The Zebra Mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) as a Model Organism for Ecotoxicological Studies: A Prior 1H NMR Spectrum Interpretation of a Whole Body Extract for Metabolism Monitoring
Abstract
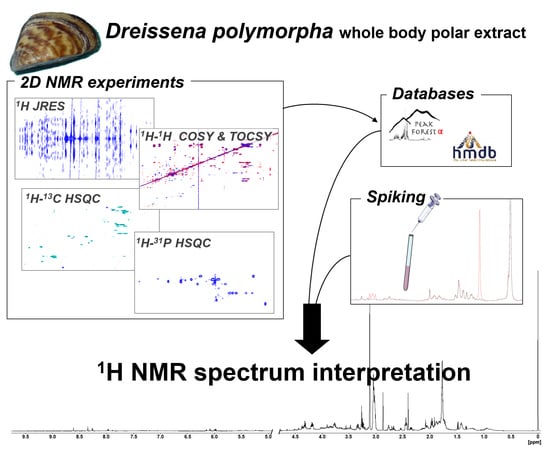
1. Introduction
2. Results
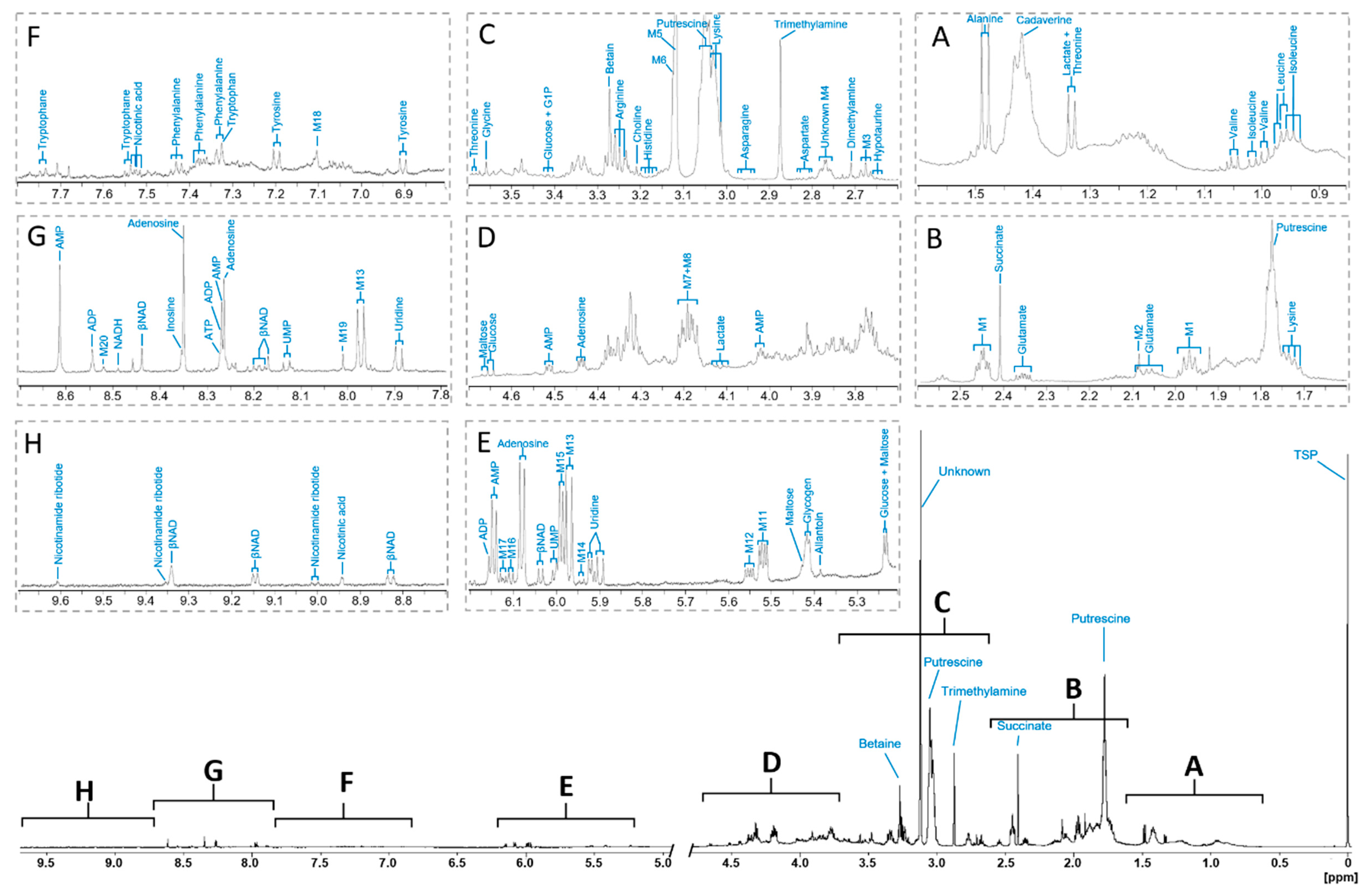
2.1. 1D 1H Reference Spectrum Annotation
2.2. Metabolites Assigned as Unknown
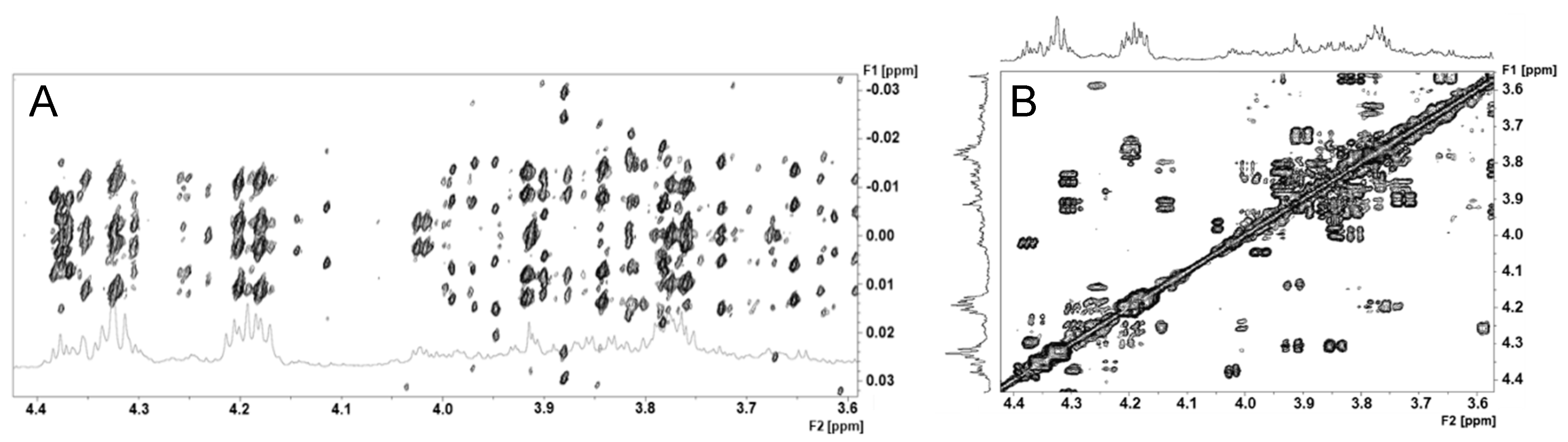
2.3. Signal Superposition in the 1H NMR Spectrum
3. Discussion
3.1. Informative Potential of NMR Based Metabolomics in D. polymorpha
3.2. Dealing with Metabolome Spectrum Complexity
3.3. Novelty of the Study
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Zebra Mussel Sampling
4.2. Sample Preparation
4.3. NMR Spectroscopy
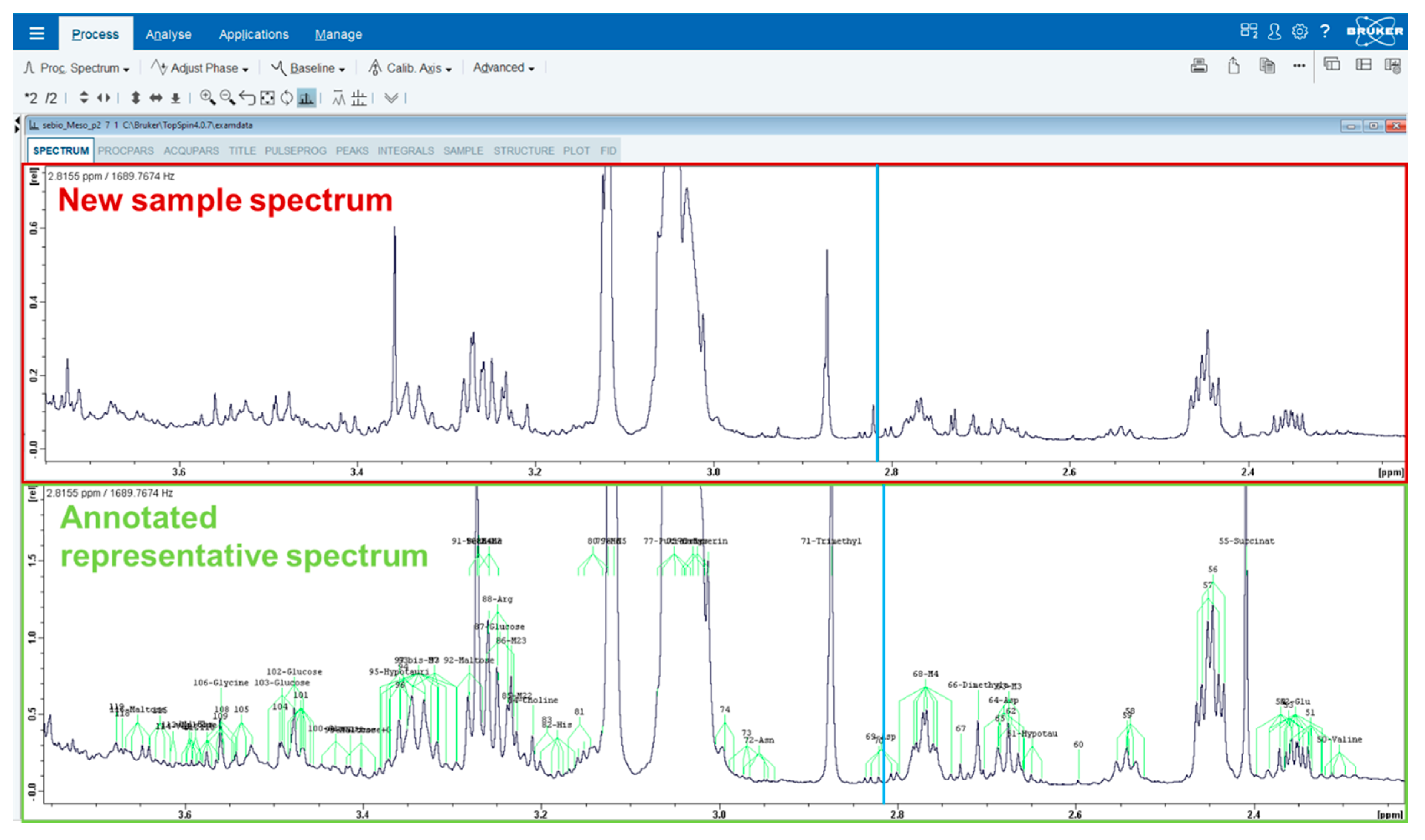
4.4. Metabolite Identification
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loos, R.; Gawlik, B.M.; Locoro, G.; Rimaviciute, E.; Contini, S.; Bidoglio, G. EU-wide survey of polar organic persistent pollutants in European river waters. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Gin, K.Y.-H.; Lin, A.Y.