High Resolution Magic Angle Spinning Proton NMR Study of Alzheimer’s Disease with Mouse Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
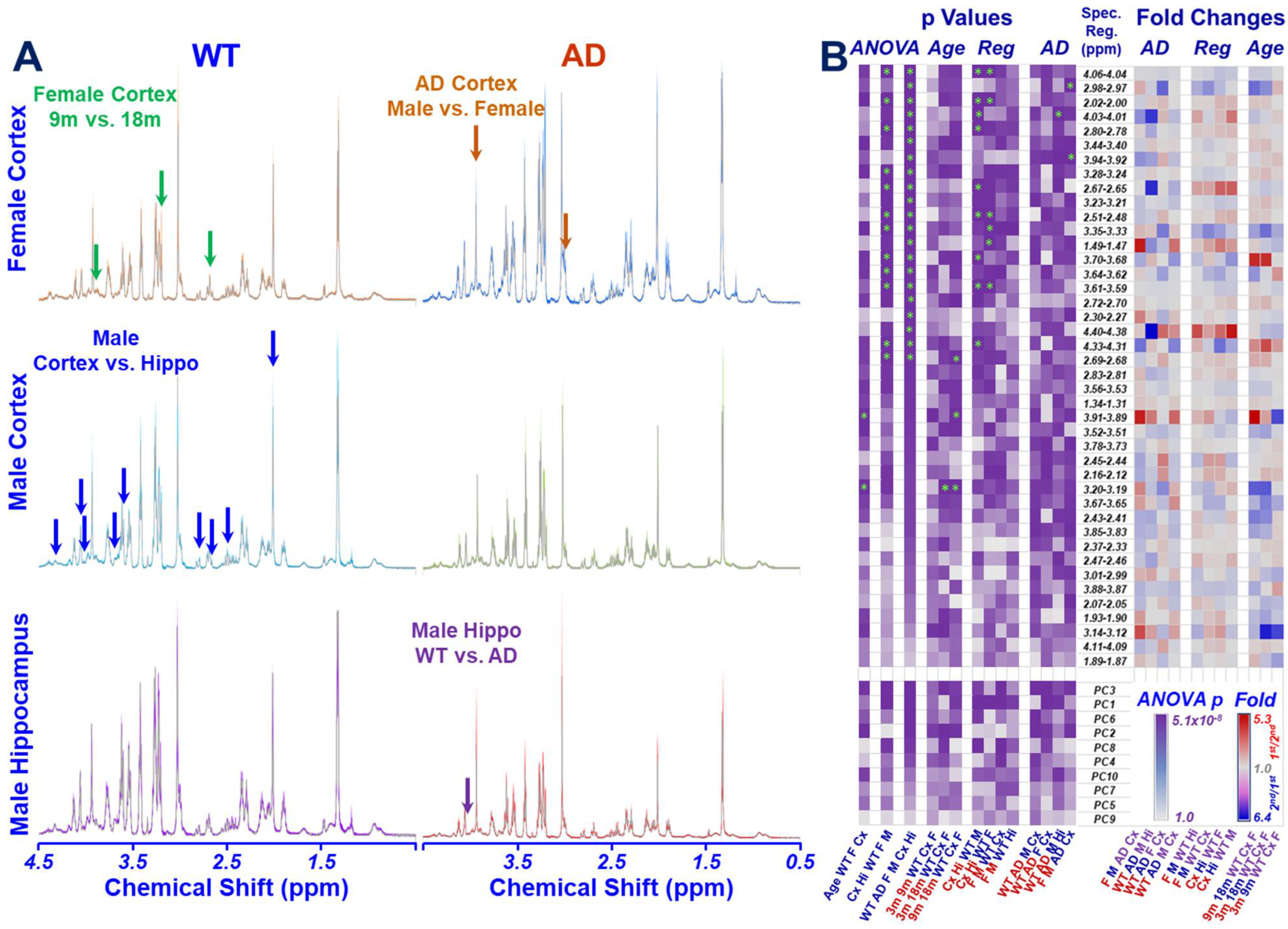
2.1. HRMAS NMR and Metabolomics
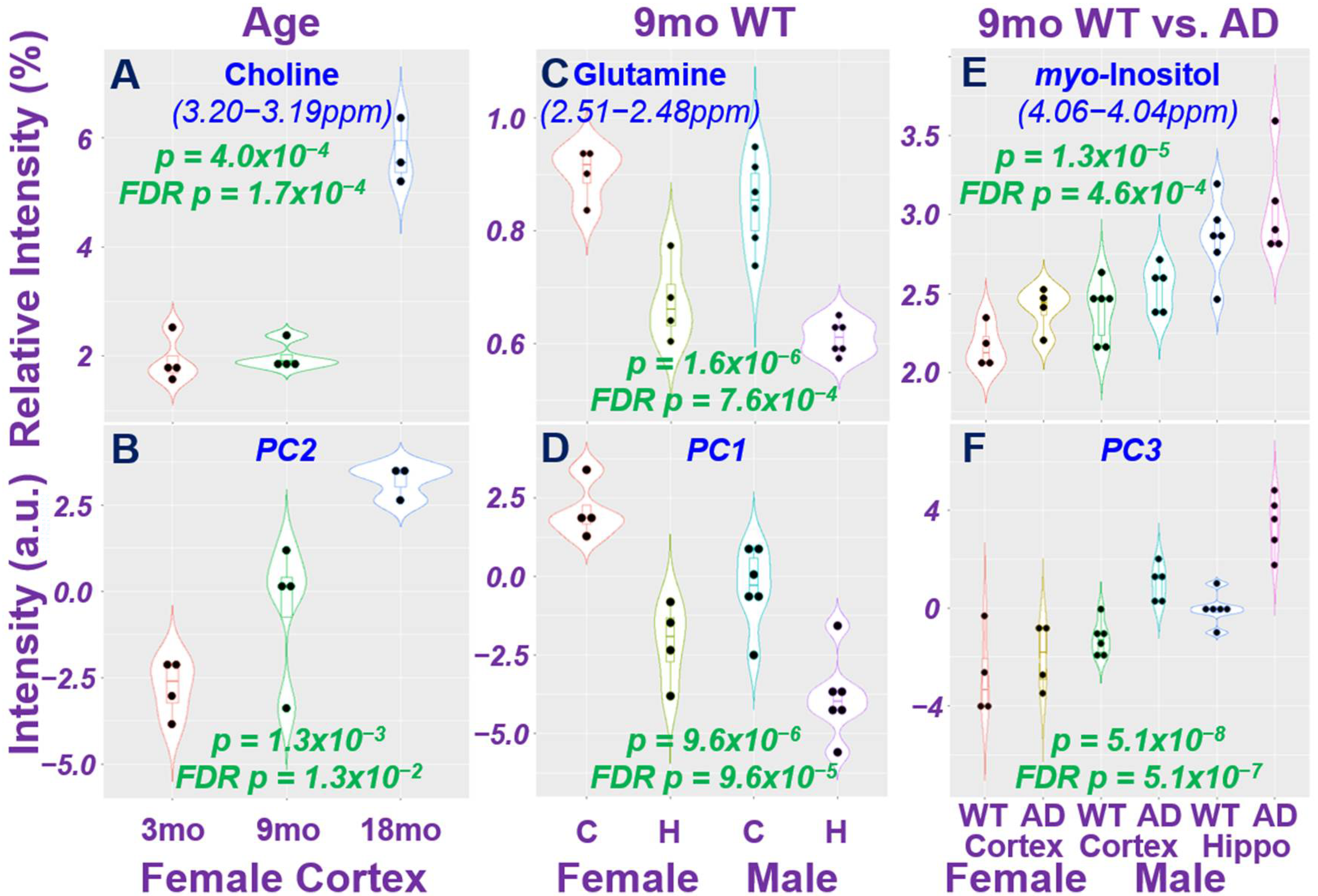
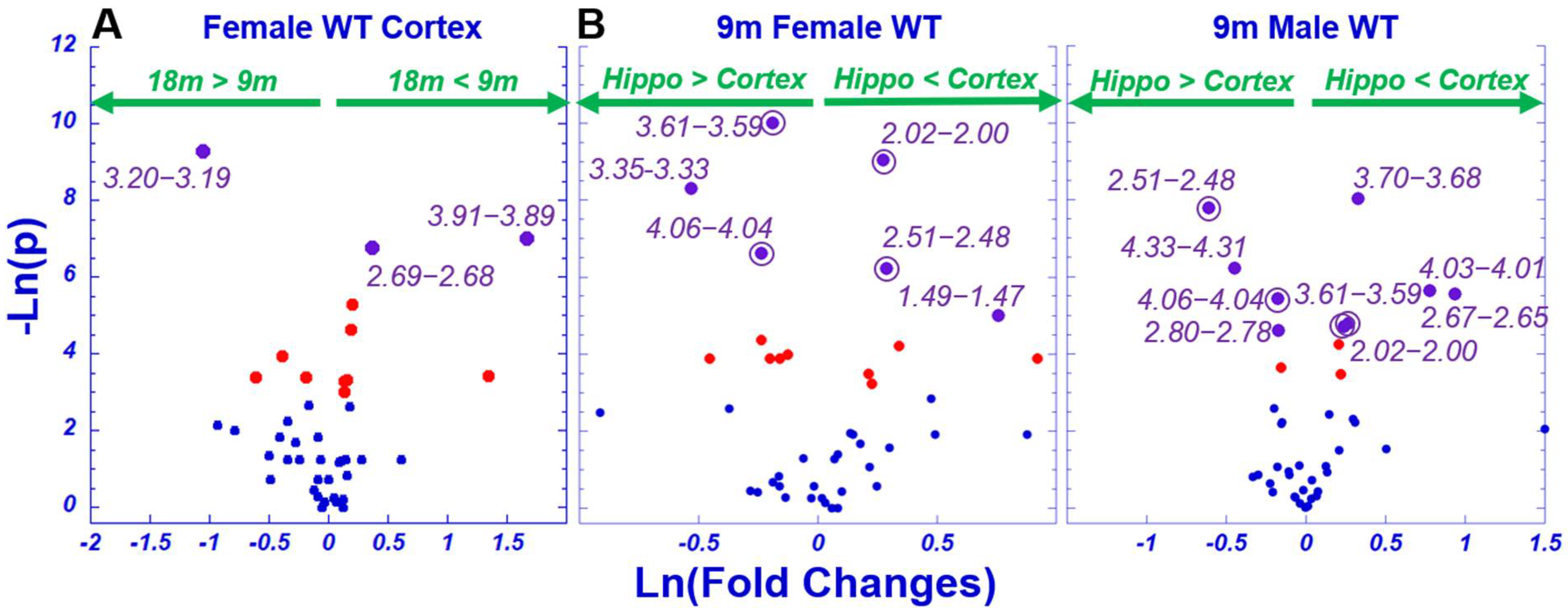
2.2. Age Difference among Females and Brain Regional Differences for 9-Month Male and Female Wild-Type Animals
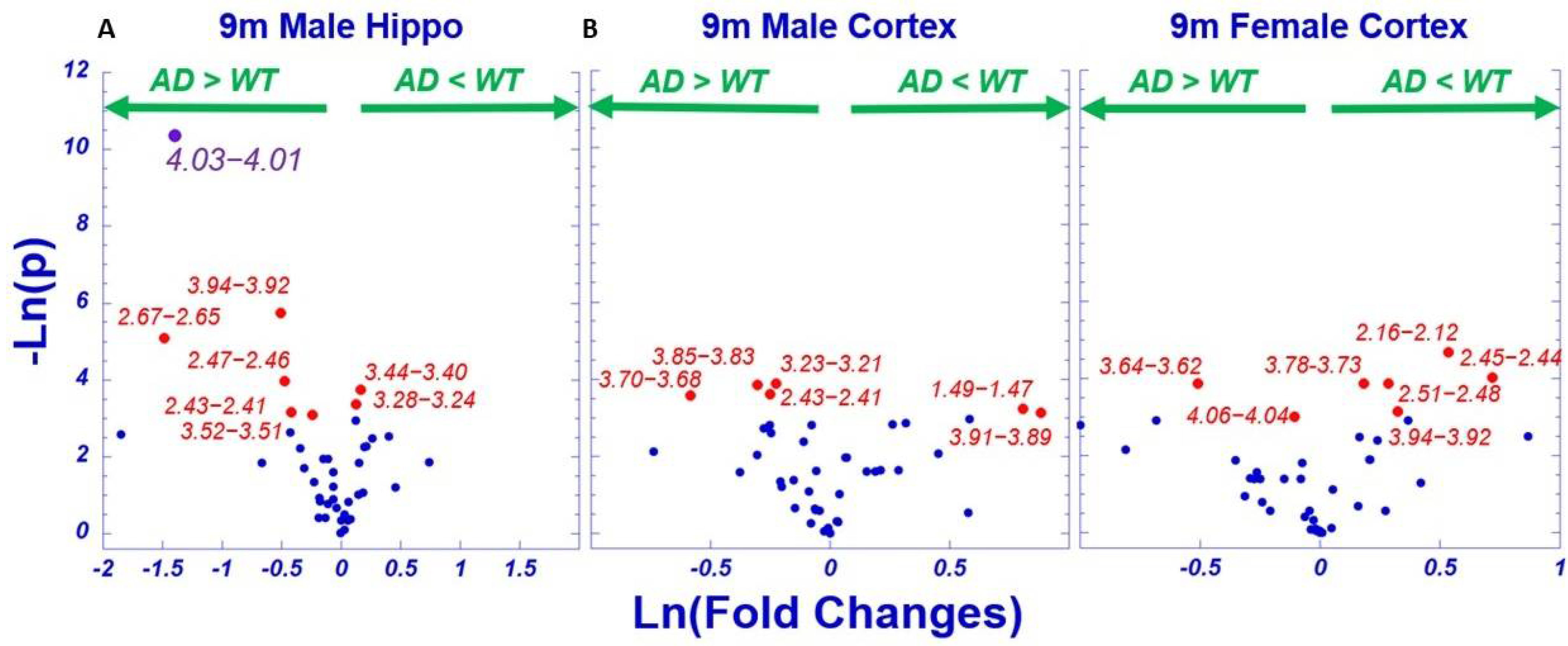
2.3. AD-Associated Metabolomics Differences for 9-Month Animals
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Models
4.2. Harvest of Mice Brain Tissues
4.3. HRMAS NMR
4.4. Data Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aging NIo. Alzheimer’s Disease Fact Sheet; National Institute of Health. Available online: https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/alzheimers-disease-fact-sheet (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Arastoo, M.; Lofthouse, R.; Penny, L.K.; Harrington, C.R.; Porter, A.; Wischik, C.M.; Palliyil, S. Current Progress and Future Directions for Tau-Based Fluid Biomarker Diagnostics in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Alafuzoff, I.; Arzberger, T.; Kretzschmar, H.; Del Tredici, K. Staging of Alzheimer disease-associated neurofibrillary pathology using paraffin sections and immunocytochemistry. Acta Neuropathol. 2006, 112, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dienel, G.A. Metabolomic Assays of Postmortem Brain Extracts: Pitfalls in Extrapolation of Concentrations of Glucose and Amino Acids to Metabolic Dysregulation In Vivo in Neurological Diseases. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 2239–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, E.; Wisniewski, T. Alzheimer’s disease: Experimental models and reality. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 133, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotz, J.; Bodea, L.G.; Goedert, M. Rodent models for Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensley, K.; Kursula, P. Collapsin Response Mediator Protein-2 (CRMP2) is a Plausible Etiological Factor and Potential Therapeutic Target in Alzheimer’s Disease: Comparison and Contrast with Microtubule-Associated Protein Tau. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2016, 53, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacovich, V.; Espindola, S.L.; Alloatti, M.; Pozo Devoto, V.; Cromberg, L.E.; Carna, M.E.; Forte, G.; Gallo, J.