Serum Metabolites Responding in a Dose-Dependent Manner to the Intake of a High-Fat Meal in Normal Weight Healthy Men Are Associated with Obesity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
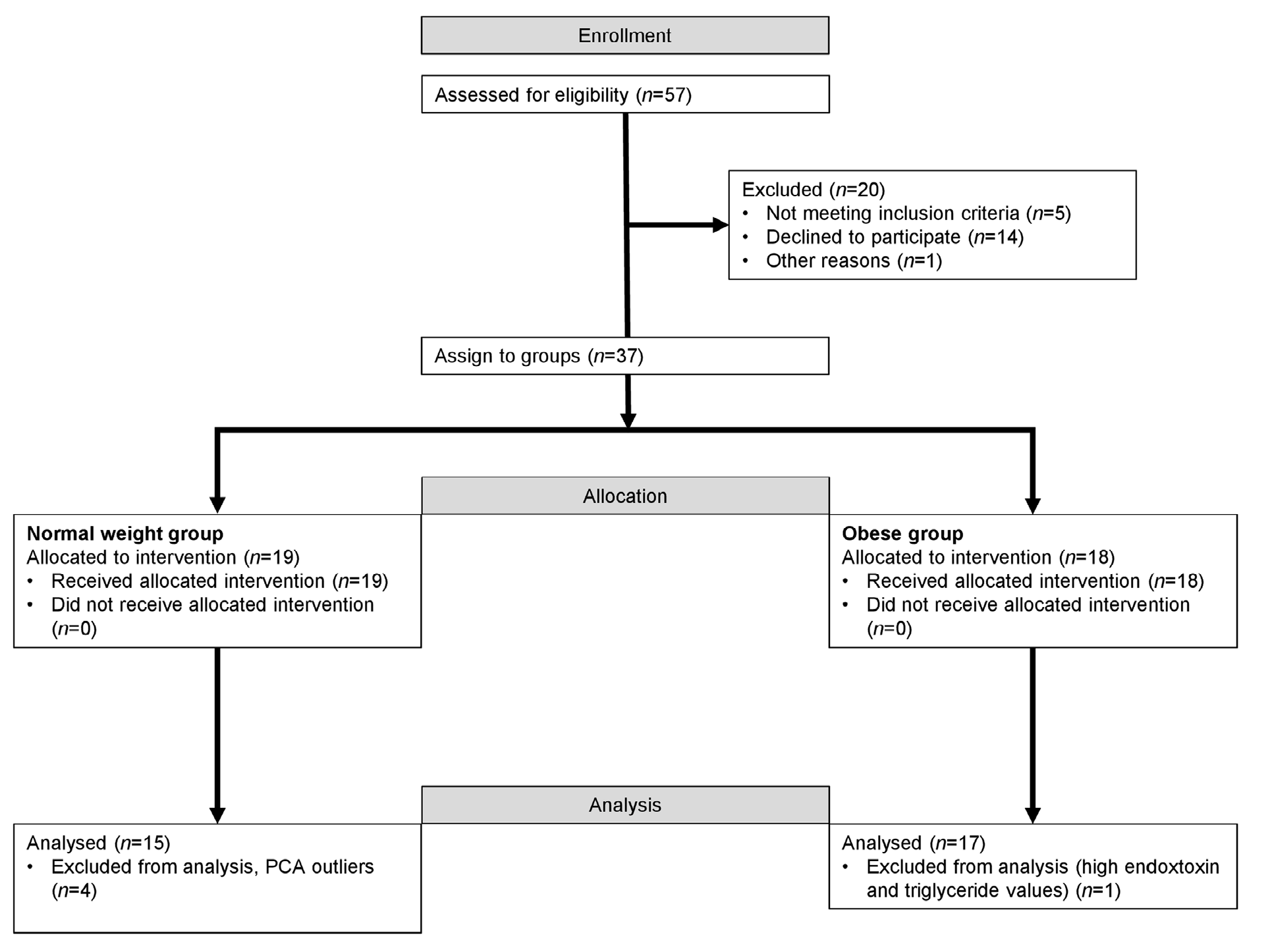
4.1. Subjects
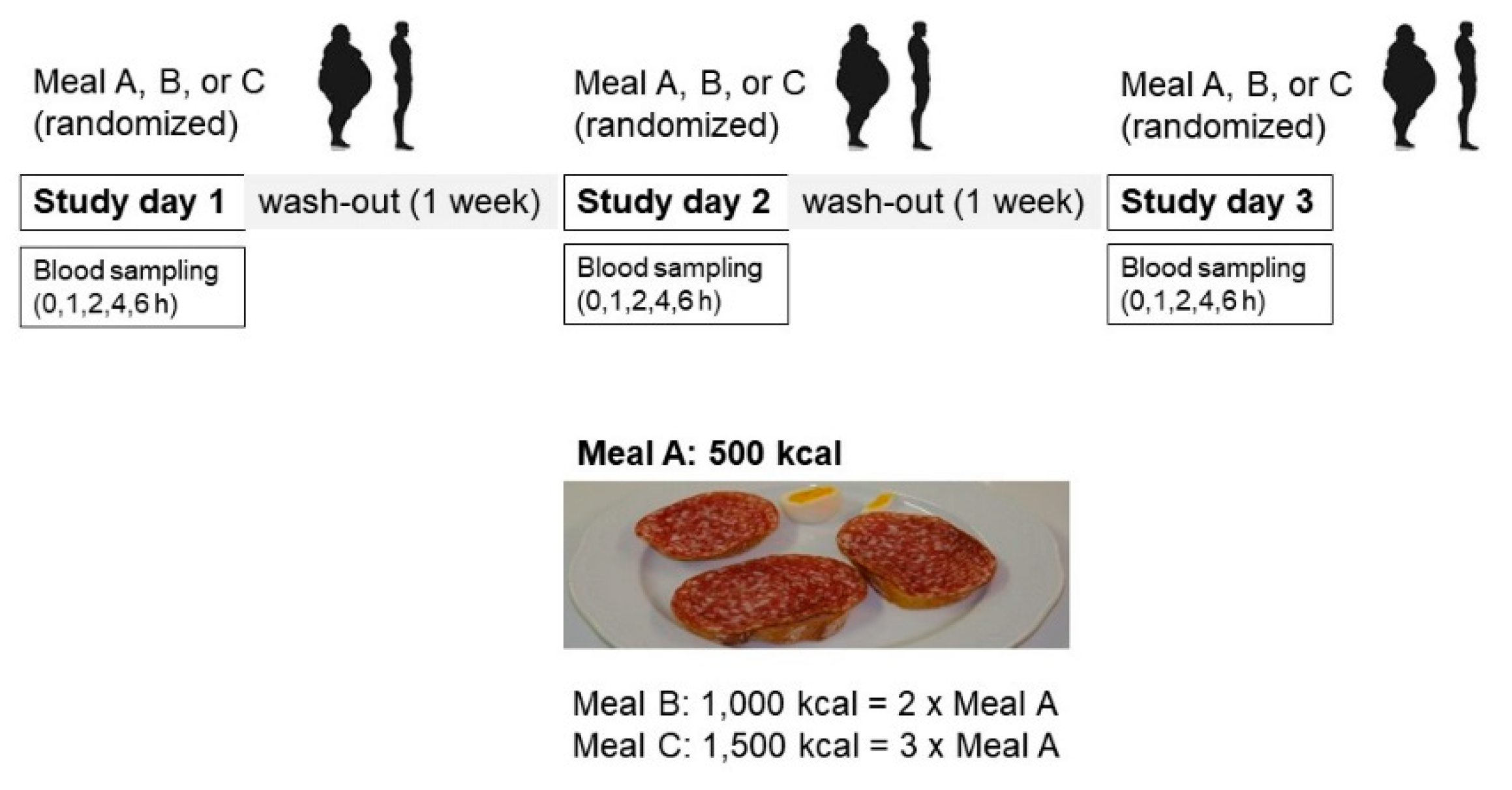
4.2. Study Design
4.3. Meal Composition
4.4. Untargeted Metabolomics with LC-MS
4.5. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis of Untargeted LC-MS Data
4.6. Measures of Amino Acids by GC-MS
4.7. Clinical Chemistry
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vázquez-Manjarrez, N.; Weinert, C.H.; Ulaszewska, M.M.; Mack, C.I.; Micheau, P.; Pétéra, M.; Durand, S.; Pujos-Guillot, E.; Egert, B.; Mattivi, F.; et al. Discovery and Validation of Banana Intake Biomarkers Using Untargeted Metabolomics in Human Intervention and Cross-sectional Studies. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 1701–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuparencu, C.; Rinnan, Å.; Dragsted, L.O. Combined Markers to Assess Meat Intake-Human Metabolomic Studies of Discovery and Validation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1900106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sri Harsha, P.S.C.; Abdul Wahab, R.; Cuparencu, C.; Dragsted, L.O.; Brennan, L. A Metabolomics Approach to the Identification of Urinary Biomarkers of Pea Intake. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes Krüger, R.; Costa Teixeira, B.; Boufleur Farinha, J.; Cauduro Oliveira Macedo, R.; Pinto Boeno, F.; Rech, A.; Lopez, P.; Silveira Pinto, R.; Reischak-Oliveira, A. Effect of exercise intensity on postprandial lipemia, markers of oxidative stress, and endothelial function after a high-fat meal. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Moreno, J.; García-Carpintero, S.; Jimenez-Lucena, R.; Haro, C.; Rangel-Zúñiga, O.A.; Blanco-Rojo, R.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; Tinahones, F.J.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Pérez-Martínez, P.; et al. Effect of Dietary Lipids on Endotoxemia Influences Postprandial Inflammatory Response. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7756–7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.; Matthan, N.R.; Ausman, L.M.; Lichtenstein, A.H. Effect of prior meal macronutrient composition on postprandial glycemic responses and glycemic index and glycemic load value determinations. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 1246–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madec, S.; Corretti, V.; Santini, E.; Ferrannini, E.; Solini, A. Effect of a fatty meal on inflammatory markers in healthy volunteers with a family history of type 2 diabetes. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irvin, M.R.; Aslibekyan, S.; Do, A.; Zhi, D.; Hidalgo, B.; Claas, S.A.; Srinivasasainagendra, V.; Horvath, S.; Tiwari, H.K.; Absher, D.M.; et al. Metabolic and inflammatory biomarkers are associated with epigenetic aging acceleration estimates in the GOLDN study. Clin. Epigenetics 2018, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Grada, C.M.; Morine, M.J.; Morris, C.; Ryan, M.; Dillon, E.T.; Walsh, M.; Gibney, E.R.; Brennan, L.; Gibney, M.J.; Roche, H.M. PBMCs reflect the immune component of the WAT transcriptome—implications as biomarkers of metabolic health in the postprandial state. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 808–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Pratico, G.; Scalbert, A.; Vergeres, G.; Kolehmainen, M.; Manach, C.; Brennan, L.; Afman, L.A.; Wishart, D.S.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; et al. A scheme for a flexible classification of dietary and health biomarkers. Genes Nutr. 2017, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragsted, L.O.; Gao, Q.; Scalbert, A.; Vergères, G.; Kolehmainen, M.; Manach, C.; Brennan, L.; Afman, L.A.; Wishart, D.S.; Andres Lacueva, C.; et al. Validation of biomarkers of food intake-Critical assessment of candidate biomarkers. Genes Nutr. 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olza, J.; Calder, P.C. Metabolic and inflammatory responses to different caloric loads of a high-fat meal are distinct between normal-weight and obese individuals. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1493–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Schwander, F.; Kopf-Bolanz, K.A.; Buri, C.; Portmann, R.; Egger, L.; Chollet, M.; McTernan, P.G.; Piya, M.; Gijs, M.A.M.; Vionnet, N.; et al. A dose-response strategy reveals differences between normal weight and obese men in their metabolic and inflammatory responses to a high-fat meal. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M.; Brennan, L.; Drevon, C.A.; van Kranen, H.; Manach, C.; Dragsted, L.O.; Roche, H.M.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Bouwman, J.; et al. Combining traditional dietary assessment methods with novel metabolomics techniques: Present efforts by the Food Biomarker Alliance. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2017, 76, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaszewska, M.M.; Weinert, C.H.; Trimigno, A.; Portmann, R.; Andres Lacueva, C.; Badertscher, R.; Brennan, L.; Brunius, C.; Bub, A.; Capozzi, F.; et al. Nutrimetabolomics: An Integrative Action for Metabolomic Analyses in Human Nutritional Studies. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, e1800384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papandreou, C.; Bulló, M.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Dennis, C.; Deik, A.; Wang, D.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; Yu, E.; Razquin, C.; Corella, D.; et al. Plasma metabolites predict both insulin resistance and incident type 2 diabetes: A metabolomics approach within the Prevención con Dieta Mediterránea (PREDIMED) study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallister, T.; Jackson, M.A.; Martin, T.C.; Zierer, J.; Jennings, A.; Mohney, R.P.; MacGregor, A.; Steves, C.J.; Cassidy, A.; Spector, T.D.; et al. Hippurate as a metabolomic marker of gut microbiome diversity: Modulation by diet and relationship to metabolic syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, E.S.; Byrne, C.S.; Morrison, D.J.; Murphy, K.G.; Preston, T.; Tedford, C.; Garcia-Perez, I.; Fountana, S.; Serrano-Contreras, J.I.; Holmes, E.; et al. Dietary supplementation with inulin-propionate ester or inulin improves insulin sensitivity in adults with overweight and obesity with distinct effects on the gut microbiota, plasma metabolome and systemic inflammatory responses: A randomised cross-over trial. Gut 2019, 68, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Pedram, P.; Cahill, F.; Zhai, G.; Randell, E.; Gulliver, W.; Sun, G. Serum metabolic biomarkers distinguish metabolically healthy peripherally obese from unhealthy centrally obese individuals. