Multi-Omics Revealing the Response Patterns of Symbiotic Microorganisms and Host Metabolism in Scleractinian Coral Pavona minuta to Temperature Stresses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
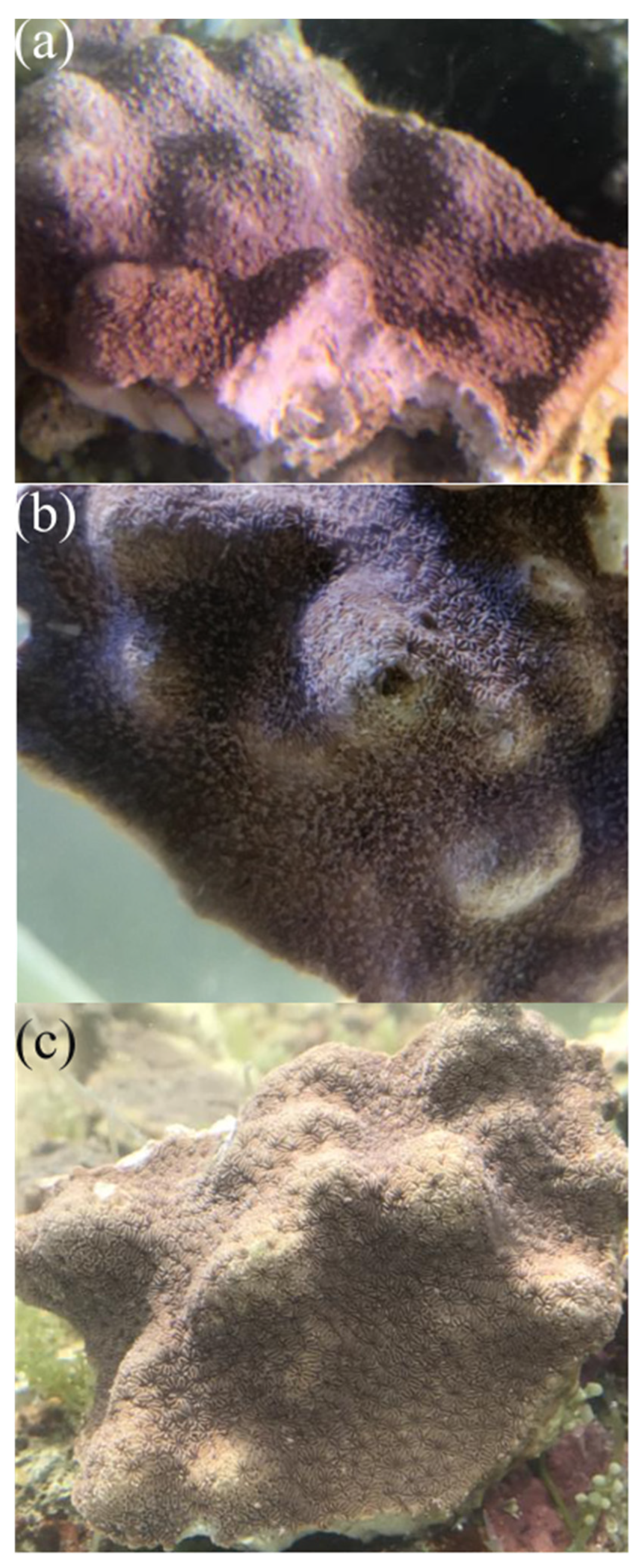
2.1. Changes in the Phenotypes of P. minuta under Temperature Stresses
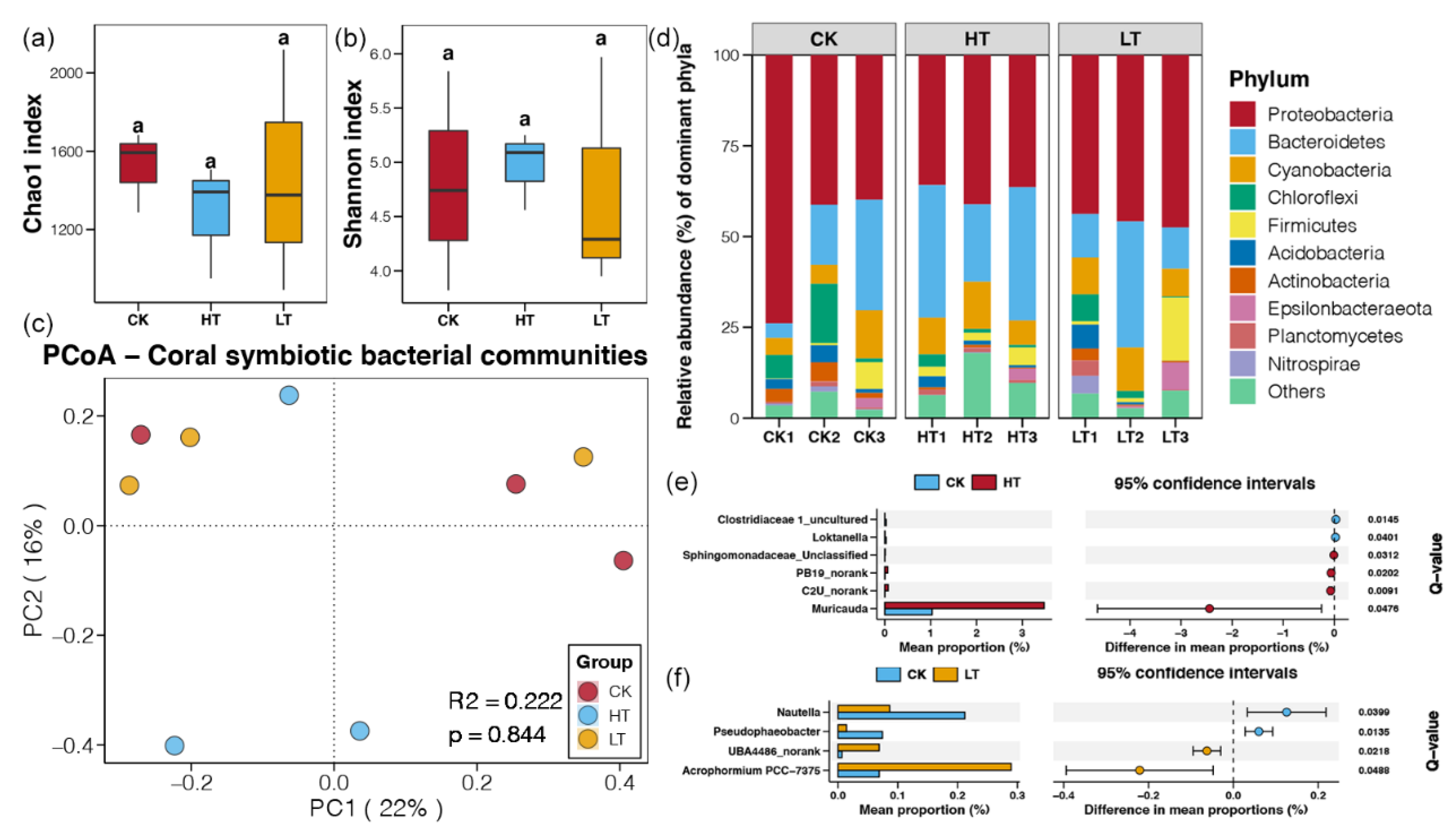
2.2. Responses of Symbiotic Bacteria under Temperature Stresses
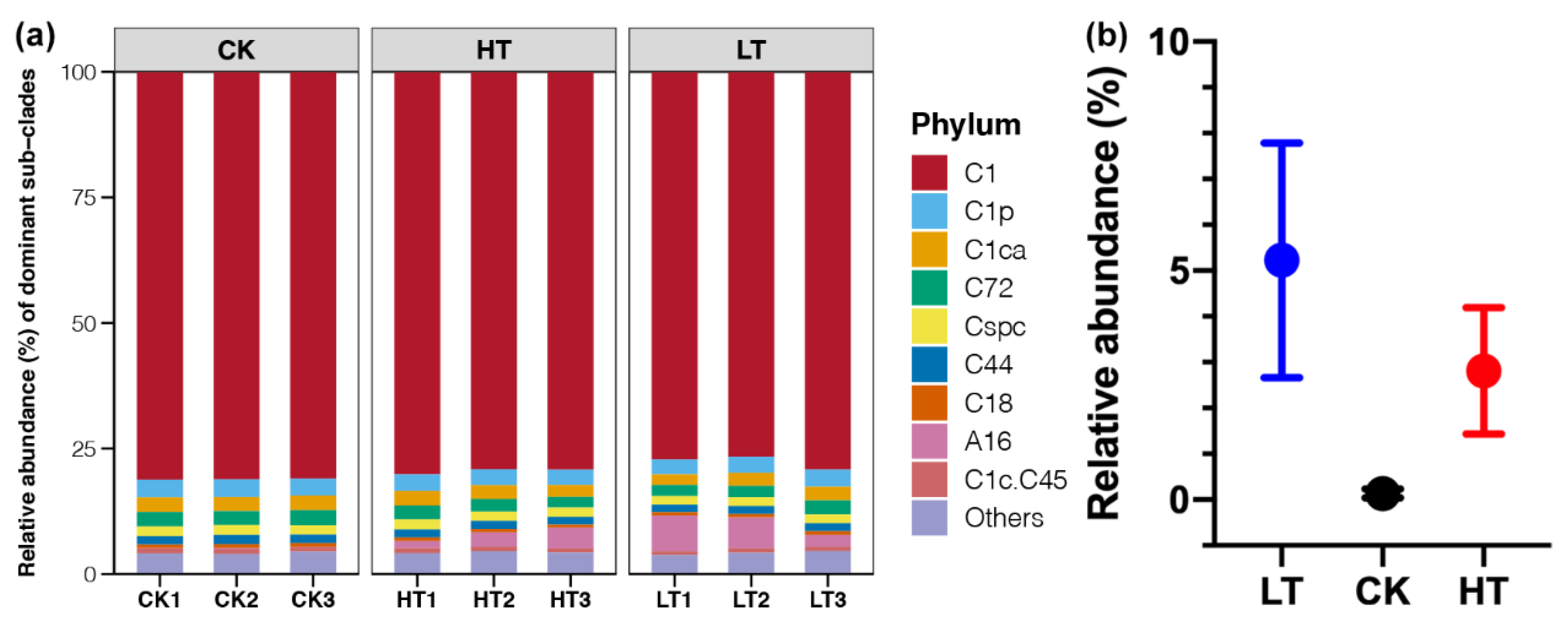
2.3. Responses of Symbiotic Dinoflagellate Communities under Different Temperature Stresses
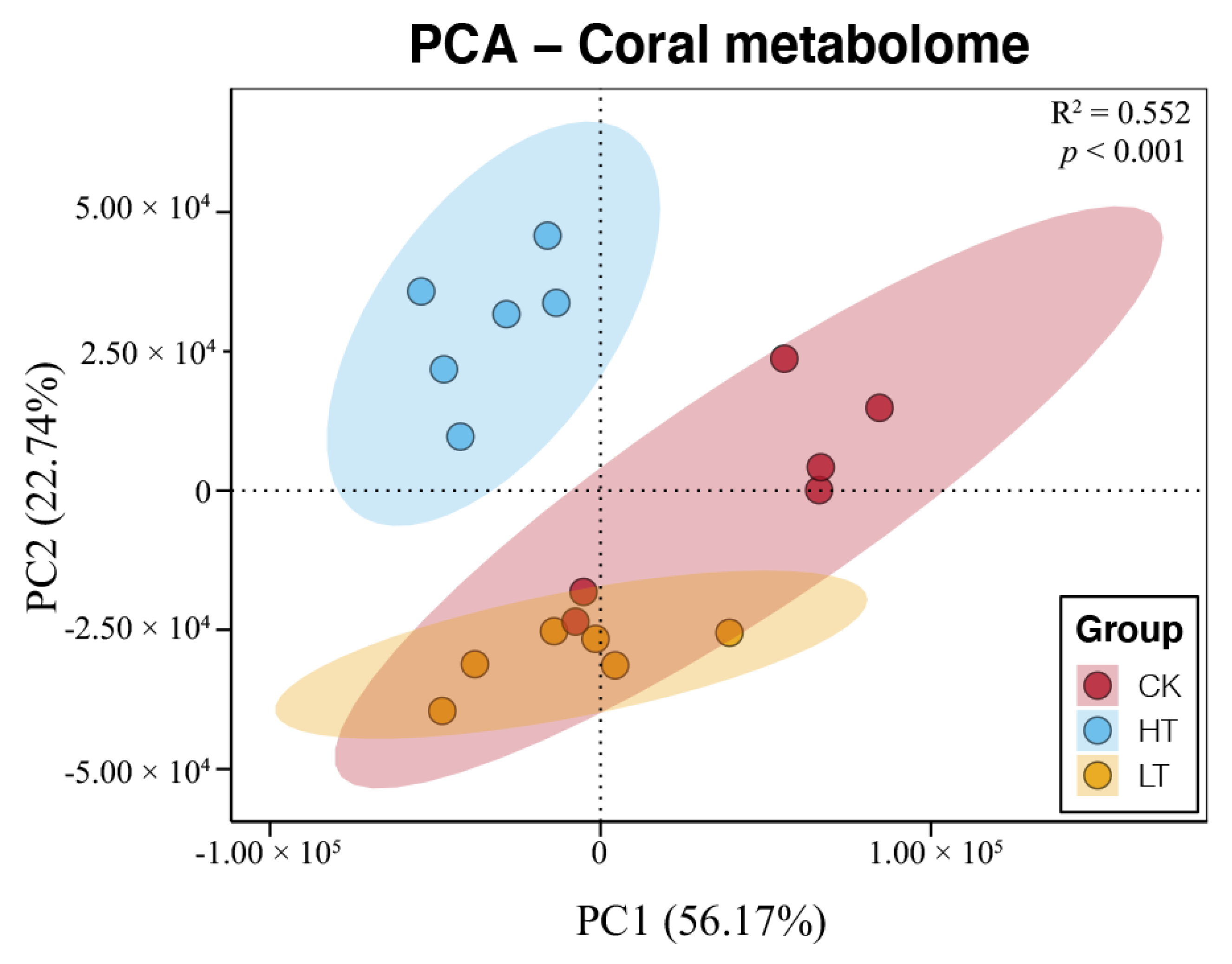
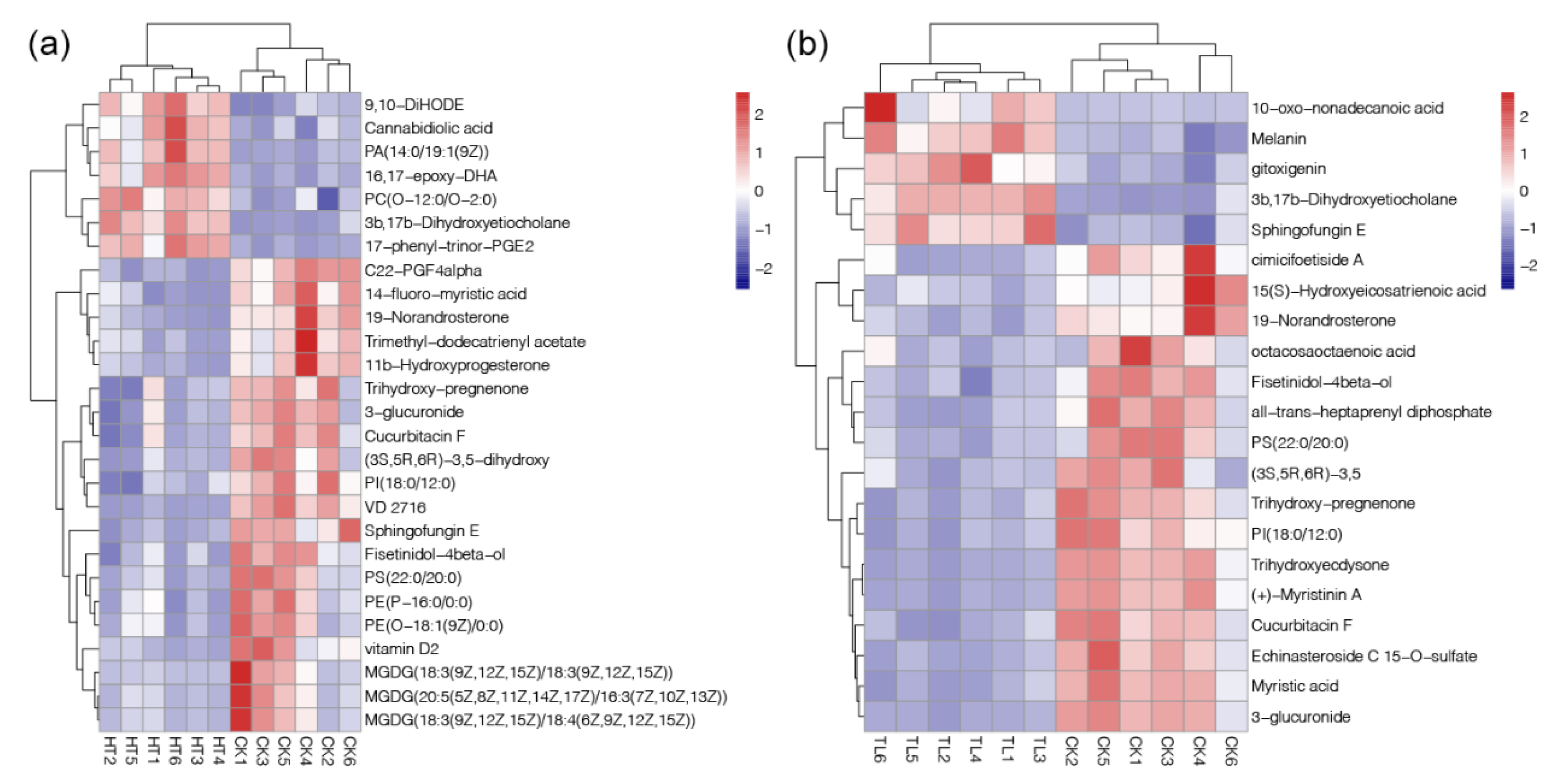
2.4. Responses of Metabolome of Corals under Different Temperature Stresses
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Specimens
4.2. Stimulation Experiments of Temperature Stresses
4.3. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
4.4. Data Processing of Microbial Communities
4.5. Metabolites Extraction and UPLC-MS Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
References
- Hughes, T.P.; Baird, A.H.; Bellwood, D.R.; Card, M.; Connolly, S.R.; Folke, C. Climate change, human impacts, and the resilience of coral reefs. Science 2003, 301, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Mumby, P.J.; Hooten, A.J.; Steneck, R.S.; Greenfield, P.; Gomez, E.; Harvell, C.D.; Sale, P.F.; Edwards, A.J.; Caldeira, K.; et al. Coral reefs under rapid climate change and ocean acidification. Science 2007, 318, 1737–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayfield, A.B.; Chen, M.N.; Meng, P.J.; Lin, H.J.; Chen, C.S.; Liu, P.J. The physiological response of the reef coral Pocillopora damicornis to elevated temperature: Results from coral reef mesocosm experiments in southern Taiwan. Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 86, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahr, K.D.; Rodgers, K.S.; Jokiel, P.L. Ocean warming drives decline in coral metabolism while acidification highlights species-specific responses. Mar. Biol. Res. 2018, 14, 924–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrou, K.; Nunn, B.L.; Padula, M.P.; Miller, D.J.; Nielsen, D.A. Broad scale proteomic analysis of heat-destabilised symbiosis in the hard coral Acropora millepora. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, T.; Cho, W.; Yum, S.; Woo, S. Holobiont transcriptome of colonial scleractinian coral Alveopora japonica. Mar. Genomics 2019, 43, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.P.; Kerry, J.T.; Baird, A.H.; Connolly, S.R.; Dietzel, A.; Eakin, C.M.; Heron, S.F.; Hoey, A.S.; Hoogenboom, M.O.; Liu, G.; et al. Global warming transforms coral reef assemblages. Nature 2018, 556, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matz, M.V.; Treml, E.A.; Aglyamova, G.V.; Bay, L.K. Potential and limits for rapid genetic adaptation to warming in a Great Barrier Reef coral. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.L.; Raina, J.B.; Kahlke, T.; Seymour, J.R.; van Oppen, M.J.; Suggett, D.J. Symbiodiniaceae-bacteria interactions: Rethinking metabolite exchange in reef-building corals as multi-partner metabolic networks. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 1675–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yu, K.; Liao, Z.; Chen, B.; Deng, C.; Yu, J.; Yao, Q.; Qin, Z.; Liang, J. Seasonal fluctuations in symbiotic bacteria and their role in environmental adaptation of the scleractinian coral Acropora pruinosa in high-latitude coral reef area of the South China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujise, L.; Yamashita, H.; Suzuki, G.; Sasaki, K.; Liao, L.M.; Koike, K. Moderate thermal stress causes active and immediate expulsion of photosynthetically damaged zooxanthellae (Symbiodinium) from corals. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garren, M.; Azam, F. Corals shed bacteria as a potential mechanism of resilience to organic matter enrichment. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jousset, A.; Bienhold, C.; Chatzinotas, A.; Gallien, L.; Gobet, A.; Kurm, V.; Küsel, K.; Rillig, M.C.; Rivett, D.W.; Salles, J.F.; et al. Where less may be more: How the rare biosphere pulls ecosystems strings. ISME J. 2017, 11, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Yu, K.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Huang, W.; Qin, Z.; Pan, Z.; Yao, Q.; Wang, W.; Wu, Z. Distinct bacterial communities associated with massive and branching scleractinian corals and potential linkages to coral susceptibility to thermal or cold stress. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicks, L.C.; Sampayo, E.M.; Gardner, J.P.; Davy, S.K. Local endemicity and high diversity characterise high-latitude coral-Symbiodinium partnerships. Coral Reefs 2010, 29, 989–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, L.A.; Voolstra, C.R.; Quigley, K.M.; Bourne, D.G.; Bay, L.K. Nutrient availability and metabolism affect the stability of coral–Symbiodiniaceae symbioses. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Yu, K.; Liang, J.; Huang, W.; Wang, G.; Su, H.; Qin, Z.; Huang, X.; Pan, Z.; Luo, W.; et al. Latitudinal variation in the molecular diversity and community composition of Symbiodiniaceae in coral from the South China Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yu, K.; Liao, Z.; Liang, J.; Deng, C.; Huang, W.; Huang, Y. Potential molecular traits underlying environmental tolerance of Pavona decussata and Acropora pruinosa in Weizhou Island, northern South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 156, 111199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roach, T.N.F.; Dilworth, J.; Martin, C.H.; Jones, A.D.; Quinn, R.A.; Drury, C. Metabolomic signatures of coral bleaching history. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, A.P.; Araújo, S.D.J.; Reis, A.M.M.; Moura, R.L.; Francini-Filho, R.B.; Pappas, G.J.; Rodrigues, T.B.; Thompson, F.L.; Krüger, R.H. Bacterial community associated with healthy and diseased reef coral Mussismilia hispida from Eastern Brazil. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 59, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Cai, L.; Zhou, G.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, W.; Tian, R.; Huang, H.; Qian, P.-Y. Temperature shapes coral-algal symbiosis in the South China Sea. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, M.; Seneca, F.O.; Yum, L.K.; Palumbi, S.R.; Voolstra, C.R. Bacterial community dynamics are linked to patterns of coral heat tolerance. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, E.; Koren, O.; Reshef, L.; Efrony, R.; Zilber-Rosenberg, I. The role of microorganisms in coral health, disease and evolution. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, D.G.; Iida, Y.; Uthicke, S.; Smithkeune, C. Changes in coral-associated microbial communities during a bleaching event. ISME J. 2008, 2, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.Q.; Jin, X.J.; Ren, L.J.; Tan, Y.H.; Xia, X.M. Unraveling heterogeneity of coral microbiome assemblages in tropical and subtropical corals in the South China Sea. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulet, T.L. Most corals may not change their symbionts. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 321, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, C.; Daniels, C.; Bayer, T.; Banguerahinestroza, E.; Barbrook, A.C.; Howe, C.J.; Voolstra, C.R. Assessing Symbiodinium diversity in scleractinian corals via next-generation sequencing-based genotyping of the ITS2 rDNA region. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 4418–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, J.D.; Takishita, K.; Ono, S.; Maruyama, T.; Tsukahara, J. Latitudinal and intracolony ITS-rDNA sequence variation in the symbiotic dinoflagellate genus Symbiodinium (Dinophyceae) in Zoanthus sansibaricus (Anthozoa: Hexacorallia). Phycol. Res. 2006, 54, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmas, S.D.; Denis, V.; Ribas-Deulofeu, L.; Loubeyres, M.; Woo, S.; Hwang, S.J.; Song, J.I.; Chen, C.A. Symbiodinium spp. associated with high-latitude scleractinian corals from Jeju Island. South Korea. Coral Reefs 2015, 34, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.J.; Yu, L.; Heidelberg, J.F.; Kirchman, D.L. Activity of abundant and rare bacteria in a coastal ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 12776–12781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, D.W.; Hernandez-Pech, X.; Iglesias-Prieto, R.; Fitt, W.K.; Schmidt, G.W. Community dynamics and physiology of Symbiodinium spp. before, during, and after a coral bleaching event. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014, 59, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, S.; Rekha, P.D.; Arun, A.B. Zeaxanthin biosynthesis by members of the genus Muricauda. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2014, 63, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajilata, M.G.; Singhal, R.S.; Kamat, M.Y. The carotenoid pigment zeaxanthin—A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2008, 7, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A. The algicidal activity of marine Loktanella sp. Gb03 on the toxic dinoflagellate Coolia Malayensis. Am.-Eurasian J. Sustain. Agric. 2016, 10, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Grotkjær, T.; Bentzon-Tilia, M.; D’Alvise, P.; Dourala, N.; Nielsen, K.F.; Gram, L. Isolation of TDA-producing Phaeobacter strains from sea bass larval rearing units and their probiotic effect against pathogenic Vibrio spp. in Artemia cultures. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 39, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hillyer, K.E. Thermal Stress and Bleaching in the Cnidarian-Dinoflagellate Symbiosis: The Application of Metabolomics. Ph.D. Thesis, Victoria University of Wellington, Wellington, New Zealand, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sogin, E.M.; Putnam, H.M.; Nelson, C.E.; Anderson, P.; Gates, R.D. Correspondence of coral holobiont metabolome with symbiotic bacteria, archaea and Symbiodinium communities. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2017, 9, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, W.; Li, M.; Wan, S.; Sui, N. Antioxidants and unsaturated fatty acids are involved in salt tolerance in peanut. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2017, 39, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plötz, T.; von Hanstein, A.S.; Krümmel, B.; Laporte, A.; Mehmeti, I.; Lenzen, S. Structure-toxicity relationships of saturated and unsaturated free fatty acids for elucidating the lipotoxic effects in human EndoC-βH1 beta-cells. BBA-Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 165525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieog, J.C.; van Oppen, M.J.H.; Cantin, N.E.; Stam, W.T.; Olsen, J.L. Real-time PCR reveals a high incidence of Symbiodinium clade D at low levels in four scleractinian corals across the Great Barrier Reef: Implications for symbiont shuffling. Coral Reefs 2017, 26, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amend, A.S.; Martiny, A.C.; Allison, S.D.; Berlemont, R.; Goulden, M.L.; Lu, Y.; Treseder, K.; Weihe, C.; Martiny, J.B. Microbial response to simulated global change is phylogenetically conserved and linked with functional potential. ISME J. 2016, 10, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Tan, G.; Wang, H.; Gai, X. Effect of biochar additions to soil on nitrogen leaching, microbial biomass and bacterial community structure. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2016, 74, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, P.; Parfrey, L.W.; Yarza, P.; Gerken, J.; Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Ludwig, W.