Urinary Free Cortisol Determination and Interferences Studies Using Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry after On-Line Solid Phase Extraction Based on TurboflowTM Chromatography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reference Steroids and Chemicals
2.2. Urinary Samples
2.3. Urinary Free Cortisol Immunoassay
2.4. Mass Spectrometry (MS)
2.5. On-Line TurboflowTM Extraction and Chromatography
2.6. Sample Preparation before LC-MS/MS Analysis
3. Method Validation
3.1. Recovery
3.2. Interferences
3.3. Linearity and Calibration Curves
3.4. Limit of Detection (LOD) and Limit of Quantification (LOQ)
3.5. Intra-Assay and Inter-Assay Precision and Accuracy
3.6. Carryover
3.7. Stability
3.8. Methods Comparison
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Extraction Method Development
4.2. Analytical Validation
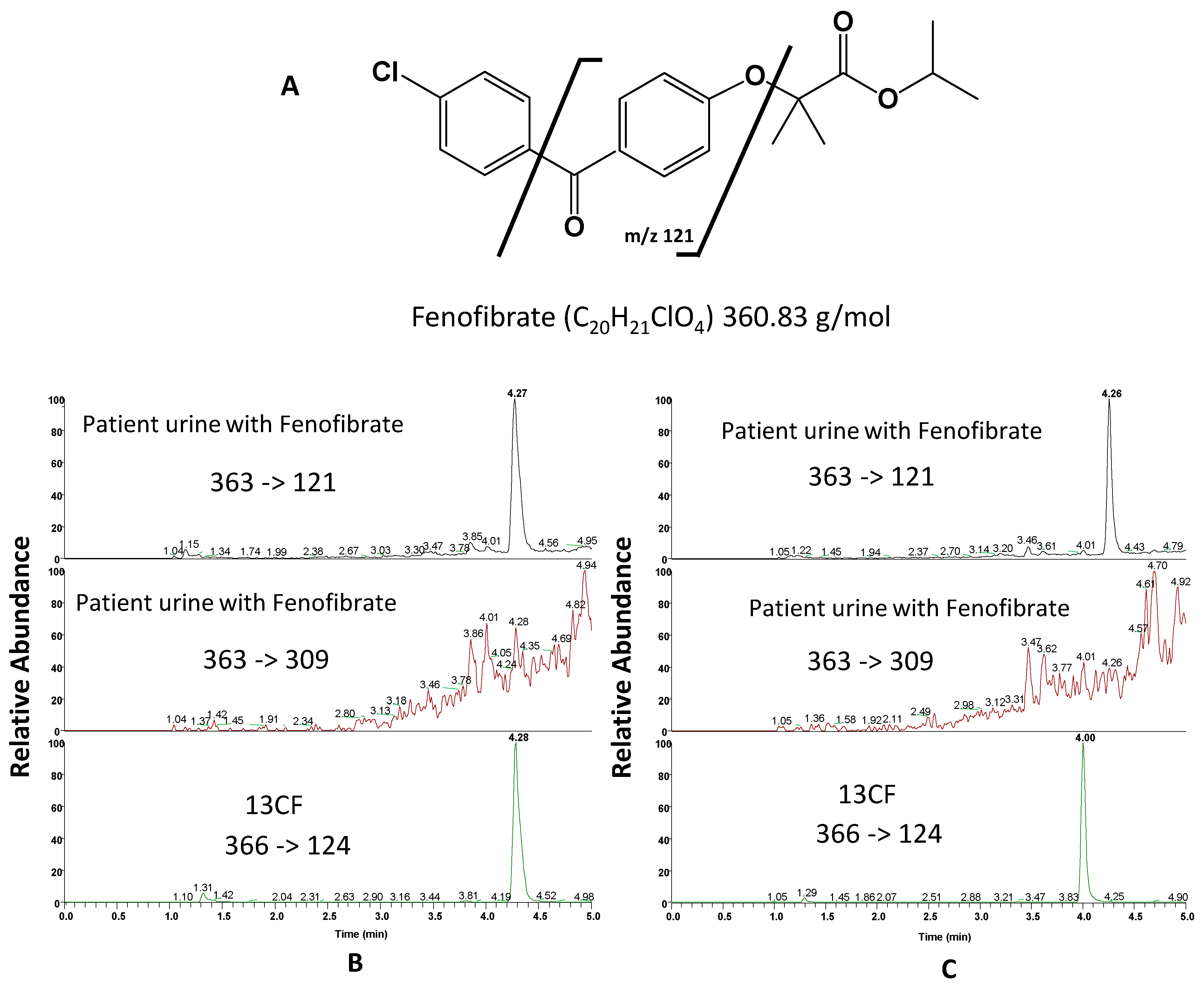
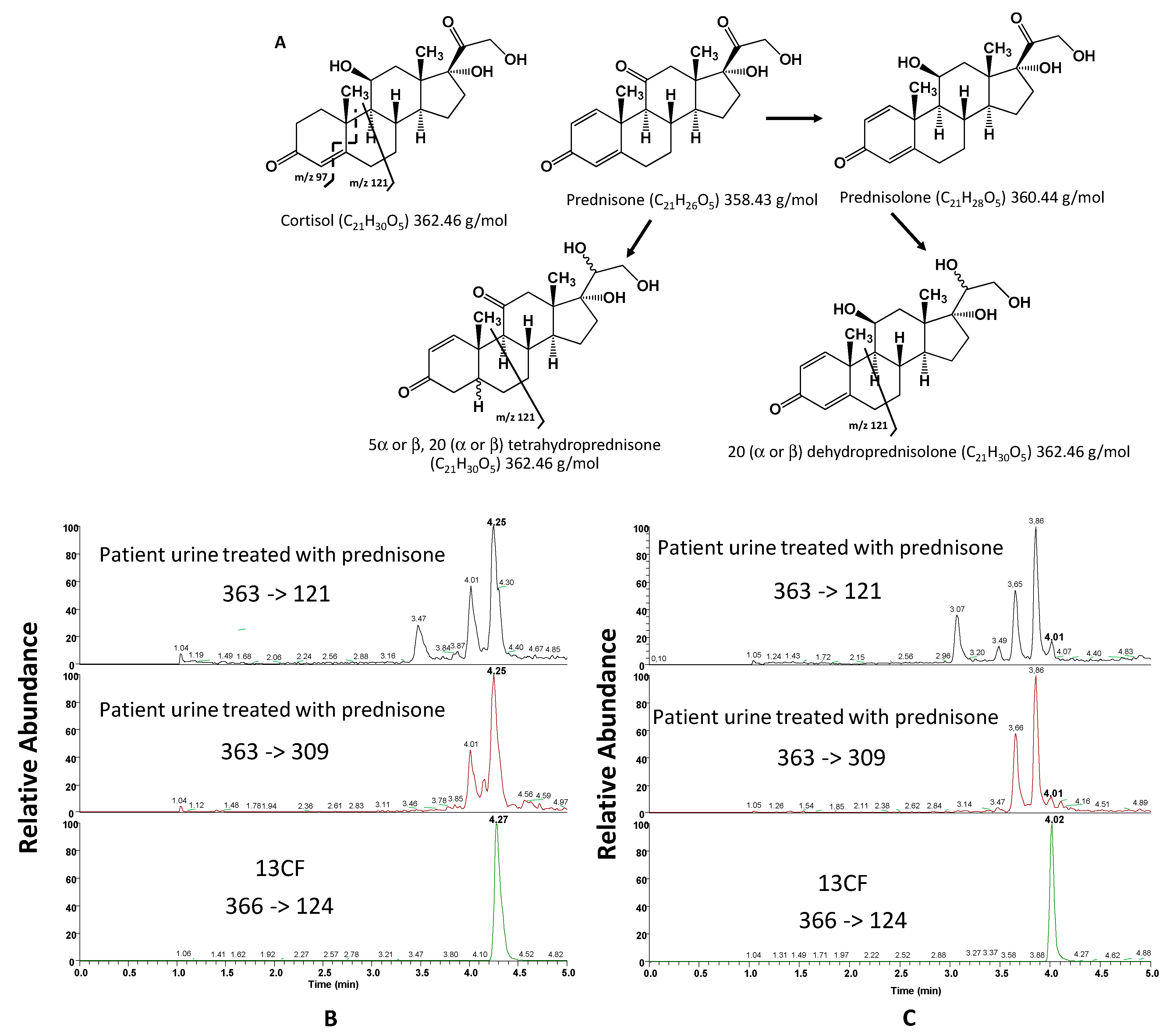
4.2.1. Interferences—Selectivity
4.2.2. Linearity and Calibration Curves
4.2.3. LOQ and LOD
4.2.4. Intra-Assay and Inter-Assay Precision and Accuracy
4.2.5. Carryover
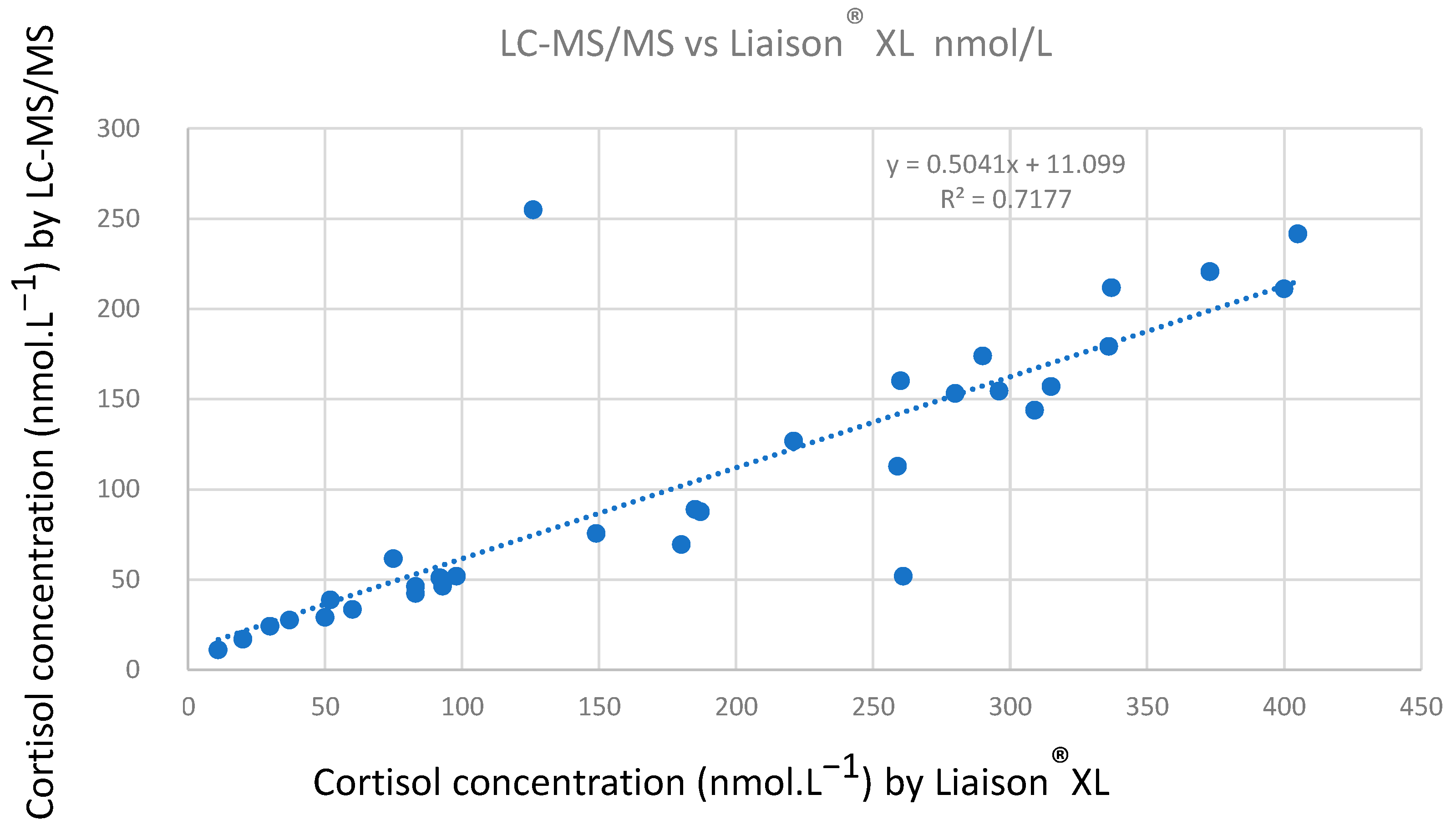
4.2.6. Methods Comparison between Liaison® XL and Proposed Method
4.2.7. Methods Comparison between LC-MS/MS Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tabarin, A.; Assié, G.; Barat, P.; Bonnet, F.; Bonneville, J.F.; Borson-Chazot, F.; Bouligand, J.; Boulin, A.; Brue, T.; Caron, P.; et al. Consensus statement by the French Society of Endocrinology (SFE) and French Society of Pediatric Endocrinology & Diabetology (SFEDP) on diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome. Ann. Endocrinol. 2022, 83, 119–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diasorin LIAISON®: Cortisol documentation. 2011. Available online: https://www.diasorin.com/en/immunodiagnostic-solutions/systems/clia-systems/liaisonr-xl (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Taylor, R.L.; Machacek, D.; Singh, R.J. Validation of a high-throughput liquid chromatograph-tandem mass spectrometry method for urinary cortisol and cortisone. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mc Whinney, B.C.; Briscoe, S.E.; Ungerer, J.P.J.; Pretorius, C.J. Measurement of cortisol, cortisone, prednisolone, dexamethasone and 11-deoxycortisol with ultra high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: Application for plasma, plasma ultrafiltrate, urine and saliva in a routine laboratory. J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 878, 2863–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, G.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Deng, H. Simultaneous measurements of cortisol and cortisone in urine and hair for the assessment of 11β-hydrosteroid dehydrogenase activity among methadone maintenance treatment patients with LC-ESI-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 969, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, A.; Raffaelli, A.; Cupisti, A.; Petri, A.; Marcocci, C.; Salvadori, P. Recent advances in the assessment of the ratios of cortisol to cortisone and of some of their metabolites in urine by LC-MS-MS. J. Mass. Spectrom. 2009, 44, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Guijo, A.; Hartmann, M.F.; Shi, L.; Remer, T.; Wudy, S.A. Determination of free cortisol and free cortisone in human urine by on-line turbulent flow chromatography coupled to fused-core chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (TFC-HPLC-MS/MS). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Liu, L.; Yin, Z.; Lu, Y. Comparison of two online extraction systems and development of the online SPE-HPLC-DAD method to simultaneously determine ten β-amino alcohol drugs in plasma. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 5816–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couchman, L. Turbulent flow chromatography in bioanalysis: A review. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2012, 26, 892–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COFRAC. Guide Technique D’accréditation de Vérification/Validation des Méthodes de Biologie Médicale. Available online: https://tools.cofrac.fr/documentation/sh-gta-04 (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- European Medicines Agency. Guideline on Bioanalytical Method Validation. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/guideline-bioanalytical-method-validation_en.pdf (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- European Medicines Agency. ICH Topic Q2 (R1) Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-q-2-r1-validation-analytical-procedures-text-methodology-step-5_en.pdf (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Krone, N.; Hughes, A.B.; Lavery, G.G.; Stewart, P.M.; Arlt, W.; Shackleton, C.H.L. Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) remains a pre-eminent discovery tool in clinical steroid investigations even in the era of fast liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS). J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 121, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushnir, M.M.; Rockwood, A.L.; Nelson, G.J.; Terry, A.H.; Meikle, A.W. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of urinary free cortisol. Clin. Chem. 2003, 49, 965–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, K.; Sudo, A. Effect of Urine pH, Storage Time, and Temperature on Stability of Catecholamines, Cortisol, and Creatinine. Clin. Chem. 1998, 44, 1759–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, J. The biochemical pharmacology of fenofibrate. Cardiology 1989, 76, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MassBank. Available online: https://massbank.eu/MassBank/RecordDisplay?id=MSBNK-Eawag-EA033604 (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Ahi, S.; Beotra, A.; Dubey, S.; Upadhyay, A.; Jain, S. Simultaneous identification of prednisolone and its ten metabolites in human urine by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Drug Test. Anal. 2012, 4, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deventer, K.; van Gansbeke, W.; Hooghe, F.; Polet, M.; van Eenoo, P. Investigation of the urinary excretion of prednisolone and metabolites after nasal administration: Relevance to doping control. In Proceedings of the Manfred Donike Workshop, 39th Workshop on Dope Analysis (Recent Advances in Doping Analysis), Cologne, Germany, 22–26 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, V.; Jusko, W.J. Simultaneous analysis of prednisone, prednisolone and their major hydroxylated metabolites in urine by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 1991, 567, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocci Jr, M.L.; Jusko, W.J. Analysis of prednisone, prednisolone and their 20β-hydroxylated metabolites by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 1981, 224, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, R.S.; Maguire, D.J.; Mortimer, R.H.; Roberts, M.S.; Cannell, G.R. Pathway and kinetics of prednisolone metabolism in the human placenta. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1993, 44, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, V.; Jusko, W.J. Bioavailability and reversible metabolism of prednisone and prednisolone in man. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 1994, 15, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, R.S.; Maguire, D.J.; Mortimer, R.H.; Cannell, G.R. Metabolism of prednisolone by the isolated perfused human placental lobule. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1991, 39, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matabosch, X.; Pozo, O.J.; Pérez-Mañá, C.; Papaseit, E.; Segur, J.; Ventura, R. Detection and characterization of prednisolone metabolites in human urine by LC-MS/MS. J. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 50, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popot, M.A.; Garcia, P.; Fournier, F.; Bonnaire, Y.; Tabet, J.C. Different approaches to the identification of a cortisol isomer compound in horse urine. Analyst 1998, 123, 2649–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevis, M.; Schänzer, W. Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Androstan-17β-ol-3-one and Androstadiene-17β-ol-3-one Isomers. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 16, 1660–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antignac, J.P.; Le Bizec, B.; Monteau, F.; Poulain, F.; André, F. Collision-induced dissociation of corticosteroids in electrospray tandem mass spectrometry and development of a screening method by high performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2000, 14, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevis, M.; Beuck, S.; Höppner, S.; Thomas, A.; Held, J.; Schäfer, M.; Oomens, J.; Schänzer, W. Structure Elucidation of the Diagnostic Product Ion at m/z 97 Derived from Androst-4-en-3-One- Based Steroids by ESI-CID and IRMPD Spectroscopy. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 23, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuzzola, A.; Mazzini, F.; Petri, A. A comprehensive study for the validation of a LC-MS/MS method for the determination of free and total forms of urinary cortisol and its metabolites. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 94, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oßwald, A.; Wang, R.; Beuschlein, F.; Hartmann, M.F.; Wudy, S.A.; Bidlingmaier, M.; Zopp, S.; Reincka, M.; Ritzel, K. Performance of LC-MS/MS and immunoassay based on 24-h urine free cortisol in diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 190, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccato, F.; Antonelli, G.; Barbot, M.; Zilio, M.; Mazzai, L.; Gatti, R.; Zaninotto, M.; Mantero, F.; Boscaro, M.; Plebani, M.; et al. The diagnostic performance of urinary free cortisol is better than the cortisol:cortisone ratio in detecting de novo Cushing’s syndrome: The use of a LC–MS/MS method in routine clinical practice. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 171, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Kalhorn, T.F.; Baillie, M.M.S.; Shen, D.D.; Thummel, K.E. Detremintion of fre and total cortisol in plasma and urine by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Ther. Drug Monit. 2007, 29, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wear, J.E.; Owen, L.J.; Duxbury, K.; Keevil, B.G. A simplified method for the measurement of urinary free cortisol using LC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B. 2007, 858, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persichilli, S.; Gervasoni, J.; Iavarone, F.; Zuppi, C. A simple liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for urinary free cortisol analysis: Suitable for routine purpose. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2010, 48, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, L.; Ducrocq, D.H.; Fraser, H.L.; Gillinngwater, S.; Evans, C.; Pickett, A.J.; Rees, D.W.; John, R.; Turkes, A. Measurement of urinary free cortisol by tandem mass spectrometry and comparison with results obtained by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and two commercial immunoassays. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2008, 45, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, G.; Artusi, C.; Marinova, M.; Brugnolo, L.; Zaninotto, M.; Scaroni, C.; Gatti, R.; Mantero, F.; Plebani, M. Cortisol and cortisone ratio in urine: LC-MS/MS method validation and preliminary clinical application. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2013, 52, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, L.J.; Haslam, S.; Adaway, J.E.; Wood, P.; Glenn, C.; Keevil, B.G. A simplified liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry assay, using on-line solid-phase extraction, for the quantitation of cortisol in saliva and comparison with a routine DELFIA method. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2010, 47, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostolanska, K.; Novotna, L.; Taborska, E.; Pes, O. Online solid-phase extraction liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry of hair cortisol using a surrogate analyte. Chem. Pap. 2019, 73, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinete, N.; Bertram, J.; Reska, M.; Lang, J.; Kraus, T. Highly selective and automated online SPE LC–MS3 method for determination of cortisol and cortisone in human hair as biomarker for stress related diseases. Talanta 2015, 134, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
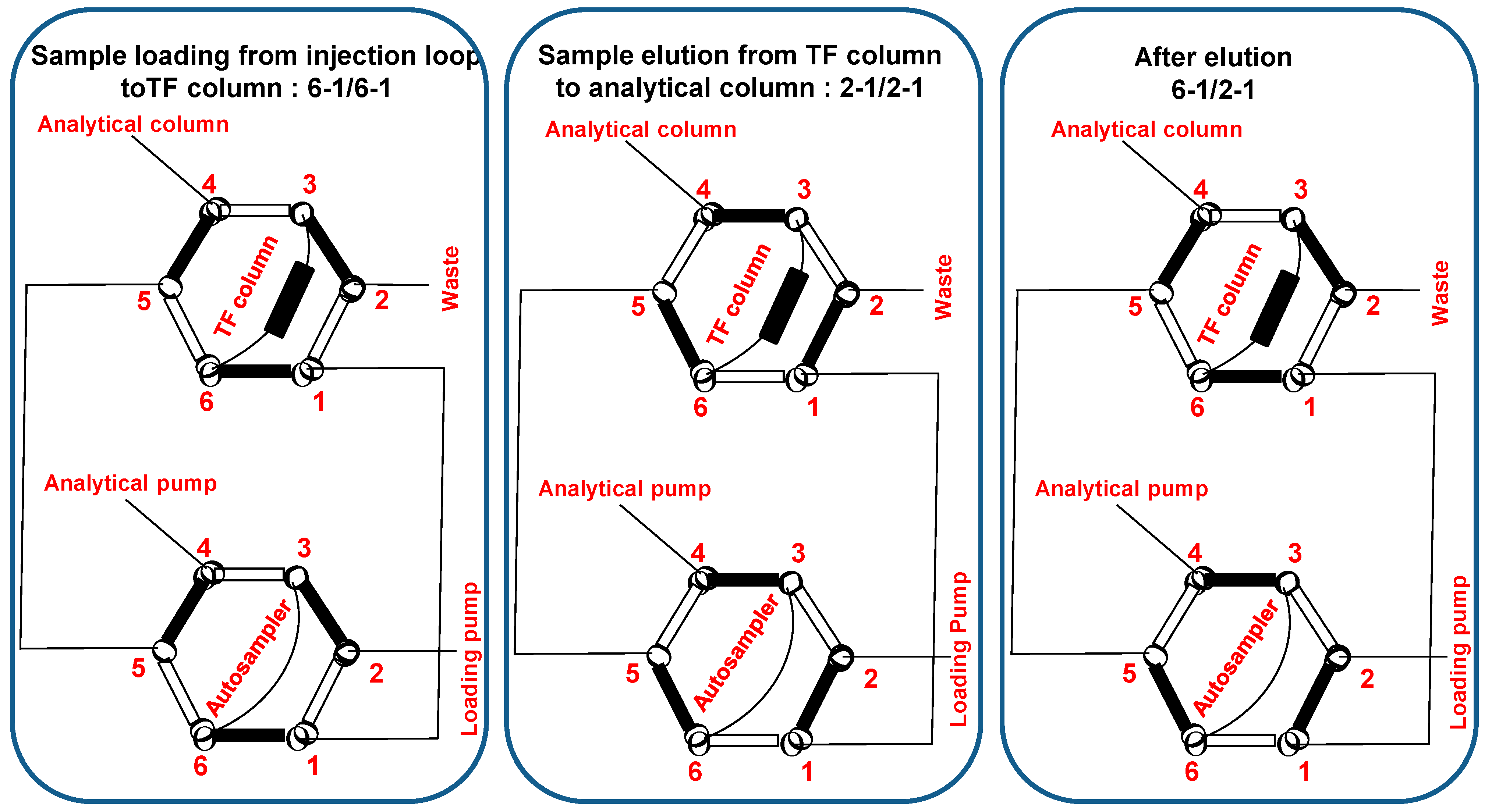
| TF Column/Tubing | Analytical Column | Loading Pump | Analytical Pump | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (min) | Valves | Flow Rate (mL/min) | Solvent | Flow Rate (mL/min) | Solvent | ||
| 6-1, 6-1 | 100% C | 0.5 | 25% B1 | ||||
| 0 | Sample loading | 2 | 100% C | 0.5 | 25% B1 | ||
| 0.5 | 2-1, 2-1 | 2 | 100% C | 0.5 | 25% B1 | ||
| 0.6 | Cortisol transfer/Cleaning tubing with D | Cortisol transfer | 2 | 100% D | 0.5 | 25% B1 | |
| 1 | Elution gradient | 2 | 100% D | 0.5 | 25% B1 | ||
| 2.7 | 0.1 | 100% D | 0.5 | ||||
| 2.9 | 2 | 100% D | 0.5 | ||||
| 3.6 | Cleaning tubing with C | 2 | 100% C | 0.5 | |||
| 4.5 | 2 | 100% C | 0.5 | 62% B1 | |||
| 4.6 | 6-1, 2-1 | Cleaning | 2 | 100% C | 0.5 | 98% B1 | |
| 5 | Equilibration with C | Equilibration with 25% B1 | 2 | 100% C | 0.5 | 25% B1 | |
| 6 | 6-1, 6-1 | 2 | 100% C | 0.5 | 25% B1 | ||
| Theoretical Values (nmol·L−1) | Average nmol·L−1 | Standard Deviation | CV (%) | Bias (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 6.65 | 6.97 | 0.56 | 8.00 | 4.44 |
