Metabolomics Benefits from Orbitrap GC–MS—Comparison of Low- and High-Resolution GC–MS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
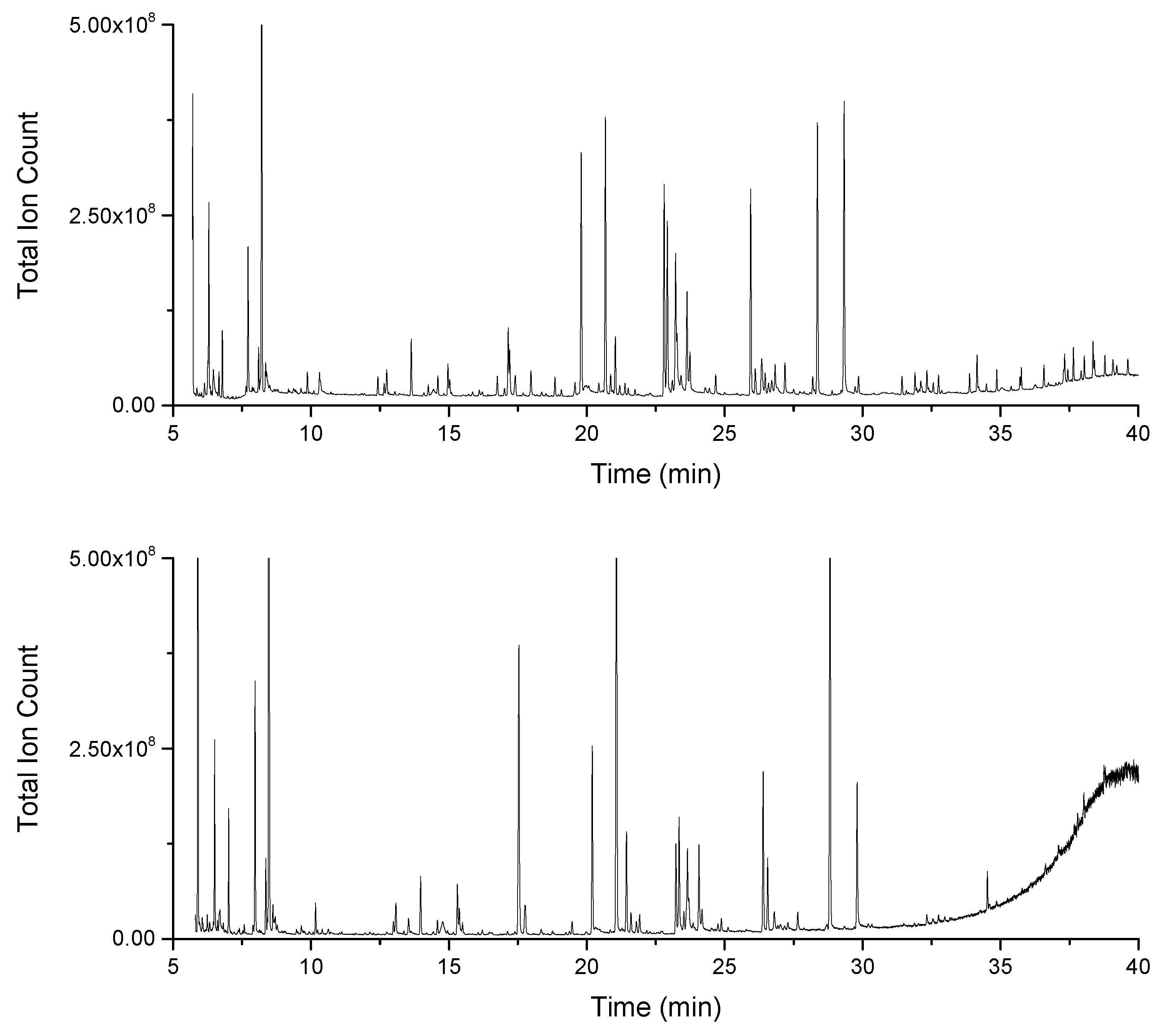
2.1. Increased Metabolic Coverage Using a Smaller Sample
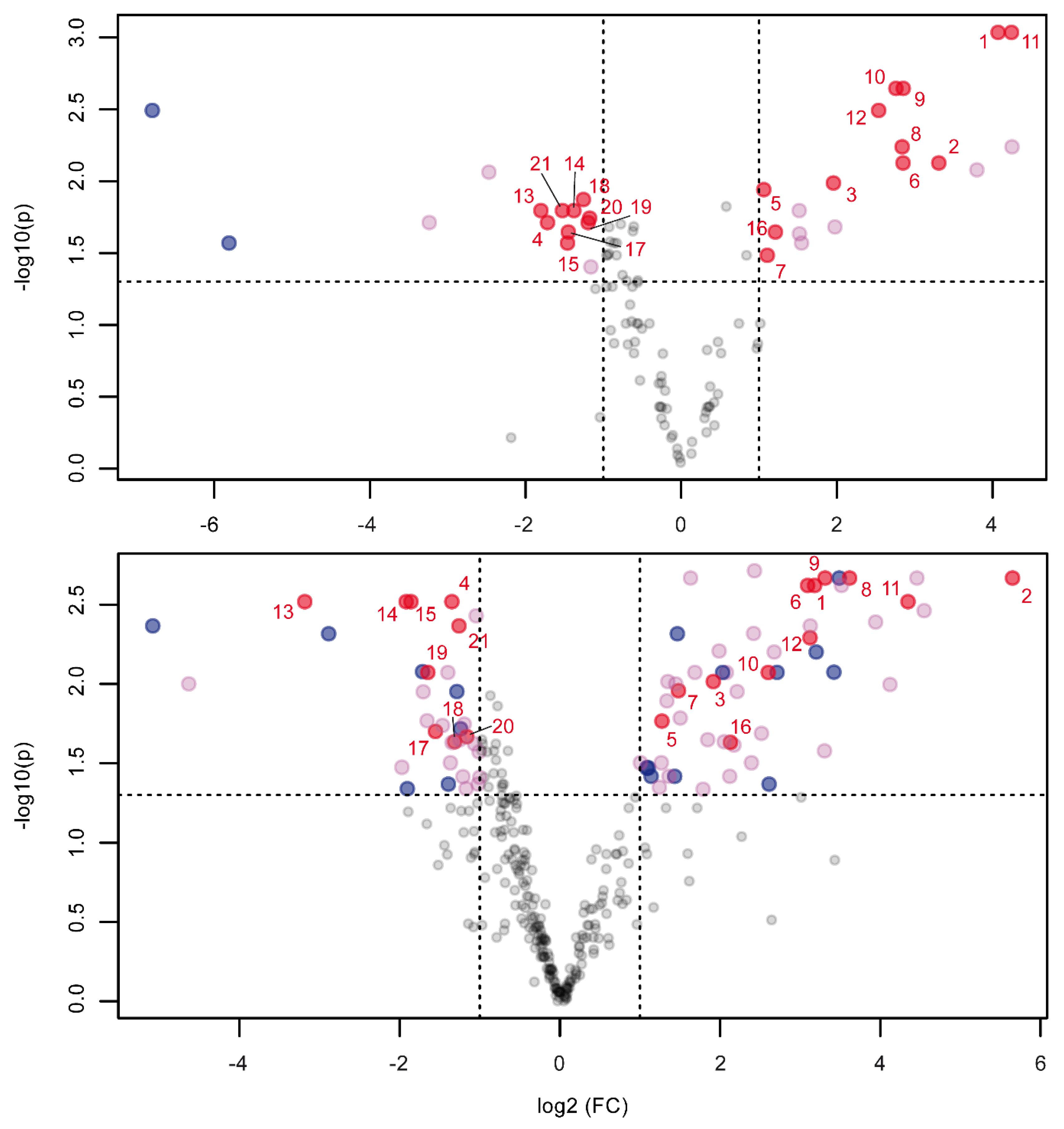
2.2. Orbitrap and Single-Quadrupole Systems Detect Different Biomarkers
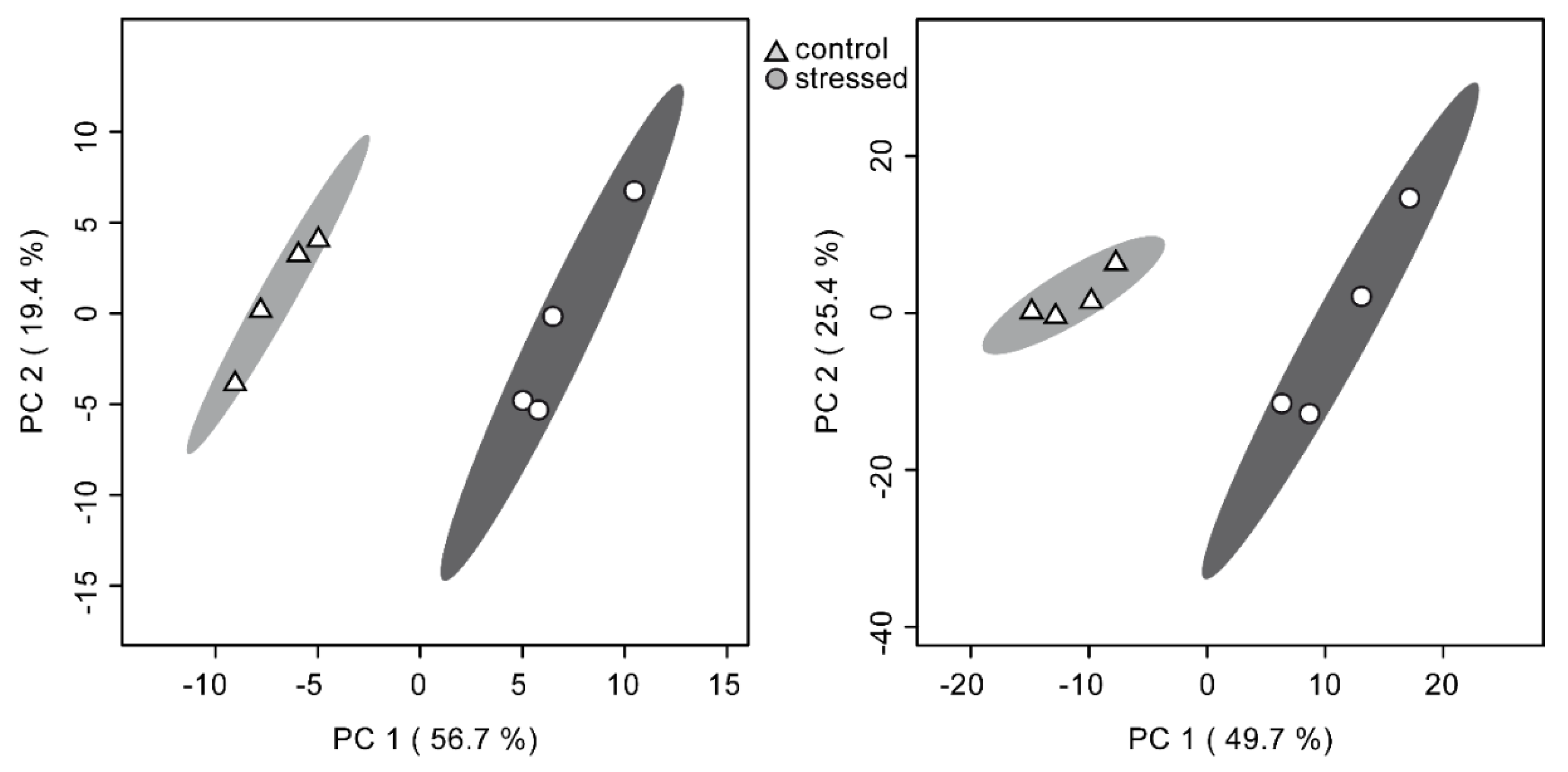
2.3. Similar Statistical Discrimination of Samples on Both Platforms
2.4. High-Resolution Data Supports Spectral Database Matching
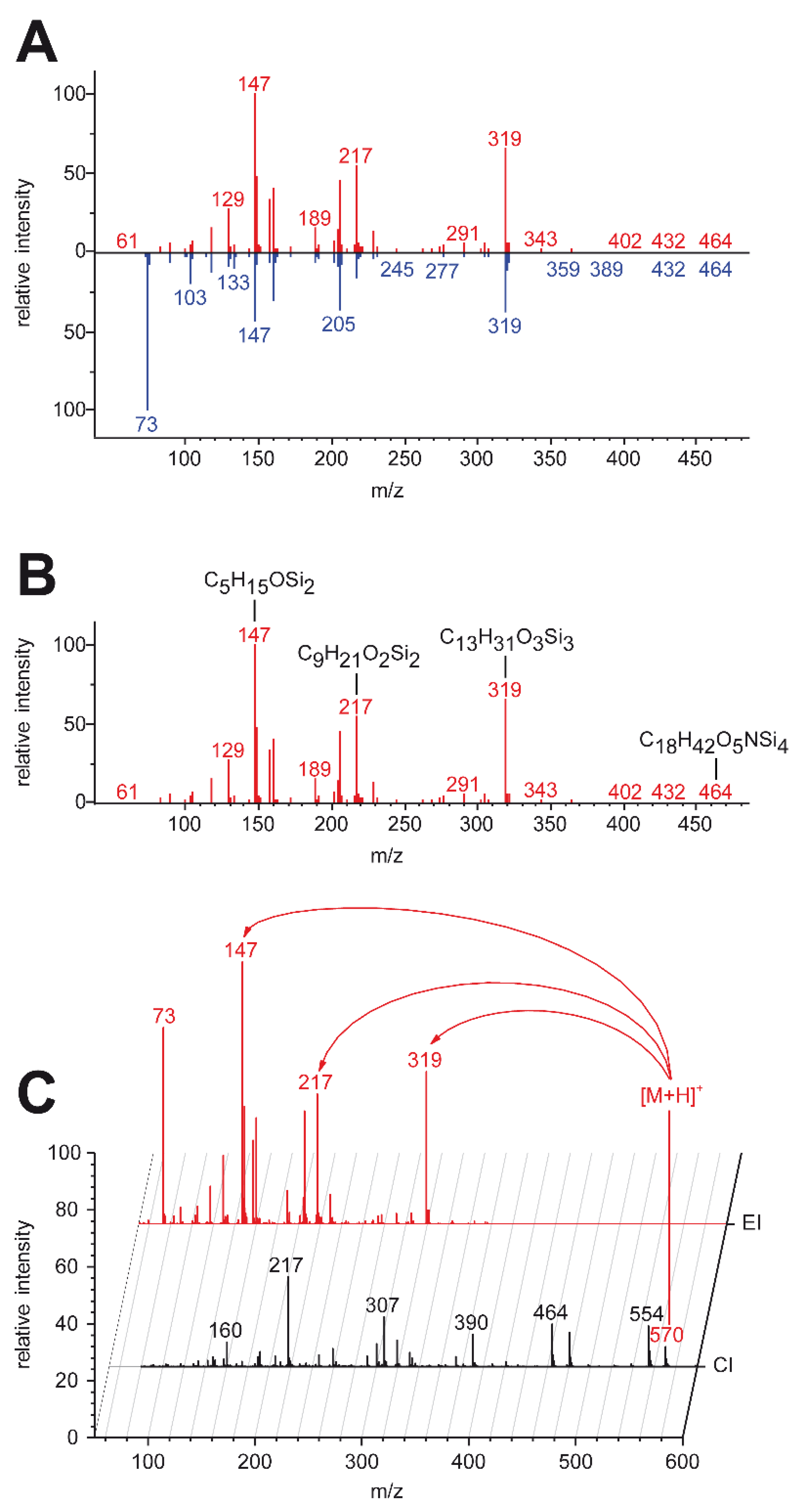
2.5. High-Resolution Data Enabled Identification of One Unknown
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Instrumentation
4.2. Standards
4.3. Cultivation
4.4. Extraction
4.5. Sample Workup
4.6. Data Collection
4.7. Data Preprocessing
4.8. Statistical Analysis
4.9. Identification Workflow
