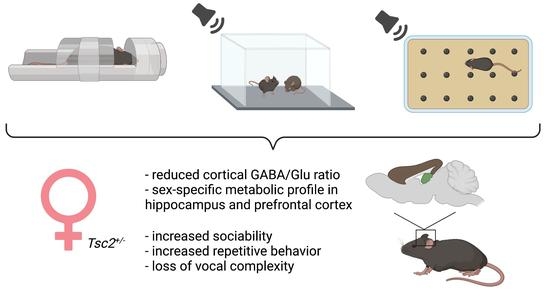
Sex-Dependent Social and Repetitive Behavior and Neurochemical Profile in Mouse Model of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
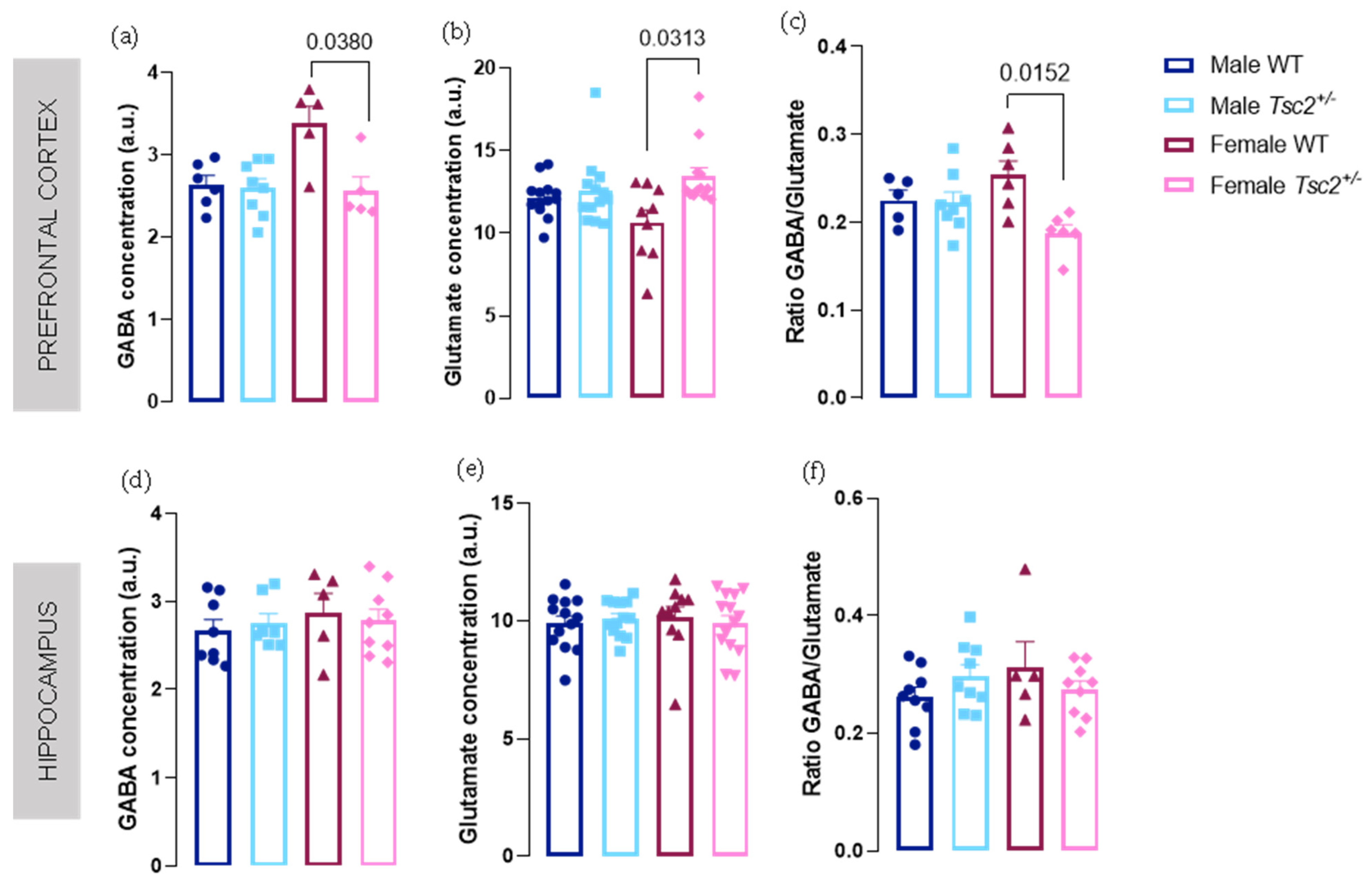
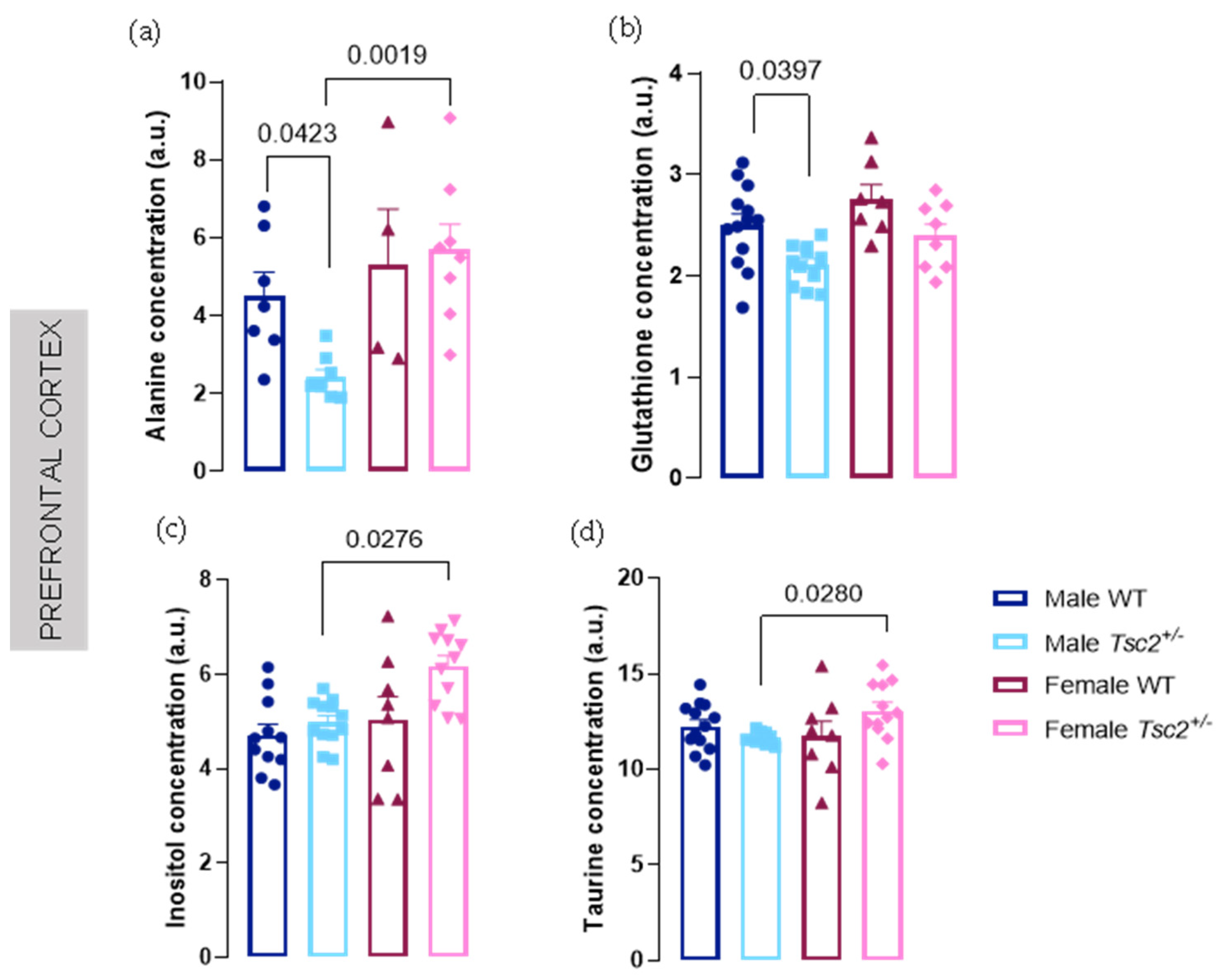
2.1. Spectroscopic Analyses
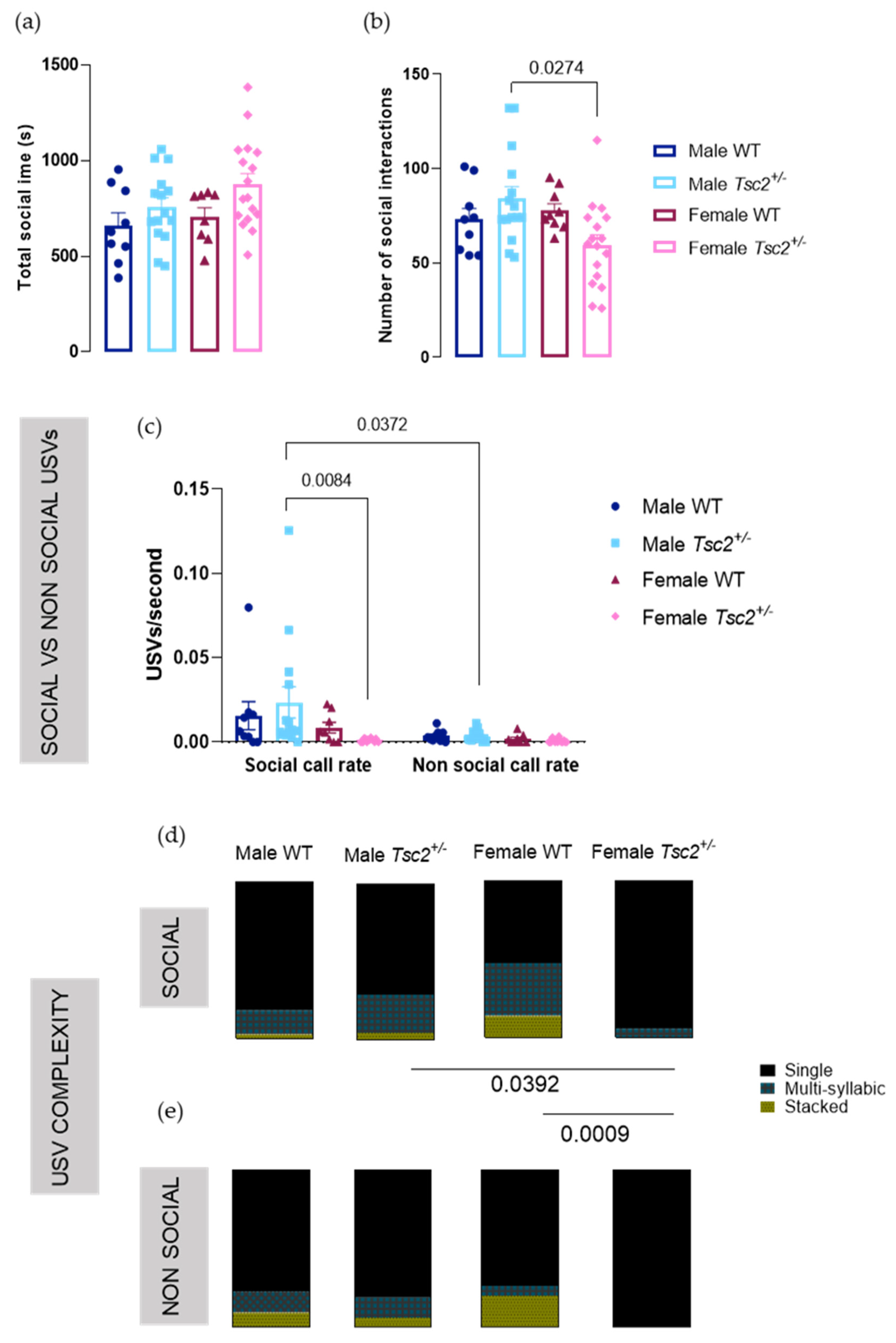
2.2. Behavioral Testing
2.2.1. Social Behavioral Test
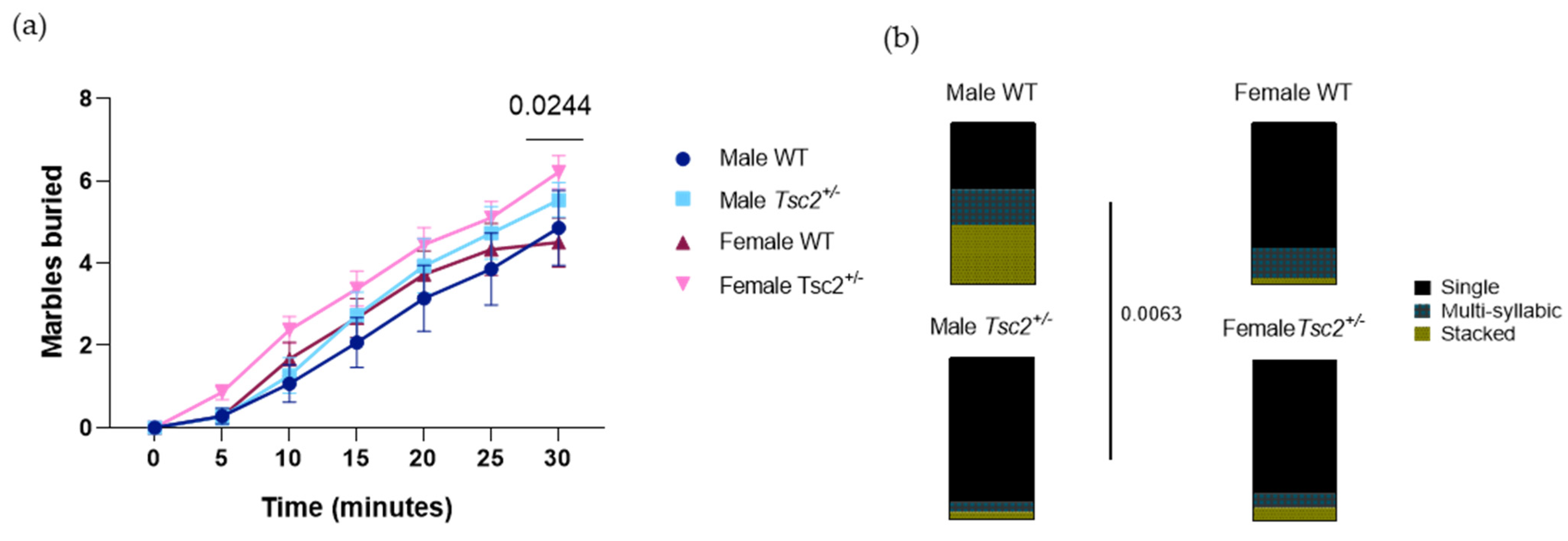
2.2.2. RRB Behavioral Test
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
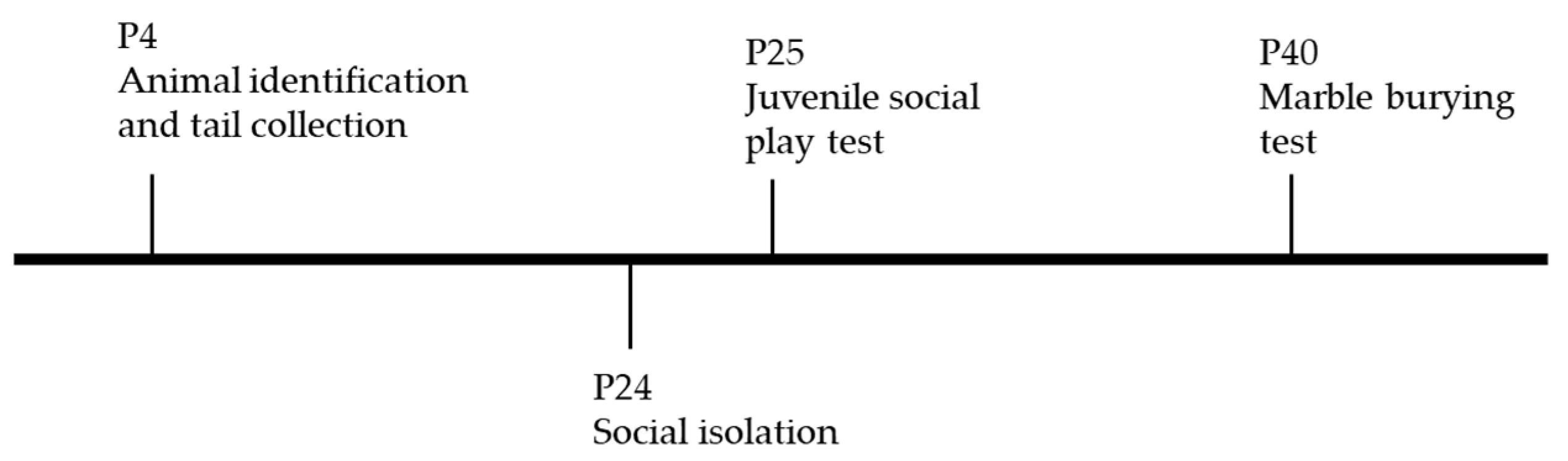
4.1. Animals
4.2. Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
4.3. Ultrasonic Vocalization Recordings and Analysis
4.4. Video Recordings
4.5. Juvenile Social Play Test
4.6. Marble-Burying Test
4.7. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baio, J.; Wiggins, L.; Christensen, D.L.; Maenner, M.J.; Daniels, J.; Warren, Z.; Kurzius-Spencer, M.; Zahorodny, W.; Rosenberg, C.R.; White, T.; et al. Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 8 Years—Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2014. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2018, 67, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. DSM-5 Task Force. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013; pp. 50–59. [Google Scholar]
- Loomes, R.; Hull, L.; Mandy, W.P.L. What Is the Male-to-Female Ratio in Autism Spectrum Disorder? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2017, 56, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse, A.J.O.; Durkin, K.; Jaquet, E.; Ziatas, K. Friendship, Loneliness and Depression in Adolescents with Asperger’s Syndrome. J. Adolesc. 2009, 32, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durkin, K.; Conti-Ramsden, G. Young People with Specific Language Impairment: A Review of Social and Emotional Functioning in Adolescence. Child. Lang. Teach. Ther. 2010, 26, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, M.O. Loneliness, Friendship, and Well-Being in Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Autism 2014, 18, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, J.K.; Werling, D.M.; Constantino, J.N.; Cantor, R.M.; Geschwind, D.H. Social Responsiveness, an Autism Endophenotype: Genomewide Significant Linkage to Two Regions on Chromosome 8. Am. J. Psychiatry 2015, 172, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sedgewick, F.; Hill, V.; Yates, R.; Pickering, L.; Pellicano, E. Gender Differences in the Social Motivation and Friendship Experiences of Autistic and Non-Autistic Adolescents. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2016, 46, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, C.H.; Luikart, B.W.; Powell, C.M.; Zhou, J.; Matheny, S.A.