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA and “All-species Living Tree Project (LTOP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D643–D648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Tzur, D.; Knox, C.; Eisner, R.; Guo, A.C.; Young, N.; Cheng, D.; Jewell, K.; Arndt, D.; Sawhney, S.; et al. HMDB: The human metabolome database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D521–D526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Chong, J.; Li, S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalystR 3.0: Toward an optimized workflow for global metabolomics. Metabolites 2020, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Comparisons | Up-Regulated | Down-Regulated |
|---|---|---|
| HT-vs-CK | 7 | 20 |
| LT-vs-CK | 6 | 15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, J.; Luo, W.; Yu, K.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; Deng, C.; Ge, R.; Su, H.; Huang, W.; Wang, G. Multi-Omics Revealing the Response Patterns of Symbiotic Microorganisms and Host Metabolism in Scleractinian Coral Pavona minuta to Temperature Stresses. Metabolites 2022, 12, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12010018
Liang J, Luo W, Yu K, Xu Y, Chen J, Deng C, Ge R, Su H, Huang W, Wang G. Multi-Omics Revealing the Response Patterns of Symbiotic Microorganisms and Host Metabolism in Scleractinian Coral Pavona minuta to Temperature Stresses. Metabolites. 2022; 12(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Jiayuan, Wenwen Luo, Kefu Yu, Yongqian Xu, Jinni Chen, Chuanqi Deng, Ruiqi Ge, Hongfei Su, Wen Huang, and Guanghua Wang. 2022. "Multi-Omics Revealing the Response Patterns of Symbiotic Microorganisms and Host Metabolism in Scleractinian Coral Pavona minuta to Temperature Stresses" Metabolites 12, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12010018
APA StyleLiang, J., Luo, W., Yu, K., Xu, Y., Chen, J., Deng, C., Ge, R., Su, H., Huang, W., & Wang, G. (2022). Multi-Omics Revealing the Response Patterns of Symbiotic Microorganisms and Host Metabolism in Scleractinian Coral Pavona minuta to Temperature Stresses. Metabolites, 12(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12010018