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 13, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gille, D.; Zangger, N.; Soneson, C.; Bütikofer, U.; Delorenzi, M.; Schwander, F.; Kopf-Bolanz, K.A.; Chollet, M.; Walther, B.; Laederach, K.; et al. Caloric dose-responsive genes in blood cells differentiate the metabolic status of obese men. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 43, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodpaster, B.H.; Sparks, L.M. Metabolic Flexibility in Health and Disease. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wopereis, S.; Stroeve, J.H.M.; Stafleu, A.; Bakker, G.C.M.; Burggraaf, J.; van Erk, M.J.; Pellis, L.; Boessen, R.; Kardinaal, A.A.F.; van Ommen, B. Multi-parameter comparison of a standardized mixed meal tolerance test in healthy and type 2 diabetic subjects: The PhenFlex challenge. Genes Nutr. 2017, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, S.; Kastenmuller, G.; Stuckler, F.; Rist, M.J.; Skurk, T.; Sailer, M.; Raffler, J.; Romisch-Margl, W.; Adamski, J.; Prehn, C.; et al. The dynamic range of the human metabolome revealed by challenges. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 2607–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Zhong, F.; Bruno, R.S.; Ballard, K.D.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J. Comparative Metabolomics Elucidates Postprandial Metabolic Modifications in Plasma of Obese Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 2850–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroeve, J.H.M.; van Wietmarschen, H.; Kremer, B.H.A.; van Ommen, B.; Wopereis, S. Phenotypic flexibility as a measure of health: The optimal nutritional stress response test. Genes Nutr. 2015, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dijk, S.J.; Mensink, M.; Esser, D.; Feskens, E.J.; Muller, M.; Afman, L.A. Responses to high-fat challenges varying in fat type in subjects with different metabolic risk phenotypes: A randomized trial. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellis, L.; van Erk, M.J.; van Ommen, B.; Bakker, G.C.; Hendriks, H.F.; Cnubben, N.H.; Kleemann, R.; van Someren, E.P.; Bobeldijk, I.; Rubingh, C.M.; et al. Plasma metabolomics and proteomics profiling after a postprandial challenge reveal subtle diet effects on human metabolic status. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiamoncini, J.; Rundle, M.; Gibbons, H.; Thomas, E.L.; Geillinger-Kastle, K.; Bunzel, D.; Trezzi, J.P.; Kiselova-Kaneva, Y.; Wopereis, S.; Wahrheit, J.; et al. Plasma metabolome analysis identifies distinct human metabotypes in the postprandial state with different susceptibility to weight loss-mediated metabolic improvements. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 5447–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman, J.; Vogels, J.T.; Wopereis, S.; Rubingh, C.M.; Bijlsma, S.; Ommen, B. Visualization and identification of health space, based on personalized molecular phenotype and treatment response to relevant underlying biological processes. BMC Med. Genom. 2012, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Broek, T.J.; Bakker, G.C.M.; Rubingh, C.M.; Bijlsma, S.; Stroeve, J.H.M.; van Ommen, B.; van Erk, M.J.; Wopereis, S. Ranges of phenotypic flexibility in healthy subjects. Genes Nutr. 2017, 12, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, M.P. Drug dosing based on weight and body surface area: Mathematical assumptions and limitations in obese adults. Pharmacotherapy 2012, 32, 856–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heni, M.; Kullmann, S.; Ketterer, C.; Guthoff, M.; Bayer, M.; Staiger, H.; Machicao, F.; Haring, H.U.; Preissl, H.; Veit, R.; et al. Differential effect of glucose ingestion on the neural processing of food stimuli in lean and overweight adults. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2014, 35, 918–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdich, C.; Toubro, S.; Buemann, B.; Lysgård Madsen, J.; Juul Holst, J.; Astrup, A. The role of postprandial releases of insulin and incretin hormones in meal-induced satiety—Effect of obesity and weight reduction. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2001, 25, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.Y.; Judd, J.T.; Taylor, P.R.; Campbell, W.S.; Nair, P.P. Influence of caloric contribution and saturation of dietary fat on plasma lipids in premenopausal women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1987, 45, 1451–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vors, C.; Pineau, G.; Drai, J.; Meugnier, E.; Pesenti, S.; Laville, M.; Laugerette, F.; Malpuech-Brugere, C.; Vidal, H.; Michalski, M.C. Postprandial Endotoxemia Linked With Chylomicrons and Lipopolysaccharides Handling in Obese Versus Lean Men: A Lipid Dose-Effect Trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 3427–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirulli, E.T.; Guo, L.; Leon Swisher, C.; Shah, N.; Huang, L.; Napier, L.A.; Kirkness, E.F.; Spector, T.D.; Caskey, C.T.; Thorens, B.; et al. Profound Perturbation of the Metabolome in Obesity Is Associated with Health Risk. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 488–500.e482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellissimo, M.P.; Cai, Q.; Ziegler, T.R.; Liu, K.H.; Tran, P.H.; Vos, M.B.; Martin, G.S.; Jones, D.P.; Yu, T.; Alvarez, J.A. Plasma High-Resolution Metabolomics Differentiates Adults with Normal Weight Obesity from Lean Individuals. Obesity 2019, 27, 1729–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.C.; Matthews, C.E.; Sampson, J.N.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Zheng, W.; Cai, Q.; Tan, Y.T.; Chow, W.H.; Ji, B.T.; Liu, D.K.; et al. Human metabolic correlates of body mass index. Metabolomics 2014, 10, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newgard, C.B. Metabolomics and Metabolic Diseases: Where Do We Stand? Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newgard, C.B.; An, J.; Bain, J.R.; Muehlbauer, M.J.; Stevens, R.D.; Lien, L.F.; Haqq, A.M.; Shah, S.H.; Arlotto, M.; Slentz, C.A.; et al. A branched-chain amino acid-related metabolic signature that differentiates obese and lean humans and contributes to insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.H. Emerging perspectives on essential amino acid metabolism in obesity and the insulin-resistant state. Adv. Nutr. 2011, 2, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.H.; Tseng, Y.J.; Wang, S.Y.; Tsai, Y.S.; Chang, C.S.; Kuo, T.C.; Yao, W.J.; Shieh, C.C.; Wu, C.H.; Kuo, P.H. The metabolome profiling and pathway analysis in metabolic healthy and abnormal obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauschert, S.; Uhl, O.; Koletzko, B.; Hellmuth, C. Metabolomic biomarkers for obesity in humans: A short review. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 64, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulet, M.M.; Chevrier, G.; Grenier-Larouche, T.; Pelletier, M.; Nadeau, M.; Scarpa, J.; Prehn, C.; Marette, A.; Adamski, J.; Tchernof, A. Alterations of plasma metabolite profiles related to adipose tissue distribution and cardiometabolic risk. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 309, E736–E746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badoud, F.; Lam, K.P.; Perreault, M.; Zulyniak, M.A.; Britz-McKibbin, P.; Mutch, D.M. Metabolomics Reveals Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Obese Individuals Differ in their Response to a Caloric Challenge. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondia-Pons, I.; Maukonen, J.; Mattila, I.; Rissanen, A.; Saarela, M.; Kaprio, J.; Hakkarainen, A.; Lundbom, J.; Lundbom, N.; Hyotylainen, T.; et al. Metabolome and fecal microbiota in monozygotic twin pairs discordant for weight: A Big Mac challenge. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 4169–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomgarden, Z. Diabetes and branched-chain amino acids: What is the link? J. Diabetes 2018, 10, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newgard, C.B. Interplay between lipids and branched-chain amino acids in development of insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, P.J.; Newgard, C.B. Branched-chain amino acids in disease. Science 2019, 363, 582–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.G.; Yim, Y.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, B.W.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, Y.W.; Kim, J.H. Fasting serum amino acids concentration is associated with insulin resistance and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 140, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, K.; Harada, S.; Takeuchi, A.; Kurihara, A.; Iida, M.; Fukai, K.; Kuwabara, K.; Kato, S.; Matsumoto, M.; Hirata, A.; et al. Association between dyslipidemia and plasma levels of branched-chain amino acids in the Japanese population without diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2019, 13, 932–939.e932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Feng, R.; Guo, F.; Li, Y.; Jiao, J.; Sun, C. Targeted metabolomic analysis reveals the association between the postprandial change in palmitic acid, branched-chain amino acids and insulin resistance in young obese subjects. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 108, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mook-Kanamori, D.O.; Römisch-Margl, W.; Kastenmüller, G.; Prehn, C.; Petersen, A.K.; Illig, T.; Gieger, C.; Wang-Sattler, R.; Meisinger, C.; Peters, A.; et al. Increased amino acids levels and the risk of developing of hypertriglyceridemia in a 7-year follow-up. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2014, 37, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakado, M.; Nagao, K.; Imaizumi, A.; Tani, M.; Toda, A.; Tanaka, T.; Jinzu, H.; Miyano, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Daimon, T.; et al. Plasma Free Amino Acid Profiles Predict Four-Year Risk of Developing Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome, Dyslipidemia, and Hypertension in Japanese Population. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Hu, W.; Fu, Z.; Sun, L.; Zhou, Y.; Gong, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhou, H. The positive association of branched-chain amino acids and metabolic dyslipidemia in Chinese Han population. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, M.; Yang, X.; Bi, M.; Na, L.; Niu, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, C. Fasting serum lipid and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate as important metabolites for detecting isolated postchallenge diabetes: Serum metabolomics via ultra-high-performance LC-MS. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, D.E.; Mandarino, L.J. Fuel selection in human skeletal muscle in insulin resistance: A reexamination. Diabetes 2000, 49, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.; Che, D.; Qin, G.; Farouk, M.H.; Hailong, J.; Rui, H. Novel Biosynthesis, Metabolism and Physiological Functions of L-Homoarginine. Curr. Protein. Pept. Sci. 2019, 20, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M.; Kayacelebi, A.A.; Batkai, S.; Jordan, J.; Tsikas, D.; Engeli, S. Plasma and tissue homoarginine concentrations in healthy and obese humans. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 1847–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Aama, J.Y.; Al Mahdi, H.B.; Salama, M.A.; Bakur, K.H.; Alhozali, A.; Mosli, H.H.; Bahijri, S.M.; Bahieldin, A.; Willmitzer, L.; Edris, S. Detection of Secondary Metabolites as Biomarkers for the Early Diagnosis and Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 2675–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brosnan, J.T.; Brosnan, M.E. Creatine: Endogenous metabolite, dietary, and therapeutic supplement. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2007, 27, 241–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazak, L.; Chouchani, E.T.; Lu, G.Z.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Bare, C.J.; Mina, A.I.; Kumari, M.; Zhang, S.; Vuckovic, I.; Laznik-Bogoslavski, D.; et al. Genetic Depletion of Adipocyte Creatine Metabolism Inhibits Diet-Induced Thermogenesis and Drives Obesity. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 660–671.e663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almanza-Aguilera, E.; Brunius, C.; Bernal-Lopez, M.R.; Garcia-Aloy, M.; Madrid-Gambin, F.; Tinahones, F.J.; Gómez-Huelgas, R.; Landberg, R.; Andres-Lacueva, C. Impact in Plasma Metabolome as Effect of Lifestyle Intervention for Weight-Loss Reveals Metabolic Benefits in Metabolically Healthy Obese Women. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 2600–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, J.; Tang, S.Y.; Jenner, A.M.; Mudway, I.; Blomberg, A.; Behndig, A.; Kasiman, K.; Lee, C.Y.; Seet, R.C.; Zhang, W.; et al. Allantoin in human plasma, serum, and nasal-lining fluids as a biomarker of oxidative stress: Avoiding artifacts and establishing real in vivo concentrations. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 1767–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalicky, J.; Muzakova, V.; Kandar, R.; Meloun, M.; Rousar, T.; Palicka, V. Evaluation of oxidative stress and inflammation in obese adults with metabolic syndrome. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2008, 46, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papandreou, C.; Li, J.; Liang, L.; Bullo, M.; Zheng, Y.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Yu, E.; Guasch-Ferre, M.; Razquin, C.; Clish, C.; et al. Metabolites related to purine catabolism and risk of type 2 diabetes incidence; modifying effects of the TCF7L2-rs7903146 polymorphism. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabado, S.; Al-Salameh, A.; Croixmarie, V.; Masson, P.; Corruble, E.; Feve, B.; Colle, R.; Ripoll, L.; Walther, B.; Boursier-Neyret, C.; et al. The human plasma-metabolome: Reference values in 800 French healthy volunteers; impact of cholesterol, gender and age. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, G.; Burton, K.J.; von Ah, U.; Butikofer, U.; Pralong, F.P.; Vionnet, N.; Portmann, R.; Vergeres, G. Metabolic Footprinting of Fermented Milk Consumption in Serum of Healthy Men. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Marcu, A.; Guo, A.C.; Liang, K.; Vazquez-Fresno, R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Karu, N.; et al. HMDB 4.0: The human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MassBank of North America (MoNA). Available online: http://mona.fiehnlab.ucdavis.edu (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Smith, C.A.; O’Maille, G.; Want, E.J.; Qin, C.; Trauger, S.A.; Brandon, T.R.; Custodio, D.E.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. METLIN: A metabolite mass spectral database. Ther. Drug Monit. 2005, 27, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Begley, P.; Zelena, E.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Anderson, N.; Brown, M.; Knowles, J.D.; Halsall, A.; Haselden, J.N.; et al. Procedures for large-scale metabolic profiling of serum and plasma using gas chromatography and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1060–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekstrøm, C.T. Miscellaneous Esoteric Statistical Scripts. 2020. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/MESS/index.html (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Noguchi, K.; Gel, Y.R.; Brunner, E.; Konietschke, F. nparLD: An R Software Package for the Nonparametric Analysis of Longitudinal Data in Factorial Experiments. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 50, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, A. Package ‘Amap’. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/amap/index.html (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Galili, T. dendextend: An R package for visualizing, adjusting and comparing trees of hierarchical clustering. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3718–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinno, A. Package ‘Conover.Test’. 2017, pp. 1–7. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/conover.test/index.html (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Begley, P.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Halsall, A.; Tseng, A.; Knowles, J.; Goodacre, R.; Kell, D.B. Development and Performance of a Gas Chromatography−Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Analysis for Large-Scale Nontargeted Metabolomic Studies of Human Serum. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 7038–7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, G.; Burton, K.J.; Rosikiewicz, M.; Freiburghaus, C.; von Ah, U.; Münger, L.H.; Pralong, F.P.; Vionnet, N.; Greub, G.; Badertscher, R.; et al. Blood lactose after dairy product intake in healthy men. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 118, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
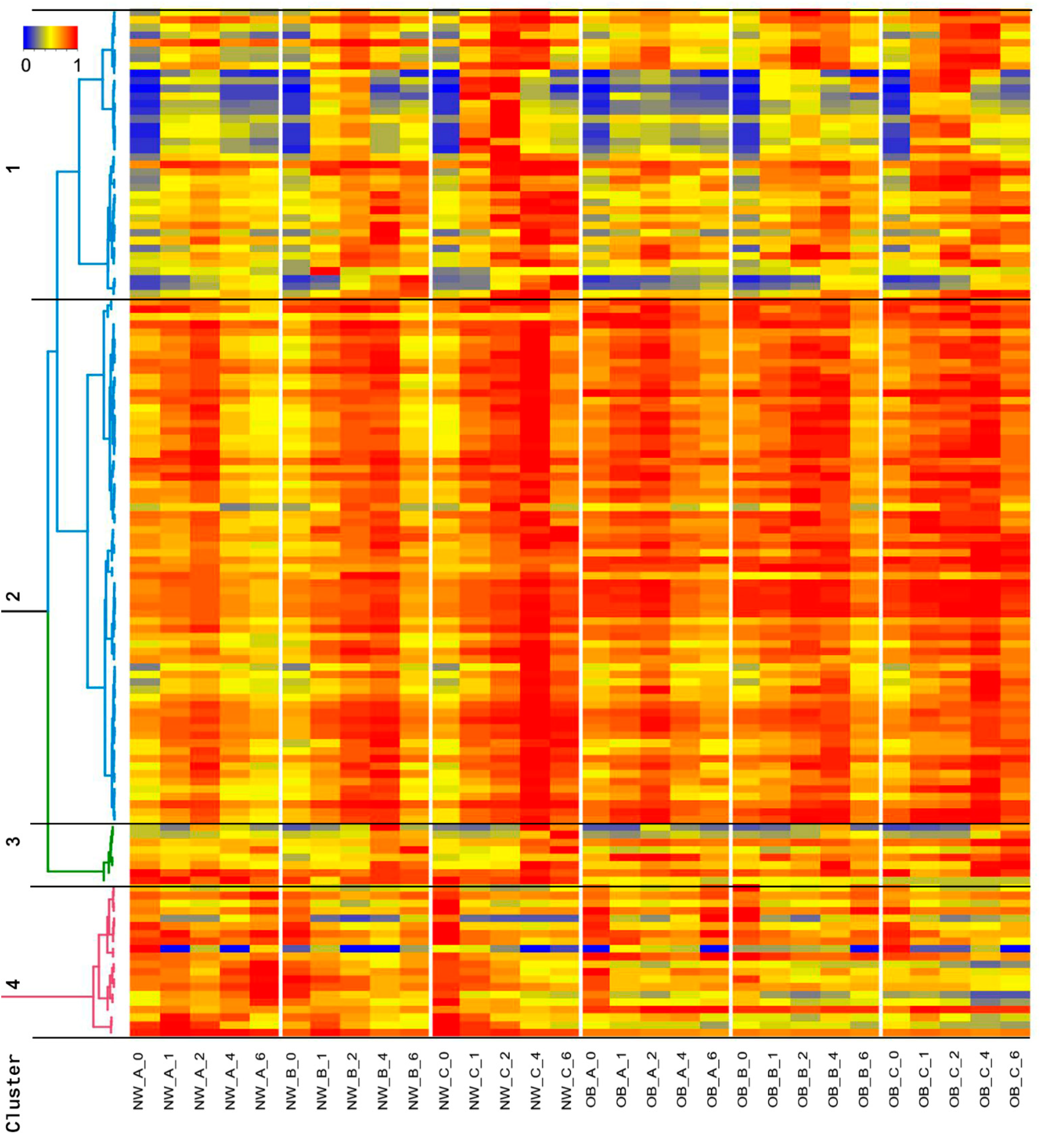

 NW group;
NW group;  OB group; meals
OB group; meals  A,
A,  B, and
B, and  C.
C.
 NW group;
NW group;  OB group; meals
OB group; meals  A,
A,  B, and
B, and  C.
