Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Coumarin-Linked 4-Anilinomethyl-1,2,3-Triazoles as Potent Inhibitors of Carbonic Anhydrases IX and XIII Involved in Tumorigenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
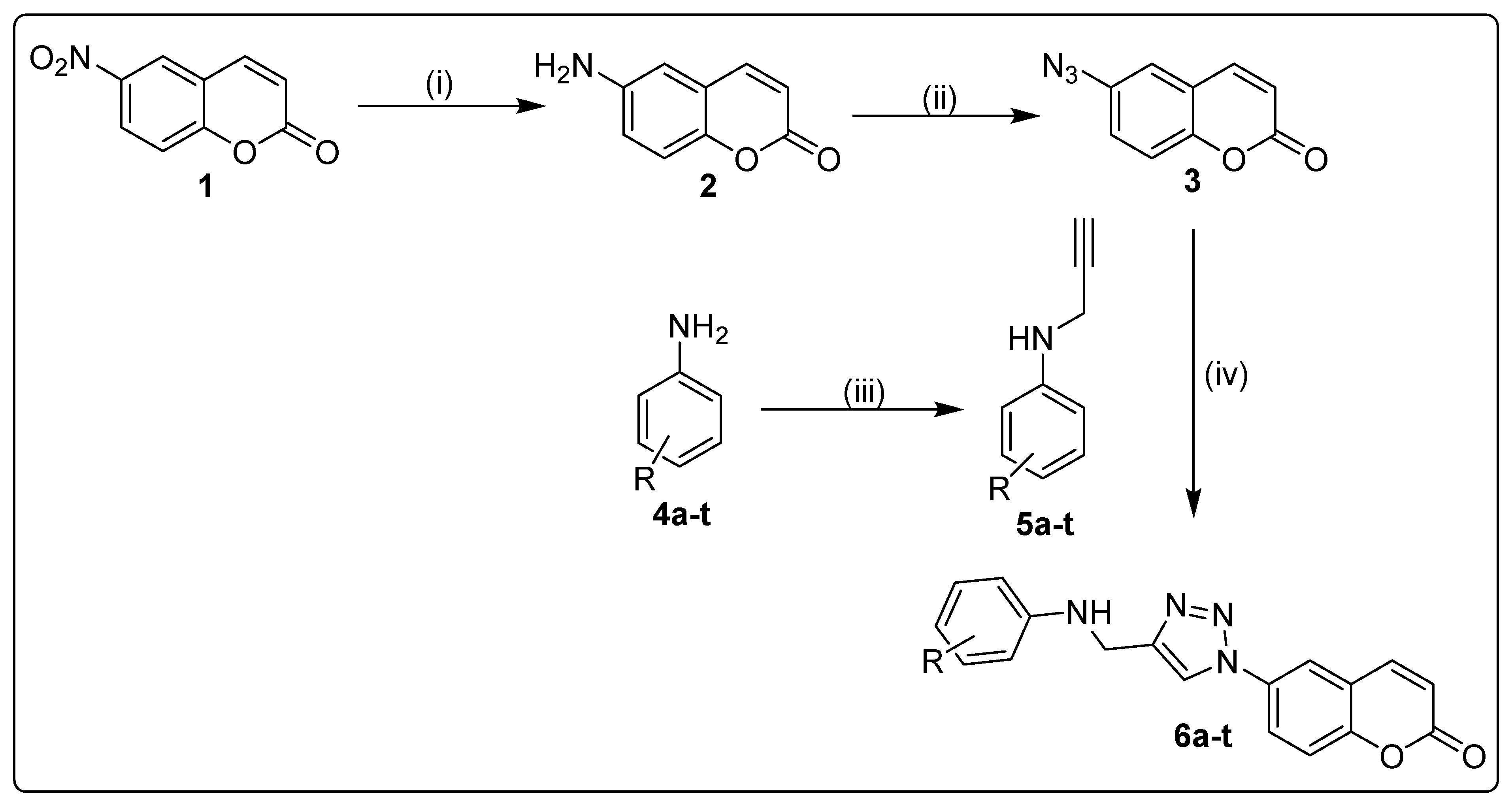
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibition
- The newly synthesized compounds, 6a–t were found to be ineffective against the cytosolic isoforms hCAs I and II (Ki > 50,000 nM).
