Dynamics of the Metabolome of Aliinostoc sp. PMC 882.14 in Response to Light and Temperature Variations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Extraction Compartment Specificity and Metabolite Diversity of Aliinostoc sp. PMC 882.14
2.2. Dynamics of Metabolite Production under Normal (Control), Higher Light, and Higher Temperature Conditions
2.2.1. Influence of Growth on Metabolite Dynamics
2.2.2. Influence of Light and Temperature Variations on the Metabolomic Dynamics
3. Discussion
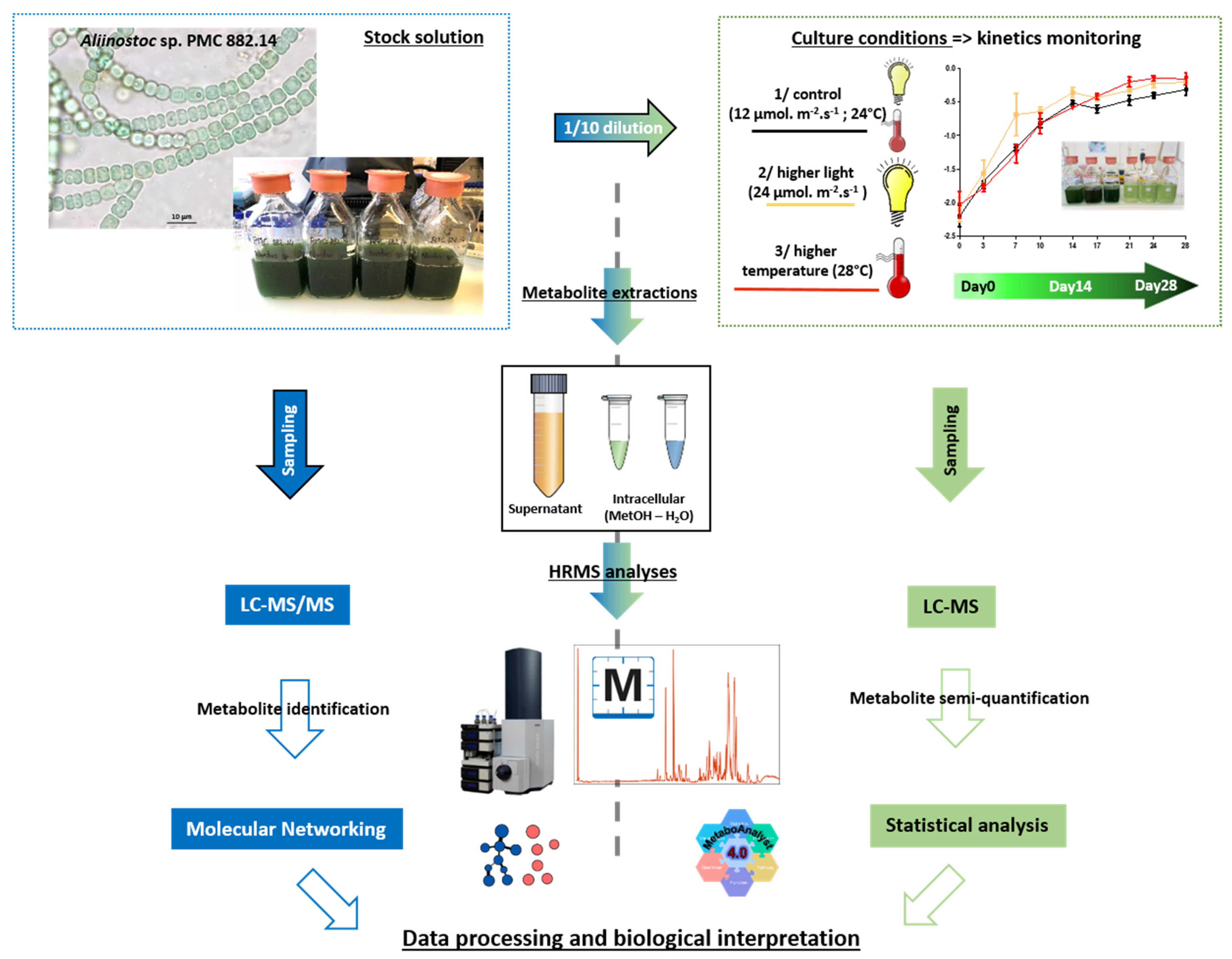
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Biological Material
4.2. Culture Conditions and Sampling
4.3. Biomass Dynamics
4.4. Metabolite Extractions
4.5. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
4.6. Simple MS Mode Analyses
4.7. MS/MS Mode Analyses
4.8. Statistical Treatments
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Whitton, B.A.; Potts, M. Ecology of Cyanobacteria II: Their Diversity in Space and Time; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Dittmann, E.; Gugger, M.; Sivonen, K.; Fewer, D.P. Natural product biosynthetic diversity and comparative genomics of the cyanobacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leão, P.N.; Engene, N.; Antunes, A.; Gerwick, W.H.; Vasconcelos, V. The chemical ecology of cyanobacteria. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 372–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerwick, W.H.; Fenner, A.M. Drug discovery from marine microbes. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Parihar, P.; Singh, M.; Bajguz, A.; Kumar, J.; Singh, S.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. Uncovering potential applications of cyanobacteria and algal metabolites in biology, agriculture and medicine: Current status and future prospects. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Sonani, R.R.; Madamwar, D. Cyanobacterial sunscreen scytonemin: Role in photoprotection and biomedical research. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 176, 1551–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, K.P.; Gacesa, R.; Long, P.F.; Young, A.R. Molecular photoprotection of human keratinocytes in vitro by the naturally occurring mycosporine-like amino acid palythine. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 178, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Welker, M.; Von Döhren, H. Cyanobacterial peptides—Nature’s own combinatorial biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 530–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kehr, J.C.; Picchi, D.G.; Dittmann, E. Natural product biosyntheses in cyanobacteria: A treasure trove of unique enzymes. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2011, 7, 1622–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demay, J.; Bernard, C.; Reinhardt, A.; Marie, B. Natural products from cyanobacteria: Focus on beneficial activities. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holland, A.; Kinnear, S. Interpreting the possible ecological role(s) of cyanotoxins: Compounds for competitive advantage and/or physiological aide? Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2239–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leflaive, J.; Ten-Hage, L. Algal and cyanobacterial secondary metabolites in freshwaters: A comparison of allelopathic compounds and toxins. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameyama, K.; Sugiura, N.; Inamori, Y.; Maekawa, T. Characteristics of microcystin production in the cell cycle ofMicrocystis viridis. Environ. Toxicol. 2004, 19, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natumi, R.; Janssen, E.M.L. Cyanopeptide co-production dynamics beyond mirocystins and effects of growth stages and nutrient availability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6063–6072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barofsky, A.; Vidoudez, C.; Pohnert, G. Metabolic profiling reveals growth stage variability in diatom exudates. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2009, 7, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, M.; Vialas, V.; Karlsen, J.; Maddalo, G.; Edfors, F.; Forsström, B.; Uhlén, M.; Käll, L.; Hudson, E.P. Growth of cyanobacteria is constrained by the abundance of light and carbon assimilation proteins. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 478–486.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: Causes, consequences, and controls. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.W.; Berry, D.L.; Boyer, G.L.; Gobler, C.J. The effects of temperature and nutrients on the growth and dynamics of toxic and non-toxic strains of Microcystis during cyanobacteria blooms. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Prajapat, G.; Abrar, M.; Ledwani, L.; Singh, A.; Agrawal, A. Cyanobacteria as efficient producers of mycosporine-like amino acids. J. Basic Microbiol. 2017, 57, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, C.; Hamlaoui, S.; Piquet, B.; Toutirais, G.; Yéprémian, C.; Reinhardt, A.; Duperron, S.; Marie, B.; Demay, J.; Bernard, C. Diversity of cyanobacteria from thermal muds (Balaruc-Les-Bains, France) with the description of Pseudochroococcus coutei gen. nov., sp. nov. FEMS Microbes 2021, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demay, J.; Halary, S.; Knittel-Obrecht, A.; Villa, P.; Duval, C.; Hamlaoui, S.; Roussel, T.; Yéprémian, C.; Reinhardt, A.; Bernard, C.; et al. Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and wound-healing properties of cyanobacteria from thermal mud of Balaruc-Les-Bains, France: A multi-approach study. Biomolecules 2020, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogle, L.M.; Williamson, R.T.; Gerwick, W.H. Somamides A and B, two new depsipeptide analogues of dolastatin 13 from a Fijian cyanobacterial assemblage of Lyngbya majuscula and Schizothrix species. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 716–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervou, S.K.; Gkelis, S.; Kaloudis, T.; Hiskia, A.; Mazur-Marzec, H. New microginins from cyanobacteria of Greek freshwaters. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 125961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Süssmuth, R.D.; Mainz, A. Nonribosomal peptide synthesis—Principles and prospects. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 3770–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.R.; Pinto, E.; Torres, M.A.; Dörr, F.; Mazur-Marzec, H.; Szubert, K.; Tartaglione, L.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Miles, C.O.; Beach, D.G.; et al. CyanoMetDB, a comprehensive public database of secondary metabolites from cyanobacteria. Water Res. 2021, 196, 117017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonova, I.; Kuzmin, A.; Deeva, D.; Sorokovikova, E.; Potapov, S.; Lomakina, A.; Belykh, O. Cyanobacteria nostoc punctiforme from abyssal benthos of lake baikal: Unique ecology and metabolic potential. Indian J. Microbiol. 2017, 57, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandclément, C.; Tannières, M.; Moréra, S.; Dessaux, Y.; Faure, D. Quorum quenching: Role in nature and applied developments. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 40, 86–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonk, L.; Visser, P.M.; Christiansen, G.; Dittmann, E.; Snelder, E.O.F.M.; Wiedner, C.; Mur, L.R.; Huisman, J. The microcystin composition of the cyanobacterium Planktothrix agardhii changes toward a more toxic variant with increasing light intensity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5177–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, M.; Kulshreshtha, J.; Singh, G.P. Growth and biopigment accumulation of cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis at different light intensities and temperature. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 1128–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Řezanka, T.; Temina, M.; Tolstikov, A.G.; Dembitsky, V.M. Natural microbial UV radiation filters—Mycosporine-like amino acids. Folia Microbiol. 2004, 49, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, H.; Waditee-Sirisattha, R. Mycosporine-like Amino Acids as Multifunctional Secondary Metabolites in Cyanobacteria: From Biochemical to Application Aspects, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volumn 59, ISBN 9780444641793. [Google Scholar]