C.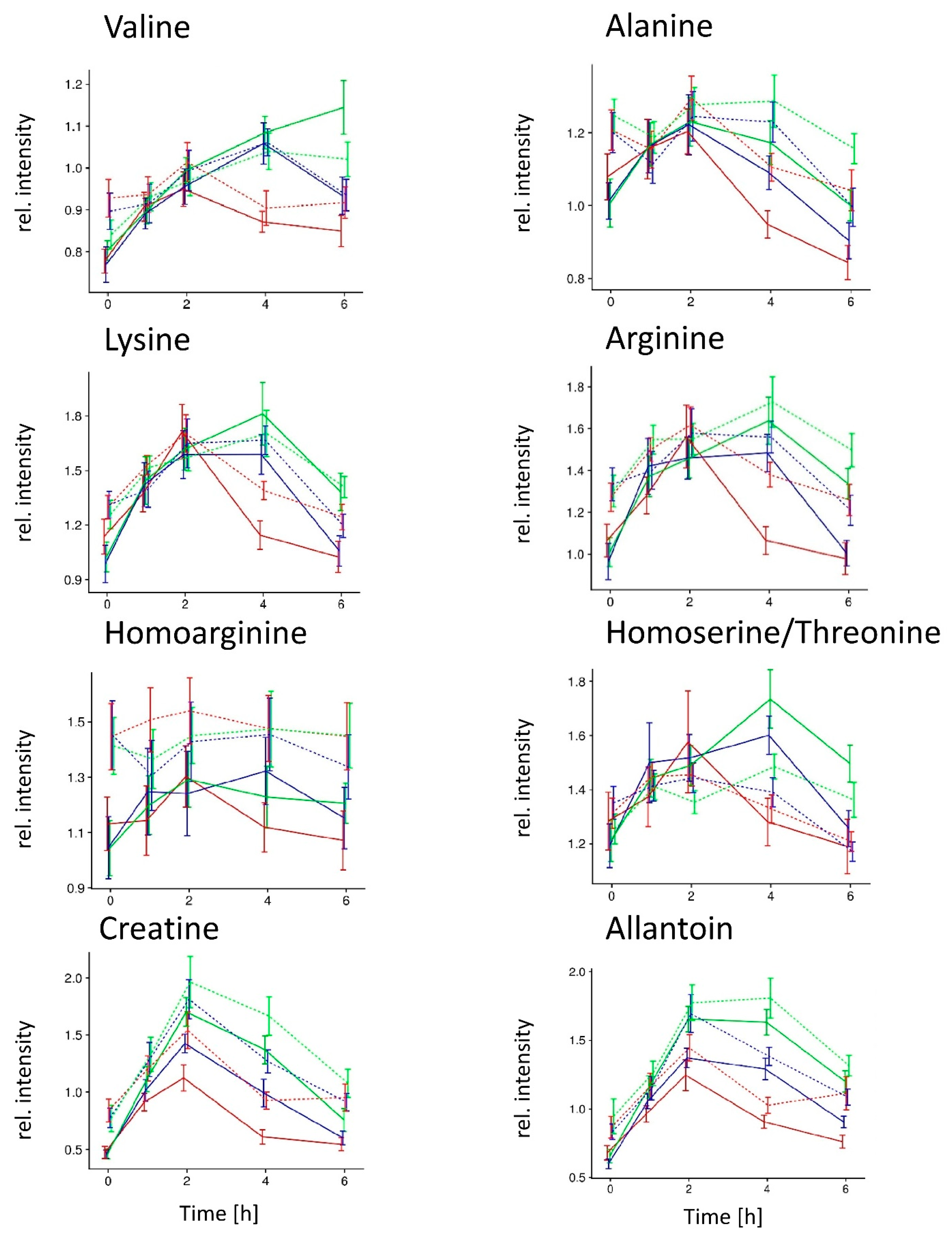
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bütikofer, U.; Burnand, D.; Portmann, R.; Blaser, C.; Schwander, F.; Kopf-Bolanz, K.A.; Laederach, K.; Badertscher, R.; Walther, B.; Vergères, G. Serum Metabolites Responding in a Dose-Dependent Manner to the Intake of a High-Fat Meal in Normal Weight Healthy Men Are Associated with Obesity. Metabolites 2021, 11, 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060392
Bütikofer U, Burnand D, Portmann R, Blaser C, Schwander F, Kopf-Bolanz KA, Laederach K, Badertscher R, Walther B, Vergères G. Serum Metabolites Responding in a Dose-Dependent Manner to the Intake of a High-Fat Meal in Normal Weight Healthy Men Are Associated with Obesity. Metabolites. 2021; 11(6):392. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060392
Chicago/Turabian StyleBütikofer, Ueli, David Burnand, Reto Portmann, Carola Blaser, Flurina Schwander, Katrin A. Kopf-Bolanz, Kurt Laederach, René Badertscher, Barbara Walther, and Guy Vergères. 2021. "Serum Metabolites Responding in a Dose-Dependent Manner to the Intake of a High-Fat Meal in Normal Weight Healthy Men Are Associated with Obesity" Metabolites 11, no. 6: 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060392
APA StyleBütikofer, U., Burnand, D., Portmann, R., Blaser, C., Schwander, F., Kopf-Bolanz, K. A., Laederach, K., Badertscher, R., Walther, B., & Vergères, G. (2021). Serum Metabolites Responding in a Dose-Dependent Manner to the Intake of a High-Fat Meal in Normal Weight Healthy Men Are Associated with Obesity. Metabolites, 11(6), 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060392





