Hopomics: Humulus lupulus Brewing Cultivars Classification Based on LC-MS Profiling and Nested Feature Selection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Study’s Background and Sample Collection
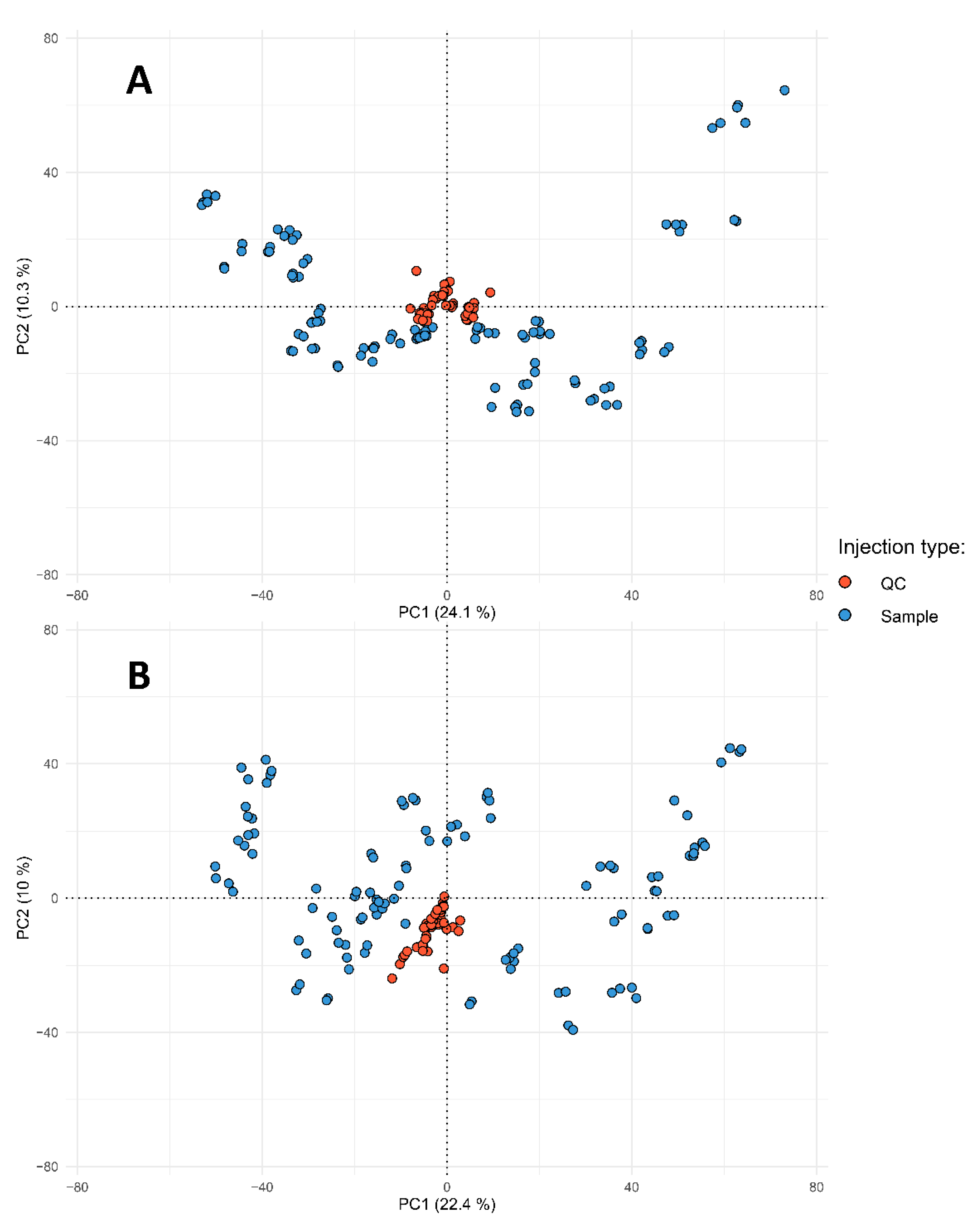
2.2. Data Pre-Treatment
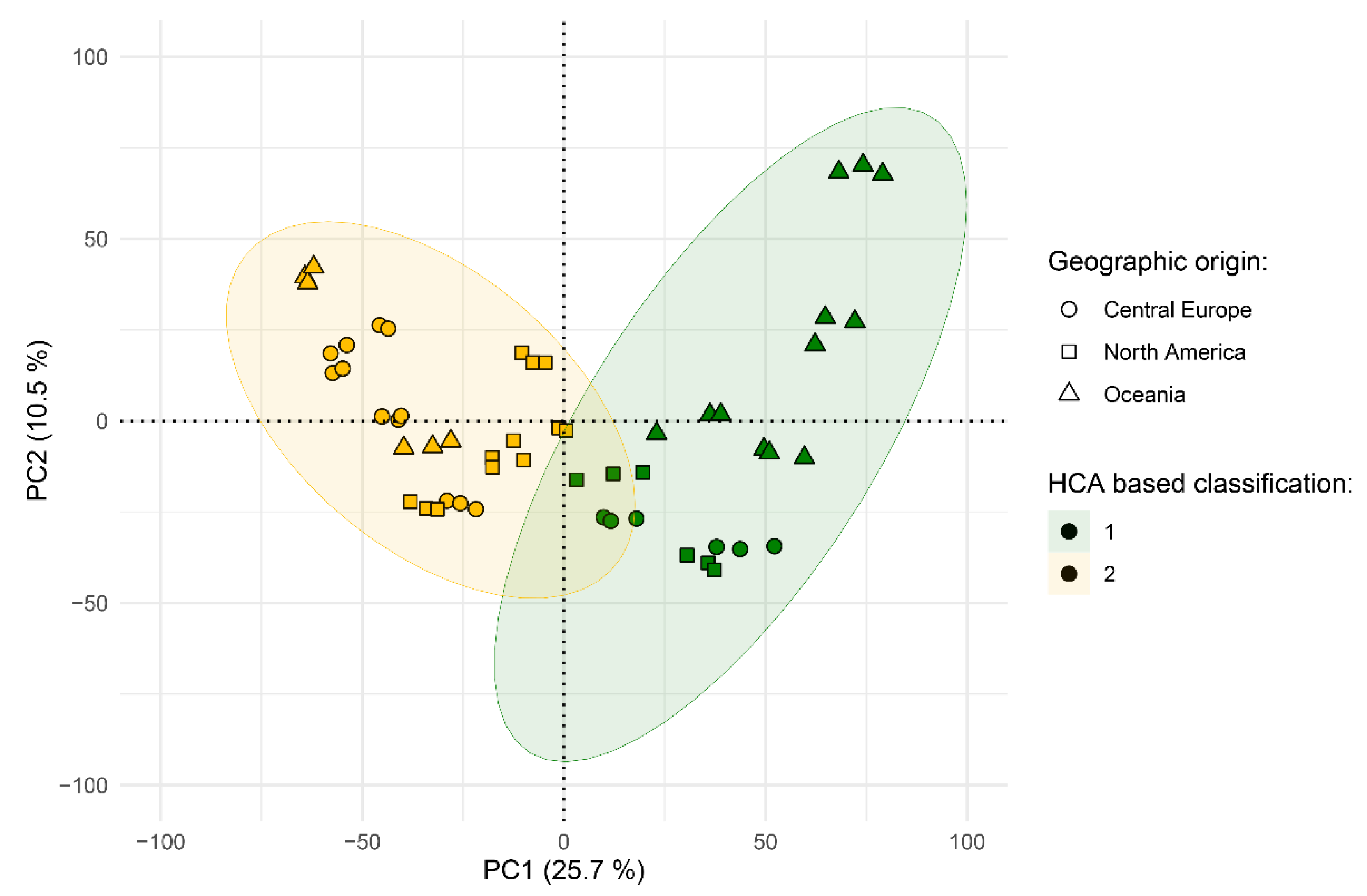
2.3. Metabolome-Based Classification
2.4. Identification of Marker Compounds
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Sample Collection and Preparation
3.3. Data Acquisition
3.4. LC-MS Profiling
3.5. Computation and Software
3.6. Semi-Supervised Classification and Feature Selection
3.7. Signal Annotation and Molecular Networks Construction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kubeš, J. Geography of World Hop Production 1990–2019. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2021, 80, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpelainen, H.; Pietiläinen, M. Hop (Humulus lupulus L.): Traditional and Present Use, and Future Potential. Econ. Bot. 2021, 75, 302–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesvadba, V.; Charvátová, J. New Fine Aroma Varieties of Hops (Humulus lupulus L.) Saaz Brilliant, Saaz Comfort, Saaz Shine and Mimosa. Kvas. Prum. 2020, 66, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Simaeys, K.R.; Féchir, M.; Gallagher, A.; Stokholm, A.; Weaver, G.; Shellhammer, T.H. Examining Chemical and Sensory Differences of New American Aroma Hops Grown in the Willamette Valley, Oregon. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2021, 79, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongelli, A.; Rodolfi, M.; Ganino, T.; Marieschi, M.; Dall’Asta, C.; Bruni, R. Italian Hop Germplasm: Characterization of Wild Humulus lupulus L. Genotypes from Northern Italy by Means of Phytochemical, Morphological Traits and Multivariate Data Analysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 70, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, J.L.; Nabuurs, M.H.; Gallant, S.T.; Kirby, C.W.; Mills, A.A.S. Phytochemical Characterization of Wild Hops (Humulus Lupulus Ssp. Lupuloides) Germplasm Resources From the Maritimes Region of Canada. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dresel, M.; van Opstaele, F.; Praet, T.; Jaskula-Goiris, B.; van Holle, A.; Naudts, D.; de Keukeleire, D.; de Cooman, L.; Aerts, G. Investigation of the Impact of the Hop Variety and the Hopping Technology on the Analytical Volatile Profile of Single-Hopped Worts and Beers. BrSc 2013, 66, 162–175. [Google Scholar]
- Dresel, M.; Dunkel, A.; Hofmann, T. Sensomics Analysis of Key Bitter Compounds in the Hard Resin of Hops (Humulus lupulus L.) and Their Contribution to the Bitter Profile of Pilsner-Type Beer. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3402–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.; Dixit, G.; Murali, T.S.; Satyamoorthy, K.; Hao, W. Genome-Based Taxonomic Classification. Genome 2019, 62, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzak, J.; Henychová, A. Evaluation of Genetic Variability within Actual Hop (Humulus lupulus L.) Cultivars by an Enlarged Set of Molecular Markers. Czech J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2018, 54, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claros, M.G.; Bautista, R.; Guerrero-Fernández, D.; Benzerki, H.; Seoane, P.; Fernández-Pozo, N. Why Assembling Plant Genome Sequences Is So Challenging. Biology 2012, 1, 439–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, S.M.; Vaitheeswaran, V.; Ambrose, S.J.; Purves, R.W.; Page, J.E. Transcriptome Analysis of Bitter Acid Biosynthesis and Precursor Pathways in Hop (Humulus Lupulus). BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champagne, A.; Boutry, M. A Comprehensive Proteome Map of Glandular Trichomes of Hop (Humulus lupulus L.) Female Cones: Identification of Biosynthetic Pathways of the Major Terpenoid-Related Compounds and Possible Transport Proteins. Proteomics 2017, 17, 1600411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresel, M.; Vogt, C.; Dunkel, A.; Hofmann, T. The Bitter Chemodiversity of Hops (Humulus lupulus L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7789–7799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liang, X.; Xiao, H.; Xu, Q. Direct Characterization of Bitter Acids in a Crude Hop Extract by Liquid Chromatography-Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 15, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.R.; Kim, K.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Park, H.J.; Jeong, H.S. Antioxidant and antitumor activities of methanolic extracts from Humulus japonicus. Korean J. Food Nutr. 2012, 25, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akazawa, H.; Kohno, H.; Tokuda, H.; Suzuki, N.; Yasukawa, K.; Kimura, Y.; Manosroi, A.; Manosroi, J.; Akihisa, T. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Tumor-Promoting Effects of 5-Deprenyllupulo-Nol C and Other Compounds from Hop (Humulus lupulus L.). Chem. Biodivers. 2012, 9, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afendi, F.M.; Okada, T.; Yamazaki, M.; Hirai-Morita, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Ikeda, S.; Takahashi, H.; Altaf-Ul-Amin, M.; Darusman, L.K.; et al. KNApSAcK Family Databases: Integrated Metabolite-Plant Species Databases for Multifaceted Plant Research. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012, 53, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moing, A.; William, A.J.; Aharoni, A.; Baker, J.; Beale, M.H.; Ben-Dor, S.; Biais, B.; Brigante, F.; Burger, Y.; Deborde, C.; et al. Comparative Metabolomics and Molecular Phylogenetics of Melon (Cucumis Melo, Cucurbitaceae) Biodiversity. Metabolites 2020, 10, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chervin, J.; Talou, T.; Audonnet, M.; Dumas, B.; Camborde, L.; Esquerré-Tugayé, M.T.; Roux, C.; Cabanac, G.; Marti, G. Deciphering the Phylogeny of Violets Based on Multiplexed Genetic and Metabolomic Approaches. Phytochemistry 2019, 163, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudzik, D.; Barbas-Bernardos, C.; García, A.; Barbas, C. Quality Assurance Procedures for Mass Spectrometry Untargeted Metabolomics. a Review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 147, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, P.; Wuolikainen, A.; Thysell, E.; Chorell, E.; Stattin, P.; Wikström, P.; Antti, H. Constrained Randomization and Multivariate Effect Projections Improve Information Extraction and Biomarker Pattern Discovery in Metabolomics Studies Involving Dependent Samples. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 1667–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godzien, J.; Alonso-Herranz, V.; Barbas, C.; Armitage, E.G. Controlling the Quality of Metabolomics Data: New Strategies to Get the Best out of the QC Sample. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Tang, J.; Yang, Q.; Sun, H.; Qiu, W.; Ma, Y.; et al. Optimization of Metabolomic Data Processing Using NOREVA. Nat. Protoc. 2022, 17, 129–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beuchel, C.; Kirsten, H.; Ceglarek, U.; Scholz, M. Metabolite-Investigator: An Integrated User-Friendly Workflow for Metabolomics Multi-Study Analysis. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 2218–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetnik, K.; Benedetti, E.; Gomari, D.P.; Schweickart, A.; Batra, R.; Buyukozkan, M.; Wang, Z.; Arnold, M.; Zierer, J.; Suhre, K.; et al. Maplet: An Extensible R Toolbox for Modular and Reproducible Metabolomics Pipelines. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 1168–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmus, R.; Ter Laak, T.L.; van Wezel, A.P.; de Voogt, P.; Schymanski, E.L. patRoon: Open source software platform for environmental mass spectrometry based non-target screening. J. Cheminform. 2021, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plyushchenko, I.V.; Fedorova, E.S.; Potoldykova, N.V.; Polyakovskiy, K.A.; Glukhov, A.I.; Rodin, I.A. Omics Untargeted Key Script: R-Based Software Toolbox for Untargeted Metabolomics with Bladder Cancer Biomarkers Discovery Case Study. J. Proteome Res. 2022, 21, 833–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stekhoven, D.J.; Bühlmann, P. Missforest-Non-Parametric Missing Value Imputation for Mixed-Type Data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadhurst, D.; Goodacre, R.; Reinke, S.N.; Kuligowski, J.; Wilson, I.D.; Lewis, M.R.; Dunn, W.B. Guidelines and Considerations for the Use of System Suitability and Quality Control Samples in Mass Spectrometry Assays Applied in Untargeted Clinical Metabolomic Studies. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turova, P.; Rodin, I.; Shpigun, O.; Stavrianidi, A. A New PARAFAC-Based Algorithm for HPLC–MS Data Treatment: Herbal Extracts Identification. Phytochem. Anal. 2020, 31, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, E.D.; Todd, D.A.; Harnly, J.M.; Cech, N.B.; Kellogg, J.J. Identification of Adulteration in Botanical Samples with Untargeted Metabolomics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 4273–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Rech, K.S.; Badshah, G.; Soares, F.L.F.; Barison, A. 1H HR-MAS NMR-Based Metabolomic Fingerprinting to Distinguish Morphological Similarities and Metabolic Profiles of Maytenus Ilicifolia, a Brazilian Medicinal Plant. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, L.M.; Amorim, T.L.; Grazul, R.M.; de Oliveira, M.A.L. Differentiation of Aromatic, Bittering and Dual-Purpose Commercial Hops from Their Terpenic Profiles: An Approach Involving Batch Extraction, GC–MS and Multivariate Analysis. Int. Food Res. J. 2020, 138, 109768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghisoni, S.; Lucini, L.; Rocchetti, G.; Chiodelli, G.; Farinelli, D.; Tombesi, S.; Trevisan, M. Untargeted Metabolomics with Multivariate Analysis to Discriminate Hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) Cultivars and Their Geographical Origin. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisoni, S.; Lucini, L.; Angilletta, F.; Rocchetti, G.; Farinelli, D.; Tombesi, S.; Trevisan, M. Discrimination of Extra-Virgin-Olive Oils from Different Cultivars and Geographical Origins by Untargeted Metabolomics. Int. Food Res. J. 2019, 121, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.I.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, S.; Nassef, M.; Badr, A.; Farag, I. A Nested Genetic Algorithm for Feature Selection in High-Dimensional Cancer Microarray Datasets. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 121, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvandeh, S.; Yeh, H.W.; Paulus, M.P.; McKinney, B.A. Consensus Features Nested Cross-Validation. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 3093–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; Johnson, K. Applied Predictive Modeling, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 500–502. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Li, T.; Qing, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, C. Structural Characterization and Osteogenic Bioactivities of a Novel: Humulus Lupulus Polysaccharide. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.H.; Oh, K.E.; Jo, Y.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Liu, Q.; Turk, A.; Jang, J.Y.; Hwang, B.Y.; Lee, K.Y.; Lee, M.K. Characterization of Tyrosinase Inhibitory Constituents from the Aerial Parts of Humulus Japonicus Using LC-MS/MS Coupled Online Assay. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, F.; Hu, Z.; Ding, H.; Tang, H.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, X. Novel Prenylated Bichalcone and Chalcone from Humulus Lupulus and Their Quinone Reductase Induction Activities. Fitoterapia 2014, 93, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohr, G.; Gerhäuser, C.; Knauft, J.; Zapp, J.; Becker, H. Anti-Inflammatory Acylphloroglucinol Derivatives from Hops (Humulus Lupulus). J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1545–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schymanski, E.L.; Jeon, J.; Gulde, R.; Fenner, K.; Ruff, M.; Singer, H.P.; Hollender, J. Identifying Small Molecules via High Resolution Mass Spectrometry: Communicating Confidence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2097–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and Community Curation of Mass Spectrometry Data with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruttkies, C.; Schymanski, E.L.; Wolf, S.; Hollender, J.; Neumann, S. MetFrag Relaunched: Incorporating Strategies beyond in Silico Fragmentation. J. Cheminform. 