-C.; Reinhard, M. Impacts of emerging organic contaminants on freshwater resources: Review of recent occurrences, sources, fate and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 6062–6069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Dinsdale, R.M.; Guwy, A.J. The occurrence of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, endocrine disruptors and illicit drugs in surface water in South Wales, UK. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3498–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Meyer, K.A.; Jackson, T.M.; Schock, T.B.; Johnson, W.E.; Bearden, D.W. Application of NMR-based metabolomics for environmental assessment in the Great Lakes using zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha). Metabolomics 2015, 11, 1302–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binelli, A.; Della Torre, C.; Magni, S.; Parolini, M. Does zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) represent the freshwater counterpart of Mytilus in ecotoxicological studies? A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 196, 386–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barjhoux, I.; Rioult, D.; Geffard, A.; Ladeiro, M.P. A new protocol for the simultaneous flow cytometric analysis of cytotoxicity and immunotoxicity on zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) hemocytes. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magniez, G.; Franco, A.; Geffard, A.; Rioult, D.; Bonnard, I.; Delahaut, L.; Joachim, S.; Daniele, G.; Vulliet, E.; Porcher, J.-M.; et al. Determination of a new index of sexual maturity (ISM) in zebra mussel using flow cytometry: Interest in ecotoxicology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 11252–11263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binelli, A.; Ricciardi, F.; Riva, C.; Provini, A. New evidences for old biomarkers: Effects of several xenobiotics on EROD and AChE activities in Zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha). Chemosphere 2006, 62, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palais, F.; Dedourge-Geffard, O.; Beaudon, A.; Pain-Devin, S.; Trapp, J.; Geffard, O.; Noury, P.; Gourlay-Francé, C.; Uher, E.; Mouneyrac, C.; et al. One-year monitoring of core biomarker and digestive enzyme responses in transplanted zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha). Ecotoxicol. Lond. Engl. 2012, 21, 888–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binelli, A.; Ricciardi, F.; Riva, C.; Provini, A. Integrated use of biomarkers and bioaccumulation data in Zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) for site-specific quality assessment. Biomark. Biochem. Indic. Expo. Response Susceptibility Chem. 2006, 11, 428–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lafontaine, Y.; Gagné, F.; Blaise, C.; Costan, G.; Gagnon, P.; Chan, H.M. Biomarkers in zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) for the assessment and monitoring of water quality of the St Lawrence River (Canada). Aquat. Toxicol. 2000, 50, 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeault, A.; Gourlay-Francé, C.; Vincent-Hubert, F.; Palais, F.; Geffard, A.; Biagianti-Risbourg, S.; Pain-Devin, S.; Tusseau-Vuillemin, M.-H. Lessons from a transplantation of zebra mussels into a small urban river: An integrated ecotoxicological assessment. Environ. Toxicol. 2010, 25, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potet, M.; Devin, S.; Pain-Devin, S.; Rousselle, P.; Giambérini, L. Integrated multi-biomarker responses in two dreissenid species following metal and thermal cross-stress. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OMICS: Complete Systems, Complete Analyses. Available online: www.setac.org/resource/resmgr/publications_and_resources/setac_tip_omics.pdf. (accessed on 25 April 2020).
