A Marked Low-Grade Inflammation and a Significant Deterioration in Metabolic Status in First-Episode Schizophrenia: A Five-Year Follow-Up Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Measurement of Biomarkers
2.3.1. Measurement of Cytokines
2.3.2. Measurement of Metabolic Syndrome Biomarkers
2.3.3. Measurement of Acylcarnitines
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. General Description of the Study Samples
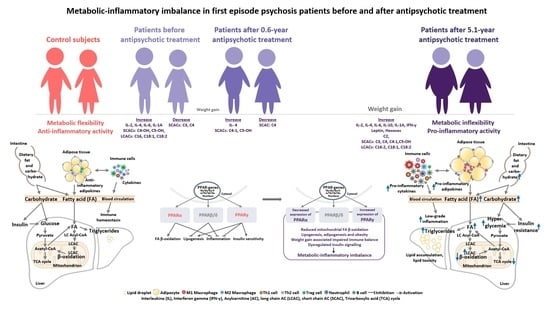
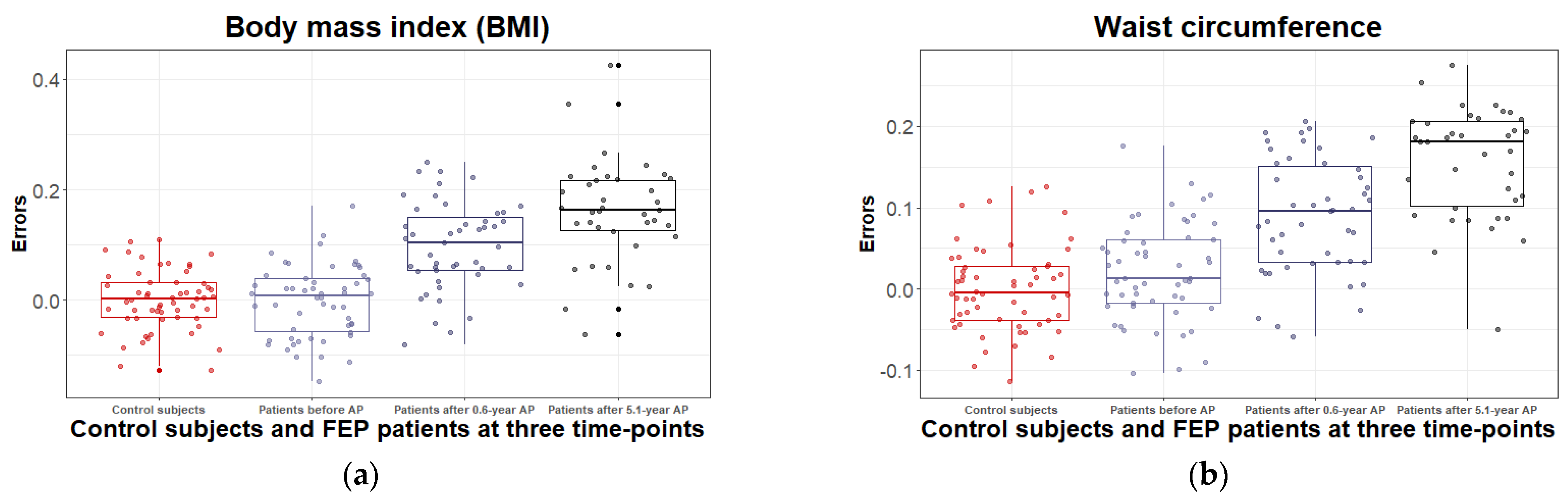
3.2. Changes in the Biomarkers, Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference of Patients with Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorder after 5.1 Years of Continuous Antipsychotic Treatment
3.2.1. Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference Change during the 5.1 Years of Disease Duration and Antipsychotic Treatment
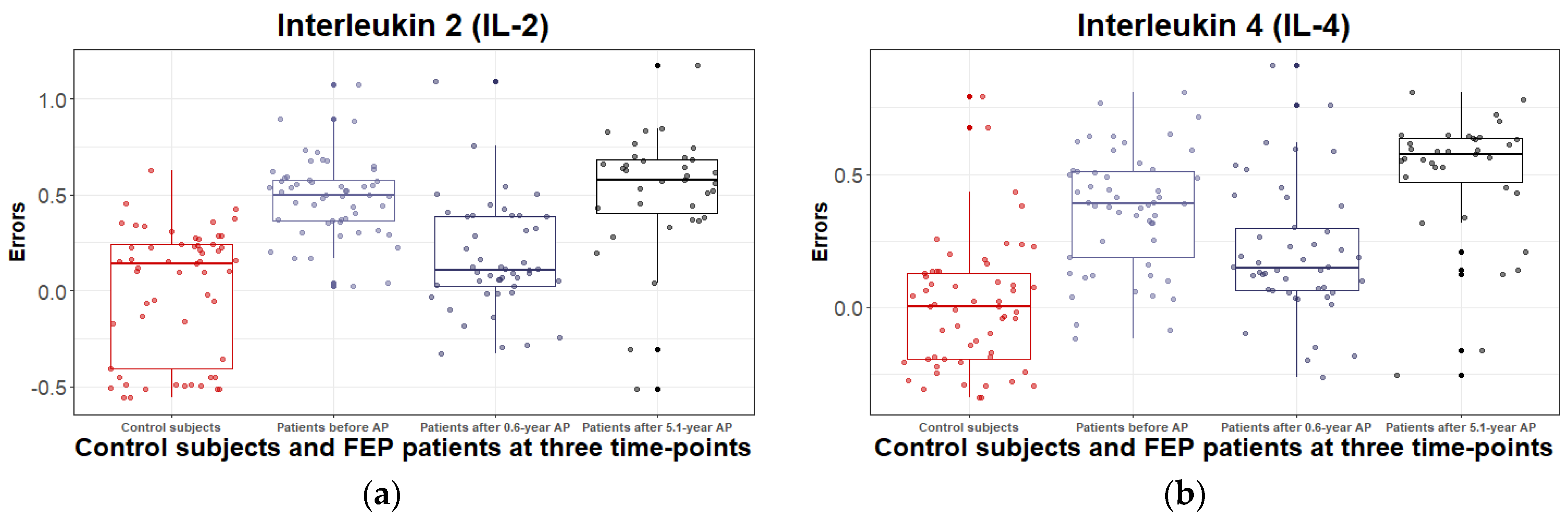
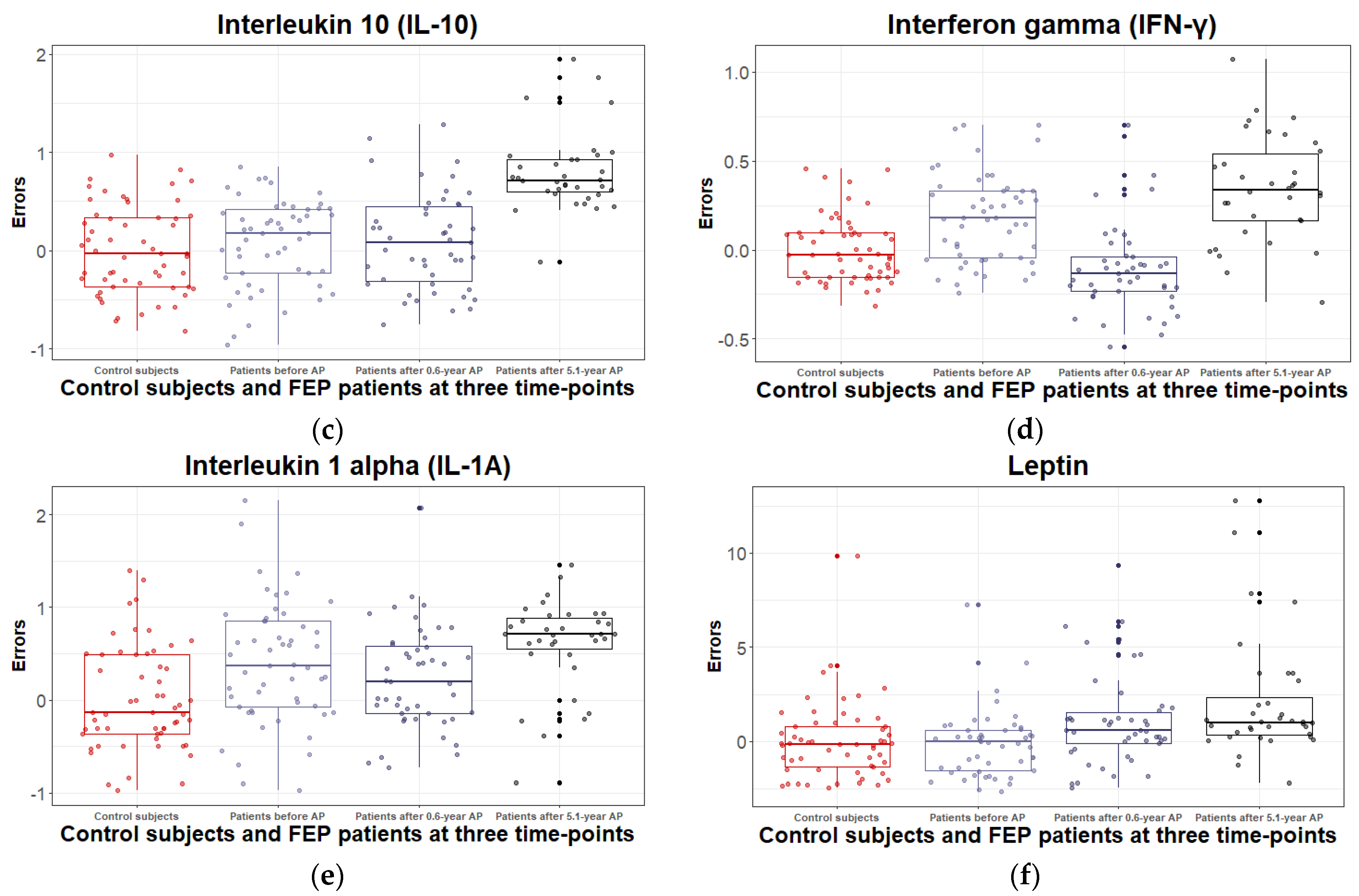
3.2.2. Inflammatory and Metabolic Biomarker Changes among Patients with Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorder: At Antipsychotic-Naïve Status, after 0.6 Years and 5.1 Years of Continuous Antipsychotic Treatment
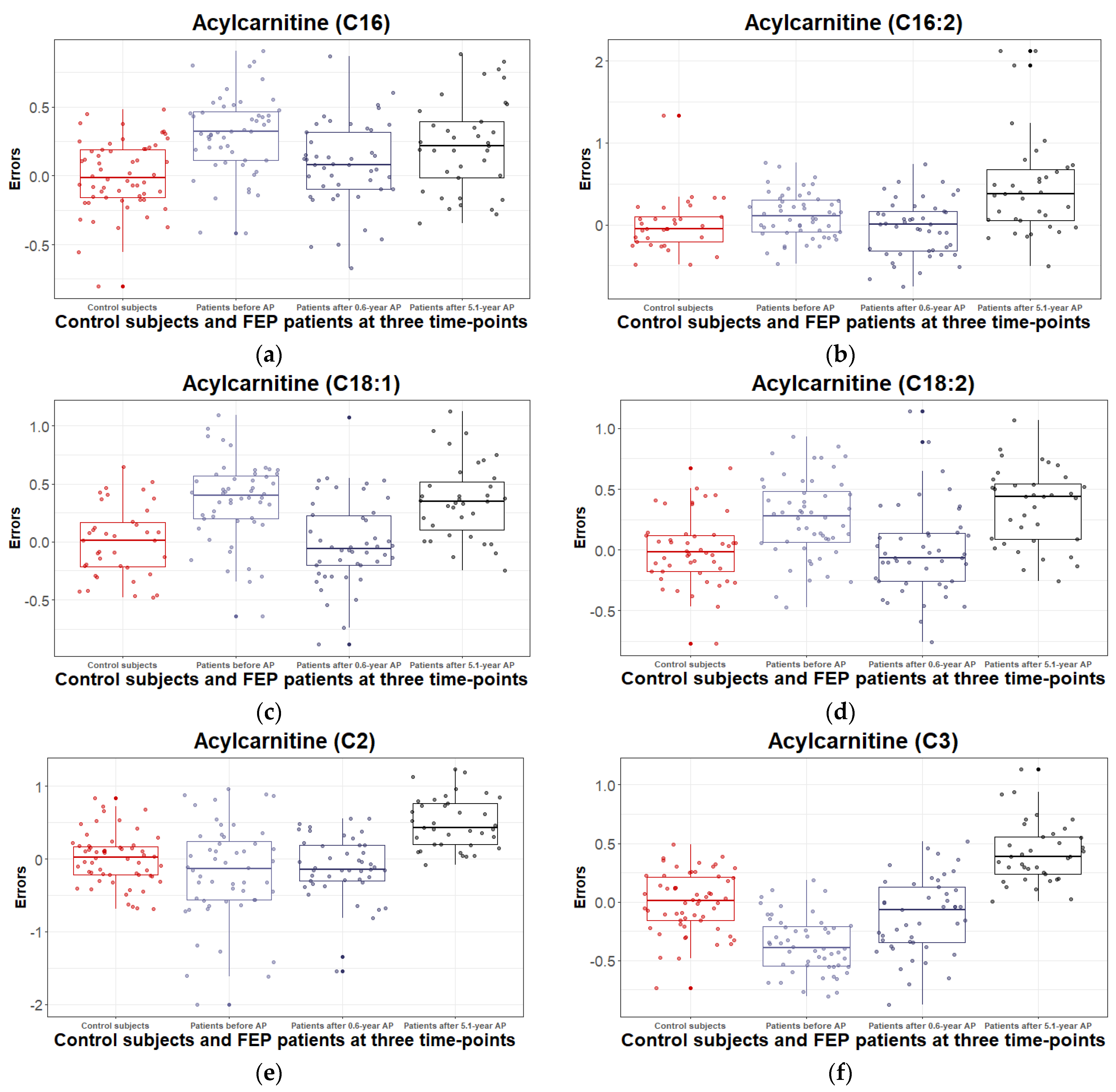
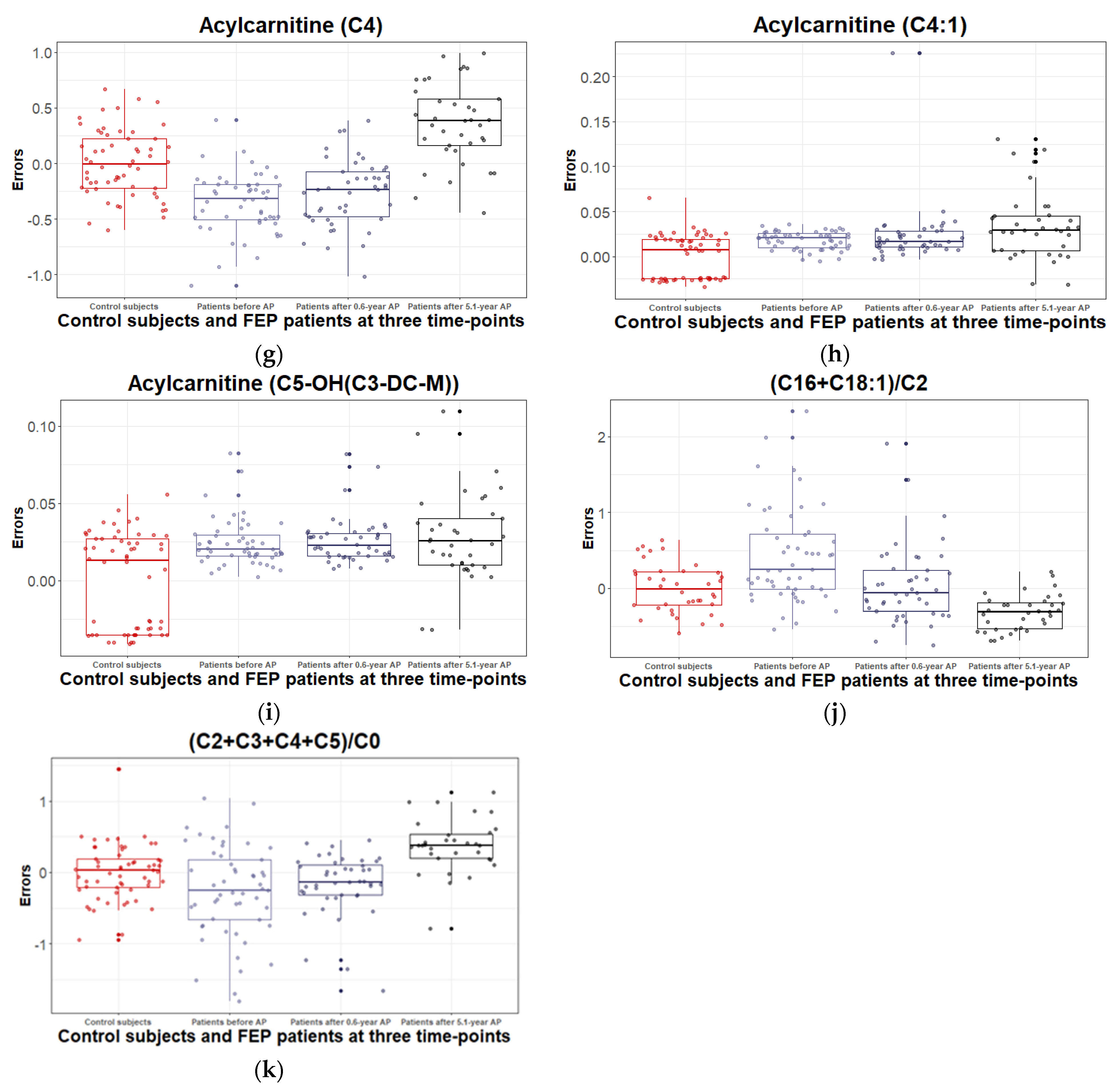
3.2.3. Levels of Acylcarnitines and Their Ratios during the 5.1 Years of Disease Duration and Antipsychotic Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitchell, A.J.; Vancampfort, D.; Sweers, K.; van Winkel, R.; Yu, W.; De Hert, M. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Metabolic Abnormalities in Schizophrenia and Related Disorders—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Schizophr. Bull. 2013, 39, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcinowicz, P.; Więdłocha, M.; Zborowska, N.; Dębowska, W.; Podwalski, P.; Misiak, B.; Tyburski, E.; Szulc, A. A Meta-Analysis of the Influence of Antipsychotics on Cytokines Levels in First Episode Psychosis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunleavy, C.; Elsworthy, R.J.; Upthegrove, R.; Wood, S.J.; Aldred, S. Inflammation in First-episode Psychosis: The Contribution of Inflammatory Biomarkers to the Emergence of Negative Symptoms, a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2022, 146, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillinger, T.; McCutcheon, R.A.; Vano, L.; Mizuno, Y.; Arumuham, A.; Hindley, G.; Beck, K.; Natesan, S.; Efthimiou, O.; Cipriani, A.; et al. Comparative Effects of 18 Antipsychotics on Metabolic Function in Patients with Schizophrenia, Predictors of Metabolic Dysregulation, and Association with Psychopathology: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, B.F.; Clegg, D.J. Metabolic Flexibility and Its Impact on Health Outcomes. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2022, 97, 761–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upthegrove, R.; Manzanares-Teson, N.; Barnes, N.M. Cytokine Function in Medication-Naive First Episode Psychosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Schizophr. Res. 2014, 155, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haring, L.; Koido, K.; Vasar, V.; Leping, V.; Zilmer, K.; Zilmer, M.; Vasar, E. Antipsychotic Treatment Reduces Psychotic Symptoms and Markers of Low-Grade Inflammation in First Episode Psychosis Patients, but Increases