- The transmembrane tumor-associated isoform hCA IX was inhibited by the compounds, 6a–t in a low to moderate nanomolar range with the Ki values ranging from 36.3 to 642.8 nM. Compound 6e possessing a 4-bromo substitution on the aniline moiety exhibited the most potent inhibition of hCA IX with a Ki value of 36.3 nM. Compound 6f is possessing a 4-isopropyl substitution on the aniline moiety and compound 6a possessing a 4-methyl substitution on the aniline moiety exhibited Ki values of 45.0 and 48.4 nM, respectively. Barring compounds 6p, 6r and 6t, all the compounds displayed Ki values < 100 nM against hCA IX. Additionally, the compounds containing electron-donating substituents on the phenyl ring of aniline displayed better inhibitory profiles over the electron-withdrawing substituents.
- The cytosolic isoform hCA XIII was inhibited by the compounds 6a–t in a low to high nanomolar range with the Ki values ranging from 90.1 to 8149 nM. Compound 6b possessing an unsubstituted phenyl ring showed the highest inhibition of hCA XIII with a Ki value of 90.1 nM. The other compounds which exhibited Ki values < 100 nM are compounds 6j, 6a, 6o and 6q with Ki values of 91.6, 92.6, 95.4 and 96.7 nM, respectively.
- Thus, it is implied from the overall results that the compounds 6a–t are highly selective inhibitors of hCAs IX and XIII over the off-target isoforms, hCAs I and II.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General
3.1.1. Synthesis of 6-Amino-2H-Chromen-2-One (2)
3.1.2. Synthesis of 6-Azido-2H-Chromen-2-One (3)
3.1.3. Synthesis of N-Propargylated Anilines (5a–t)
3.1.4. Synthesis of Coumarin-Triazole Hybrids (6a–t)
3.2. CA Inhibition
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, D.L.; Yuan, A.T.; Korkola, N.C.; Stillman, M.J. Interplay between Carbonic Anhydrases and Metallothioneins: Structural Control of Metalation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrases and metabolism. Metabolites 2018, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Structure and function of carbonic anhydrases. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 2023–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alterio, V.; Di Fiore, A.; Ambrosio, K.D.; Supuran, C.T.; de Simone, G. Multiple binding modes of inhibitors to carbonic anhydrases: How to design specific drugs targeting 15 different isoforms? Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 4421–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, S.K.; Cormerais, Y.; Pouysségur, J. Hypoxia and cellular metabolism in tumour pathophysiology. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 2439–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatum, J.L.; Kelloff, G.J.; Gillies, R.J.; Arbeit, J.M.; Brown, J.M.; Chao, K.C.; Chapman, J.D.; Eckelman, W.C.; Fyles, A.W.; Giaccia, A.J.; et al. Hypoxia: Importance in tumor biology, noninvasive measurement by imaging, and value of its measurement in the management of cancer therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2006, 82, 699–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiche, J.; Brahimi-Horn, M.C.; Pouysségur, J. Tumour hypoxia induces a metabolic shift causing acidosis: A common feature in cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 771–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahimi-Horn, M.C.; Bellot, G.; Pouysségur, J. Hypoxia and energetic tumour metabolism. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2011, 21, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastorekova, S.; Parkkila, S.; Zavada, J. Tumor-associated carbonic anhydrases and their clinical significance. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2006, 42, 167–216. [Google Scholar]
- Guler, O.O.; De Simone, G.; Supuran, C.T. Drug design studies of the novel antitumor targets carbonic anhydrase IX and XII. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mboge, M.Y.; Mahon, B.P.; McKenna, R.; Frost, S.C. Carbonic Anhydrases: Role in pH Control and Cancer. Metabolites 2018, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorekova, S.; Gillies, R.J. The role of carbonic anhydrase IX in cancer development: Links to hypoxia, acidosis, and beyond. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019, 38, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibition and the Management of Hypoxic Tumors. Metabolites 2017, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilvo, M.; Supuran, C.T.; Parkkila, S. Characterization and inhibition of the recently discovered carbonic anhydrase isoforms CA XIII, XIV and XV. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yogosawa, S.; Nakayama, J.; Nishi, M.; Ryo, A.; Yoshida, K. Carbonic anhydrase 13 suppresses bone metastasis in breast cancer. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2021, 27, 100332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, F.; Pinna, C.; Dallavalle, S.; Tamborini, L.; Pinto, A. An Overview of Coumarin as a Versatile and Readily Accessible Scaffold with Broad-Ranging Biological Activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, A.; Carta, F.; Nocentini, A.; Winum, J.Y.; Zalubovskis, R.; Akdemir, A.; Onnis, V.; Eldehna, W.M.; Capasso, C.; Simone, G.; et al. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Targeting Metabolism and TumorMicroenvironment. Metabolites 2020, 10, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maresca, A.; Temperini, C.; Vu, H.; Pham, N.B.; Poulsen, S.A.; Scozzafava, A.; Quinn, R.J.; Supuran, C.T. Non-zinc mediated inhibition of carbonic anhydrases: Coumarins are a new class of suicide inhibitors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3057–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thacker, P.S.; Angeli, A.; Argulwar, O.S.; Tiwari, P.L.; Arifuddin, M.; Supuran, C.T. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of coumarin linked 1,2,4-oxadiazoles as selective carbonic anhydrase IX and XII inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 98, 103739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozorov, K.; Zhao, J.; Aisa, H.A. 1,2,3-Triazole-containing hybrids as leads in medicinal chemistry: A recent overview. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 3511–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Coumarin carbonic anhydrase inhibitors from natural sources. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 1462–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinchilli, K.K.; Angeli, A.; Thacker, P.S.; Korra, L.N.; Biswas, R.; Arifuddin, M.; Supuran, C.T. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of 1,2,3-Triazole-Linked Triazino [5, 6-B]Indole-Benzene Sulfonamide Conjugates as Potent Carbonic Anhydrase I, II, IX, and XIII Inhibitors. Metabolites 2020, 10, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Gu, L.; Wang, B.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zeng, S.; Shen, Z. Discovery of novel coumarin derivatives as potent and orally bio-available BRD4 inhibitors based on scaffold hopping. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, V.D.; de Faria, B.M.; Colombo, E.; Ascari, L.; Freitas, G.P.; Flores, L.S.; Cordeiro, Y.; Romão, L.; Buarque, C.D. Design, synthesis, structural characterization and in vitro evaluation of new 1,4-disubstituted-1,2,3-triazole derivatives against glioblastoma cells. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 83, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z.; Yang, S.; Yan, R. AgNO2 as the NO Source for the Synthesis of Substituted Pyrazole N-Oxides from N-Propargylamines. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 5928–5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifah, R.G. The carbon dioxide hydration activity of carbonic anhydrase. I. Stop-flowkinetic studies on the native human isoenzymes B and C. J. Biol. Chem. 1971, 246, 2561–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, M.A.; Eldehna, W.M.; Nocentini, A.; Fahim, S.H.; Bonardi, A.; Elgazar, A.A.; Kryštof, V.; Soliman, D.H.; Abdel-Aziz, H.A.; Gratteri, P.; et al. Sulfonamide-based ring-fused analogues for CAN508 as novel carbonic anhydrase inhibitors endowed with antitumor activity: Design, synthesis, and in vitro biological evaluation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 189, 112019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clima, L.; Craciun, B.; Angeli, A.; Petreni, A.; Bonardi, A.; Nocentini, A.; Carta, F.; Gratteri, P.; Pinteala, M.; Supuran, C.T. Synthesis, Computational Studies and Assessment of in Vitro Activity of Squalene Derivatives as Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2020, 15, 2052–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, M.; Eladwy, R.A.; Nocentini, A.; El Hadi, S.R.A.; Ghabbour, H.A.; Abdel-Megeed, A.; Eldehna, W.M.; Abdel-Aziz, H.A.; Supuran, C.T. Synthesis of bulky-tailed sulfonamides incorporating pyrido[2,3-d][1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrimidin-1(5H)-yl) moieties and evaluation of their carbonic anhydrases I, II, IV and IX inhibitory effects. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 2210–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, P.S.; Alvala, M.; Arifuddin, M.; Angeli, A.; Supuran, C.T. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of coumarin-3-carboxamides as selective carbonic anhydrase IX and XII inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 86, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
