Hyperpolarized Metabolic MRI—Acquisition, Reconstruction, and Analysis Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pulse Sequence Methods
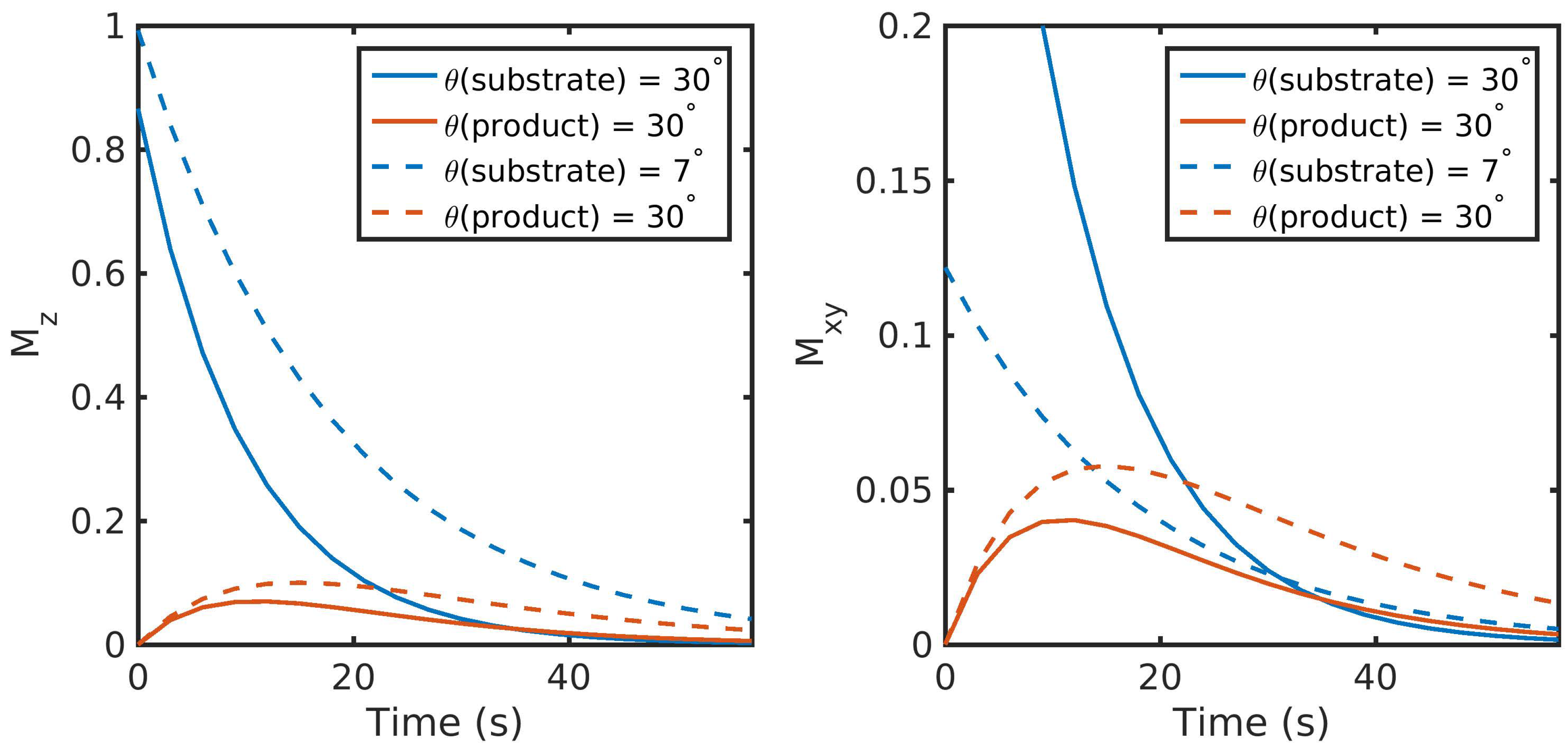
2.1. RF Excitation and Imaging Timing
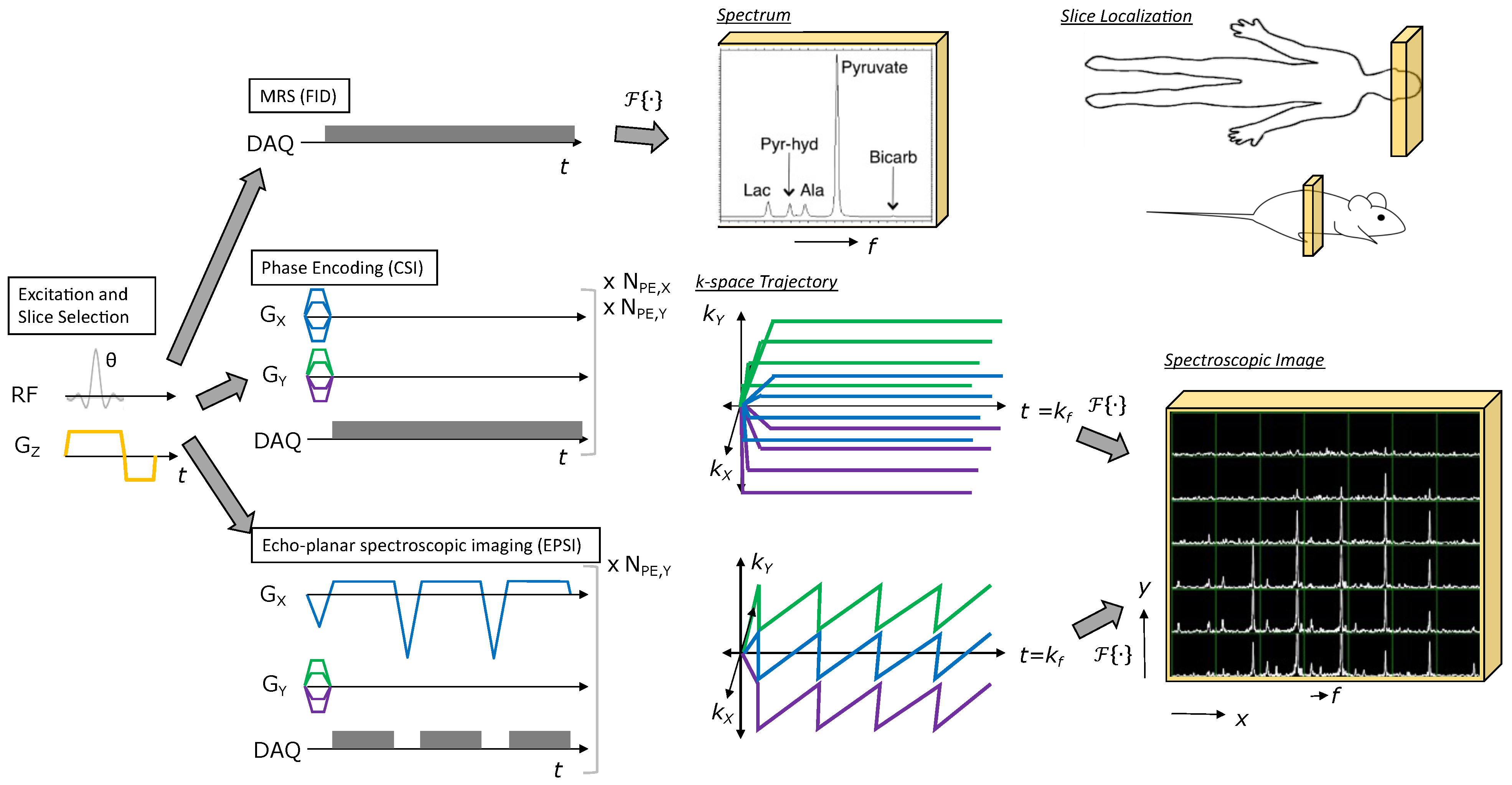
2.2. Data Acquisition and Reconstruction Strategies
2.2.1. Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Imaging (MRSI)
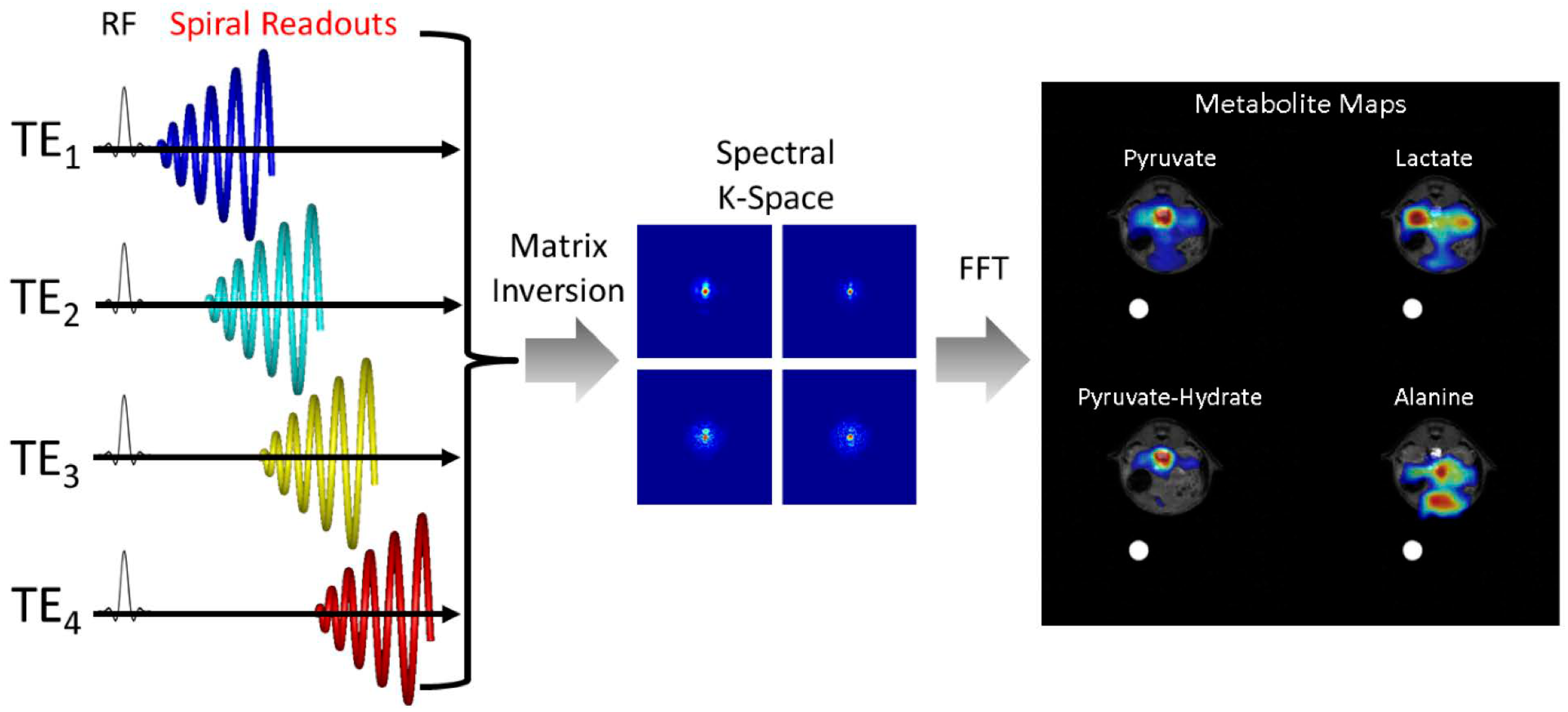
2.2.2. Model-Based Chemical Shift Encoding
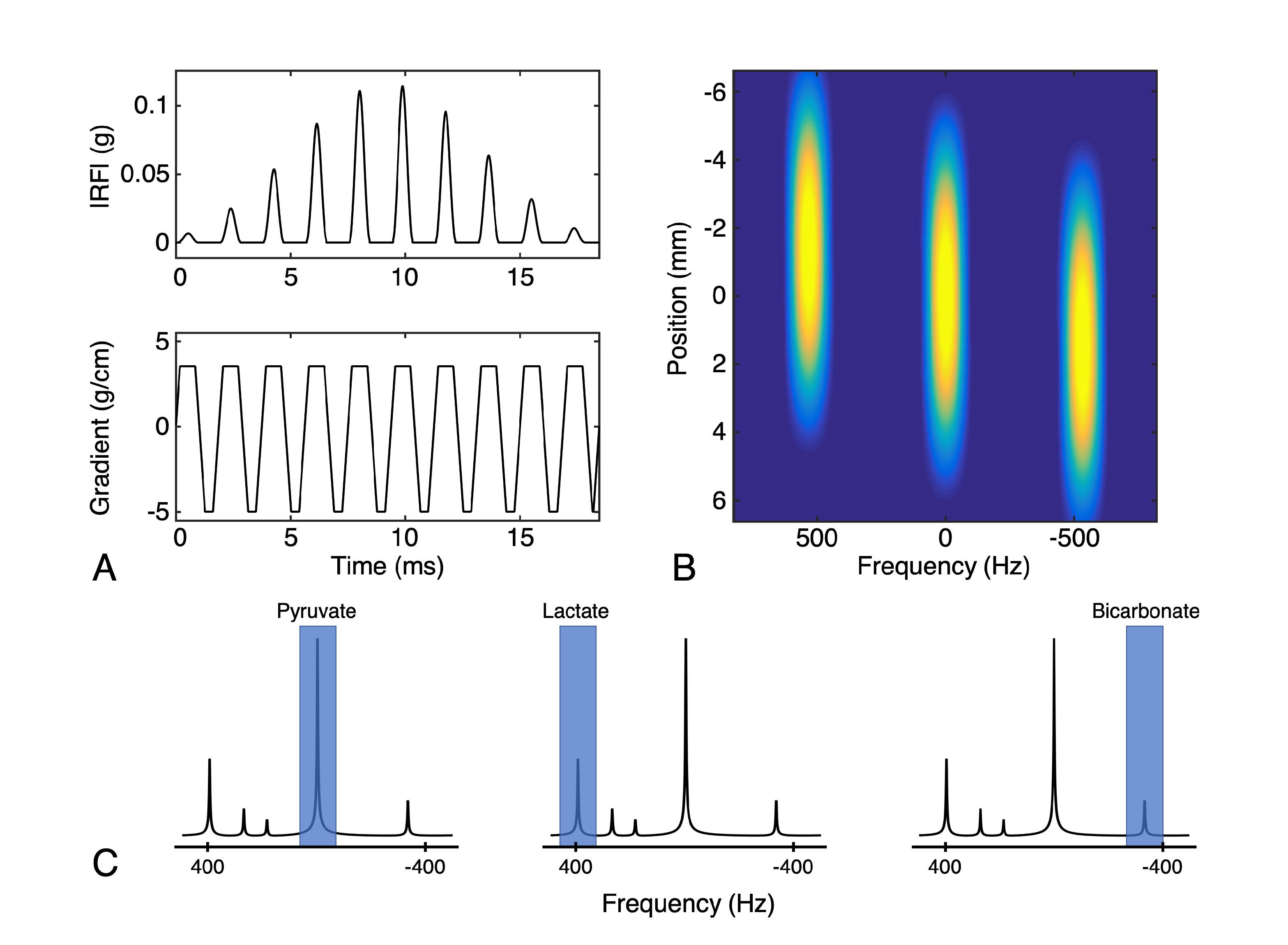
2.2.3. Metabolite-Selective Imaging
2.2.4. Refocused Imaging Methods
2.2.5. Acceleration Methods
2.2.6. Calibration Methods
3. Data Analysis Methods
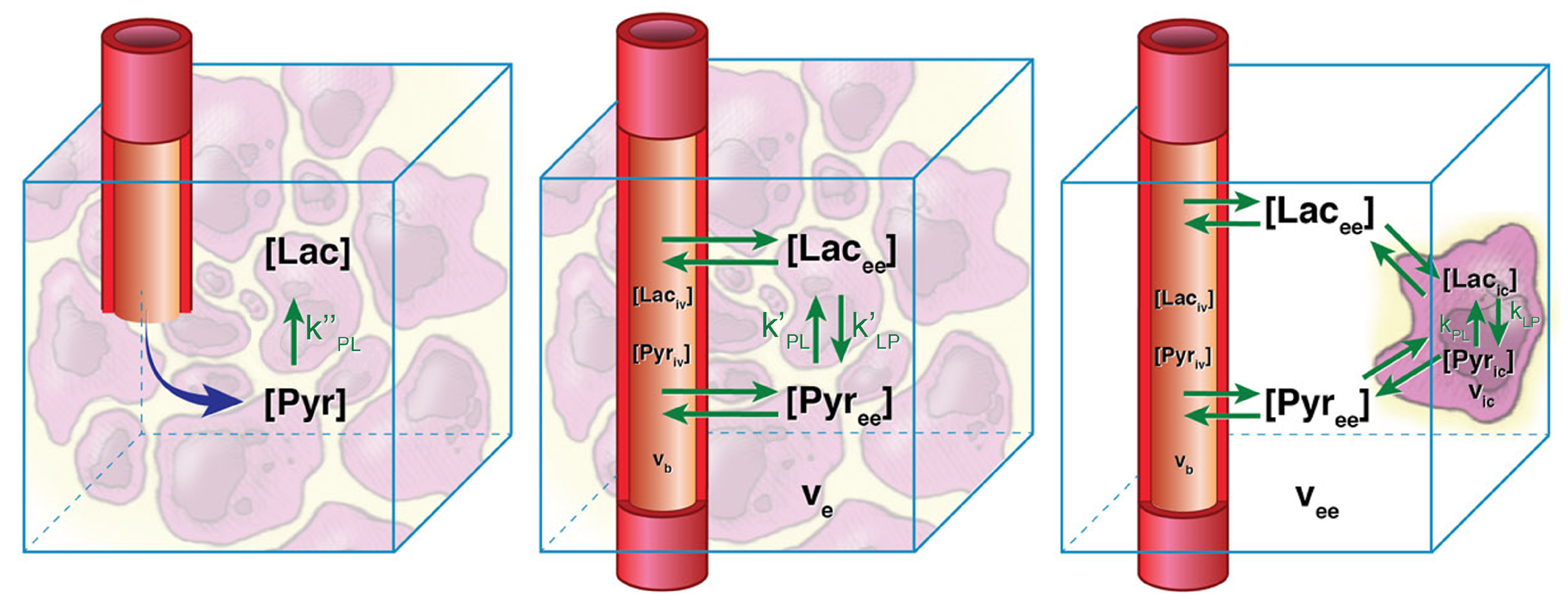
3.1. Kinetic Modeling
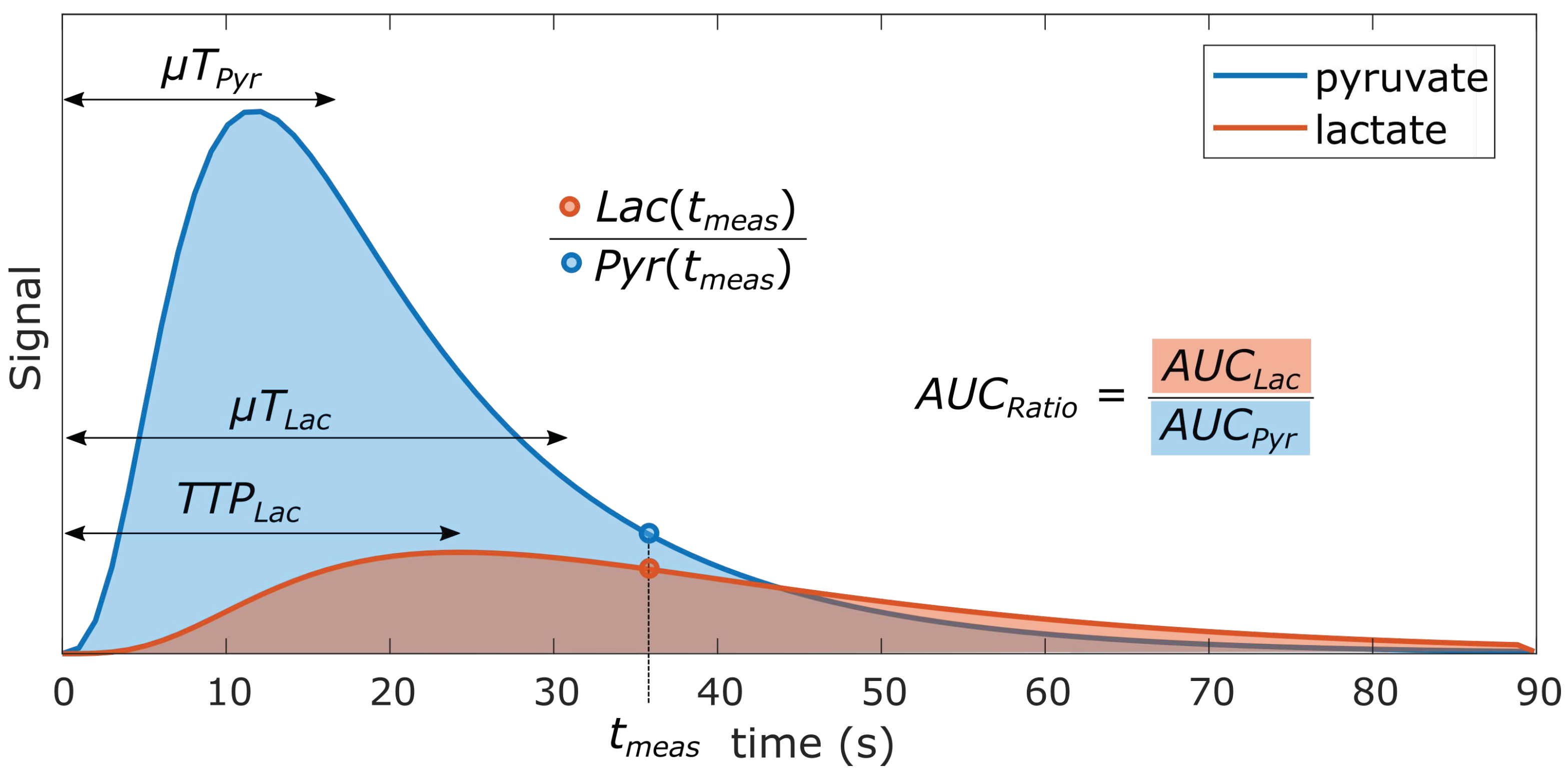
3.2. Model-Free Metrics
3.2.1. Single time-point Metabolite Ratio
3.2.2. Area-under-curve (AUC) Metabolite Ratio
4. Final Remarks
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.J.; Ohliger, M.A.; Larson, P.E.Z.; Gordon, J.W.; Bok, R.A.; Slater, J.; Villanueva-Meyer, J.E.; Hess, C.P.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Vigneron, D.B. Hyperpolarized 13C MRI: State of the Art and Future Directions. Radiology 2019, 182391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golman, K.; Zandt, R.I.; Lerche, M.; Pehrson, R.; Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J.H. Metabolic Imaging by Hyperpolarized 13C Magnetic Resonance Imaging for In vivo Tumor Diagnosis. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 10855–10860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golman, K.; Ardenkjaer Larsen, J.H.; Petersson, J.S.; Maansson, S.; Leunbach, I. Molecular imaging with endogenous substances. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10435–10439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, F.A.; Kettunen, M.I.; Hu, D.E.; Jensen, P.R.; Zandt, R.I.T.; Karlsson, M.; Gisselsson, A.; Nelson, S.K.; Witney, T.H.; Bohndiek, S.E.; et al. Production of hyperpolarized [1,4-13C2]malate from [1,4-13C2]fumarate is a marker of cell necrosis and treatment response in tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19801–19806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaumeil, M.M.; Larson, P.E.Z.; Yoshihara, H.A.I.; Danforth, O.M.; Vigneron, D.B.; Nelson, S.J.; Pieper, R.O.; Phillips, J.J.; Ronen, S.M. Non-invasive in vivo assessment of IDH1 mutational status in glioma. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, F.A.; Kettunen, M.I.; Day, S.E.; Hu, D.E.; Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J.H.; Zandt, R.I.T.; Jensen, P.R.; Karlsson, M.; Golman, K.; Lerche, M.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of pH in vivo using hyperpolarized 13C-labelled bicarbonate. Nature 2008, 453, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, D.R.; Rowlands, B.; Dodd, M.S.; Page, L.L.; Ball, V.; Carr, C.A.; Clarke, K.; Tyler, D.J. Hyperpolarized butyrate: A metabolic probe of short chain fatty acid metabolism in the heart. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 71, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, P.R.; Peitersen, T.; Karlsson, M.; In ’t Zandt, R.; Gisselsson, A.; Hansson, G.; Meier, S.; Lerche, M.H. Tissue-specific short chain fatty acid metabolism and slow metabolic recovery after ischemia from hyperpolarized NMR in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 36077–36082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshari, K.R.