Metabolomic Studies in Inner Ear Pathologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
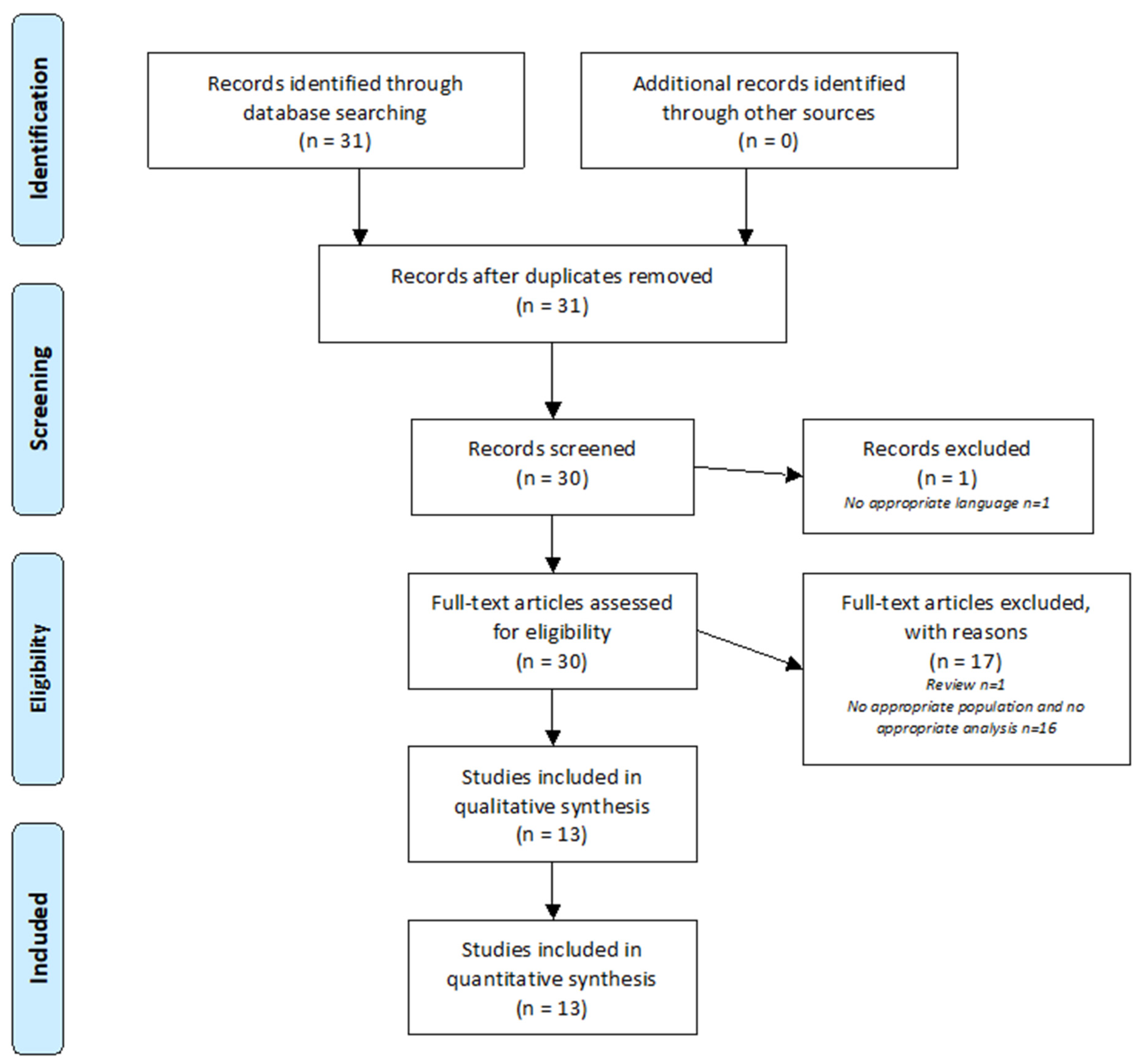
2. Methods
2.1. Research Strategy
2.2. Selection Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
3. Results
3.1. Types of Samples
3.2. Analytical Techniques
3.3. Animal Studies
3.3.1. Mice
3.3.2. Rats
3.3.3. Guinea Pigs
3.4. Human Biomarker Research
3.4.1. Urine Sample
3.4.2. Perilymph Sample
3.4.3. Plasma Sample
3.4.4. In Vitro Cells
4. Discussion
4.1. Slow Progression of SNHL-Related Metabolomics Studies
4.2. What Is the Most Promising Biological Fluid for Studies of SNHL?
4.3. Progress in Metabolomic Analysis Methods on Constrained Biological Fluids
4.4. Next Steps Needed in the Field of Metabolomic Studies
5. Limits
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stevens, G.; Flaxman, S.; Brunskill, E.; Mascarenhas, M.; Mathers, C.D.; Finucane, M. Global Burden of Disease Hearing Loss Expert Group. Global and regional hearing impairment prevalence: An analysis of 42 studies in 29 countries. Eur. J. Public Health 2013, 23, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kral, A.; O’Donoghue, G.M. Profound deafness in childhood. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1438–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, L.L.; Tucci, D.L. Hearing Loss in Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2465–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blarney, P.; Arndt, P.; Bergeron, F.; Bredberg, G.; Brimacombe, J.; Facer, G.; Larky, J.; Lindström, B.; Nedzelski, J.; Peterson, A.; et al. Factors affecting auditory performance of postlinguistically deaf adults using cochlear implants. Audiol. Neurootol. 1996, 1, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.C.; Ryan, A.F. Mechanisms of sensorineural cell damage, death and survival in the cochlea. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodacre, R. Metabolomics shows the way to new discoveries. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Carta, F.; Lussu, M.; Bandino, F.; Noto, A.; Peppi, M.; Chuchueva, N.; Atzori, L.; Fanos, V.; Puxeddu, R.; Antonio, N.; et al. Metabolomic analysis of urine with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A preliminary study. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2017, 44, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavel, S.; Lefèvre, A.; Bakhos, D.; Dufour-Rainfray, D.; Blasco, H.; Emond, P. Validation of metabolomics analysis of human perilymph fluid using liquid chromatography-mass spectroscopy. Hear. Res. 2018, 367, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diémé, B.; Lefèvre, A.; Nadal-Desbarats, L.; Galineau, L.; Hounoum, B.M.; Montigny, F.; Blasco, H.; Andres, C.; Emond, P.; Mavel, S. Workflow methodology for rat brain metabolome exploration using NMR, LC-MS and GC-MS analytical platforms. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 142, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuster-García, C.; García-Bohórquez, B.; Rodríguez-Muñoz, A.; Aller, E.; Jaijo, T.; Millán, J.; García-García, G. Usher Syndrome: Genetics of a Human Ciliopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, C.; Riahi, Z.; Chantot-Bastaraud, S.; Smagghe, L.; Letexier, M.; Marcaillou, C.; Lefèvre, G.M.; Hardelin, J.-P.; El-Amraoui, A.; Singh-Estivalet, A.; et al. An innovative strategy for the molecular diagnosis of Usher syndrome identifies causal biallelic mutations in 93% of European patients. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 24, 1730–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, H.A.; Pich, A.; Schröder, A.; Scheper, V.; Lilli, G.; Reuter, G.; Lenarz, T. Proteome Analysis of Human Perilymph Using an Intraoperative Sampling Method. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 1911–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lysaght, A.C.; Kao, S.-Y.; Paulo, J.A.; Merchant, S.N.; Steen, H.; Stankovic, K.M. Proteome of human perilymph. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 3845–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, T.-T.; Blasco, H.; Emond, P.; Andres, C.; Lefevre, A.; Lescanne, E.; Bakhos, D. Relationship between Metabolomics Profile of Perilymph in Cochlear-Implanted Patients and Duration of Hearing Loss. Metabolites 2019, 9, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, T.; Yamashita, D.; Irino, Y.; Kitamoto, J.; Fukuda, Y.; Inokuchi, G.; Hasegawa, S.; Otsuki, N.; Yoshida, M.; Nibu, K.-I. Metabolomic profiling in inner ear fluid by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry in guinea pig cochlea. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 606, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirttilä, K.; Pierre, P.V.; Haglöf, J.; Engskog, M.; Hedeland, M.; Laurell, G.; Arvidsson, T.; Pettersson, C. An LCMS-based untargeted metabolomics protocol for cochlear perilymph: Highlighting metabolic effects of hydrogen gas on the inner ear of noise exposed Guinea pigs. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransson, A.E.; Kisiel, M.; Pirttilä, K.; Pettersson, C.; Pierre, P.V.; Laurell, G.F.E. Hydrogen Inhalation Protects against Ototoxicity Induced by Intravenous Cisplatin in the Guinea Pig. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Lee, H.-J.; Wan, G.; Wang, G.-P.; Zhang, L.; Sajjakulnukit, P.; Schacht, J.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Corfas, G. Auditory metabolomics, an approach to identify acute molecular effects of noise trauma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, P.V.; Haglöf, J.; Linder, B.; Engskog, M.K.R.; Arvidsson, T.; Pettersson, C.; Fransson, A.; Laurell, G. Cisplatin-induced metabolome changes in serum: An experimental approach to identify markers for ototoxicity. Acta Otolaryngol. 2017, 137, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaboon, N.E.; Banaganapalli, B.; Nasser, K.; Razeeth, M.; Alsaedi, M.S.; Rashidi, O.M.; Abdelwehab, L.S.; Alahmadi, T.S.; Safdar, O.Y.; Shaik, J.; et al. Exome sequencing and metabolomic analysis of a chronic kidney disease and hearing loss patient family revealed RMND1 mutation induced sphingolipid metabolism defects. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y. Plasma metabolomic profiling in workers with noise-induced hearing loss: A pilot study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 68539–68550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Ding, Y.; Liu, P.-Z.; Song, H.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-P.; Li, M.; Shi, J.-R. Investigation of the Material Basis Underlying the Correlation between Presbycusis and Kidney Deficiency in Traditional Chinese Medicine via GC/MS Metabolomics. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 762092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Zhu, Y.; Aa, J.; Smith, P.F.; De Ridder, D.; Wang, G.; Zheng, Y. Brain Metabolic Changes in Rats following Acoustic Trauma. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kather, M.; Koitzsch, S.; Breit, B.; Plontke, S.; Kammerer, B.; Liebau, A. Metabolic reprogramming of inner ear cell line HEI-OC1 after dexamethasone application. Metabolomics 2021, 17, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodoridis, G.A.; Gika, H.G.; Want, E.J.; Wilson, I. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry based global metabolite profiling: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 711, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shew, M.; Wichova, H.; Peter, M.S.; Warnecke, A.; Staecker, H. Distinct MicroRNA Profiles in the Perilymph and Serum of Patients With Menière’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 646928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, H.A.; Pich, A.; Prenzler, N.K.; Lenarz, T.; Harre, J.; Staecker, H.; Durisin, M.; Warnecke, A. Personalized Proteomics for Precision Diagnostics in Hearing Loss: Disease-Specific Analysis of Human Perilymph by Mass Spectrometry. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 21241–21254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollard, M.E.; Stanley, E.G.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.; Holmes, E. NMR-based metabonomic approaches for evaluating physiologica influences on biofluid composition. NMR Biomed. 2005, 18, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Wang, P.; Han, Y.; Wang, X. Recent and potential developments of biofluid analyses in metabolomics. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Puel, J.L. Toward Cochlear Therapies. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 2477–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, M.W.; Heavens, R.P.; Baldwin, B.A. Auditory evoked potentials recorded from conscious sheep. Brain Res. Bull. 1985, 15, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibel, V.A.; Lavinsky, L.; De Oliveira, J.A. Morphometric study of the external and middle ear anatomy in sheep: A possible model for ear experiments. Clin. Anat. 2006, 19, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Authors, Year | Participants | Pathology | Sample | Metabolomic Technique | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gaboon NEA et al., 2020 [17] | Hu | Mitochondrial disease | Blood | LCMS | Metabolomic analysis of renal disease with HL induced by a RMND1 mutation revealed ceramide accumulation |
| Trinh TT et al., 2019 [11] | Hu | SNHL | Perilymph | LCMS | Relationship between metabolomics profile and duration of HL |
| Mavel S et al., 2018 [6] | Hu | SNHL | Perilymph | LCMS | Feasibility of metabolomic analysis of human perilymph |
| Carta F et al., 2017 [5] | Hu | Metabolomic study of urine in sudden HL | Urine | NMR spectrometry | Metabolomic profiles differ depending on auditory recovery following dexamethasone treatment |
| Dong Y et al., 2013 [19] | Hu | Presbyacusis and renal dysfunction | Urine | GCMS | Difference in metabolomic profile for patients with renal failure, with and without hearing impairment |
| Miao L et al., 2021 [18] | Hu | NIHL | Blood | LCMS | NIHL-induced changes in the plasma profile |
| Pirttilä K et al., 2019 [13] | GP | NIHL | Perilymph | LCMS | Difference in terms of metabolomic profiles between NIHL and NH |
| Fransson A et al., 2017 [14] | GP | Ototoxicity to cisplatin | Perilymph | LCMS | Cisplatin-induced changes in the perilymph metabolomic profile |
| Videhult Pierre et al., 2017 [16] | GP | Ototoxicity to cisplatin | Blood | LCMS | Cisplatin-induced changes in the serum metabolome |
| Fujita T et al., 2015 [12] | GP | NIHL | Perilymph | GCMS | NIHL-induced changes in the perilymph metabolomic profile |
| Ji L et al., 2019 [15] | Mouse | NIHL | Perilymph Temporal bone | LCMS | NIHL-induced changes in the temporal bone metabolomic profile |
| He J et al., 2017 [20] | Rat | NIHL | Cerebral tissue | GCMS | Cerebral metabolic changes in rats after exposure to acoustic trauma |
| Kather M et al., 2021 [21] | Cells (in vitro model) | Research | Cell line HEI-OC1 | GCMS | Dexamethasone-induced metabolic changes in a ciliated cell line under both growth conditions |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boullaud, L.; Blasco, H.; Trinh, T.-T.; Bakhos, D. Metabolomic Studies in Inner Ear Pathologies. Metabolites 2022, 12, 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12030214
Boullaud L, Blasco H, Trinh T-T, Bakhos D. Metabolomic Studies in Inner Ear Pathologies. Metabolites. 2022; 12(3):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12030214
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoullaud, Luc, Hélène Blasco, Thuy-Trân Trinh, and David Bakhos. 2022. "Metabolomic Studies in Inner Ear Pathologies" Metabolites 12, no. 3: 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12030214
APA StyleBoullaud, L., Blasco, H., Trinh, T.-T., & Bakhos, D. (2022). Metabolomic Studies in Inner Ear Pathologies. Metabolites, 12(3), 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12030214