Their Body Mass Index. Schizophr. Res. 2015, 169, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balõtšev, R.; Haring, L.; Koido, K.; Leping, V.; Kriisa, K.; Zilmer, M.; Vasar, V.; Piir, A.; Lang, A.; Vasar, E. Antipsychotic Treatment Is Associated with Inflammatory and Metabolic Biomarkers Alterations among First-Episode Psychosis Patients: A 7-Month Follow-up Study. Early Interv. Psychiatry 2019, 13, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balõtšev, R.; Koido, K.; Vasar, V.; Janno, S.; Kriisa, K.; Mahlapuu, R.; Ljubajev, U.; Parksepp, M.; Veiksaar, P.; Volke, V.; et al. Inflammatory, Cardio-Metabolic and Diabetic Profiling of Chronic Schizophrenia. Eur. Psychiatry 2017, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiak, B.; Stańczykiewicz, B.; Łaczmański, Ł.; Frydecka, D. Lipid Profile Disturbances in Antipsychotic-Naive Patients with First-Episode Non-Affective Psychosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Schizophr. Res. 2017, 190, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancampfort, D.; Stubbs, B.; Mitchell, A.J.; De Hert, M.; Wampers, M.; Ward, P.B.; Rosenbaum, S.; Correll, C.U. Risk of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Components in People with Schizophrenia and Related Psychotic Disorders, Bipolar Disorder and Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Psychiatry 2015, 14, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorena, K.; Jachimowicz-Duda, O.; Ślęzak, D.; Robakowska, M.; Mrugacz, M. Adipokines and Obesity. Potential Link to Metabolic Disorders and Chronic Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiernan, K.; MacIver, N.J. The Role of the Adipokine Leptin in Immune Cell Function in Health and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 622468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalik, S.J.; Goodpaster, B.H.; Kelley, D.E.; Chace, D.H.; Vockley, J.; Toledo, F.G.S.; DeLany, J.P. Increased Levels of Plasma Acylcarnitines in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes and Identification of a Marker of Glucolipotoxicity. Obesity 2010, 18, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dambrova, M.; Makrecka-Kuka, M.; Kuka, J.; Vilskersts, R.; Nordberg, D.; Attwood, M.M.; Smesny, S.; Sen, Z.D.; Guo, A.C.; Oler, E.; et al. Acylcarnitines: Nomenclature, Biomarkers, Therapeutic Potential, Drug Targets, and Clinical Trials. Pharmacol. Rev. 2022, 74, 506–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, S.E.; Evans, A.M. Carnitine and Acylcarnitines: Pharmacokinetic, Pharmacological and Clinical Aspects. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2012, 51, 553–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schooneman, M.G.; Vaz, F.M.; Houten, S.M.; Soeters, M.R. Acylcarnitines: Reflecting or Inflicting Insulin Resistance? Diabetes 2013, 62, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnefont, J. Carnitine Palmitoyltransferases 1 and 2: Biochemical, Molecular and Medical Aspects. Mol. Asp. Med. 2004, 25, 495–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowsky, J.M.; Knotts, T.A.; Ono-Moore, K.D.; McCoin, C.S.; Huang, S.; Schneider, D.; Singh, S.; Adams, S.H.; Hwang, D.H. Acylcarnitines Activate Proinflammatory Signaling Pathways. AJP Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E1378–E1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichane, S.; Dahal Lamichane, B.; Kwon, S.