Proteomics and Metabolomics Profiling of Pork Exudate Reveals Meat Spoilage during Storage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
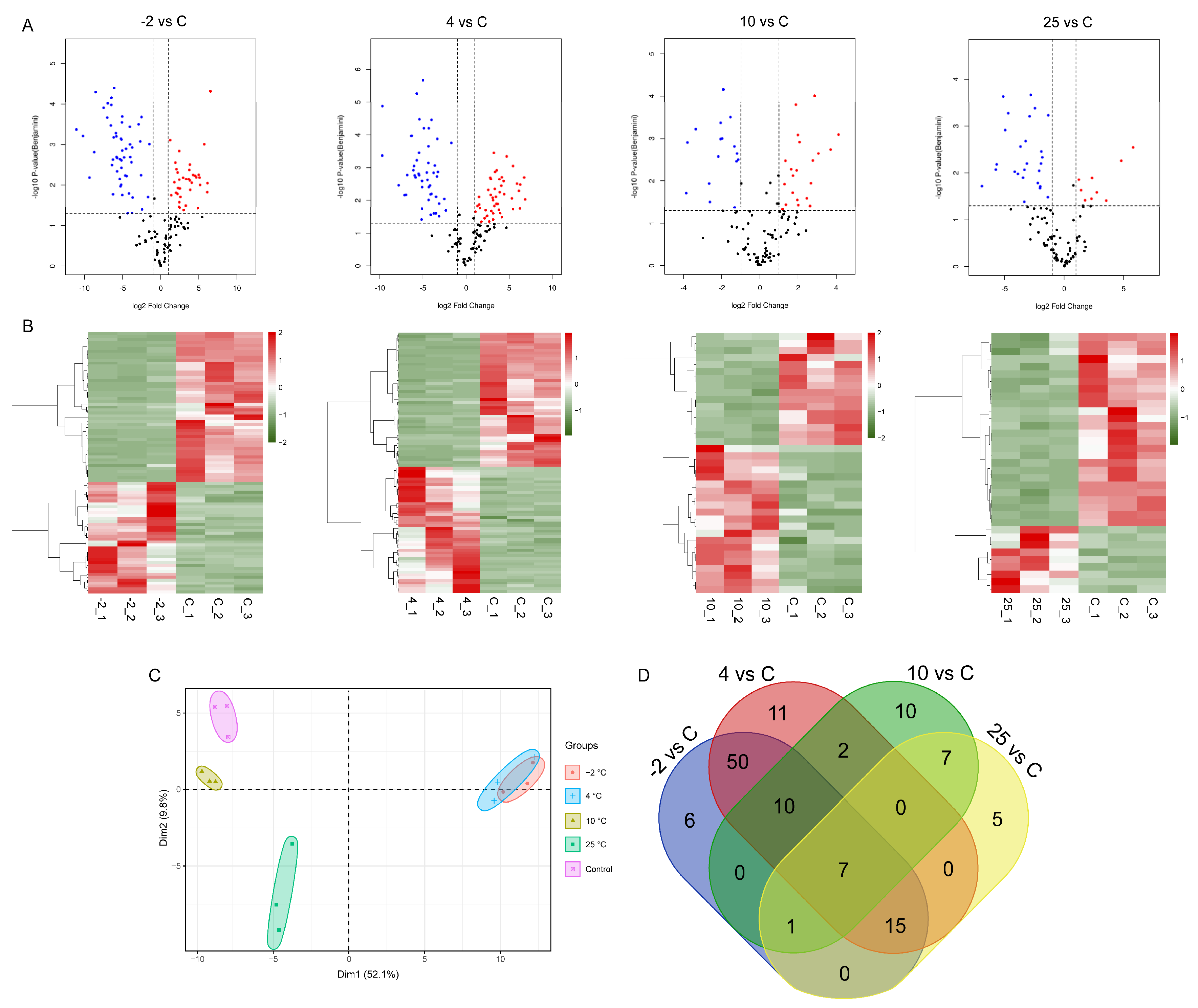
2.1. Identification of Peptides/Proteins by Quantitative Proteomics Analysis
2.2. Identification and Analysis of Differentially Abundant Proteins
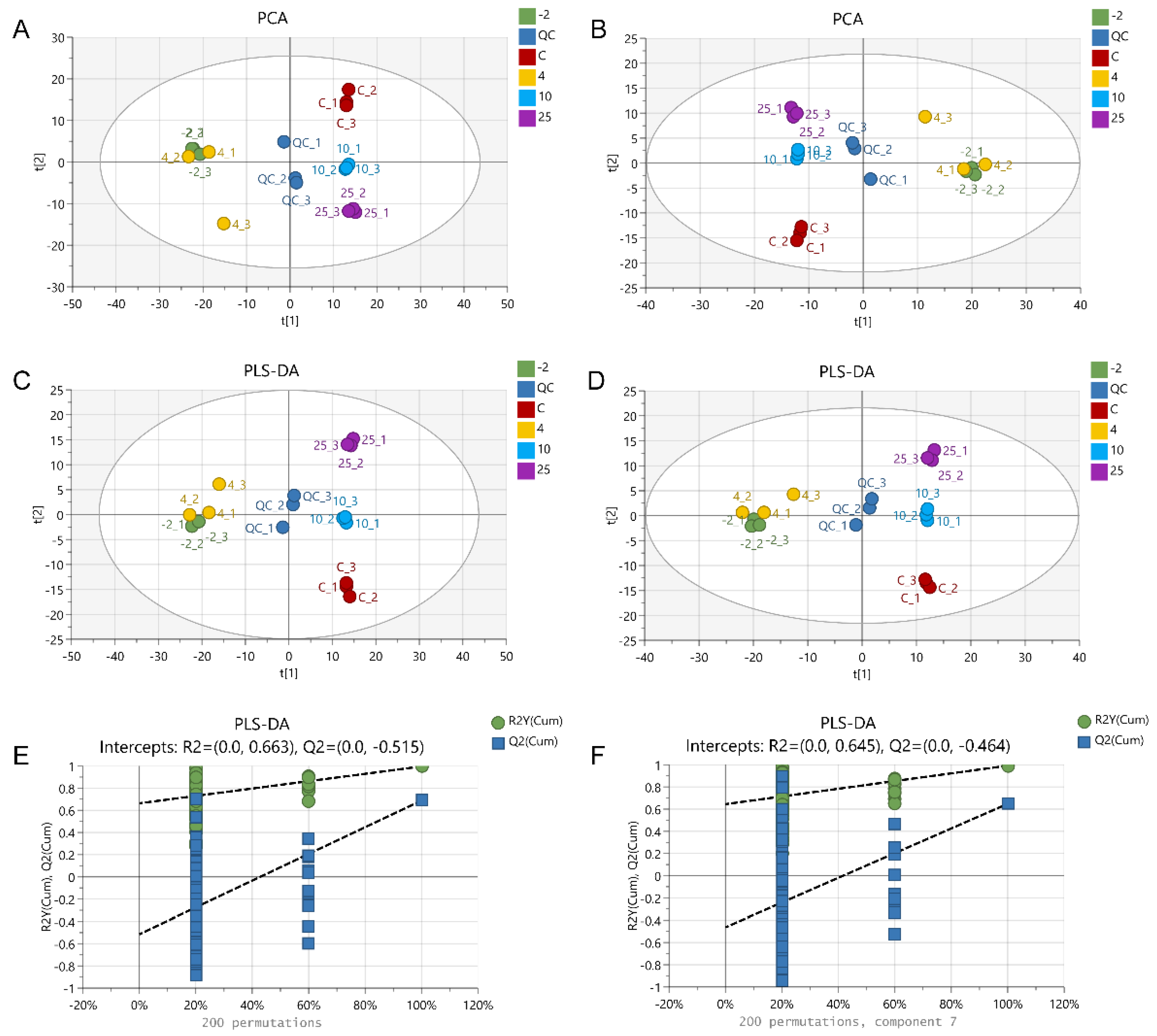
2.3. The Metabolic Profile Changes during Pork Spoilage
2.4. Screening of Differentially Abundant Metabolites
2.5. Analysis of the Correlation between Meat Quality and Omics Data
2.6. Analysis of Potential Protein Markers Associated with Pork Spoilage
2.7. Analysis of Potential Metabolite Markers Associated with Pork Spoilage
2.7.1. Organic Acids and Fatty Acids
2.7.2. Esters
2.7.3. Nucleosides and Nucleotides
2.7.4. Peptides/Amino Acids
2.7.5. Lipids, Carbohydrates, and Others
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection
3.2. Proteomics Analysis of Pork Exudate
3.3. Metabolomics Analysis of Pork Exudate
3.4. Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Metabolites
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pereira, P.M.d.C.C.; Vicente, A.F.d.R.B. Meat nutritional composition and nutritive role in the human diet. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Hopkins, D.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Dong, P.; Wang, X.; Mao, Y.; Luo, X.; Fowler, S.M. Preliminary investigation of the use of Raman spectroscopy to predict beef spoilage in different types of packaging. Meat Sci. 2020, 165, 108136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Ding, H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Wu, P.; Xie, K.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, G.; Dai, G.; Wu, H. Characterization of chilled chicken spoilage using an integrated microbiome and metabolomics analysis. Food Res. Int. 2021, 144, 110328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Geng, W.; Haruna, S.A.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Y.; Ouyang, Q.; Chen, Q. Identification of characteristic volatiles and metabolomic pathway during pork storage using HS-SPME-GC/MS coupled with multivariate analysis. Food Chem. 2021, 373, 131431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, N.; Wada, R.; Fukushima, H.; Tanaka, R.; Kono, S.; Okazaki, E. Effect of long-term storage, ultra-low temperature, and freshness on the quality characteristics of frozen tuna meat. Int. J. Refrig. 2020, 112, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, E.J.; Park, D.H.; Ji, Y.R.; Kang, G.; Choi, M.-J. Deep freezing to maintain the freshness of pork loin during long-term storage. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-García, A.; Herrera, A.; Fernández-Valle, M.; Cambero, M.; Castejón, D. Evaluation of E-beam irradiation and storage time in pork exudates using NMR metabolomics. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, R.D. The eating quality of meat-IV Water-holding capacity and juiciness. In Lawrie’ s Meat Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 419–459. [Google Scholar]