- Kultschar, B.; Dudley, E.; Wilson, S.; Llewellyn, C.A. Intracellular and extracellular metabolites from the cyanobacterium chlorogloeopsis fritschii, PCC 6912, during 48 hours of UV-B exposure. Metabolites 2019, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinu, F.R.; Granucci, N.; Daniell, J.; Han, T.-L.; Carneiro, S.; Rocha, I.; Nielsen, J.; Villas-Boas, S.G. Metabolite secretion in microorganisms: The theory of metabolic overflow put to the test. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cano, M.; Holland, S.C.; Artier, J.; Burnap, R.L.; Ghirardi, M.; Morgan, J.A.; Yu, J. Glycogen synthesis and metabolite overflow contribute to energy balancing in cyanobacteria. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yéprémian, C.; Catherine, A.; Bernard, C.; Congestri, R.; Elersek, T.; Pilkaityte, R. Chlorophyll a extraction and determination. In Handbook of Cyanobacterial Monitoring and Cyanotoxin Analysis; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2017; pp. 331–334. [Google Scholar]
- Catherine, A.; Maloufi, S.; Congestri, R.; Viaggiu, E.; Pilkaityte, R. Cyanobacterial samples: Preservation, enumeration, and biovolume measurements. In Handbook of Cyanobacterial Monitoring and Cyanotoxin Analysis; Wiley, J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2017; pp. 315–330. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with global natural products social molecular networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, M.R.; Pinto, E.; Torres, M.A.; Dörr, F.; Mazur-Marzec, H.; Szubert, K.; Tartaglione, L.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Miles, C.O.; Beach, D.G.; et al. S75 | CyanoMetDB | Comprehensive Database of Secondary Metabolites from Cyanobacteria. 2021. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/4562688#.YXlLgp5BxPY (accessed on 14 March 2020).
- Chong, J.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. Using MetaboAnalyst 4.0 for comprehensive and integrative metabolomics data analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2019, 68, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, Y.C.; Speed, T.P. A multivariate empirical Bayes statistic for replicated microarray time course data. Ann. Stat. 2006, 34, 2387–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le Moigne, D.; Demay, J.; Reinhardt, A.; Bernard, C.; Kim Tiam, S.; Marie, B. Dynamics of the Metabolome of Aliinostoc sp. PMC 882.14 in Response to Light and Temperature Variations. Metabolites 2021, 11, 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11110745
Le Moigne D, Demay J, Reinhardt A, Bernard C, Kim Tiam S, Marie B. Dynamics of the Metabolome of Aliinostoc sp. PMC 882.14 in Response to Light and Temperature Variations. Metabolites. 2021; 11(11):745. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11110745
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe Moigne, Damien, Justine Demay, Anita Reinhardt, Cécile Bernard, Sandra Kim Tiam, and Benjamin Marie. 2021. "Dynamics of the Metabolome of Aliinostoc sp. PMC 882.14 in Response to Light and Temperature Variations" Metabolites 11, no. 11: 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11110745
APA StyleLe Moigne, D., Demay, J., Reinhardt, A., Bernard, C., Kim Tiam, S., & Marie, B. (2021). Dynamics of the Metabolome of Aliinostoc sp. PMC 882.14 in Response to Light and Temperature Variations. Metabolites, 11(11), 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11110745