| S2 | 29.15 | 29.7 | 1.18 | 3.99 | 1.86 |
| S3 | 132.87 | 122.76 | 4.32 | 3.46 | −5.83 |
| S4 | 89.50 | 86.44 | 4.28 | 4.95 | −3.42 |
| S5 | 411.74 | 409.63 | 11.88 | 3.01 | −4.21 |
| S6 | 1069.89 | 1081.24 | 9.16 | 0.84 | 2.26 |
| (a) | ||||
| Pool | Average (nmol·L−1) | Standard Deviation | CV (%) | |
| QC2 | 23.9 | 1.5 | 6.2 | |
| P1 | 97.9 | 2.1 | 2.1 | |
| P2 | 361.4 | 11.7 | 3.2 | |
| P3 | 784.1 | 17.0 | 2.2 | |
| (b) | ||||
| QC1 | QC3 | QC4 | QC5 | |
| Target nmol·L−1 | 6.90 | 44.16 | 209.76 | 334.00 |
| Average nmol·L−1 | 7.3 | 39.0 | 206.1 | 332.4 |
| CV (%) | 5.8 | 6.9 | 7.8 | 3.4 |
| Bias (%) | 5.2 | −11.6 | −1.8 | −0.5 |
| Reference | Sample | Extraction Mode | Cortisol Retention Time Injection Interval | LOQ or LCCR * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [33] | Plasma (250 μL)/Urine (1 mL) | Liquid–liquid extraction using 3 mL of ethyl acetate | 5.3 min | LOQ 0.5 ng/mL |
| [3] | Urine (500 μL) | Liquid–liquid extraction using 4.5 mL of methylene chloride | 1.5 min | LCCR 7 nmol·L−1 |
| [34] | Urine (100 μL) | Injection volume: 50 μL Precipitation with trichloroacetic acid and centrifugation | 2 min | LOQ 2.5 nmol·L−1 |
| [35] | Urine (500 μL) | Precipitation with methanol and filtration | 6.84 min | LCCR 7 nmol·L−1 |
| [30] | Urine (125 μL) | Injection volume: 20 μL Solid phase extraction with Oasis® HLB | 13 min | LOQ 0.3 ng/mL |
| [36] | Urine (1 mL) | Solid phase extraction with Oasis® HLB | 2.6 min | LOQ 2 nmol·L−1 |
| [4] | Acidified plasma (250 μL), urine (50 μL), saliva (250 μL), ultrafiltrate of plasma (250 μL) | Solid phase extraction with Oasis® HLB | 1.46 min | LOQ in plasma 3.75 nmol·L−1 |
| [37] | Urine (500 μL) diluted by 10 | On-line extraction (Zorbax Extend-C18 cartridge) | 4.4 min | 5 nmol·L−1 |
| [38] | Saliva (200 μL) | Injection volume: 50 μL On-line extraction (Phenomenex C8) | 3 min | 2 nmol·L−1 |
| [39] | Hair (8 mg) in 1.8 mL of MeOH | 1.6 mL evaporated, residue dissolved in 500 μL Injection volume 50 μL On-line extraction with cartridge (2 × 4 mm, C18, Phenomenex®) | 6.3 min | 0.8 pg/mg |
| [40] | Hair (50 mg) in 2 mL of MeOH | 50 μL of supernatant On-line extraction with Restricted Acess Material phase (Lichrospher® RP-8-ADS (25 μm, 24 mm × 4 mm) | 11.5 min | 2 pg/mg |
