A Serum Metabolite Classifier for the Early Detection of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-Positive Hepatocellular Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
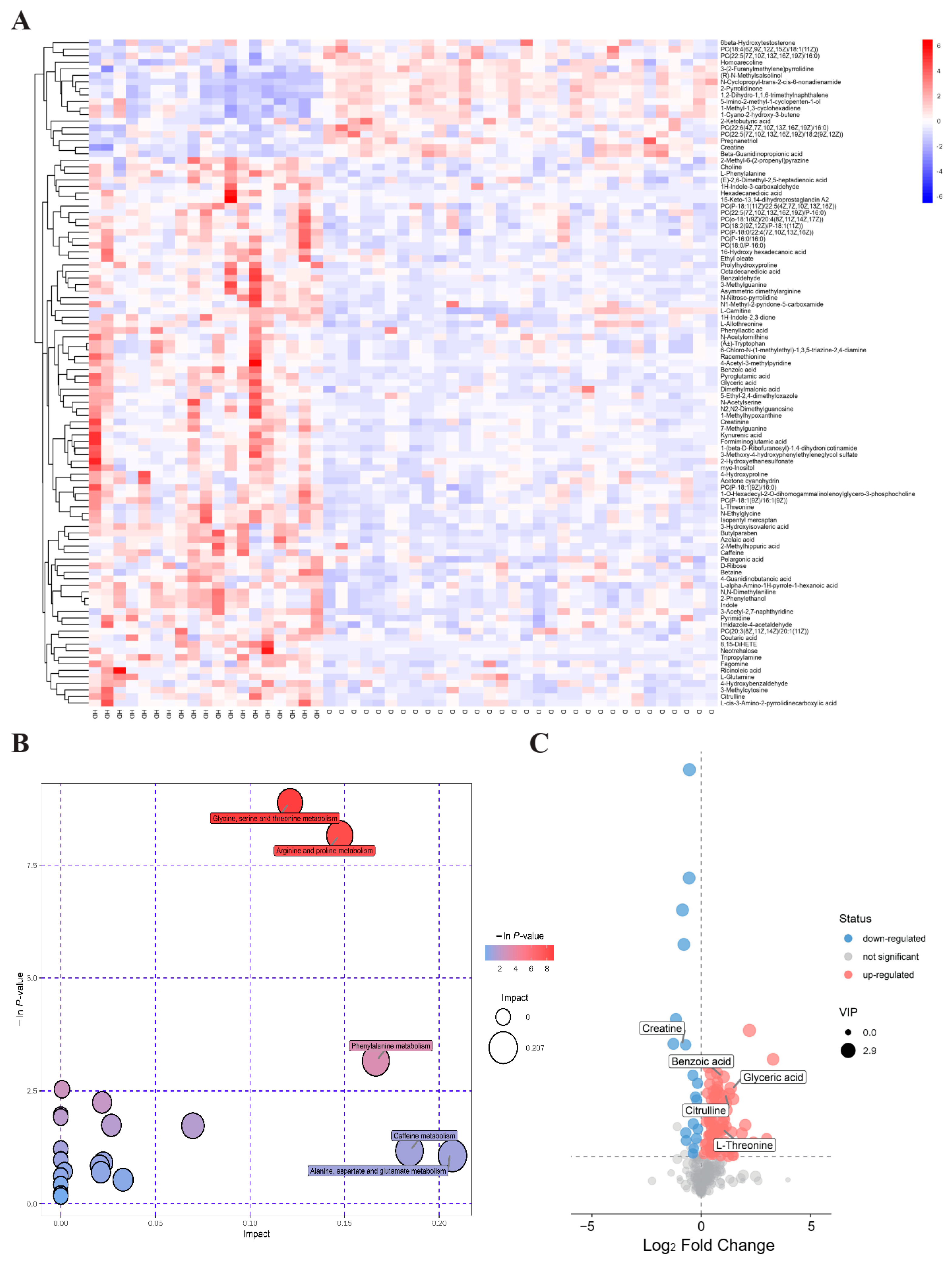
2.1. Serum Metabolomic Profiling Identified Significantly Dysregulated Metabolites in T2DM(+) HCC
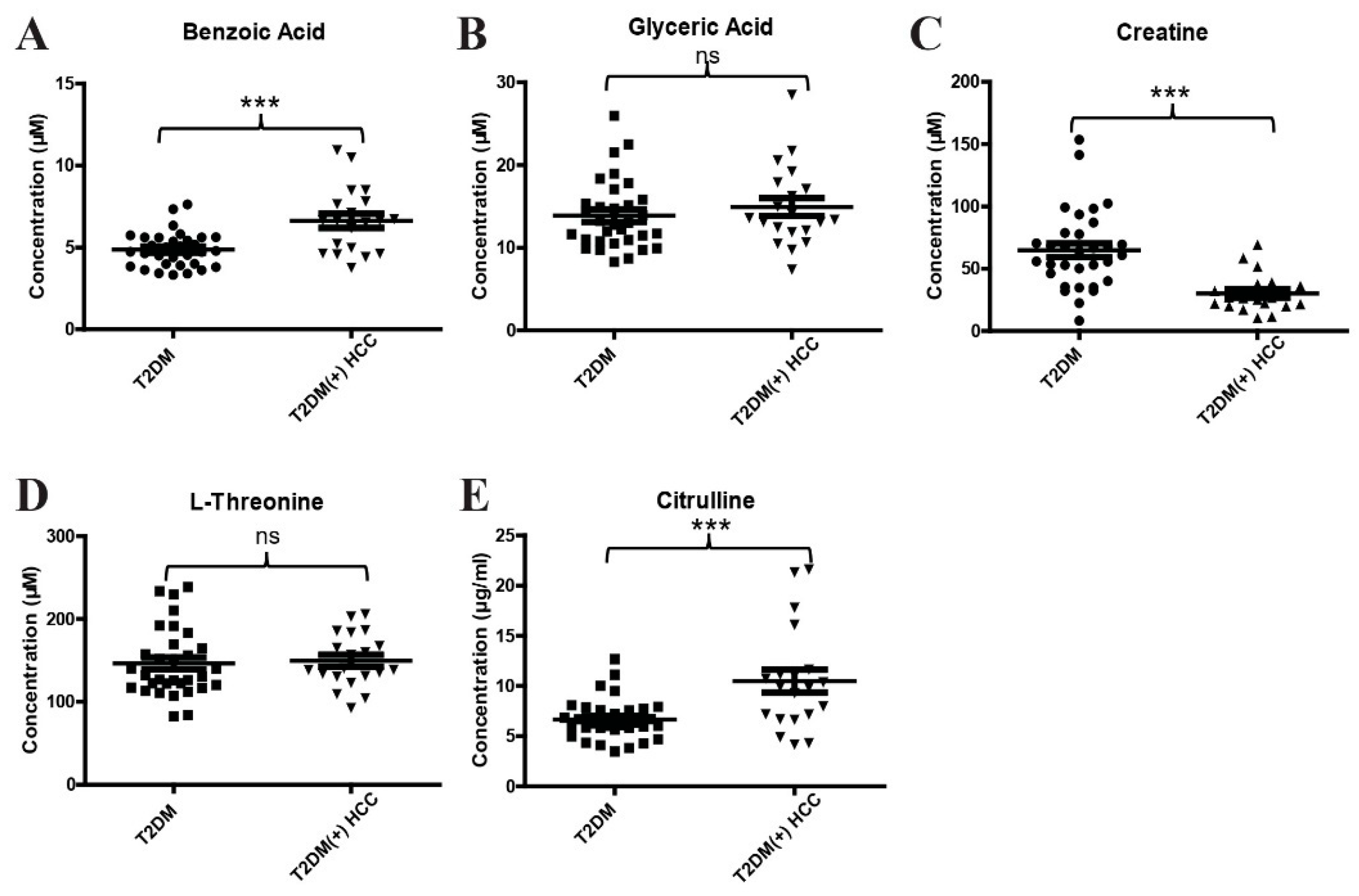
2.2. Validation of Differential Metabolites by Targeted Metabolite Analyses
2.3. Evaluation of the Diagnostic Performance of the Metabolite Classifier That Incorporates Benzoic Acid, Creatine, and Citrulline
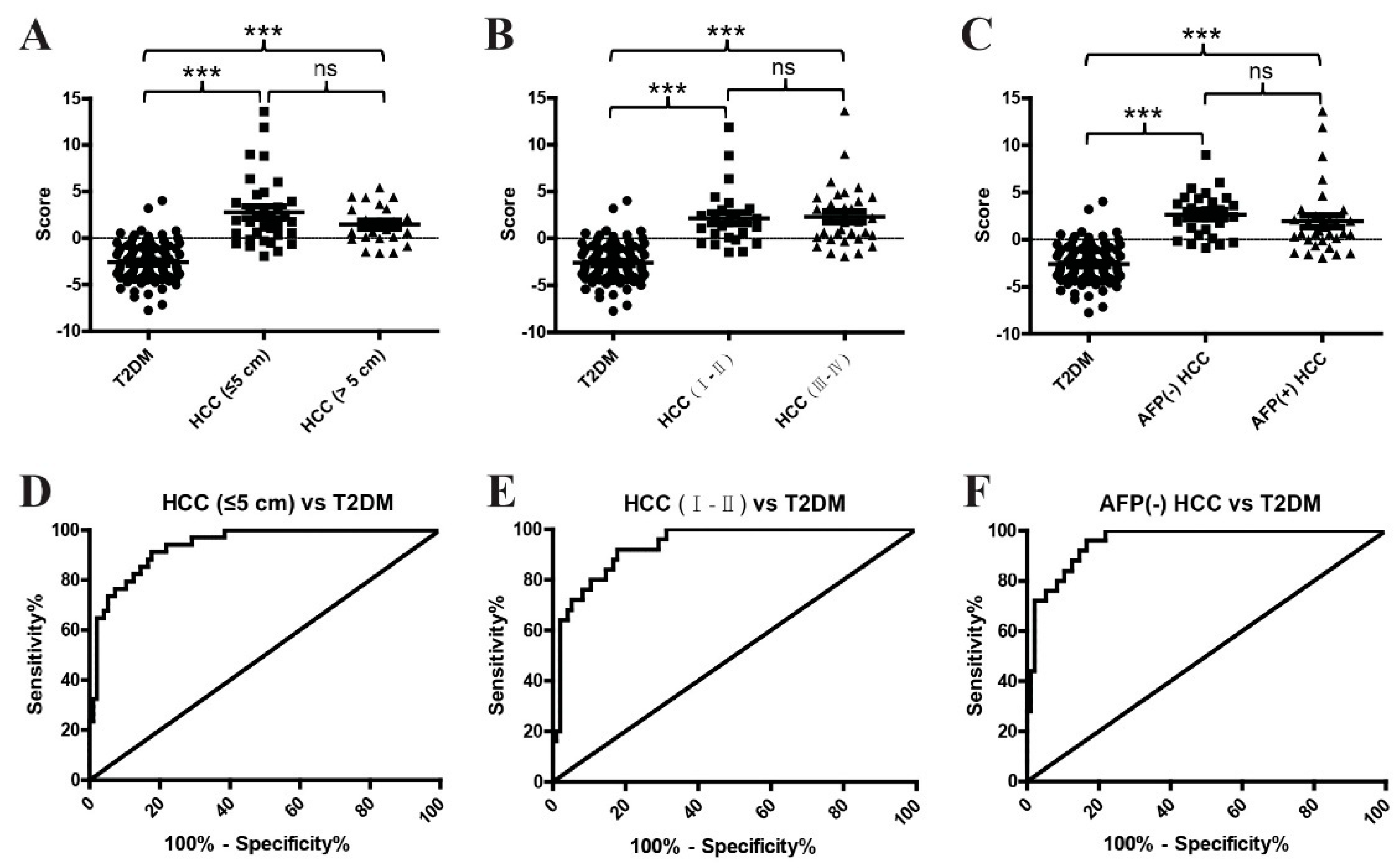
2.4. The Diagnostic Performance of the Metabolite Classifier in Small-Size, Early-Stage, and AFP-Negative T2DM(+) HCC
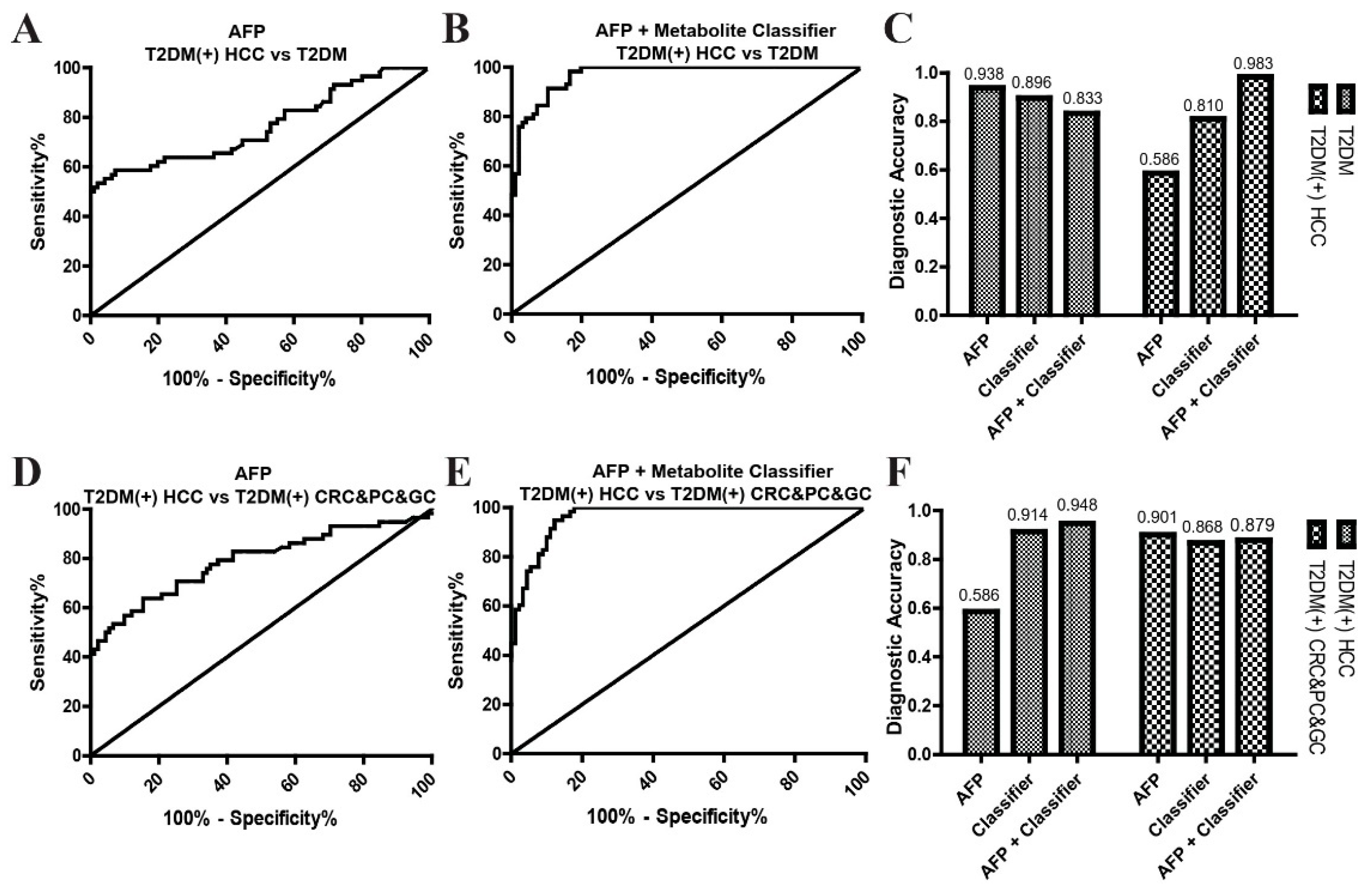
2.5. The Combination of the Metabolite Classifier and AFP in the Diagnosis of T2DM(+) HCC
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Study Population
5.2. Chemicals and Reagents
5.3. Measurement of Clinical Indicators
5.4. Untargeted Metabolomic Analyses
5.5. Targeted Metabolite Analyses
5.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGlynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2021, 73 (Suppl. 1), 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Pikarsky, E.; Sangro, B.; Schwartz, M.; Sherman, M.; Gores, G. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, E.G.; Farinati, F.; Ciccarese, F.; Pecorelli, A.; Rapaccini, G.L.; Di Marco, M.; Benvegnù, L.; Caturelli, E.; Zoli, M.; Borzio, F.; et al. Prognosis of untreated hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2015, 61, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Serag, H.B.; Tran, T.; Everhart, J.E. Diabetes increases the risk of chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davila, J.A.; Morgan, R.O.; Shaib, Y.; McGlynn, K.A.; El-Serag, H.B. Diabetes increases the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States: A population based case control study. Gut 2005, 54, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, W.P.; Wang, R.; Jin, A.; Yu, M.C.; Yuan, J.M. Diabetes mellitus and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: Findings from the Singapore Chinese Health Study. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasmari, A.J.; Welch, A.; Liu, G.; Leslie, D.; McGarrity, T.; Riley, T. Independent of Cirrhosis, Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk Is Increased with Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome. Am. J. Med. 2017, 130, 746.e1–746.