-M.; Bruno, L.; Stokin, G.B.; et al. Tau Isoforms Imbalance Impairs the Axonal Transport of the Amyloid Precursor Protein in Human Neurons. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, T.; Hu, Y.; Verghese, P.B.; Bateman, R.J.; Braunstein, J.B.; Fogelman, I.; Budur, K.; Florian, H.; Mendonca, N.; Holtzman, D.M. Preclinical and Clinical Development of ABBV-8E12, a Humanized Anti-Tau Antibody, for Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Tauopathies. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 4, 236–241. [Google Scholar]
- Huynh, T.V.; Liao, F.; Francis, C.M.; Robinson, G.O.; Serrano, J.R.; Jiang, H.; Roh, J.; Finn, M.B.; Sullivan, P.M.; Esparza, T.J.; et al. Age-Dependent Effects of apoE Reduction Using Antisense Oligonucleotides in a Model of beta-amyloidosis. Neuron 2017, 96, 1013–1023.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran-Prado, M.; Frontinan, J.; Santiago-Mora, R.; Peinado, J.R.; Parrado-Fernandez, C.; Gomez-Almagro, M.V.; Moreno, M.; López-Domínguez, J.A.; Villalba, J.M.; Alcaín, F.J. Coenzyme Q10 protects human endothelial cells from beta-amyloid uptake and oxidative stress-induced injury. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, M.M.; Caamano-Gutierrez, E.; Gant, M.S.; Grosman, R.X.; Madine, J. Using an NMR metabolomics approach to investigate the pathogenicity of amyloid-beta and alpha-synuclein. Metab. Off. J. Metab. Soc. 2017, 13, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Assche, R.; Temmerman, L.; Dias, D.A.; Boughton, B.; Boonen, K.; Braeckman, B.P.; Schoofs, L.; Roessner, U. Metabolic profiling of a transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans Alzheimer model. Metab. Off. J. Metab. Soc. 2015, 11, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.Y.; Bingham, E.J.; Twine, S.M.; Geiger, J.D.; Ghribi, O. Metabolomic Identification in Cerebrospinal Fluid of the Effects of High Dietary Cholesterol in a Rabbit Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Metabolomics 2012, 2, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, J.; Correia, M.; Martins, I.; Henriques, A.G.; Delgadillo, I.; da Cruz, E.S.O.; Nunes, A. FTIR and Raman Spectroscopy Applied to Dementia Diagnosis Through Analysis of Biological Fluids. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2016, 52, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Dominguez, R.; Gonzalez-Dominguez, A.; Sayago, A.; Fernandez-Recamales, A. Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomic Multiplatform for Alzheimer’s Disease Research. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1750, 125–137. [Google Scholar]
