Probiotic Ameliorating Effects of Altered GABA/Glutamate Signaling in a Rodent Model of Autism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods:
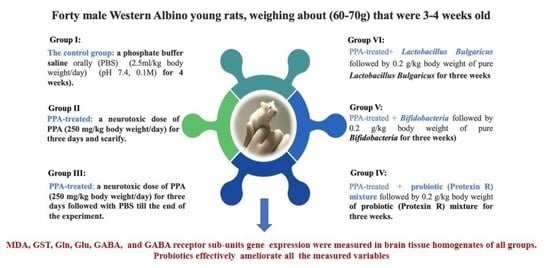
3.1. Animals
3.2. Preparation of Brain Tissue Homogenates
3.3. Biochemical Analyses
3.3.1. ELISA Measurements of GABA-Signaling-Related Markers
3.3.2. Measurement of Lipid Peroxidation Concentration
3.3.3. Assay of Glutathione (GSH)
3.4. Gene Expression
3.5. Microbial Analysis
3.5.1. Fecal Collection and Preparation for Microbial Analysis
3.5.2. Bacterial Enumeration and Identification
3.5.3. Statistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quaak, I.; Brouns, M.R.; Van De Bor, M. The Dynamics of Autism Spectrum Disorders: How Neurotoxic Compounds and Neurotransmitters Interact. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 3384–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Essa, M.M.; Braidy, N.; Vijayan, K.R.; Subash, S.; Guillemin, G.J. Excitotoxicity in the Pathogenesis of Autism. Neurotox. Res. 2013, 23, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ansary, A. GABA and Glutamate Imbalance in Autism and Their Reversal as Novel Hypothesis for Effective Treatment Strategy. Autism Dev. Disord. 2020, 18, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerriero, R.M.; Giza, C.C.; Rotenberg, A. Glutamate and GABA Imbalance Following Traumatic Brain Injury. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2015, 15, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The Microbiome-Gut-Brain Axis in Health and Disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 46, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.-K.; Shin, C. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Novel Treatments. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuaish, S.; Al-Otaibi, N.; Abujamel, T.; Alzahrani, S.; Alotaibi, S.; AlShawakir, Y.; Aabed, K.; El-Ansary, A. Fecal Transplant and Bifidobacterium Treatments Modulate Gut Clostridium Bacteria and Rescue Social Impairment and Hippocampal BDNF Expression in a Rodent Model of Autism. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzoli, R.; Pessione, E. The Neuro-endocrinological Role of Microbial Glutamate and GABA Signaling. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boonchooduang, N.; Louthrenoo, O.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C. Possible links between gut–microbiota and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorders in children and adolescents. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 3391–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunes, R.; Poluektova, E.; Dyachkova, M.; Klimina, K.; Kovtun, A.; Averina, O.; Orlova, V.; Danilenko, V. GABA production and structure of gadB / gadC genes in Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains from human microbiota. Anaerobe 2016, 42, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.A.; Forsythe, P.; Chew, M.V.; Escaravage, E.; Savignac, H.