Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Gestational Diabetes: Analysis of Maternal Serum and Cord Blood Pairs and Comparison of Dietary- and Insulin-Dependent GDM
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Baseline Characteristics
2.2. Comparisons between Groups
- (1)
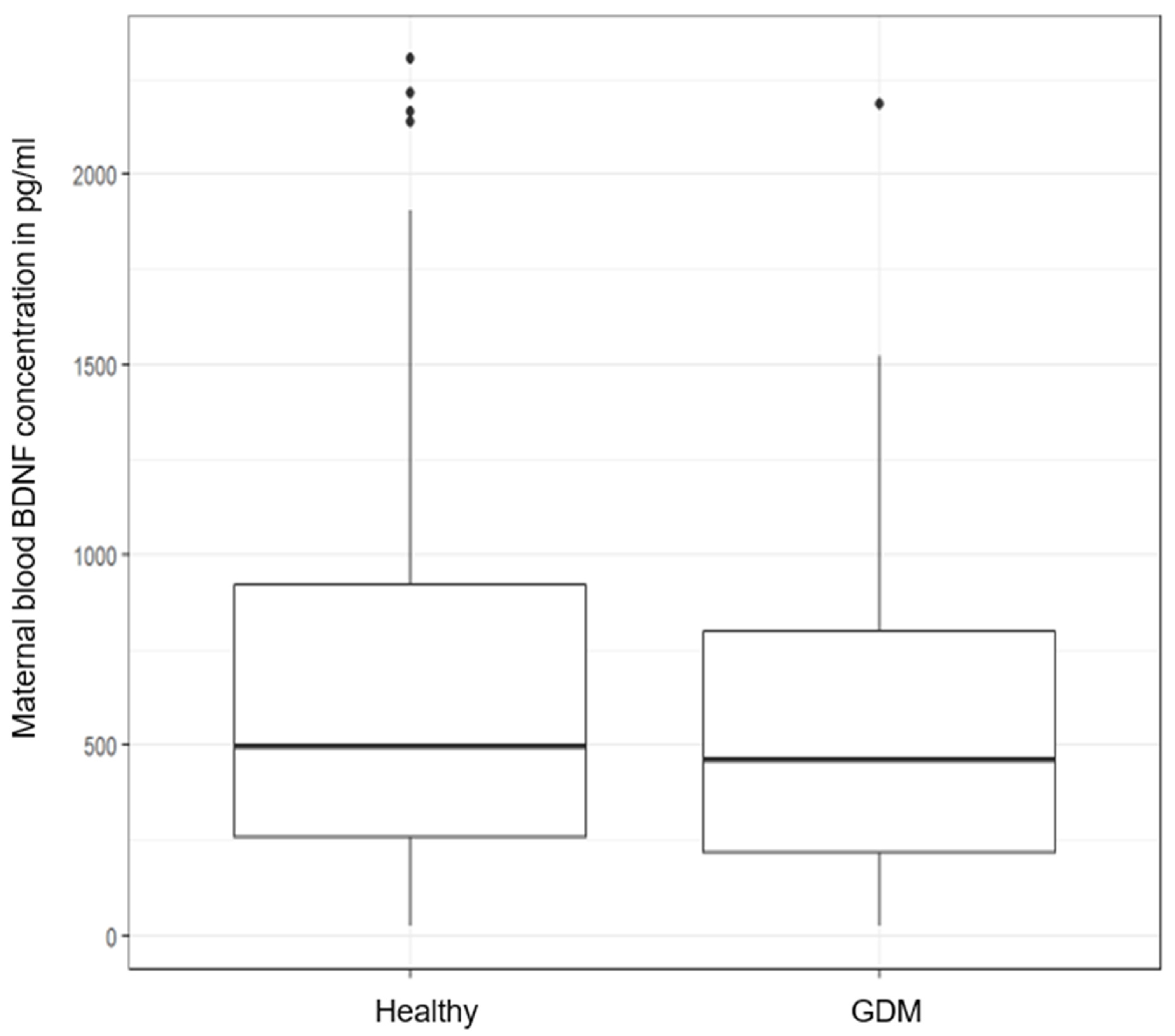
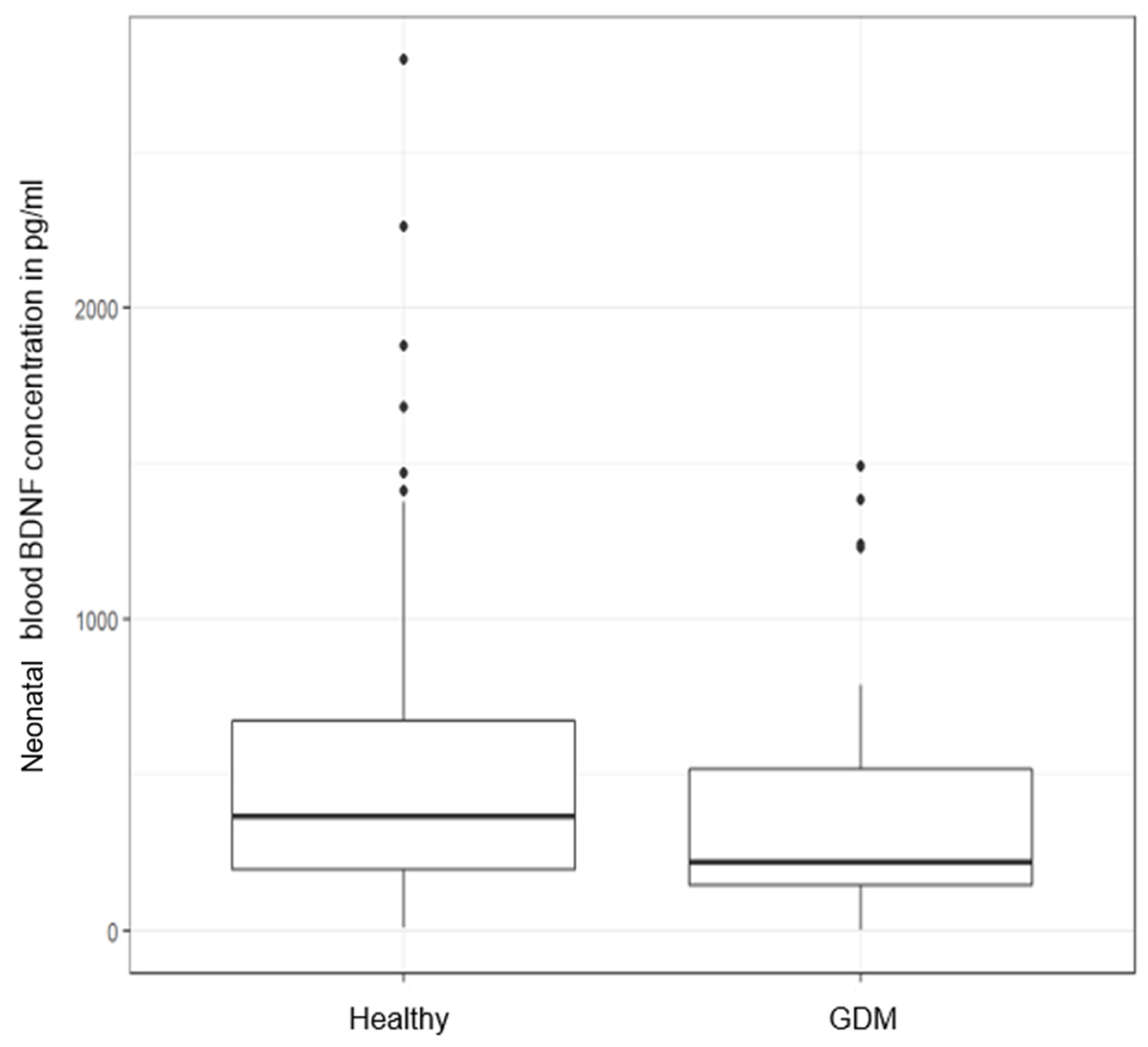
- Maternal and neonatal BDNF: healthy (n = 173) vs. all GDM (n = 60)
- (2)
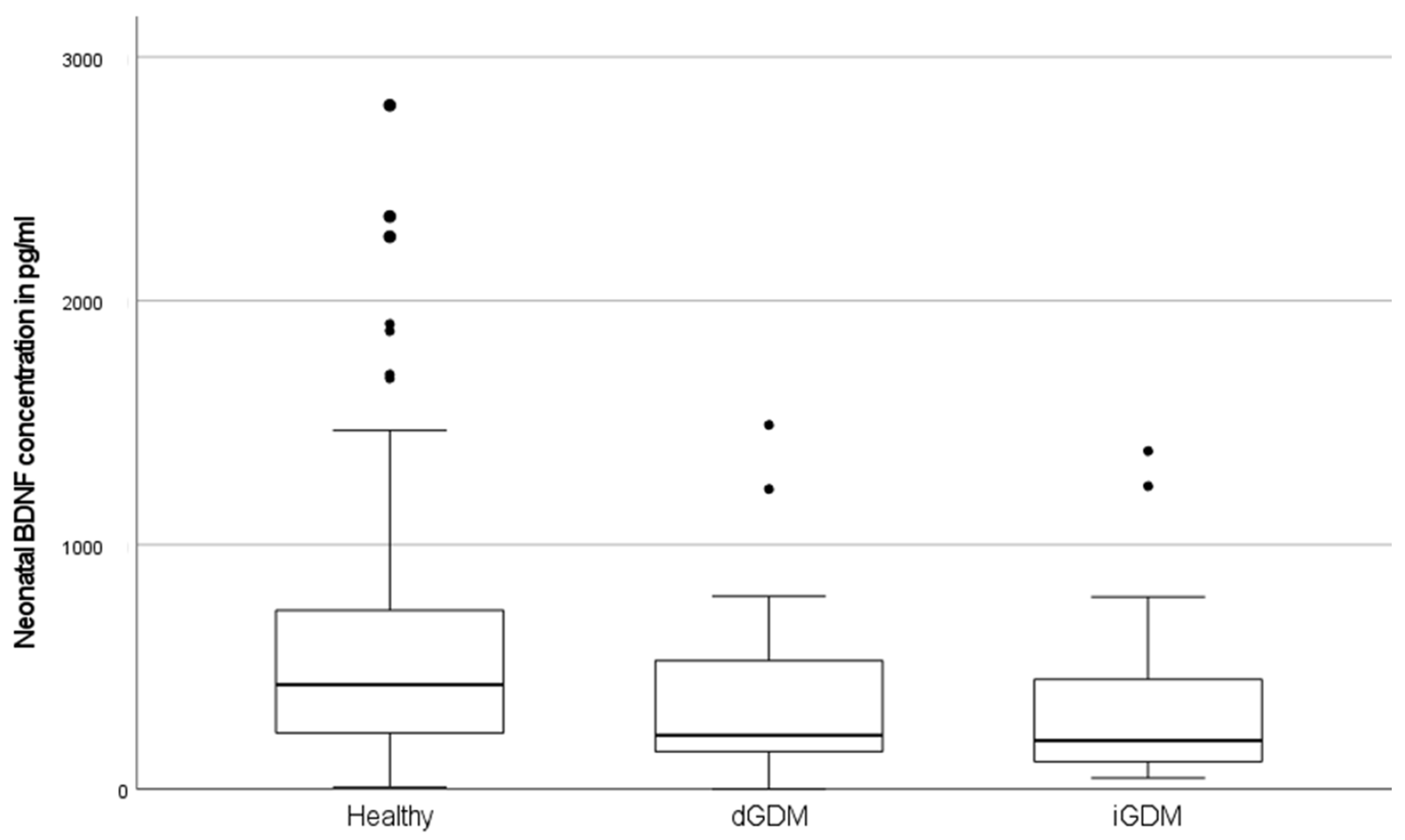
- Maternal and neonatal BDNF: healthy (A; n = 173) vs. dGDM (B; n = 29) vs. iGDM (C; n = 31)
2.3. Multiple Regression Analysis
2.4. Matching
3. Discussion
3.1. BDNF in Diabetes Mellitus
3.2. BDNF in GDM
3.3. Neonatal BDNF in Umbilical Cord Blood
3.4. Maternal BDNF
3.5. Factors Contributing to BDNF Concentration
4. Material and Methods
5. Conclusions
Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas 9th Edition. Available online: www.diabetesatlas.org/upload/resources/material/20200302_133351_IDFATLAS9e-final-web.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Sacks, D.A.; Hadden, D.R.; Maresh, M.; Deerochanawong, C.; Dyer, A.R.; Metzger, B.E.; Lowe, L.P.; Coustan, D.R.; Hod, M.; Oats, J.J.; et al. Frequency of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus at Collaborating Centers Based on IADPSG Consensus Panel–Recommended Criteria. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abouzeid, M.; Versace, V.; Janus, E.D.; Davey, M.-A.; Philpot, B.; Oats, J.; Dunbar, J.A. A Population-Based Observational Study of Diabetes during Pregnancy in Victoria, Australia, 1999–2008. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e005394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- HAPO Study Cooperative Research Group; Metzger, B.E.; Lowe, L.P.; Dyer, A.R.; Trimble, E.R.; Chaovarindr, U.; Coustan, D.R.; Hadden, D.R.; McCance, D.R.; Hod, M.; et al. Hyperglycemia and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1991–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozanska, O.; Uruska, A.; Zozulinska-Ziolkiewicz, D. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ornoy, A. Growth and Neurodevelopmental Outcome of Children Born to Mothers with Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Rev. 2005, 3, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Lieshout, R.J.; Voruganti, L.P. Diabetes Mellitus during Pregnancy and Increased Risk of Schizophrenia in Offspring: A Review of the Evidence and Putative Mechanisms. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2008, 33, 395–404. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, P.A. BDNF: No Gain Without Pain? Neuroscience 2014, 283, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Cory, S.; Kidane, A.H.; Shirkey, N.J.; Marshak, S. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and the Development of Structural Neuronal Connectivity. Dev. Neurobiol. 2010, 70, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eyileten, C.; Kaplon-Cieslicka, A.; Mirowska-Guzel, D.; Małek, L.; Postula, M. Antidiabetic Effect of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Its Association with Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 2823671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonra, J.R.; Ono, M.; Liu, X.; Garcia, K.; Jackson, C.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Wiegand, S.J.; Wong, V. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Improves Blood Glucose Control and Alleviates Fasting Hyperglycemia in C57BLKS-Lepr(db)/lepr(db) Mice. Diabetes 1999, 48, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briana, D.D.; Malamitsi-Puchner, A. Developmental Origins of Adult Health and Disease: The Metabolic Role of BDNF from Early Life to Adulthood. Metabolism 2018, 81, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’angelo, A.; Ceccanti, M.; Petrella, C.; Greco, A.; Tirassa, P.; Rosso, P.; Ralli, M.; Ferraguti, G.; Fiore, M.; Messina, M.P. Role of Neurotrophins in Pregnancy, Delivery and Postpartum. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2020, 247, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, R.; Wessels, J.M.; Foster, W.G. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Expression and Function in the Mammalian Reproductive Tract. Hum. Reprod. Update 2020, 26, 545–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Tatsumi, K.; Kondoh, E.; Chigusa, Y.; Mogami, H.; Fujii, T.; Yura, S.; Kakui, K.; Konishi, I. Differential Expression and the Anti-apoptotic Effect of Human Placental Neurotrophins and Their Receptors. Placenta 2011, 32, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayeur, S.; Lukaszewski, M.A.; Breton, C.; Storme, L.; Vieau, D.; Lesage, J. Do Neurotrophins Regulate the Feto-Placental Development? Med. Hypotheses 2011, 76, 726–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujinami, A.; Ohta, K.; Obayashi, H.; Fukui, M.; Hasegawa, G.; Nakamura, N.; Kozai, H.; Imai, S.; Ohta, M. Serum Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Relationship to Glucose Metabolism and Biomarkers of Insulin Resistance. Clin. Biochem. 2008, 41, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Lang, N.; Cheng, Z.-F. Serum Levels of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Are Associated with Diabetes Risk, Complications, and Obesity: A Cohort Study from Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 5492–5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ola, M.S.; Nawaz, M.I.; Abu El-Asrar, A.; Abouammoh, M.; Alhomida, A.S. Reduced Levels of Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) in the Serum of Diabetic Retinopathy Patients and in the Retina of Diabetic Rats. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 33, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Tang, D.-D.; Yin, E.-G.; Wei, L.-L.; Chen, P.; Deng, S.-P.; Tu, L.-L. Diagnostic Significance of Serum Levels of Nerve Growth Factor and Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 5943–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyuk, B.; Degirmencioglu, S.; Atalay, H.; Guzel, S.; Acar, A.; Çelebi, A.; Ekizoğlu, I.; Simsek, C. Relationship between Levels of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Metabolic Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2014, 2014, 978143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, M.; Itakura, Y.; Tsuchida, A.; Nakagawa, T.; Taiji, M. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Prevents the Development of Diabetes in Prediabetic Mice. Biomed. Res. 2008, 29, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagahara, A.H.; Tuszynski, M.H. Potential Therapeutic Uses of BDNF in Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lommatzsch, M.; Zingler, D.; Schuhbaeck, K.; Schloetcke, K.; Zingler, C.; Schuff-Werner, P.; Virchow, J.C. The Impact of Age, Weight and Gender on BDNF Levels in Human Platelets and Plasma. Neurobiol. Aging 2005, 26, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christian, L.M.; Mitchell, A.M.; Gillespie, S.L.; Palettas, M. Serum Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Across Pregnancy and Postpartum: Associations with Race, Depressive Symptoms, and Low Birth Weight. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2016, 74, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flöck, A.; Weber, S.K.; Ferrari, N.; Fietz, C.; Graf, C.; Fimmers, R.; Gembruch, U.; Merz, W.M. Determinants of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) In Umbilical Cord and Maternal Serum. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2016, 63, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colucci-D’Amato, L.; Speranza, L.; Volpicelli, F. Neurotrophic Factor BDNF, Physiological Functions and Therapeutic Potential in Depression, Neurodegeneration and Brain Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björkholm, C.; Monteggia, L.M. BDNF—A Key Transducer of Antidepressant Effects. Neuropharmacology 2015, 102, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suwa, M.; Kishimoto, H.; Nofuji, Y.; Nakano, H.; Sasaki, H.; Radak, Z.; Kumagai, S. Serum Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Level Is Increased and Associated with Obesity in Newly Diagnosed Female Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Metabolism 2006, 55, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.; Yoo, J.H.; Kang, S.; Woo, J.H.; Shin, K.O.; Kim, K.B.; Cho, S.Y.; Roh, H.T.; Kim, Y.I. The Effects of 12 Weeks Regular Aerobic Exercise on Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor and Inflammatory Factors in Juvenile Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2014, 26, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Q.-Y.; Zhang, H.-X.; Wang, C.-C.; Sun, H.; Sun, S.-Q.; Wang, Y.-H.; Yan, H.-T.; Yang, X.-J. Placental and Cord Blood Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor Levels Are Decreased in Nondiabetic Macrosomia. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2017, 296, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briana, D.D.; Papastavrou, M.; Boutsikou, M.; Marmarinos, A.; Gourgiotis, D.; Malamitsi-Puchner, A. Differential Expression of Cord Blood Neurotrophins in Gestational Diabetes: The Impact of Fetal Growth Abnormalities. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2017, 31, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, A.; Khaire, A.; Gundu, S.; Wadhwani, N.; Chandhiok, N.; Gupte, S.; Joshi, S. Placental Neurotrophin Levels in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2021, 81, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.-H.; Liu, T.-Y.; Chen, I.-T.; Ou-Yang, M.-C.; Huang, L.-T.; Tsai, C.-C.; Chen, C.-C. Correlations between Serum BDNF Levels and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Infants of Mothers with Gestational Diabetes. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2021, 62, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayman, M.G.; Inal, Z.O.; Hayiroglu, F.; Ozturk, E.N.Y.; Gezginc, K. Foetal Umbilical Cord Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Levels in Pregnancy with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2022, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardar, R.; Hami, J.; Soleimani, M.; Joghataei, M.-T.; Shirazi, R.; Golab, F.; Namjoo, Z.; Zandieh, Z. Maternal Diabetes-Induced Alterations in the Expression of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in the Developing Rat Hippocampus. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2021, 114, 101946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.A. Brainwork in the Ovary: Kisspeptin and BDNF Signaling Converge to Ensure Oocyte Survival. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 2751–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlando, G.; Leone, S.; Ferrante, C.; Chiavaroli, A.; Mollica, A.; Stefanucci, A.; Macedonio, G.; Dimmito, M.P.; Leporini, L.; Menghini, L.; et al. Effects of Kisspeptin-10 on Hypothalamic Neuropeptides and Neurotransmitters Involved in Appetite Control. Molecules 2018, 23, 3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrante, C.; Recinella, L.; Leone, S.; Chiavaroli, A.; Di Nisio, C.; Martinotti, S.; Mollica, A.; Macedonio, G.; Stefanucci, A.; Dvorácskó, S.; et al. Anorexigenic Effects Induced by RVD-hemopressin(α) Administration. Pharmacol. Rep. 2017, 69, 1402–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Hervada, A.D.; Pascual, A.L.C. Criterios Diagnósticos de la Diabetes Gestacional: El Debate Continúa. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2015, 62, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups Consensus Panel; Metzger, B.E.; Gabbe, S.G.; Persson, B.; Buchanan, T.A.; Catalano, P.A.; Damm, P.; Dyer, A.R.; de Leiva, A.; Hod, M.; et al. International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups Recommendations on the Diagnosis and Classification of Hyperglycemia in Pregnancy. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2020. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, S14–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| KERRYPNX | Healthy (n = 173) | dGDM (n = 29) | iGDM (n = 31) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal data: | ||||
| Age (years) | 0.0501 | |||
| mean ± SD | 33.0 ± 5.0 | 32.1 ± 5.7 | 35.2 ± 5.2 | |
| BMI before pregnancy (kg/m2) | <0.001 A vs. B A vs. C | |||
| mean ± SD | 26.5 ± 20.4 | 28.9 ± 8.1 | 32.7 ± 12.4 | |
| BMI before pregnancy, category (kg/m²) % (n) | - | |||
| <30 | 92.5 (160) | 65.5 (19) | 54.8 (17) | |
| 30–34.9 | 3.5 (6) | 13.8 (4) | 16.1 (5) | |
| >35 | 4.1 (7) | 20.7 (6) | 29.0 (9) | |
| BMI at delivery (kg/m²) | <0.001 | |||
| mean ± SD | 28.5 ± 4.9 | 33.0 ± 7.5 | 34.4 ± 8.7 | |
| missing (n) | (1) | - | - | |
| BMI at delivery, category (kg/m²) % (n) | - | |||
| <30 | 68.6 (118) | 41.4 (12) | 38.7 (12) | |
| 30–34.9 | 23.8 (41) | 27.6 (8) | 16.1 (5) | |
| >35 | 7.6 (13) | 31.0 (9) | 45.2 (14) | |
| missing (n) | (1) | - | - | |
| Platelet count (n/µL) | 0.490 | |||
| mean ± SD | 223.1 ± 81.6 | 230.7 ± 49.3 | 230.9 ± 77.8 | |
| missing (n) | (7) | (2) | - | |
| Smoker % (n) | ||||
| yes | - (0) | 3.4 (1) | 3.2 (1) | |
| unknown | 10.4 (18) | 13.8 (4) | 9.7 (3) | 0.124 |
| BDNF serum concentration (pg/mL) | 0.652 | |||
| mean ± SD | 664.6 ± 562.4 | 593.1 ± 446.1 | 541.0 ± 446.1 | |
| Neonatal data: | ||||
| BDNF serum concentration (pg/mL) | 0.004 | |||
| mean ± SD | 541.3 ± 463.9 | 374.6 ± 342.0 | 330.2 ± 326.3 | A vs. B |
| missing (n) | (3) | - | - | A vs. C |
| Gestational age at delivery, (weeks) | ||||
| mean ± SD | 39.7 ± 2.0 | 39.9 ± 1.2 | 39.0 ± 1.5 | 0.008 |
| missing (n) | (1) | - | - | A vs. C |
| Neonatal sex % (n) | 0.845 | |||
| male | 53.8 (93) | 48.3 (14) | 54.8 (17) | |
| female | 46.2 (80) | 51.7 (15) | 45.2 (14) | |
