Oxylipins as Potential Regulators of Inflammatory Conditions of Human Lactation
Abstract
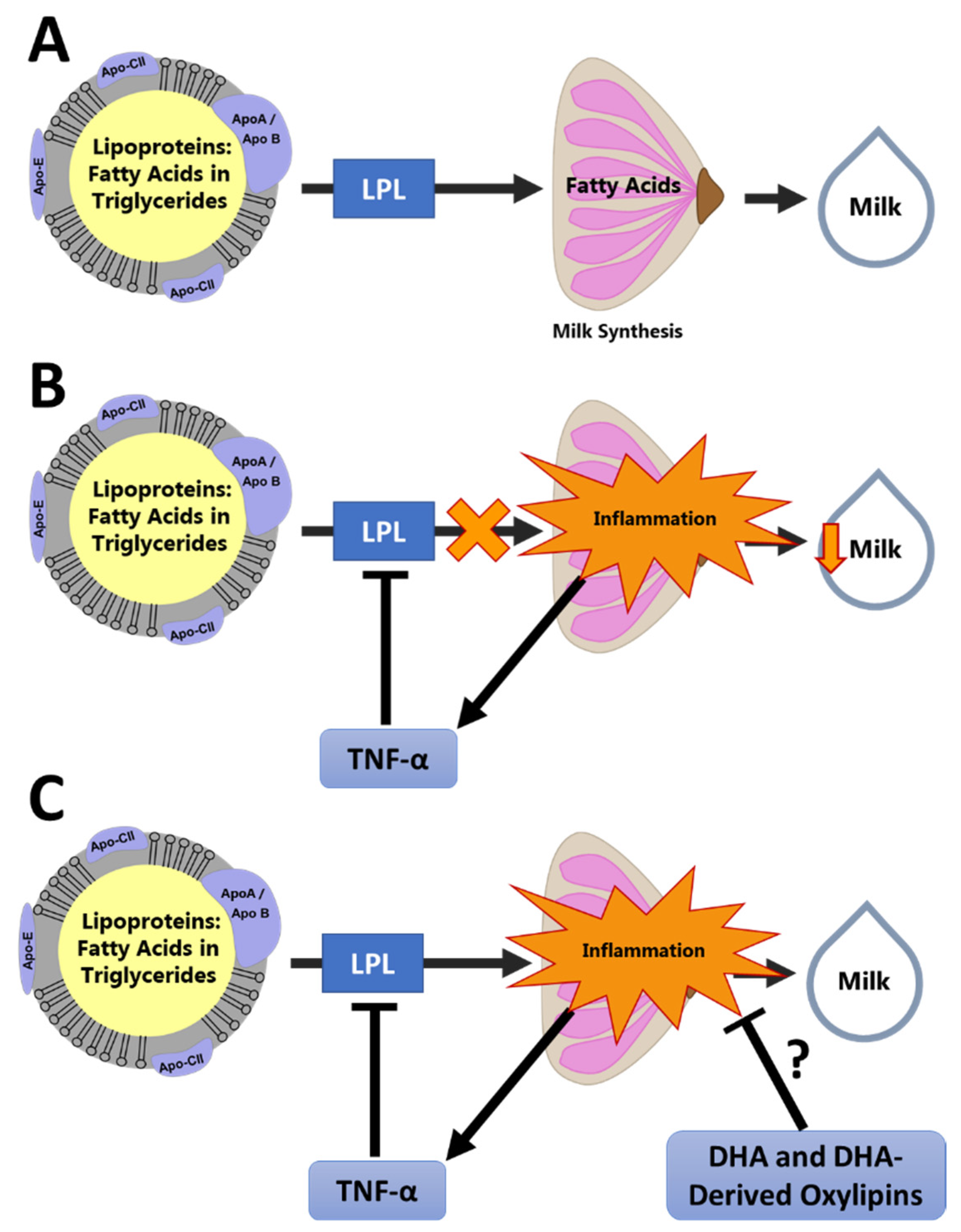
1. Introduction
2. Inflammatory Disorders of Lactation
3. Oxylipins during Lactation
3.1. Milk Oxylipins
3.2. Circulating Oxylipins
4. Oxylipins and Chronic Low-Grade Inflammation during Lactation
5. Gaps in Knowledge
6. Technical Challenges in Measuring Milk Oxylipins
- The total milk fat concentration;
- Potential matrix effects of milk affecting the extraction efficiency;
- High lipase activity in human milk.
7. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eidelman, A.; Schanier, R. Breastfeeding and the Use of Human Milk. Pediatrics 2012, 129, 600–603. [Google Scholar]
- Meek, J.Y.; Noble, L.; Breastfeeding, S. On Breastfeeding and the Use of Human Milk. Policy Statement. Pediatrics 2022, 150, e2022057988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunderson, E.P. Impact of Breastfeeding on Maternal Metabolism: Implications for Women with Gestational Diabetes Topical Collection on Diabetes and Pregnancy. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2014, 14, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunderson, E.P.; Kim, C.; Quesenberry, C.P.; Marcovina, S.; Walton, D.; Azevedo, R.A.; Fox, G.; Elmasian, C.; Young, S.; Salvador, N.; et al. Lactation Intensity and Fasting Plasma Lipids, Lipoproteins, Non-Esterified Free Fatty Acids, Leptin and Adiponectin in Postpartum Women with Recent Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: The SWIFT Cohort. Metabolism. 2014, 63, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmera, V.H.; Terrault, N.A.; VanWagner, L.B.; Sarkar, M.; Lewis, C.E.; Carr, J.J.; Gunderson, E.P. Longer Lactation Duration Is Associated with Decreased Prevalence of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Women. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkegaard, H.; Bliddal, M.; Støvring, H.; Rasmussen, K.M.; Gunderson, E.P.; Køber, L.; Sørensen, T.I.A.; Nohr, E.A. Breastfeeding and Later Maternal Risk of Hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease—The Role of Overall and Abdominal Obesity. Prev. Med. 2018, 114, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, M.L.; Bernard, P.S.; Kroenke, C.H.; Factor, R.E.; Habel, L.A.; Weltzien, E.K.; Castillo, A.; Gunderson, E.P.; Maxfield, K.S.; Stijleman, I.J.; et al. Breastfeeding, PAM50 Tumor Subtype, and Breast Cancer Prognosis and Survival. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, djv087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartick, M.C.; Schwarz, E.B.; Green, B.D.; Jegier, B.J.; Reinhold, A.G.; Colaizy, T.T.; Bogen, D.L.; Schaefer, A.J.; Stuebe, A.M. Suboptimal Breastfeeding in the United States: Maternal and Pediatric Health Outcomes and Costs. Matern. Child Nutr. 2017, 13, e12366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan-Fogarty, Y.; Becker, G.; Moles, R.; O’Regan, B. Backcasting to Identify Food Waste Prevention and Mitigation Opportunities for Infant Feeding in Maternity Services. Waste Manag. 2017, 61, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.P. A Commentary on the Carbon Footprint of Milk Formula: Harms to Planetary Health and Policy Implications. Int. Breastfeed. J. 2019, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Immunization Survey. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/breastfeeding/data/nis_data/results.html (accessed on 8 September 2022).
