HPLC–(Q)-TOF-MS-Based Study of Plasma Metabolic Profile Differences Associated with Age in Pediatric Population Using an Animal Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
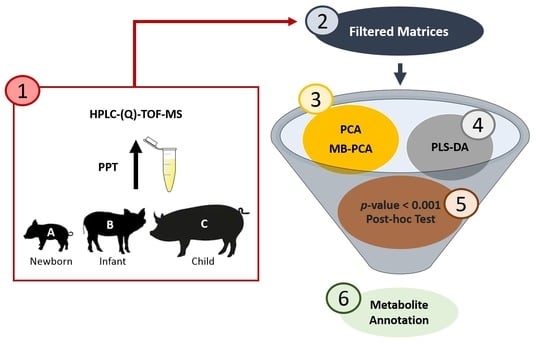
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagent and Solutions
2.2. Study Design and Sample Collection
2.3. Plasma Sample Treatment and QC Sample Preparation
2.4. HPLC–(Q)-TOF-MS Analysis
2.5. Data Preprocessing
2.6. Multivariate Analysis
2.7. Univariate Analysis
2.8. MS/MS-Based Metabolites Annotation
3. Results
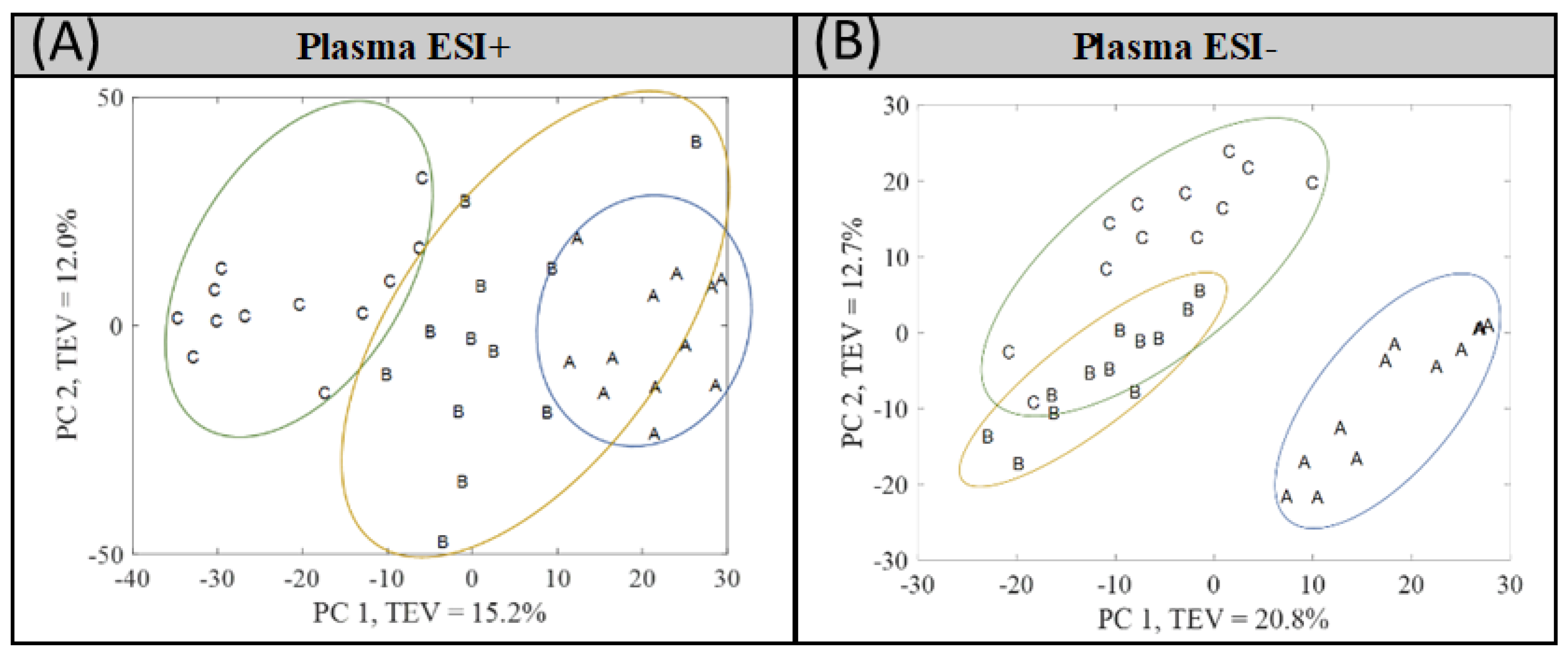
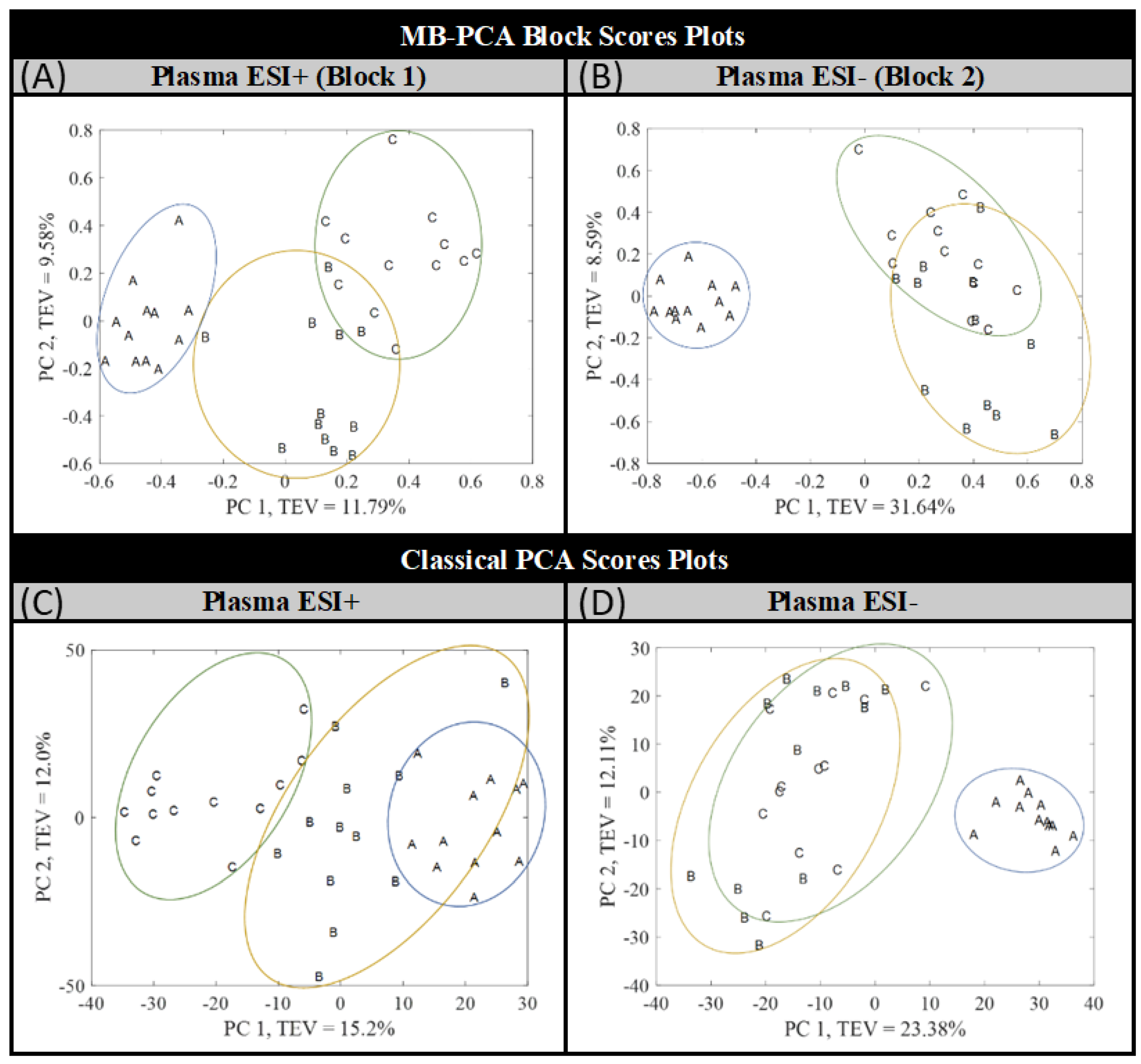
3.1. Multivariate Analysis
3.2. Univariate Analysis
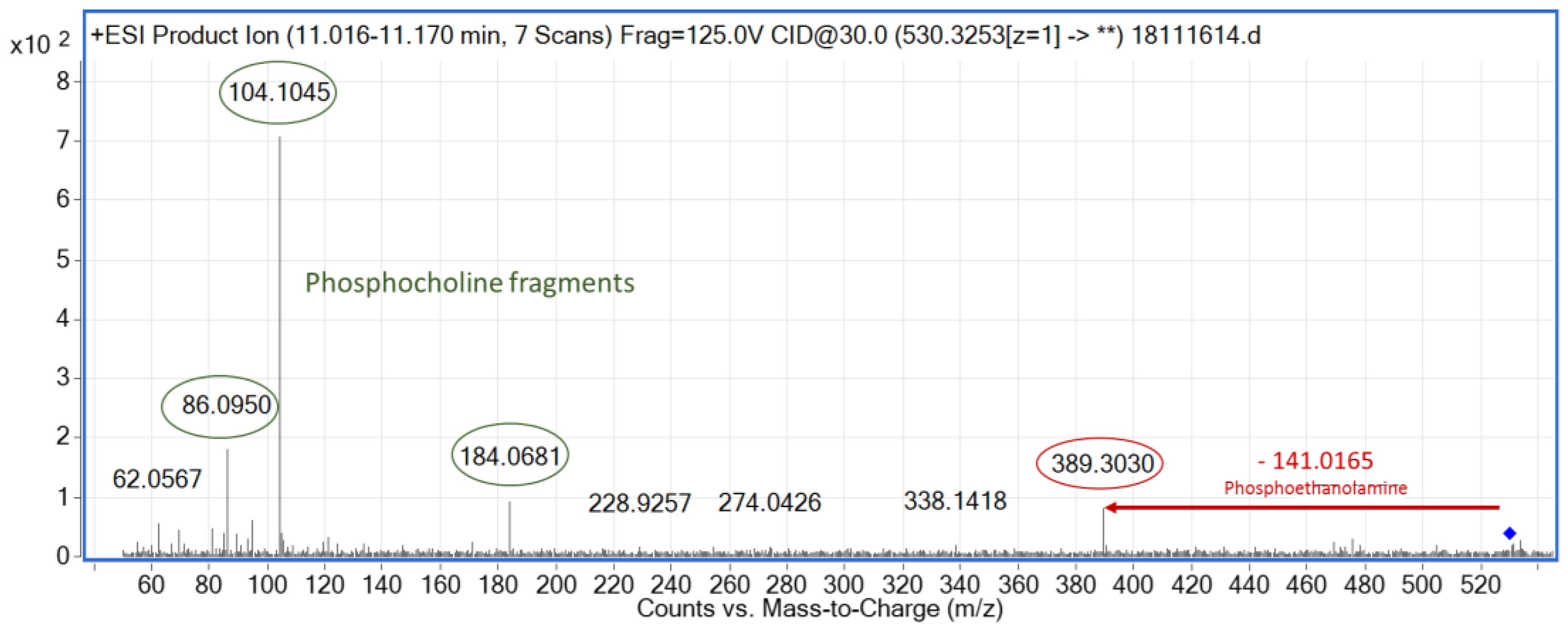
3.3. MS/MS-Based Metabolite Annotation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kimland, E.; Odlind, V. Off-Label Drug Use in Pediatric Patients. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 91, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Rosenbaum, S. Developmental Pharmacokinetics in Pediatric Populations. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 19, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kshirsagar, N.; Swaminathan, S.; Jog, P.; Dalwai, S.; Mathur, R.; Shekhar, C.; Meibohm, B.; Gupta, Y.K.; Shafiq, N.; Sunkara, G.; et al. Regulatory and Ethical Issues in Pediatric Clinical Research: Recommendations from a Panel Discussion. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 57, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tefera, Y.G.; Gebresillassie, B.M.; Mekuria, A.B.; Abebe, T.B.; Erku, D.; Seid, N.; Beshir, H.B. Off-label drug use in hospitalized children: A prospective observational study at Gondar University Referral Hospital, Northwestern Ethiopia. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2017, 5, e00304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, J.; Conroy, S.; Avery, A.; Corns, H.; Choonara, I. Unlicensed and off label prescribing of drugs in general practice. Arch. Dis. Child. 2000, 83, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, R.; Wood, B. Drug Dosage for Children. Lancet 1967, 290, 1350–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lack, J.A.; E Stuart-Taylor, M. Calculation of drug dosage and body surface area of children. Br. J. Anaesth. 1997, 78, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, H.K.; Marriott, J.F. Paediatric pharmacokinetics: Key considerations. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 79, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, S.P.; Nakayama, Y.; Matsuda, F.; Uchikata, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Matsubara, A.; Fukusaki, E. Current metabolomics: Practical applications. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2013, 115, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, M.G.; Ganguly, R.; Rich, K.A.; Fox, A.; Mattox, L.; Keckley, E.; Joseph, M.; Malbrue, R.; Youngblood, B.; Krishna, V.; et al. Continual cerebrospinal fluid sampling in the neonatal domestic piglet for biomarker and discovery studies. J. Neurosci. Methods 2021, 366, 109403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterloo, B.C.; Premkumar, M.; Stoll, B.; Olutoye, O.; Thymann, T.; Sangild, P.T.; Burrin, D.G. Dual purpose use of preterm piglets as a model of pediatric GI disease. Veter-Immunol. Immunopathol. 2014, 159, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, M.E.; González, O.; Albóniga, O.E.; Alonso, M.L.; Alonso, R.M. Metabolomic analysis for the study of maturation in pediatrics: Effect of confounding factors in a pilot study. Electrophoresis 2017, 38, 2323–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalabre, A.; Jobard, E.; Demède, D.; Gaillard, S.; Pontoizeau, C.; Mouriquand, P.; Elena-Herrmann, B.; Mure, P.-Y. Evolution of Newborns’ Urinary Metabolomic Profiles according to Age and Growth. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 3732–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sussulini, A. Erratum to: Chapters 1 and 11 of Metabolomics: From Fundamentals to Clinical Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 965, pp. E1–E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Smith, C.A.; Brandon, T.R.; Uritboonthai, W.; Qin, C.; Trauger, A.S.A.; Siuzdak, G. Solvent-Dependent Metabolite Distribution, Clustering, and Protein Extraction for Serum Profiling with Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2005, 78, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cajka, T.; Fiehn, O. Toward Merging Untargeted and Targeted Methods in Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics and Lipidomics. Anal. Chem. 2015, 88, 524–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, R.; Abliz, Z. Methods used to increase the comprehensive coverage of urinary and plasma metabolomes by MS. Bioanalysis 2016, 8, 981–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issaq, H.J.; Xiao, Z.; Veenstra, T.D. Serum and Plasma Proteomics. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 3601–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S. Advances in metabolite identification. Bioanalysis 2011, 3, 1769–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, W.J.; Dunn, W.B. From mass to metabolite in human untargeted metabolomics: Recent advances in annotation of metabo-lites applying liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry data. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 120, 115324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, J.D.; Tabb, D.L.; Mallick, P. Employing ProteoWizard to convert raw mass spectrometry data. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2014, 46, 13.24.1–13.24.9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tautenhahn, R.; Böttcher, C.; Neumann, S. Highly sensitive feature detection for high resolution LC/MS. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.A.; Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS: Processing Mass Spectrometry Data for Metabolite Profiling Using Nonlinear Peak Alignment, Matching, and Identification. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libiseller, G.; Dvorzak, M.; Kleb, U.; Gander, E.; Eisenberg, T.; Madeo, F.; Neumann, S.; Trausinger, G.; Sinner, F.; Pieber, T.; et al. IPO: A tool for automated optimization of XCMS parameters. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albóniga, O.E.; González, O.; Alonso, R.M.; Xu, Y.; Goodacre, R. Optimization of XCMS parameters for LC–MS metabolomics: An assessment of automated versus manual tuning and its effect on the final results. Metabolomics 2020, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhl, C.; Tautenhahn, R.; Boettcher, C.; Larson, T.R.; Neumann, S. CAMERA: An integrated strategy for compound spectra ex-traction and annotation of liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry data sets. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Begley, P.; Zelena, E.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Anderson, N.; Brown, M.; Knowles, J.D.; Halsall, A.; Haselden, J.N.; et al. Procedures for large-scale metabolic profiling of serum and plasma using gas chromatography and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1060–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viant, M.R.; Kurland, I.J.; Jones, M.R.; Dunn, W. How close are we to complete annotation of metabolomes? Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2017, 36, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worley, B.; Powers, R. Multivariate analysis in metabolomics. Curr. Metab. 2013, 1, 92–107. [Google Scholar]
- Gromski, P.S.; Muhamadali, H.; Ellis, D.I.; Xu, Y.; Correa, E.; Turner, M.L.; Goodacre, R. A tutorial review: Metabolomics and partial least squares-discriminant analysis—A marriage of convenience or a shotgun wedding. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 879, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Marsal, S.; Juliã, A. Analytical Methods in Untargeted Metabolomics: State of the Art in 2015. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, R.; Xiang, Y.; Harrington, P.B. Diagnosis of patients with chronic kidney disease by using two fuzzy classifiers. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2016, 153, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, R.M.; Correa, D.N.; Rocha, W.F.C.; Scafi, F.J.O.; Poppi, R.J. Discrimination between authentic and counterfeit banknotes using raman spectroscopy and PLS-DA with uncertainty estimation. Microchem. J. 2013, 109, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromski, P.S.; Correa, E.; Vaughan, A.A.; Wedge, D.; Turner, M.; Goodacre, R. A comparison of different chemometrics approaches for the robust classification of electronic nose data. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 7581–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Pérez, R.; Fernández, L.; Marco, S. Overoptimism in cross-validation when using partial least squares-discriminant analysis for omics data: A systematic study. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5981–5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, E.; Saccenti, E.; Smilde, A.K.; Westerhuis, J.A. Double-check: Validation of diagnostic statistics for PLS-DA models in metabolomics studies. Metabolomics 2011, 8, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Correa, E.; Goodacre, R. Integrating multiple analytical platforms and chemometrics for comprehensive metabolic profiling: Application to meat spoilage detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 5063–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Goodacre, R. Multiblock principal component analysis: An efficient tool for analyzing metabolomics data which contain two influential factors. Metabolomics 2011, 8, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhuis, J.A.; Kourti, T.; Macgregor, J.F. Analysis of multiblock and hierarchical PCA and PLS models. J. Chemom. 1998, 12, 301–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; O’Maille, G.; Want, E.J.; Qin, C.; Trauger, S.A.; Brandon, T.R.; Custidio, D.E.; Darlene, E.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. METLIN: A metabolite mass spectral database. Ther. Drug. Monit. 2005, 27, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Tzur, D.; Knox, C.; Eisner, R.; Guo, A.C.; Young, N.; Cheng, D.; Jewell, K.; Arndt, D.; Sawhney, S.; et al. HMDB: The Human Metabolome Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D521–D526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistrik, R. mzCLOUD: A spectral tree library for the identification of “unknown unknowns”. Abstracts of Papers. In Proceedings of the 255th ACS National Meeting & Exposition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–22 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Li, R.; Zhou, J.; Zuniga, A.; Stanislaus, A.E.; Wu, Y.; Huan, T.; Zheng, J.; Shi, Y.; Wishart, D.S.; et al. MyCompoundID: Using an Evidence-Based Metabolome Library for Metabolite Identification. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3401–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, V.B.; Dennis, E.A.; Wakelam, M.J.O.; Subramaniam, S. LIPID MAPS: Serving the next generation of lipid researchers with tools, resources, data, and training. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaaw2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochat, B. Proposed Confidence Scale and ID Score in the Identification of Known-Unknown Compounds Using High Resolution MS Data. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 28, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godzien, J.; Ciborowski, M.; Martinez-Alcazar, M.P.; Samczuk, P.; Kretowski, A.; Barbas, C. Rapid and reliable identification of phospholipids for untargeted metabolomics with LC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS. J. Proteome. Res. 2015, 14, 3204–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Han, X.; Mancuso, D.J.; Abendschein, D.R.; Gross, R.W. Accumulation of long-chain acylcarnitine and 3-hydroxy acylcarnitine molecular species in diabetic myocardium: Identification of alterations in mitochondrial fatty acid processing in diabetic my-ocardium by shotgun lipidomics. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 5234–5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.H., 4th; Poston, P.A.; Karnes, H.T. A quantitative method for acylcarnitines and amino acids using high resolution chro-matography and tandem mass spectrometry in newborn screening dried blood spot analysis. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2012, 903, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuniga, A.; Li, L. Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for comprehensive analysis of urinary acylcarnitines. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 689, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciborowski, M.; Teul, J.; Martín-Ventura, J.L.; Egido, J.; Barbas, C. Metabolomics with LC-QTOF-MS Permits the Prediction of Disease Stage in Aortic Abdominal Aneurysm Based on Plasma Metabolic Fingerprint. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quehenberger, O.; Armando, A.M.; Brown, A.H.; Milne, S.B.; Myers, D.S.; Merrill, A.H.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Jones, K.N.; Kelly, S.; Shaner, R.L.; et al. Lipidomics reveals a remarkable diversity of lipids in human plasma. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 3299–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quehenberger, O.; Dennis, E.A. The Human Plasma Lipidome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1812–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailte, I.; Lingelem, A.B.D.; Kavaliauskiene, S.; Bergan, J.; Kvalvaag, A.S.; Myrann, A.