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Cryan, J.F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16050–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pellegrini-Giampietro, D.; Cherici, G.; Alesiani, M.; Carla, V.; Moroni, F. Excitatory amino acid release and free radical formation may cooperate in the genesis of ischemia-induced neuronal damage. J. Neurosci. 1990, 10, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richter, C.; Kass, G.E. Oxidative stress in mitochondria: Its relationship to cellular Ca2+ homeostasis, cell death, proliferation, and differentiation. Chem. Interact. 1991, 77, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schor, N.F. Inactivation of mammalian brain glutamine synthetase by oxygen radicals. Brain Res. 1988, 456, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.M.; Swanson, R.A. Astrocyte glutamate transport: Review of properties, regulation, and physiological functions. Glia 2000, 32, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ansary, A.K.; Ben Bacha, A.; Kotb, M. Etiology of autistic features: The persisting neurotoxic effects of propionic acid. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Ansary, A. Data of multiple regressions analysis between selected biomarkers related to glutamate excitotoxicity and oxidative stress in Saudi autistic patients. Data Brief 2016, 7, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aldbass, A.M.; Bhat, R.S.; El-Ansary, A. Protective and therapeutic potency of N-acetyl-cysteine on propionic acid-induced biochemical autistic features in rats. J. Neuroinflamm. 2013, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Gadani, Y.; El-Ansary, A.; Attas, O.; Al-Ayadhi, L. Metabolic biomarkers related to oxidative stress and antioxidant status in Saudi autistic children. Clin. Biochem. 2009, 42, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khemakhem, A.M.; Frye, R.E.; El-Ansary, A.; Al-Ayadhi, L.; Ben Bacha, A. Novel biomarkers of metabolic dysfunction is autism spectrum disorder: Potential for biological diagnostic markers. Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 1983–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duranti, S.; Ruiz, L.; Lugli, G.A.; Tames, H.; Milani, C.; Mancabelli, L.; Mancino, W.; Longhi, G.; Carnevali, L.; Sgoifo, A.; et al. Bifidobacterium adolescentis as a key member of the human gut microbiota in the production of GABA. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelli, L.S.; Samsam, A.; Naser, S.A. Propionic Acid Induces Gliosis and Neuro-inflammation through Modulation of PTEN/AKT Pathway in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Chang, N.; Wang, D.; Shan, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Feng, H.; Zhang, L.; et al. Preservation of GABA A Receptor Function by PTEN Inhibition Protects Against Neuronal Death in Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2010, 41, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wasilewska, J.; Klukowski, M. Gastrointestinal symptoms and autism spectrum disorder: Links and risks—A possible new overlap syndrome. Pediatr. Health Med. Ther. 2015, 6, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doenyas, C. Novel Personalized Dietary Treatment for Autism Based on the Gut-Immune-Endocrine-Brain Axis. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdellatif, B.; McVeigh, C.; Bendriss, G.; Chaari, A. The Promising Role of Probiotics in Managing the Altered Gut in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagleson, K.; Gravielle, M.; McFadyen-Ketchum, L.S.; Russek, S.; Farb, D.; Levitt, P. Genetic disruption of the autism spectrum disorder risk gene PLAUR induces GABAA receptor subunit changes. Neuroscience 2010, 168, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leblanc, J.J.; Fagiolini, M. Autism: A “Critical Period” Disorder? Neural Plast. 2011, 2011, 921680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, A.-K.; Krumsiek, J.; Wägele, B.; Theis, F.J.; Wichmann, H.-E.; Gieger, C.; Suhre, K. On the hypothesis-free testing of metabolite ratios in genome-wide and metabolome-wide association studies. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Otaish, H.; Al-Ayadhi, L.; Bjørklund, G.; Chirumbolo, S.; Urbina, M.A.; El-Ansary, A. Relationship between absolute and relative ratios of glutamate, glutamine and GABA and severity of autism spectrum disorder. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 33, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, U.; Möhler, H. Analysis of GABAA Receptor Function and Dissection of the Pharmacology of Benzodiazepines and General Anesthetics Through Mouse Genetics. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2004, 44, 475–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; Kaupmann, K. Don’t worry ‘B’ happy!: A role for GABAB receptors in anxiety and depression. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 26, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, R.L.; Kang, J.-Q.; Gallagher, M.J. GABAA Receptor Subunit Mutations and Genetic Epilepsies. In Jasper’s Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies [Internet], 4th ed; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, J.O.; Whelan, K.; Stagg, A.J.; Gobin, P.; Al-Hassi, H.O.; Rayment, N.; Kamm, M.A.; Knight, S.C.; Forbes, A. Clinical, microbiological, and immunological effects of fructo-oligosaccharide in patients with Crohn’s disease. Gut 2006, 55, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, N.; Liu, L. Microbial response to acid stress: Mechanisms and applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benjamin, J.L.; Hedin, C.; Koutsoumpas, A.; Ng, S.C.; McCarthy, N.; Hart, A.L.; Kamm, M.A.; Sanderson, J.D.; Knight, S.C.; Forbes, A.; et al. Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of fructo-oligosaccharides in active Crohn’s disease. Gut 2011, 60, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Dera, H.; Alrafaei, B.; AL Tamimi, M.I.; Alfawaz, H.A.; Bhat, R.S.; Soliman, D.A.; Abuaish, S.; El-Ansary, A. Leaky gut biomarkers in casein- and gluten-rich diet fed rat model of autism. Transl. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Broek, M.F.L.; De Boeck, I.; Claes, I.J.J.; Nizet, V.; Lebeer, S. Multifactorial inhibition of lactobacilli against the respiratory tract pathogen Moraxella catarrhalis. Benef. Microbes 2018, 9, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, C.