Disruption of GPR35 Signaling in Bone Marrow-Derived Cells Does Not Influence Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis in Hyperlipidemic Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
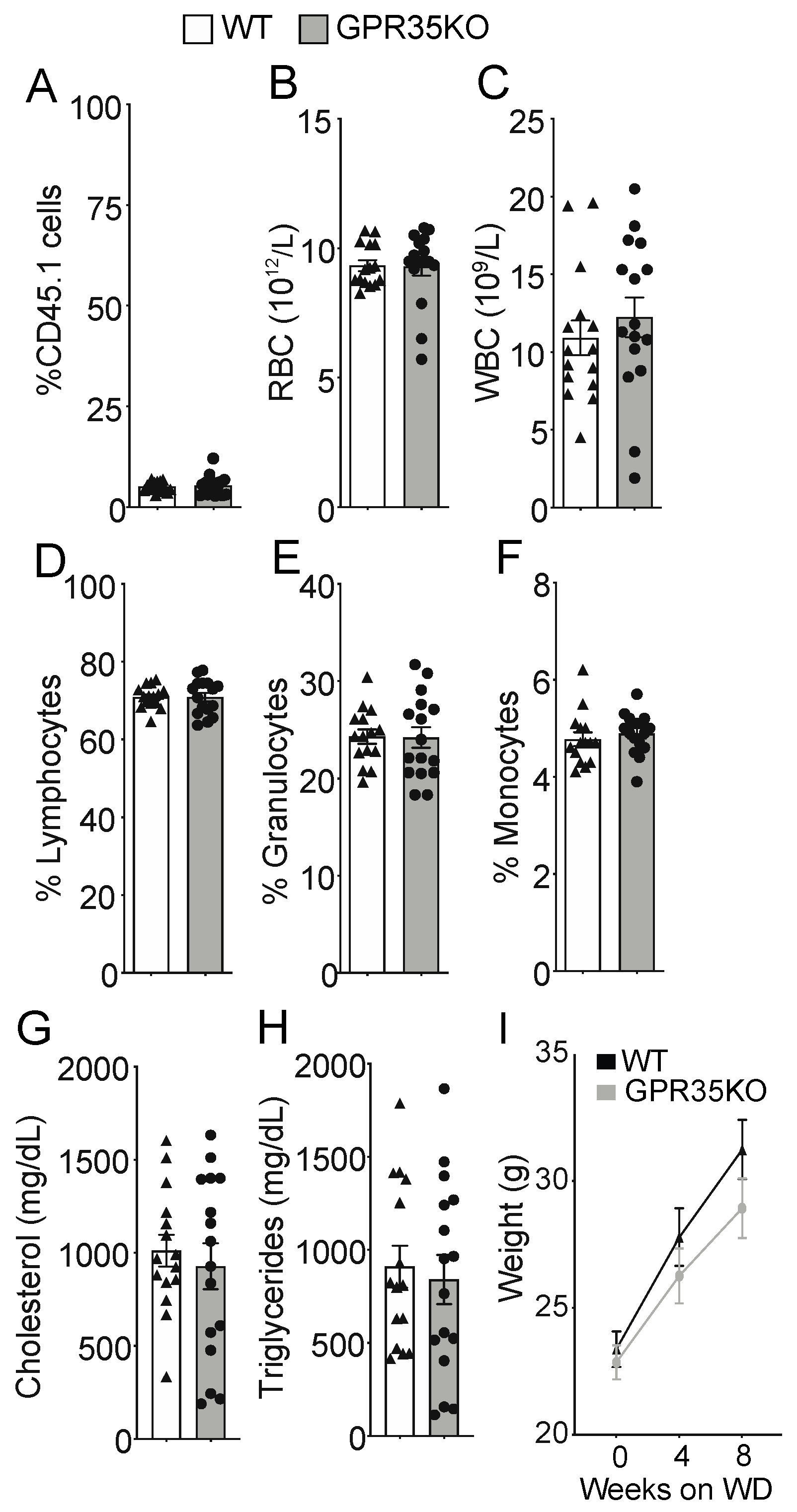
2.1. GPR35KO and WT Chimeric Mice Show No Differences in Blood Parameters
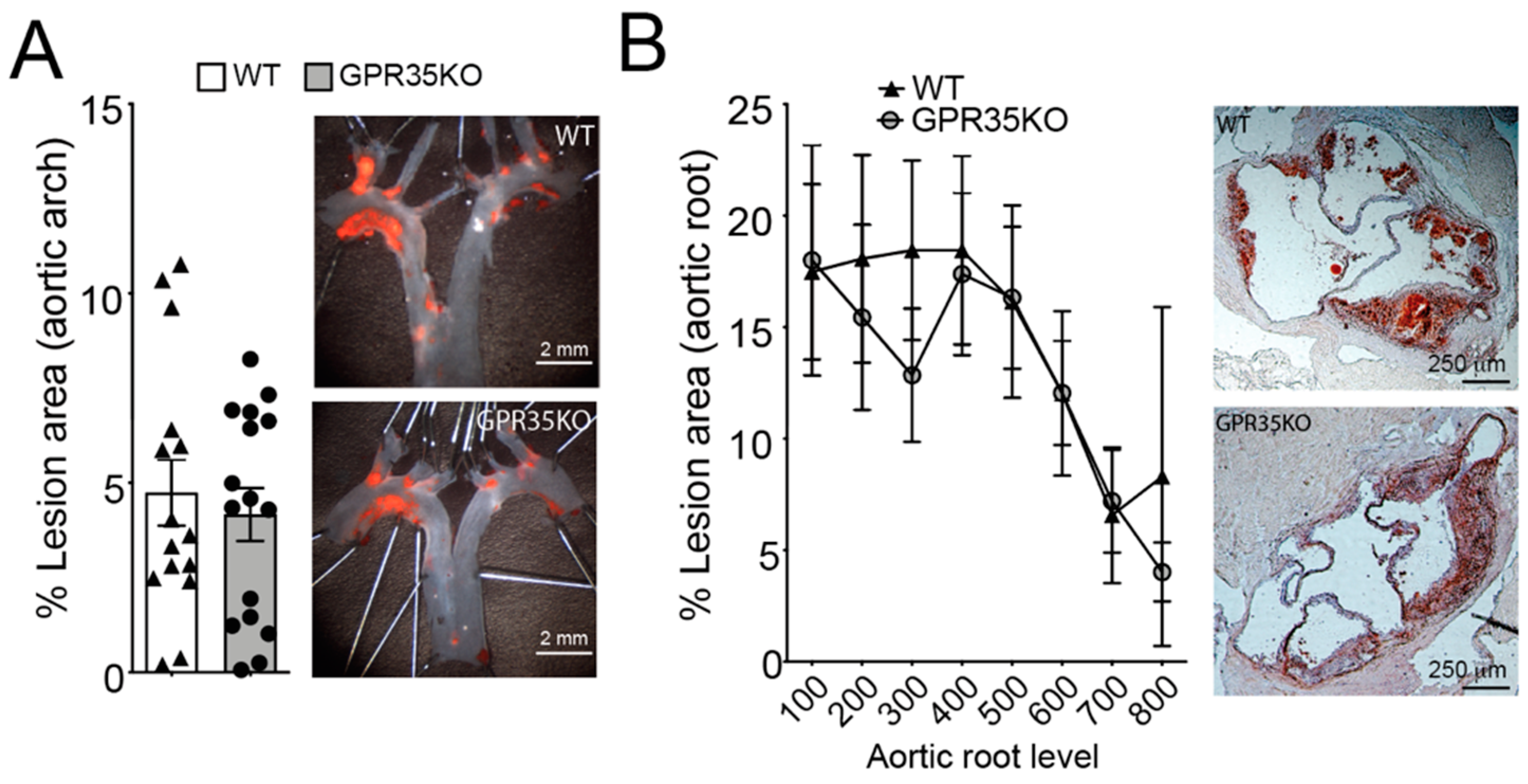
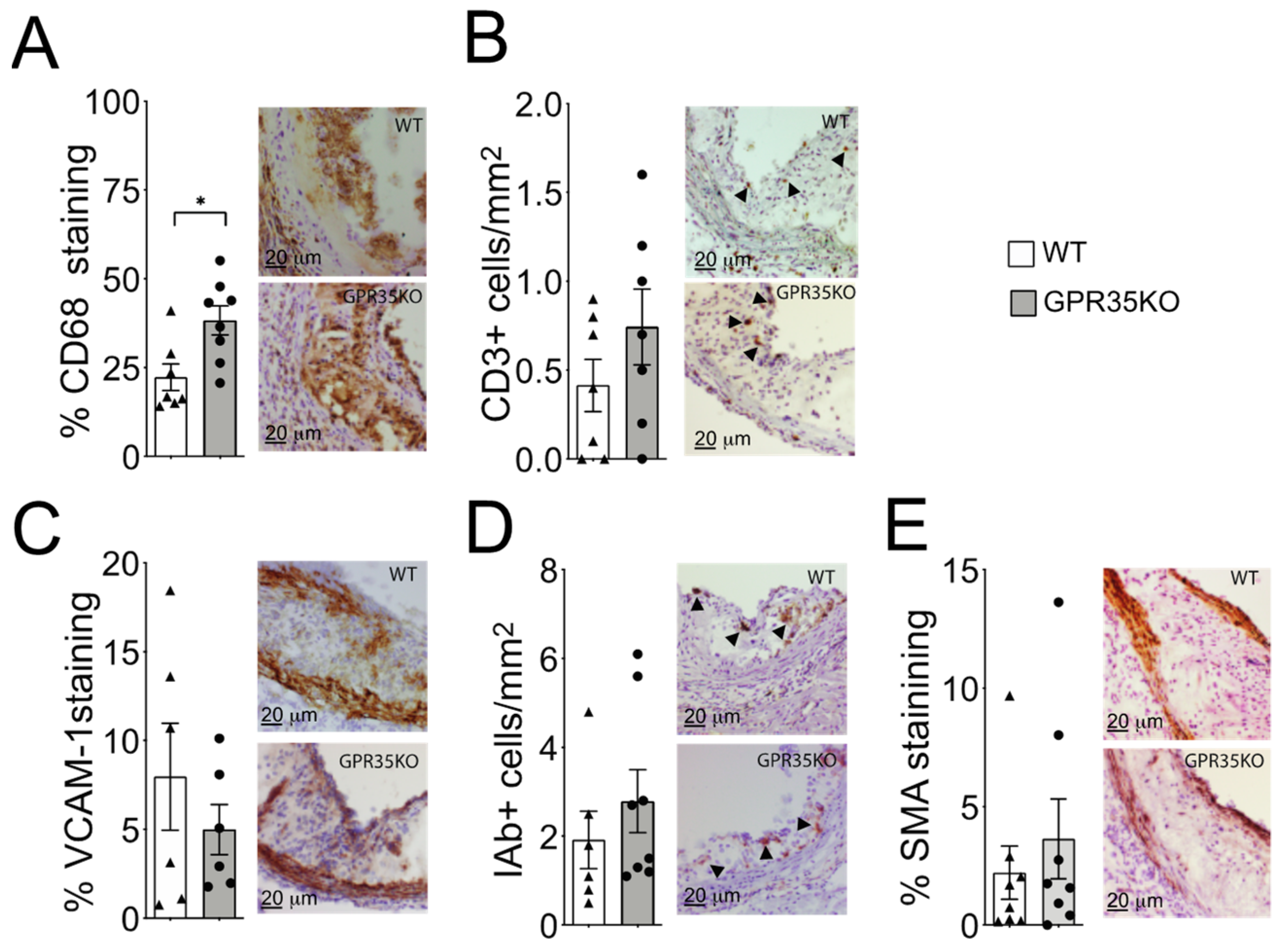
2.2. GPR35 Deficiency in Bone Marrow-Derived Cells Does Not Influence Atherosclerosis and Vascular Inflammation
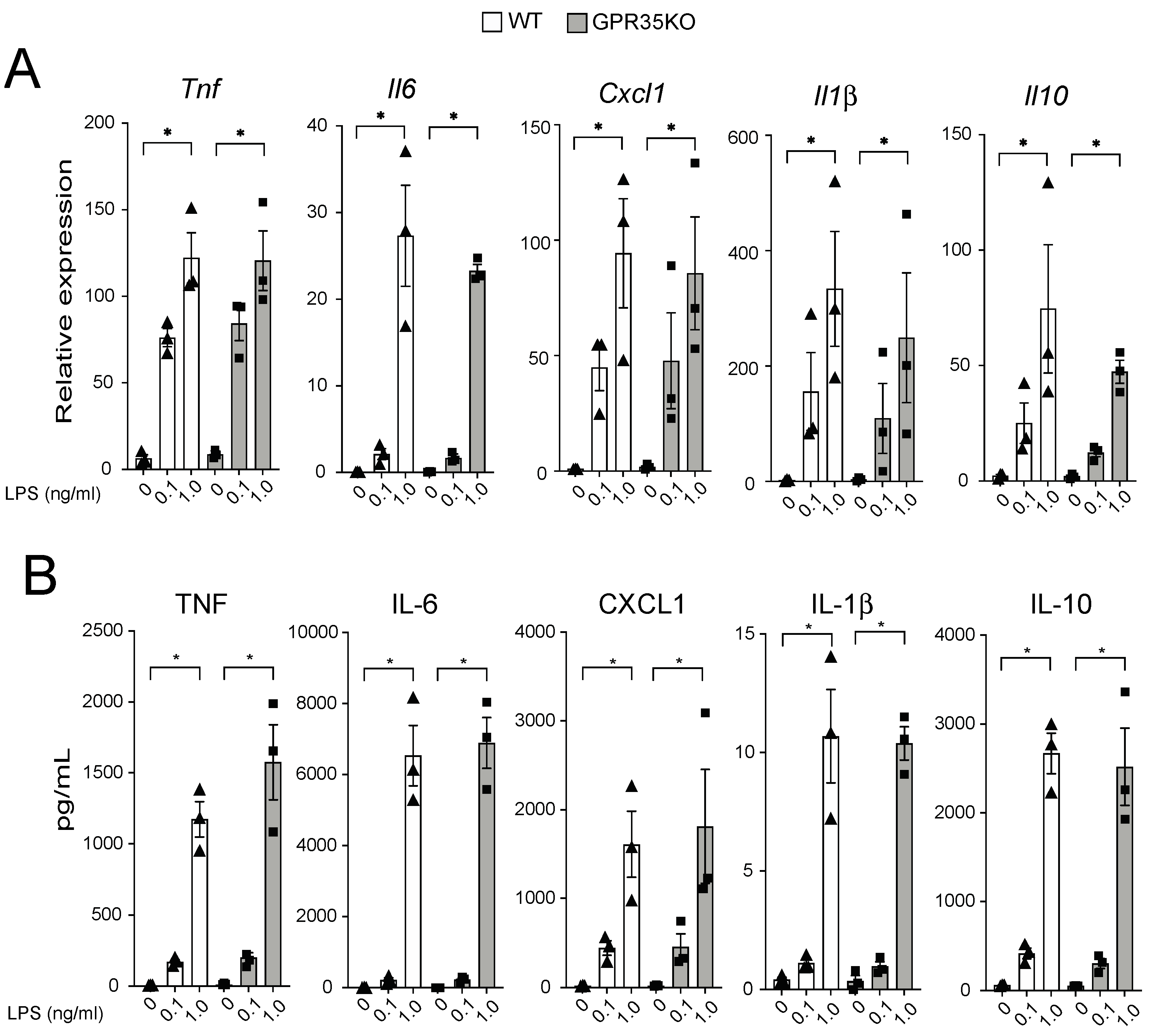
2.3. GPR35KO- and WT-Derived Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages (BMDM) Respond Similarly in a Dose Response Manner to LPS Stimulation
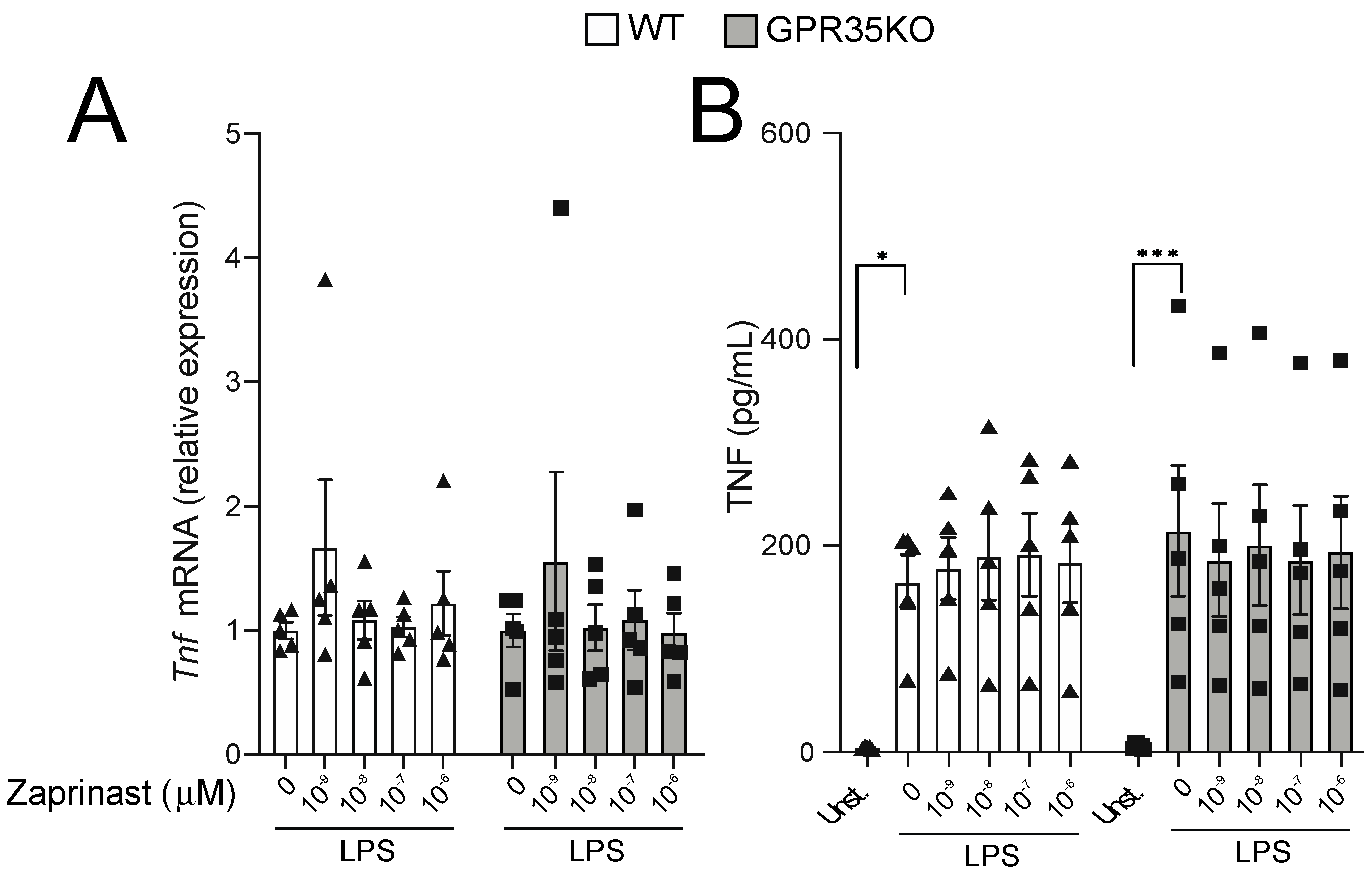
2.4. GPR35 Signaling Does Not Influence Macrophage Responses to LPS
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Bone Marrow Transplantation
4.2. Tissue Collection, Lesion Analysis, and Immunohistochemistry
4.3. Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophage (BMDM) Experiments
4.4. mRNA Isolation and Analysis