-G.; Skotland, T.; Sandvig, K. Addition of lysophospholipids with large head groups to cells inhibits Shiga toxin binding. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindou, H.; Shimizu, T. Acyl-CoA:Lysophospholipid acyltransferases. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, B.; Schiller, J. Lysophospholipids: Their generation, physiological role and detection. are they important disease markers? Mini. Rev. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatomi, Y.; Kurano, M.; Ikeda, H.; Igarashi, K.; Kano, K.; Aoki, J. Lysophospholipids in laboratory medicine. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2018, 94, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostoni, C.; Bruzzese, M.G. Fatty acids: Their biochemical and functional classification. Pediatr. Medica Chir. 1992, 14, 473–479. [Google Scholar]
- Cavedon, C.T.; Bourdoux, P.; Mertens, K.; Van Thi, H.V.; Herremans, N.; De Laet, C.; Goyens, P. Age-Related Variations in Acylcarnitine and Free Carnitine Concentrations Measured by Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Novak, M.; Wieser, P.B.; Buch, M.; Hahn, P. Acetylcarnitine and Free Carnitine in Body Fluids before and after Birth. Pediatr. Res. 1979, 13, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Algorithm | Parameter | ESI+ | ESI− |
|---|---|---|---|
| CentWave | ppm | 31.68 | 31 |
| peakwidth | 22.01, 81.26 | 20, 80 | |
| mzdiff | −0.0123 | −0.0120 | |
| Obiwarp | profStep | 0.7324 | 1 |
| gapInit | 0.7552 | 0.9280 | |
| gapExtend | 2.400 | 2.688 | |
| Density | Bw | 0.250 | 0.879 |
| mzwid | 0.0270 | 0.0342 |
| Plasma ESI+ | Plasma ESI− | |
|---|---|---|
| Total number after matrix filtering | 2207 | 1855 |
| ANOVA and FDR (p < 0.001) | 225 | 489 |
| Post-hoc Tukey HSD test (A ≠ B ≠ C) | 36 | 89 |
| Fulfil normality | 26 | 73 |
| Do not fulfil normality | 10 | 16 |
| Kruskal–Wallis (p <0.001) | 1 | 1 |
| Total significant features | 27 | 74 |
| Plasma ESI+ | Plasma ESI− | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m/z | RT (Min) | Regulation a | q-Value | Annotation | Ion Specie | m/z | RT (Min) | Regulation a | q-Value | Annotation | Ion Specie |
| 400.1157 | 6.6 | Up | 1.2 × 10−5 | Unknown | 398.0972 | 6.5 | Up | 4.55 × 10−9 | Unknown | - | |
| 364.0715 | 6.8 | Up | 4.43 × 10−5 | Unknown | 343.0242 | 6.8 | Up | 5.52 × 10−8 | Unknown | - | |
| 271.9848 | 6.8 | Up | 6.24 × 10−5 | Unknown | 457.0161 | 6.8 | Up | 3.70 × 10−9 | Unknown | - | |
| 212.5111 | 6.9 | Up | 1.06 × 10−5 | Unknown | 428.1105 | 7.7 | Up | 5.00 × 10−6 | Unknown | - | |
| 211.0713 | 10.4 | Up | 5.86 × 10−5 | Unknown | 415.1959 | 8.0 | Up | 1.16 × 10−9 | Unknown | - | |