- Leprêtre, M.; Almunia, C.; Armengaud, J.; Salvador, A.; Geffard, A.; Palos-Ladeiro, M. The immune system of the freshwater zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, decrypted by proteogenomics of hemocytes and plasma compartments. J. Proteomics 2019, 202, 103366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotton, B.; Paris, A.; Le Manach, S.; Blond, A.; Duval, C.; Qiao, Q.; Catherine, A.; Combes, A.; Pichon, V.; Bernard, C.; et al. Specificity of the metabolic signatures of fish from cyanobacteria rich lakes. Chemosphere 2019, 226, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bundy, J.G.; Davey, M.P.; Viant, M.R. Environmental metabolomics: A critical review and future perspectives. Metabolomics 2008, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markley, J.L.; Brüschweiler, R.; Edison, A.S.; Eghbalnia, H.R.; Powers, R.; Raftery, D.; Wishart, D.S. The future of NMR-based metabolomics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 43, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weckwerth, W. Metabolomics in systems biology. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2003, 54, 669–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappello, T. NMR-based metabolomics of aquatic organisms. eMagRes 2020, 9, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnefille, B.; Gomez, E.; Alali, M.; Rosain, D.; Fenet, H.; Courant, F. Metabolomics assessment of the effects of diclofenac exposure on Mytilus galloprovincialis: Potential effects on osmoregulation and reproduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H.; Jia, X.; Cai, W. Gender-specific metabolic responses in gonad of mussel Perna viridis to triazophos. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 123, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, T.; Fernandes, D.; Maisano, M.; Casano, A.; Bonastre, M.; Bebianno, M.J.; Mauceri, A.; Fasulo, S.; Porte, C. Sex steroids and metabolic responses in mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis exposed to drospirenone. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 143, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.-K.; Jung, Y.-S.; Park, J.-C.; Seo, J.; Choi, M.-S.; Hwang, G.-S. Characterizing the effect of heavy metal contamination on marine mussels using metabolomics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1874–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappello, T.; Maisano, M.; Mauceri, A.; Fasulo, S. 1H NMR-based metabolomics investigation on the effects of petrochemical contamination in posterior adductor muscles of caged mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 142, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Wang, Q.; Wu, H.; Tan, Q.; Wang, W.-X. A metabolomic study on the biological effects of metal pollutions in oysters Crassostrea sikamea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 102, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Wang, W.-X. Bioaccumulation and metabolomics responses in oysters Crassostrea hongkongensis impacted by different levels of metal pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagana Gowda, G.A.; Raftery, D. Can NMR solve some significant challenges in metabolomics? J. Magn. Reson. 2015, 260, 144–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viant, M.R.; Kurland, I.J.; Jones, M.R.; Dunn, W.B. How close are we to complete annotation of metabolomes? Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2017, 36, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dona, A.C.; Kyriakides, M.; Scott, F.; Shephard, E.A.; Varshavi, D.; Veselkov, K.; Everett, J.R. A guide to the identification of metabolites in NMR-based metabonomics/metabolomics experiments. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, J.R. A new paradigm for known metabolite identification in metabonomics/metabolomics: Metabolite identification efficiency. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, M.D.; Dumontier, M.; Aalbersberg, I.J.; Appleton, G.; Axton, M.; Baak, A.; Blomberg, N.; Boiten, J.-W.; da Santos, L.B.S.; Bourne, P.E.; et al. The FAIR guiding principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pupier, M.; Nuzillard, J.-M.; Wist, J.; Schlörer, N.E.; Kuhn, S.; Erdelyi, M.; Steinbeck, C.; Williams, A.J.; Butts, C.; Claridge, T.D.W.; et al. NMReDATA, a standard to report the NMR assignment and parameters of organic compounds. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2018, 56, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlpine, J.B.; Chen, S.-N.; Kutateladze, A.; MacMillan, J.B.; Appendino, G.; Barison, A.; Beniddir, M.A.; Biavatti, M.W.; Bluml, S.; Boufridi, A.; et al. The value of universally available raw NMR data for transparency, reproducibility, and integrity in natural product research. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 35–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antony, N.D.; Peter, L. JCAMP-DX for NMR. Appl. Spectrosc. 