Mass Spectrometry-Based Lipidomics Reveals Differential Changes in the Accumulated Lipid Classes in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
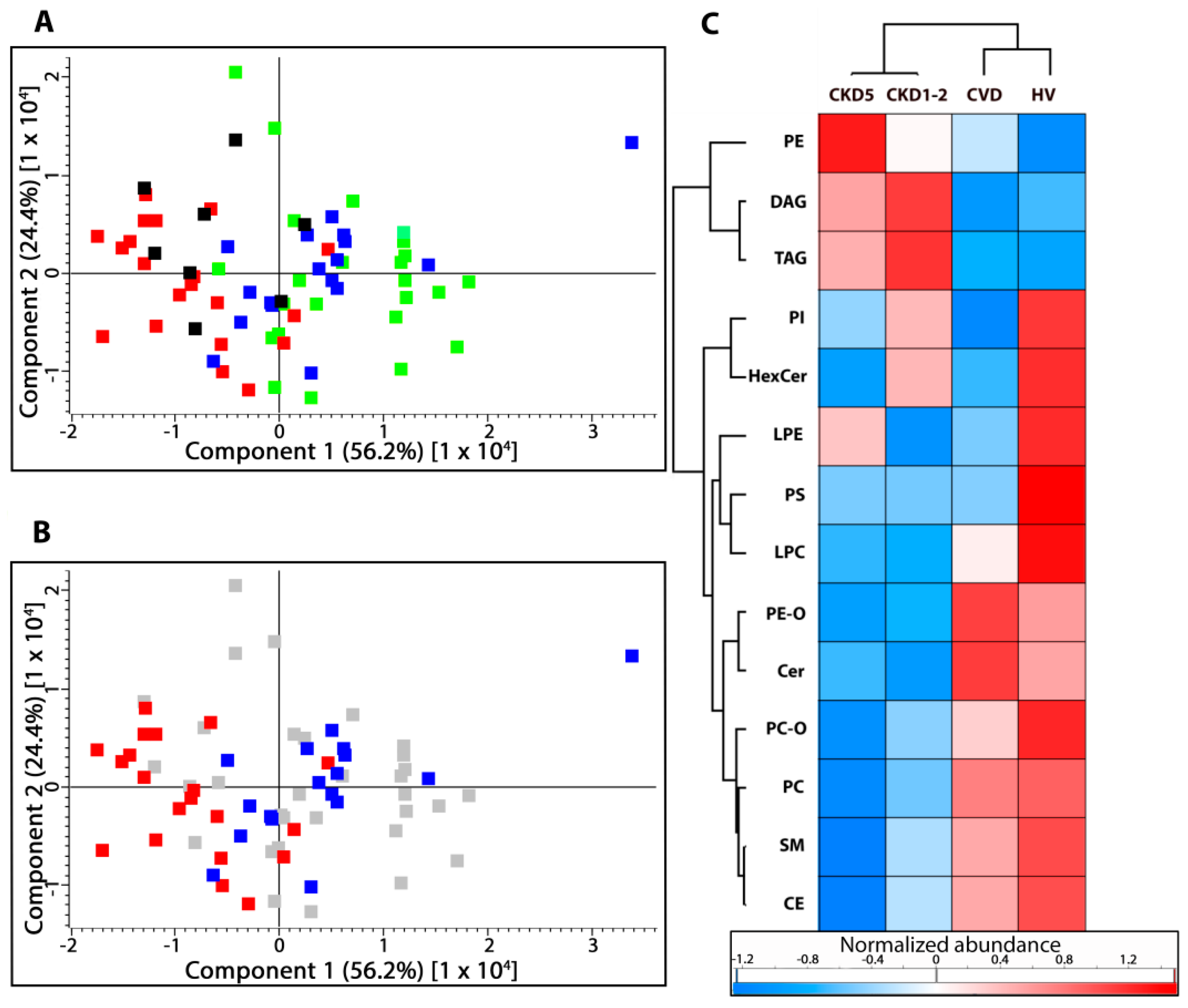
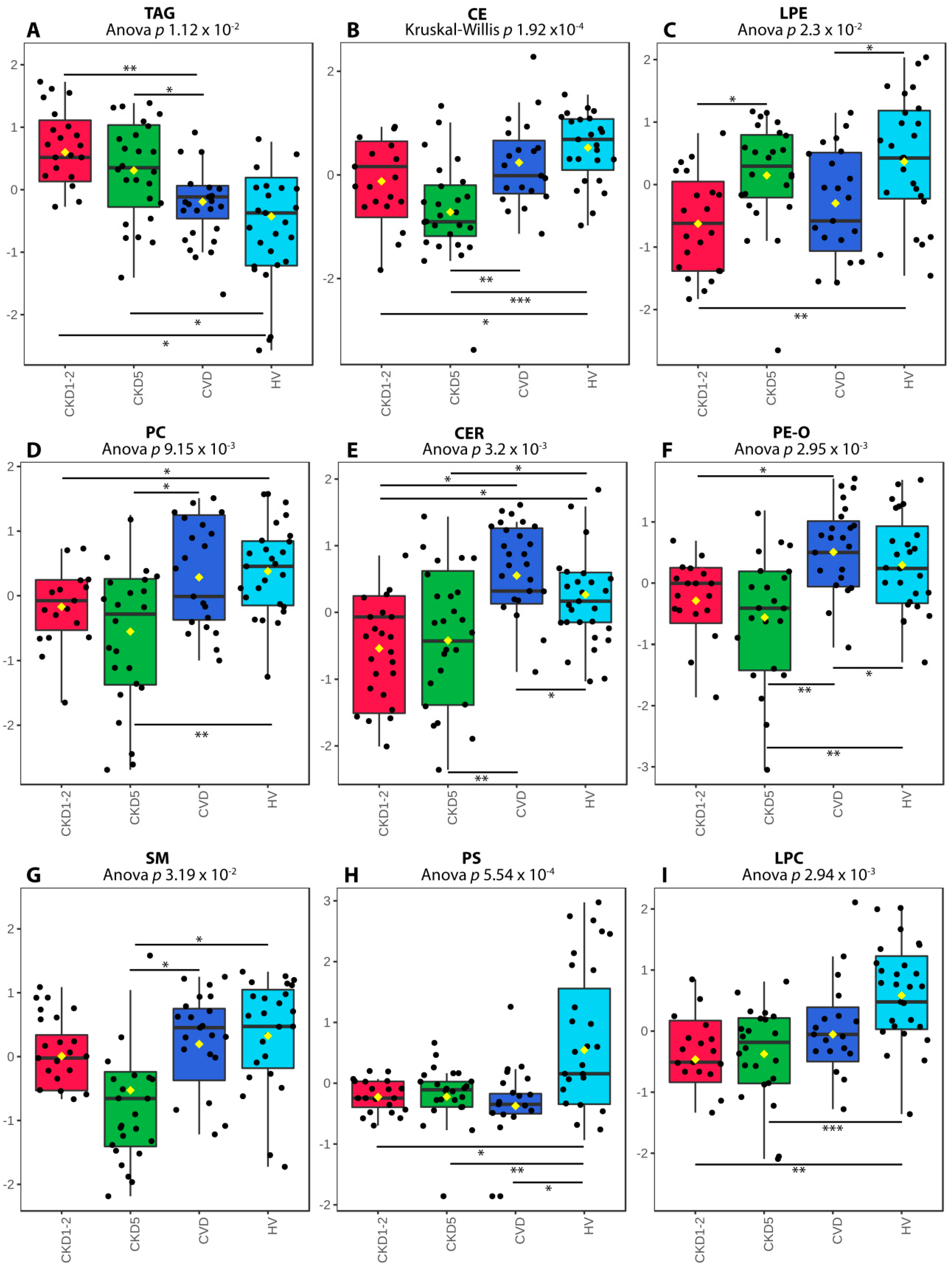
2.1. Lipid Classes Analysis Using Shotgun Approach
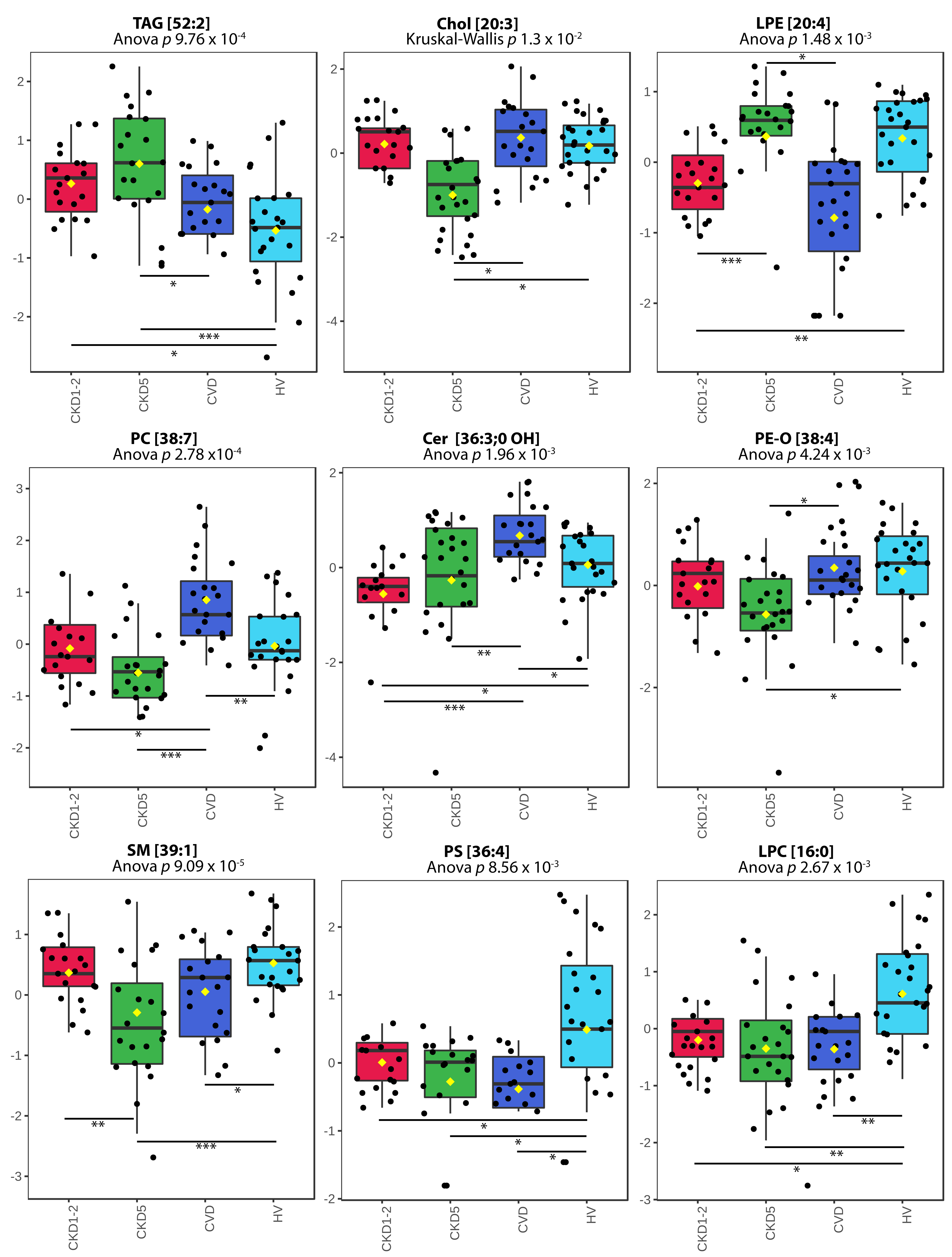
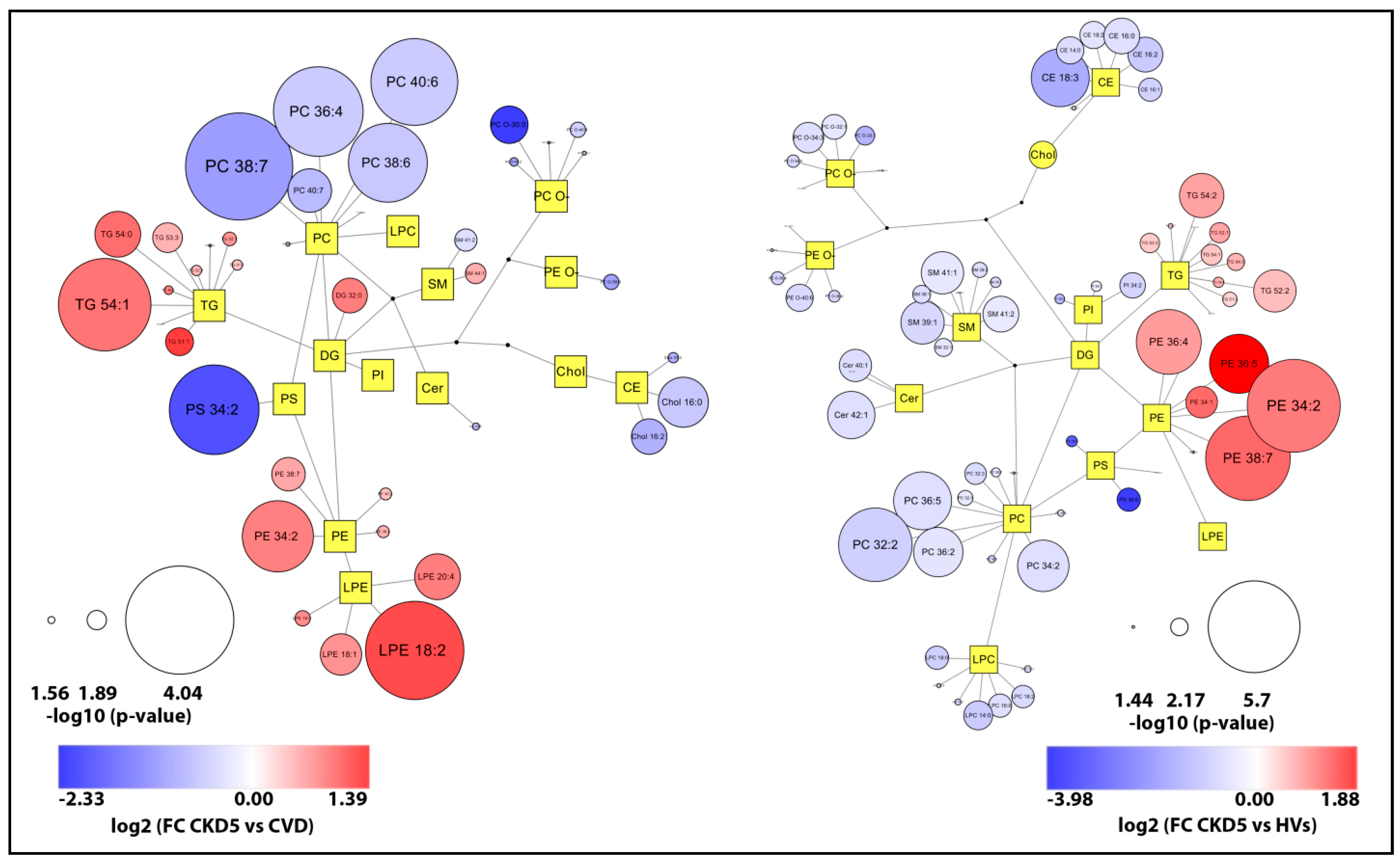
2.2. Lipid Species Analysis Utilizing Shotgun Approach
2.3. Analysis of Selected Lipid Precursor and Components Using GC-MS Profiling
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Subject and Samples
4.2. Lipid Extraction Method
4.3. Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Lipid Fractions (Shotgun-Based Lipidomics)
4.4. Data Processing and Identification of Lipid Species
4.5. Functional Analysis
4.6. GC-MS Analysis of Plasma Samples for Identification of Selected Lipid-Related Compounds
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levin, A.; Stevens, P.; Bilous, R. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 1e150. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, S.; Kon, V. Mechanisms for increased cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney dysfunction. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2009, 18, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ecder, T. Early diagnosis saves lives: Focus on patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Briasoulis, A.; Bakris, G.L. Chronic Kidney Disease as a Coronary Artery Disease Risk Equivalent. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2013, 15, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santo, N.G.; Cirillo, M.; Perna, A.; De Santo, L.S.; Anastasio, P.; Pollastro, M.R.; De Santo, R.M.; Iorio, L.; Cotrufo, M.; Rossi, F. The heart in uremia: Role of hypertension, hypotension, and sleep apnea. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2001, 38, S38–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olechnowicz-Tietz, S.; Gluba, A.; Paradowska, A.; Banach, M.; Rysz, J. The risk of atherosclerosis in patients with chronic kidney disease. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2013, 45, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Beto, J.A.; Coronado, B.E.; Eknoyan, G.; Foley, R.N.; Kasiske, B.L.; Klag, M.J.; Mailloux, L.U.; Manske, C.L.; Meyer, K.B.; et al. Controlling the epidemic of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease: What do we know? What do we need to learn? Where do we go from here? National Kidney Foundation Task Force on Cardiovascular Disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1998, 32, 853–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffrin, E.L.; Lipman, M.L.; Mann, J.F.E. Chronic kidney disease: Effects on the cardiovascular system. Circulation 2007, 116, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jager, D.J.; Grootendorst, D.C.; Jager, K.J.; Van Dijk, P.C.; Tomas, L.M.J.; Ansell, D.; Collart, F.; Finne, P.; Heaf, J.G.; De Meester, J.; et al. Cardiovascular and noncardiovascular mortality among patients starting dialysis. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2009, 302, 1782–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunath, C.N.; Rawal, J.R.; Irani, P.M.; Madhu, K. Atherogenic dyslipidemia. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 17, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Block, G.; Humphreys, M.H.; Kopple, J.D. Reverse epidemiology of cardiovascular risk factors in maintenance dialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 793–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Coresh, J.; Eustace, J.A.; Longenecker, J.C.; Jaar, B.; Fink, N.E.; Tracy, R.P.; Powe, N.R.; Klag, M.J. Association Between Cholesterol Level and Mortality in Dialysis Patients. JAMA 2004, 291, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baigent, C.; Landray, M.J.; Wheeler, D.C. Misleading associations between cholesterol and vascular outcomes in dialysis patients: The need for randomized trials. Semin. Dial. 2007, 20, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, J.; Weir, M. The unique character of cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease and its implications for treatment with lipid-lowering drugs. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 2, 766–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdivielso, J.M.; Rodríguez-Puyol, D.; Pascual, J.; Barrios, C.; Bermúdez-López, M.; Sánchez-Niño, M.D.; Pérez-Fernández, M.; Ortiz, A. Atherosclerosis in Chronic Kidney Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 1938–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Mukku, V.K.; Ahmad, M. Coronary artery disease in patients with chronic kidney disease: A clinical update. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2013, 9, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannock, L. Dyslipidemia in Chronic Kidney Disease; MDText.com, Inc.: Portland, OR, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Obialo, C.I.; Ofili, E.O.; Norris, K.C. Statins and Cardiovascular Disease Outcomes in Chronic Kidney Disease: Reaffirmation vs. Repudiation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luczak, M.; Formanowicz, D.; Marczak, Ł.; Suszyńska-Zajczyk, J.; Pawliczak, E.; Wanic-Kossowska, M.; Stobiecki, M. ITRAQ-based proteomic analysis of plasma reveals abnormalities in lipid metabolism proteins in chronic kidney disease-related atherosclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, A.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Chariyavilaskul, P.; Dhaun, N.; Melville, V.; Goddard, J.; Webb, D.J.; Pitt, A.R.; Spickett, C.M. Top-down lipidomics of low density lipoprotein reveal altered lipid profiles in advanced chronic kidney disease. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshinnia, F.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Karnovsky, A.; Soni, T.; Wang, X.; Xie, D.; Yang, W.; Shafi, T.; Weir, M.R.; He, J.; et al. Lipidomic Signature of Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease in the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort. Kidney Int. Rep. 2016, 1, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekroos, K.; Jänis, M.; Tarasov, K.; Hurme, R.; Laaksonen, R. Lipidomics: A Tool for Studies of Atherosclerosis. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2010, 12, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.-Y.; Cheng, X.; Lin, R.-C. Lipidomics Applications for Discovering Biomarkers of Diseases in Clinical Chemistry. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 313, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holčapek, M.; Červená, B.; Cífková, E.; Lísa, M.; Chagovets, V.; Vostálová, J.; Bancířová, M.; Galuszka, J.; Hill, M. Lipidomic analysis of plasma, erythrocytes and lipoprotein fractions of cardiovascular disease patients using UHPLC/MS, MALDI-MS and multivariate data analysis. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 990, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graessler, J.; Schwudke, D.; Schwarz, P.E.H.; Herzog, R.; Shevchenko, A.; Bornstein, S.R. Top-down lipidomics reveals ether lipid deficiency in blood plasma of hypertensive patients. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holčapek, M.; Liebisch, G.; Ekroos, K. Lipidomic Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 4249–4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surma, M.A.; Herzog, R.; Vasilj, A.; Klose, C.; Christinat, N.; Morin-Rivron, D.; Simons, K.; Masoodi, M.; Sampaio, J.L. An automated shotgun lipidomics platform for high throughput, comprehensive, and quantitative analysis of blood plasma intact lipids. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2015, 117, 1540–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cajka, T.; Fiehn, O. Comprehensive analysis of lipids in biological systems by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Trends Analyt. Chem. 2014, 61, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matyash, V.; Liebisch, G.; Kurzchalia, T.V.; Shevchenko, A.; Schwudke, D. Lipid extraction by methyl-tert-butyl ether for high-throughput lipidomics. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwudke, D.; Schuhmann, K.; Herzog, R.; Bornstein, S.R.; Shevchenko, A. Shotgun Lipidomics on High Resolution Mass Spectrometers. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a004614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandya, V.; Rao, A.; Chaudhary, K. Lipid abnormalities in kidney disease and management strategies. World J. Nephrol. 2015, 4, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolasevic, I.; Žutelija, M.; Mavrinac, V.; Orlic, L. Dyslipidemia in patients with chronic kidney disease: Etiology and management. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2017, 10, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimihodimos, V.; Dounousi, E.; Siamopoulos, K.C. Dyslipidemia in Chronic Kidney Disease: An Approach to Pathogenesis and Treatment. Am. J. Nephrol. 2008, 28, 958–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.S.; Jung, M.H.; Yeo, H.D.; Kim, H.J.; Yang, J.I.; Roh, G.S.; Chang, S.H.; Park, D.J. N-acetylcysteine attenuates glycerol-induced acute kidney injury by regulating MAPKs and Bcl-2 family proteins. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homsi, E.; Janino, P.; De Faria, J.B.L. Role of caspases on cell death, inflammation, and cell cycle in glycerol-induced acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, S.; Souza, L.C.R.; Cronin, M.T.; Waaga-Gasser, A.M.; Grossi, M.F.; Franco, G.R.; Tagliati, C.A. Biomarkers and in vitro strategies for nephrotoxicity and renal disease assessment. Nephrol. Ren. Dis. 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, G.C.; Carrero, J.J.; Heimbürger, O.; Barany, P.; Stenvinkel, P. Plasma Fatty Acids in Chronic Kidney Disease: Nervonic Acid Predicts Mortality. J. Ren. Nutr. 2012, 22, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczuko, M.; Kaczkan, M.; Drozd, A.; Maciejewska, D.; Palma, J.; Owczarzak, A.; Marczuk, N.; Rutkowski, P.; Małgorzewicz, S. Comparison of Fatty Acid Profiles in a Group of Female Patients with Chronic Kidney Diseases (CKD) and Metabolic Syndrome (MetS)–Similar Trends of Changes, Different Pathophysiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, Z.; Kárpáti, I.; Paragh, G.; Buris, L.; Kakuk, G. Relative abundance of some free fatty acids in plasma of uremic patients: Relationship between fatty acids, lipid parameters, and diseases. Nephron 1997, 77, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, T.C.; Miyazaki-Anzai, S.; Masuda, M.; Levi, M.; Demer, L.L.; Tintut, Y.; Miyazaki, M. Increased lipogenesis and stearate accelerate vascular calcification in calcifying vascular cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 23938–23949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Lorenzo, M.; Gonzalez-Calero, L.; Ramos-Barron, A.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Gomez-Alamillo, C.; García-Segura, J.M.; Ortiz, A.; Arias, M.; Vivanco, F.; Alvarez-Llamas, G. Urine metabolomics insight into acute kidney injury point to oxidative stress disruptions in energy generation and H2S availability. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminzadeh, M.A.; Vaziri, N.D. Downregulation of the renal and hepatic hydrogen sulfide (H2S)-producing enzymes and capacity in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perna, A.F.; Luciano, M.G.; Ingrosso, D.; Pulzella, P.; Sepe, I.; Lanza, D.; Violetti, E.; Capasso, R.; Lombardi, C.; De Santo, N.G. Hydrogen sulphide-generating pathways in haemodialysis patients: A study on relevant metabolites and transcriptional regulation of genes encoding for key enzymes. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 3756–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perna, A.F.; Luciano, M.G.; Ingrosso, D.; Raiola, I.; Pulzella, P.; Sepe, I.; Lanza, D.; Violetti, E.; Capasso, R.; Lombardi, C.; et al. Hydrogen sulfide, the third gaseous signaling molecule with cardiovascular properties, is decreased in hemodialysis patients. J. Ren. Nutr. 2010, 20, S11–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luczak, M.; Formanowicz, D.; Marczak, Ł.; Pawliczak, E.; Wanic-Kossowska, M.; Figlerowicz, M.; Stobiecki, M. Deeper insight into chronic kidney disease-related atherosclerosis: Comparative proteomic studies of blood plasma using 2DE and mass spectrometry. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseki, K.; Ikemiya, Y.; Iseki, C.; Takishita, S. Proteinuria and the risk of developing end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 1468–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpatrick, R.D.; McAllister, C.J.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Derose, S.F.; Kopple, J.D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Association between Serum Lipids and Survival in Hemodialysis Patients and Impact of Race. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luczak, M.; Suszynska-Zajczyk, J.; Marczak, L.; Formanowicz, D.; Pawliczak, E.; Wanic-Kossowska, M.; Stobiecki, M. Label-free quantitative proteomics reveals differences in molecular mechanism of atherosclerosis related and non-related to chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayrard, N.; Ficheux, A.; Duranton, F.; Guzman, C.; Szwarc, I.; Vetromile, F.; Cazevieille, C.; Brunet, P.; Servel, M.