- Enche Ady, C.N.A.; Lim, S.M.; Teh, L.K.; Salleh, M.Z.; Chin, A.V.; Tan, M.P.; Poi, P.J.H.; Kamaruzzaman, S.B.; Majeed, A.B.A.; Ramasamy, K. Metabolomic-guided discovery of Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers from body fluid. J. Neurosci. Res. 2017, 95, 2005–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marksteiner, J.; Oberacher, H.; Humpel, C. Acyl-Alkyl-Phosphatidlycholines are Decreased in Saliva of Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease as Identified by Targeted Metabolomics. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2019, 68, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, S.; Huan, T.; Tran, T.; Zheng, J.; Camicioli, R.; Li, L.; Dixon, R.A. Alzheimer’s Biomarkers From Multiple Modalities Selectively Discriminate Clinical Status: Relative Importance of Salivary Metabolomics Panels, Genetic, Lifestyle, Cognitive, Functional Health and Demographic Risk Markers. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, T.; Tran, T.; Zheng, J.; Sapkota, S.; MacDonald, S.W.; Camicioli, R.; Dixon, R.A.; Li, L. Metabolomics Analyses of Saliva Detect Novel Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2018, 65, 1401–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Geddes, T.; Han, B.; Bahado-Singh, R.O.; Wilson, G.D.; Imam, K.; Maddens, M.; Graham, S.F. Diagnostic Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease as Identified in Saliva using 1H NMR-Based Metabolomics. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2017, 58, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socha, E.; Koba, M.; Koslinski, P. Amino acid profiling as a method of discovering biomarkers for diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases. Amino Acids 2019, 51, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Dominguez, R.; Sayago, A.; Fernandez-Recamales, A. High-Throughput Direct Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics to Characterize Metabolite Fingerprints Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis. Metabolites 2018, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leeuw, F.A.; Peeters, C.F.W.; Kester, M.I.; Harms, A.C.; Struys, E.A.; Hankemeier, T.; van