1993, 47, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladeiro, M.P.; Aubert, D.; Villena, I.; Geffard, A.; Bigot, A. Bioaccumulation of human waterborne protozoa by zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha): Interest for water biomonitoring. Water Res. 2014, 48, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contardo-Jara, V.; Lorenz, C.; Pflugmacher, S.; Nützmann, G.; Kloas, W.; Wiegand, C. Exposure to human pharmaceuticals carbamazepine, ibuprofen and bezafibrate causes molecular effects in Dreissena polymorpha. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 105, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolini, M.; Pedriali, A.; Binelli, A. Application of a biomarker response index for ranking the toxicity of five pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) to the bivalve Dreissena polymorpha. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 64, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacker, T.S.; Duchen, M.R. Investigating mitochondrial redox state using NADH and NADPH autofluorescence. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 100, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, S. From heterochromatin islands to the NAD world: A hierarchical view of aging through the functions of mammalian sirt1 and systemic NAD biosynthesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Compte, A.; Álvarez-Muñoz, D.; Solé, M.; Cáceres, N.; Barceló, D.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S. Comprehensive study of sulfamethoxazole effects in marine mussels: Bioconcentration, enzymatic activities and metabolomics. Environ. Res. 2019, 173, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M. The KEGG database. Novartis Found. Symp. 2002, 247, 91–103. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, J.L.; Souza, M.M. Osmotic stress and muscle tissue volume response of a freshwater bivalve. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2008, 151, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, M.B.; Ferraris, J.D. Intracellular organic osmolytes: Function and regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 7309–7313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, T.; Giannetto, A.; Parrino, V.; Maisano, M.; Oliva, S.; De Marco, G.; Guerriero, G.; Mauceri, A.; Fasulo, S. Baseline levels of metabolites in different tissues of mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis (Bivalvia: Mytilidae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genomics Proteomics 2018, 26, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kournoutou, G.G.; Pytharopoulou, S.; Leotsinidis, M.; Kalpaxis, D.L. Changes of polyamine pattern in digestive glands of mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis under exposure to cadmium. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 165, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Qiu, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Xin, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Song, L. The inhibitory role of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) on immunomodulation of Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 52, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, T.; Maisano, M.; Giannetto, A.; Natalotto, A.; Parrino, V.; Mauceri, A.; Spanò, N. Pen shell Pinna nobilis L. (Mollusca: Bivalvia) from different peculiar environments: Adaptive mechanisms of osmoregulation and neurotransmission. Eur. Zool. J. 2019, 86, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagné, F.; André, C.; Gélinas, M. Neurochemical effects of benzodiazepine and morphine on freshwater mussels. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 152, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, T.; Maisano, M.; Giannetto, A.; Parrino, V.; Mauceri, A.; Fasulo, S. Neurotoxicological effects on marine mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis caged at petrochemical contaminated areas (eastern Sicily, Italy): 1H NMR and immunohistochemical assays. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 169, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, C.; Viant, M.R. Two-dimensional J-resolved NMR spectroscopy: Review of a key methodology in the metabolomics toolbox. Phytochem. Anal. 2010, 21, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Meyer, T.; Sinnaeve, D.; van Gasse, B.; Tsiporkova, E.; Rietzschel, E.R.; de Buyzere, M.L.; Gillebert, T.C.; Bekaert, S.; Martins, J.C.; van Criekinge, W. NMR-Based characterization of metabolic alterations in hypertension using an adaptive, intelligent binning algorithm. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 3783–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deborde, C.; Fontaine, J.-X.; Jacob, D.; Botana, A.; Nicaise, V.; Richard-Forget, F.; Lecomte, S.; Decourtil, C.; Hamade, K.; Mesnard, F.; et al. Optimizing 1D 1H-NMR profiling of plant samples for high throughput analysis: Extract preparation, standardization, automation and spectra processing. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BioStatFlow: Statistical Analysis Workflow for “OMICS” Data. Available online: biostatflow.org (accessed on 25 April 2020).