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Creek, D.J.; Dunn, W.B.; Fiehn, O.; Griffin, J.L.; Hall, R.D.; Lei, Z.T.; Mistrik, R.; Neumann, S.; Schymanski, E.L.; Sumner, L.W.; et al. Metabolite identification: Are you sure? And how do your peers gauge your confidence? Metabolomics 2014, 10, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaženović, I.; Kind, T.; Torbašinović, H.; Obrenović, S.; Mehta, S.S.; Tsugawa, H.; Wermuth, T.; Schauer, N.; Jahn, M.; Biedendieck, R.; et al. Comprehensive comparison of in silico MS/MS fragmentation tools of the CASMI contest: Database boosting is needed to achieve 93% accuracy. J. Cheminform. 2017, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, W.B.; Erban, A.; Weber, R.J.M.; Creek, D.J.; Brown, M.; Breitling, R.; Hankemeier, T.; Goodacre, R.; Neumann, S.; Kopka, J.; et al. Mass appeal: Metabolite identification in mass spectrometry-focused untargeted metabolomics. Metabolomics 2013, 9, S44–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viant, M.R.; Kurland, I.J.; Jones, M.R.; Dunn, W.B. How close are we to complete annotation of metabolomes? Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2017, 36, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Rivera, G.; Ballesteros-Vivas, D.; Parada-Alfonso, F.; Ibanez, E.; Cifuentes, A. Recent applications of high resolution mass spectrometry for the characterization of plant natural products. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 112, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Marcu, A.; Guo, A.C.; Liang, K.; Vazquez-Fresno, R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.R.; Karu, N.; et al. HMDB 4.0: The human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D608–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horai, H.; Arita, M.; Kanaya, S.; Nihei, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Suwa, K.; Ojima, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Tanaka, S.; Aoshima, K.; et