- Li, R.; Fein, S.B.; Chen, J.; Grummer-Strawn, L.M. Why Mothers Stop Breastfeeding: Mothers’ Self-Reported Reasons for Stopping during the First Year. Pediatrics 2008, 122, S69–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenta, S.M.; Nigussie, T.Z. Individual- And Community-Level Risk Factors Associated with Childhood Diarrhea in Ethiopia: A Multilevel Analysis of 2016 Ethiopia Demographic and Health Survey. Int. J. Pediatr. 2021, 2021, 8883618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, S.L.; Combest, C. Role of breast—feeding in the prevention and treatment of diarrhoea. J. Diarrhoeal Dis. Res. 1990, 8, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kelleher, S.L. Biological Underpinnings of Breastfeeding Challenges: The Role of Genetics, Diet, and Environment on Lactation Physiology. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 311, E405–E422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuebe, A. We Need Patient-Centered Research in Breastfeeding Medicine. Breastfeed. Med. 2021, 16, 349–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nommsen-Rivers, L.A.; Wagner, E.A.; Roznowski, D.M.; Riddle, S.W.; Ward, L.P.; Thompson, A. Measures of Maternal Metabolic Health as Predictors of Severely Low Milk Production. Breastfeed. Med. 2022, 17, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, R.E.; Harvatine, K.J.; Ross, A.C.; Wagner, E.A.; Riddle, S.W.; Gernand, A.D.; Nommsen-Rivers, L.A. Fatty Acid Transfer from Blood to Milk Is Disrupted in Mothers with Low Milk Production, Obesity, and Inflammation. J. Nutr. 2022, nxac220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbs, M.; Leng, S.; Devassy, J.G.; Monirujjaman, M.; Aukema, H.M. Advances in Our Understanding of Oxylipins Derived from Dietary PUFAs. Adv. Nutr. An Int. Rev. J. 2015, 6, 513–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, G.C.; Walker, R.E. An Overview of the Biologic Effects of Omega-6 Oxylipins in Humans. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2018, 137, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, G.A.; Troxler, H.; Klinke, G.; Rogler, D.; Braegger, C.; Hersberger, M. High Levels of Anti-Inflammatory and pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators Lipoxins and Resolvins and Declining Docosahexaenoic Acid Levels in Human Milk during the First Month of Lactation. Lipids Health Dis. 2013, 12, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnardottir, H.; Orr, S.K.; Dalli, J.; Serhan, C.N. Human Milk Proresolving Mediators Stimulate Resolution of Acute Inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2016, 9, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, D.T.; Palac, H.L.; Baillif, V.; Van Goethem, E.; Dubourdeau, M.; Van Horn, L.; Martin, C.R. Long Chain Fatty Acids and Related Pro-Inflammatory, Specialized pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators and Their Intermediates in Preterm Human Milk during the First Month of Lactation. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2017, 121, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyall, S.C.; Balas, L.; Bazan, N.G.; Brenna, J.T.; Chiang, N.; da Costa Souza, F.; Dalli, J.; Durand, T.; Galano, J.M.; Lein, P.J.; et al. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Fatty Acid-Derived Lipid Mediators: Recent Advances in the Understanding of Their Biosynthesis, Structures, and Functions. Prog. Lipid Res. 2022, 86, 101165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelopoulou, A.; Field, D.; Ryan, C.A.; Stanton, C.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P. The Microbiology and Treatment of Human Mastitis. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 207, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omranipour, R.; Vasigh, M. Mastitis, Breast Abscess, and Granulomatous Mastitis. In Diseases of the Breast During Pregnancy and Lactation; Alipour, S., Omranipour, R., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 1252, pp. 53–61. ISBN 9783030415969. [Google Scholar]