4.5. Cytokine Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mathers, C.D.; Boerma, T.; Ma Fat, D. Global and regional causes of death. Br. Med. Bull. 2009, 92, 7–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabas, I.; Williams, K.J.; Boren, J. Subendothelial lipoprotein retention as the initiating process in atherosclerosis: Update and therapeutic implications. Circulation 2007, 116, 1832–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketelhuth, D.F.J.; Lutgens, E.; Back, M.; Binder, C.J.; Van den Bossche, J.; Daniel, C.; Dumitriu, I.E.; Hoefer, I.; Libby, P.; O’Neill, L.; et al. Immunometabolism and atherosclerosis: Perspectives and clinical significance: A position paper from the Working Group on Atherosclerosis and Vascular Biology of the European Society of Cardiology. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 115, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husted, A.S.; Trauelsen, M.; Rudenko, O.; Hjorth, S.A.; Schwartz, T.W. GPCR-Mediated Signaling of Metabolites. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 777–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Simonavicius, N.; Wu, X.; Swaminath, G.; Reagan, J.; Tian, H.; Ling, L. Kynurenic acid as a ligand for orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR35. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 22021–22028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lattin, J.E.; Schroder, K.; Su, A.I.; Walker, J.R.; Zhang, J.; Wiltshire, T.; Saijo, K.; Glass, C.K.; Hume, D.A.; Kellie, S.; et al. Expression analysis of G Protein-Coupled Receptors in mouse macrophages. Immun. Res. 2008, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, J.Y.; Wu, X.; Summer, S.; Whoriskey, J.; Saris, C.; Reagan, J.D. G-protein-coupled receptor 35 is a target of the asthma drugs cromolyn disodium and nedocromil sodium. Pharmacology 2010, 86, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, B.; Donas, C.; Wuggenig, P.; Diaz, O.E.; Morales, R.A.; Melhem, H.; Swiss, I.B.D.C.I.; Hernandez, P.P.; Kaymak, T.; Das, S.; et al. Lysophosphatidic Acid-Mediated GPR35 Signaling in CX3CR1(+) Macrophages Regulates Intestinal Homeostasis. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 107979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, S.M.; Hou, Y.; Li, H.; O’Meara, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, J.M. Disruption of GPR35 Exacerbates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 2910–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, A.E.; Caltabiano, G.; Kent, T.C.; Jenkins, L.; McCallum, J.E.; Hudson, B.D.; Nicklin, S.A.; Fawcett, L.; Markwick, R.; Charlton, S.J.; et