A New Pipeline for the Normalization and Pooling of Metabolomics Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Description of the Study Population
2.2. Data Cleaning and Imputation
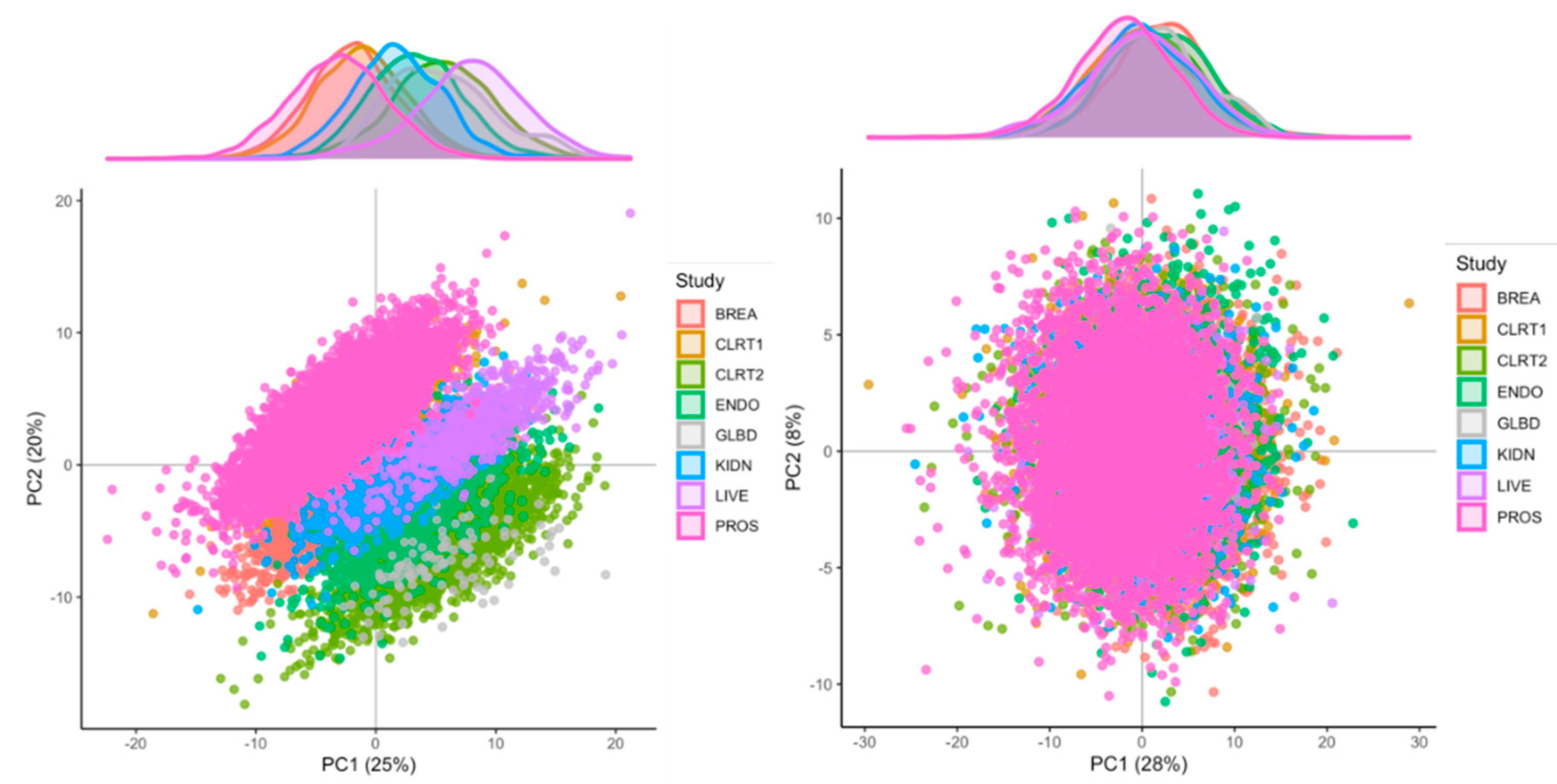
2.3. Identification of Major Sources of Variations
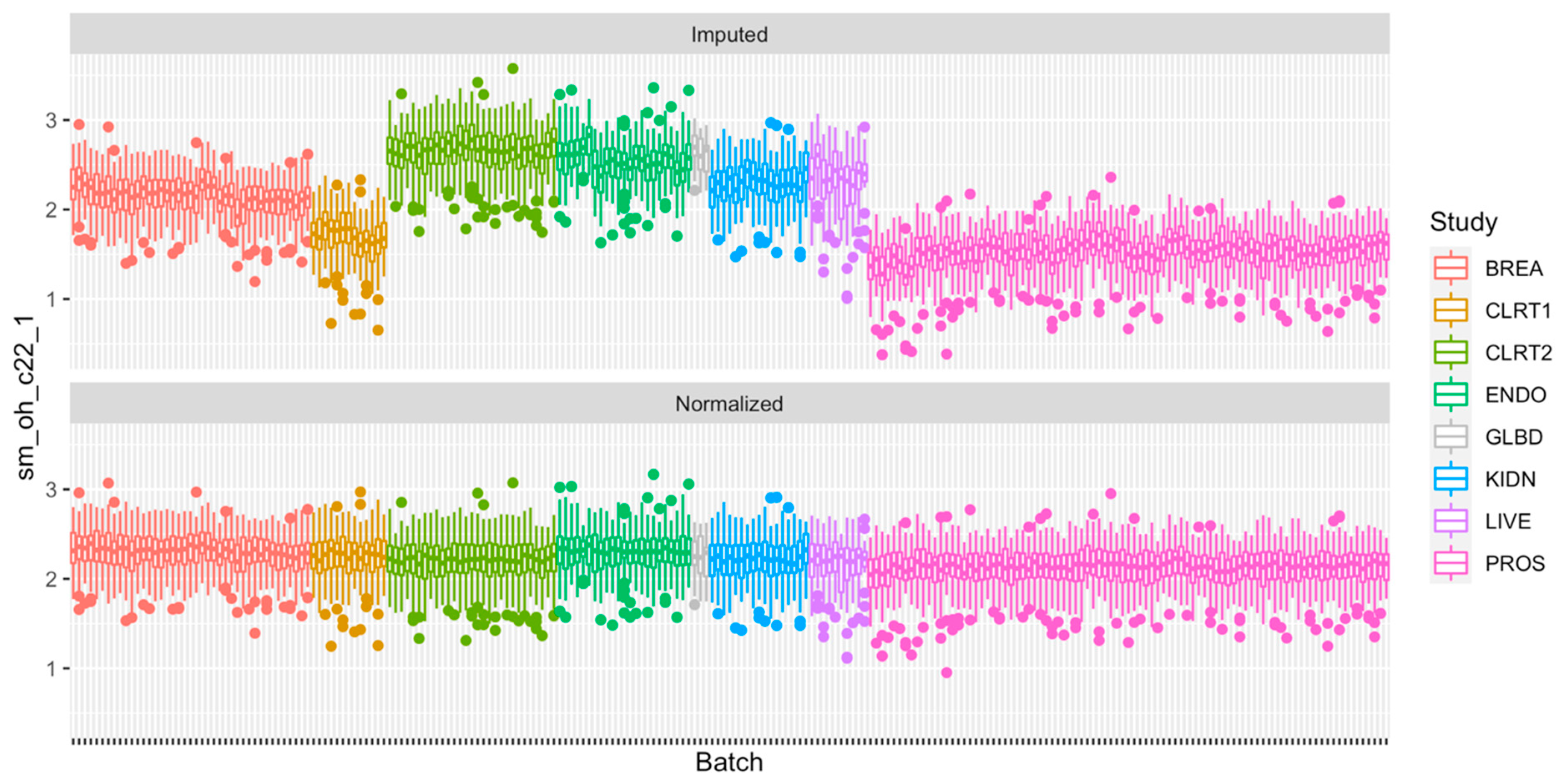
2.4. Normalization of the Measurements
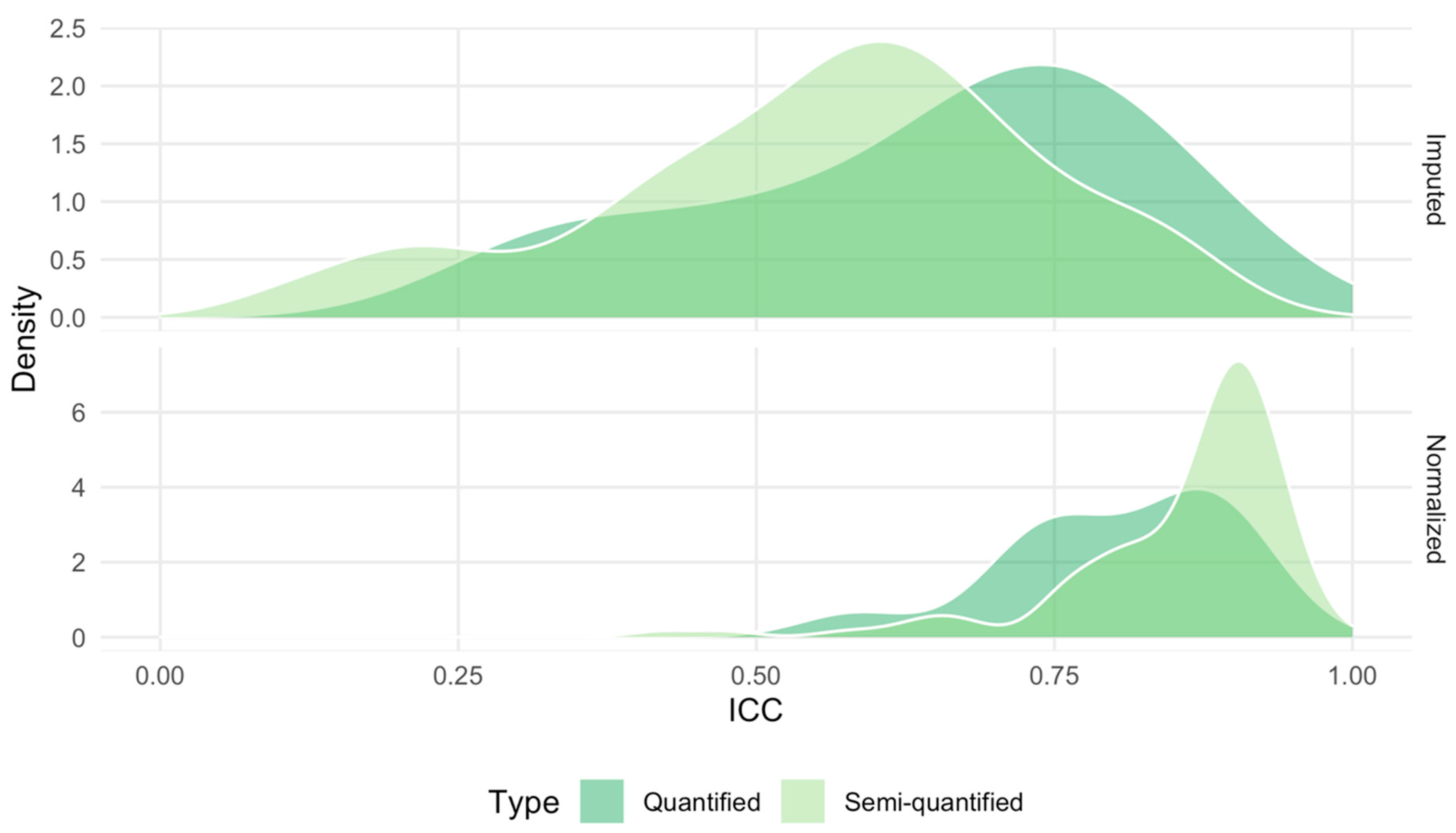
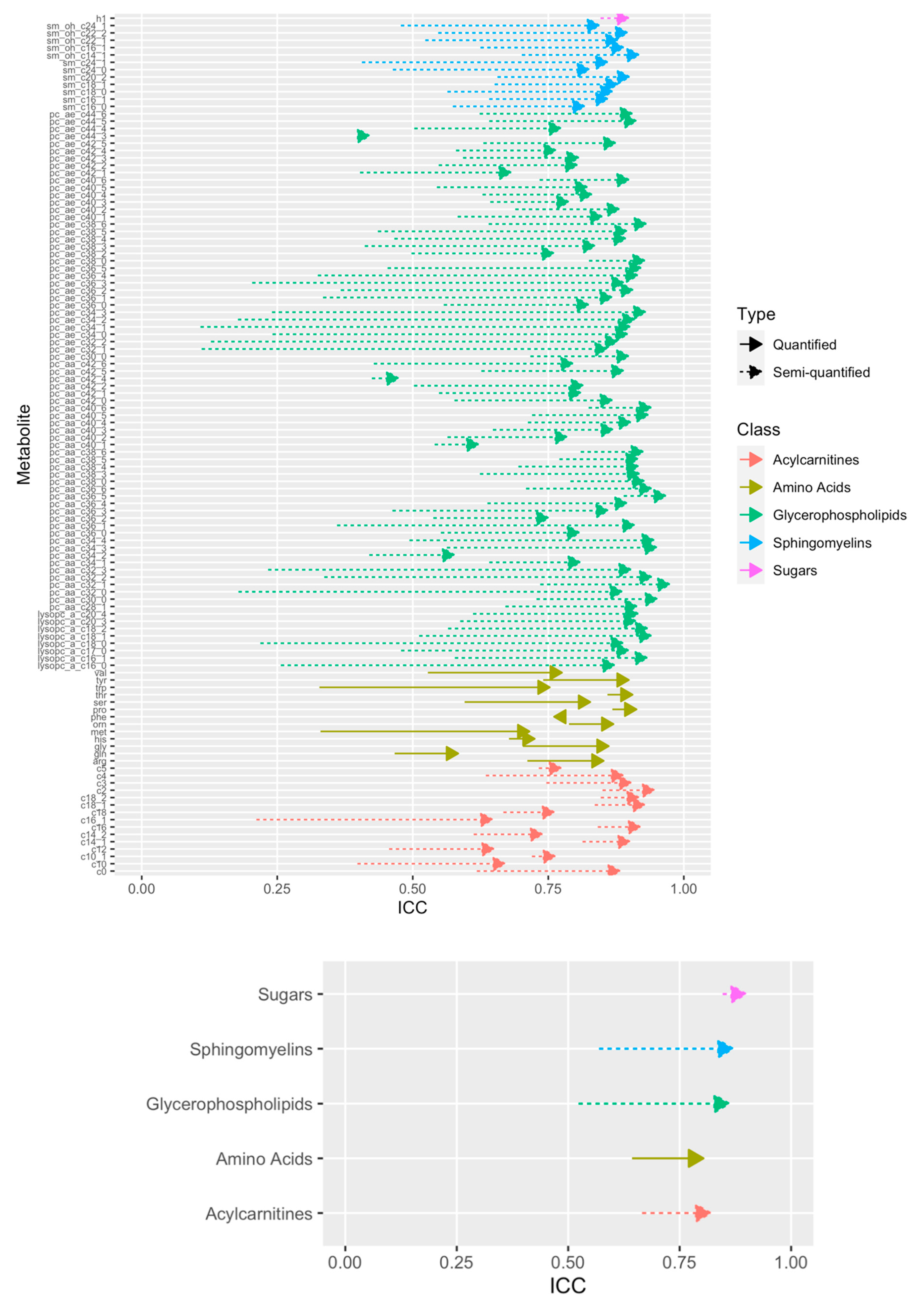
2.5. Technical Reproducibility of Measurements before and after Normalization
2.6. Impact of Normalization When Relating a Given Phenotype to the Metabolites
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. The EPIC Study
4.2. The Pipeline to Normalize Data
4.2.1. Step 1: Data Cleaning
4.2.2. Step 2: Data Imputation
4.2.3. Step 3: Data Normalization, Part 1: Identification of Sources of Variation
4.2.4. Step 4: Data Normalization, Part 2: Correction for the Unwanted Sources of Variation
4.3. Computation of the Intraclass Correlation Coefficient Using Duplicated Samples
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
References
- Beger, R.D. A Review of Applications of Metabolomics in Cancer. Metabolites 2013, 3, 552–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pirhaji, L.; Milani, P.; Leidl, M.; Curran, T.; Avila, J.; Clish, C.B.; White, F.; Saghatelian, M.L.A.; Fraenkel, E. Revealing disease-associated pathways by network integration of untargeted metabolomics. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scalbert, A.; Huybrechts, I.; Gunter, M.J. The Food Exposome. In Unraveling the Exposome; Dagnino, S., Macherone, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 217–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebani, A.; Bekri, S. Paving the Way to Precision Nutrition through Metabolomics. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, L.; Brunius, C.; Johansson, I.; Bergdahl, I.; Rolandsson, O.; Van Guelpen, B.; Winkvist, A.; Hanhineva, K.; Landberg, R. Plasma metabolite biomarkers of boiled and filtered coffee intake and their association with type 2 diabetes risk. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 287, 405–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; Chung, W.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Toledo, E.; Corella, D.; Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Tobias, D.K.; Tabung, F.K.; Hu, J.; et al. The Mediterranean diet, plasma metabolome, and cardiovascular disease risk. Eur. Hear. J. 2020, 41, 2645–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, N.; Thomas, D.C.; Leitzmann, M.; Stepien, M.; Chajès, V.; Philip, T.; Vineis, P.; Bamia, C.; Boutron-Ruault, M.-C.; Sandanger, T.M.; et al. Are Metabolic Signatures Mediating the Relationship between Lifestyle Factors and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk? Results from a Nested Case–Control Study in EPIC. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2018, 27, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- His, M.; Viallon, V.; Dossus, L.; Gicquiau, A.; Achaintre, D.; Scalbert, A.; Ferrari, P.; Romieu, I.; Onland-Moret, N.C.; Weiderpass, E.; et al. Prospective analysis of circulating metabolites and breast cancer in EPIC. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.A.; Fensom, G.K.; Rinaldi, S.; Scalbert, A.; Appleby, P.N.; Achaintre, D.; Gicquiau, A.; Gunter, M.J.; Ferrari, P.; Kaaks, R.; et al. Patterns in metabolite profile are associated with risk of more aggressive prostate cancer: A prospective study of 3057 matched case–control sets from EPIC. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 146, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kliemann, N.; Viallon, V.; Murphy, N.; Beeken, R.J.; Rothwell, J.A.; Rinaldi, S.; Assi, N.; van Roekel, E.H.; Schmidt, J.A.; Borch, K.B.; et al. Metabolic signatures of greater body size and their associations with risk of colorectal and endometrial cancers in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmands, W.M.B.; Barupal, D.K.; Scalbert, A. MetMSLine: An automated and fully integrated pipeline for rapid processing of high-resolution LC-MS metabolomic datasets. Bioinformatics 2014, 31, 788–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stanstrup, J.; Broeckling, C.D.; Helmus, R.; Hoffmann, N.; Mathé, E.; Naake, T.; Nicolotti, L.; Peters, K.; Rainer, J.; Salek, R.M.; et al. The metaRbolomics Toolbox in Bioconductor and beyond. Metabolites 2019, 9, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fages, A.; Ferrari, P.; Monni, S.; Dossus, L.; Floegel, A.; Mode, N.; Johansson, M.; Travis, R.C.; Bamia, C.; Sánchez-Pérez, M.-J.; et al. Investigating sources of variability in metabolomic data in the EPIC study: The Principal Component Partial R-square (PC-PR2) method. Metabolomics 2014, 10, 1074–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauhiainen, A.; Madhu, B.; Narita, M.; Narita, M.; Griffiths, J.; Tavaré, S. Normalization of metabolomics data with applications to correlation maps. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2155–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Do, K.T.; Wahl, S.; Raffler, J.; Molnos, S.; Laimighofer, M.; Adamski, J.; Suhre, K.; Strauch, K.; Peters, A.; Gieger, C.; et al. Characterization of missing values in untargeted MS-based metabolomics data and evaluation of missing data handling strategies. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schiffman, C.; Petrick, L.; Perttula, K.; Yano, Y.; Carlsson, H.; Whitehead, T.; Metayer, C.; Hayes, J.; Rappaport, S.; Dudoit, S. Filtering procedures for untargeted LC-MS metabolomics data. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siskos, A.P.; Jain, P.; Römisch-Margl, W.; Bennett, M.; Achaintre, D.; Asad, Y.; Marney, L.; Richardson, L.; Koulman, A.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Interlaboratory Reproducibility of a Targeted Metabolomics Platform for Analysis of Human Serum and Plasma. Anal. Chem. 2016, 89, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan, A.; Song, Y.; Gail, M.H.; Betensky, R.; Rosner, B.; Ziegler, R.G.; Smith-Warner, S.A.; Wang, M. Design and analysis considerations for combining data from multiple biomarker studies. Stat. Med. 2018, 38, 1303–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.; Li, C.; Rabinovic, A. Adjusting batch effects in microarray expression data using empirical Bayes methods. Biostatistics 2006, 8, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leek, J.T.; Johnson, W.; Parker, H.S.; Jaffe, A.; Storey, J. The sva package for removing batch effects and other unwanted variation in high-throughput experiments. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 882–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alter, O.; Brown, P.O.; Botstein, D. Singular value decomposition for genome-wide expression data processing and modeling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10101–10106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leek, J.; Storey, J.D. Capturing Heterogeneity in Gene Expression Studies by Surrogate Variable Analysis. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3, 1724–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riboli, E.; Hunt, K.J.; Slimani, N.; Ferraria, P.; Norata, T.; Fahey, M.; Charrondierea, U.R.; Hemona, B.; Casagrandea, C.; Vignata, J.; et al. European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC): Study populations and data collection. Public Health Nutr. 2002, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossus, L.; Kouloura, E.; Biessy, C.; Viallon, V.; Siskos, A.P.; Dimou, N.; Rinaldi, S.; Merritt, M.A.; Allen, N.; Fortner, R.; et al. Prospective analysis of circulating metabolites and endometrial cancer risk. Gynecol. Oncol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepien, M.; Duarte-Salles, T.; Fedirko, V.; Floegel, A.; Barupal, D.; Rinaldi, S.; Achaintre, D.; Assi, N.; Tjonneland, A.; Overvad, K.; et al. Alteration of amino acid and biogenic amine metabolism in hepatobiliary cancers: Findings from a prospective cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 138, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guida, F.; Severi, G.; Giles, G.; Johansson, M. Metabolomics and risk of kidney cancer. Rev. D’épidémiologie St. Publique 2018, 66, S291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.A.; Fensom, G.K.; Rinaldi, S.; Scalbert, A.; Appleby, P.N.; Achaintre, D.; Gicquiau, A.; Gunter, M.J.; Ferrari, P.; Kaaks, R.; et al. Pre-diagnostic metabolite concentrations and prostate cancer risk in 1077 cases and 1077 matched controls in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindström, M.; Tohmola, N.; Renkonen, R.; Hämäläinen, E.; Schalin-Jäntti, C.; Itkonen, O. Comparison of serum serotonin and serum 5-HIAA LC-MS/MS assays in the diagnosis of serotonin producing neuroendocrine neoplasms: A pilot study. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 482, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrari, P.; Al-Delaimy, W.K.; Slimani, N.; Boshuizen, H.C.; Roddam, A.; Orfanos, P.; Skeie, G.; Rodríguez-Barranco, M.; Thiebaut, A.; Johansson, G.; et al. An Approach to Estimate Between- and Within-Group Correlation Coefficients in Multicenter Studies: Plasma Carotenoids as Biomarkers of Intake of Fruits and Vegetables. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 162, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troyanskaya, O.G.; Cantor, M.; Sherlock, G.; Brown, P.O.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Botstein, D.; Altman, R.B. Missing value estimation methods for DNA microarrays. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habra, H.; Kachman, M.; Bullock, K.; Clish, C.; Evans, C.R.; Karnovsky, A. metabCombiner: Paired Untargeted LC-HRMS Metabolomics Feature Matching and Concatenation of Disparately Acquired Data Sets. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 5028–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Zanetti, K.A.; Temprosa, M.; Albanes, D.; Appel, N.; Barrera, C.B.; Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Boerwinkle, E.; Casas, J.P.; Clish, C.; et al. The Consortium of Metabolomics Studies (COMETS): Metabolomics in 47 Prospective Cohort Studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 188, 991–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Acronym | Number of Samples | Matrix | Laboratory | MS Instrument | LC Instrument | Kit Used |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BREA | 3172 | Citrate plasma 1 | IARC | SCIEX QTRAP 5500 | Agilent 1290 | p180 |
| CLRT1 | 946 | Citrate plasma | IARC | SCIEX Triple Quad 4500 | Agilent 1290 | p180 |
| CLRT2 | 2295 | Serum | HZM 3 | SCIEX API 4000 | Agilent 1200 | p150 |
| ENDO | 1706 | Citrate plasma | ICL 4 | SCIEX API 4000 | Agilent 1290 | p180 |
