The Dose–Response Effect of Fluoride Exposure on the Gut Microbiome and Its Functional Pathways in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiment
2.2. DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.3. Sequencing Data Analysis
2.4. Microbiome Co-Abundance Groups (CAGs)
2.5. Functional Prediction via Tax4fun2 Package
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Distribution of the Gut Microbiome with Fluoride Exposure
3.2. Influence of Fluoride Exposure on Gut Microbiome in Genus
3.3. Effect of Fluoride Exposure on Gut Microbiome in Species
3.4. Functional Changes in the Gut Microbiome with Fluoride Exposure
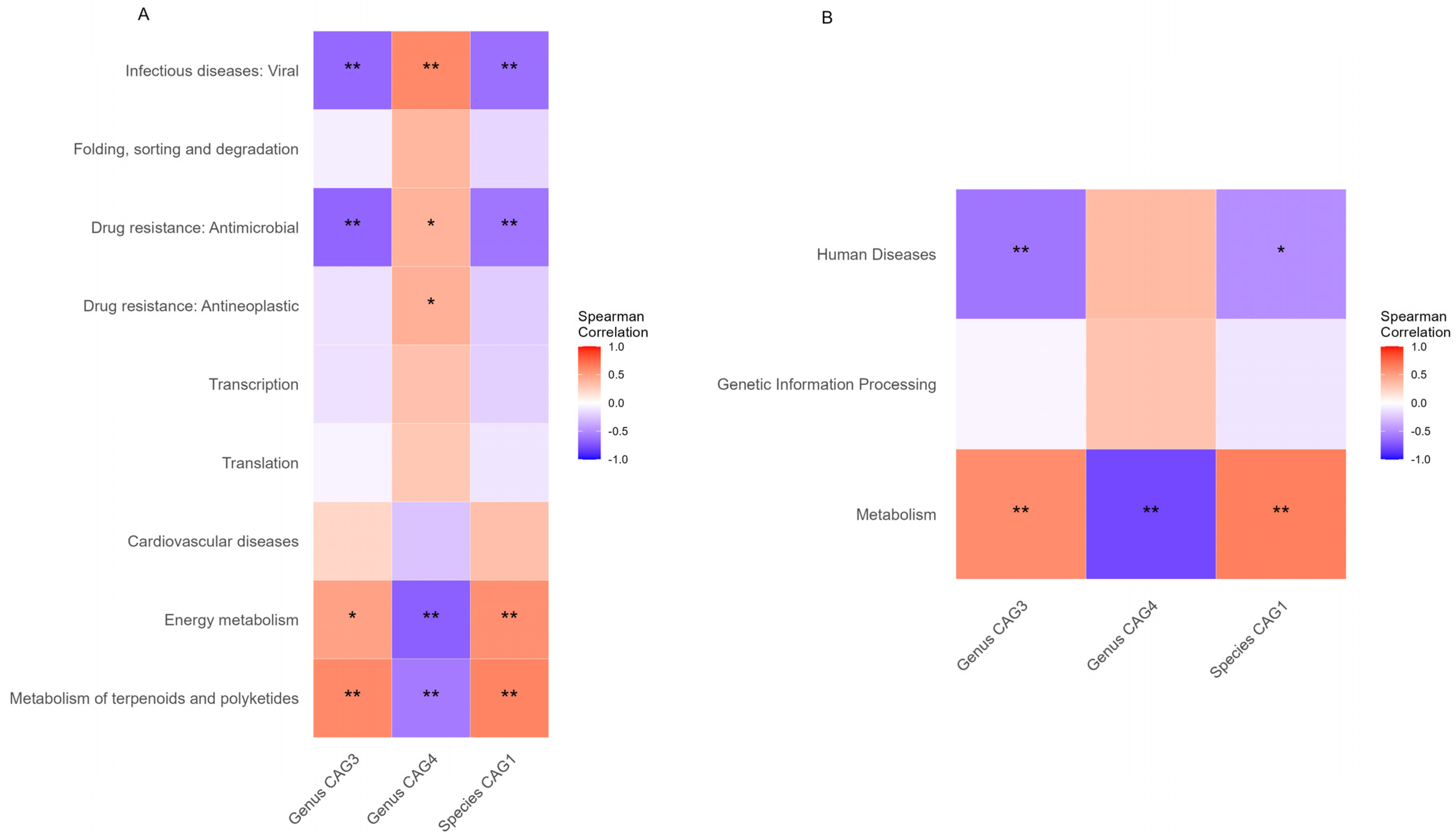
3.5. Associations between Functional Alterations and Gut Microbiome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pramanik, S.; Saha, D. The genetic influence in fluorosis. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 56, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozsvath, D.L. Fluoride and environmental health: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio./Technol. 2009, 8, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrone, P.; Giordano, M.; Giustino, S.; Guarino, F.M. Enduring fluoride health hazard for the Vesuvius area population: The case of AD 79 Herculaneum. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, M.M.; Lakhkar, B.B.; Patil, S.S. Curse of Fluorosis. Indian J. Pediatr. 2018, 85, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meenakshi; Maheshwari, R.C. Fluoride in drinking water and its removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Z.; Wang, L.; Sun, D. Endemic Fluorosis. In Endemic Disease in China; Sun, D., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 61–96. [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda, K.; Hsu, T.; Gallini, C.A.; McLver, L.J.; Schwager, E.; Shi, A.; DuLong, C.R.; Schwager, R.N.; Abu-Ali, G.S.; Franzosa, E.A.; et al. Fluoride Depletes Acidogenic Taxa in Oral but Not Gut Microbial Communities in Mice. mSystems 2017, 2, e00047-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, H.; Chen, L.; Kong, M.; Qiu, L.; Lü, P.; Wu, P.; Yang, Y.; Chen, K. Toxic effects of fluoride on organisms. Life Sci. 2018, 198, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, C.; Qin, Y.; Han, X.; Gao, J.; Zhang, A.; Luo, P.; Pan, X. Analysis of the microRNA Profile of Coal-Burning Endemic Fluorosis Using Deep Sequencing and Bioinformatic Approaches. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 103, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Abo, R.P.; Schlieper, K.A.; Graffam, M.E.; Levine, S.; Wishnok, J.S.; Swenberg, J.A.; Tannenbaum, S.R.; Fox, J.G. Arsenic exposure perturbs the gut microbiome and its metabolic profile in mice: An integrated metagenomics and metabolomics analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, H.W.; Lin, L.; Miao, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, B.H. Intestinal barrier damage involved in intestinal microflora changes in fluoride-induced mice. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Niu, R.; Li, R.; Yue, B.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Q.; Wang, J.; Sun, Z. Fluoride-Induced Alteration in the Diversity and Composition of Bacterial Microbiota in Mice Colon. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 196, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.W.; Miao, C.Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, S.Q.; Zhou, B.H. Fluoride-induced rectal barrier damage and microflora disorder in mice. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 7596–7607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelakkot, C.; Ghim, J.; Ryu, S.H. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H. Study on the Characteristics of Gut Microbiota for Children with Dental Fluorosis in Drinking Water-Born Endemic Fluorosis Areas; Zhengzhou University: Zhengzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.L.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Liston, A.; Raes, J. How informative is the mouse for human gut microbiota research? Dis. Model Mech. 2015, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, N.; Ma, Y.; Meng, X.; Sowanou, A.; Wu, L.; Huang, W.; Gao, Y.; Pei, J. Effect of Fluoride in Drinking Water on Fecal Microbial Community in Rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wemheuer, F.; Taylor, J.A.; Daniel, R.; Johnston, E.; Meinicke, P.; Thomas, T.; Wemheuer, B. Tax4Fun2: Prediction of habitat-specific functional profiles and functional redundancy based on 16S rRNA gene sequences. Environ. Microbiome 2020, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, F.Y.; Liu, J.; Shi, C.; Tang, K.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Q.; Gao, X.; Wang, N.; et al. The reciprocal changes in dominant species with complete metabolic functions explain the decoupling phenomenon of microbial taxonomic and functional composition in a grassland. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1113157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesi, J.R.; Ravel, J. The vocabulary of microbiome research: A proposal. Microbiome 2015, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Kinross, J.; Burcelin, R.; Gibson, G.; Jia, W.; Pettersson, S. Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science 2012, 336, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, G.; Garg, N.; Debelius, J.; Knight, R.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Mazmanian, S.K. Specialized metabolites from the microbiome in health and disease. Cell. Metab. 