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Bok, R.; Larson, P.E.Z.; Vigneron, D.B.; Wilson, D.M. Hyperpolarized 13C dehydroascorbate as an endogenous redox sensor for in vivo metabolic imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18606–18611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshari, K.R.; Wilson, D.M. Chemistry and biochemistry of 13C hyperpolarized magnetic resonance using dynamic nuclear polarization. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 1627–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitt, M.H. Spin Dynamics: Basics of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Farrar, T.C.; Druck, S.J.; Shoup, R.R.; Becker, E.D. Temperature-Dependent Carbon-13 Relaxation Studies of Small Molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972, 94, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, M.H. Long live the singlet state! J. Magn. Reson. 2019, 306, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardenkjær-Larsen, J.H.; Fridlund, B.; Gram, A.; Hansson, G.; Hansson, L.; Lerche, M.H.; Servin, R.; Thaning, M.; Golman, K. Increase in signal-to-noise ratio of < 10,000 times in liquid-state NMR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10158–10163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Mulkern, R.; Tseng, C.H.; Williamson, D.; Patz, S.; Kraft, R.; Walsworth, R.L.; Jolesz, F.A.; Albert, M.S. Gradient-Echo Imaging Considerations for Hyperpolarized 129Xe MR. J. Magn. Reson. B 1996, 113, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, P.E.Z.; Kerr, A.B.; Chen, A.P.; Lustig, M.S.; Zierhut, M.L.; Hu, S.; Cunningham, C.H.; Pauly, J.M.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Vigneron, D.B. Multiband excitation pulses for hyperpolarized 13C dynamic chemical-shift imaging. J. Magn. Reson. 2008, 194, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maidens, J.; Gordon, J.W.; Arcak, M.; Larson, P.E.Z. Optimizing Flip Angles for Metabolic Rate Estimation in Hyperpolarized Carbon-13 MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 2403–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagashima, K. Optimum pulse flip angles for multi-scan acquisition of hyperpolarized NMR and MRI. J. Magn. Reson. 2008, 190, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Reed, G.D.; Pauly, J.M.; Kerr, A.B.; Larson, P.E.Z. Optimal variable flip angle schemes for dynamic acquisition of exchanging hyperpolarized substrates. J. Magn. Reson. 2013, 234, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, C.M.; Fuentes, D.; Larson, P.E.Z.; Kundra, V.; Vigneron, D.B.; Bankson, J.A. Effects of excitation angle strategy on quantitative analysis of hyperpolarized pyruvate. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 81, 3754–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, P.E.Z.; Chen, H.Y.; Gordon, J.; Maidens, J.; Mammoli, D.; Van Criekinge, M.; Bok, R.; Aggarwal, R.; Ferrone, M.; Slater, J.B.; et al. Analysis Methods for Human Hyperpolarized 13C-pyruvate Studies. In Proceedings of the ISMRM Annual Meeting, Paris, France, 16–21 June 2018; p. 3850. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, Y.F.; Josan, S.; Senadheera, L.; Park, J.M.; Takahashi, A.M.; Jang, T.; Merchant, M.; Balchandani, P.; Tropp, J.; Mayer, D.; et al. Non-CPMG Echo-Train Sequence for T2 Mapping and Large SNR Gain in Hyperpolarized 13C Imaging. In Proceedings of the ISMRM 20th Annual Meeting, Melboune, Australia, 5–11 May 2012; p. 4295. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, H.; Sukumar, S.; von Morze, C.; Bok, R.A.; Marco-Rius, I.; Kerr, A.; Reed, G.D.; Milshteyn, E.; Ohliger, M.A.; Kurhanewicz, J.; et al. Spectrally selective three-dimensional dynamic balanced steady-state free precession for hyperpolarized C-13 metabolic imaging with spectrally selective radiofrequency pulses. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, J.; Maansson, S.; Johansson, E.; Petersson, J.S.; Olsson, L.E. Hyperpolarized 13C MR angiography using trueFISP. Magn. Reson. Med. 2003, 50, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Bok, R.; Qin, H.; Reed, G.; VanCriekinge, M.; Santos, R.D.; Overall, W.; Santos, J.; Gordon, J.; Wang, Z.J.; et al. A metabolite-specific 3D stack-of-spiral bSSFP sequence for improved lactate imaging in hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate studies on a 3T clinical scanner. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Lustig, M.; Balakrishnan, A.; Larson, P.E.Z.; Bok, R.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Nelson, S.J.; Goga, A.; Pauly, J.M.; Vigneron, D.B. 3D compressed sensing for highly accelerated hyperpolarized (13)C MRSI with in vivo applications to transgenic mouse models of cancer. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 63, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, P.E.Z.; Hu, S.; Lustig, M.; Kerr, A.B.; Nelson, S.J.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Pauly, J.M.; Vigneron, D.B. Fast dynamic 3D MR spectroscopic imaging with compressed sensing and multiband excitation pulses for hyperpolarized 13C studies. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 65, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.X.; Merritt, M.E.; Sherry, A.D.; Malloy, C.R. Accelerated chemical shift imaging of hyperpolarized 13C metabolites. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 76, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, M.A.; Lau, A.Z.; Chen, A.P.; Gu, Y.; Nagendran, J.; Barry, J.; Hu, X.; Dyck, J.R.; Tyler, D.J.; Clarke, K.; et al. Hyperpolarized 13C magnetic resonance reveals early- and late-onset changes to in vivo pyruvate metabolism in the failing heart. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2013, 15, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, B.T.; Chen, H.Y.; Gordon, J.; Mammoli, D.; Sriram, R.; Autry, A.W.; Le Page, L.M.; Chaumeil, M.; Shin, P.; Slater, J.; et al. First hyperpolarized [2-13C]pyruvate MR studies of human brain metabolism. J. Magn. Reson. 2019, 309, 106617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.B.; Serrao, E.M.; Kennedy, B.W.C.; Hu, D.E.; Kettunen, M.I.; Brindle, K.M. Magnetic resonance imaging of tumor glycolysis using hyperpolarized (13)C-labeled glucose. Nat. Med. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, S.J.; Yen, Y.; Wolber, J.; Chen, A.P.; Albers, M.J.; Bok, R.; Zhang, V.; Tropp, J.; Nelson, S.; Vigneron, D.B.; et al. In vivo 13 carbon metabolic imaging at 3T with hyperpolarized 13C-1-pyruvate. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007, 58, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golman, K.; in ’t Zandt, R.; Thaning, M. Real-time metabolic imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11270–11275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, Y.F.; Kohler, S.J.; Chen, A.P.; Tropp, J.; Bok, R.; Wolber, J.; Albers, M.J.; Gram, K.A.; Zierhut, M.L.; Park, I.; et al. Imaging considerations for in vivo 13C metabolic mapping using hyperpolarized 13C-pyruvate. Magn. Reson. Med. 2009, 62, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, D.; Levin, Y.S.; Hurd, R.E.; Glover, G.H.; Spielman, D.M. Fast metabolic imaging of systems with sparse spectra: Application for hyperpolarized 13C imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2006, 56, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, M.S.; Lee, J.; Walker, C.M.; Sandulache, V.C.; Hennel, F.; Lai, S.Y.; Bankson, J.A. Radial spectroscopic MRI of hyperpolarized [1-(13) C] pyruvate at 7 tesla. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Lustig, M.; Larson, P.E.Z. Concentric rings K-space trajectory for hyperpolarized (13) C MR spectroscopic imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 75, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, I.; Larson, P.E.Z.; Gordon, J.W.; Carvajal, L.; Chen, H.Y.; Bok, R.; Criekinge, M.V.; Ferrone, M.; Slater, J.B.; Xu, D.; et al. Development of methods and feasibility of using hyperpolarized carbon-13 imaging data for evaluating brain metabolism in patient studies. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 80, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miloushev, V.Z.; Granlund, K.L.; Boltyanskiy, R.; Lyashchenko, S.K.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Mellinghoff, I.K.; Brennan, C.W.; Tabar, V.; Yang, T.J.; Holodny, A.I.; et al. Metabolic Imaging of the Human Brain with Hyperpolarized 13C Pyruvate Demonstrates 13C Lactate Production in Brain Tumor Patients. Cancer Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, S.J.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Vigneron, D.B.; Larson, P.E.Z.; Harzstark, A.L.; Ferrone, M.; van Criekinge, M.; Chang, J.W.; Bok, R.; Park, I.; et al. Metabolic Imaging of Patients with Prostate Cancer Using Hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 198ra108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granlund, K.L.; Tee, S.S.; Vargas, H.A.; Lyashchenko, S.K.; Reznik, E.; Fine, S.; Laudone, V.; Eastham, J.A.; Touijer, K.A.; Reuter, V.E.; et al. Hyperpolarized MRI of Human Prostate Cancer Reveals Increased Lactate with Tumor Grade Driven by Monocarboxylate Transporter 1. Cell Metab. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Y.; Larson, P.E.Z.; Gordon, J.W.; Bok, R.A.; Ferrone, M.; van Criekinge, M.; Carvajal, L.; Cao, P.; Pauly, J.M.; Kerr, A.B.; et al. Technique development of 3D dynamic CS-EPSI for hyperpolarized 13 C pyruvate MR molecular imaging of human prostate cancer. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Y.; Aggarwal, R.; Bok, R.A.; Ohliger, M.A.; Zhu, Z.; Lee, P.; Gordon, J.W.; Criekinge, M.V.; Carvajal, L.; Slater, J.B.; et al. Hyperpolarized 13 C-pyruvate MRI detects real-time metabolic flux in prostate cancer metastases to bone and liver: A clinical feasibility study. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.; Latifoltojar, A.; Neves, J.B.; Papoutsaki, M.V.; Gong, F.; Comment, A.; Costa, A.S.H.; Glaser, M.; Tran-Dang, M.A.; El Sheikh, S.; et al. First-in-human in vivo non-invasive assessment of intra-tumoral metabolic heterogeneity in renal cell carcinoma. BJR Case Rep. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stødkilde-Jørgensen, H.; Laustsen, C.; Hansen, E.S.S.; Schulte, R.; Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J.H.; Comment, A.; Frøkiær, J.; Ringgaard, S.; Bertelsen, L.B.; Ladekarl, M.; et al. Pilot Study Experiences with Hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate MRI in Pancreatic Cancer Patients. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeder, S.B.; Brittain, J.H.; Grist, T.M.; Yen, Y.F. Least-squares chemical shift separation for (13)C metabolic imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2007, 26, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesinger, F.; Weidl, E.; Menzel, M.I.; Janich, M.A.; Khegai, O.; Glaser, S.J.; Haase, A.; Schwaiger, M.; Schulte, R.F. IDEAL spiral CSI for dynamic metabolic MR imaging of hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 68, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.W.; Niles, D.J.; Fain, S.B.; Johnson, K.M. Joint spatial-spectral reconstruction and k-t spirals for accelerated 2D spatial/1D spectral imaging of 13C dynamics. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 71, 1435–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiens, C.N.; Friesen-Waldner, L.J.; Wade, T.P.; Sinclair, K.J.; McKenzie, C.A. Chemical shift encoded imaging of hyperpolarized (13) C pyruvate. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 74, 1682–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niles, D.J.; Gordon, J.W.; Huang, G.; Reese, S.; Adamson, E.B.; Djamali, A.; Fain, S.B. Evaluation of renal metabolic response to partial ureteral obstruction with hyperpolarized 13 C MRI. NMR Biomed. 2018, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.Z.; Miller, J.J.; Robson, M.D.; Tyler, D.J. Simultaneous assessment of cardiac metabolism and perfusion using copolarized [1-13 C]pyruvate and 13 C-urea. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 77, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durst, M.; Koellisch, U.; Frank, A.; Rancan, G.; Gringeri, C.V.; Karas, V.; Wiesinger, F.; Menzel, M.I.; Schwaiger, M.; Haase, A.; et al. Comparison of acquisition schemes for hyperpolarised ¹³C imaging. NMR Biomed. 2015, 28, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grist, J.T.; McLean, M.A.; Riemer, F.; Schulte, R.F.; Deen, S.S.; Zaccagna, F.; Woitek, R.; Daniels, C.J.; Kaggie, J.D.; Matys, T.; et al. Quantifying normal human brain metabolism using hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate and magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage 2019, 189, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, C.H.; Chen, A.P.; Lustig, M.; Hargreaves, B.A.; Lupo, J.; Xu, D.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Hurd, R.E.; Pauly, J.M.; Nelson, S.J.; et al. Pulse sequence for dynamic volumetric imaging of hyperpolarized metabolic products. J. Magn. Reson. 2008, 193, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, A.Z.; Chen, A.P.; Hurd, R.E.; Cunningham, C.H. Spectral–spatial excitation for rapid imaging of DNP compounds. NMR Biomed. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.W.; Vigneron, D.B.; Larson, P.E.Z. Development of a symmetric echo planar imaging framework for clinical translation of rapid dynamic hyperpolarized (13) C imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.Z.; Chen, A.P.; Ghugre, N.R.; Ramanan, V.; Lam, W.W.; Connelly, K.A.; Wright, G.A.; Cunningham, C.H. Rapid multislice imaging of hyperpolarized 13C pyruvate and bicarbonate in the heart. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 64, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, J.W.; Chen, H.Y.; Autry, A.; Park, I.; Van Criekinge, M.; Mammoli, D.; Milshteyn, E.; Bok, R.; Xu, D.; Li, Y.; et al. Translation of Carbon-13 EPI for hyperpolarized MR molecular imaging of prostate and brain cancer patients. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 81, 2702–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, C.H.; Lau, J.Y.C.; Chen, A.P.; Geraghty, B.J.; Perks, W.J.; Roifman, I.; Wright, G.A.; Connelly, K.A. Hyperpolarized 13C Metabolic MRI of the Human HeartNovelty and Significance: Initial Experience. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.J.; Lau, A.Z.; Tyler, D.J. Susceptibility-induced distortion correction in hyperpolarized echo planar imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 2135–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geraghty, B.J.; Lau, J.Y.C.; Chen, A.P.; Cunningham, C.H. Dual-Echo EPI sequence for integrated distortion correction in 3D time-resolved hyperpolarized 13C MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wright, A.J.; Hesketh, R.L.; Hu, D.e.; Brindle, K.M. A referenceless Nyquist ghost correction workflow for echo planar imaging of hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate and [1-13C]lactate. NMR Biomed. 2018, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, G.D.; von Morze, C.; Bok, R.; Koelsch, B.L.; Van Criekinge, M.; Smith, K.J.; Shang, H.; Larson, P.E.Z.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Vigneron, D.B. High resolution (13)C MRI with hyperpolarized urea: In vivo T(2) mapping and (15)N labeling effects. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2014, 33, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milshteyn, E.; Morze, C.V.; Gordon, J.W.; Zhu, Z.; Larson, P.E.Z.; Vigneron, D.B. High spatiotemporal resolution bSSFP imaging of hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate and [1-13C]lactate with spectral suppression of alanine and pyruvate-hydrate. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 80, 1048–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffler, K. Tomographic imaging with nonuniform angular sampling. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1999, 23, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Morze, C.; Sukumar, S.; Reed, G.D.; Larson, P.E.Z.; Bok, R.A.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Vigneron, D.B. Frequency-specific SSFP for hyperpolarized (13)C metabolic imaging at 14.1 T. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 31, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leupold, J.; Maansson, S.; Petersson, J.S.; Hennig, J.; Wieben, O. Fast multiecho balanced SSFP metabolite mapping of (1)H and hyperpolarized (13)C compounds. MAGMA 2009, 22, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varma, G.; Wang, X.; Vinogradov, E.; Bhatt, R.S.; Sukhatme, V.P.; Seth, P.; Lenkinski, R.E.; Alsop, D.C.; Grant, A.K. Selective spectroscopic imaging of hyperpolarized pyruvate and its metabolites using a single-echo variable phase advance method in balanced SSFP. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustig, M.; Donoho, D.L.; Santos, J.M.; Pauly, J.M. Compressed Sensing MRI. IEEE Signal Proc. Mag. 2008, 25, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wespi, P.; Steinhauser, J.; Kwiatkowski, G.; Kozerke, S. High-resolution hyperpolarized metabolic imaging of the rat heart using k–t PCA and k–t SPARSE. NMR Biomed. 