Glycosphingolipid Levels in Urine Extracellular Vesicles Enhance Prediction of Therapeutic Response in Lupus Nephritis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Glycosphingolipids in Urine Extracellular Vesicles May Serve as Biomarkers to Predict Therapeutic Response
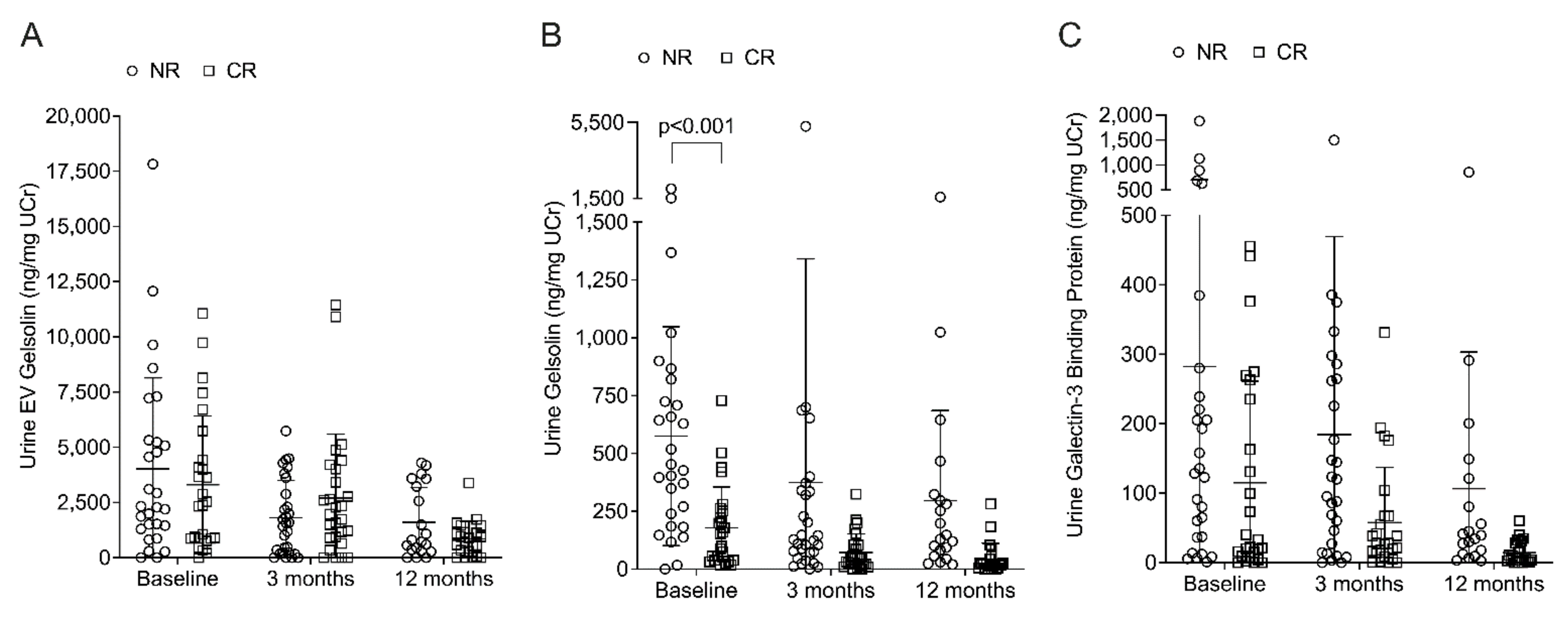
2.2. Urine Proteins Elevated in Non-Responders, but May Not Predict Therapeutic Response
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement and Human Samples
4.2. Urine Extracellular Vesicle Isolation
4.3. Lipidomic Analyses
4.4. Protein Analyses
4.5. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wallace, D.J. Dubois’ Lupus Erythematosus and Related Syndromes, 9th ed.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rovin, B.H.; Teng, Y.K.O.; Ginzler, E.M.; Arriens, C.; Caster, D.J.; Romero-Diaz, J.; Gibson, K.; Kaplan, J.; Lisk, L.; Navarra, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of voclosporin versus placebo for lupus nephritis (AURORA 1): A double-blind, randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 2070–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furie, R.; Rovin, B.H.; Houssiau, F.; Malvar, A.; Teng, Y.O.; Contreras, G.; Amoura, Z.; Yu, X.; Mok, C.-C.; Santiago, M.B.; et al. Two-Year, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Belimumab in Lupus Nephritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1117–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, S.V.; Almaani, S.; Brodsky, S.; Rovin, B.H. Update on Lupus Nephritis: Core Curriculum 2020. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arazi, A.; Rao, D.A.; Berthier, C.C.; Davidson, A.; Liu, Y.; Hoover, P.J.; Chicoine, A.; Eisenhaure, T.M.; Jonsson, A.H.; Li, S.; et al. The immune cell landscape in kidneys of patients with lupus nephritis. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 902–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, S.V.; Malvar, A.; Song, H.; Alberton, V.; Lococo, B.; Vance, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, L.; Birmingham, D.; Rovin, B.H. Molecular imaging of the kidney in lupus nephritis to characterize response to treatment. Transl. Res. 2016, 182, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolaou, O.; Kousios, A.; Hadjisavvas, A.; Lauwerys, B.; Sokratous, K.; Kyriacou, K. Biomarkers of systemic lupus erythematosus identified using mass spectrometry-based proteomics: A systematic review. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 21, 993–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragón, C.C.; Tafúr, R.-A.; Suárez-Avellaneda, A.; Martínez, T.; Salas, A.D.L.; Tobón, G.J. Urinary biomarkers in lupus nephritis. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2020, 3, 100042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radin, M.; Miraglia, P.; Barinotti, A.; Fenoglio, R.; Roccatello, D.; Sciascia, S. Prognostic and Diagnostic Values of Novel Serum and Urine Biomarkers in Lupus Nephritis: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Nephrol. 