2014, 20, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffie, C.G.; Bucci, V.; Stein, R.R.; McKenney, P.T.; Ling, L.; Gobourne, A.; No, D.; Liu, H.; Kinnebrew, M.; Viale, A.; et al. Precision microbiome reconstitution restores bile acid mediated resistance to Clostridium difficile. Nature 2015, 517, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From Dietary Fiber to Host Physiology: Short-Chain Fatty Acids as Key Bacterial Metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, B.O.; Bäckhed, F. Signals from the gut microbiota to distant organs in physiology and disease. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natividad, J.M.; Lamas, B.; Pham, H.P.; Michel, M.L.; Rainteau, D.; Bridonneau, C.; da Costa, G.; van Hylckama Vlieg, J.; Sovran, B.; Chamignon, C.; et al. Bilophila wadsworthia aggravates high fat diet induced metabolic dysfunctions in mice. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.B.; Gonzalez, E.L.; Choy, K.; Faull, K.F.; Jewell, T.; Arellano, A.; Liang, J.; Yu, K.B.; Paramo, J.; Hsiao, E.Y. Gut microbiota Turicibacter strains differentially modify bile acids and host lipids. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, K.; Ma, K.; Luo, W.; Shen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xiao, M.; Tong, T.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Roseburia intestinalis: A Beneficial Gut Organism From the Discoveries in Genus and Species. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 757718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.S.B.; Raes, J.; Bork, P. The Human Gut Microbiome: From Association to Modulation. Cell 2018, 172, 1198–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Mukherjee, K.; Ghosh, S.K.; Saha, B. Sources and toxicity of fluoride in the environment. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2013, 39, 2881–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, N.; Pandey, G.; Labhasetwar, P.K. Global Fluoride Occurrence, Available Technologies for Fluoride Removal and Electrolytic Defluoridation: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 2357–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JK, F. Fluoride in Drinking-Water; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Godebo, T.R.; Jeuland, M.; Tekle-Haimanot, R.; Shankar, A.; Alemayehu, B.; Assefa, G.; Whitford, G.; Wolfe, A. Bone quality in fluoride-exposed populations: A novel application of the ultrasonic method. Bone Rep. 2020, 12, 100235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Gong, Y.; Li, H.; Xie, C.; Xu, Q.; Dong, X.; Elwan, H.A.M.; Zou, X. Alterations in cecal microbiota and intestinal barrier function of laying hens fed on fluoride supplemented diets. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 193, 110372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.K.M.; Aragão, W.A.B.; Bittencourt, L.O.; Puty, B.; Dionizio, A.; Souza, M.P.C.; Buzalaf, M.A.R.; de Oliveira, E.H.; Crespo-Lopez, M.E.; Lima, R.R. Fluoride exposure during pregnancy and lactation triggers oxidative stress and molecular changes in hippocampus of offspring rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, J.; Wu, P.; Manthari, R.K.; Zhao, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, J. Self-recovery study of the adverse effects of fluoride on small intestine: Involvement of pyroptosis induced inflammation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppel, N.; Maini Rekdal, V.; Balskus, E.P. Chemical transformation of xenobiotics by the human gut microbiota. Science 2017, 356, eaag2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhu, D.; Yang, R.; Wu, Z.; Xu, N.; Chen, F.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H.; Li, M.; Hou, K. Gut microbiota diversity in middle-aged and elderly patients with end-stage diabetic kidney disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Chen, M.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y. A systematic review and meta-analysis of gut microbiota in diabetic kidney disease: Comparisons with diabetes mellitus, non-diabetic kidney disease, and healthy individuals. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1018093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Sun, J.; Liu, C.; Yu, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Geng, Y.; Wang, Z. Compositional Alterations of Gut Microbiota in Patients with Diabetic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, R.; Bai, M.; Zhao, J.; Wang, D.; Ning, X.; Sun, S. A Comparative Study of the Gut Microbiota Associated With Immunoglobulin a Nephropathy and Membranous Nephropathy. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 557368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.H.; Huang, S.J.; Li, X.; Liu, X.S.; Du, Q.L. Response of gut microbiota to serum metabolome changes in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnant patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 7338–7351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamoudi, M.U.; Hosie, S.; Shindler, A.E.; Wood, J.L.; Franks, A.E.; Hill-Yardin, E.L. Comparing the Gut Microbiome in Autism and Preclinical Models: A Systematic Review. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 905841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Liang, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, T.; Liu, X.; Duan, J.; Duan, J.A.; Zhu, Y. Integrated gut microbiota and fecal metabolome analyses of the effect of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on D-galactose-induced premature ovarian insufficiency. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 7209–7221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Yan, J.; Hu, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Hou, D.X.; He, J.; Wu, S. Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Oxidative Status by β-Carotene in Late Pregnant Sows. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 612875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Mao, R.; Zhang, C. Mendelian randomization supports causality between gut microbiota and chronic hepatitis B. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1243811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Lin, M.; You, L.; Chen, T.; Liang, Z.; Li, D.; Xie, C.; Xiao, G.; Ye, P.; Kong, Y.; et al. Gut Microbiota Profile in Adult Patients with Idiopathic Nephrotic Syndrome. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 8854969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivaraj, S.; Chan, A.; Pasini, E.; Chen, E.; Lawendy, B.; Verna, E.; Watt, K.; Bhat, M. Enteric dysbiosis in liver and kidney transplant recipients: A systematic review. Transpl. Int. 2020, 33, 1163–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, S.; El-Mowafy, M.; Elgaml, A.; El-Mesery, M.; El Shabrawi, A.; Elegezy, M.; Hammami, R.; Mottawea, W. Alterations of the Treatment-Naive Gut Microbiome in Newly Diagnosed Hepatitis C Virus Infection. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.; You, H.J.; Bajaj, J.S.; Joo, S.K.; Yu, J.; Park, S.; Kang, H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; et al. Distinct signatures of gut microbiome and metabolites associated with significant fibrosis in non-obese NAFLD. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H.R.; Sales Martinez, S.; Stebliankin, V.; Tamargo, J.A.; Campa, A.; Narasimhan, G.; Hernandez, J.; Rodriguez, J.A.B.; Teeman, C.; Johnson, A.; et al. Diet Quality and Liver Health in People Living with HIV in the MASH Cohort: A Multi-Omic Analysis of the Fecal Microbiome and Metabolome. Metabolites 2023, 13, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyupoglu, N.D.; Ergunay, K.; Acikgoz, A.; Akyon, Y.; Yilmaz, E.; Yildiz, B.O. Gut Microbiota and Oral Contraceptive Use in Overweight and Obese Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e4792–e4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaq, H.M.; Mohammad, I.S.; Hussain, R.; Parveen, R.; Shirazi, J.H.; Fan, Y.; Shahzad, M.; Hayat, K.; Li, H.; Ihsan, A.; et al. Gut-Thyroid axis: How gut microbial dysbiosis associated with euthyroid thyroid cancer. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 2014–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Yue, Y.; He, T.; Huang, C.; Qu, B.; Lv, W.; Lai, H.Y. The Association Between the Gut Microbiota and Parkinson’s Disease, a Meta-Analysis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 636545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; You, Z.; Jia, L.; Wang, F. Autism spectrum disorder is associated with gut microbiota disorder in children. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzo, P.; Capri, F.C.; Vecchioni, L.; Realmuto, S.; Scalisi, L.; Cottone, S.; Nuzzo, D.; Alduina, R. Comparison of the Intestinal Microbiome of Italian Patients with Multiple Sclerosis and Their Household Relatives. Life 2021, 11, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, R.; Wang, J.