- Castejón, D.; García-Segura, J.M.; Escudero, R.; Herrera, A.; Cambero, M.I. Metabolomics of meat exudate: Its potential to evaluate beef meat conservation and aging. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 901, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Cooper, B.; Sobreira, T.; Kim, Y.H.B.J.F. Utilizing pork exudate metabolomics to reveal the impact of aging on meat quality. Foods 2021, 10, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, T.; Zhao, X.; Xu, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Gao, F. Physiochemical properties, protein and metabolite profiles of muscle exudate of chicken meat affected by wooden breast myopathy. Food Chem. 2020, 316, 126271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, E.; Coe, M.; Grose, C.; Martin, D.; Greenwood, D.R. Metabolomics approach to assess the relative contributions of the volatile and non-volatile composition to expert quality ratings of pinot noir wine quality. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 13380–13396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Pedrouso, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Gagaoua, M.; Franco, D. Application of proteomic technologies to assess the quality of raw pork and pork products: An overview from farm-to-fork. Biology 2020, 9, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Jin, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Konno, K.; Zhu, B.; Dong, X. Effects of super-chilling storage on shelf-life and quality indicators of Coregonus peled based on proteomics analysis. Food Res. Int. 2021, 143, 110229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Hu, J.; Chen, W. Analysis of the relationship between microorganisms and flavour development in dry-cured grass carp by high-throughput sequencing, volatile flavour analysis and metabolomics. Food Chem. 2022, 368, 130889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Pang, J.; Liang, P. Differential proteomics analysis of Penaeus vannamei muscles with quality characteristics by TMT quantitative proteomics during low-temperature storage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 3247–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrie, R.A.; Ledward, D. Lawrie’s Meat Science; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Nieminen, T.T.; Dalgaard, P.; Björkroth, J. Volatile organic compounds and Photobacterium phosphoreum associated with spoilage of modified-atmosphere-packaged raw pork. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 218, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dave, D.; Ghaly, A.E. Meat spoilage mechanisms and preservation techniques: A critical review. Am. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2011, 6, 486–510. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Gao, R.; Li, H.; Wu, S.; Fang, J.; Ma, K.; Yang, J.; Yan, X.; Dong, F. Evaluating potential markers of spoilage foods using a metabolic profiling approach. Food Anal. Methods 2015, 8, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Luca, A.; Elia, G.; Mullen, A.M.; Hamill, R.M. Monitoring post mortem changes in porcine muscle through 2-D DIGE proteome analysis of Longissimus muscle exudate. Proteome Sci. 