Mucopolysaccharidosis Type 1 among Children—Neuroradiological Perspective Based on Single Centre Experience and Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Manifestations
3. Differential Diagnosis Difficulties
4. Radiological Point of View
5. Neuroimaging
6. Patients Presentation
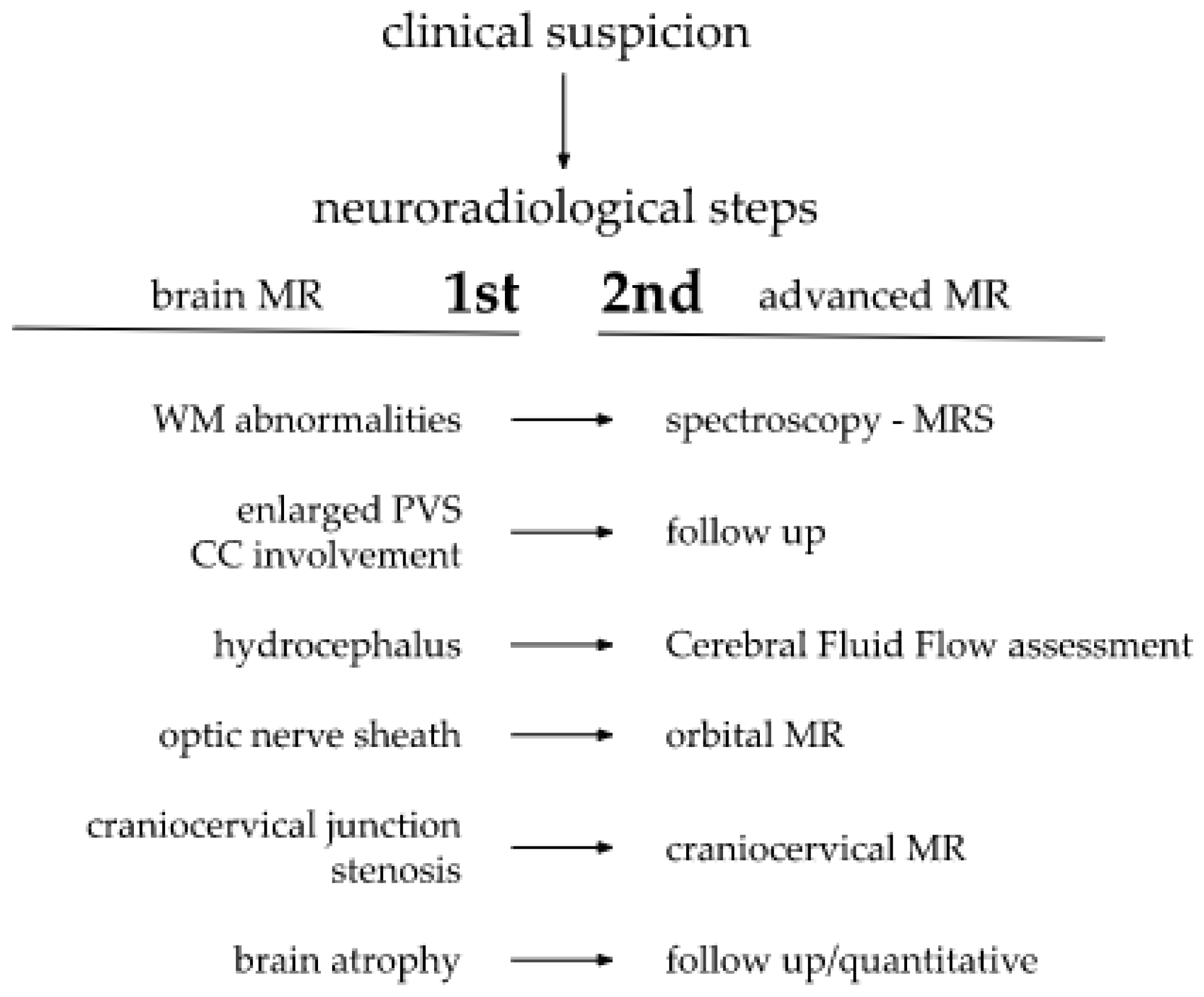
7. Neuroimaging—Methods
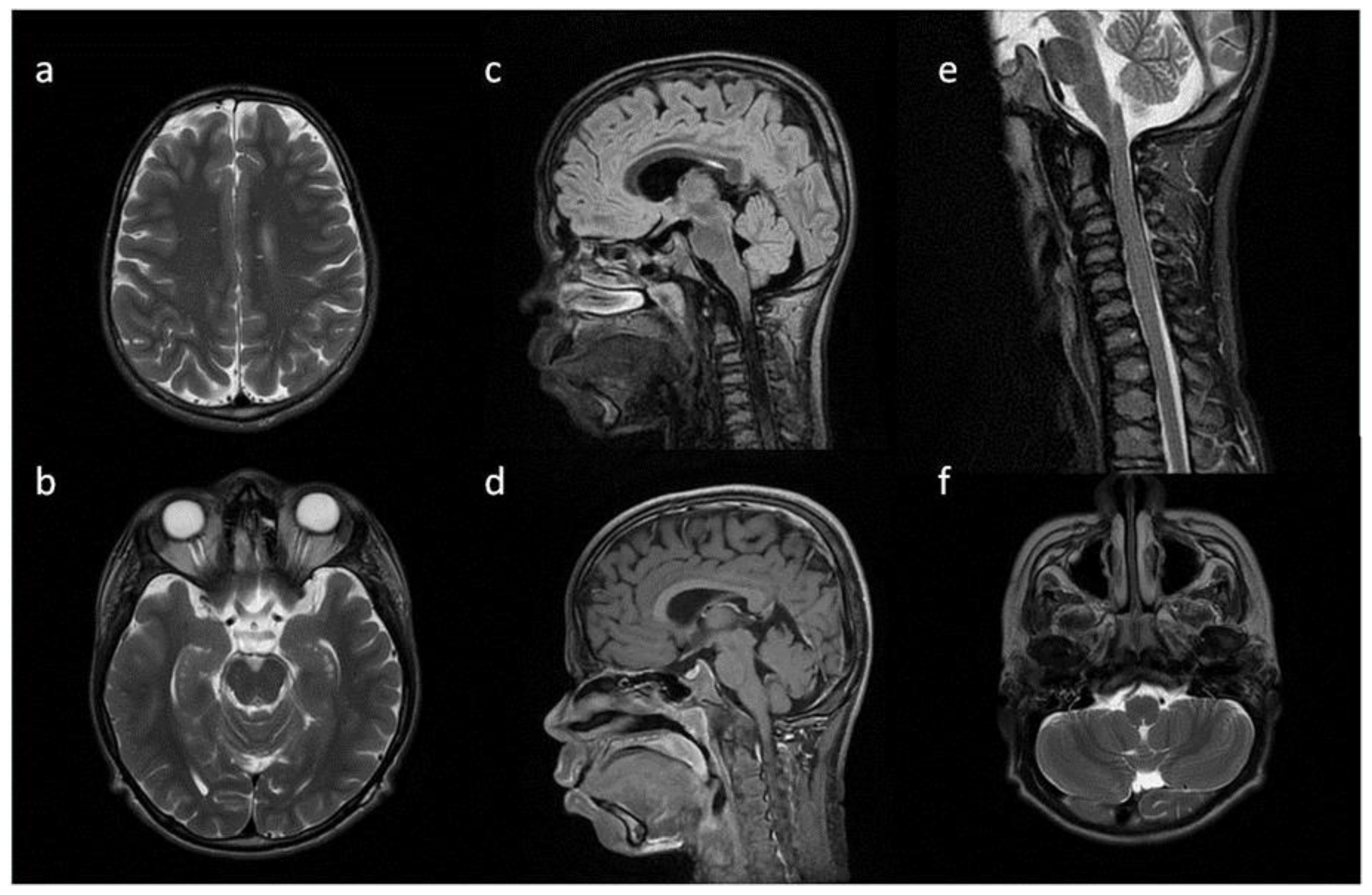
8. Brain, Head and Spine—Radiological Symptoms
| Patient No | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| age at exam | 4 mo | 3 yo | 1 y 2 mo | 1 y 11 mo | 3 y 2 mo | 14 yo |
| radiological imaging | ||||||
| WM signal abnormalities | + | + | + | |||
| areas of delayed myelination | + | + | + | + | + | |
| enlarged perivascular spaces | + | + | + | + | ||
| narrow corpus callosum | + | +/− | + | + | ||
| prominent ventricular system | +/− | + | +/− | + | + | |
| arachnoid cyst | + | + | ||||
| optic nerve sheath enlargement | + | + | ||||
| J-shaped sella turcica | + | + | + | +/− | + | +/− |
| craniocervical junction distortion | + | +/− | + | + | ||
| posterior fossa horns | + | + | + | + | ||
| fluid effusion temporal bone | + | + | + | + | +/− | |
| closed sagittal suture | + | + | + | |||
| vertebral bodies deformity | + | + | ||||
| intervertebral disc anomalies | + | + | ||||
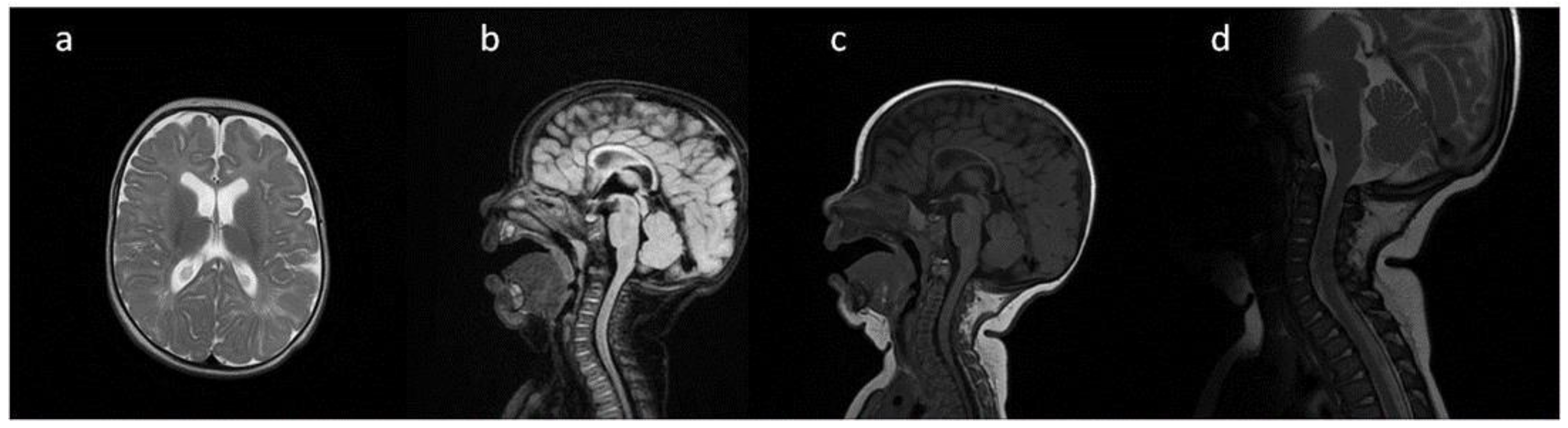
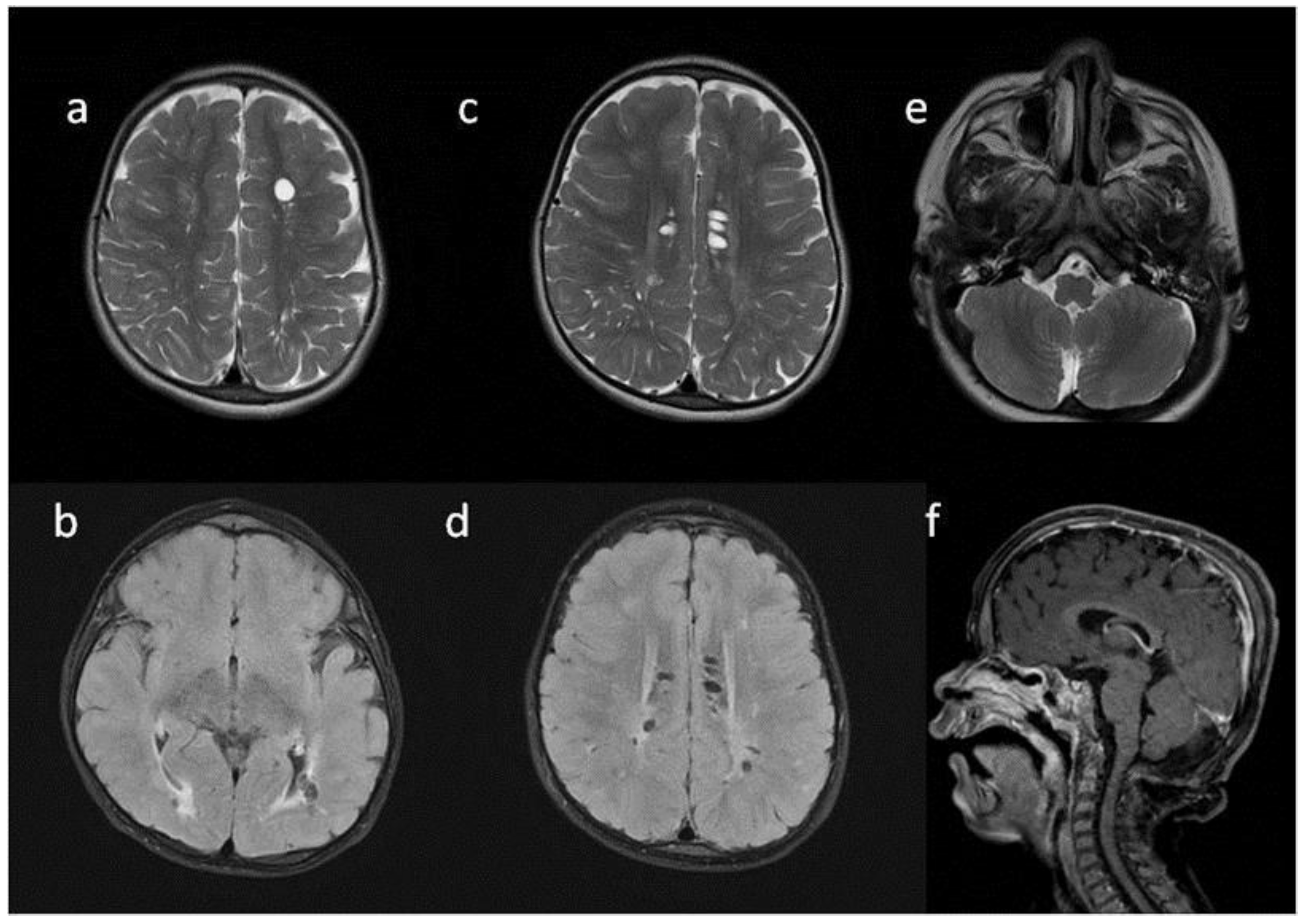
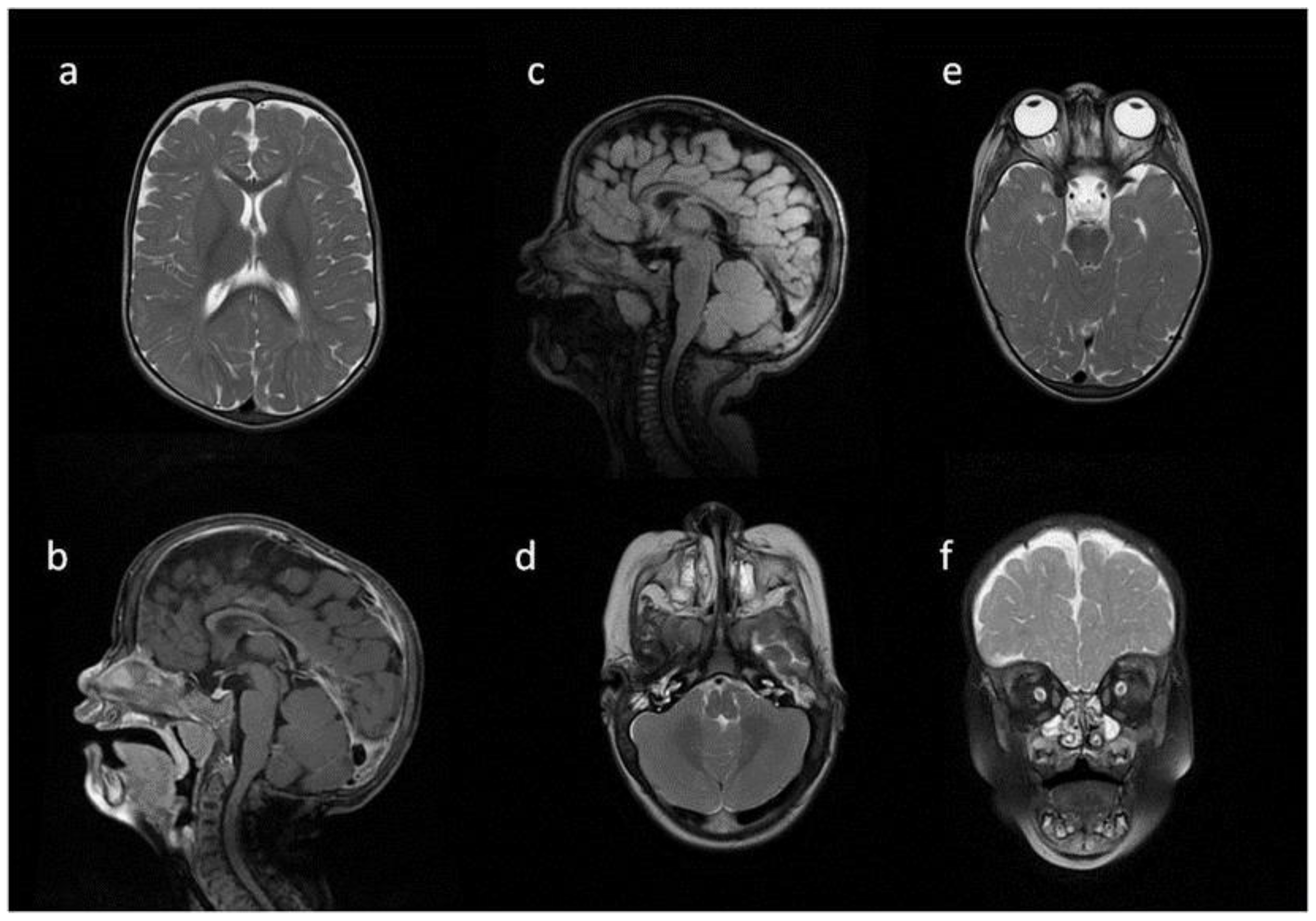
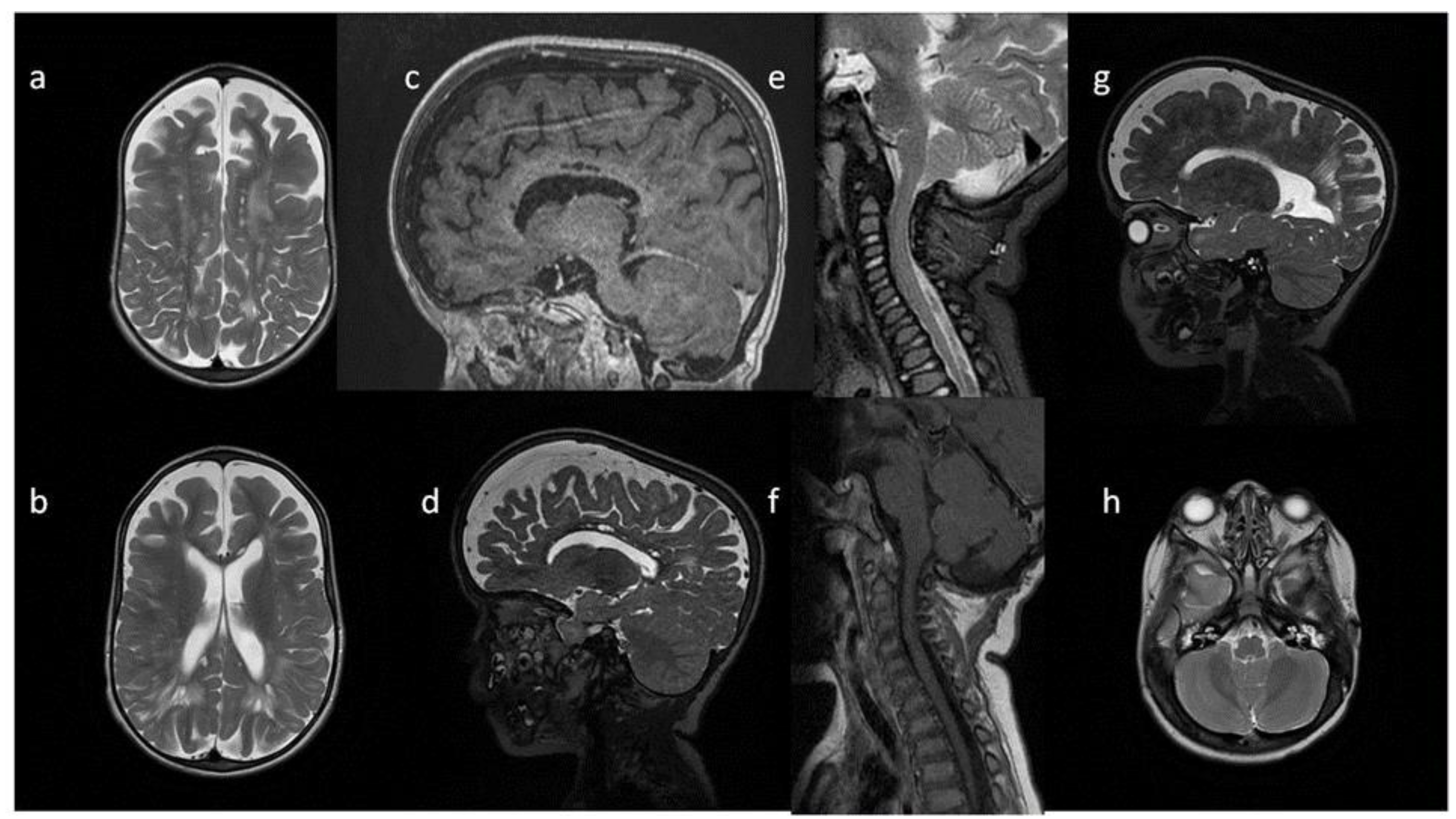

9. Discussion
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CC | corpus callosum |
| CSF | cerebrospinal fluid |
| DQ | developmental quotient |
| ERT | enzyme replacement therapy |
| GAGs | glycosaminoglycans |
| HSCT | hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
| HSPC | hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell |
| IDUA | alpha-L-iduronidase |
| IHOMS | internal hypertrophy of the occipitomastoid suture |
| MPS 1 | Mucopolysaccharidosis type 1 |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| MRS | magnetic resonance spectroscopy |
| PVS | perivascular spaces |
| WM | white matter |
| WMA | white matter abnormalities |
References