2021, 52, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanarsa, K.; Soomro, S.; Zhang, T.; Strachan, B.; Pedroza, C.; Nidhi, M.; Cicalese, P.; Gidley, C.; Dasari, S.; Mohan, S.; et al. Quantitative planar array screen of 1000 proteins uncovers novel urinary protein biomarkers of lupus nephritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1349–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitorino, R.; Ferreira, R.; Guedes, S.; Amado, F.; Thongboonkerd, V. What can urinary exosomes tell us? Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 3265–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowling, T.K.; Mather, A.R.; Thiyagarajan, T.; Hernández-Corbacho, M.J.; Powers, T.W.; Jones, E.E.; Snider, A.J.; Oates, J.C.; Drake, R.R.; Siskind, L.J. Renal Glycosphingolipid Metabolism Is Dysfunctional in Lupus Nephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 26, 1402–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sundararaj, K.; Rodgers, J.I.; Marimuthu, S.; Siskind, L.J.; Bruner, E.; Nowling, T.K. Neuraminidase activity mediates IL-6 production by activated lupus-prone mesangial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2018, 314, F630–F642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingwood, C.A. Glycosphingolipid Functions. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a004788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mather, A.R.; Siskind, L.J. Glycosphingolipids and kidney disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2011, 721, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupre, T.V.; Siskind, L.J. The role of sphingolipids in acute kidney injury. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2018, 70, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, C.T.; Østergaard, O.; Rekvig, O.P.; Sturfelt, G.; Jacobsen, S.; Heegaard, N.H.H. Galectin-3 binding protein links circulating microparticles with electron dense glomerular deposits in lupus nephritis. Lupus 2015, 24, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodgers, J.; Sundararaj, K.; Bruner, E.; Wolf, B.; Nowling, T.K. The role of neuraminidase 1 (NEU1) in cytokine release by primary mouse mesangial cells and disease outcomes in murine lupus nephritis. Autoimmunity 2021, 54, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wei, W.; Liu, M.-L. Extracellular vesicles and lupus nephritis—New insights into pathophysiology and clinical implications. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luís, M.S.F.; Bultink, I.E.M.; Silva, J.A.P.D.; E Voskuyl, A.; Inês, L.S. Early predictors of renal outcome in patients with proliferative lupus nephritis: A 36-month cohort study. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 5134–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helget, L.N.; Dillon, D.J.; Wolf, B.; Parks, L.P.; Self, S.E.; Bruner, E.T.; Oates, E.E.; Oates, J.C. Development of a lupus nephritis suboptimal response prediction tool using renal histopathological and clinical laboratory variables at the time of diagnosis. Lupus Sci. Med. 2021, 8, e000489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, H.; Li, W.H.; Meng, H.X.; Fan, Y.Z.; Li, W.J.; Ji, Y.T.