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Baker, S.J.; Parada, L.F. Pten Regulates Neuronal Arborization and Social Interaction in Mice. Neuron 2006, 50, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabuchi, K.; Blundell, J.; Etherton, M.R.; Hammer, R.E.; Liu, X.; Powell, C.M.; Südhof, T.C. A Neuroligin-3 Mutation Implicated in Autism Increases Inhibitory Synaptic Transmission in Mice. Science 2007, 318, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamain, S.; Radyushkin, K.; Hammerschmidt, K.; Granon, S.; Boretius, S.; Varoqueaux, F.; Ramanantsoa, N.; Gallego, J.; Ronnenberg, A.; Winter, D.; et al. Reduced Social Interaction and Ultrasonic Communication in a Mouse Model of Monogenic Heritable Autism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1710–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peça, J.; Feliciano, C.; Ting, J.T.; Wang, W.; Wells, M.F.; Venkatraman, T.N.; Lascola, C.D.; Fu, Z.; Feng, G. Shank3 Mutant Mice Display Autistic-like Behaviours and Striatal Dysfunction. Nature 2011, 472, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkogkas, C.G.; Khoutorsky, A.; Ran, I.; Rampakakis, E.; Nevarko, T.; Weatherill, D.B.; Vasuta, C.; Yee, S.; Truitt, M.; Dallaire, P.; et al. Autism-Related Deficits via Dysregulated EIF4E-Dependent Translational Control. Nature 2013, 493, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clipperton-Allen, A.E.; Page, D.T. Pten Haploinsufficient Mice Show Broad Brain Overgrowth but Selective Impairments in Autism-Relevant Behavioral Tests. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 3490–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasciuto, E.; Borrie, S.C.; Kanellopoulos, A.K.; Santos, A.R.; Cappuyns, E.; D’Andrea, L.; Pacini, L.; Bagni, C. Autism Spectrum Disorders: Translating Human Deficits into Mouse Behavior. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2015, 124, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarlane, H.G.; Kusek, G.K.; Yang, M.; Phoenix, J.L.; Bolivar, V.J.; Crawley, J.N. Autism-like Behavioral Phenotypes in BTBR T+tf/J Mice. Genes Brain Behav. 2008, 7, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.; O’Connor, M.; Templet, S.; Moghaddam, M.; Di Via Ioschpe, A.; Sinclair, A.; Zhu, L.Q.; Xu, W.; Man, H.Y. NEXMIF/KIDLIA Knock-out Mouse Demonstrates Autism-Like Behaviors, Memory Deficits, and Impairments in Synapse Formation and Function. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.L.; Pride, M.C.; Edmiston, E.; Yang, M.; Silverman, J.L.; Crawley, J.N.; Van de Water, J. Autism-Specific Maternal Autoantibodies Produce Behavioral Abnormalities in an Endogenous Antigen-Driven Mouse Model of Autism. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 2994–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etherton, M.R.; Blaiss, C.A.; Powell, C.M.; Südhof, T.C. Mouse Neurexin-1α Deletion Causes Correlated Electrophysiological and Behavioral Changes Consistent with Cognitive Impairments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17998–18003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pobbe, R.L.H.; Pearson, B.L.; Defensor, E.B.; Bolivar, V.J.; Blanchard, D.C.; Blanchard, R.J. Expression of Social Behaviors of C57BL/6J versus BTBR Inbred Mouse Strains in the Visible Burrow System. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 214, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, M.D.; Shah, C.R.; Muller, C.L.; Crawley, J.N.; Carneiro, A.M.D.; Veenstra-VanderWeele, J. Absence of Preference for Social Novelty and Increased Grooming in Integrin Β3 Knockout Mice: Initial Studies and Future Directions. Autism Res. 2011, 4, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodeo, D.A.; Jones, J.H.; Sweeney, J.A.; Ragozzino, M.E. Differences in BTBR T+ Tf/J and C57BL/6J Mice on Probabilistic Reversal Learning and Stereotyped Behaviors. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 227, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, J.; Jones, K.; Miller, E.; Ariza, J.; Noctor, S.; Van de Water, J.; Martínez-Cerdeño, V. Embryonic Intraventricular Exposure to Autism-Specific Maternal Autoantibodies Produces Alterations in Autistic-like Stereotypical Behaviors in Offspring Mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 266, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sungur, A.Ö.; Vörckel, K.J.; Schwarting, R.K.W.; Wöhr, M. Repetitive Behaviors in the Shank1 Knockout Mouse Model for Autism Spectrum Disorder: Developmental Aspects and Effects of Social Context. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 234, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheaha, D.; Bumrungsri, S.; Chatpun, S.; Kumarnsit, E. Characterization of in Utero Valproic Acid Mouse Model of Autism by Local Field Potential in the Hippocampus and the Olfactory Bulb. Neurosci. Res. 2015, 98, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaan, C.; Corley, M.J.; Eulalio, T.; Leite-ahyo, K.; Pang, A.P.S.; Fang, R.; Khadka, V.S.; Maunakea, A.K.; Ward, M.A. Juvenile Shank3b Deficient Mice Present with Behavioral Phenotype Relevant to Autism Spectrum Disorder. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 356, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reith, R.M.; McKenna, J.; Wu, H.; Hashmi, S.S.; Cho, S.H.; Dash, P.K.; Gambello, M.J. Loss of Tsc2 in Purkinje Cells Is Associated with Autistic-like Behavior in a Mouse Model of Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 51, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartzer, J.J.; Careaga, M.; Onore, C.E.; Rushakoff, J.A.; Berman, R.F.; Ashwood, P. Maternal Immune Activation and Strain Specific Interactions in the Development of Autism-like Behaviors in Mice. Transl. Psychiatry 2013, 3, e240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moy, S.S.; Riddick, N.V.; Nikolova, V.D.; Teng, B.L.; Agster, K.L.; Nonneman, R.J.; Young, N.B.; Baker, L.K.; Nadler, J.J.; Bodfish, J.W. Repetitive Behavior Profile and Supersensitivity to Amphetamine in the C58/J Mouse Model of Autism. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 259, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shriberg, L.D.; Paul, R.; McSweeny, J.L.; Klin, A.; Cohen, D.J.; Volkmar, F.R. Speech and Prosody Characteristics of Adolescents and Adults With High-Functioning Autism and Asperger Syndrome. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2001, 44, 1097–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabout, J.; Serreau, P.; Ey, E.; Bellier, L.; Aubin, T.; Bourgeron, T.; Granon, S. Adult Male Mice Emit Context-Specific Ultrasonic Vocalizations That Are Modulated by Prior Isolation or Group Rearing Environment. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, H.S.; Lipina, T.V.; Roder, J.C. Ultrasonic Vocalizations in Mice during Exploratory Behavior Are Context-Dependent. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wöhr, M.; Roullet, F.I.; Hung, A.Y.; Sheng, M.; Crawley, J.N. Communication Impairments in Mice Lacking Shank1: Reduced Levels of Ultrasonic Vocalizations and Scent Marking Behavior. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmeisser, M.J.; Ey, E.; Wegener, S.; Bockmann, J.; Stempel, A.V.; Kuebler, A.; Janssen, A.L.; Udvardi, P.T.; Shiban, E.; Spilker, C.; et al. Autistic-like Behaviours and Hyperactivity in Mice Lacking ProSAP1/Shank2. Nature 2012, 486, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Bozdagi, O.; Scattoni, M.L.; Wöhr, M.; Roullet, F.I.; Katz, A.M.; Abrams, D.N.; Kalikhman, D.; Simon, H.; Woldeyohannes, L.; et al. Reduced Excitatory Neurotransmission and Mild Autism-Relevant Phenotypes in Adolescent Shank3 Null Mutant Mice. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 6525–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ey, E.; Torquet, N.; Le Sourd, A.M.; Leblond, C.S.; Boeckers, T.M.; Faure, P.; Bourgeron, T. The Autism ProSAP1/Shank2 Mouse Model Displays Quantitative and Structural Abnormalities in Ultrasonic Vocalisations. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 256, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene-Colozzi, E.A.; Sadowski, A.R.; Chadwick, E.; Tsai, P.T.; Sahin, M. Both Maternal and Pup Genotype Influence Ultrasonic Vocalizations and Early Developmental Milestones in Tsc2+/− Mice. Epilepsy Res. Treat. 2014, 2014, 784137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, A.; Hammerschmidt, K.; Tantra, M.; Krueger, D.; Brose, N.; Ehrenreich, H. Juvenile Manifestation of Ultrasound Communication Deficits in the Neuroligin-4 Null Mutant Mouse Model of Autism. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 270, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bicks, L.K.; Koike, H.; Akbarian, S.; Morishita, H. Prefrontal Cortex and Social Cognition in Mouse and Man. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J. Neuroanatomical Substrates of Rodent Social Behavior: The Medial Prefrontal Cortex and Its Projection Patterns. Front. Neural Circuits 2017, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, M.; Jang, H.J.; Park, M.; Miller, E.M.; Cox, J.; Taliaferro, J.P.; Parker, N.F.; Bhave, V.; Hur, H.; Liang, Y.; et al. Combined Social and Spatial Coding in a Descending Projection from the Prefrontal Cortex. Cell 2017, 171, 1663–1677.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banker, S.M.; Gu, X.; Schiller, D.; Foss-Feig, J.H. Hippocampal Contributions to Social and Cognitive Deficits in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 44, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehpara Farhat, S.; Mahboob, A.; Iqbal, G.; Ahmed, T. Aluminum-Induced Cholinergic Deficits in Different Brain Parts and Its Implications on Sociability and Cognitive Functions in Mouse. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 177, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jupp, B.; Sawiak, S.J.; Van Der Veen, B.; Lemstra, S.; Toschi, C.; Barlow, R.L.; Pekcec, A.; Bretschneider, T.; Nicholson, J.R.; Robbins, T.W.; et al. Diminished Myoinositol in Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex Modulates the Endophenotype of Impulsivity. Cereb. Cortex 2020, 30, 3392–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Min, L.; Li, M.; Shao, F. Juvenile Social Isolation Leads to Schizophrenia-like Behaviors via Excess Lactate Production by Astrocytes. Brain Res. Bull. 2021, 174, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, D.M.; Schenk, A.K.; Yang, S.B.; Jan, Y.N.; Jan, L.Y. Altered Ultrasonic Vocalizations in a Tuberous Sclerosis Mouse Model of Autism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11074–11079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidstone, J.; Uljarević, M.; Sullivan, J.; Rodgers, J.; McConachie, H.; Freeston, M.; Le Couteur, A.; Prior, M.; Leekam, S. Relations among Restricted and Repetitive Behaviors, Anxiety and Sensory Features in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2014, 8, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baribeau, D.A.; Vigod, S.; Pullenayegum, E.; Kerns, C.M.; Mirenda, P.; Smith, I.M.; Vaillancourt, T.; Volden, J.; Waddell, C.; Zwaigenbaum, L.; et al. Repetitive Behavior Severity as an Early Indicator of Risk for Elevated Anxiety Symptoms in Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2020, 59, 890–899.