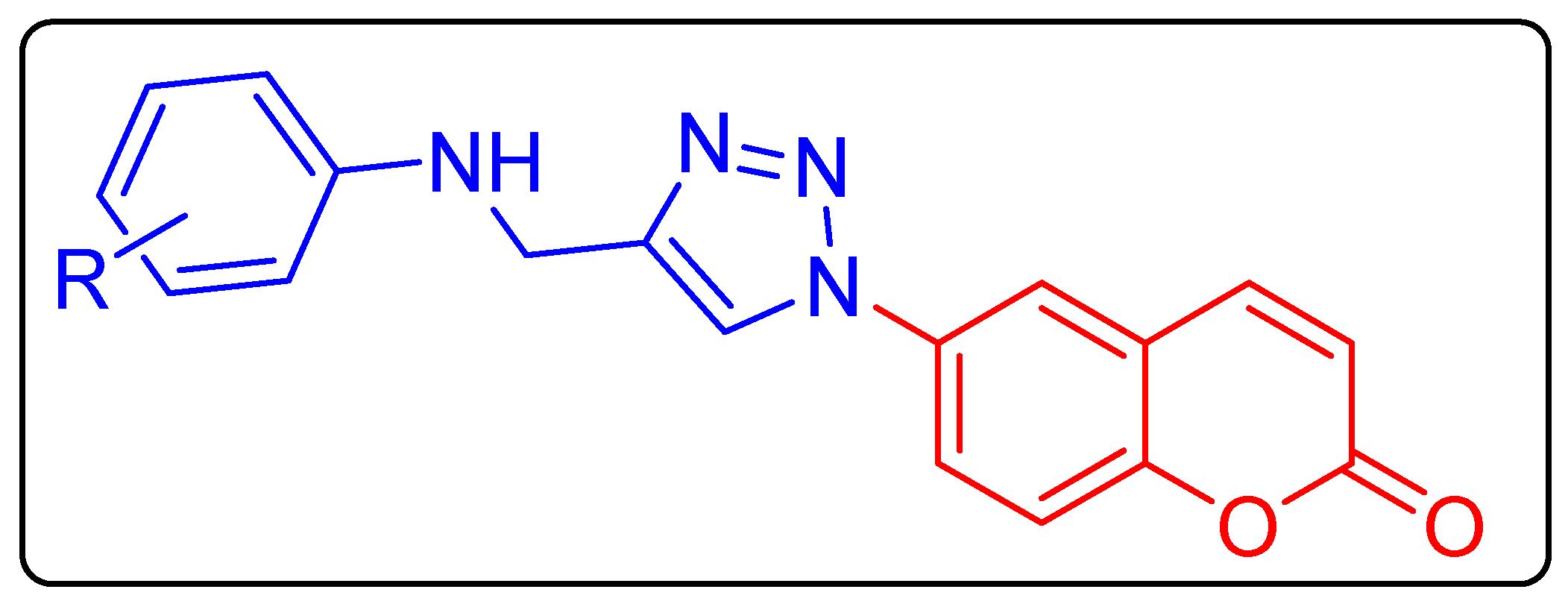

| Ki (nM) * | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | Structure | hCA I | hCAII | hCA IX | hCA XIII |
| 6a | 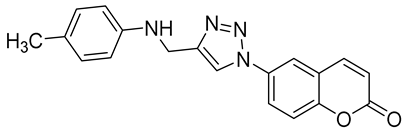 | >50,000 | >50,000 | 48.4 | 92.6 |
| 6b |  | >50,000 | >50,000 | 60.8 | 90.1 |
| 6c |  | >50,000 | >50,000 | 73.3 | 950.5 |
| 6d |  | >50,000 | >50,000 | 151.9 | 897.6 |
| 6e |  | >50,000 | >50,000 | 36.3 | 883.2 |
| 6f |  | >50,000 | >50,000 | 45.0 | 8149 |
| 6g | 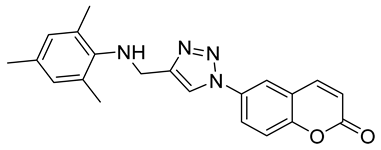 | >50,000 | >50,000 | 64.8 | 902.7 |
| 6h |  | >50,000 | >50,000 | 73.0 | 905.4 |
| 6i | 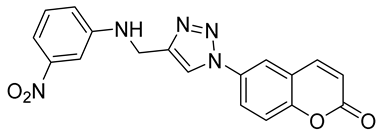 | >50,000 | >50,000 | 85.7 | 896.1 |
| 6j |  | >50,000 | >50,000 | 304.9 | 91.8 |
| 6k | 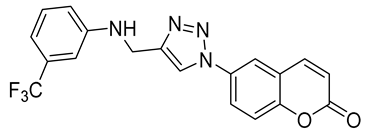 | >50,000 | >50,000 | 69.1 | 6426 |
| 6l | 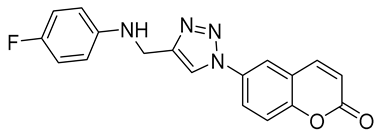 | >50,000 | >50,000 | 86.1 | 839.8 |
| 6m | 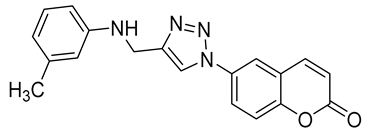 | >50,000 | >50,000 | 80.1 | 795.2 |
| 6n |  | >50,000 | >50,000 | 89.3 | 703.4 |
| 6o | 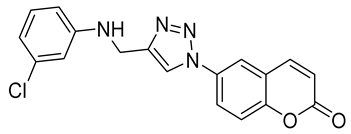 | >50,000 | >50,000 | 92.7 | 95.4 |
| 6p | 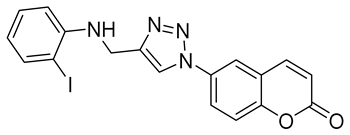 | >50,000 | >50,000 | 573.9 | 594.4 |
| 6q |  | >50,000 | >50,000 | 96.4 | 96.7 |
| 6r | 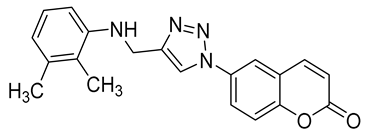 | >50,000 | >50,000 | 462.1 | 550.1 |
| 6s |  | >50,000 | >50,000 | 90.9 | 664.4 |
| 6t |  | >50,000 | >50,000 | 642.8 | 6034 |
| AAZ | 250 | 12.1 | 25.8 | 17.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thacker, P.S.; Tiwari, P.L.; Angeli, A.; Srikanth, D.; Swain, B.; Arifuddin, M.; Supuran, C.T. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Coumarin-Linked 4-Anilinomethyl-1,2,3-Triazoles as Potent Inhibitors of Carbonic Anhydrases IX and XIII Involved in Tumorigenesis. Metabolites 2021, 11, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11040225
Thacker PS, Tiwari PL, Angeli A, Srikanth D, Swain B, Arifuddin M, Supuran CT. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Coumarin-Linked 4-Anilinomethyl-1,2,3-Triazoles as Potent Inhibitors of Carbonic Anhydrases IX and XIII Involved in Tumorigenesis. Metabolites. 2021; 11(4):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11040225
Chicago/Turabian StyleThacker, Pavitra S., Prerna L. Tiwari, Andrea Angeli, Danaboina Srikanth, Baijayantimala Swain, Mohammed Arifuddin, and Claudiu T. Supuran. 2021. "Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Coumarin-Linked 4-Anilinomethyl-1,2,3-Triazoles as Potent Inhibitors of Carbonic Anhydrases IX and XIII Involved in Tumorigenesis" Metabolites 11, no. 4: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11040225
APA StyleThacker, P. S., Tiwari, P. L., Angeli, A., Srikanth, D., Swain, B., Arifuddin, M., & Supuran, C. T. (2021). Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Coumarin-Linked 4-Anilinomethyl-1,2,3-Triazoles as Potent Inhibitors of Carbonic Anhydrases IX and XIII Involved in Tumorigenesis. Metabolites, 11(4), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11040225