| 200.2004 | 11.1 | Up | 2.35 × 10−4 | Unknown | 586.3141 | 10.0 | Up | 3.42 × 10−7 | LPC (20:5) | [M-COOH]− | |
| 714.2590 | 9.3 | Down | 2.28 × 10−5 | Unknown | 615.3475 | 10.7 | Up | 5.34 × 10−6 | LPC class | - | |
| 356.2795 | 9.7 | Down | 5.67 × 10−5 | Acylcarnitine | - | 411.2371 | 8.2 | Down | 1.00 × 10−14 | Unknown | - |
| 628.2926 | 10.5 | Down | 4.53 × 10−5 | Unknown | 350.2097 | 9.0 | Down | 2.68 × 10−9 | Unknown | - | |
| 544.3400 | 10.5 | Down | 2.51 × 10−4 | LPC (20:4) | [M+H]+ | 497.3464 | 9.4 | Down | 5.38 × 10−8 | Unknown | - |
| 300.6346 | 10.6 | Down | 1.74 × 10−4 | Unknown | 513.3004 | 9.9 | Down | 7.34 × 10−5 | Unknown | - | |
| 530.3254 | 11.0 | Down | 4.34 × 10−4 | LPE (22:4) | [M+H]+ | 447.3090 | 10.7 | Down | 1.51 × 10−10 | Unknown | - |
| LPC (17:1) | [M+Na]+ | 973.6249 | 10.9 | Down | 2.20 × 10−6 | Unknown | - | ||||
| 548.3703 | 11.5 | Down | 1.58 × 10−4 | LPC (20:2) | [M+H]+ | 478.2922 | 10.9 | Down | 1.72 × 10−5 | LPE (18:1) | [M-H]− |
| 235.0707 | 5.6 | Other | 2.32 × 10−4 | Unknown | - | ||||||
| 315.1055 | 6.0 | Other | 6.89 × 10−6 | Unknown | - | ||||||
| 230.0111 | 6.5 | Other | 3.96 × 10−6 | Unknown | - | ||||||
| 117.6456 | 8.1 | Other | 1.91 × 10−8 | Unknown | - | ||||||
| 815.5669 | 8.9 | Other | 1.38 × 10−4 | Unknown | - | ||||||
| 436.2815 | 11.0 | Other | 1.33 × 10−7 | LPE (15:1) | [M-H]− | ||||||
| 526.3490 | 11.5 | Other | 5.49 × 10−11 | Unknown | - | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albóniga, O.E.; González-Mendia, O.; Blanco, M.E.; Alonso, R.M. HPLC–(Q)-TOF-MS-Based Study of Plasma Metabolic Profile Differences Associated with Age in Pediatric Population Using an Animal Model. Metabolites 2022, 12, 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080739
Albóniga OE, González-Mendia O, Blanco ME, Alonso RM. HPLC–(Q)-TOF-MS-Based Study of Plasma Metabolic Profile Differences Associated with Age in Pediatric Population Using an Animal Model. Metabolites. 2022; 12(8):739. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080739
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbóniga, Oihane E., Oskar González-Mendia, María E. Blanco, and Rosa M. Alonso. 2022. "HPLC–(Q)-TOF-MS-Based Study of Plasma Metabolic Profile Differences Associated with Age in Pediatric Population Using an Animal Model" Metabolites 12, no. 8: 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080739
APA StyleAlbóniga, O. E., González-Mendia, O., Blanco, M. E., & Alonso, R. M. (2022). HPLC–(Q)-TOF-MS-Based Study of Plasma Metabolic Profile Differences Associated with Age in Pediatric Population Using an Animal Model. Metabolites, 12(8), 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080739