| GLBD | 112 | Serum 2 | HZM 3 | SCIEX API 4000 | Agilent 1200 | p180 |
| LIVE | 662 | Serum | IARC | SCIEX QTRAP 5500 | Agilent 1290 | p180 |
| KIDN | 1213 | Citrate plasma | IARC | SCIEX QTRAP 5500 | Agilent 1290 | p180 |
| PROS | 6020 | Citrate plasma | IARC | SCIEX Triple Quad 4500 | Agilent 1290 | p180 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Viallon, V.; His, M.; Rinaldi, S.; Breeur, M.; Gicquiau, A.; Hemon, B.; Overvad, K.; Tjønneland, A.; Rostgaard-Hansen, A.L.; Rothwell, J.A.; et al. A New Pipeline for the Normalization and Pooling of Metabolomics Data. Metabolites 2021, 11, 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11090631
Viallon V, His M, Rinaldi S, Breeur M, Gicquiau A, Hemon B, Overvad K, Tjønneland A, Rostgaard-Hansen AL, Rothwell JA, et al. A New Pipeline for the Normalization and Pooling of Metabolomics Data. Metabolites. 2021; 11(9):631. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11090631
Chicago/Turabian StyleViallon, Vivian, Mathilde His, Sabina Rinaldi, Marie Breeur, Audrey Gicquiau, Bertrand Hemon, Kim Overvad, Anne Tjønneland, Agnetha Linn Rostgaard-Hansen, Joseph A. Rothwell, and et al. 2021. "A New Pipeline for the Normalization and Pooling of Metabolomics Data" Metabolites 11, no. 9: 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11090631
APA StyleViallon, V., His, M., Rinaldi, S., Breeur, M., Gicquiau, A., Hemon, B., Overvad, K., Tjønneland, A., Rostgaard-Hansen, A. L., Rothwell, J. A., Lecuyer, L., Severi, G., Kaaks, R., Johnson, T., Schulze, M. B., Palli, D., Agnoli, C., Panico, S., Tumino, R., ... Ferrari, P. (2021). A New Pipeline for the Normalization and Pooling of Metabolomics Data. Metabolites, 11(9), 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11090631