2018, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geraghty, B.J.; Lau, J.Y.C.; Chen, A.P.; Cunningham, C.H. Accelerated 3D echo-planar imaging with compressed sensing for time-resolved hyperpolarized 13C studies. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 77, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, P.; Shin, P.J.; Park, I.; Najac, C.; Marco-Rius, I.; Vigneron, D.B.; Nelson, S.J.; Ronen, S.M.; Larson, P.E.Z. Accelerated high-bandwidth MR spectroscopic imaging using compressed sensing. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 76, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVience, S.J.; Mayer, D. Speeding up dynamic spiral chemical shift imaging with incoherent sampling and low-rank matrix completion. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 77, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.R.; Peterson, E.T.; Gordon, J.W.; Niles, D.J.; Rowland, I.J.; Kurpad, K.N.; Fain, S.B. In vivo imaging and spectroscopy of dynamic metabolism using simultaneous 13C and 1H MRI. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grist, J.T.; Hansen, E.S.S.; Sánchez-Heredia, J.D.; McLean, M.A.; Tougaard, R.; Riemer, F.; Schulte, R.F.; Kaggie, J.D.; Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J.H.; Laustsen, C.; et al. Creating a clinical platform for carbon-13 studies using the sodium-23 and proton resonances. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.M.; Wade, T.P.; Friesen-Waldner, L.J.; McKenzie, C.A. Optimizing SNR for multi-metabolite hyperpolarized carbon-13 MRI using a hybrid flip-angle scheme. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 84, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durst, M.; Koellisch, U.; Gringeri, C.; Janich, M.A.; Rancan, G.; Frank, A.; Wiesinger, F.; Menzel, M.I.; Haase, A.; Schulte, R.F. Bolus tracking for improved metabolic imaging of hyperpolarised compounds. J. Magn. Reson. 2014, 243C, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.Y.; Walker, C.M.; Michel, K.A.; Venkatesan, A.M.; Lai, S.Y.; Bankson, J.A. Influence of parameter accuracy on pharmacokinetic analysis of hyperpolarized pyruvate. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 3239–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, P.E.Z.; Chen, H.Y.; Gordon, J.W.; Korn, N.; Maidens, J.; Arcak, M.; Tang, S.; Criekinge, M.; Carvajal, L.; Mammoli, D.; et al. Investigation of analysis methods for hyperpolarized 13C-pyruvate metabolic MRI in prostate cancer patients. NMR Biomed. 2018, 31, e3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miloushev, V.Z.; Di Gialleonardo, V.; Salamanca-Cardona, L.; Correa, F.; Granlund, K.L.; Keshari, K.R. Hyperpolarized 13C pyruvate mouse brain metabolism with absorptive-mode EPSI at 1T. J. Magn. Reson. 2017, 275, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, S.E.; Kettunen, M.I.; Gallagher, F.A.; Hu, D.E.; Lerche, M.; Wolber, J.; Golman, K.; Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J.H.; Brindle, K.M. Detecting tumor response to treatment using hyperpolarized 13C magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1382–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, R.J.; Schornack, P.A.; Secomb, T.W.; Raghunand, N. Causes and effects of heterogeneous perfusion in tumors. Neoplasia 1999, 1, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Milshteyn, E.; Reed, G.; Gordon, J.; Bok, R.