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, L.; Jin, X.M.; et al. The value of decreased plasma gelsolin levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis in diagnosis and disease activity evaluation. Lupus 2013, 22, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, S.; Heras, M.; Herrero, P.; Amigó, N.; Garcés, E.; Girona, J.; Correig, X.; Canela, N.; Castro, A. Gelsolin: A new biomarker of disease activity in SLE patients associated with HDL-c. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovin, B.H.; Van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Aranow, C.; Wagner, C.; Gordon, R.; Zhuang, Y.; Belkowski, S.; Hsu, B. A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Treatment with Sirukumab (CNTO 136) in Patients with Active Lupus Nephritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2174–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, X.; Tang, J.; Jin, X. Plasma gelsolin levels are decreased and correlate with fibrosis in IgA nephropathy. Exp. Biol. Med. 2013, 238, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idborg, H.; Eketjäll, S.; Pettersson, S.; Gustafsson, J.T.; Zickert, A.; Kvarnström, M.; Oke, V.; Jakobsson, P.-J.; Gunnarsson, I.; Svenungsson, E. TNF-α and plasma albumin as biomarkers of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus Sci. Med. 2018, 5, e000260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, A.; Buyon, J.; Mohan, C.; Zhang, T.; Belmont, H.; Izmirly, P.; Clancy, R.; Trujillo, J.M.; Fine, D.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Integrated urine proteomics and renal single-cell genomics identify an IFN-γ response gradient in lupus nephritis. JCI Insight 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovin, B.H.; Furie, R.; Latinis, K.; Looney, R.J.; Fervenza, F.C.; Sanchez-Guerrero, J.; Maciuca, R.; Zhang, D.; Garg, J.P.; Brunetta, P.; et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in patients with active proliferative lupus nephritis: The lupus nephritis assessment with rituximab study. Arthritis Care Res. 2012, 64, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furie, R.; Nicholls, K.; Cheng, T.; Houssiau, F.; Burgos-Vargas, R.; Chen, S.; Hillson, J.L.; Meadows-Shropshire, S.; Kinaszczuk, M.; Merrill, J.T. Efficacy and Safety of Abatacept in Lupus Nephritis: A Twelve-Month, Randomized, Double-Blind Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2013, 66, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, F.E., Jr.; Lee, K.L.; Califf, R.M.; Pryor, D.B.; Rosati, R.A. Regression modelling strategies for improved prognostic prediction. Stat. Med. 1984, 3, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeDell, E.; Petersen, M.; van der Laan, M. Computationally efficient confidence intervals for cross-validated area under the ROC curve estimates. Electron. J. Stat. 2015, 9, 1583–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | LUNAR NR (n = 9) | LUNAR CR (n = 5) | Abatacept NR (n = 19) | Abatacept CR (n = 15) | MUSC CR (n = 6) | Cohort Comparisons | All NR (n = 28) | All CR (n = 26) | All NR vs. CR p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR p-Value | CR p-Value | |||||||||