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Itzchak, E.; Koller, J.; Zachor, D.A. Characterization and Prediction of Anxiety in Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Longitudinal Study. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2020, 48, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodgers, J.; Glod, M.; Connolly, B.; McConachie, H. The Relationship between Anxiety and Repetitive Behaviours in Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2012, 42, 2404–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.S.; Gonzales, E.L.; Kim, K.C.; Yang, S.M.; Kim, J.W.; Mabunga, D.F.; Cheong, J.H.; Han, S.H.; Bahn, G.H.; Shin, C.Y. The Transgenerational Inheritance of Autism-like Phenotypes in Mice Exposed to Valproic Acid during Pregnancy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.C.; Cole, T.B.; Costa, L.G. Prenatal and Early-Life Diesel Exhaust Exposure Causes Autism-like Behavioral Changes in Mice. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.M.; Plachez, C.; Huang, S. Sex-Dependent Motor Deficit and Increased Anxiety-like States in Mice Lacking Autism-Associated Gene Slit3. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouser, M.; Speed, H.E.; Dewey, C.M.; Reimers, J.M.; Widman, A.J.; Gupta, N.; Liu, S.; Jaramillo, T.C.; Bangash, M.; Xiao, B.; et al. Loss of Predominant Shank3 Isoforms Results in Hippocampus-Dependent Impairments in Behavior and Synaptic Transmission. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 18448–18468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, I.Y.; Ding, A.Y.; Li, Q.; McAlonan, G.M.; Wu, E.X. Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Reveals N-Acetylaspartate Reduction in Hippocampus and Cingulate Cortex after Fear Conditioning. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2012, 204, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gapp, K.; Corcoba, A.; van Steenwyk, G.; Mansuy, I.M.; Duarte, J.M.N. Brain Metabolic Alterations in Mice Subjected to Postnatal Traumatic Stress and in Their Offspring. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 37, 2423–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, E.; Granon, S.; Chauveau, F. Social Context Increases Ultrasonic Vocalizations during Restraint in Adult Mice. Anim. Cogn. 2020, 23, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Screven, L.A.; Dent, M.L. Perception of Ultrasonic Vocalizations by Socially Housed and Isolated Mice. eNeuro 2019, 6, ENEURO.0049-19.2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werling, D.M.; Geschwind, D.H. Sex Differences in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2013, 26, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignoli, A.; La Briola, F.; Peron, A.; Turner, K.; Vannicola, C.; Saccani, M.; Magnaghi, E.; Scornavacca, G.F.; Canevini, M.P. Autism Spectrum Disorder in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex: Searching for Risk Markers. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2015, 10, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, A.; Shepherd, C. A Prevalence Study of Autism in Tuberous Sclerosis. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 1993, 23, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saré, R.M.; Lemons, A.; Figueroa, C.; Song, A.; Levine, M.; Smith, C.B. Sex-Selective Effects on Behavior in a Mouse Model of Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. eNeuro 2020, 7, ENEURO.0379-19.2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Huang, G.B.; Muna, S.S.; Bagalkot, T.R.; Jin, H.M.; Chae, H.J.; Chung, Y.C. Effects of Chronic Social Defeat Stress on Behavior and Choline Acetyltransferase, 78-KDa Glucose-Regulated Protein, and CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein (C/EBP) Homologous Protein in Adult Mice. Psychopharmacology 2013, 228, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, J.; Violante, I.R.; Sereno, J.; Leitão, R.A.; Cai, Y.; Abrunhosa, A.; Silva, A.P.; Silva, A.J.; Castelo-Branco, M. Testing the Excitation/Inhibition Imbalance Hypothesis in a Mouse Model of the Autism Spectrum Disorder: In Vivo Neurospectroscopy and Molecular Evidence for Regional Phenotypes. Mol. Autism 2017, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Xu, X.; Pan, L.; Zhu, W.; Fu, X.; Guo, L.; Lu, Q.; Wang, J. Pharmacologic Activation of Cholinergic Alpha7 Nicotinic Receptors Mitigates Depressive-like Behavior in a Mouse Model of Chronic Stress. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gitik, M.; Holliday, E.D.; Leung, M.; Yuan, Q.; Logue, S.F.; Tikkanen, R.; Goldman, D.; Gould, T.J. Choline Ameliorates Adult Learning Deficits and Reverses Epigenetic Modification of Chromatin Remodeling Factors Related to Adolescent Nicotine Exposure. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2018, 155, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Hong, K.B.; Kim, S.; Suh, H.J.; Jo, K. Creatine and Taurine Mixtures Alleviate Depressive-like Behaviour in Drosophila Melanogaster and Mice via Regulating Akt and ERK/BDNF Pathways. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claghorn, G.C.; Thompson, Z.; Wi, K.; Van, L.; Garland, T. Caffeine Stimulates Voluntary Wheel Running in Mice without Increasing Aerobic Capacity. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 170, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoba, A.; Gruetter, R.; Do, K.Q.; Duarte, J.M.N. Social Isolation Stress and Chronic Glutathione Deficiency Have a Common Effect on the Glutamine-to-Glutamate Ratio and Myo-Inositol Concentration in the Mouse Frontal Cortex. J. Neurochem. 