Towards Unbiased Evaluation of Ionization Performance in LC-HRMS Metabolomics Method Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Evaluation of Selectivity
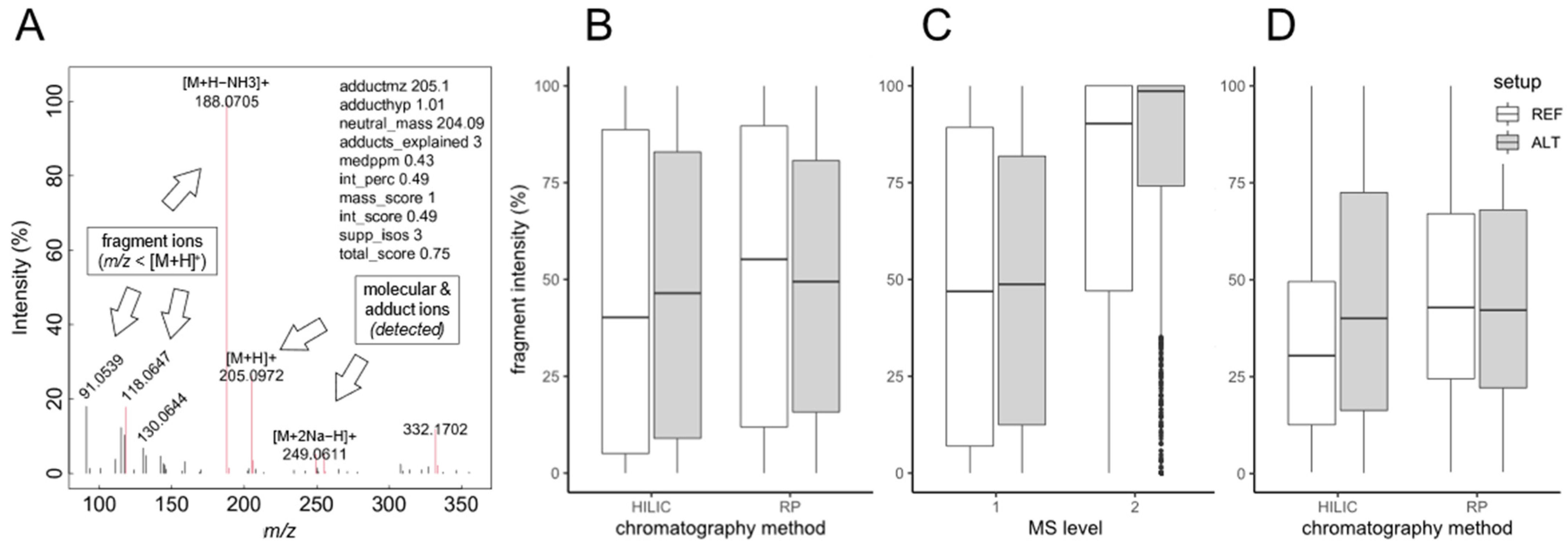
2.2. Evaluation of In-Source Fragmentation
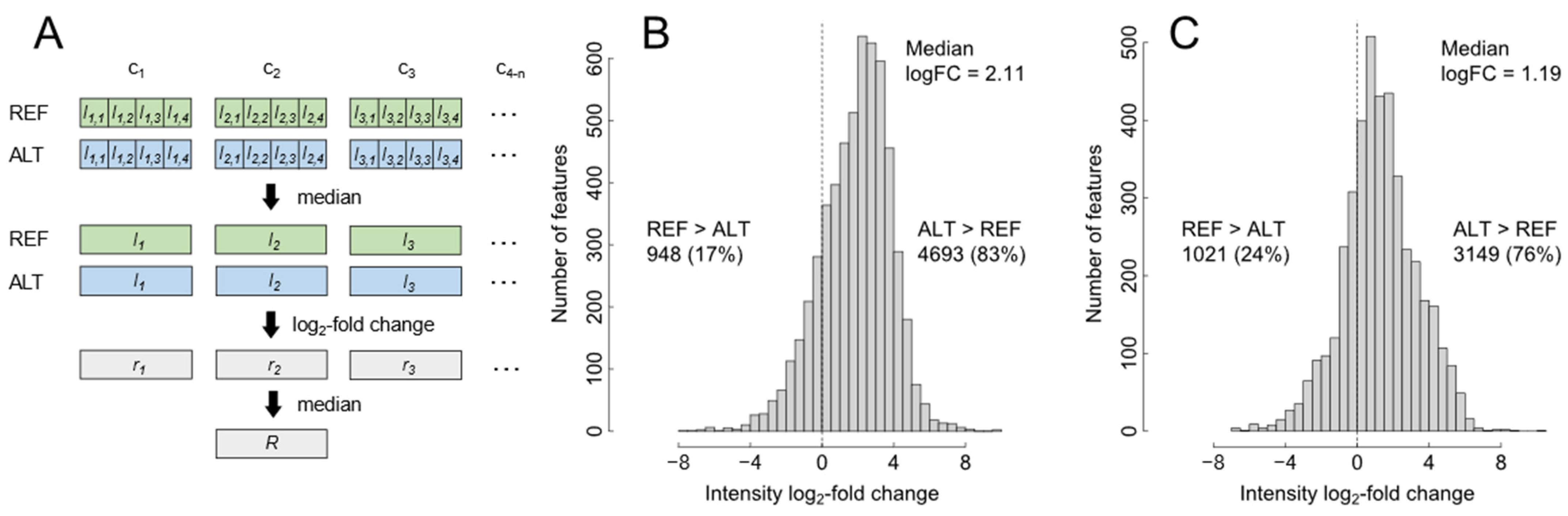
2.3. Evaluation of Ion Suppression
2.4. Evaluation of Chemical Comprehensiveness
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Test Sample and Chemical Standards
4.2. LC-HRMS Analysis
4.3. Matrix Effect Assay
4.4. Feature Analysis
4.4.1. Peak Detection
4.4.2. Peak Alignment
4.4.3. Chromatographic Deconvolution
4.4.4. Identification and Classification
4.4.5. Linear Regression Analysis
4.4.6. Further Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashrafian, H.; Sounderajah, V.; Glen, R.; Ebbels, T.; Blaise, B.J.; Kalra, D.; Kultima, K.; Spjuth, O.; Tenori, L.; Salek, R.M.; et al. Metabolomics: The Stethoscope for the Twenty-First Century. Med. Princ. Pract. 2021, 30, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcon-Barrera, J.C.; Kostidis, S.; Ondo-Mendez, A.; Giera, M. Recent Advances in Metabolomics Analysis for Early Drug Development. Drug Discov. Today 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olesti, E.; González-Ruiz, V.; Wilks, F.M.; Boccard, J.; Rudaz, S. Approaches in Metabolomics for Regulatory Toxicology Applications. Analyst 2021, 146, 1820–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alseekh, S.; Aharoni, A.; Brotman, Y.; Contrepois, K.; D’Auria, J.; Ewald, J.; Ewald, C.J.; Fraser, P.D.; Giavalisco, P.; Hall, R.D.; et al. Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics: A Guide for Annotation, Quantification and Best Reporting Practices. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudzik, D.; Barbas-Bernardos, C.; García, A.; Barbas, C. Quality Assurance Procedures for Mass Spectrometry Untargeted Metabolomics. a Review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 147, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortmayr, K.; Causon, T.J.; Hann, S.; Koellensperger, G. Increasing Selectivity and Coverage in LC-MS Based Metabolome Analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 82, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.H. Mass Spectrometry: A Textbook, 3rd ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-54397-0. [Google Scholar]
- Manisali, I.; Chen, D.D.Y.; Schneider, B.B. Electrospray Ionization Source Geometry for Mass Spectrometry: Past, Present, and Future. Trends Anal. Chem. 2006, 25, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordehai, A.; Fjeldsted, J. Agilent Jet Stream Thermal Gradient Focusing Technology; Agilent Technologies Technical Note; Publication Number 5990-3494; Agilent Technologies: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wendt, K.; Baessmann, C.; Zey, T.; Hillis, J.; Weinmann, W. Enhanced Determination of Alcohol Biomarkers Using Mass Spectrometry with the New IonBooster Source; Bruker Daltonics: Billerica, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Huppertz, L.M.; Kneisel, S.; Auwärter, V.; Kempf, J. A Comprehensive Library-Based, Automated Screening Procedure for 46 Synthetic Cannabinoids in Serum Employing Liquid Chromatography-Quadrupole Ion Trap Mass Spectrometry with High-Temperature Electrospray Ionization. J. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 49, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carboni, A.; Helmus, R.; Parsons, J.R.; Kalbitz, K.; de Voogt, P. A Method for the Determination of Fullerenes in Soil and Sediment Matrices Using Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Heated Electrospray Quadrupole Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1433, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Bennett, B.D.; Rabinowitz, J.D. Analytical Strategies for LC–MS-Based Targeted Metabolomics. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 871, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandher, R.; Naegele, E.; Fischer, S.M.; Raynaud, F.I. Raynaud Improvement in the Number of Analytic Features Detected by Non-Targeted Metabolomic Analysis: Influence of the Chromatographic System and the Ionization Technique; INTECH Open Access Publisher: London, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-953-51-0046-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhl, C.; Tautenhahn, R.; Böttcher, C.; Larson, T.R.; Neumann, S. CAMERA: An Integrated Strategy for Compound Spectra Extraction and Annotation of Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry Data Sets. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaeger, C.; Méret, M.; Schmitt, C.A.; Lisec, J. Compound Annotation in LC-HRMS-Based Metabolomics: Robust Adduct Ion Determination as a Prerequisite to Structure Prediction in Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectra. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 31, 1261–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furey, A.; Moriarty, M.; Bane, V.; Kinsella, B.; Lehane, M. Ion Suppression; A Critical Review on Causes, Evaluation, Prevention and Applications. Talanta 2013, 115, 104–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feunang, Y.D.; Eisner, R.; Knox, C.; Chepelev, L.; Hastings, J.; Owen, G.; Fahy, E.; Steinbeck, C.; Subramanian, S.; Bolton, E.; et al. ClassyFire: Automated Chemical Classification with a Comprehensive, Computable Taxonomy. J. ChemInform. 2016, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsugawa, H.; Kind, T.; Nakabayashi, R.; Yukihira, D.; Tanaka, W.; Cajka, T.; Saito, K.; Fiehn, O.; Arita, M. Hydrogen Rearrangement Rules: Computational MS/MS Fragmentation and Structure Elucidation Using MS-FINDER Software. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 7946–7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulipani, S.; Mora-Cubillos, X.; Jáuregui, O.; Llorach, R.; García-Fuentes, E.; Tinahones, F.J.; Andres-Lacueva, C. New and Vintage Solutions to Enhance the Plasma Metabolome Coverage by LC-ESI-MS Untargeted Metabolomics: The Not-So-Simple Process of Method Performance Evaluation. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 2639–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, M.M.; Adamko, D.J.; El-Aneed, A. Mass Spectrometric Based Approaches in Urine Metabolomics and Biomarker Discovery. Mass Spec. Rev. 2017, 36, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietmair, S.; Timmins, N.E.; Gray, P.P.; Nielsen, L.K.; Krömer, J.O. Towards Quantitative Metabolomics of Mammalian Cells: Development of a Metabolite Extraction Protocol. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 404, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, D.Y.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Park, H.S.; Fiehn, O.; Kim, K.H. Evaluation and Optimization of Metabolome Sample Preparation Methods for Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 2169–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinney, K.W.; Ballihaut, G.; Bedner, M.; Benford, B.S.; Camara, J.E.; Christopher, S.J.; Davis, W.C.; Dodder, N.G.; Eppe, G.; Lang, B.E.; et al. Development of a Standard Reference Material for Metabolomics Research. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11732–11738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, J.W.; Adams, K.J.; Adamski, J.; Asad, Y.; Borts, D.; Bowden, J.A.; Byram, G.; Dang, V.; Dunn, W.B.; Fernandez, F.; et al. International Ring Trial of a High Resolution Targeted Metabolomics and Lipidomics Platform for Serum and Plasma Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 14407–14416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szerkus, O.; Mpanga, A.Y.; Siluk, D.; Kaliszan, R.; Markuszewski, M.J. Optimization of the Electrospray Ionization Source with the Use of the Design of Experiments Approach for the LC–MS-MS Determination of Selected Metabolites in Human Urine. Spectrosc. Suppl. 2016, 14, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Pedro, L.; Van Voorhis, W.C.; Quinn, R.J. Optimization of Electrospray Ionization by Statistical Design of Experiments and Response Surface Methodology: Protein-Ligand Equilibrium Dissociation Constant Determinations. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 27, 1520–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liigand, J.; Kruve, A.; Liigand, P.; Laaniste, A.; Girod, M.; Antoine, R.; Leito, I. Transferability of the Electrospray Ionization Efficiency Scale between Different Instruments. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 26, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, O.D.; Sumner, S.J.; Li, S.; Barnes, S.; Du, X. Detailed Investigation and Comparison of the XCMS and MZmine 2 Chromatogram Construction and Chromatographic Peak Detection Methods for Preprocessing Mass Spectrometry Metabolomics Data. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 8689–8695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-F.; Lu, W.; Rabinowitz, J.D. Avoiding Misannotation of In-Source Fragmentation Products as Cellular Metabolites in Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 2273–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kind, T.; Tsugawa, H.; Cajka, T.; Ma, Y.; Lai, Z.; Mehta, S.S.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Barupal, D.K.; Showalter, M.R.; Arita, M.; et al. Identification of Small Molecules Using Accurate Mass MS/MS Search. Mass Spec. Rev. 2017, 37, 513–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksenov, A.A.; Laponogov, I.; Zhang, Z.; Doran, S.L.F.; Belluomo, I.; Veselkov, D.; Bittremieux, W.; Nothias, L.F.; Nothias-Esposito, M.; Maloney, K.N.; et al. Auto-Deconvolution and Molecular Networking of Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Data. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Hooft, J.J.J.; Wandy, J.; Young, F.; Padmanabhan, S.; Gerasimidis, K.; Burgess, K.E.V.; Barrett, M.P.; Rogers, S. Unsupervised Discovery and Comparison of Structural Families across Multiple Samples in Untargeted Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 7569–7577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmid, R.; Petras, D.; Nothias, L.-F.; Wang, M.; Aron, A.T.; Jagels, A.; Tsugawa, H.; Rainer, J.; Garcia-Aloy, M.; Dührkop, K.; et al. Ion Identity Molecular Networking for Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics in the GNPS Environment. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, C.A.; Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS: Processing Mass Spectrometry Data for Metabolite Profiling Using Nonlinear Peak Alignment, Matching, and Identification. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaeger, C.; Lisec, J. Towards Unbiased Evaluation of Ionization Performance in LC-HRMS Metabolomics Method Development. Metabolites 2022, 12, 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12050426
Jaeger C, Lisec J. Towards Unbiased Evaluation of Ionization Performance in LC-HRMS Metabolomics Method Development. Metabolites. 2022; 12(5):426. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12050426
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaeger, Carsten, and Jan Lisec. 2022. "Towards Unbiased Evaluation of Ionization Performance in LC-HRMS Metabolomics Method Development" Metabolites 12, no. 5: 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12050426
APA StyleJaeger, C., & Lisec, J. (2022). Towards Unbiased Evaluation of Ionization Performance in LC-HRMS Metabolomics Method Development. Metabolites, 12(5), 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12050426