2016, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djoumbou-Feunang, Y.; Pon, A.; Karu, N.; Zheng, J.; Li, C.; Arndt, D.; Gautam, M.; Allen, F.; Wishart, D.S. Cfm-Id 3.0: Significantly Improved Esi-Ms/Ms Prediction and Compound Identification. Metabolites 2019, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron, A.T.; Gentry, E.C.; McPhail, K.L.; Nothias, L.F.; Nothias-Esposito, M.; Bouslimani, A.; Petras, D.; Gauglitz, J.M.; Sikora, N.; Vargas, F.; et al. Reproducible Molecular Networking of Untargeted Mass Spectrometry Data Using GNPS. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 1954–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.A.; Porzel, A.; Schmidt, J.; Wessjohann, L.A. Metabolite Profiling and Fingerprinting of Commercial Cultivars of Humulus lupulus L. (Hop): A Comparison of MS and NMR Methods in Metabolomics. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 492–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srečec, S.; Rezić, T.; Šantek, B.; Marić, V. Hop Pellets Type 90: Influence of Manufacture and Storage on Losses of α-Acids. Acta Aliment. 2009, 38, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Česlová, L.; Holčapek, M.; Fidler, M.; Drštičková, J.; Lísa, M. Characterization of Prenylflavonoids and Hop Bitter Acids in Various Classes of Czech Beers and Hop Extracts Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 7249–7257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, M.; Gigliobianco, M.R.; Peregrina, D.V.; Sagratini, G.; Censi, R.; di Martino, P. Quantification of Phenolic Compounds in Different Types of Crafts Beers, Worts, Starting and Spent Ingredients by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1612, 460622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessner, D.; Chambers, M.; Burke, R.; Agus, D.; Mallick, P. ProteoWizard: Open Source Software for Rapid Proteomics Tools Development. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2534–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.A.; Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS: Processing Mass Spectrometry Data for Metabolite Profiling Using Nonlinear Peak Alignment, Matching, and Identification. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libiseller, G.; Dvorzak, M.; Kleb, U.; Gander, E.; Eisenberg, T.; Madeo, F.; Neumann, S.; Trausinger, G.; Sinner, F.; Pieber, T.; et al. IPO: A Tool for Automated Optimization of XCMS Parameters. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thévenot, E.A.; Roux, A.; Xu, Y.; Ezan, E.; Junot, C. Analysis of the human adult urinary metabolome variations with age, body mass index, and gender by implementing a comprehensive workflow for univariate and OPLS statistical analyses. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 3322–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Cultivar | Region of Growth | Genetic Origin [10] | Type | New Labels |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saaz | Central Europe | European | Aroma | 2 |