- Filteau, S.M.; Lietz, G.; Mulokozi, G.; Bilotta, S.; Henry, C.J.K.; Tomkins, A.M. Milk Cytokines and Subclinical Breast Inflammation in Tanzanian Women: Effects of Dietary Red Palm Oil or Sunflower Oil Supplementation. Immunology 1999, 97, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willumsen, J.F.; Filteau, S.M.; Coutsoudis, A.; Uebel, K.E.; Newell, M.L.; Tomkins, A.M. Subclinical Mastitis as a Risk Factor for Mother-Infant HIV Transmission. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2000, 478, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filteau, S.M.; Rice, A.L.; Ball, J.J.; Chakraborty, J.; Stoltzfus, R.; De Francisco, A.; Willumsen, J.F. Breast Milk Immune Factors in Bangladeshi Women Supplemented Postpartum with Retinol or β-Carotene. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Solomons, N.W.; Scott, M.E.; Koski, K.G. Subclinical Mastitis (SCM) and Proinflammatory Cytokines Are Associated with Mineral and Trace Element Concentrations in Human Breast Milk. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 46, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuaillon, E.; Viljoen, J.; Dujols, P.; Cambonie, G.; Rubbo, P.A.; Nagot, N.; Bland, R.M.; Badiou, S.; Newell, M.L.; Van De Perre, P. Subclinical Mastitis Occurs Frequently in Association with Dramatic Changes in Inflammatory/Anti-Inflammatory Breast Milk Components. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 81, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wren-Atilola, H.M.; Solomons, N.W.; Scott, M.E.; Koski, K.G. Infant Growth Faltering Linked to Subclinical Mastitis, Maternal Faecal–Oral Contamination, and Breastfeeding. Matern. Child Nutr. 2019, 15, e12756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasonka, L.; Makasa, M.; Marshall, T.; Chisenga, M.; Sinkala, M.; Chintu, C.; Kaseba, C.; Kasolo, F.; Gitau, R.; Tomkins, A.; et al. Risk Factors for Subclinical Mastitis among HIV-Infected and Uninfected Women in Lusaka, Zambia. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2006, 20, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makasa, M.; Kasonka, L.; Chisenga, M.; Sinkala, M.; Chintu, C.; Tomkins, A.; Filteau, S. Early Growth of Infants of HIV-Infected and Uninfected Zambian Women. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2007, 12, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Jewell, S.; Grummer-Strawn, L.M. Maternal Obesity and Breast-Feeding Practices. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.L.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Sørensen, T.I.A.; Rasmussen, K.M. High Prepregnant Body Mass Index Is Associated with Early Termination of Full and Any Breastfeeding in Danish Women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nommsen-Rivers, L.A.; Chantry, C.J.; Peerson, J.M.; Cohen, R.J.; Dewey, K.G. Delayed Onset of Lactogenesis among First-Time Mothers Is Related to Maternal Obesity and Factors Associated with Ineffective Breastfeeding. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marasco, L.A. Unsolved Mysteries of the Human Mammary Gland: Defining and Redefining the Critical Questions from the Lactation Consultant’s Perspective. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2015, 19, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foong, S.C.; Tan, M.L.; Foong, W.C.; Marasco, L.A.; Ho, J.J.; Ong, J.H. Oral Galactagogues (Natural Therapies or Drugs) for Increasing Breast Milk Production in Mothers of Non-Hospitalised Term Infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 2020, CD011505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nommsen-Rivers, L.; Thompson, A.; Riddle, S.; Ward, L.; Wagner, E.; King, E. Feasibility and Acceptability of Metformin to Augment Low Milk Supply: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Hum. Lact. 2019, 35, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Brouckaert, P.; Olivecrona, T. Rapid Downregulation of Adipose Tissue Lipoprotein Lipase Activity on Food Deprivation: Evidence That TNF-α Is Involved. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 286, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracey, K.J.; Cerami, A. Metabolic Responses to Cachectin/TNF. A Brief Review. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1990, 587, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, M.C.; Picciano, M.F. Regulation of Milk Lipid Secretion and Composition. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1997, 17, 159–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, R.H. The Brain and Immune System Prompt Energy Shortage in Chronic Inflammation and Ageing. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetzl, E.J.; Weller, P.F.; Sun, F.F. The Regulation of Human Eosinophil Function by Endogenous Mono-Hydroxy-Eicosatetraenoic Acids (HETEs). J. Immunol. 1980, 124, 926–933. [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl, E.J.; Brash, A.R.; Tauber, A.I.; Oates, J.A.; Hubbard, W.C. Modulation of Human Neutrophil Function by Monohydroxy-Eicosatetraenoic Acids. Immunology 1980, 39, 491–501. [Google Scholar]