| Mode of delivery % (n) | 0.001 | |||
| vaginal birth | 59.3 (102) | 75.0 (22) | 25.8 (8) | |
| instrumental | 5.8 (10) | 3.6 (1) | 9.7 (3) | |
| elective cesarean | 27.9 (48) | 14.3 (4) | 61.3 (19) | |
| emergency cesarean | 7.0 (12) | 7.1 (2) | 3.2 (1) | |
| missing (n) | (1) | (1) | - | |
| Birth weight (g) | 0.559 | |||
| mean ± SD | 3392.4 ± 577.0 | 3352.3 ± 359.0 | 3496.8 ± 618.7 | |
| Birth weight percentile | 0.077 | |||
| mean ± SD | 50.4 ± 28.4 | 46.4 ± 24.9 | 61.5 ± 27.4 | |
| Umbilical artery cord pH | 0.804 | |||
| mean ± SD | 7.3 ± 0.1 | 7.3 ± 0.1 | 7.3 ± 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaskolski, M.R.; Diedrich, A.K.; Odainic, A.; Schmidt, S.V.; Schmitz, M.-T.; Strizek, B.; Gembruch, U.; Merz, W.M.; Flöck, A. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Gestational Diabetes: Analysis of Maternal Serum and Cord Blood Pairs and Comparison of Dietary- and Insulin-Dependent GDM. Metabolites 2022, 12, 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12060482
Jaskolski MR, Diedrich AK, Odainic A, Schmidt SV, Schmitz M-T, Strizek B, Gembruch U, Merz WM, Flöck A. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Gestational Diabetes: Analysis of Maternal Serum and Cord Blood Pairs and Comparison of Dietary- and Insulin-Dependent GDM. Metabolites. 2022; 12(6):482. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12060482
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaskolski, Michael Robert, Anna Katharina Diedrich, Alexandru Odainic, Susanne Viktoria Schmidt, Marie-Therese Schmitz, Brigitte Strizek, Ulrich Gembruch, Waltraut Maria Merz, and Anne Flöck. 2022. "Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Gestational Diabetes: Analysis of Maternal Serum and Cord Blood Pairs and Comparison of Dietary- and Insulin-Dependent GDM" Metabolites 12, no. 6: 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12060482
APA StyleJaskolski, M. R., Diedrich, A. K., Odainic, A., Schmidt, S. V., Schmitz, M.-T., Strizek, B., Gembruch, U., Merz, W. M., & Flöck, A. (2022). Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Gestational Diabetes: Analysis of Maternal Serum and Cord Blood Pairs and Comparison of Dietary- and Insulin-Dependent GDM. Metabolites, 12(6), 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12060482