- Barkovich, A.J.; Raybaud, C. Pediatric Neuroimaging; Wolters Kluwer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, H.S.; Ashton, L.J.; Eyre, H.J.; Baker, E.; Brooks, D.A.; Callen, D.F.; Sutherland, G.R.; Morris, C.P.; Hopwood, J.J. Chromosomal localization of the human alpha-L-iduronidase gene (IDUA) to 4p16.3. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1990, 47, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kubaski, F.; Poswar, F.D.O.; Michelin-Tirelli, K.; Burin, M.G.; Rojas-Málaga, D.; Brusius-Facchin, A.C.; Leistner-Segal, S.; Giugliani, R. Diagnosis of Mucopolysaccharidoses. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurecka, A.; Ługowska, A.; Golda, A.; Czartoryska, B.; Tylki-Szymańska, A. Prevalence rates of mucopolysaccharidoses in Poland. J. Appl. Genet. 2014, 56, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Peracha, H.; Ballhausen, D.; Wiesbauer, A.; Rohrbach, M.; Gautschi, M.; Mason, R.W.; Giugliani, R.; Suzuki, Y.; Orii, K.E.; et al. Epidemiology of mucopolysaccharidoses. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 121, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussoren, E.; Keulemans, J.; van Diggelen, O.P.; Oemardien, L.F.; Timmermans, R.G.; van der Ploeg, A.T.; Ruijter, G.J. Residual α-l-iduronidase activity in fibroblasts of mild to severe Mucopolysaccharidosis type I patients. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2013, 109, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijay, S.; Wraith, J.E. Clinical presentation and follow-up of patients with the attenuated phenotype of mucopolysaccharidosis type I. Acta Paediatr. 2007, 94, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, L.A.; Giugliani, R.; Guffon, N.; Jones, S.A.; Keenan, H.A.; Munoz-Rojas, M.V.; Okuyama, T.; Viskochil, D.; Whitley, C.B.; Wijburg, F.A.; et al. Genotype-phenotype relationships in mucopolysaccharidosis type I (MPS I): Insights from the International MPS I Registry. Clin. Genet. 2019, 96, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosse, S.D.; Lam, W.K.; Wiggins, L.D.; Kemper, A.R. Cognitive outcomes and age of detection of severe mucopolysaccharidosis type 1. Anesthesia Analg. 2017, 19, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tylki-Szymańska, A.; De Meirleir, L.; Di Rocco, M.; Fathalla, W.M.; Guffon, N.; Lampe, C.; Lund, A.; Parini, R.; Wijburg, F.A.; Zeman, J.; et al. Easy-to-use algorithm would provide faster diagnoses for mucopolysaccharidosis type I and enable patients to receive earlier treatment. Acta Paediatr. 2018, 107, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aco, K.; Underhill, L.; Rangachari, L.; Arn, P.; Cox, G.F.; Giugliani, R.; Okuyama, T.; Wijburg, F.; Kaplan, P. Diagnosis and treatment trends in mucopolysaccharidosis I: Findings from the MPS I Registry. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2012, 171, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimaz, R.; La Torre, F. Mucopolysaccharidoses. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2013, 16, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiely, B.T.; Kohler, J.L.; Coletti, H.Y.; Poe, M.D.; Escolar, M.L. Early disease progression of Hurler syndrome. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017, 12, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.M.; Lindstrom, K.; Kyosen, S.O.; Munoz-Rojas, M.V.; Thibault, N.; Polgreen, L.E. Short stature as a presenting symptom of attenuated Mucopolysaccharidosis type I: Case report and clinical insights. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2018, 18, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, S.D.K.; Jonckheere, A.I. MPS I: Early diagnosis, bone disease and treatment, where are we now? J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2021, 44, 1289–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, E.G.; Nestrasil, I.; Rudser, K.; Delaney, K.; Kovac, V.; Ahmed, A.; Yund, B.; Orchard, P.J.; Eisengart, J.B.; Niklason, G.R.; et al. Neurocognition across the spectrum of mucopolysaccharidosis type I: Age, severity, and treatment. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2015, 116, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampe, C.; Eisengart, J.; Lund, T.; Orchard, P.; Swietlicka, M.; Wesley, J.; McIvor, R. Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I: A Review of the Natural History and Molecular Pathology. Cells 2020, 9, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, M.C.; Lam, J.M. Cutaneous Manifestations of Mucopolysaccharidoses. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2016, 33, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Makler, V.; Goldstein, C.L.; Hoernschemeyer, D. Chiari I malformation and syringomyelia in mucopolysaccharidosis type I (Hurler syndrome) treated with posterior fossa decompression: Case report and review of the literature. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2017, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, S.; Lavery, C.; Broomfield, A. The diagnostic journey of patients with mucopolysaccharidosis I: A real-world survey of patient and physician experiences. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2016, 8, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.; Khan, S.; Stapleton, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Wynn, R.; Yabe, H.; Chinen, Y.; Boelens, J.J.; Mason, R.W.; et al. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Mucopolysaccharidoses: Past, Present, and Future. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, e226–e246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muenzer, J.; Wraith, J.E.; Clarke, L.A.; the International Consensus Panel on the Management and Treatment of Mucopolysaccharidosis I. Mucopolysaccharidosis I: Management and Treatment Guidelines. Pediatrics 2009, 123, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontesilli, S.; Baldoli, C.; Della Rosa, P.A.; Cattoni, A.; Bernardo, M.E.; Meregalli, P.; Gasperini, S.; Motta, S.; Fumagalli, F.; Tucci, F.; et al. Evidence of Treatment Benefits in Patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I-Hurler in Long-term Follow-up Using a New Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scoring System. J. Pediatr. 2021, 240, 297–301.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guffon, N.; Pettazzoni, M.; Pangaud, N.; Garin, C.; Lina-Granade, G.; Plault, C.; Mottolese, C.; Froissart, R.; Fouilhoux, A. Long term disease burden post-transplantation: Three decades of observations in 25 Hurler patients successfully treated with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentner, B.; Tucci, F.; Galimberti, S.; Fumagalli, F.; De Pellegrin, M.; Silvani, P.; Camesasca, C.; Pontesilli, S.; Darin, S.; Ciotti, F.; et al. Hematopoietic Stem- and Progenitor-Cell Gene Therapy for Hurler Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1929–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, N.; Langan, T.J.; Stapleton, M.; Kubaski, F.; Mason, R.W.; Singh, R.; Kobayashi, H.; Yamaguchi, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Orii, K.; et al. Newborn screening of mucopolysaccharidoses: Past, present, and future. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 65, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, C.-K.; Lee, C.-L.; Tu, R.-Y.; Lo, Y.-T.; Sisca, F.; Chang, Y.-H.; Liu, M.-Y.; Liu, H.-Y.; Chen, H.-J.; Kao, S.-M.; et al. Nationwide Newborn Screening Program for Mucopolysaccharidoses in Taiwan and an Update of the “Gold Standard” Criteria Required to Make a Confirmatory Diagnosis. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möllmann, C.; Lampe, C.G.; Müller-Forell, W.; Scarpa, M.; Harmatz, P.; Schwarz, M.; Beck, M.; Lampe, C. Development of a Scoring System to Evaluate the Severity of Craniocervical Spinal Cord Compression in Patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis IVA (Morquio A Syndrome). In JIMD Reports; Zschocke, J., Gibson, K.M., Brown, G., Morava, E., Peters, V., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 11, pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafeiriou, D.; Batzios, S. Brain and Spinal MR Imaging Findings in Mucopolysaccharidoses: A Review. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 34, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.R.; Naikmasur, V.G.; Sattur, A. Hurler syndrome: Orofacial, dental, and skeletal findings of a case. Skelet. Radiol. 2014, 44, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breyer, S.R.; Muschol, N.; Schmidt, M.; Rupprecht, M.; Babin, K.; Herrmann, J.; Stücker, R. Hip Morphology in MPS-1H Patients: An MRI-based Study. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2018, 38, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas-Jilwan, M.; AlSayed, M. Mucopolysaccharidoses: Overview of neuroimaging manifestations. Pediatr. Radiol. 2018, 48, 1503–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damar, Ç.; Derinkuyu, B.E.; Kiliçkaya, M.A.B.O.; Öztürk, M.; Öztunali, Ç.; Alimli, A.G.; Boyunağa, Ö.L.; Uçar, M.; Ezgü, F.S.; Tümer, L.; et al. Posterior fossa horns; a new calvarial finding of mucopolysaccharidoses with well-known cranial MRI features. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 50, 1048–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovac, V.; Shapiro, E.G.; Rudser, K.D.; Mueller, B.A.; Eisengart, J.B.; Delaney, K.A.; Ahmed, A.; King, K.E.; Yund, B.D.; Cowan, M.J.; et al. Quantitative brain MRI morphology in severe and attenuated forms of mucopolysaccharidosis type I. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2022, 135, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, K.E.; Rudser, K.D.; Nestrasil, I.; Kovac, V.; Delaney, K.A.; Wozniak, J.R.; Mueller, B.A.; Lim, K.O.; Eisengart, J.B.; Mamak, E.G.; et al. Attention and corpus callosum volumes in individuals with mucopolysaccharidosis type I. Neurology 2019, 92, e2321–e2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Sukegawa, K.; Aoki, M.; Ito, A.; Suzuki, K.; Sakaguchi, H.; Watanabe, M.; Isogai, K.; Mizuno, S.; Hoshi, H.; et