al. The antiallergic mast cell stabilizers lodoxamide and bufrolin as the first high and equipotent agonists of human and rat GPR35. Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 85, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agudelo, L.Z.; Ferreira, D.M.S.; Cervenka, I.; Bryzgalova, G.; Dadvar, S.; Jannig, P.R.; Pettersson-Klein, A.T.; Lakshmikanth, T.; Sustarsic, E.G.; Porsmyr-Palmertz, M.; et al. Kynurenic Acid and Gpr35 Regulate Adipose Tissue Energy Homeostasis and Inflammation. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 378–392.e375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Epelman, S.; Lavine, K.J.; Randolph, G.J. Origin and functions of tissue macrophages. Immunity 2014, 41, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feil, S.; Fehrenbacher, B.; Lukowski, R.; Essmann, F.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Schaller, M.; Feil, R. Transdifferentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells to macrophage-like cells during atherogenesis. Circ. Res. 2014, 115, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, A.E.; Lappin, J.E.; Taylor, D.L.; Nicklin, S.A.; Milligan, G. GPR35 as a Novel Therapeutic Target. Front. Endocrinol. 2011, 2, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.V.; Bielak, L.F.; Peyser, P.A.; Turner, S.T.; Sheedy, P.F., 2nd; Boerwinkle, E.; Kardia, S.L. Application of machine learning algorithms to predict coronary artery calcification with a sibship-based design. Genet. Epidemiol. 2008, 32, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Min, K.D.; Asakura, M.; Liao, Y.; Nakamaru, K.; Okazaki, H.; Takahashi, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Ito, S.; Takahashi, A.; Asanuma, H.; et al. Identification of genes related to heart failure using global gene expression profiling of human failing myocardium. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 393, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirthgen, E.; Hoeflich, A.; Rebl, A.; Gunther, J. Kynurenic Acid: The Janus-Faced Role of an Immunomodulatory Tryptophan Metabolite and Its Link to Pathological Conditions. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baumgartner, R.; Berg, M.; Matic, L.; Polyzos, K.P.; Forteza, M.J.; Hjorth, S.A.; Schwartz, T.W.; Paulsson-Berne, G.; Hansson, G.K.; Hedin, U.; et al. Evidence that a deviation in the kynurenine pathway aggravates atherosclerotic disease in humans. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 289, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingenberg, R.; Gerdes, N.; Badeau, R.M.; Gistera, A.; Strodthoff, D.; Ketelhuth, D.F.; Lundberg, A.M.; Rudling, M.; Nilsson, S.K.; Olivecrona, G.; et al. Depletion of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells promotes hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoletti, A.; Kaveri, S.; Caligiuri, G.; Bariety, J.; Hansson, G.K. Immunoglobulin treatment reduces atherosclerosis in apo E knockout mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Goncalves, R.; Mosser, D.M. The isolation and characterization of murine macrophages. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baumgartner, R.; Casagrande, F.B.; Mikkelsen, R.B.; Berg, M.; Polyzos, K.A.; Forteza, M.J.; Arora, A.; Schwartz, T.W.; Hjorth, S.A.; Ketelhuth, D.F.J. Disruption of GPR35 Signaling in Bone Marrow-Derived Cells Does Not Influence Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis in Hyperlipidemic Mice. Metabolites 2021, 11, 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11070411
Baumgartner R, Casagrande FB, Mikkelsen RB, Berg M, Polyzos KA, Forteza MJ, Arora A, Schwartz TW, Hjorth SA, Ketelhuth DFJ. Disruption of GPR35 Signaling in Bone Marrow-Derived Cells Does Not Influence Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis in Hyperlipidemic Mice. Metabolites. 2021; 11(7):411. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11070411
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaumgartner, Roland, Felipe B. Casagrande, Randi B. Mikkelsen, Martin Berg, Konstantinos A. Polyzos, Maria J. Forteza, Aastha Arora, Thue W. Schwartz, Siv A. Hjorth, and Daniel F. J. Ketelhuth. 2021. "Disruption of GPR35 Signaling in Bone Marrow-Derived Cells Does Not Influence Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis in Hyperlipidemic Mice" Metabolites 11, no. 7: 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11070411
APA StyleBaumgartner, R., Casagrande, F. B., Mikkelsen, R. B., Berg, M., Polyzos, K. A., Forteza, M. J., Arora, A., Schwartz, T. W., Hjorth, S. A., & Ketelhuth, D. F. J. (2021). Disruption of GPR35 Signaling in Bone Marrow-Derived Cells Does Not Influence Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis in Hyperlipidemic Mice. Metabolites, 11(7), 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11070411