| [14] | Urine (500 μL) | Injection volume: 200 μL On-line extraction (C18 Phenomenex) | Injection interval: 8 min | LCCR 10 μg/L |
| [6] | Urine (50 μL) diluted by 20 | Injection volume (diluted urine): 60 μL On-line extraction (Poros) | 4.07 min | LCCR 5 ng/mL |
| [7] | Urine (100 μL) | Injection volume: 20 μL On-line extraction (Turbulent Flow Chromatography: C18 HTLC column) | 5.70 min | LOQ 1 ng/mL |
| Proposed method | Urine (10 μL) diluted by 10 | Injection volume: 10 μL On-line extraction (TurboflowTM XL C2) | 4.3 min | LOQ 1.65 nmol·L−1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonnet-Serrano, F.; Nakib, S.; Zientek, C.; Guignat, L.; Guibourdenche, J.; Bertherat, J.; Menet, M.-C. Urinary Free Cortisol Determination and Interferences Studies Using Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry after On-Line Solid Phase Extraction Based on TurboflowTM Chromatography. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13101063
Bonnet-Serrano F, Nakib S, Zientek C, Guignat L, Guibourdenche J, Bertherat J, Menet M-C. Urinary Free Cortisol Determination and Interferences Studies Using Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry after On-Line Solid Phase Extraction Based on TurboflowTM Chromatography. Metabolites. 2023; 13(10):1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13101063
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonnet-Serrano, Fidéline, Samir Nakib, Corinne Zientek, Laurence Guignat, Jean Guibourdenche, Jerôme Bertherat, and Marie-Claude Menet. 2023. "Urinary Free Cortisol Determination and Interferences Studies Using Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry after On-Line Solid Phase Extraction Based on TurboflowTM Chromatography" Metabolites 13, no. 10: 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13101063
APA StyleBonnet-Serrano, F., Nakib, S., Zientek, C., Guignat, L., Guibourdenche, J., Bertherat, J., & Menet, M.-C. (2023). Urinary Free Cortisol Determination and Interferences Studies Using Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry after On-Line Solid Phase Extraction Based on TurboflowTM Chromatography. Metabolites, 13(10), 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13101063