al. Evaluation of Accumulated Mucopolysaccharides in the Brain of Patients with Mucopolysaccharidoses by 1H-Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy before and after Bone Marrow Transplantation. Pediatr. Res. 2001, 49, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parini, R.; Deodato, F.; Di Rocco, M.; Lanino, E.; Locatelli, F.; Messina, C.; Rovelli, A.; Scarpa, M. Open issues in Mucopolysaccharidosis type I-Hurler. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baronio, F.; Zucchini, S.; Zulian, F.; Salerno, M.; Parini, R.; Cattoni, A.; Deodato, F.; Gaeta, A.; Bizzarri, C.; Gasperini, S.; et al. Proposal of an Algorithm to Early Detect Attenuated Type I Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS Ia) among Children with Growth Abnormalities. Medicina 2022, 58, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, T. Newborn Screening in Japan—2021. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2022, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwee, R.M.; Kwee, T.C. Virchow-Robin Spaces at MR Imaging. Radiographics 2007, 27, 1071–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheus, M.G.; Castillo, M.; Smith, J.K.; Armao, D.; Towle, D.; Muenzer, J. Brain MRI findings in patients with mucopolysaccharidosis types I and II and mild clinical presentation. Neuroradiology 2004, 46, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmucci, S.; Attinà, G.; Lanza, M.L.; Belfiore, G.; Cappello, G.; Foti, P.V.; Milone, P.; Di Bella, D.; Barone, R.; Fiumara, A.; et al. Imaging findings of mucopolysaccharidoses: A pictorial review. Insights Imaging 2013, 4, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachman, R.; Martin, K.W.; Castro, S.; Basto, M.A.; Adams, A.; Teles, E.L. Radiologic and neuroradiologic findings in the mucopolysaccharidoses. J. Pediatr. Rehabil. Med. 2010, 3, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauch, R.A.; Friloux, L.A., 3rd; Lott, I.T. MR imaging of cavitary lesions in the brain with Hurler/Scheie. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1989, 10, S1–S3. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lücke, T.; Das, A.M.; Hartmann, H.; Sykora, K.-W.; Donnerstag, F.; Schmid-Ott, G.; Grigull, L. Developmental outcome in five children with Hurler syndrome after stem cell transplantation: A pilot study. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 49, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miebach, E.; Church, H.; Cooper, A.; Mercer, J.; Tylee, K.; Wynn, R.F.; Wraith, J.E. The craniocervical junction following successful haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for mucopolysaccharidosis type I H (Hurler syndrome). J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2011, 34, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashworth, J.L.; Biswas, S.; Wraith, E.; Lloyd, I.C. The ocular features of the mucopolysaccharidoses. Eye 2005, 20, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| System Affected | Problem |
|---|---|
| General appearance | coarse facies short stature |
| Musculoskeletal | dysostosis multiplex gibbus kyphosis scoliosis hip dysplasia genu valgum joint stiffness and contractures odontoid hypoplasia |
| Neurological | cognitive impairment hydrocephalus carpal tunnel hearing loss |
| Respiratory/ENT | recurrent respiratory infections otitis media |
| Cardiovascular | valvular disease heart failure arrhythmias |
| Ophthalmology | corneal clouding glaucoma retinal changes |
| Gastrointestinal | hepatomegaly splenomegaly inguinal/umbilical hernia IBS/diarrhoea * |
| Skin lesions (non-specific) | thickened skin excessive hair growth extensive melanocytosis |
| Dysostosis Multiplex | |
|---|---|
| skull | shape changes of sella turcica craniosynostosis macrocephaly thickened calvarium oral and dental abnormalities |
| spine | craniocervical junction anomalies cord compression spinal deformities |
| other bones | inadequate modelling of long bones clavicles with widened ends “oar shaped” ribs metacarpals deformation flared iliac bones with flattened acetabulum bilateral coxa valga deformity increased risk of osteoporosis/osteopenia |
| Neuroimaging Findings—Main Changes |
|---|
| white matter signal abnormalities enlarged perivascular spaces brain atrophy hydrocephalus spinal canal stenosis involvement of corpus callosum |
| Patient No | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| diagnosis age current age sex | 4 mo 8 mo F | 2 y 10 mo 10 y 5 mo F | 1 y 2 mo 1 y 3 mo F | 2 y 4 mo 3 y 10 mo F | 1 y 10 mo 15 y 5 mo M |
| clinical features | |||||
| level of urinary GAGs at diagnosis | 462 mg/g creatinine (N: 90.0–208.0) | 459.95 mg/g creatinine (N: 90.0–208.0) | 179.2 mg/mmol creatinine (N: 9.52–26.9) | 745 mg/g creatinine (N: 90.0–208.0) | 509 mg/g creatinine (N: 83.0–161.0) |