- Griffith, C.M.; Williams, P.B.; Tinoco, L.W.; Dinges, M.M.; Wang, Y.; Larive, C.K. 1H NMR metabolic profiling of earthworm (Eisenia fetida) coelomic fluid, coelomocytes, and tissue: Identification of a new metabolite—Malylglutamate. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 3407–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.; Ding, C.; Dang, F.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X. NMR-based metabolic toxicity of low-level Hg exposure to earthworms. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikunov, A.P.; Johnson, C.B.; Lee, H.; Stoskopf, M.K.; Macdonald, J.M. Metabolomic investigations of american oysters using 1H-NMR spectroscopy. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2578–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanana, H.; Simon, G.; Kervarec, N.; Mohammadou, B.A.; Cérantola, S. HRMAS NMR as a tool to study metabolic responses in heart clam Ruditapes decussatus exposed to Roundup®. Talanta 2012, 97, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerambrun, E.; Delahaut, L.; Geffard, A.; David, E. Differentiation of sympatric zebra and quagga mussels in ecotoxicological studies: A comparison of morphometric data, gene expression, and body metal concentrations. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 154, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradwell, M.J.; Fan, T.W.M.; Lane, A.N. Analysis of phosphorylated metabolites in crayfish extracts by two-dimensional 1H-31P NMR heteronuclear total correlation spectroscopy (heteroTOCSY). Anal. Biochem. 1998, 263, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakforest Database. Available online: https://alpha.peakforest.org/webapp/ (accessed on 25 April 2020).
- Wishart, D.S.; Tzur, D.; Knox, C.; Eisner, R.; Guo, A.C.; Young, N.; Cheng, D.; Jewell, K.; Arndt, D.; Sawhney, S.; et al. HMDB: The human metabolome database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D521–D526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, J.T.; Beggel, S.; Auerswald, K.; Stoeckle, B.C.; Geist, J. Establishing mussel behavior as a biomarker in ecotoxicology. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 170, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ożgo, M.; Urbańska, M.; Hoos, P.; Imhof, H.K.; Kirschenstein, M.; Mayr, J.; Michl, F.; Tobiasz, R.; von Wesendonk, M.; Zimmermann, S.; et al. Invasive zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) threatens an exceptionally large population of the depressed river mussel (Pseudanodonta complanata) in a postglacial lake. Ecol. Evol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Metabolite | 1H Chemical Shift (ppm) | Confidence Level |
|---|---|---|
| Proteinogenic amino acids | ||
| Alanine | 1.483 (d), 3.783 (q) | 2+ |
| Arginine | 1.924 (m8), 3.249 (t), 3.776 (dd) | 2+ |
| ▸Asparagine | 2.956 (dd) | 1 |
| Aspartate | 2.681 (q), 2.818 (dd), 3.899 (dd) | 2+ |
| Glutamate | 2.061 (m6), 2.099 (m6), 2.136 (m12), 2.354 (m8), 3.760 (dd) | 2+ |
| ▸Glycine | 3.56 (s) | 1 |
| ▸Histidine | 3.183 (3), 7.965 (s) | 1 |
| Isoleucine | 0.944 (t), 1.016 (d) | 2+ |
| Leucine | 0.959 (d), 0.972 (d) | 2+ |
| ▸Lysine | 1.482 (m8), 1.729 (m4), 3.030 (t) | 1 |
| ▸Phenylalanine | 7.331 (d), 7.378 (m3), 7.418 (s), 7.430 (s), 7.442 (s) | 1 |
| Threonine | 1.333 (d), 3.588 (d) | 2+ |
| ▸Tryptophan | 7.203 (t), 7.87 (t), 7.544 (d), 7.740 (d) | 1 |