Vlijmen, H.W.T.; van der Lee, S.J.; van Duijn, C.M.; Scheltens, P.; et al. Blood-based metabolic signatures in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017, 8, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.F.; Chevallier, O.P.; Elliott, C.T.; Holscher, C.; Johnston, J.; McGuinness, B.; Kehoe, P.G.; Passmore, A.P.; Green, B.D. Untargeted metabolomic analysis of human plasma indicates differentially affected polyamine and L-arginine metabolism in mild cognitive impairment subjects converting to Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Dominguez, R.; Garcia, A.; Garcia-Barrera, T.; Barbas, C.; Gomez-Ariza, J.L. Metabolomic profiling of serum in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease by capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis 2014, 35, 3321–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Suzuki, I.; Nakamura, T.; Bernier, F.; Aoshima, K.; Oda, Y. Identification of a new plasma biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease using metabolomics technology. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Wang, J.; Page, D.; Asthana, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Carlsson, C.; Okonkwo, O.C.; Li, L. Comparative Evaluation of MS-based Metabolomics Software and Its Application to Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibanez, C.; Simo, C.; Barupal, D.K.; Fiehn, O.; Kivipelto, M.; Cedazo-Minguez, A.; Cifuentes, A. A new metabolomic workflow for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1302, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trushina, E.; Dutta, T.; Persson, X.M.; Mielke, M.M.; Petersen, R.C. Identification of altered metabolic pathways in plasma and CSF in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease using metabolomics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barupal, D.K.; Fan, S.; Wancewicz, B.; Cajka, T.; Sa, M.; Showalter, M.R.; Baillie, R.; Tenenbaum, J.D.; Louie, G.; Kaddurah-Daouk, R.; et al. Generation and quality control of lipidomics data for the alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative cohort. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MahmoudianDehkordi, S.; Arnold, M.; Nho, K.; Ahmad, S.; Jia, W.; Xie, G.; Louie, G.; Kueider-Paisley, A.; Moseley, M.A.; Thompson, J.W.; et al. Altered bile acid profile associates with cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease—An emerging role for gut microbiome. Alzheimer’s Dement. J. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2019, 15, 76–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nho, K.; Kueider-Paisley, A.; MahmoudianDehkordi, S.; Arnold, M.; Risacher, S.L.; Louie, G.; Blach, C.; Baillie, R.; Han, X.; Kastenmüller, G.; et al. Altered bile acid profile in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: Relationship to neuroimaging and CSF biomarkers. Alzheimer’s Dement. J. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2019, 15, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, I.; Vos, S.; Vandenberghe, R.; Scheltens, P.; Engelborghs, S.; Frisoni, G.; Molinuevo, J.L.; Wallin, A.; Lleó, A.; Popp, J.; et al. The EMIF-AD Multimodal Biomarker Discovery study: Design, methods and cohort characteristics. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2018, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varma, V.R.; Oommen, A.M.; Varma, S.; Casanova, R.; An, Y.; Andrews, R.M.; O’Brien, R.; Pletnikova, O.; Troncoso, J.C.; Toledo, J.; et al. Brain and blood metabolite signatures of pathology and progression in Alzheimer disease: A targeted metabolomics study. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanova, R.; Varma, S.; Simpson, B.; Kim, M.; An, Y.; Saldana, S.; Riveros, C.; Moscato, P.; Griswold, M.; Sonntag, D.; et al. Blood metabolite markers of preclinical Alzheimer’s disease in two longitudinally followed cohorts of older individuals. Alzheimer’s Dement. J. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2016, 12, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Begley, P.; Church, S.J.; Patassini, S.; Hollywood, K.A.; Jullig, M.; Curtis, M.A.; Waldvogel, H.J.; Faull, R.L.M.; Unwin, R.D.; et al. Graded perturbations of metabolism in multiple regions of human brain in Alzheimer’s disease: Snapshot of a pervasive metabolic disorder. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1862, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, T.; Mizuno, H.; Toyo’oka, T.; Akatsu, H.; Inoue, K.; Todoroki, K. Isotope Corrected Chiral and Achiral Nontargeted Metabolomics: An Approach for High Accuracy and Precision Metabolomics Based on Derivatization and Its Application to Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4396–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oresic, M.; Anderson, G.; Mattila, I.; Manoucheri, M.; Soininen, H.; Hyotylainen, T.; Basignani, C. Targeted Serum Metabolite Profiling Identifies Metabolic Signatures in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease, Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus and Brain Tumor. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouraki, V.; Preis, S.R.; Yang, Q.; Beiser, A.; Li, S.; Larson, M.G.; Weinstein, G.; Wang, T.J.; Gerszten, R.E.; Vasan, R.S. Association of amine biomarkers with incident dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in the Framingham Study. Alzheimer’s Dement. J. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2017, 13, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Cunningham, E.L.; Passmore, A.P.; McGuinness, B.; McAuley, D.F.; Beverland, D.; O’Brien, S.; Mawhinney, T.; Schott, J.M.; Zetterberg, H.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Spermidine, Glutamine and Putrescine Predict Postoperative Delirium Following Elective Orthopaedic Surgery. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snowden, S.G.; Ebshiana, A.A.; Hye, A.; An, Y.; Pletnikova, O.; O’Brien, R.; Troncoso, J.; Legido-Quigley, C.; Thambisetty, M. Association between fatty acid metabolism in the brain and Alzheimer disease neuropathology and cognitive performance: A nontargeted metabolomic study. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jager, P.L.; Ma, Y.; McCabe, C.; Xu, J.; Vardarajan, B.N.; Felsky, D.; Klein, H.-U.; White, C.C.; Peters, M.A.; Lodgson, B.; et al. A multi-omic atlas of the human frontal cortex for aging and Alzheimer’s disease research. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motsinger-Reif, A.A.; Zhu, H.; Kling, M.A.; Matson, W.; Sharma, S.; Fiehn, O.; Reif, D.M.; Appleby, D.H.; Doraiswamy, P.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; et al. Comparing metabolomic and pathologic biomarkers alone and in combination for discriminating Alzheimer’s disease from normal cognitive aging. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2013, 1, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.L.; Ma, M.J.; Becerra, L.; Ptak, T.; Tracey, I.; Lackner, A.; González, R.G. Quantitative neuropathology by high resolution magic angle spinning proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 6408–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.L. High Resolution Magic Angle Spinning NMR for Intact Biological Specimens Analyses: Initial Discovery, Recent Developments, and Future Directions. NMR Biomed. 