| alpha-L-iduro- nidase activity at diagnosis | 0 umol/L/h * (cut-off value > 1.5) | 0.01 nmol/mg protein/18 h ** (N: 88.5–169.5) | 0.2 umol/L/h * (cut-off value > 1.5) | 0.3 umol/L/h * (cut-off value > 1.5) | 0.01 nmol/mg protein/18 h ** (N: 88.5–169.5) |
| mutations in the alpha-L-iduronidase gene | p.Gln63Ter and p.Arg621Ter | p.Gln63Ter and p.Arg621Ter | in progress | homozygous c.1045_1047delGAC/p.(Asp349del) | not done |
| family history | MPS type 1 in older sister | MPS type 1 in younger sister | unencumbered | suspicion of multiple sclerosis in father | unencumbered |
| developmental stages at psychomotor skills | wide range (asymmetrical body muscle tone) | correct physical and delayed mental and speech development | delayed (sitting from 11 mo, does not walk alone, words 13 mo) | delayed (walk from 2 y 4 mo, words 12 mo, halted speech development) | wide range (walk from 15 mo, words 12 mo, sentences 3 yo) |
| treatment | ERT since 5 mo old, qualified for HSCT | ERT 3 to 5 yo; HSCT at 4 y 4 mo | qualified for ERT | ERT since 2 y 6 mo old, qualified for HSCT | ERT since 2 years old until now |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Machnikowska-Sokołowska, M.; Myszczuk, A.; Wieszała, E.; Wieja-Błach, D.; Jamroz, E.; Paprocka, J. Mucopolysaccharidosis Type 1 among Children—Neuroradiological Perspective Based on Single Centre Experience and Literature Review. Metabolites 2023, 13, 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020209
Machnikowska-Sokołowska M, Myszczuk A, Wieszała E, Wieja-Błach D, Jamroz E, Paprocka J. Mucopolysaccharidosis Type 1 among Children—Neuroradiological Perspective Based on Single Centre Experience and Literature Review. Metabolites. 2023; 13(2):209. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020209
Chicago/Turabian StyleMachnikowska-Sokołowska, Magdalena, Aleksandra Myszczuk, Emilia Wieszała, Dominika Wieja-Błach, Ewa Jamroz, and Justyna Paprocka. 2023. "Mucopolysaccharidosis Type 1 among Children—Neuroradiological Perspective Based on Single Centre Experience and Literature Review" Metabolites 13, no. 2: 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020209
APA StyleMachnikowska-Sokołowska, M., Myszczuk, A., Wieszała, E., Wieja-Błach, D., Jamroz, E., & Paprocka, J. (2023). Mucopolysaccharidosis Type 1 among Children—Neuroradiological Perspective Based on Single Centre Experience and Literature Review. Metabolites, 13(2), 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020209