-M. Pivotal Roles of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPARs) and Their Signal Cascade for Cellular and Whole-Body Energy Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toobian, D.; Ghosh, P.; Katkar, G.D. Parsing the Role of PPARs in Macrophage Processes. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 783780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cariello, M.; Piccinin, E.; Moschetta, A. Transcriptional Regulation of Metabolic Pathways via Lipid-Sensing Nuclear Receptors PPARs, FXR, and LXR in NASH. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 11, 1519–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambele, M.A.; Dhanraj, P.; Giles, R.; Pepper, M.S. Adipogenesis: A Complex Interplay of Multiple Molecular Determinants and Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.B. The Role of PPARs in Inflammation and Immunity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2002, 71, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Sharma, S.; Gupta, P.; Saini, A.; Kaushal, C. The Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor: A Family of Nuclear Receptors Role in Various Diseases. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2011, 2, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strosznajder, A.K.; Wójtowicz, S.; Jeżyna, M.J.; Sun, G.Y.; Strosznajder, J.B. Recent Insights on the Role of PPAR-β/δ in Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration, and Its Potential Target for Therapy. NeuroMol. Med. 2021, 23, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, N.; Vaseghi, G.; Haghjooy-Javanmard, S. Crosstalk between Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors And Toll-Like Receptors: A Systematic Review. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 9, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. The ICD–10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders: Clinical Descriptions and Diagnostic Guidelines; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, D.M.; Murphy, A.L.; O’Donnell, H.; Centorrino, F.; Baldessarini, R.J. International Consensus Study of Antipsychotic Dosing. Am. J. Psychiatry 2010, 167, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriisa, K.; Leppik, L.; Balõtšev, R.; Ottas, A.; Soomets, U.; Koido, K.; Volke, V.; Innos, J.; Haring, L.; Vasar, E.; et al. Profiling of Acylcarnitines in First Episode Psychosis before and after Antipsychotic Treatment. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 3558–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parksepp, M.; Leppik, L.; Koch, K.; Uppin, K.; Kangro, R.; Haring, L.; Vasar, E.; Zilmer, M. Metabolomics Approach Revealed Robust Changes in Amino Acid and Biogenic Amine Signatures in Patients with Schizophrenia in the Early Course of the Disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parksepp, M.; Haring, L.; Kilk, K.; Koch, K.; Uppin, K.; Kangro, R.; Zilmer, M.; Vasar, E. The Expanded Endocannabinoid System Contributes to Metabolic and Body Mass Shifts in First-Episode Schizophrenia: A 5-Year Follow-Up Study. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overall, J.E.; Gorham, D.R. The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale. Psychol. Rep. 1962, 10, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Minor, B.L.; Elliott, V.; Fernandez, M.; O’Neal, L.; McLeod, L.; Delacqua, G.; Delacqua, F.; Kirby, J.; et al. The REDCap Consortium: Building an International Community of Software Platform Partners. J. Biomed. Inform. 2019, 95, 103208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap)—A Metadata-Driven Methodology and Workflow Process for Providing Translational Research Informatics Support. J. Biomed. Inform. 2009, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leo, G.; Sardanelli, F. Statistical Significance: P Value, 0.05 Threshold, and Applications to Radiomics—Reasons for a Conservative Approach. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2020, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D.; DebRoy, S.; Sarkar, D. Nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models; New Prairie Press: Manhattan, KS, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- StataCorp. Stata Statistical Software: Release 13; StataCorp: College Station, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis (Use R!), 2nd ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. [Google Scholar]
- Prestwood, T.R.; Asgariroozbehani, R.; Wu, S.; Agarwal, S.M.; Logan, R.W.; Ballon, J.S.; Hahn, M.K.; Freyberg, Z. Roles of Inflammation in Intrinsic Pathophysiology and Antipsychotic Drug-Induced Metabolic Disturbances of Schizophrenia. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 402, 113101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancampfort, D.; Wampers, M.; Mitchell, A.J.; Correll, C.U.; De Herdt, A.; Probst, M.; De Hert, M. A Meta-Analysis of Cardio-Metabolic Abnormalities in Drug Naïve, First-Episode and Multi-Episode Patients with Schizophrenia versus General Population Controls. World Psychiatry 2013, 12, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigaard, J.; Frederiksen, K.; Tjønneland, A.; Thomsen, B.L.; Overvad, K.; Heitmann, B.L.; Sørensen, T.I.A. Waist Circumference and Body Composition in Relation to All-Cause Mortality in Middle-Aged Men and Women. Int. J. Obes. 2005, 29, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, B.E.; Schwarz, M.; Myint, A.M. The Metabolic Syndrome in Schizophrenia: Is Inflammation a Contributing Cause? J. Psychopharmacol. (Oxf.) 2012, 26, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroken, R.A.; Sommer, I.E.; Steen, V.M.; Dieset, I.; Johnsen, E. Constructing the Immune Signature of Schizophrenia for Clinical Use and Research; An Integrative Review Translating Descriptives Into Diagnostics. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potvin, S.; Stip, E.; Sepehry, A.A.; Gendron, A.; Bah, R.; Kouassi, E. Inflammatory Cytokine Alterations in Schizophrenia: A Systematic Quantitative Review. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 63, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Knovich, M.A.; Coffman, L.G.; Torti, F.M.; Torti, S.V. Serum Ferritin: Past, Present and Future. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Gen. Subj. 2010, 1800, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. Serum Ferritin Is an Important Inflammatory Disease Marker, as It Is Mainly a Leakage Product from Damaged Cells. Metallomics 2014, 6, 748–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, D.R.; Rapaport, M.H.; Miller, B.J. A Meta-Analysis of Blood Cytokine Network Alterations in Psychiatric Patients: Comparisons between Schizophrenia, Bipolar Disorder and Depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1696–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boerrigter, D.; Weickert, T.W.; Lenroot, R.; O’Donnell, M.; Galletly, C.; Liu, D.; Burgess, M.; Cadiz, R.; Jacomb, I.; Catts, V.S.; et al. Using Blood Cytokine Measures to Define High Inflammatory Biotype of Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Disorder. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childers, E.; Bowen, E.F.W.; Rhodes, C.H.; Granger, R. Immune-Related Genomic Schizophrenic Subtyping Identified in DLPFC Transcriptome. Genes 2022, 13, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.R.; Zhang, L.; Lizano, P. Inflammation Subtypes and Translating Inflammation-Related Genetic Findings in Schizophrenia and Related Psychoses: A Perspective on Pathways for Treatment Stratification and Novel Therapies. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 2022, 30, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuzzi, E.; Bartoli, F.; Crocamo, C.; Clerici, M.; Carrà, G. Acute Variations of Cytokine Levels after Antipsychotic Treatment in Drug-Naïve Subjects with a First-Episode Psychosis: A Meta-Analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 77, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.J.; Buckley, P.; Seabolt, W.; Mellor, A.; Kirkpatrick, B. Meta-Analysis of Cytokine Alterations in Schizophrenia: Clinical Status and Antipsychotic Effects. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 70, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-K.; Myint, A.-M.; Lee, B.-H.; Han, C.-S.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, D.-J.; Leonard, B.E. Th1, Th2 and Th3 Cytokine Alteration in Schizophrenia. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2004, 28, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugino, H.; Futamura, T.; Mitsumoto, Y.; Maeda, K.; Marunaka, Y. Atypical Antipsychotics Suppress Production of Proinflammatory Cytokines and Up-Regulate Interleukin-10 in Lipopolysaccharide-Treated Mice. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 33, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momtazmanesh, S.; Zare-Shahabadi, A.; Rezaei, N. Cytokine Alterations in Schizophrenia: An Updated Review. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.-L.; Bai, W.; Li, X.-H.; Huang, H.; Cui, X.-L.; Cheung, T.; Su, Z.-H.; Yuan, Z.; Ng, C.H.; Xiang, Y.-T. Schizophrenia and Inflammation Research: A Bibliometric Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 907851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monji, A.; Kato, T.; Kanba, S. Cytokines and Schizophrenia: Microglia Hypothesis of Schizophrenia: Cytokines and Schizophrenia. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 63, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purves-Tyson, T.D.; Weber-Stadlbauer, U.; Richetto, J.; Rothmond, D.A.; Labouesse, M.A.; Polesel, M.; Robinson, K.; Shannon Weickert, C.; Meyer, U. Increased Levels of Midbrain Immune-Related Transcripts in Schizophrenia and in Murine Offspring after Maternal Immune Activation. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 849–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedraz-Petrozzi, B.; Elyamany, O.; Rummel, C.; Mulert, C. Effects of Inflammation on the Kynurenine Pathway in Schizophrenia-a Systematic Review. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickens, A.M.; Sen, P.; Kempton, M.J.; Barrantes-Vidal, N.; Iyegbe, C.; Nordentoft, M.; Pollak, T.; Riecher-Rössler, A.; Ruhrmann, S.; Sachs, G.; et al. Dysregulated Lipid Metabolism Precedes Onset of Psychosis. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 89, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coentre, R.; Levy, P.; Góis, C.; Figueira, M.L. Metabolic Syndrome Following a First Episode of Psychosis: Results of a 1-Year Longitudinal Study Conducted in Metropolitan Lisbon, Portugal. J. Int. Med. Res. 2022, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Torres, N.; Rocha-Gonzalez, I.; Alameda, L.; Rodriguez-Gangoso, A.; Vilches, A.; Canal-Rivero, M.; Crespo-Facorro, B.; Ruiz-Veguilla, M. Metabolic Syndrome in Antipsychotic-Naïve Patients with First-Episode Psychosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Psychol. Med. 2021, 51, 2307–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragoo, J.L.; Shapiro, S.A.; Bradsell, H.; Frank, R.M. The Essential Roles of Human Adipose Tissue: Metabolic, Thermoregulatory, Cellular, and Paracrine Effects. J. Cartil. Jt. Preserv. 2021, 1, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretz, D.; Le Foll, C.; Rizwan, M.Z.; Lutz, T.A.; Tups, A. Hyperleptinemia as a Contributing Factor for the Impairment of Glucose Intolerance in Obesity. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragguett, R.-M.; Hahn, M.; Messina, G.; Chieffi, S.; Monda, M.; De Luca, V. Association between Antipsychotic Treatment and Leptin Levels across Multiple Psychiatric Populations: An Updated Meta-Analysis. Hum. Psychopharmacol. Clin. Exp. 2017, 32, e2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potvin, S.; Zhornitsky, S.; Stip, E. Antipsychotic-Induced Changes in Blood Levels of Leptin in Schizophrenia: A Meta-Analysis. Can. J. Psychiatry Rev. Can. Psychiatr. 2015, 60, S26–S34. [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs, B.; Wang, A.K.; Vancampfort, D.; Miller, B.J. Are Leptin Levels Increased among People with Schizophrenia versus Controls? A Systematic Review and Comparative Meta-Analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2016, 63, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathis, D. Immunological Goings-on in Visceral Adipose Tissue. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginhoux, F.; Schultze, J.L.; Murray, P.J.; Ochando, J.; Biswas, S.K. New Insights into the Multidimensional Concept of Macrophage Ontogeny, Activation and Function. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Kokoeva, M.V.; Inouye, K.; Tzameli, I.; Yin, H.; Flier, J.S. TLR4 Links Innate Immunity and Fatty Acid–Induced Insulin Resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 3015–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snel, M.; Jonker, J.T.; Schoones, J.; Lamb, H.; de Roos, A.; Pijl, H.; Smit, J.W.A.; Meinders, A.E.; Jazet, I.M. Ectopic Fat and Insulin Resistance: Pathophysiology and Effect of Diet and Lifestyle Interventions. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltiel, A.R.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammatory Mechanisms Linking Obesity and Metabolic Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves-Bezerra, M.; Cohen, D.E. Triglyceride Metabolism in the Liver. In Comprehensive Physiology, Terjung, R., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–22. ISBN 978-0-470-65071-4. [Google Scholar]