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, J.; Ma, X.; Gou, X.; He, X.; Cheng, C.; Wang, W.; Zheng, J.; et al. Relationship between gut microbiota and lymphocyte subsets in Chinese Han patients with spinal cord injury. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 986480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Sun, S.; Wu, X.; Yang, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Intestinal environmental disorders associate with the tissue damages induced by perfluorooctane sulfonate exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Jia, H.; Zhou, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, M.; Zou, Z. Variations in gut microbiota and fecal metabolic phenotype associated with depression by 16S rRNA gene sequencing and LC/MS-based metabolomics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 138, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, L.; Bin, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, K.; Li, Q. Blood Bacterial 16S rRNA Gene Alterations in Women With Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 814520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Shang, L.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y. Gut Microbiome Characteristics in IgA Nephropathy: Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis from Observational Studies. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 904401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.N.; Joo, E.J.; Cheong, H.S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.L.; Shin, H.; Chang, Y.; Ryu, S. Gut Microbiota and Risk of Persistent Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, C.; Beaumont, M.; Pallister, T.; Villar, J.; Goodrich, J.K.; Clark, A.; Pascual, J.; Ley, R.E.; Spector, T.D.; Bell, J.T.; et al. Gut-Microbiota-Metabolite Axis in Early Renal Function Decline. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Qin, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ning, X.; Sun, S. The Specific Alteration of Gut Microbiota in Diabetic Kidney Diseases-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 908219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voroneanu, L.; Burlacu, A.; Brinza, C.; Covic, A.; Balan, G.G.; Nistor, I.; Popa, C.; Hogas, S.; Covic, A. Gut Microbiota in Chronic Kidney Disease: From Composition to Modulation towards Better Outcomes-A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Xie, S.; Lv, D.; Wang, P.; He, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, Q.