| Tettnanger | European | Aroma | 2 | |
| Hallertau Mittelfruh | North American | Aroma | 2 | |
| Perle | European | Dual use | 2 | |
| Nugget | North American | Dual use | 1 | |
| Styrian Cardinal | North American | Dual use | 1 | |
| Amarillo | North America | North American | Aroma | 2 |
| Fuggle | European | Aroma | 2 | |
| Willamette | European | Aroma | 2 | |
| Cashmere | North American | Dual use | 1 | |
| Mosaic | North American | Dual use | 1 | |
| Cascade | North American | Aroma | 2 | |
| Kohatu | Oceania | North American | Aroma | 2 |
| Wai-iti | European | Aroma | 2 | |
| Nelson Sauvin | North American | Dual use | 1 | |
| Galaxy | North American | Dual use | 1 | |
| Waimea | North American | Dual use | 1 | |
| Ella | North American | Aroma | 1 |
| Compound Name | Retention Time, Min | m/z | Ion Type | Predicted Molecular Formula (Error, ppm) | VIP from PLS | Fold Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Isoxanthohumol | 10.46 | 353.1384 | [M-H]− | C21H22O5 (0.26) | 1.73 | 1.45 |
| 2 | Unknown | 11.4 | 399.1443 | [M-H]− | C22H24O7 (3.67) | 1.24 | 1.06 |
| 3 | Cohumulone | 19.37 | 347.1886 | [M-H]− | C20H28O5 (0.53) | 1.42 | 2.15 |
| 4 | Posthumulone | 17.43 | 333.1694 | [M-H]− | C19H26O5 (0.8) | 1.56 | 2.23 |
| 5 | Humulone | 21.59 | 361.202 | [M-H]− | C21H30O5 (1.95) | 1.46 | 0.31 |
| 6 | Prehumulone | 23.2 | 375.2172 | [M-H]− | C22H32O5 (0.57) | 1.35 | 2.33 |
| 7 | Unknown | 20.33 | 385.2371 | [M + H]+ | --- | 1.31 | 1.11 |
| 8 | Unknown | 10.01 | 410.196 | [M + H]+ | --- | 1.71 | 0.93 |
| 9 | Unknown | 16.1 | 371.1811 | [M + H]+ | C23H32O4 (0.67) | 1.42 | 1.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ikhalaynen, Y.A.; Plyushchenko, I.V.; Rodin, I.A. Hopomics: Humulus lupulus Brewing Cultivars Classification Based on LC-MS Profiling and Nested Feature Selection. Metabolites 2022, 12, 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100945
Ikhalaynen YA, Plyushchenko IV, Rodin IA. Hopomics: Humulus lupulus Brewing Cultivars Classification Based on LC-MS Profiling and Nested Feature Selection. Metabolites. 2022; 12(10):945. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100945
Chicago/Turabian StyleIkhalaynen, Yuriy Andreevich, Ivan Victorovich Plyushchenko, and Igor Alexandrovich Rodin. 2022. "Hopomics: Humulus lupulus Brewing Cultivars Classification Based on LC-MS Profiling and Nested Feature Selection" Metabolites 12, no. 10: 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100945
APA StyleIkhalaynen, Y. A., Plyushchenko, I. V., & Rodin, I. A. (2022). Hopomics: Humulus lupulus Brewing Cultivars Classification Based on LC-MS Profiling and Nested Feature Selection. Metabolites, 12(10), 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100945