| Age, years, mean (SD) | 31.1 (13.0) | 24.4 (5.9) | 31.2 (5.8) | 35.4 (7.9) | 32.0 (8.5) | 0.978 | 0.011 | 31.2 (8.54) | 32.5 (8.57) | 0.573 |
| Race, n (%) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.031 | |||||||
| Black | 1 | 2 | 1 | 6 | 1 (3.57) | 9 (34.6) | ||||
| Hispanic | 5 | 3 | 5 (17.86) | 3 (11.5) | ||||||
| Other/Asian | 12 | 7 | 12 (42.86) | 7 (26.9) | ||||||
| White | 3 | 7 | 7 | 10 (35.71) | 7 (26.9) | |||||
| LN Class, n (%) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.032 | |||||||
| I | 1 | 0. (0.00) | 1 (3.85) | |||||||
| III, IV | 6 | 5 | 13 | 13 | 2 | 19 (67.9) | 20 (71.4) | |||
| III + V, IV + V | 3 | 6 | 2 | 9 (32.1) | 2 (7.14) | |||||
| V | 2 | 0 (0.00) | 2 (7.14) | |||||||
| no biopsy | 1 | 0 (0.00) | 1 (3.85) | |||||||
| C3 Comp, mean (SD) | 72.6 (29.3) | 75.3 (18.4) | 56.6 (21.4) | 70.7 (22.2) | 59.9 (22.2) | 0.142 | 0.683 | 62.0 (25.0) | 69.1 (29.1) | 0.270 |
| C4 Comp, mean (SD) | 12.9 (8.2) | 11.4 (4.7) | 13.7 (5.6) | 15.3 (6.7) | 9.9 (2.6) | 0.373 | 0.151 | 13.4 (6.43) | 14.34 (6.43) | 0.624 |
| Anti-dsDNA, median (IQR) | 66.3 (322.1) | 66.4 (1009.5) | 89.8 (256.7) | 76.6 (189.0) | 174.0 (167.0) | 0.797 | 0.617 | 71.9 (249.1) | 94.0 (168.2) | 0.560 |
| UPr:UCr, mean (SD) | 3.0 (2.6) | 2.3 (1.8) | 3.4 (2.6) | 1.4 (1.6) | 1.5 (1.9) | 0.606 | 0.097 | 3.28 (2.56) | 1.59 (1.66) | 0.006 |
| eGFR, mean (SD) | 67.5 (34.2) | 125.4 (17.4) | 88.6 (33.1) | 102.3 (23.2) | 122.5 (26.9) | 0.116 | 0.059 | 81.8 (34.3) | 111.4 (24.8) | <0.001 |
| Serum Creatinine, mean (SD) | 1.3 (0.7) | 0.7 (0.2) | 1.0 (0.5) | 0.8 (0.3) | 0.7 (0.2) | 0.099 | 0.431 | 1.1 (0.57) | 0.75 (0.24) | 0.005 |
| Marker | Non-Responders (n = 28) Median (IQR; min, max) | Complete Responders (n = 26) Median (IQR; min, max) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| HexCer C16 | 1.52 (1.70; 0.04, 9.79) | 0.29 (0.52; 0.01, 2.36) | <0.001 |
| HexCerC18 | 0.13 (0.29; 0.00, 1.37) | 0.03 (0.08; 0.00, 0.23) | <0.001 |
| HexCer C20 | 0.39 (0.92; 0.05, 4.14) | 0.08 (0.18; 0.00, 0.70) | <0.001 |
| HexCer C22:1 | 0.09 (0.14; 0.02, 1.68) | 0.04 (0.08; 0.00, 0.18) | 0.003 |
| HexCer C22 | 0.93 (1.97; 0.19, 8.80) | 0.29 (0.57; 0.02, 2.11) | <0.001 |
| HexCer C24:1 | 0.92 (2.02; 0.13, 11.60) | 0.17 (0.39; 0.01, 2.26) | <0.001 |
| HexCer C24 | 1.03 (1.74; 0.08, 11.40) | 0.26 (0.42; 0.01, 1.97) | <0.001 |
| HexCer Total | 5.33 (8.67; 0.56, 44.80) | 1.21 (1.69; 0.07, 9.23) | <0.001 |
| LacCer C16 | 4.63 (6.12; 0.11, 19.00) | 0.71 (1.49; 0.00, 5.44) | <0.001 |
| LacCer C18 | 0.21 (0.36; 0.00, 1.01) | 0.04 (0.09; 0.00, 0.28) | <0.001 |
| LacCer C20 | 0.15 (0.32; 0.00, 0.88) | 0.03 (0.08; 0.00, 0.20) | <0.001 |
| LacCer C22:1 | 0.10 (0.18; 0.00, 0.36) | 0.03 (0.06; 0.00, 0.20) | 0.001 |
| LacCer C22 | 0.88 (1.31; 0.01, 3.09) | 0.18 (0.32; 0.00, 1.59) | <0.001 |
| LacCer C24:1 | 4.52 (5.89; 0.06, 16.2) | 0.55 (1.55; 0.02, 6.29) | <0.001 |
| LacCer C24 | 0.82 (1.17; 0.06, 4.06) | 0.24 (0.44; 0.01, 1.69) | <0.001 |
| LacCer Total | 12.90 (15.60; 0.26, 44.20) | 1.85 (3.85; 0.04, 15.10) | <0.001 |
| Marker | AUC | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| HexCer C16 | 0.88 | 0.011 * |
