inflammatory responses. Binding of FFAR2 by SCFAs may provide a molecular link between diet, gastrointestinal bacterial metabolism, immunity, and inflammatory responses. This study examined the concentration of FFAR2 and found that it decreased along with that of acetic acid. Notably, FFAR2 expression may be associated with neurotoxicity and may be involved in brain development and neuronal differentiation as a potential drug target against several neurological diseases [37,38,39]. Schmidt et al. found that FFAR2 is mainly expressed on neutrophils, eosinophils, immune cells, and neuronal cells [40], but the neuronal cell function of FFAR2 has not been well explored. Razazan et al. indicated that the acetic acid-activated FFAR2-signaling pathway is associated with AD progression [10]. AD is the most common neurodegenerative disease in the elderly population [41],and has an increasing prevalence and no currently available effective preventive therapy or treatment. Amyloid β (Aβ) accumulation and formation of intracellular neurofibrillary tangles are characteristics of AD, causing neuronal changes and decreased memory function and learning capacity [42,43]. There is substantial evidence that neurodegeneration in AD pathology is caused by increased Aβ accumulation [44,45,46,47,48,49]. However, treatments targeting the reduction of Aβ levels have not yet been successful. A study by Kim et al. exploring the transition from wild-type mice to an AD mouse model of healthy microbiota transfer found that the decrease in the formation of Aβ plaques and neurogenic fibrous tangles was due to a change in the intestinal microbiota toward a normal trend, reduced neurotoxicity, and improved cognition, confirming the link between the gut and the brain in AD patients [50]. The results suggest that repression of the FFAR2-signaling pathway contributes to Aβ accumulation, increases Aβ-stimulated neuronal toxicity, and decreases neuronal cell survival. FFAR2 has also been confirmed to be richly expressed in human neuronal cells [10], and has been reported in human and mouse brain genome databases [51,52]. FFAR2 is also expressed in neuronal cells, indicating that it may have important effects on neuronal proliferation, differentiation, and activation, or other functions, further confirming that FFAR2 plays an integral role in neurons. These results show that the activation of FFAR2 may play a critical role in neuronal cells to reduce senescence and increase neuroprotection. Our study results indicated that the FFAR2 mRNA expression level was significantly reduced in the Cd group compared with that in the control group, suggesting that FFAR2 may be implicated in the regulatory mechanism of the gut–brain axis in Cd-induced neurodevelopmental toxicity.
5. Conclusions
Our study found that exposure at an environmentally relevant concentration of Cd (5 µg/L) altered the microbial composition and the concentrations of SCFAs. There was a positive correlation between acetic acid and Phascolarctobacterium and Candidatus Saccharimonas (R = 0.842, p < 0.01; R= 0.767, p < 0.01) and a negative correlation between isobutyric acid and Blautia glucerasea (R = −0.673, p < 0.05); all these bacteria were associated with neurotoxicity. Moreover, in terms of the mechanisms involved in the regulation of neuroprotective effects of FFAR2, FFAR2 must be activated first. SCFAs are one of its activators, and acetic acid in SCFAs is the major ligand of FFAR2. Our results indicated that compared with the control group, the concentration of acetic acid was decreased in the Cd group, which ultimately led to a decrease in FFAR2 expression in the Cd group. In summary, environmentally relevant concentrations of Cd can reduce the relative abundance of SCFA-producing intestinal flora, leading to a decrease in acetic acid concentrations, which in turn leads to a decrease in FFAR2 concentrations. Therefore, we hypothesize that Cd is implicated in the mechanism of neurodevelopmental toxicity through the gut–brain axis, demonstrating that FFAR2 might be a new potential target for the treatment of neurodevelopmental toxicity and neurodegenerative diseases.
