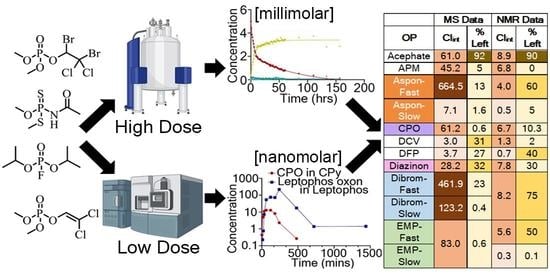
Targeted Metabolomics of Organophosphate Pesticides and Chemical Warfare Nerve Agent Simulants Using High- and Low-Dose Exposure in Human Liver Microsomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
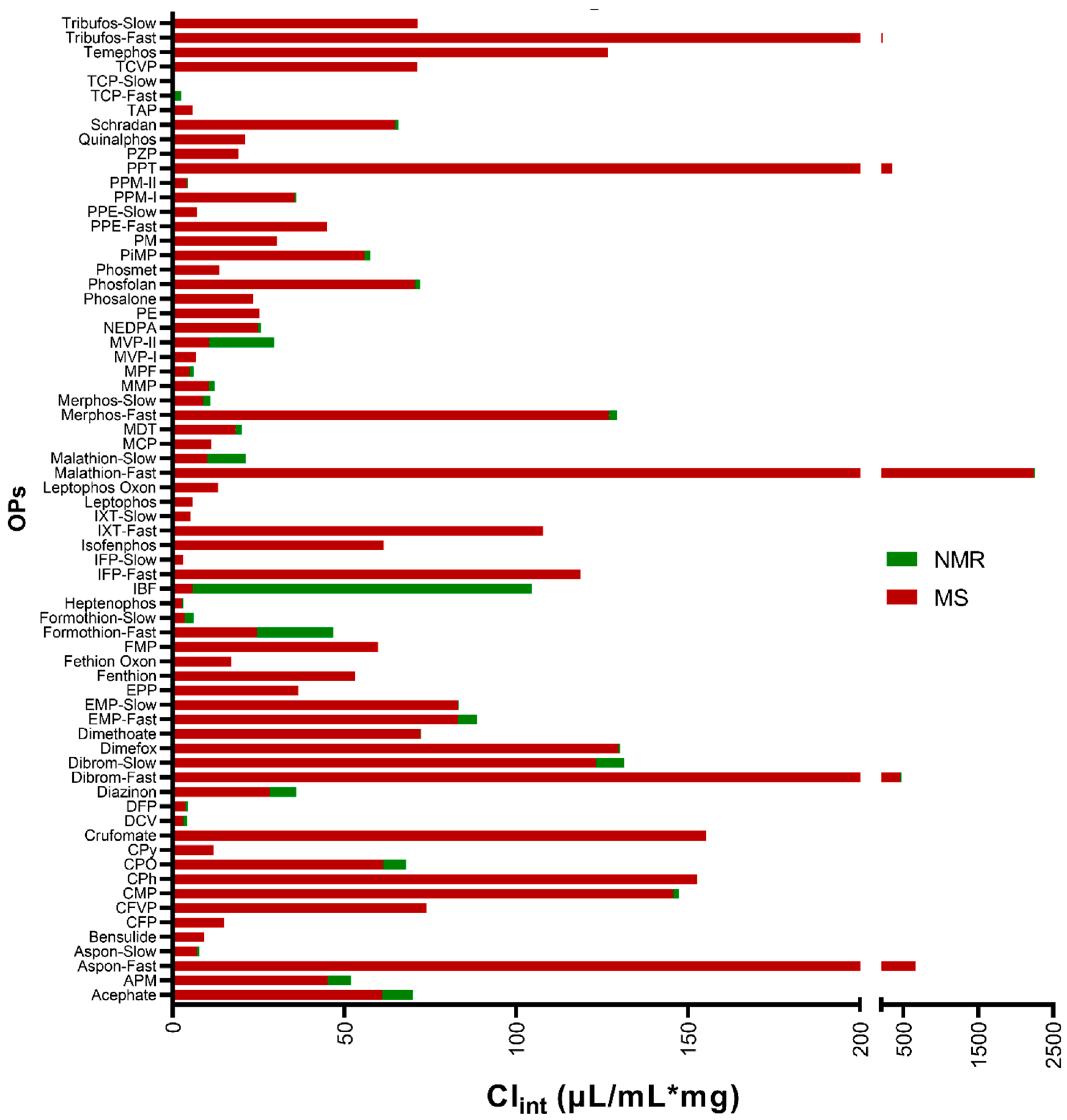
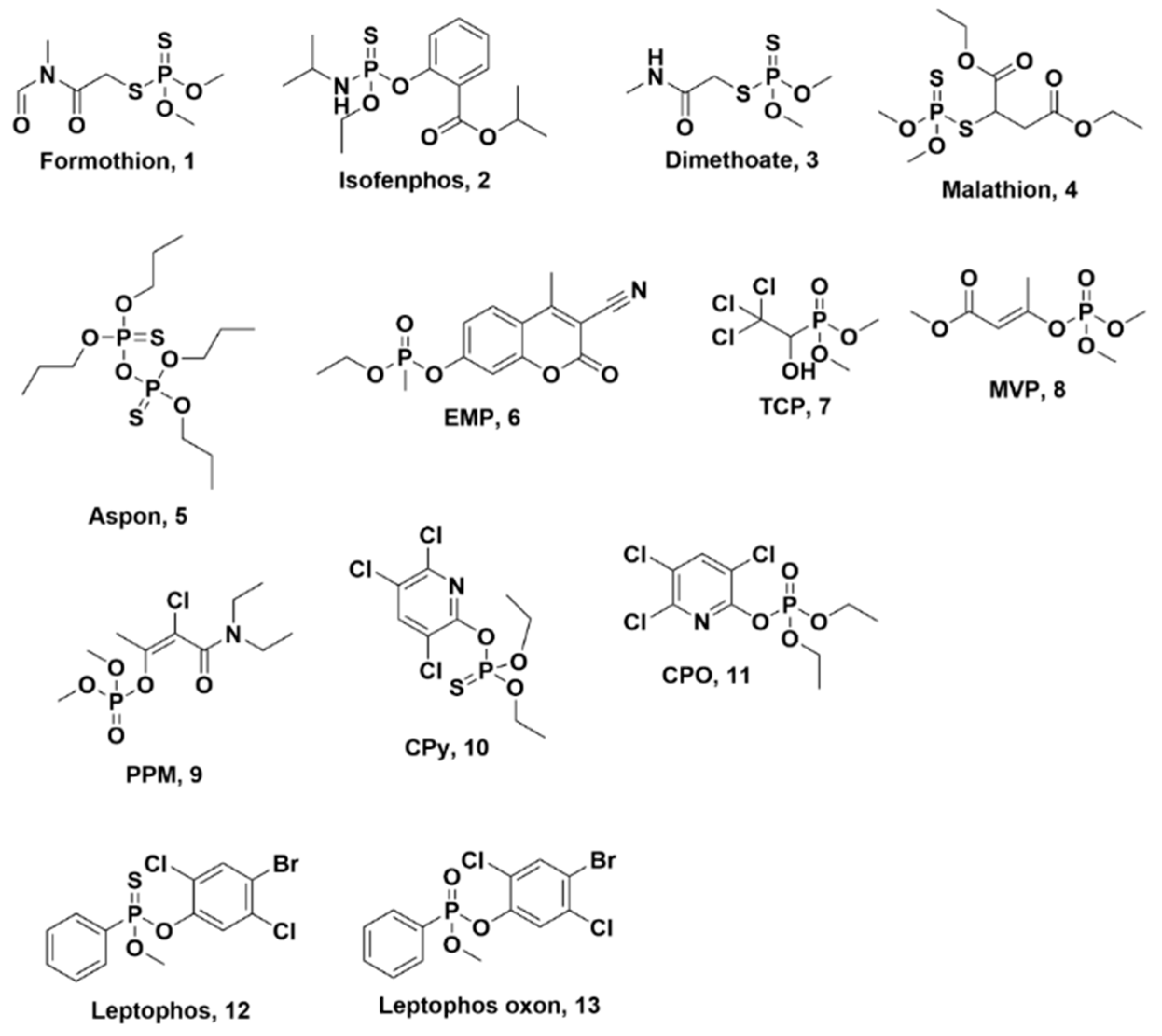
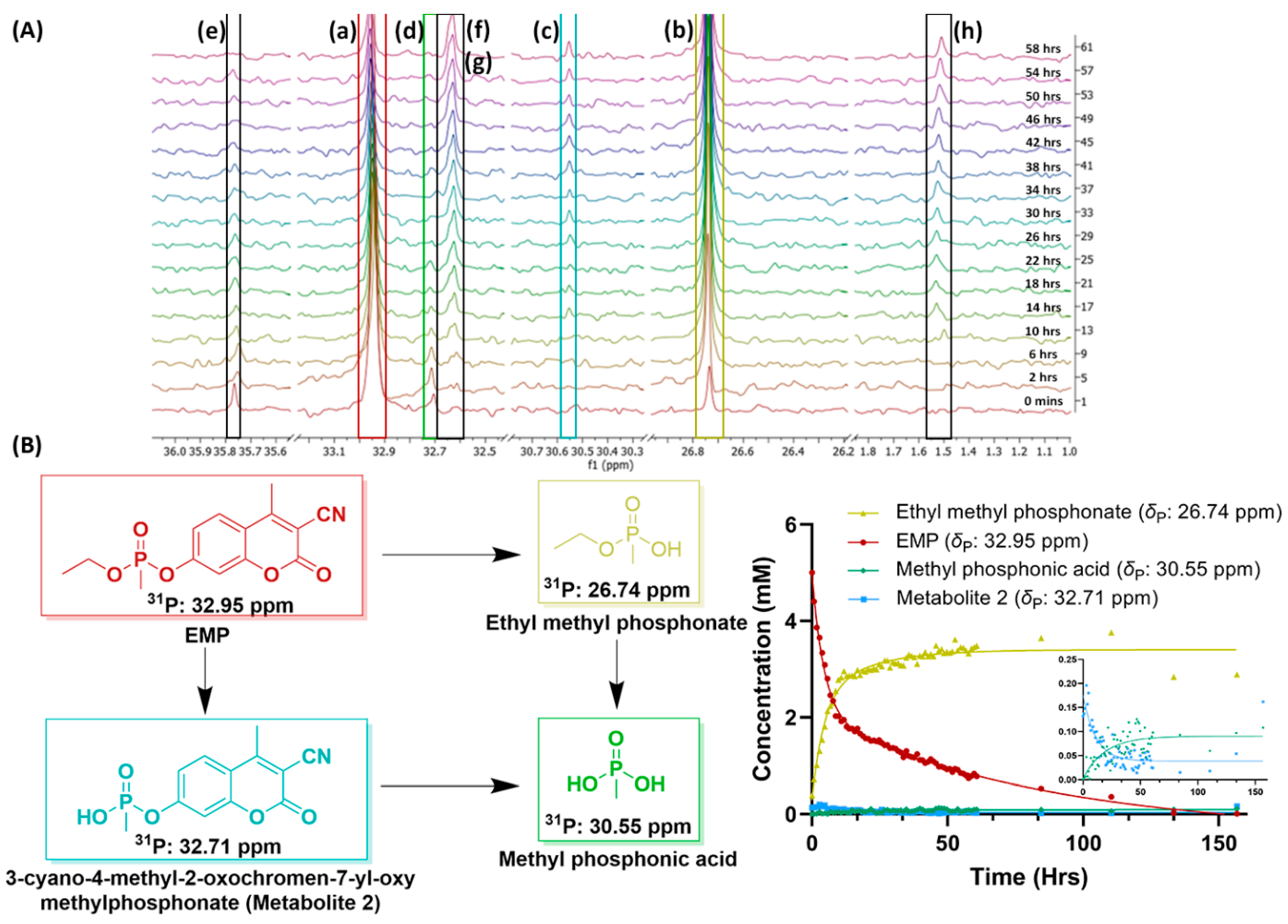
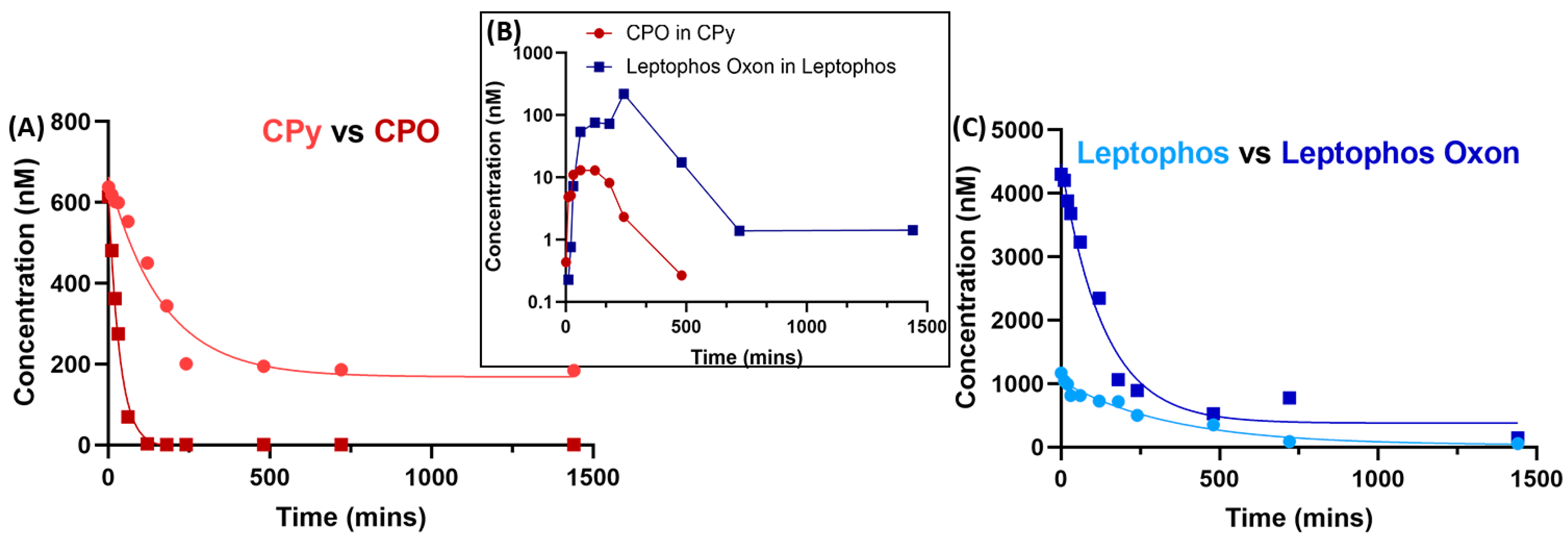
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boedeker, W.; Watts, M.; Clausing, P.; Marquez, E. The global distribution of acute unintentional pesticide poisoning: Estimations based on a systematic review. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robb, E.L.; Baker, M.B. Organophosphate Toxicity; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Fallon Nevada: FAQs: Organophosphates. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nceh/clusters/fallon/organophosfaq.htm#:~:text=Organophosphates%20are%20the%20most%20widely,in%20the%20body%20called%20acetylcholinesterase (accessed on 9 May 2022).
- Mew, E.J.; Padmanathan, P.; Konradsen, F.; Eddleston, M.; Chang, S.S.; Phillips, M.R.; Gunnell, D. The global burden of fatal self-poisoning with pesticides 2006–15: Systematic review. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 219, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, P.R.; Hayes, B.D.; Erickson, T.B.; Boyer, E.W. Novichok agents: A historical, current, and toxicological perspective. Toxicol. Commun. 2018, 2, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Gupta, R.D. Organophosphorus Nerve Agents: Types, Toxicity, and Treatments. J. Toxicol. 2020, 2020, 3007984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, H.; Van der Schans, M.J.; Koller, M.; Spruit, H.E.T.; Worek, F.; Thiermann, H.; Noort, D. Fatal sarin poisoning in Syria 2013: Forensic verification within an international laboratory network. Forensic Toxicol. 2018, 36, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartin, J.S. Gulf War illnesses: Causes and controversies. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2000, 75, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colovic, M.B.; Krstic, D.Z.; Lazarevic-Pasti, T.D.; Bondzic, A.M.; Vasic, V.M. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: Pharmacology and toxicology. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2013, 11, 315–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawdsley, S.E. Burden of Proof: The Debate Surrounding Aerotoxic Syndrome. J. Contemp. Hist. 2022, 57, 959–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main, A.R. Mode of Action of Anticholinesterases. Pharmacol. Ther. 1979, 6, 579–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenberg, A.; Benabbas, R.; De Souza, I.S.; Conigliaro, A.; Paladino, L.; Warman, E.; Sinert, R.; Wiener, S.W. Utility of 2-Pyridine Aldoxime Methyl Chloride (2-PAM) for Acute Organophosphate Poisoning: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Med. Toxicol. 2018, 14, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrs, T.C. Diazepam in the treatment of organophosphorus ester pesticide poisoning. Toxicol. Rev. 2003, 22, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBlanc, F.N. A severe organophosphate poisoning requiring the use of atropine drip. Clin. Toxicol. 1986, 24, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanger, U.M.; Schwab, M. Cytochrome P450 enzymes in drug metabolism: Regulation of gene expression, enzyme activities, and impact of genetic variation. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 138, 103–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Chambers, J.E. Kinetic parameters of desulfuration and dearylation of parathion and chlorpyrifos by rat liver microsomes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1994, 32, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foxenberg, R.J.; McGarrigle, B.P.; Knaak, J.B.; Kostyniak, P.J.; Olson, J.R. Human hepatic cytochrome p450-specific metabolism of parathion and chlorpyrifos. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2007, 35, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abass, K.; Turpeinen, M.; Pelkonen, O. An evaluation of the cytochrome P450 inhibition potential of selected pesticides in human hepatic microsomes. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2009, 44, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawfik Khattab, A.M.; Zayed, A.A.; Ahmed, A.I.; AbdelAal, A.G.; Mekdad, A.A. The role of PON1 and CYP2D6 genes in susceptibility to organophosphorus chronic intoxication in Egyptian patients. Neurotoxicology 2016, 53, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Androutsopoulos, V.P.; Kanavouras, K.; Tsatsakis, A.M. Role of paraoxonase 1 (PON1) in organophosphate metabolism: Implications in neurodegenerative diseases. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 256, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellison, C.A.; Tian, Y.; Knaak, J.B.; Kostyniak, P.J.; Olson, J.R. Human hepatic cytochrome P450-specific metabolism of the organophosphorus pesticides methyl parathion and diazinon. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2012, 40, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernasconi, C.; Pelkonen, O.; Andersson, T.B.; Strickland, J.; Wilk-Zasadna, I.; Asturiol, D.; Cole, T.; Liska, R.; Worth, A.; Muller-Vieira, U.; et al. Validation of in vitro methods for human cytochrome P450 enzyme induction: Outcome of a multi-laboratory study. Toxicol. Vitro 2019, 60, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meek, E.C.; Chambers, H.W.; Coban, A.; Funck, K.E.; Pringle, R.B.; Ross, M.K.; Chambers, J.E. Synthesis and in vitro and in vivo inhibition potencies of highly relevant nerve agent surrogates. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 126, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, N.; Tian, X.; Liu, T.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wen, Q.; Xu, B.; Qi, B.; Gao, J.; et al. Content and activity of human liver microsomal protein and prediction of individual hepatic clearance in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohutsky, M.A.; Chien, J.Y.; Ring, B.J.; Wrighton, S.A. Predictions of the in vivo clearance of drugs from rate of loss using human liver microsomes for phase I and phase II biotransformations. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cyprotex. Microsomal Stability Assay. Available online: https://www.cyprotex.com/admepk/in-vitro-metabolism/microsomal-stability (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Backus, B.T. EPA Memorandum Reg; No. 476-1713 Apson 6-E; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1982; pp. 54–57.