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Ferrannini, E.; Groop, L.; Henry, R.R.; Herman, W.H.; Holst, J.J.; Hu, F.B.; Kahn, C.R.; Raz, I.; Shulman, G.I.; et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilidis, K.K.; Kasimis, J.C.; Lopez, D.S.; Ntzani, E.E.; Ioannidis, J.P. Type 2 diabetes and cancer: Umbrella review of meta-analyses of observational studies. BMJ 2015, 350, g7607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suh, S.; Kim, K.W. Diabetes and Cancer: Cancer Should Be Screened in Routine Diabetes Assessment. Diabetes Metab. J. 2019, 43, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogurtsova, K.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Huang, Y.; Linnenkamp, U.; Guariguata, L.; Cho, N.H.; Cavan, D.; Shaw, J.E.; Makaroff, L.E. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 128, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Hu, F.B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, F.; Singal, A.G. Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current Best Practice and Future Direction. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beudeker, B.J.B.; Boonstra, A. Circulating biomarkers for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820931734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newgard, C.B. Metabolomics and Metabolic Diseases: Where Do We Stand? Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satriano, L.; Lewinska, M.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Banales, J.M.; Andersen, J.B. Metabolic rearrangements in primary liver cancers: Cause and consequences. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 748–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimhofer, T.; Fye, H.; Taylor-Robinson, S.; Thursz, M.; Holmes, E. Proteomic and metabonomic biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma: A comprehensive review. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1141–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, P.; Yin, P.; Hua, R.; Tan, Y.; Li, Z.; Qiu, G.; Yin, Z.; Xie, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; et al. A Large-scale, multicenter serum metabolite biomarker identification study for the early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.C.; Sun, L.Q.; Shao, L.; Yi, L.Z.; Li, N.; Fan, X.G. Establishment of a pattern recognition metabolomics model for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 4607–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrarini, A.; Di Poto, C.; He, S.; Tu, C.; Varghese, R.S.; Kara Balla, A.; Jayatilake, M.; Li, Z.; Ghaffari, K.; Fan, Z.; et al. Metabolomic Analysis of Liver Tissues for Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 3067–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Han, M.L.; Xing, H.; Li, Z.L.; Yuan, D.Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.D.; Li, C.; Liang, L.; et al. Tissue and serum metabolomic phenotyping for diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 1741–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Xie, G.; Wang, X.; Fan, J.; Qiu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Qi, X.; Cao, Y.; Su, M.; Wang, X.; et al. Serum and urine metabolite profiling reveals potential biomarkers of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2011, 10, M110.004945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.; Zhu, B.; Zheng, R.; Zhao, X.; Yin, P.; Lu, X.; Jiao, B.; Xu, G.; Yao, Z. Development of urinary pseudotargeted LC-MS-based metabolomics method and its application in hepatocellular carcinoma biomarker discovery. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 906–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, P.J.; Bazelier, M.T.; Leufkens, H.G.; de Vries, F.; De Bruin, M.L. The risk of colorectal cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes: Associations with treatment stage and obesity. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, Y.; Kartsonaki, C.; Guo, Y.; Bragg, F.; Yang, L.; Bian, Z.; Chen, Y.; Iona, A.; Millwood, I.Y.; Lv, J.; et al. Diabetes, plasma glucose and incidence of pancreatic cancer: A prospective study of 0.5 million Chinese adults and a meta-analysis of 22 cohort studies. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sekikawa, A.; Fukui, H.; Maruo, T.; Tsumura, T.; Okabe, Y.; Osaki, Y. Diabetes mellitus increases the risk of early gastric cancer development. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.K.; Das, B.K.; Choudhary, S.; Gupta, D.; Patil, U.K. Diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma: A pathophysiological link and pharmacological management. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banales, J.M.; Iñarrairaegui, M.; Arbelaiz, A.; Milkiewicz, P.; Muntane, J.; Muñoz-Bellvis, L.; La Casta, A.; Gonzalez, L.M.; Arretxe, E.; Alonso, C.; et al. Serum Metabolites as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Cholangiocarcinoma, Hepatocellular Carcinoma, and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. Hepatology 2019, 70, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Q.; Tan, Y.; Yin, P.; Ye, G.; Gao, P.; Lu, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, G. Metabolic characterization of hepatocellular carcinoma using nontargeted tissue metabolomics. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 4992–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, J.; Qin, W.X.; Li, Z.L.; Xu, A.J.; Xing, H.; Wu, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.D.; Li, C.; Liang, L.; et al. Tissue and serum metabolite profiling reveals potential biomarkers of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 488, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wainwright, P.; Scorletti, E.; Byrne, C.D. Type 2 Diabetes and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Risk Factors and Pathogenesis. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2017, 17, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, H.; Chen, J.; Sekar, K.; Shi, M.; Xie, T.; Hui, K.M. Clinical and metabolomics analysis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients with diabetes mellitus. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakehashi, A.; Suzuki, S.; Ishii, N.; Okuno, T.; Kuwae, Y.; Fujioka, M.; Gi, M.; Stefanov, V.; Wanibuchi, H. Accumulation of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine, L-arginine and Glucose Metabolites by Liver Tumor Cells Are the Important Characteristic Features of Metabolic Syndrome and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis-Associated Hepatocarcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Liu, X.; Cheng, C.; Yu, W.; Yi, P. Metabolism of Amino Acids in Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 603837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieu, E.L.; Nguyen, T.; Rhyne, S.; Kim, J. Amino acids in cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepien, M.; Keski-Rahkonen, P.; Kiss, A.; Robinot, N.; Duarte-Salles, T.; Murphy, N.; Perlemuter, G.; Viallon, V.; Tjønneland, A.; Rostgaard-Hansen, A.L.; et al. Metabolic perturbations prior to hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis: Findings from a prospective observational cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 148, 609–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Lu, Q.; Liu, X.; Cong, H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Lin, D. Application of 1H NMR-based metabonomics in the study of metabolic profiling of human hepatocellular carcinoma and liver cirrhosis. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 782–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, I.J.; Aliev, A.E.; Crossey, M.M.; Dawood, M.; Al-Mahtab, M.; Akbar, S.M.; Rahman, S.; Riva, A.; Williams, R.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D. Urinary nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of a Bangladeshi cohort with hepatitis-B hepatocellular carcinoma: A biomarker corroboration study. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 4191–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, F.F.; Song, Y.N.; Lu, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.Y.; Su, S.B. Analysis of plasma metabolic profile, characteristics and enzymes in the progression from chronic hepatitis B to hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging 2020, 12, 14949–14965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladep, N.G.; Dona, A.C.; Lewis, M.R.; Crossey, M.M.; Lemoine, M.; Okeke, E.; Shimakawa, Y.; Duguru, M.; Njai, H.F.; Fye, H.K.; et al. Discovery and validation of urinary metabotypes for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in West Africans. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, R.; Cheng, J.; Fan, C.; Shi, X.; Cao, Y.; Sun, B.; Ding, H.; Hu, C.; Dong, F.; Yan, X. Serum Metabolomics to Identify the Liver Disease-Specific Biomarkers for the Progression of Hepatitis to Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, R.; Zhang, X.; Rong, Z.; Xiu, B.; Yang, X.; Wang, C.; Hao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Duan, C.; et al. Non-invasive detection of hepatocellular carcinoma serum metabolic profile through surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 2475–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jee, S.H.; Kim, M.; Kim, M.; Yoo, H.J.; Kim, H.; Jung, K.J.; Hong, S.; Lee, J.H. Metabolomics Profiles of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in a Korean Prospective Cohort: The Korean Cancer Prevention Study-II. Cancer Prev. Res. 2018, 11, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, K.H.; Cheng, M.L.; Lo, C.J.; Lin, Y.H.; Lai, M.W.; Lin, W.R.; Yeh, C.T. Plasma phenylalanine and glutamine concentrations correlate with subsequent hepatocellular carcinoma occurrence in liver cirrhosis patients: An exploratory study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Society, C.D. Guideline for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in China (2020 edition). Chin. J. Diabetes 2021, 13, 315–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, W.M.; Jenner, A.M.; Proudfoot, J.M.; McKinley, A.J.; Hodgson, J.M.; Halliwell, B.; Croft, K.D. A metabolite profiling approach to identify biomarkers of flavonoid intake in humans. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 2309–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, G.F.; Meier-Augenstein, W.; Stöckler, S.; Surtees, R.; Rating, D.; Nyhan, W.L. Physiology and pathophysiology of organic acids in cerebrospinal fluid. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1993, 16, 648–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Fernandez, M.; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, P.; Anon Alvarez, M.E.; Rodriguez, F.; Menéndez, F.V.; Alonso, J.I. Simultaneous determination of creatinine and creatine in human serum by double-spike isotope dilution liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 3755–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Xie, M.; Han, J.; Yuan, D.; Yang, T.; Xie, Y. Development and validation of a rapid, selective, and sensitive LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of D- and L-amino acids in human serum: Application to the study of hepatocellular carcinoma. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 2517–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, X.; Kline, J.A.; Wang, M. Development, validation, and comparison of four methods to simultaneously quantify l-arginine, citrulline, and ornithine in human plasma using hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography and electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 1005, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
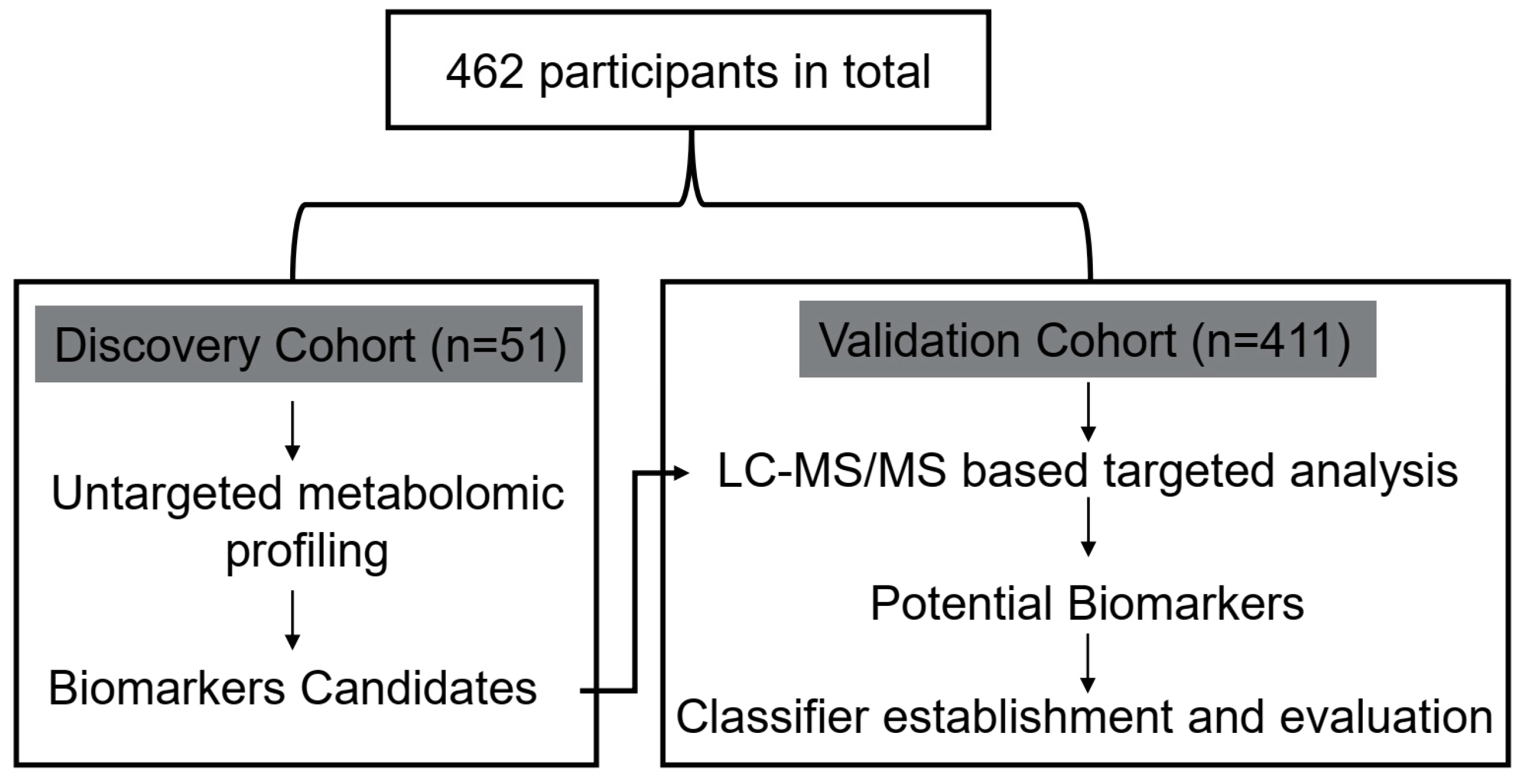
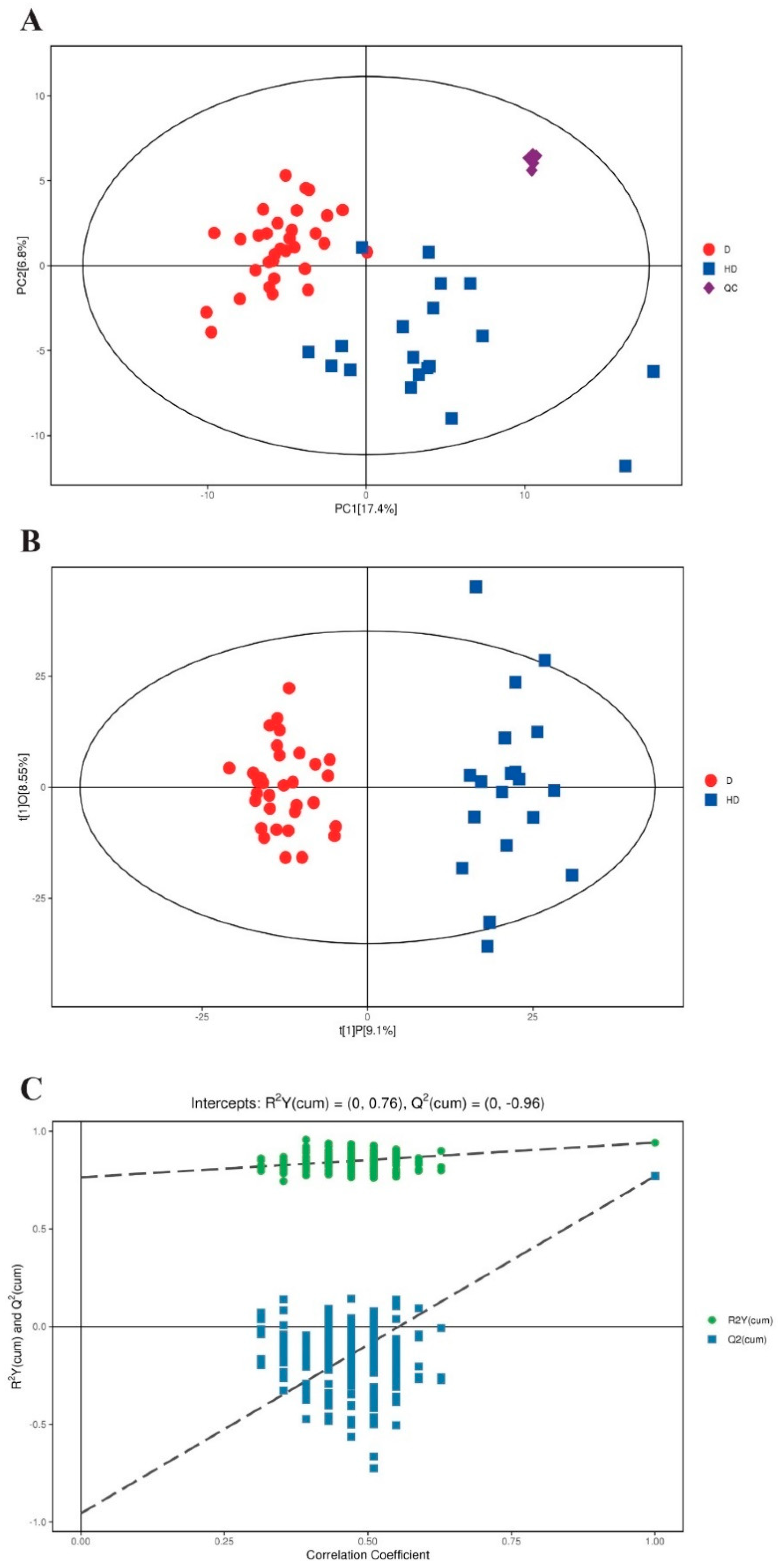



| Discovery Cohort | Validation Cohort | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | T2DM | T2DM(+) HCC | NC | T2DM | T2DM(+) HCC | T2DM(−) HCC | T2DM(+) CRC | T2DM(+) PC | T2DM(+) GC |
| N = 32 | N = 19 | N = 94 | N = 96 | N = 58 | N = 72 | N = 46 | N = 23 | N = 22 | |
| Age | 56.47 ± 11.37 | 64.32 ± 9.21 | 43.56 ± 15.02 | 55.15 ± 12.92 | 61.48 ± 9.70 | 56.11 ± 12.97 | 68.20 ± 10.99 | 69.04 ± 7.99 | 67.50 ± 11.49 |
| Gender Male/Female | 20/12 | 17/2 | 32/62 | 65/31 | 49/9 | 57/15 | 28/18 | 16/7 | 15/7 |
| FBG (mmol/L) | 7.43 ± 1.43 | 9.75 ± 4.94 | 4.99 ± 0.42 | 8.17 ± 2.37 | 8.60 ± 3.69 | 5.10 ± 0.55 | 7.72 ± 2.02 | 7.88 ± 2.41 | 8.80 ± 4.23 |
| AFP >7/≤7 ng/mL | 3/29 | 11/8 | 2/92 | 6/90 | 34/24 | 43/29 | 2/44 | 3/20 | 4/18 |