- Serhan, C.N. Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators Are Leads for Resolution Physiology. Nature 2014, 510, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, A.A.; Kim, H.Y. Cytochrome P Epoxygenase Pathway of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1851, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laiho, K.; Lampi, A.M.; Hämäläinen, M.; Moilanen, E.; Piironen, V.; Arvola, T.; Syrjänen, S.; Isolauri, E. Breast Milk Fatty Acids, Eicosanoids, and Cytokines in Mothers with and without Allergic Disease. Pediatr. Res. 2003, 53, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, A.; Mitchell, M.D. Prostaglandins in Human Milk. Arch. Dis. Child. 1980, 55, 950–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neu, J.; Wu-Wang, C.Y.; Measel, C.P.; Gimotty, P. Prostaglandin Concentrations in Human Milk. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1988, 47, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Kurudimov, K.; German, J.B.; Taha, A.Y. Distribution of Free and Esterified Oxylipins in Cream, Cell, and Skim Fractions of Human Milk. Lipids 2020, 55, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, B.F.; Dias, F.F.G.; de Souza Vieira, T.M.F.; Leite Nobrega de Moura Bell, J.M.; Taha, A.Y. Method Optimization of Oxylipin Hydrolysis in Nonprocessed Bovine Milk Indicates That the Majority of Oxylipins Are Esterified. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 1791–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, P.; Smith, E.R.; Lee, S.E.; Vargas, A.J.; Bremer, A.A.; Raiten, D.J. The Need to Study Human Milk as a Biological System. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 113, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitino, M.A.; Alashmali, S.M.; Hopperton, K.E.; Unger, S.; Pouliot, Y.; Doyen, A.; O’Connor, D.L.; Bazinet, R.P. Oxylipin Concentration, but Not Fatty Acid Composition, Is Altered in Human Donor Milk Pasteurised Using Both Thermal and Non-Thermal Techniques. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 122, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nessel, I.; Khashu, M.; Dyall, S.C. The Effects of Storage Conditions on Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, Lipid Mediators, and Antioxidants in Donor Human Milk—A Review. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2019, 149, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gouveia-Figueira, S.; Domellöf, M.; Zivkovic, A.M.; Nording, M.L. Oxylipins, Endocannabinoids, and Related Compounds in Human Milk: Levels and Effects of Storage Conditions. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2016, 122, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blüher, M. The Distinction of Metabolically “healthy” from “Unhealthy” Obese Individuals. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2010, 21, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia-Figueira, S.; Nording, M.L. Validation of a Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method Using Combined Extraction of 37 Oxylipins and 14 Endocannabinoid-Related Compounds Including Prostamides from Biological Matrices. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2015, 121, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre-Gouabau, M.C.; Moyon, T.; Cariou, V.; Antignac, J.P.; Qannari, E.M.; Croyal, M.; Soumah, M.; Guitton, Y.; David-Sochard, A.; Billard, H.; et al. Breast Milk Lipidome Is Associated with Early Growth Trajectory in Preterm Infants. Nutrients 2018, 10, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavangira, V.; Gandy, J.C.; Zhang, C.; Ryman, V.E.; Daniel Jones, A.; Sordillo, L.M. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Influence Differential Biosynthesis of Oxylipids and Other Lipid Mediators during Bovine Coliform Mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 6202–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryman, V.E.; Pighetti, G.M.; Lippolis, J.D.; Gandy, J.C.; Applegate, C.M.; Sordillo, L.M. Quantification of Bovine Oxylipids during Intramammary Streptococcus Uberis Infection. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2015, 121, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.J.; Mavangira, V.; Gandy, J.C.; Zhang, C.; Jones, A.D.; Sordillo, L.M. Differences in the Oxylipid Profiles of Bovine Milk and Plasma at Different Stages of Lactation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4980–4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llauradó-Calero, E.; Badiola, I.; Delpino-Rius, A.; Lizardo, R.; Torrallardona, D.; Esteve-Garcia, E.; Tous, N. Fish Oil Rich in Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid in Sow Diets Modifies Oxylipins and Immune Indicators in Colostrum and Milk. Animal 2021, 15, 100403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.M.; Rosario, R.; Brito, A.; Agrawal, K.; Fanter, R.; Lietz, G.; Haskell, M.; Engle-Stone, R.; Newman, J.W.; La Frano, M.R. Multiassay Nutritional Metabolomics Profiling of Low Vitamin A Status versus Adequacy Is Characterized by Reduced Plasma Lipid Mediators among Lactating Women in the Philippines: A Pilot Study. Nutr. Res. 2022, 104, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, K.P.; Gibson, R.A.; Yelland, L.N.; Leemaqz, S.; Gomersall, J.; Liu, G.; Makrides, M. Effect of Omega-3 Lcpufa Supplementation on Maternal Fatty Acid and Oxylipin Concentrations during Pregnancy. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2020, 162, 102181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsden, C.E.; Makrides, M.; Yuan, Z.X.; Horowitz, M.S.; Zamora, D.; Yelland, L.N.; Best, K.; Jensen, J.; Taha, A.Y.; Gibson, R.A. Plasma Oxylipins and Unesterified Precursor Fatty Acids Are Altered by DHA Supplementation in Pregnancy: Can They Help Predict Risk of Preterm Birth? Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2020, 153, 102041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Frano, M.R.; Carmichael, S.L.; Ma, C.; Hardley, M.; Shen, T.; Wong, R.; Rosales, L.; Borkowski, K.; Pedersen, T.L.; Shaw, G.M.; et al. Impact of Post-Collection Freezing Delay on the Reliability of Serum Metabolomics in Samples Reflecting the California Mid-Term Pregnancy Biobank. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkowski, K.; Newman, J.W.; Aghaeepour, N.; Mayo, J.A.; Blazenović, I.; Fiehn, O.; Stevenson, D.K.; Shaw, G.M.; Carmichael, S.L. Mid-Gestation Serum Lipidomic Profile Associations with Spontaneous Preterm Birth Are Influenced by Body Mass Index. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, M.; Ulu, A.; Yuil-Valdes, A.G.; Mukherjee, M.; Thoene, M.; Van Ormer, M.; Slotkowski, R.; Lyden, E.; Berry, A.A.; Hanson, C.K.; et al. Omega-6 and Omega-3 Fatty Acid-Derived Oxylipins from the Lipoxygenase Pathway in Maternal and Umbilical Cord Plasma at Delivery and Their Relationship with Infant Growth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putman, A.K.; Brown, J.L.; Gandy, J.C.; Abuelo, A.; Sordillo, L.M. Oxylipid Profiles of Dairy Cattle Vary throughout the Transition into Early Mammary Gland Involution. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 2481–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olagaray, K.E.; Bradford, B.J.; Sordillo, L.M.; Gandy, J.C.; Mamedova, L.K.; Swartz, T.H.; Jackson, T.D.; Persoon, E.K.; Shugart, C.S.; Youngs, C.R. Postpartum Meloxicam Administration Alters Plasma Haptoglobin, Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid, and Oxylipid Concentrations in Postpartum Ewes. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, K.; Ticiani, E.; Sprícigo, J.F.W.; Carvalho, M.R.; Mion, B.; Bertolini, M.; Contreras, G.A.; Ribeiro, E.S. Dynamics of Lipid Droplets in the Endometrium and Fatty Acids and Oxylipins in the Uterine Lumen, Blood, and Milk of Lactating Cows during Diestrus. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 3676–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryman, V.E.; Packiriswamy, N.; Sordillo, L.M. Apoptosis of Endothelial Cells by 13-HPODE Contributes to Impairment of Endothelial Barrier Integrity. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 9867138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, T.C.; Wallace, R.J.; Moate, P.J.; Mosley, E.E. Board-Invited Review: Recent Advances in Biohydrogenation of Unsaturated Fatty Acids within the Rumen Microbial Ecosystem. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 86, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, T.M.; De Castro, C.A.; Dubascoux, S.; Michael, A.; Giu, F.; Billeaud, C.; Picaud, J.; Agosti, M.; Al-jashi, I.; Pereira, A.B.; et al. Subclinical Mastitis in a European Multicenter and Growth. Nutrients 2020, 12, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bzikowska-Jura, A.; Czerwonogrodzka-Senczyna, A.; Olędzka, G.; Szostak-Węgierek, D.; Weker, H.; Wesołowska, A. Maternal Nutrition and Body Composition during Breastfeeding: Association with Human Milk Composition. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, C.R.; Lipsmeyer, M.E.; Turner, D.E.; Andres, A. Human Milk Composition Differs by Maternal BMI in the First 9 Months Postpartum. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nommsen, L.A.; Lovelady, C.A.; Heinig, M.J.; Lönnerdal, B.; Dewey, K.G. Determinants of Energy, Protein, Lipid, and Lactose Concentrations in Human Milk during the First 12 Mo of Lactation: The DARLING Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 53, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruel, M.T.; Dewey, K.G.; Martínez, C.; Flores, R.; Brown, K.H. Validation of Single Daytime Samples of Human Milk to Estimate the 24-h Concentration of Lipids in Urban Guatemalan Mothers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 65, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopperton, K.E.; Pitino, M.A.; Chouinard-Watkins, R.; Shama, S.; Sammut, N.; Bando, N.; Williams, B.A.; Walton, K.; Kiss, A.; Unger, S.L.; et al. Determinants of Fatty Acid Content and Composition of Human Milk Fed to Infants Born Weighing <1250 G. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Garza Puentes, A.; Caballero, M.; Martí Alemany, A.; Chisguano Tonato, A.M.; Montes Goyanes, R.; Castellote, A.I.; Martín-Dinares, L.; Segura, M.T.; García-Valdés, L.; Campos, D.; et al. SUN-PO291: Breast Milk Fatty Acids Influence Infant Growth and Cognition: The Preobe Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, Y.; Marano, D.; Oliveira, E.; Moreira, M.E. Impact of Pre-Pregnancy Excessive Body Weight on the Composition of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Breast Milk: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 71, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkow, S.E.; Freed, L.M.; Hamosh, M.; Bitman, J.; Wood, D.L.; Happ, B.; Hamosh, P. Lipases and Lipids in Human Milk: Effect of Freeze–Thawing and Storage. Pediatr. Res. 1984, 18, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koletzko, B. Human Milk Lipids. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 69, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertino, E.; Giribaldi, M.; Baro, C.; Giancotti, V.; Pazzi, M.; Peila, C.; Tonetto, P.; Arslanoglu, S.; Moro, G.E.; Cavallarin, L.; et al. Effect of Prolonged Refrigeration on the Lipid Profile, Lipase Activity, and Oxidative Status of Human Milk. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 56, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.M.; Hundrieser, K.H.; Ross, S.; Brown, P.B. Effect of Temperature and Length of Storage on Serum-Stimulated and Serum-Independent Lipolytic Activities in Human Milk. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1984, 3, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parent Fatty Acid | Enzymatic Pathway | Oxylipin Class (Abbreviation) |
|---|---|---|
| Linoleic Acid | LOX | Hydroxy octadecadienoic acids (HODEs) |
| LOX | Hydroperoxy octadecadienoic acids (HpODEs) | |
| LOX | Oxo octadecadienoic acid (oxo-ODEs) | |
| LOX | Trihydroxy octadecamonoenoic acids (TriHOMEs) | |
| CYP 450Ep | Epoxy octadecamonoenoic acids (EpOMEs) | |
| CYP 450Ep | Dihydroxy octadecamonoenoic acids (DiHOMEs) | |
| Alpha-linolenic Acid (ALA) | LOX | Hydroxy octadecatrienoic acids (HOTrEs) |
| CYP 450Ep | Epoxy octadecadienoic acids (EpODEs) | |
| CYP 450Ep | Dihydroxy octadecadienoic acids (DiHODEs) | |
| Arachidonic Acid (ArA) | COX | 2-series prostaglandins (PG2s) |
| COX | Keto prostaglandins (keto-PGs) | |
| COX | 2-series thromboxanes (TX2s) | |
| LOX | Hydroxy eicosatetraenoic acids (HETEs) | |
| LOX | Oxo eicosatetraenoic acids (oxo-ETEs) | |
| LOX | 4-series leukotrienes (LT4s) | |
| CYP 450Ep | Epoxy eicosatrienoic acids (EpETrEs) | |
| CYP 450Ep | Dihydroxy eicosatrienoic acids (DiHETrEs) | |
| Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) | COX | 3-series prostaglandins (PG3s) |
| COX | 3-series thromboxanes (TX3s) | |
| LOX | Hydroxy eicosapentaenoic acids (HEPEs) | |
| LOX | 3- and 5-series leukotrienes (LT3,5s) | |
| CYP 450Ep | Epoxy eicosatetraenoic acids (EpETEs) | |
| CYP 450Ep | Dihydroxy eicosatetraenoic acids (DiHETEs) | |
| Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) | LOX | Hydroxy docosahexaenoic acids (HDoHEs) |
| CYP 450Ep | Epoxy docosapentaenoic acids (EpDPEs) | |
| CYP 450Ep | Dihydroxy docosapentaenoic acids (DiHDPEs) | |
| ArA, EPA, and DHA | LOX | Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators (SPMs) |