-C.; Dai, Y.; Luo, Q.; Ji, Y.; Wang, K.; Deng, S.; Yu, J.; Xu, M.; Du, X.; et al. Symptom improvement in children with autism spectrum disorder following bumetanide administration is associated with decreased GABA/glutamate ratios. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santocchi, E.; Guiducci, L.; Prosperi, M.; Calderoni, S.; Gaggini, M.; Apicella, F.; Tancredi, R.; Billeci, L.; Mastromarino, P.; Grossi, E.; et al. Effects of Probiotic Supplementation on Gastrointestinal, Sensory and Core Symptoms in Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 550593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afroz, K.F.; Reyes, N.; Young, K.; Parikh, K.; Misra, V.; Alviña, K. Altered gut microbiome and autism like behavior are associated with parental high salt diet in male mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, S.J.; Tong, T.; Chew, J.; Lim, W.L. Antidepressive Mechanisms of Probiotics and Their Therapeutic Potential. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jackson, S.J.; Andrews, N.; Ball, D.; Bellantuono, I.; Gray, J.; Hachoumi, L.; Holmes, A.; Latcham, J.; Petrie, A.; Potter, P.; et al. Does age matter? The impact of rodent age on study outcomes. Lab. Anim. 2017, 51, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beutler, E.; Duron, O.; Kelly, B.M. Improved Methods for Determination of Blood Gluthatione. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1963, 61, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seol, D.; Choe, H.; Zheng, H.; Jang, K.; Ramakrishnan, P.S.; Lim, T.H.; Martin, J.A. Selection of reference genes for normalization of quantitative real-time PCR in organ culture of the rat and rabbit intervertebral disc. BMC Res. Notes 2011, 4, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Peng, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.; Wei, H. Isolation and identification of quercetin degrading bacteria from human fecal microbes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Control | PPA | PPA+ | PPA + BIF | PPA + LAC | PPA + MIX | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TBARS | 10.17 ± 3.528 | 43.61 ± 5.181 a** | 51.24 ± 6.843 a** | 33.30 ± 6.274 ac** | 40.68 ± 6.111 a** | 47.09 ± 10.41 a** |
| GSH | 81.62 ± 19.59 | 26.21 ± 15.94 a* | 41.16 ± 24.21 | 69.70 ± 45.15 | 27.39 ± 11.51 | 90.67 ± 27.27 bce* |
| GST | 18.55 ± 3.219 | 5.690 ± 3.775 | 9.010 ± 3.237 | 17.83 ± 6.741 | 6.135 ± 2.628 | 18.38 ± 5.644 |
| Glutamine | 136.4 ± 16.95 | 58.41 ± 14.36 a** | 77.76 ± 14.39 a** | 113.3 ± 16.67 bc* | 58.74 ± 10.18 d* | 72.11 ± 18.05 d** |
| Glutamate | 3.883 ± 0.6326 | 1.061 ± 0.2552 | 1.931 ± 0.4517 | 2.773 ± 0.8548 | 1.214 ± 0.1813 | 2.033 ± 0.7631 |
| GABA | 283.5 ± 59.00 | 143.0 ± 24.02 a** | 152.3 ± 34.06 a* | 347.8 ± 80.01 bc* | 142.0 ± 29.95 d* | 278.7 ± 67.55 b* |
| GABARA | 9.912 ± 1.587 | 1.752 ± 0.8360 a** | 3.096 ± 0.9080 a** | 6.479 ± 2.550 bd* | 1.324 ± 0.7396 a* | 4.493 ± 2.594 a* |
| Control | PPA | PPA+ | PPA + BIF | PPA + LAC | PPA + MIX | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
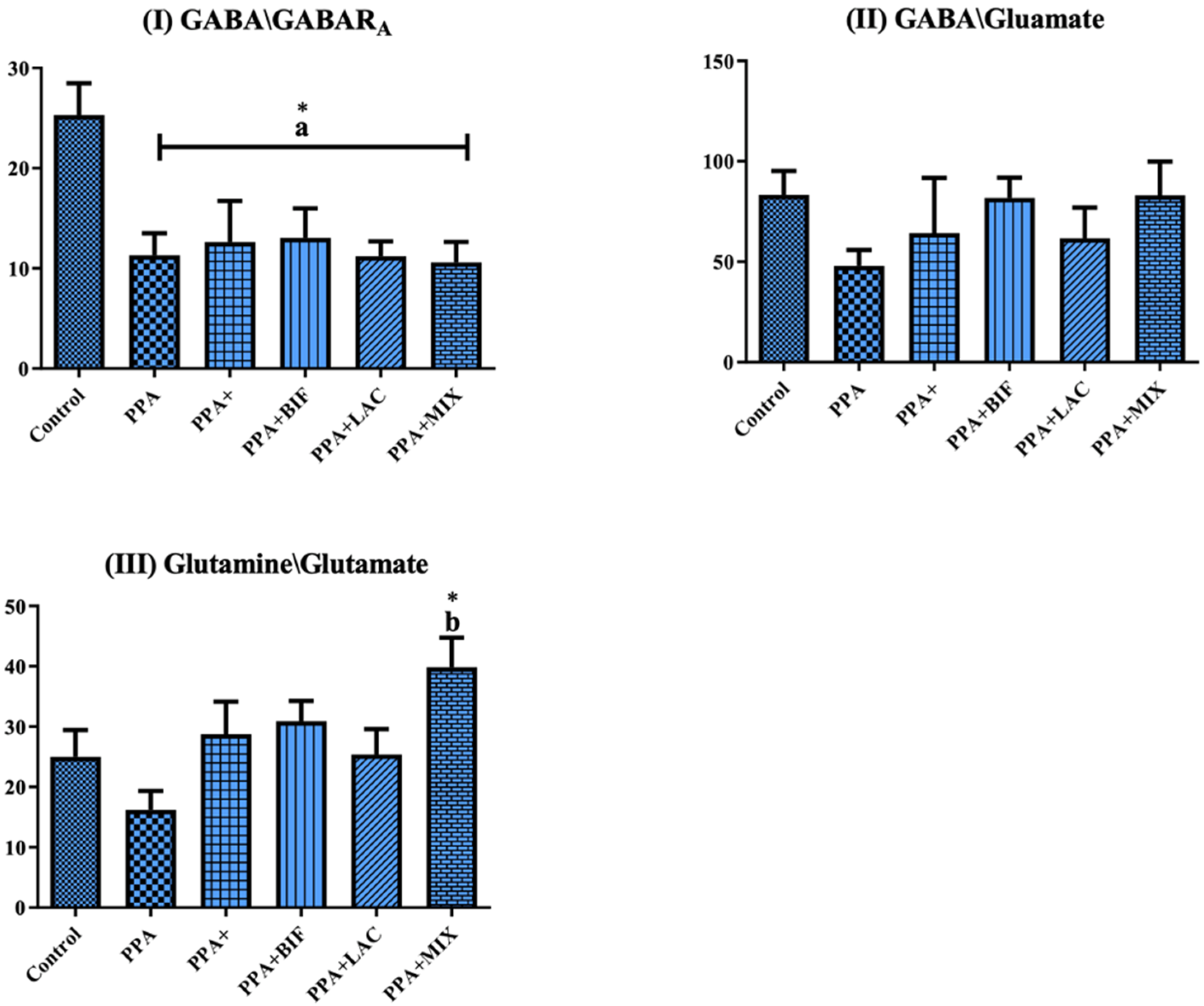
| GABA/GABARA | 25.32 ± 7.092 | 11.32 ± 5.397 a* | 12.64 ± 10.00 a* | 13.05 ± 8.337 a* | 11.21 ± 3.899 a* | 10.59 ± 5.425 a* |