| Pathway | Total | Hits | p Value | Impact | Metabolite | MS2 Score | VIP | p Value | FC | Log_FC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycine, Serine and Threonine Metabolism | 48 | 6 | 0.0001 | 0.1212 | Choline | 0.9998 | 1.8147 | 0.0003 | 1.2297 | 0.2983 |
| Glyceric acid | 0.9378 | 2.4864 | 0.0002 | 2.5316 | 1.3401 | |||||
| Betaine | 0.9994 | 1.7816 | 0.0027 | 1.2823 | 0.3588 | |||||
| L-Threonine | 0.8118 | 1.2569 | 0.0051 | 1.8870 | 0.9161 | |||||
| Creatine | 0.9999 | 1.6842 | 5.52 × 10−6 | 0.6108 | −0.7112 | |||||
| L-Allothreonine | 0.8758 | 1.4867 | 0.0083 | 1.3063 | 0.3855 | |||||
| Arginine and Proline Metabolism | 77 | 7 | 0.0003 | 0.1474 | L-Glutamine | 0.6030 | 1.1105 | 0.0370 | 1.3353 | 0.4172 |
| Citrulline | 0.9887 | 2.3293 | 0.0003 | 2.4283 | 1.2800 | |||||
| N-Acetylornithine | 0.7652 | 1.1535 | 0.0307 | 1.5949 | 0.6735 | |||||
| Hydroxyproline | 0.9951 | 1.1415 | 0.0350 | 1.5815 | 0.6613 | |||||
| Creatine | 0.9999 | 1.6842 | 5.52 × 10−6 | 0.6108 | −0.7112 | |||||
| Creatinine | 0.9998 | 1.7932 | 0.0084 | 1.3825 | 0.4672 | |||||
| 4-Guanidinobutanoic acid | 0.9866 | 1.8229 | 0.0001 | 1.3149 | 0.3950 | |||||
| Phenylalanine Metabolism | 45 | 3 | 0.0422 | 0.1665 | L-Phenylalanine | 0.9937 | 2.2553 | 0.0001 | 1.3532 | 0.4363 |
| Phenylethyl alcohol | 0.9373 | 2.1139 | 0.0001 | 1.6448 | 0.7179 | |||||
| Benzoic acid | 0.9950 | 2.6529 | 0.0001 | 2.0267 | 1.0192 |
| AUC (95%CI) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzoic acid | 0.87 (0.81–0.93) | 72.41 | 86.46 | <0.0001 |
| Creatine | 0.73 (0.65–0.81) | 71.93 | 70.83 | <0.0001 |
| Citrulline | 0.67 (0.58–0.76) | 65.52 | 65.63 | 0.0003 |
| Groups | AUC (95%CI) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2DM(+) HCC vs. T2DM | 0.93 (0.89–0.97) | 80.70 | 89.58 | <0.0001 |
| T2DM(+) HCC vs. T2DM(+) CRC&PC&GC | 0.93 (0.89–0.97) | 91.23 | 86.67 | <0.0001 |
| Variables | N | Classifier Score | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n = 29) | High (n = 29) | |||
| Age | 0.79 | |||
| ≤60 y | 29 | 14 | 15 | |
| >60 y | 29 | 15 | 14 | |
| Gender | 0.28 | |||
| Male | 49 | 26 | 23 | |
| Female | 9 | 3 | 6 | |
| BMI | 0.57 | |||
| ≥24 kg/m2 | 41 | 22 | 19 | |
| <24 kg/m2 | 17 | 7 | 10 | |
| FBG (mmol/L) | 0.55 | |||
| 8.91 ± 3.57 | 8.31 ± 3.84 | |||
| AFP | 0.06 | |||
| >7 ng/mL | 33 | 20 | 13 | |
| ≤7 ng/mL | 25 | 9 | 16 | |
| HBV | 0.10 | |||
| Positive | 38 | 22 | 16 | |
| Negative | 20 | 7 | 13 | |
| HCV | 0.15 | |||
| Positive | 2 | 2 | 0 | |
| Negative | 56 | 27 | 29 | |