Author Contributions
J.Y.: methodology and writing—original draft. J.L.: methodology and writing—original draft. X.Z.: methodology. Q.Z.: methodology. J.W.: writing—original draft. Q.C.: writing—original draft. X.M.: conceptualization and supervision. Y.X.: conceptualization, supervision, and writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81973071, 81773473 to XM) and Medical Science and Technology Research Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (no. A2021195 to YX).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All zebrafish work was approved by the Ethical Review Committee of Southern Medical University, China.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Zhao, X.M.; Yao, L.A.; Ma, Q.L.; Zhou, G.J.; Wang, L.; Fang, Q.L.; Xu, Z.C. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of cadmium in water and sediment in Longjiang River, China: Implication on water quality management after pollution accident. Chemosphere 2018, 194, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyder, O.; Chung, M.; Cosgrove, D.; Herman, J.M.; Li, Z.; Firoozmand, A.; Gurakar, A.; Koteish, A.; Pawlik, T.M. Cadmium exposure and liver disease among US adults. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2013, 17, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, Q.; Li, M.; Chen, P.; Huang, C.; Duan, X.; Lu, L.; Li, J.; Chu, R.; Xie, D.; Song, H.; et al. Sex-Dependent Effects of Cadmium Exposure in Early Life on Gut Microbiota and Fat Accumulation in Mice. Environ. Health Perspect 2017, 125, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Guo, Z.; Xiao, X.; Peng, C.; Shi, L.; Ran, H.; Xu, W. Atmospheric deposition as a source of cadmium and lead to soil-rice system and associated risk assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Shen, J. Exposing to cadmium stress cause profound toxic effect on microbiota of the mice intestinal tract. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Lan, T.; Yuan, B.; Chen, J.; Hu, J.; Ren, W.; Chen, Z. Cadmium-induced microsatellite instability in the kidneys and leukocytes of C57BL/6J mice. Environ. Toxicol. 2015, 30, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zou, F.; Meng, X. Effects of ecologically relevant concentrations of cadmium on locomotor activity and microbiota in zebrafish. Chemosphere 2020, 257, 127220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroszkiewicz, J.; Groblewska, M.; Mroczko, B. The Role of Gut Microbiota and Gut-Brain Interplay in Selected Diseases of the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Gallausiaux, C.; Marinelli, L.; Blottière, H.M.; Larraufie, P.; Lapaque, N. SCFA: Mechanisms and functional importance in the gut. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2021, 80, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razazan, A.; Karunakar, P.; Mishra, S.P.; Sharma, S.; Miller, B.; Jain, S.; Yadav, H. Activation of Microbiota Sensing—Free Fatty Acid Receptor 2 Signaling Ameliorates Amyloid-β Induced Neurotoxicity by Modulating Proteolysis-Senescence Axis. Front. Aging. Neurosci. 2021, 13, 735933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurisu, R.; Takai, M.; Takamoto, M.; Tsujiuchi, T. Effects of free fatty acid receptor-2 (FFAR2)-mediated signaling on the regulation of cellular functions in osteosarcoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 646, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahuguna, A.; Bharadwaj, S.; Chauhan, A.K.; Kang, S.C. Inhibitory insights of strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa var. Seolhyang) root extract on tyrosinase activity using computational and in vitro analysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 2773–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Yu, L.; Tian, F.; Zhai, Q.; Fan, L.; Chen, W. Gut microbiota: A target for heavy metal toxicity and a probiotic protective strategy. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Qi, Z.; Hou, H.; Qian, L.; Gao, J.; Zhang, X.X. Structural and functional alterations of gut microbiome in mice induced by chronic cadmium exposure. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marizzoni, M.; Cattaneo, A.; Mirabelli, P.; Festari, C.; Lopizzo, N.; Nicolosi, V.; Mombelli, E.; Mazzelli, M.; Luongo, D.; Naviglio, D.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Lipopolysaccharide as Mediators between Gut Dysbiosis and Amyloid Pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 78, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, A.V.; Sadler, R.K.; Llovera, G.; Singh, V.; Roth, S.; Heindl, S.; Sebastian Monasor, L.; Verhoeven, A.; Peters, F.; Parhizkar, S.; et al. Microbiota-derived short chain fatty acids modulate microglia and promote Aβ plaque deposition. Elife 2021, 10, e59826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarawneh, R.; Penhos, E. The gut microbiome and Alzheimer’s disease: Complex and bidirectional interactions. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 141, 104814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giridharan, V.V.; Barichello De Quevedo, C.E.; Petronilho, F. Microbiota-gut-brain axis in the Alzheimer’s disease pathology—An overview. Neurosci. Res. 2022, 181, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiatrak, B.; Balon, K.; Jawień, P.; Bednarz, D.; Jęśkowiak, I.; Szeląg, A. The Role of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in the Development of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y.; Liu, K.; Ren, L.; Ji, Y. The Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiota Caused by Low-Dose Cadmium Aggravate the Injury of Mice Liver through Increasing Intestinal Permeability. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Abo, R.P.; Schlieper, K.A.; Graffam, M.E.; Levine, S.; Wishnok, J.S.; Swenberg, J.A.; Tannenbaum, S.R.; Fox, J.G. Arsenic exposure perturbs the gut microbiome and its metabolic profile in mice: An integrated metagenomics and metabolomics analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M.; Kortenkamp, A. Cadmium exposures and deteriorations of cognitive abilities: Estimation of a reference dose for mixture risk assessments based on a systematic review and confidence rating. Environ. Health 2022, 21, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michels, N.; Van de Wiele, T.; De Henauw, S. Chronic Psychosocial Stress and Gut Health in Children: Associations with Calprotectin and Fecal Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Psychosom. Med. 2017, 79, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zheng, P.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Tan, X.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; et al. Landscapes of bacterial and metabolic signatures and their interaction in major depressive disorders. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba8555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrov, V.A.; Saltykova, I.V.; Zhukova, I.A.; Alifirova, V.M.; Zhukova, N.G.; Dorofeeva, Y.B.; Tyakht, A.V.; Kovarsky, B.A.; Alekseev, D.G.; Kostryukova, E.S.; et al. Analysis of Gut Microbiota in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Bull Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 162, 734–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Nallar, E.; Bendall, M.L.; Pérez-Losada, M.; Sabuncyan, S.; Severance, E.G.; Dickerson, F.B.; Schroeder, J.R.; Yolken, R.H.; Crandall, K.A. Composition, taxonomy and functional diversity of the oropharynx microbiome in individuals with schizophrenia and controls. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yolken, R.H.; Severance, E.G.; Sabunciyan, S.; Gressitt, K.L.; Chen, O.; Stallings, C.; Origoni, A.; Katsafanas, E.; Schweinfurth, L.A.; Savage, C.L.; et al. Metagenomic Sequencing Indicates That the Oropharyngeal Phageome of Individuals with Schizophrenia Differs from That of Controls. Schizophr. Bull. 2015, 41, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Hu, S.; Liang, Y. Analysis of gut microbiota diversity and auxiliary diagnosis as a biomarker in patients with schizophrenia: A cross-sectional study. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 197, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, P.; Hold, G.L.; Flint, H.J. The gut microbiota, bacterial metabolites and colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lai, J.; Zhang, P.; Ding, J.; Jiang, J.; Liu, C.; Huang, H.; Zhen, H.; Xi, C.; Sun, Y.; et al. Multi-omics analyses of serum metabolome, gut microbiome and brain function reveal dysregulated microbiota-gut-brain axis in bipolar depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 4123–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltysova, M.; Tomova, A.; Ostatnikova, D. Gut Microbiota Profiles in Children and Adolescents with Psychiatric Disorders. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Chiu, A.T.G.; Li, V.W.Y.; Zhang, X.; Yeung, W.L.; Chan, S.H.S.; Tun, H.M. The role of the gut-microbiome-brain axis in metabolic remodeling amongst children with cerebral palsy and epilepsy. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1109469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarmeas, N.; Stern, Y.; Mayeux, R.; Manly, J.J.; Schupf, N.; Luchsinger, J.A. Mediterranean diet and mild cognitive impairment. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEvoy, C.T.; Guyer, H.; Langa, K.M.; Yaffe, K. Neuroprotective Diets Are Associated with Better Cognitive Function: The Health and Retirement Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2017, 65, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardener, S.; Gu, Y.; Rainey-Smith, S.R.; Keogh, J.B.; Clifton, P.M.; Mathieson, S.L.; Taddei, K.; Mondal, A.; Ward, V.K.; Scarmeas, N.; et al. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet and Alzheimer’s disease risk in an Australian population. Transl. Psychiatry 2012, 2, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Luo, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, G.; Jiang, D.; Cao, R.; Huang, H.; Luo, D.; et al. Profiling the differences of gut microbial structure between schizophrenia patients with and without violent behaviors based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Int. J. Legal. Med. 2021, 135, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragano, N.R.V.; Solon, C.; Ramalho, A.F.; de Moura, R.F.; Razolli, D.S.; Christiansen, E.; Azevedo, C.; Ulven, T.; Velloso, L.A. Polyunsaturated fatty acid receptors, GPR40 and GPR120, are expressed in the hypothalamus and control energy homeostasis and inflammation. J. Neuroinflammation 2017, 14, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falomir-Lockhart, L.J.; Cavazzutti, G.F.; Giménez, E.; Toscani, A.M. Fatty Acid Signaling Mechanisms in Neural Cells: Fatty Acid Receptors. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Fujimura, Y.; Kameya, N.; Nakamura, S.; Arakawa, K.; Morita, H. Fecal metabolite of a gnotobiotic mouse transplanted with gut microbiota from a patient with Alzheimer’s disease. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 2144–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.; Smith, N.J.; Christiansen, E.; Tikhonova, I.G.; Grundmann, M.; Hudson, B.D.; Ward, R.J.; Drewke, C.; Milligan, G.; Kostenis, E.; et al. Selective orthosteric free fatty acid receptor 2 (FFA2) agonists: Identification of the structural and chemical requirements for selective activation of FFA2 versus FFA3. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 10628–10640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, T.; Stefansson, H.; Steinberg, S.; Jonsdottir, I.; Jonsson, P.V.; Snaedal, J.; Bjornsson, S.; Huttenlocher, J.; Levey, A.I.; Lah, J.J.; et al. Variant of TREM2 associated with the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Srivastav, S.; Yadav, A.K.; Srikrishna, S.; Perry, G. Overview of Alzheimer’s Disease and Some Therapeutic Approaches Targeting Aβ by Using Several Synthetic and Herbal Compounds. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 7361613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuboyama, T.; Yang, X.; Tohda, C. Natural Medicines and Their Underlying Mechanisms of Prevention and Recovery from Amyloid Β-Induced Axonal Degeneration in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, R.; Shively, C.A.; Register, T.C.; Craft, S.; Yadav, H. Gut microbiome-Mediterranean diet interactions in improving host health. F1000Research 2019, 8, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, R.; Neth, B.J.; Wang, S.; Mishra, S.P.; Craft, S.; Yadav, H. Gut mycobiome and its interaction with diet, gut bacteria and alzheimer’s disease markers in subjects with mild cognitive impairment: A pilot study. EBioMedicine 2020, 59, 102950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doifode, T.; Giridharan, V.V.; Generoso, J.S.; Bhatti, G.; Collodel, A.; Schulz, P.E.; Forlenza, O.V.; Barichello, T. The impact of the microbiota-gut-brain axis on Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 164, 105314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xu, J.; Ling, Y.; Wang, F.; Gong, T.; Yang, C.; Ye, S.; Ye, K.; Wei, D.; Song, Z.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation alleviated Alzheimer’s disease-like pathogenesis in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.P.; Karunakar, P.; Taraphder, S.; Yadav, H. Free Fatty Acid Receptors 2 and 3 as Microbial Metabolite Sensors to Shape Host Health: Pharmacophysiological View. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, T.J.; Gates, E.J.; Ranger, A.L.; Klegeris, A. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) alone or in combination regulate select immune functions of microglia-like cells. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 105, 103493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, Y.; Choi, H.; Kim, W.; Park, S.; Lee, D.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, H.; Hyun, D.W.; et al. Transfer of a healthy microbiota reduces amyloid and tau pathology in an Alzheimer’s disease animal model. Gut 2020, 69, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Human Proten Atlas. Available online: http://www.proteinatlas.org (accessed on 11 March 2022).
- ALLEN BRAIN MAP 2021. Available online: https://portal.brain-map.org/ (accessed on 25 May 2022).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).