| GABA/Glutamate | 83.27 ± 26.58 | 47.92 ± 19.39 | 64.26 ± 67.62 | 81.82 ± 28.73 | 61.63 ± 40.50 | 83.06 ± 44.28 |
| Glutamine/glutamate | 25.00 ± 9.945 | 16.18 ± 7.730 | 28.72 ± 13.32 | 30.90 ± 9.489 | 25.38 ± 11.18 | 39.86 ± 12.84 b* |
| Control | PPA | PPA+ | PPA + BIF | PPA + LAC | PPA + MIX | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GABARA1 | 1 ± 0.409 | 0.0716 ± 0.0089 * | 1.878 ± 0.086 * | 2.493 ± 0.291 ** | 2.049 ± 0.0789 * | 0.0371 ± 0.00073 ** |
| GABARA2 | 1 ± 0.162 | 0.0116 ± 0.007 ** | 0.924 ± 0.056401 * | 1.574 ± 0.336 * | 0.310 ± 0.044 * | 0.0259 ± 0.0026 ** |
| GABARA3 | 1 ± 0.027 | 0.00036 ± 5.18046 × 10−5 ** | 0.648 ± 0.024 ** | 1.132 ± 0.119 ** | 0.256 ± 0.0213 ** | 0.00059 ± 0.00015 ** |
| GABARA5 | 1 ± 0.108 | 0.0070 ± 0.0011 ** | 0.564 ± 0.030 ** | 0.683 ± 0.038 ** | 0.142 ± 0.004 ** | 0.019 ± 0.002 ** |
| GABARB2 | 1 ± 0.0195 | 0.066 ± 0.0137 * | 1.076 ± 0.135 * | 1.608 ± 0.269 * | 0.677 ± 0.662 | 0.038 ± 0.00196 ** |
| GABARB3 | 1 ± 0.158 | 0.00025 ± 0.00011 * | 1.089 ± 0.0064 * | 2.099 ± 0.215 ** | 0.561 ± 0.087 * | 6.81 × 10−5 ± 8.92 × 10−5 * |
| GABARG2 | 1 ± 0.199 | 0.0410 ± 0.00322 * | 0.611 ± 0.028 * | 1.181 ± 0.1609 * | 0.2875 ± 0.0266 * | 0.01715 ± 0.0017 * |
| Isolated Organisms | Media and Incubation Conditions | Control | PPA+ | PPA + BIF | PPA + LAC | PPA + MIX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enterobacteriaceae (Gram-negative rod, lactose fermenters) | MCA/aerobic 37 °C/24 h | + | - | ++ | +++ | ++ |
| Staphylococcus and/or Bacilli (Gram-positive cocci/rod or Gram-negative rod) | NA/aerobic 37 °C/24 h | - | - | +++ | + | ++ |
| Moraxella spp. | MHA/aerobic 37 °C/24 h | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Gram-negative | ||||||
| Gram-positive/Gram-negative rod and positive cocci | Blood/aerobic 37 °C/24 h | - | ++ | ++ | - | + |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bin-Khattaf, R.M.; Alonazi, M.A.; Al-Dbass, A.M.; Almnaizel, A.T.; Aloudah, H.S.; Soliman, D.A.; El-Ansary, A.K. Probiotic Ameliorating Effects of Altered GABA/Glutamate Signaling in a Rodent Model of Autism. Metabolites 2022, 12, 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080720
Bin-Khattaf RM, Alonazi MA, Al-Dbass AM, Almnaizel AT, Aloudah HS, Soliman DA, El-Ansary AK. Probiotic Ameliorating Effects of Altered GABA/Glutamate Signaling in a Rodent Model of Autism. Metabolites. 2022; 12(8):720. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080720
Chicago/Turabian StyleBin-Khattaf, Rawan M., Mona A. Alonazi, Abeer M. Al-Dbass, Ahmad T. Almnaizel, Hisham S. Aloudah, Dina A. Soliman, and Afaf K. El-Ansary. 2022. "Probiotic Ameliorating Effects of Altered GABA/Glutamate Signaling in a Rodent Model of Autism" Metabolites 12, no. 8: 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080720
APA StyleBin-Khattaf, R. M., Alonazi, M. A., Al-Dbass, A. M., Almnaizel, A. T., Aloudah, H. S., Soliman, D. A., & El-Ansary, A. K. (2022). Probiotic Ameliorating Effects of Altered GABA/Glutamate Signaling in a Rodent Model of Autism. Metabolites, 12(8), 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080720