2017, 142, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottomley, P. Spatial Localization in NMR Spectroscopy in vivo. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1987, 508, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkáč, I.; Starčuk, Z.; Choi, I.-Y.; Gruetter, R. In Vivo 1 H NMR Spectroscopy of Rat Brain at 1 Ms Echo Time. Magn. Reson. Med. 1999, 41, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provencher, S.W. Automatic Quantitation of Localized in Vivo 1H Spectra with LCModel. NMR Biomed. 2001, 14, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, K.H.; Rissman, E.F. Sex Differences in Juvenile Mouse Social Behavior Are Influenced by Sex Chromosomes and Social Context. Genes Brain Behav. 2011, 10, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terranova, M.L.; Laviola, G. Scoring of Social Interactions and Play in Mice During Adolescence. Curr. Protoc. Toxicol. 2005, 26, 13.10.1–13.10.11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanford School of Medicine Mouse Species Ethogram. Available online: http://mousebehavior.org/ethogram/ (accessed on 17 March 2021).
- Angoa-Pérez, M.; Kane, M.J.; Briggs, D.I.; Francescutti, D.M.; Kuhn, D.M. Marble Burying and Nestlet Shredding as Tests of Repetitive, Compulsive-like Behaviors in Mice. JoVE J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 82, e50978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferreira, H.; Sousa, A.C.; Sereno, J.; Martins, J.; Castelo-Branco, M.; Gonçalves, J. Sex-Dependent Social and Repetitive Behavior and Neurochemical Profile in Mouse Model of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Metabolites 2022, 12, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12010071
Ferreira H, Sousa AC, Sereno J, Martins J, Castelo-Branco M, Gonçalves J. Sex-Dependent Social and Repetitive Behavior and Neurochemical Profile in Mouse Model of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Metabolites. 2022; 12(1):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12010071
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreira, Helena, Ana Catarina Sousa, José Sereno, João Martins, Miguel Castelo-Branco, and Joana Gonçalves. 2022. "Sex-Dependent Social and Repetitive Behavior and Neurochemical Profile in Mouse Model of Autism Spectrum Disorder" Metabolites 12, no. 1: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12010071
APA StyleFerreira, H., Sousa, A. C., Sereno, J., Martins, J., Castelo-Branco, M., & Gonçalves, J. (2022). Sex-Dependent Social and Repetitive Behavior and Neurochemical Profile in Mouse Model of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Metabolites, 12(1), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12010071