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, Z.; Vigneron, D.B.; Larson, P.E.Z. A regional bolus tracking and real-time B1 calibration method for hyperpolarized 13 C MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 81, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazey, T.; Reed, G.D.; Garbow, J.R.; von Morze, C. Metabolite-specific echo planar imaging of hyperpolarized 13C-pyruvate at 4. In 7T. In Proceedings of the ISMRM, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 15–20 May 2021; p. 5102. [Google Scholar]
- Schulte, R.F.; Sacolick, L.; Deppe, M.H.; Janich, M.A.; Schwaiger, M.; Wild, J.M.; Wiesinger, F. Transmit gain calibration for nonproton MR using the Bloch-Siegert shift. NMR Biomed. 2011, 24, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zierhut, M.L.; Yen, Y.F.; Chen, A.P.; Bok, R.; Albers, M.J.; Zhang, V.; Tropp, J.; Park, I.; Vigneron, D.B.; Kurhanewicz, J.; et al. Kinetic modeling of hyperpolarized 13C1-pyruvate metabolism in normal rats and TRAMP mice. J. Magn. Reson. 2010, 202, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khegai, O.; Schulte, R.F.; Janich, M.A.; Menzel, M.I.; Farrell, E.; Otto, A.M.; Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J.H.; Glaser, S.J.; Haase, A.; Schwaiger, M.; et al. Apparent rate constant mapping using hyperpolarized [1-(13)C]pyruvate. NMR Biomed. 2014, 27, 1256–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankson, J.A.; Walker, C.M.; Ramirez, M.S.; Stefan, W.; Fuentes, D.; Merritt, M.E.; Lee, J.; Sandulache, V.C.; Chen, Y.; Phan, L.; et al. Kinetic Modeling and Constrained Reconstruction of Hyperpolarized [1-13C]-Pyruvate Offers Improved Metabolic Imaging of Tumors. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 4708–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyperpolarized-MRI-Toolbox. Available online: https://github.com/LarsonLab/hyperpolarized-mri-toolbox (accessed on 11 June 2021).
- Daniels, C.J.; McLean, M.A.; Schulte, R.F.; Robb, F.J.; Gill, A.B.; McGlashan, N.; Graves, M.J.; Schwaiger, M.; Lomas, D.J.; Brindle, K.M.; et al. A comparison of quantitative methods for clinical imaging with hyperpolarized (13)C-pyruvate. NMR Biomed. 2016, 29, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, D.K.; Orton, M.R.; Mariotti, E.; Boult, J.K.R.; Panek, R.; Jafar, M.; Parkes, H.G.; Jamin, Y.; Miniotis, M.F.; Al-Saffar, N.M.S.; et al. Model free approach to kinetic analysis of real-time hyperpolarized 13C magnetic resonance spectroscopy data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Larson, P.E.Z.; Gordon, J.W. Hyperpolarized Metabolic MRI—Acquisition, Reconstruction, and Analysis Methods. Metabolites 2021, 11, 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060386
Larson PEZ, Gordon JW. Hyperpolarized Metabolic MRI—Acquisition, Reconstruction, and Analysis Methods. Metabolites. 2021; 11(6):386. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060386
Chicago/Turabian StyleLarson, Peder Eric Zufall, and Jeremy W. Gordon. 2021. "Hyperpolarized Metabolic MRI—Acquisition, Reconstruction, and Analysis Methods" Metabolites 11, no. 6: 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060386
APA StyleLarson, P. E. Z., & Gordon, J. W. (2021). Hyperpolarized Metabolic MRI—Acquisition, Reconstruction, and Analysis Methods. Metabolites, 11(6), 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060386