| Cirrhosis | 0.13 | |||
| Yes | 43 | 24 | 19 | |
| No | 15 | 5 | 10 | |
| Alcohol Consumption | 0.75 | |||
| Yes | 13 | 6 | 7 | |
| No | 45 | 23 | 22 | |
| Tumor Size | 0.79 | |||
| >5 cm | 23 | 12 | 11 | |
| ≤5 cm | 35 | 17 | 18 | |
| Tumor Number | 0.57 | |||
| =1 | 40 | 19 | 21 | |
| >1 | 18 | 10 | 8 | |
| CNLC Stage | 0.79 | |||
| Ⅰ–Ⅱ | 25 | 13 | 12 | |
| Ⅲ–Ⅳ | 33 | 16 | 17 | |
| Vascular invasion | 0.79 | |||
| Yes | 23 | 11 | 12 | |
| No | 35 | 18 | 17 | |
| Groups | AUC (95%CI) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCC (≤5 cm) vs. T2DM | 0.94 (0.90–0.98) | 91.18 | 82.29 | <0.0001 |
| HCC (Ⅰ–Ⅱ) vs. T2DM | 0.94 (0.89–0.98) | 92 | 82.29 | <0.0001 |
| AFP(−) HCC vs. T2DM | 0.96 (0.92–0.99) | 96 | 83.33 | <0.0001 |
| Groups | AUC (95%CI) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFP | ||||
| T2DM(+) HCC vs. T2DM | 0.76 (0.68–0.85) | 56.90 | 92.91 | <0.0001 |
| T2DM(+) HCC vs. T2DM(+) CRC&PC&GC | 0.79 (0.71–0.87) | 56.90 | 89.01 | <0.0001 |
| AFP + Classifier | ||||
| T2DM(+) HCC vs. T2DM | 0.97 (0.95–0.99) | 98.28 | 83.33 | <0.0001 |
| T2DM(+) HCC vs. T2DM(+) CRC&PC&GC | 0.96 (0.94–0.99) | 94.83 | 87.78 | <0.0001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, L.-L.; Han, Y.; Pei, L.; Yue, Z.-H.; Liu, B.-Y.; Cui, J.-W.; Jia, M.; Wang, H. A Serum Metabolite Classifier for the Early Detection of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-Positive Hepatocellular Cancer. Metabolites 2022, 12, 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12070610
Cao L-L, Han Y, Pei L, Yue Z-H, Liu B-Y, Cui J-W, Jia M, Wang H. A Serum Metabolite Classifier for the Early Detection of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-Positive Hepatocellular Cancer. Metabolites. 2022; 12(7):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12070610
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Lin-Lin, Yi Han, Lin Pei, Zhi-Hong Yue, Bo-Yu Liu, Jing-Wen Cui, Mei Jia, and Hui Wang. 2022. "A Serum Metabolite Classifier for the Early Detection of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-Positive Hepatocellular Cancer" Metabolites 12, no. 7: 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12070610
APA StyleCao, L.-L., Han, Y., Pei, L., Yue, Z.-H., Liu, B.-Y., Cui, J.-W., Jia, M., & Wang, H. (2022). A Serum Metabolite Classifier for the Early Detection of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-Positive Hepatocellular Cancer. Metabolites, 12(7), 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12070610