2013, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Z.; Dai, C.; Bassey, A.P.; Tang, C.; Han, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhou, G. Identification of potential peptide marker (s) for evaluating pork meat freshness via mass spectrometry-based peptidomics during storage under different temperatures. Foods 2022, 11, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, J.; Hu, W.; Chen, J.; Li, H. Protein changes in post mortem large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) monitored by SDS-PAGE and proteome analysis. Food Control 2014, 41, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Chu, P.-H.; Huang, C.; Cheng, C.-F.; Martone, M.E.; Knoll, G.; Shelton, G.D.; Evans, S.; Chen, J. Ablation of Cypher, a PDZ-LIM domain Z-line protein, causes a severe form of congenital myopathy. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Qin, N.; Zhang, L.; Lv, J.; Li, Q.; Luo, Y. Effects of different concentrations of metal ions on degradation of adenosine triphosphate in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) fillets stored at 4 °C: An in vivo study. Food Chem. 2016, 211, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, S.; Sato, M.; Shiraiwa, Y.; Iwamoto, K. Molecular characterization of adenosine 5′-monophosphate deaminase-the key enzyme responsible for the umami taste of nori (Porphyra yezoensis Ueda, Rhodophyta). Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 13, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, E.; Matarneh, S.; Scheffler, T.; Gerrard, D. Perimortal muscle metabolism and its effects on meat quality. In New Aspects of Meat Quality; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 63–89. [Google Scholar]
- Wongwichian, C.; Klomklao, S.; Panpipat, W.; Benjakul, S.; Chaijan, M. Interrelationship between myoglobin and lipid oxidations in oxeye scad (Selar boops) muscle during iced storage. Food Chem. 2015, 174, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-D.; Lee, S.Y.; Jung, E.-Y.; Song, S.; Hur, S.J. Quantitative changes in peptides derived from proteins in beef tenderloin (psoas major muscle) and striploin (longissimus lumborum muscle) during cold storage. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y. iTRAQ based proteomic profile analysis for goat Longissimus thoracis under repeated freeze-thaw treatments. LWT 2020, 134, 109934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Clerens, S.; Farouk, M.M. LC MS/MS identification of large structural proteins from bull muscle and their degradation products during post mortem storage. Food Chem. 2014, 150, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, G.; Jiang, Y.; Li, M.; Bai, L.; Li, X. Effect of muscle-fiber type on glycogenin-1 gene expression and its relationship with the glycolytic potential and pH of pork. Genet. Mol. Res. 2013, 12, 3383–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Wu, W.; Tian, X.; Hou, M.; Dai, R.; Li, X. Unraveling proteome changes of Holstein beef M. semitendinosus and its relationship to meat discoloration during post-mortem storage analyzed by label-free mass spectrometry. J. Proteom. 