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, J.; et al. Alteration of the gut microbiota in Chinese population with chronic kidney disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohia, S.; Vlahou, A.; Zoidakis, J. Microbiome in Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): An Omics Perspective. Toxins 2022, 14, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Sternes, P.R.; Guo, X.K.; Zhao, H.; Xu, C.; Xu, H. Autoimmune diseases exhibit shared alterations in the gut microbiota. Rheumatology 2023, kead364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Song, J.; Ke, P.; Kong, L.; Lei, B.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, G.; Chen, J.; et al. The gut microbiome is associated with brain structure and function in schizophrenia. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleine Bardenhorst, S.; Cereda, E.; Severgnini, M.; Barichella, M.; Pezzoli, G.; Keshavarzian, A.; Desideri, A.; Pietrucci, D.; Aho, V.T.E.; Scheperjans, F.; et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in Parkinson disease: A systematic review and pooled analysis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2023, 30, 3581–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, B.; Adiguzel, E.; Gursel, I.; Yilmaz, B.; Gursel, M. Intestinal Microbiota in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0145878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komiya, S.; Naito, Y.; Okada, H.; Matsuo, Y.; Hirota, K.; Takagi, T.; Mizushima, K.; Inoue, R.; Abe, A.; Morimoto, Y. Characterizing the gut microbiota in females with infertility and preliminary results of a water-soluble dietary fiber intervention study. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2020, 67, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Y.; Han, J.; Wu, L.; Fang, C.; Li, W.G.; Gu, J.M.; Deng, T.; Qin, C.J.; Nie, J.Y.; Zeng, X.T. Alterations of gut microbiota diversity, composition and metabonomics in testosterone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia rats. Mil. Med. Res. 2022, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, D.Q.; Liu, J.R.; Zhang, J.; Vaziri, N.D.; Zhuang, S.; Chen, H.; Feng, Y.L.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Y.Y. Unilateral ureteral obstruction causes gut microbial dysbiosis and metabolome disorders contributing to tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, P.; Chi, L.; Bodnar, W.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, B.; Bian, X.; Stewart, J.; Fry, R.; Lu, K. Gut Microbiome Toxicity: Connecting the Environment and Gut Microbiome-Associated Diseases. Toxics 2020, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thayer, K.A.; Heindel, J.J.; Bucher, J.R.; Gallo, M.A. Role of environmental chemicals in diabetes and obesity: A National Toxicology Program workshop review. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananthakrishnan, A.N. Epidemiology and risk factors for IBD. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
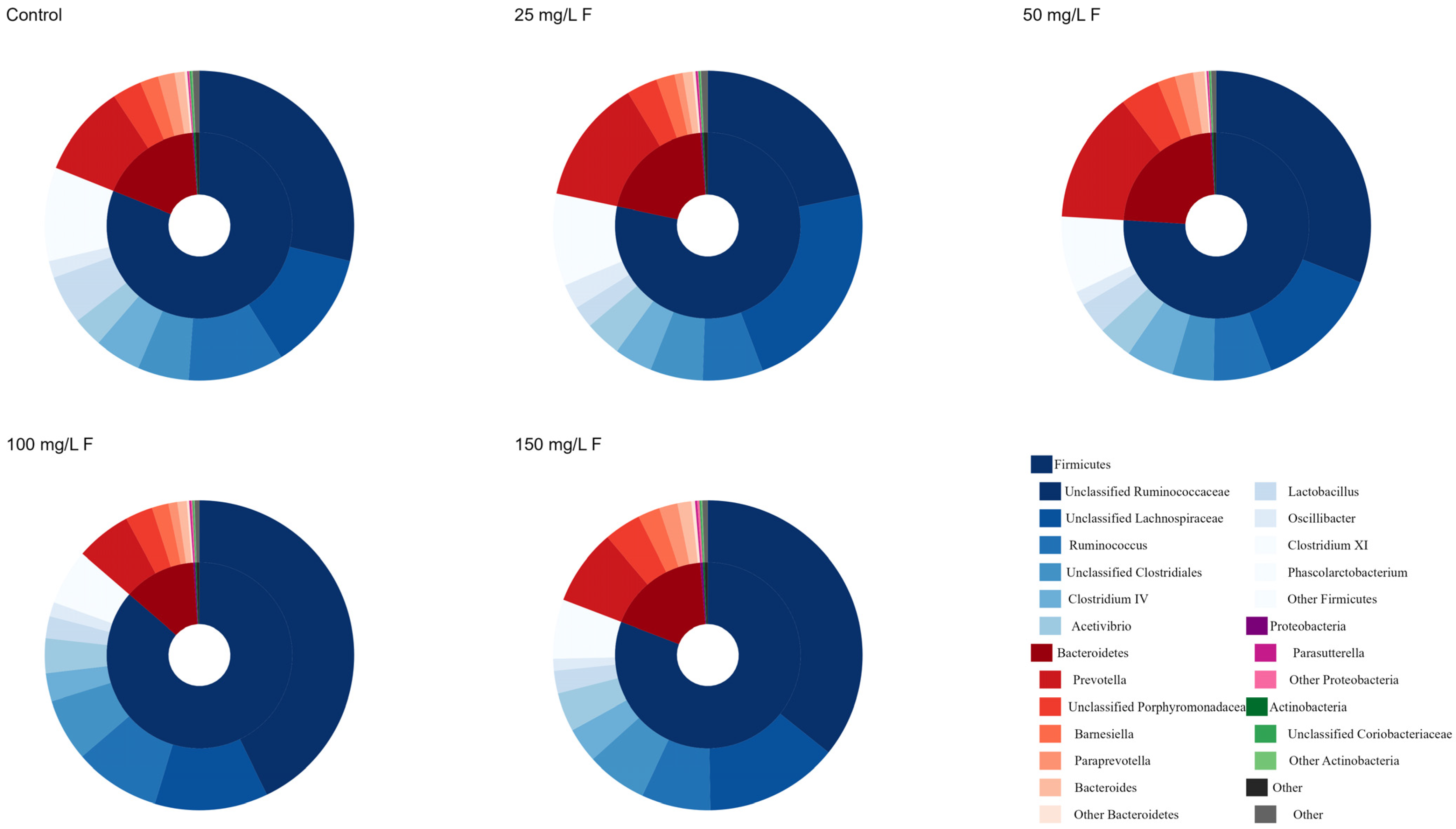
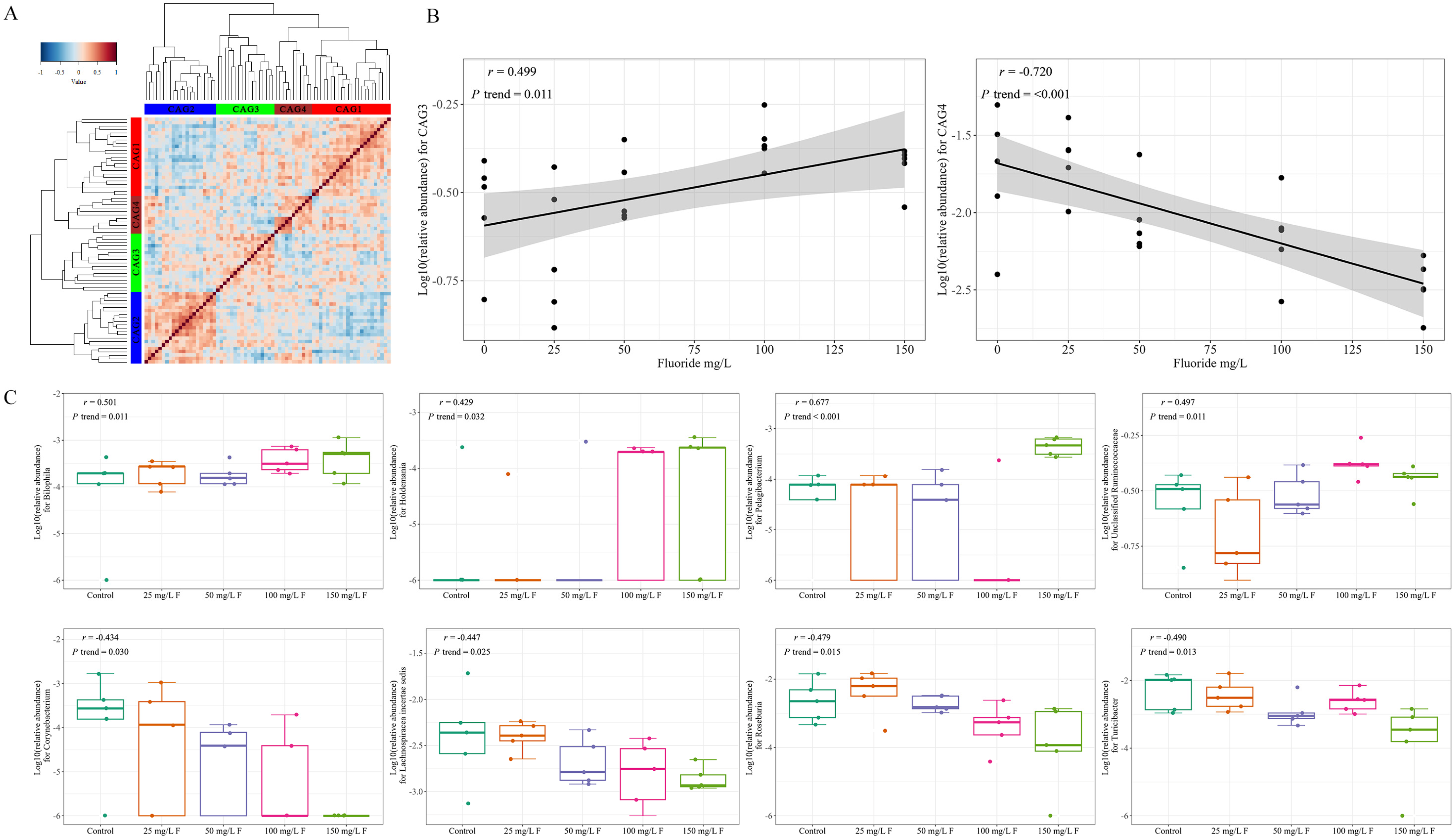

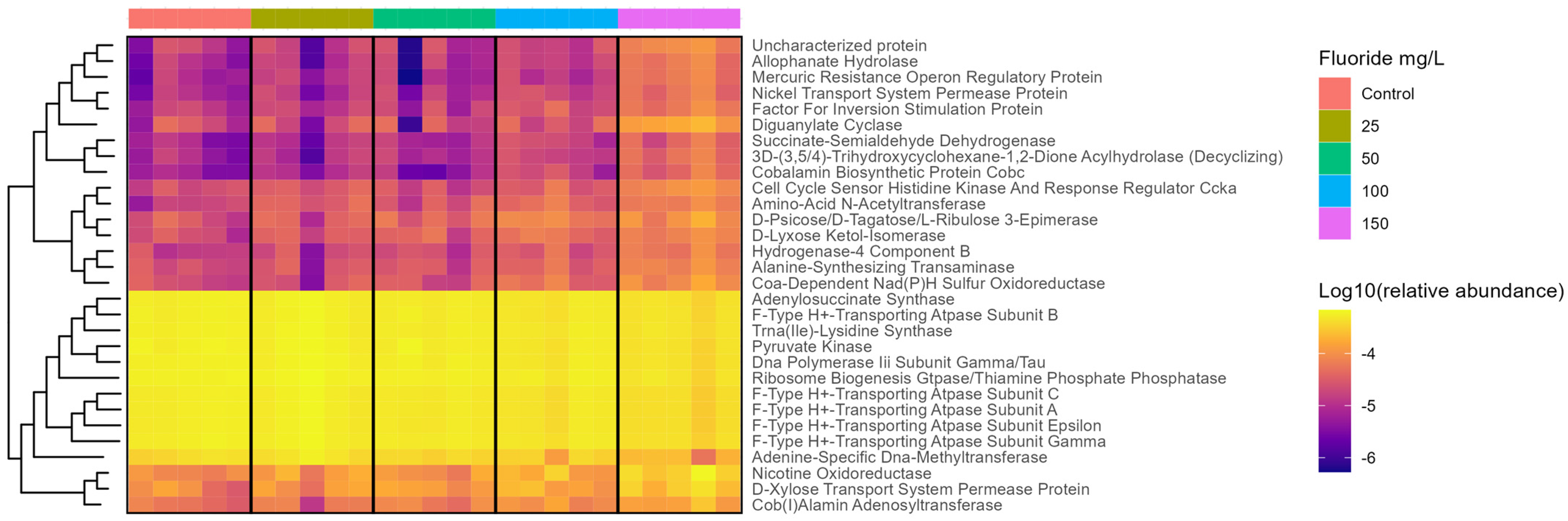