| Study (First Author, Year) | Species | Sample Size | Oxylipin Pool | Oxylipin Classes Quantified | Sample Type | Study Oxylipin Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weiss, 2013 [21] | Human | n = 30 |
|
|
| 17-HDoHE decreases across first 4 weeks of lactation in mothers of pre-term infants; Other pro-resolving mediator and precursor concentrations remain stable. |
| Gouveia-Figueira, 2015 [59] | Human | n = 3 |
|
|
| Many oxylipins were detectable in human milk, but extraction efficiency was lower in human milk than many other biological sample types. |
| Arnardottir, 2016 [22] | Human | n = 13 |
|
|
| Lipid mediator concentrations were recorded for donor milk from commercial supplier; Concentrations differed between donors with and without mastitis by principal components analysis. |
| Wu, 2016 [57] | Human | n = 1 |
|
|
| Some oxylipin concentrations increase significantly with extended storage, especially when held for any period of time at -20oC or above. |
| Robinson, 2017 [23] | Human | n = 30 |
|
|
| Oxylipin concentrations stayed stable across 4 weeks of lactation in mothers delivering full-term. |
| Alexandre-Gouabau, 2017 [60] | Human | n = 22 |
|
|
| 10,11-dihydro-20-trihydroxy-LTB4 and PGs were associated with faster infant growth trajectories; 11-dihydro-2,3-dinor-TXB2 was associated with slower infant growth trajectories. |
| Pitino, 2019 [55] | Human | n = 17 (pooled) |
|
|
| Oxylipin profiles were altered significantly with different pasteurization techniques. |
| Gan, 2020 [52] | Human | n = 5 (pooled) |
|
|
| Non-esterified oxylipins were most abundant in skim milk, while esterified oxylipins were most abundant in cream layer and cell pellet; Over 90% of milk oxylipins were derived from linoleic acid. |
| Mavangira, 2015 [61] | Bovine | n = 24 |
|
|
| Many oxylipin classes had increased concentrations in dairy cows with mastitis. |
| Ryman, 2015 [62] | Bovine | n = 8 |
|
|
| Milk from cows with S. uberis infection was higher in HODEs and 11-HETE. |
| Kuhn, 2017 [63] | Bovine | n = 36 |
|
|
| Most oxylipin concentrations increased with time across lactation. |
| Teixeira, 2021 [53] | Bovine | Pooled milk from storage tanks |
|
|
| Over 95% of oxylipins in milk were bound; Approximately 90% of milk oxylipins were linoleic acid-derived oxylipins; Lipid extraction followed by base hydrolysis in methanol was the best method for measuring total oxylipins. |
| Llaurado-Calero, 2021 [64] | Porcine | n = 36 |
|
|
| Fish oil feeding improved piglet growth and survival; Fish oil feeding increased concentrations of most milk oxylipins. |
| Study (First Author, Year) | Species | Sample Size | Oxylipin Pool | Oxylipin Classes Quantified | Sample Type | Study Oxylipin Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Johnson, 2022 [65] | Human | n = 10 |
|
|
| Low plasma Vitamin A was associated with lower plasma concentrations of many oxylipins in lactating mothers. |
| Mavangira, 2015 [61] | Bovine | n = 24 |
|
|
| Multiple oxylipin classes had elevated concentrations in dairy cows with mastitis. |
| Kuhn, 2017 [63] | Bovine | n = 36 |
|
|
| 20-HETE decreased and 9(10)-DiHOME increased from the periparturient to mid-lactation stage; 13-oxo-ODE decreased across the entire lactation. |
| Putman, 2019 [71] | Bovine | n = 10 |
|
|
| Many oxylipins spike in concentration around the time of dry-off and may be involved in the process of involution. |
| Olagaray, 2020 [72] | Ovine | n = 36 |
|
|
| Treatment with meloxicam after birth reduced concentrations of some oxylipins, primarily 9(10)-DiHOME, in postpartum ewes. |
| King, 2021 [73] | Bovine | n = 30 |
|
|
| Plasma oxylipins stay stable throughout early to late diestrous stage; Uterine oxylipins spike in late diestrous stage. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walker, R.E. Oxylipins as Potential Regulators of Inflammatory Conditions of Human Lactation. Metabolites 2022, 12, 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100994
Walker RE. Oxylipins as Potential Regulators of Inflammatory Conditions of Human Lactation. Metabolites. 2022; 12(10):994. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100994
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalker, Rachel E. 2022. "Oxylipins as Potential Regulators of Inflammatory Conditions of Human Lactation" Metabolites 12, no. 10: 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100994
APA StyleWalker, R. E. (2022). Oxylipins as Potential Regulators of Inflammatory Conditions of Human Lactation. Metabolites, 12(10), 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100994