- Muoio, D.M. Metabolic Inflexibility: When Mitochondrial Indecision Leads to Metabolic Gridlock. Cell 2014, 159, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Liang, L.; Gao, X.; Zhang, H.; Yao, P.; Hu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, F.; Jin, Q.; Li, H.; et al. Early Prediction of Developing Type 2 Diabetes by Plasma Acylcarnitines: A Population-Based Study. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morze, J.; Wittenbecher, C.; Schwingshackl, L.; Danielewicz, A.; Rynkiewicz, A.; Hu, F.B.; Guasch-Ferré, M. Metabolomics and Type 2 Diabetes Risk: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatti, J.S.; Bhatti, G.K.; Reddy, P.H. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Metabolic Disorders-A Step towards Mitochondria Based Therapeutic Strategies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 1066–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Wang, D.; Pan, Z.; McIntyre, R.S.; Brietzke, E.; Subramanieapillai, M.; Nozari, Y.; Wang, J. Metabolic Profiling for Water-Soluble Metabolites in Patients with Schizophrenia and Healthy Controls in a Chinese Population: A Case-Control Study. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 21, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Chen, Y.; McIntyre, R.S.; Yan, L. Acyl-Carnitine Plasma Levels and Their Association with Metabolic Syndrome in Individuals with Schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 293, 113458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougarne, N.; Weyers, B.; Desmet, S.J.; Deckers, J.; Ray, D.W.; Staels, B.; De Bosscher, K. Molecular Actions of PPARα in Lipid Metabolism and Inflammation. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 760–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahli, W.; Michalik, L. PPARs at the Crossroads of Lipid Signaling and Inflammation. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 23, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, S.; Stienstra, R. The Role and Regulation of the Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor Alpha in Human Liver. Biochimie 2017, 136, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shao, Y.Y.; Ballock, R.T. Leptin Antagonizes Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor- γ Signaling in Growth Plate Chondrocytes. PPAR Res. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janani, C.; Ranjitha Kumari, B.D. PPAR Gamma Gene–A Review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2015, 9, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Sánchez, K.; Vargas, L.; Urrutia, Y.; Beltrán, I.; Rossi, A.B.; Lozano, H.Y.; Guarín, J.; Losada-Barragán, M. PPARα and PPARβ/δ Are Negatively Correlated with Proinflammatory Markers in Leukocytes of an Obese Pediatric Population. J. Inflamm. 2020, 17, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheggi, S.; Pinna, G.; Braccagni, G.; De Montis, M.G.; Gambarana, C. PPARα Signaling: A Candidate Target in Psychiatric Disorder Management. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolezzi, J.M.; Santos, M.J.; Bastías-Candia, S.; Pinto, C.; Godoy, J.A.; Inestrosa, N.C. PPARs in the Central Nervous System: Roles in Neurodegeneration and Neuroinflammation: PPARs in the CNS and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biol. Rev. 2017, 92, 2046–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chase, K.A.; Rosen, C.; Gin, H.; Bjorkquist, O.; Feiner, B.; Marvin, R.; Conrin, S.; Sharma, R.P. Metabolic and Inflammatory Genes in Schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 225, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Squassina, A.; Congiu, D.; Chillotti, C.; Niola, P.; Galderisi, S.; Pistis, M.; Del Zompo, M. Investigation of Endocannabinoid System Genes Suggests Association between Peroxisome Proliferator Activator Receptor-α Gene (PPARA) and Schizophrenia. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 23, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, I.; Hankemeier, T.; van der Graaf, P.H.; Knibbe, C.A.J.; van Hasselt, J.G.C. Integrating Clinical Metabolomics-Based Biomarker Discovery and Clinical Pharmacology to Enable Precision Medicine. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 109, S15–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Participants | Comparison between FEPb and CSs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSs | FEPb | FEP(0.6-year) | FEP(5.1-year) | FEPb and CSs | |
| Participants | 58 | 54 | 47 | 38 | |
| Age (years), mean ± SD (range) | 24.7 ± 4.5 (19.1–39.3) | 26.6 ± 6.1 (18.7–41.1) | 27.3 ± 6.4 (19.3–41.7) | 31.8 ± 5.9 (23.7–46.2) | t(110) = 1.87, ns |
| Men (%) | 24 (44%) | 31 (57%) | 27 (51%) | 23 (43%) | χ2(1) = 3.58, ns |
| Current cigarette smokers (n%) | 15 (26%) | 18 (33%) | 16 (30%) | 20 (37%) | χ2(1) = 0.33, ns |
| BMI (kg/m2) mean ± SD | 22.6 ± 2.8 | 22.8 ± 3.0 | 25.3 ± 3.9 a | 27.8 ± 4.7 b,c | t(110) = 0.34, ns |
| Waist circum- ference (cm) mean ± SD | 77.9 ± 12.6 | 81.0 ± 9.89 | 86.3 ± 11.2 a | 94.4 ± 11.2 b,c | t(110) = −1.68, ns |
| BPRS score mean ± SD (range) | - | 49.9 ± 15.4 (13–85) | 22.9 ± 12.7 a (2–48) | 14.2 ± 10.5 b,c (0–49) | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parksepp, M.; Haring, L.; Kilk, K.; Taalberg, E.; Kangro, R.; Zilmer, M.; Vasar, E. A Marked Low-Grade Inflammation and a Significant Deterioration in Metabolic Status in First-Episode Schizophrenia: A Five-Year Follow-Up Study. Metabolites 2022, 12, 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100983
Parksepp M, Haring L, Kilk K, Taalberg E, Kangro R, Zilmer M, Vasar E. A Marked Low-Grade Inflammation and a Significant Deterioration in Metabolic Status in First-Episode Schizophrenia: A Five-Year Follow-Up Study. Metabolites. 2022; 12(10):983. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100983
Chicago/Turabian StyleParksepp, Madis, Liina Haring, Kalle Kilk, Egon Taalberg, Raul Kangro, Mihkel Zilmer, and Eero Vasar. 2022. "A Marked Low-Grade Inflammation and a Significant Deterioration in Metabolic Status in First-Episode Schizophrenia: A Five-Year Follow-Up Study" Metabolites 12, no. 10: 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100983
APA StyleParksepp, M., Haring, L., Kilk, K., Taalberg, E., Kangro, R., Zilmer, M., & Vasar, E. (2022). A Marked Low-Grade Inflammation and a Significant Deterioration in Metabolic Status in First-Episode Schizophrenia: A Five-Year Follow-Up Study. Metabolites, 12(10), 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100983