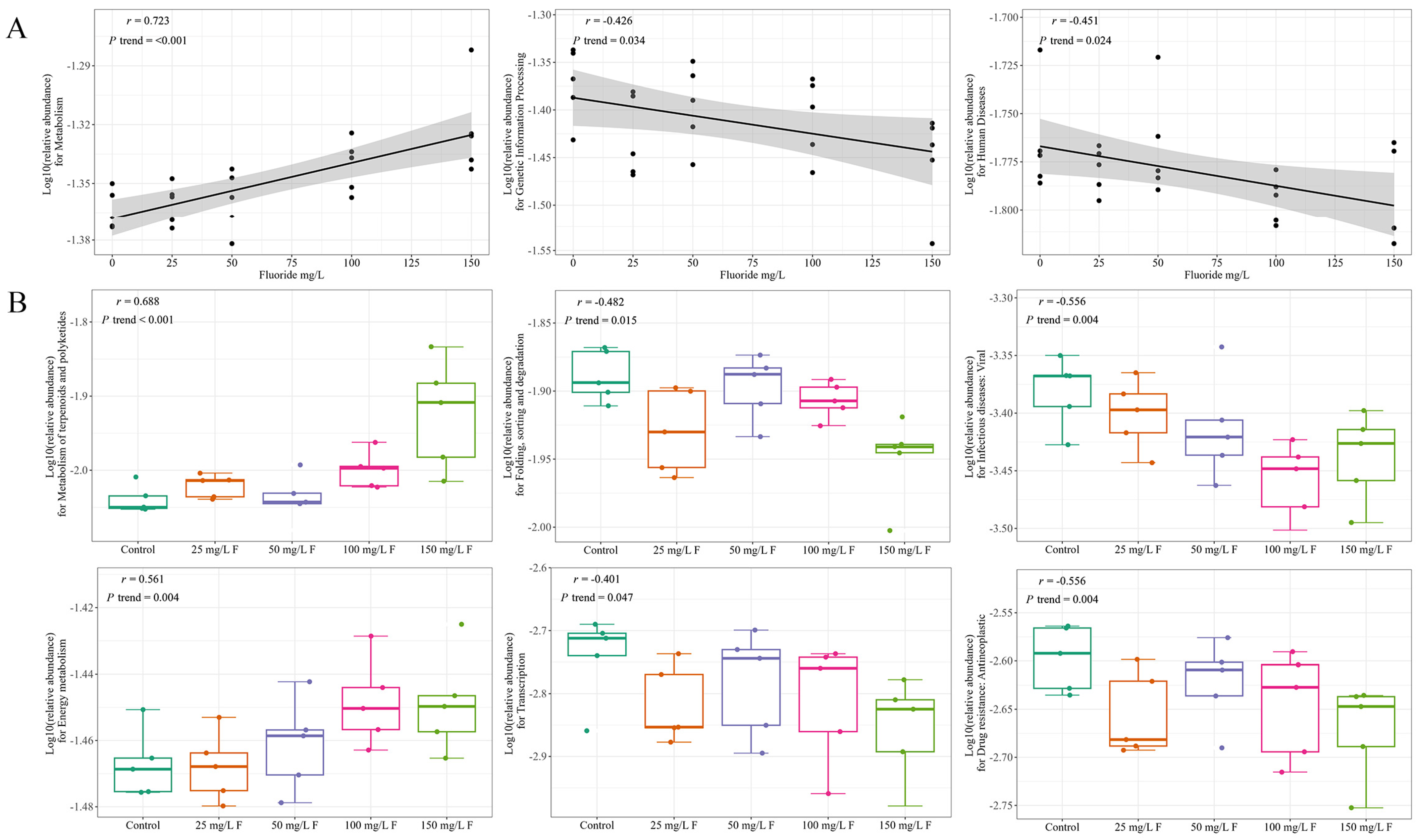
| Phylum | Control | 25 mg/L F | 50 mg/L F | 100 mg/L F | 150 mg/L F | F | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Firmicutes | 81.12 ± 18.73 | 78.33 ± 9.95 | 75.97 ± 13.54 | 86.36 ± 6.66 | 80.84 ± 9.48 | 0.490 | 0.743 |
| Bacteroidetes | 17.71 ± 18.35 | 20.55 ± 9.75 | 23.09 ± 13.51 | 12.62 ± 6.76 | 17.94 ± 9.75 | 0.502 | 0.735 |
| Proteobacteria | 0.25 ± 0.11 | 0.35 ± 0.19 | 0.24 ± 0.12 | 0.35 ± 0.13 | 0.51 ± 0.12 | 2.995 | 0.043 |
| Actinobacteria | 0.31 ± 0.24 | 0.27 ± 0.12 | 0.24 ± 0.12 | 0.22 ± 0.09 | 0.29 ± 0.15 | 0.283 | 0.885 |
| MetaCyc Pathways of Level 3 | Correlation Coefficient | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Metabolism | 0.723 | <0.001 |
| Genetic Information Processing | −0.426 | 0.034 |
| Human Diseases | −0.451 | 0.024 |
| MetaCyc Pathways of Level 3 | MetaCyc Pathways of Level 2 | Correlation Coefficient | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic Information Processing | Translation | −0.399 | 0.048 |
| Genetic Information Processing | Folding, sorting, and degradation | −0.482 | 0.015 |
| Genetic Information Processing | Transcription | −0.401 | 0.047 |
| Human Diseases | Drug resistance: Antimicrobial | −0.442 | 0.027 |
| Human Diseases | Drug resistance: Antineoplastic | −0.411 | 0.041 |
| Human Diseases | Infectious diseases: Viral | −0.556 | 0.004 |
| Human Diseases | Cardiovascular diseases | 0.399 | 0.048 |
| Metabolism | Energy metabolism | 0.561 | 0.004 |
| Metabolism | Metabolism of terpenoids and polyketides | 0.688 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mo, Z.; Wang, J.; Meng, X.; Li, A.; Li, Z.; Que, W.; Wang, T.; Tarnue, K.F.; Ma, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. The Dose–Response Effect of Fluoride Exposure on the Gut Microbiome and Its Functional Pathways in Rats. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13111159
Mo Z, Wang J, Meng X, Li A, Li Z, Que W, Wang T, Tarnue KF, Ma X, Liu Y, et al. The Dose–Response Effect of Fluoride Exposure on the Gut Microbiome and Its Functional Pathways in Rats. Metabolites. 2023; 13(11):1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13111159
Chicago/Turabian StyleMo, Zhe, Jian Wang, Xinyue Meng, Ailin Li, Zhe Li, Wenjun Que, Tuo Wang, Korto Fatti Tarnue, Xu Ma, Ying Liu, and et al. 2023. "The Dose–Response Effect of Fluoride Exposure on the Gut Microbiome and Its Functional Pathways in Rats" Metabolites 13, no. 11: 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13111159
APA StyleMo, Z., Wang, J., Meng, X., Li, A., Li, Z., Que, W., Wang, T., Tarnue, K. F., Ma, X., Liu, Y., Yan, S., Wu, L., Zhang, R., Pei, J., & Wang, X. (2023). The Dose–Response Effect of Fluoride Exposure on the Gut Microbiome and Its Functional Pathways in Rats. Metabolites, 13(11), 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13111159