| HexCer C18 | 0.86 | 0.009 * |
| HexCer C20 | 0.89 | 0.003 * |
| HexCer C22:1 | 0.85 | 0.069 |
| HexCer C22 | 0.87 | 0.011 * |
| HexCer C24:1 | 0.90 | 0.001 * |
| HexCer C24 | 0.87 | 0.015 * |
| HexCer Total | 0.89 | 0.003 * |
| LacCer C16 | 0.88 | 0.012 * |
| LacCer C18 | 0.87 | 0.023 * |
| LacCer C20 | 0.85 | 0.106 |
| LacCer C22:1 | 0.84 | 0.178 |
| LacCer C22 | 0.87 | 0.147 |
| LacCer C24:1 | 0.87 | 0.037 * |
| LacCer C24 | 0.87 | 0.039 * |
| LacCer Total | 0.88 | 0.022 * |
| Marker | Non-Responders Median (IQR; min, max) | Complete Responders Median (IQR; min, max) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| EV Gelsolin | 461.2 (779.1; 0.00, 3564) | 490.2 (697.7; 0.0, 1627) | 1.000 |
| Urine Gelsolin | 440.0 (561.0; 0.00, 2018) | 126.0 (212.6; 17.4, 729.4) | <0.001 * |
| Urine LGALS3BP | 132.0 (222.6; 1.0, 1880) | 27.8 (225.9; 0.0, 455.5) | 0.237 |
| Eotaxin2 | 9.1 (12.3; 1.6, 59.6) | 7.2 (8.1; 0.6, 37.3) | 1.000 |
| MCP2 | 8.1 (26.8; 0.0, 71.8) | 5.3 (5.2; 0, 18.6) | 1.000 |
| BCA1 | 1.0 (1.7; 0.2, 9.4) | 0.4 (0.4; 0.2, 4.2) | 1.000 |
| IL16 | 17.5 (19.1; 0.2, 46.0) | 3.6 (7.2; 0.0, 21.7) | 0.237 |
| 6CKine | 0.0 (19.9; 0.0, 255.3) | 0.0 (7.6; 0, 18.3) | 1.000 |
| TPO | 62.9 (91.2; 12.9, 901.6) | 34.2 (26.1; 13.0, 218.3) | 1.000 |
| SCF | 13.5 (14.4; 0.3, 50.9) | 11.1 (16.9; 2.4, 49.7) | 1.000 |
| TSLP | 1.2 (8.26; 0.1, 51.0) | 0.7 (0.6; 0.0, 1.14) | 0.189 |
| IL33 | 4.94 (18.7; 0.3, 120.3) | 3.1 (1.6; 0.7, 11.5) | 0.823 |
| IL20 | 80.1 (131.5; 0.0, 2496.2) | 52.8 (55.1; 0, 133.4) | 1.000 |
| IL23 | 60.5 (98.8; 1.6, 1737.5) | 21.4 (29.8; 0.0, 58.4) | 0.537 |
| CTACK | 1.1 (1.2; 0.0, 21.0) | 0.4 (0.2; 0.0, 0.9) | 0.108 |
| SDF1 a + b | 70.0 (352.1; 0.0, 1522.1) | 61.0 (65.7; 0.0, 184.9) | 1.000 |
| ENA78 | 9.0 (20.3; 0.0, 149.4) | 6.5 (5.9; 0.0, 14.2) | 1.000 |
| MIP1d | 48.9 (73.3; 0.0, 368.7) | 21.3 (28.1; 0.0, 59.5) | 0.946 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Troyer, B.; Rodgers, J.; Wolf, B.J.; Oates, J.C.; Drake, R.R.; Nowling, T.K. Glycosphingolipid Levels in Urine Extracellular Vesicles Enhance Prediction of Therapeutic Response in Lupus Nephritis. Metabolites 2022, 12, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020134
Troyer B, Rodgers J, Wolf BJ, Oates JC, Drake RR, Nowling TK. Glycosphingolipid Levels in Urine Extracellular Vesicles Enhance Prediction of Therapeutic Response in Lupus Nephritis. Metabolites. 2022; 12(2):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020134
Chicago/Turabian StyleTroyer, Brian, Jessalyn Rodgers, Bethany J. Wolf, James C. Oates, Richard R. Drake, and Tamara K. Nowling. 2022. "Glycosphingolipid Levels in Urine Extracellular Vesicles Enhance Prediction of Therapeutic Response in Lupus Nephritis" Metabolites 12, no. 2: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020134
APA StyleTroyer, B., Rodgers, J., Wolf, B. J., Oates, J. C., Drake, R. R., & Nowling, T. K. (2022). Glycosphingolipid Levels in Urine Extracellular Vesicles Enhance Prediction of Therapeutic Response in Lupus Nephritis. Metabolites, 12(2), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020134