2021, e4684. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.L.; Newell, K.; Mallory, A.E.; Hyman, B.T.; Gonzalez, R.G. Quantification of neurons in Alzheimer and control brains with ex vivo high resolution magic angle spinning proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy and stereology. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2002, 20, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, U.; Stute, L.; Hofling, C.; Hartlage-Rubsamen, M.; Matysik, J.; Roβner, S.; Alia, A. Sex- and age-specific modulation of brain GABA levels in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 62, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, D.C.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, D.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, G.Y.; Rhim, H.S.; Choi, H.Y.; Lee, C.U.; Choe, B.Y. Regional metabolic alteration of Alzheimer’s disease in mouse brain expressing mutant human APP-PS1 by 1H HR-MAS. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 211, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytan, N.; Choi, J.K.; Carreras, I.; Brinkmann, V.; Kowall, N.W.; Jenkins, B.G.; Dedeoglu, A. Fingolimod modulates multiple neuroinflammatory markers in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paban, V.; Manrique, C.; Filali, M.; Maunoir-Regimbal, S.; Fauvelle, F.; Alescio-Lautier, B. Therapeutic and preventive effects of methylene blue on Alzheimer’s disease pathology in a transgenic mouse model. Neuropharmacology 2014, 76 Pt A, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.K.; Carreras, I.; Dedeoglu, A.; Jenkins, B.G. Detection of increased scyllo-inositol in brain with magnetic resonance spectroscopy after dietary supplementation in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. Neuropharmacology 2010, 59, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, E.; Jung, Y.S.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.S.; Park, M.; Jeong, J.; Lee, S.K.; Yoon, H.G.; Hwang, G.S.; Namkoong, K. Metabolomic signatures in peripheral blood associated with Alzheimer’s disease amyloid-beta-induced neuroinflammation. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2014, 42, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.M.; Han, H.B.; Zhang, Q.F.; Bai, H. Application of modern neuroimaging technology in the diagnosis and study of Alzheimer’s disease. Neural. Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Velazquez, R.; Ferreira, E.; Knowles, S.; Fux, C.; Rodin, A.; Winslow, W.; Oddo, S. Lifelong choline supplementation ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease pathology and associated cognitive deficits by attenuating microglia activation. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e13037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, H.; Dong, Y.; Shi, H.N.; Culley, D.J.; Crosby, G.; Marcantonio, E.R.; Tanzi, R.E.; Xie, Z. Anesthetics isoflurane and desflurane differently affect mitochondrial function, learning, and memory. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wu, X.; Lu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Knapp, A.; Yue, Y.; Xu, T.; Xie, Z. The mitochondrial pathway of anesthetic isoflurane-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 4025–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraju, V.; Young, K.; Maudsley, A.A. Proton NMR chemical shifts and coupling constants for brain metabolites. NMR Biomed. 2000, 13, 129–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Füzesi, M.V.; Muti, I.H.; Berker, Y.; Li, W.; Sun, J.; Habbel, P.; Nowak, J.; Xie, Z.; Cheng, L.L.; Zhang, Y. High Resolution Magic Angle Spinning Proton NMR Study of Alzheimer’s Disease with Mouse Models. Metabolites 2022, 12, 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12030253
Füzesi MV, Muti IH, Berker Y, Li W, Sun J, Habbel P, Nowak J, Xie Z, Cheng LL, Zhang Y. High Resolution Magic Angle Spinning Proton NMR Study of Alzheimer’s Disease with Mouse Models. Metabolites. 2022; 12(3):253. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12030253
Chicago/Turabian StyleFüzesi, Mark V., Isabella H. Muti, Yannick Berker, Wei Li, Joseph Sun, Piet Habbel, Johannes Nowak, Zhongcong Xie, Leo L. Cheng, and Yiying Zhang. 2022. "High Resolution Magic Angle Spinning Proton NMR Study of Alzheimer’s Disease with Mouse Models" Metabolites 12, no. 3: 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12030253
APA StyleFüzesi, M. V., Muti, I. H., Berker, Y., Li, W., Sun, J., Habbel, P., Nowak, J., Xie, Z., Cheng, L. L., & Zhang, Y. (2022). High Resolution Magic Angle Spinning Proton NMR Study of Alzheimer’s Disease with Mouse Models. Metabolites, 12(3), 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12030253