2017, 154, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyri, A.A.; Doulgeraki, A.I.; Blana, V.A.; Panagou, E.Z.; Nychas, G.-J.E. Potential of a simple HPLC-based approach for the identification of the spoilage status of minced beef stored at various temperatures and packaging systems. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 150, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Sha, K.; Feng, X.; Liu, H. Post-thawing metabolite profile and amino acid oxidation of thawed pork tenderloin by HVEF-A short communication. Food Chem. 2019, 291, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajala, L.O.; Ogunlowo, O.M.; Okafor, M.C.; Onwukeme, V.I.; Ezem, S.N. Chemoprotective studies of some preservatives against spoilage microorganisms associated with stored roselle juice and their resultant effects on the juice’s pH and ascorbic acid. Curr. Adv. Chem. Biochem. 2021, 9, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Liu, S.; Ma, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.J.F.R.I. Evaluation of the spoilage heterogeneity of meat-borne Leuconostoc mesenteroides by metabonomics and in-situ analysis. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaburi, A.; Piombino, P.; Nychas, G.-J.; Villani, F.; Ercolini, D. Bacterial populations and the volatilome associated to meat spoilage. Food Microbiol. 2015, 45, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekhit, A.E.-D.A.; Holman, B.W.; Giteru, S.G.; Hopkins, D.L. Total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) and its role in meat spoilage: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 280–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H.; Song, S.; Luo, Y. Comparison of postmortem changes in ATP-related compounds, protein degradation and endogenous enzyme activity of white muscle and dark muscle from common carp (Cyprinus carpio) stored at 4 °C. LWT 2017, 78, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-Y.; Wang, H.-H.; Han, Y.-W.; Xing, T.; Ye, K.-P.; Xu, X.-L.; Zhou, G.-H. Evaluation of the spoilage potential of bacteria isolated from chilled chicken in vitro and in situ. Food Microbiol. 2017, 63, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comi, G. Spoilage of meat and fish. In The Microbiological Quality of Food; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 179–210. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, R.; Xia, Q.; Zhou, C.; Geng, F.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; He, J.; Pan, D.; Cao, J. LC-MS/MS-based metabolomics and sensory evaluation characterize metabolites and texture of normal and spoiled dry-cured hams. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gänzle, M.G. Lactic metabolism revisited: Metabolism of lactic acid bacteria in food fermentations and food spoilage. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 2, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granafei, S.; Losito, I.; Palmisano, F.; Cataldi, T.R. Identification of isobaric lyso-phosphatidylcholines in lipid extracts of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) fillets by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution Fourier-transform mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 6391–6404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kong, Q.; Sun, Z.; Liu, J. Freshness analysis based on lipidomics for farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) stored at different times. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhou, D.-Y.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Yin, F.-W.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Li, D.-Y.; Shahidi, F. Hydrolysis and oxidation of lipids in mussel Mytilus edulis during cold storage. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Guo, Y.; Luo, R.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, T.; Hu, Q.; Bo, S. Spoilage marker metabolites and pathway analysis in chilled tan sheep meat based on GC-MS. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2018, 24, 635–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.S.; Kwon, M.; Heo, S.; Kim, M.G.; Kim, G.-B. Characterization of the biodiversity of the spoilage microbiota in chicken meat using next generation sequencing and culture dependent approach. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2017, 37, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Accession No. | Protein Name | Gene Name | Peptide Counts | Mol. Weight [kDa] | Ratio (p < 0.05) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −2 vs. C | 4 vs. C | 10 vs. C | 25 vs. C | |||||
| A0A287A435 | LIM domain-binding protein 3 | LDB3 | 207 | 65.603 | 0.015 | 0.019 | 0.342 | 0.090 |
| A0A288CG57 | Elongation factor 1-alpha | EEF1A1 | 14 | 49.07 | 0.016 | 0.013 | 0.493 | 0.143 |
| B5SYT7 | AMP deaminase | AMPD1 | 21 | 86.502 | 0.005 | 0.013 | 0.267 | 0.021 |
| F1SHX0 | Nebulin | NEB | 358 | 772.72 | 0.070 | 0.102 | 0.420 | 0.030 |
| F1SKC4 | Glycogenin 1 | GYG1 | 21 | 37.309 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.441 | 0.151 |
| I3LJI1 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit NDUFA4 | NDUFA4 | 2 | 15.368 | 0.012 | 0.023 | 0.098 | 0.041 |
| P02189 | Myoglobin | MB | 47 | 17.084 | 0.137 | 0.087 | 0.401 | 0.251 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, F.; Wei, Z.; Bai, Y.; Li, C.; Zhou, G.; Kristiansen, K.; Wang, C. Proteomics and Metabolomics Profiling of Pork Exudate Reveals Meat Spoilage during Storage. Metabolites 2022, 12, 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12070570
Zhao F, Wei Z, Bai Y, Li C, Zhou G, Kristiansen K, Wang C. Proteomics and Metabolomics Profiling of Pork Exudate Reveals Meat Spoilage during Storage. Metabolites. 2022; 12(7):570. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12070570
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Fan, Zhenqian Wei, Yun Bai, Chunbao Li, Guanghong Zhou, Karsten Kristiansen, and Chong Wang. 2022. "Proteomics and Metabolomics Profiling of Pork Exudate Reveals Meat Spoilage during Storage" Metabolites 12, no. 7: 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12070570
APA StyleZhao, F., Wei, Z., Bai, Y., Li, C., Zhou, G., Kristiansen, K., & Wang, C. (2022). Proteomics and Metabolomics Profiling of Pork Exudate Reveals Meat Spoilage during Storage. Metabolites, 12(7), 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12070570