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem in 2021: New data content and improved web interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1388–D1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, K.A.; Tzilivakis, J.; Warner, D.J.; Green, A. An international database for pesticide risk assessments and management. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2016, 22, 1050–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2016, 7, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misik, J.; Pavlikova, R.; Cabal, J.; Kuca, K. Acute toxicity of some nerve agents and pesticides in rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 38, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.D.; Goldsmith, M.; Ashani, Y.; Simo, Y.; Mullokandov, G.; Bar, H.; Ben-David, M.; Leader, H.; Margalit, R.; Silman, I.; et al. Directed evolution of hydrolases for prevention of G-type nerve agent intoxication. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amitai, G.; Gaidukov, L.; Adani, R.; Yishay, S.; Yacov, G.; Kushnir, M.; Teitlboim, S.; Lindenbaum, M.; Bel, P.; Khersonsky, O.; et al. Enhanced stereoselective hydrolysis of toxic organophosphates by directly evolved variants of mammalian serum paraoxonase. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 1906–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amitai, G.; Adani, R.; Yacov, G.; Yishay, S.; Teitlboim, S.; Tveria, L.; Limanovich, O.; Kushnir, M.; Meshulam, H. Asymmetric fluorogenic organophosphates for the development of active organophosphate hydrolases with reversed stereoselectivity. Toxicology 2007, 233, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivam, S.P.; Hoskins, B.; Ho, I.K. An assessment of comparative acute toxicity of diisopropyl-fluorophosphate, tabun, sarin, and soman in relation to cholinergic and GABAergic enzyme activities in rats. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1984, 4, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, H.M.; Houston, J.B. Substrate depletion approach for determining in vitro metabolic clearance: Time dependencies in hepatocyte and microsomal incubations. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2004, 32, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millan, D.; Rojas, M.; Tapia, R.A.; Pavez, P. Microwave-assisted nucleophilic degradation of organophosphorus pesticides in propylene carbonate. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 7868–7875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitt, D.M.; Belabassi, Y.; Suhy, J.; Berkman, C.E.; Thompson, C.M. Chemoenzymatic resolution of rac-malathion. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2014, 25, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferri, D.; Barba-Bon, A.; Costero, A.M.; Gaviña, P.; Parra, M.; Gil, S. An Au(III)–amino alcohol complex for degradation of organophosphorus pesticides. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 106941–106944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, F.M.; D’Aniello, A.; Volpe, M.T.; Meneguz, A.; Testai, E. Malathion bioactivation in the human liver: The contribution of different cytochrome p450 isoforms. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2005, 33, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sams, C.; Cocker, J.; Lennard, M.S. Biotransformation of chlorpyrifos and diazinon by human liver microsomes and recombinant human cytochrome P450s (CYP). Xenobiotica 2004, 34, 861–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskela, H.; Andjelkovic, B.; Pettersson, A.; Rapinoja, M.L.; Kuitunen, M.L.; Vanninen, P. pH-Dependent Piecewise Linear Correlation of (1)H,(31)P Chemical Shifts: Application in NMR Identification of Nerve Agent Metabolites in Urine Samples. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8495–8500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.Y.; Wagner, G.W.; Mondloch, J.E.; Peterson, G.W.; DeCoste, J.B.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K. Effective, Facile, and Selective Hydrolysis of the Chemical Warfare Agent VX Using Zr6-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 10829–10833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.R.; Hutson, D.H. Organophosphorus insecticides. In Metabolic Pathways of Agrochemicals: Part 2: Insecticides and Fungicides; Plimmer, J., Ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 1999; Volume 2, pp. 187–522. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Saga, Y.; Onozawa, S.Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Sato, K.; Fukaya, N.; Han, L.B. Wet and Dry Processes for the Selective Transformation of Phosphonates to Phosphonic Acids Catalyzed by Bronsted Acids. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 14411–14419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, J.; Zhang, H.; Kenaan, C.; Hollenberg, P.F. Mechanism-Based Inactivation of Human Cytochrome P450 2B6 by Chlorpyrifos. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 1484–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Cao, Y.; Rose, R.L.; Brimfield, A.A.; Dai, D.; Goldstein, J.A.; Hodgson, E. Metabolism of Chlorpyrifos by Human Cytochrome P450 Isoforms and Human, Mouse, and Rat Liver Microsomes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2001, 29, 1201–1204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mutch, E.; Williams, F.M. Diazinon, chlorpyrifos and parathion are metabolised by multiple cytochromes P450 in human liver. Toxicology 2006, 224, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croom, E.L.; Wallace, A.D.; Hodgson, E. Human variation in CYP-specific chlorpyrifos metabolism. Toxicology 2010, 276, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foxenberg, R.J.; Ellison, C.A.; Knaak, J.B.; Ma, C.; Olson, J.R. Cytochrome P450-specific human PBPK/PD models for the organophosphorus pesticides: Chlorpyrifos and parathion. Toxicology 2011, 285, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agarwal, G.; Tichenor, H.; Roo, S.; Lane, T.R.; Ekins, S.; McElroy, C.A. Targeted Metabolomics of Organophosphate Pesticides and Chemical Warfare Nerve Agent Simulants Using High- and Low-Dose Exposure in Human Liver Microsomes. Metabolites 2023, 13, 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13040495
Agarwal G, Tichenor H, Roo S, Lane TR, Ekins S, McElroy CA. Targeted Metabolomics of Organophosphate Pesticides and Chemical Warfare Nerve Agent Simulants Using High- and Low-Dose Exposure in Human Liver Microsomes. Metabolites. 2023; 13(4):495. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13040495
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgarwal, Garima, Hunter Tichenor, Sarah Roo, Thomas R. Lane, Sean Ekins, and Craig A. McElroy. 2023. "Targeted Metabolomics of Organophosphate Pesticides and Chemical Warfare Nerve Agent Simulants Using High- and Low-Dose Exposure in Human Liver Microsomes" Metabolites 13, no. 4: 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13040495
APA StyleAgarwal, G., Tichenor, H., Roo, S., Lane, T. R., Ekins, S., & McElroy, C. A. (2023). Targeted Metabolomics of Organophosphate Pesticides and Chemical Warfare Nerve Agent Simulants Using High- and Low-Dose Exposure in Human Liver Microsomes. Metabolites, 13(4), 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13040495