| Tyrosine | 6.902 (2), 7.196 (2) | 2+ |
| Valine | 0.994 (d), 1.047 (d), 2.304 (dd), 3.613 (d) | 2+ |
| Amine and amide compounds and osmolites | ||
| ▸Choline | 3.210 (s) | 1 |
| Phosphocholine | 3.227 (s) | 2− |
| Glycerophosphocholine | 3.233 (s) | 2− |
| Cadaverine | 1.419 (m5), 1.733 (m6), 3.024 (t) | 2+ |
| Putrescine | 1.775 (m9), 3.052 (m5) | 2+ |
| Trimethylamine | 2.874 (s) | 2+ |
| Dimethylamine | 2.709 (s) | 2+ |
| Betaine | 3.272 (s), 3.913 (s) | 2+ |
| Hypotaurine | 2.650 (t), 3.357 (t) | 2+ |
| Allantoin | 5.387 (s) | 2− |
| Carboxylic acids | ||
| Succinic acid | 2.409 (s) | 2+ |
| Lactic acid | 1.331 (d), 4.114 (dd) | 2+ |
| Nicotinic acid | 7.525 (qd), 8.253 (m8), 8.941 (s) | 2+ |
| γ-aminobutyric acid | 1.967 (m5), 2.446 (t), 2.452 (t) | 2− |
| Nucleotides–Nucleosides | ||
| ▸Adenosine | 3.842 (dd), 3.918 (dd), 4.305 (dd), 4.439 (dd), 6.083 (d), 8.263 (s), 8.350 (s) | 1 |
| Inosine | 8.239 (s), 8.355 (s) | 2+ |
| Uridine | 4.369 (t), 5.900 (d), 5.924 (d), 7.889 (d) | 2+ |
| ▸ATP | 4.413 (m), 8.273 (s) | 1 |
| ▸ADP | 6.156 (d), 8.271 (s), 8.545 (s) | 1 |
| ▸AMP | 4.017 (d), 4.025 (d), 4.376 (m), 4.415 (qd), 6.147 (d), 8.268 (s), 8.615 (s) | 1 |
| ▸UMP | 6.001 (m3), 8.130 (d) | 1 |
| NMN | 8.997 - 9.113 (d), 9.354 (s), 9.606 (s) | 2− |
| Coenzymes | ||
| ▸βNAD | 4.428 (m4), 4.489 (m4), 4.514 (qd), 4.546 (m), 6.040 (d), 8.169 (s), 8.118 (dd), 8.439 (s), 8.828 (dd), 9.145 (d), 9.340 (s) | 1 |
| ▸NADH | 8.490 (s) | 1 |
| Carbohydrates | ||
| ▸Glucose | (3.246 (d), 3.402 (dd), 3.430 (t), 3.477 (t), 3.491 (t), 3.727 (t), 4.650 (d), 5.237 (d) | 1 |
| ▸Maltose | 3.281 (t), 4.414 (s), 3.596 (2), 3.653 (dd), 3.698 (d), 3.725 (m6), 4.663 (d), 5.237 (d), 5.430 (2) | 1 |
| ▸Glycogen | 1.187 (t), 5.414 (br), 5.418 (br) | 1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prud’homme, S.M.; Hani, Y.M.I.; Cox, N.; Lippens, G.; Nuzillard, J.-M.; Geffard, A. The Zebra Mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) as a Model Organism for Ecotoxicological Studies: A Prior 1H NMR Spectrum Interpretation of a Whole Body Extract for Metabolism Monitoring. Metabolites 2020, 10, 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10060256
Prud’homme SM, Hani YMI, Cox N, Lippens G, Nuzillard J-M, Geffard A. The Zebra Mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) as a Model Organism for Ecotoxicological Studies: A Prior 1H NMR Spectrum Interpretation of a Whole Body Extract for Metabolism Monitoring. Metabolites. 2020; 10(6):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10060256
Chicago/Turabian StylePrud’homme, Sophie Martine, Younes Mohamed Ismail Hani, Neil Cox, Guy Lippens, Jean-Marc Nuzillard, and Alain Geffard. 2020. "The Zebra Mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) as a Model Organism for Ecotoxicological Studies: A Prior 1H NMR Spectrum Interpretation of a Whole Body Extract for Metabolism Monitoring" Metabolites 10, no. 6: 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10060256
APA StylePrud’homme, S. M., Hani, Y. M. I., Cox, N., Lippens, G., Nuzillard, J.-M., & Geffard, A. (2020). The Zebra Mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) as a Model Organism for Ecotoxicological Studies: A Prior 1H NMR Spectrum Interpretation of a Whole Body Extract for Metabolism Monitoring. Metabolites, 10(6), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10060256