-F.; Argilés, À.; et al. Consequences of increasing convection onto patient care and protein removal in hemodialysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeboah, J.; McNamara, C.; Jiang, X.C.; Tabas, I.; Herrington, D.M.; Burke, G.L.; Shea, S. Association of plasma sphingomyelin levels and incident coronary heart disease events in an adult population: Multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pongrac Barlovic, D.; Harjutsalo, V.; Sandholm, N.; Forsblom, C.; Groop, P.H. Sphingomyelin and progression of renal and coronary heart disease in individuals with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Bosch, J.P.; Lewis, J.B.; Greene, T.; Rogers, N.; Roth, D. A More Accurate Method To Estimate Glomerular Filtration Rate from Serum Creatinine: A New Prediction Equation. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999, 130, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Clinical Guideline Centre (UK). Chronic Kidney Disease (Partial Update): Early Identification and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Adults in Primary and Secondary Care; NICE Clinical Guidelines, No. 182; National Clinical Guideline Centre: London, UK, 2014; pp. 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Herzog, R.; Schuhmann, K.; Schwudke, D.; Sampaio, J.L.; Bornstein, S.R.; Schroeder, M.; Shevchenko, A. LipidXplorer: A software for consensual cross-platform lipidomics. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.-M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis Chemical Analysis Working Group (CAWG) Metabolomics Standards Initiative (MSI). Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molenaar, M.R.; Jeucken, A.; Wassenaar, T.A.; van de Lest, C.H.A.; Brouwers, J.F.; Helms, J.B. LION/web: A web-based ontology enrichment tool for lipidomic data analysis. Gigascience 2019, 8, giz061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.; Mann, M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Psychogios, N.; Young, N.; Wishart, D.S. MetaboAnalyst: A web server for metabolomic data analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W652–W660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| HV | CKD1-2 | CKD5 | CVD | p -Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age [years] | 51 ± 16 | 63 ± 5 | 61 ± 14 | 58 ± 10 | 0.04 |
| Males | 75% | 75% | 75% | 75% | 0.64 |
| eGFR [ml/min/1.73 m2] | 102 ± 11 | 70 ± 6 | 6 ± 4 | 96 ± 11 | <0.01 |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 24 ± 2 | 29 ± 4 | 25 ± 3 | 28 ± 4 | 0.08 |
| Arterial hypertension | 0% | 100% | 100% | 100% | <0.01 |
| Glucose [mM] | 4 ± 0.5 | 5.6 ± 0.5 | 5.8 ± 0.4 | 5.41 ± 0.6 | <0.01 |
| Anticoagulant treatment | 0% | 79% | 54% | 87.5% | <0.01 |
| Statin treatment | 0% | 87.5% | 67% | 75% | <0.01 |
| Blood pressure treatment | 0% | 100% | 100% | 100% | <0.01 |
| Total cholesterol [mg/dL] | 190 ± 24 | 199 ± 46 | 170 ± 29 | 187 ± 49 | <0.01 |
| HDL cholesterol [mg/dL] | 65 ± 16 | 62 ± 19 | 44 ± 10 | 53 ± 13 | <0.01 |
| LDL cholesterol [mg/dL] | 90 ± 28 | 131 ± 39 | 84 ± 27 | 101 ± 41 | <0.01 |
| Triacylglycerols [mg/dL] | 101 ± 56 | 129 ± 66 | 127 ± 60 | 101 ± 42 | <0.01 |
| hsCRP [mg/L] | 1.53 ± 0.4 | 2.32 ± 2.1 | 16.67 ± 11 | 2.17 ± 4.6 | <0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marczak, L.; Idkowiak, J.; Tracz, J.; Stobiecki, M.; Perek, B.; Kostka-Jeziorny, K.; Tykarski, A.; Wanic-Kossowska, M.; Borowski, M.; Osuch, M.; et al. Mass Spectrometry-Based Lipidomics Reveals Differential Changes in the Accumulated Lipid Classes in Chronic Kidney Disease. Metabolites 2021, 11, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11050275
Marczak L, Idkowiak J, Tracz J, Stobiecki M, Perek B, Kostka-Jeziorny K, Tykarski A, Wanic-Kossowska M, Borowski M, Osuch M, et al. Mass Spectrometry-Based Lipidomics Reveals Differential Changes in the Accumulated Lipid Classes in Chronic Kidney Disease. Metabolites. 2021; 11(5):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11050275
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarczak, Lukasz, Jakub Idkowiak, Joanna Tracz, Maciej Stobiecki, Bartłomiej Perek, Katarzyna Kostka-Jeziorny, Andrzej Tykarski, Maria Wanic-Kossowska, Marcin Borowski, Marcin Osuch, and et al. 2021. "Mass Spectrometry-Based Lipidomics Reveals Differential Changes in the Accumulated Lipid Classes in Chronic Kidney Disease" Metabolites 11, no. 5: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11050275
APA StyleMarczak, L., Idkowiak, J., Tracz, J., Stobiecki, M., Perek, B., Kostka-Jeziorny, K., Tykarski, A., Wanic-Kossowska, M., Borowski, M., Osuch, M., Formanowicz, D., & Luczak, M. (2021). Mass Spectrometry-Based Lipidomics Reveals Differential Changes in the Accumulated Lipid Classes in Chronic Kidney Disease. Metabolites, 11(5), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11050275