al. MassBank: A public repository for sharing mass spectral data for life sciences. J. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 45, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.X.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruttkies, C.; Schymanski, E.L.; Wolf, S.; Hollender, J.; Neumann, S. MetFrag relaunched: Incorporating strategies beyond in silico fragmentation. J. Cheminform. 2016, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhrkop, K.; Fleischauer, M.; Ludwig, M.; Aksenov, A.A.; Melnik, A.V.; Meusel, M.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Rousu, J.; Bocker, S. SIRIUS 4: A rapid tool for turning tandem mass spectra into metabolite structure information. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Kind, T.; Nakabayashi, R.; Yukihira, D.; Tanaka, W.; Cajka, T.; Saito, K.; Fiehn, O.; Arita, M. Hydrogen Rearrangement Rules: Computational MS/MS Fragmentation and Structure Elucidation Using MS-FINDER Software. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 7946–7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djoumbou-Feunang, Y.; Pon, A.; Karu, N.; Zheng, J.M.; Li, C.; Arndt, D.; Gautam, M.; Allen, F.; Wishart, D.S. CFM-ID 3.0: Significantly Improved ESI-MS/MS Prediction and Compound Identification. Metabolites 2019, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, A.C.; Hauschild, J.P.; Quarmby, S.T.; Krumwiede, D.; Lange, O.; Lemke, R.A.S.; Grosse-Coosmann, F.; Horning, S.; Donohue, T.J.; Westphall, M.S.; et al. Development of a GC/Quadrupole-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer, Part I: Design and Characterization. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 10036–10043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, A.C.; Balloon, A.J.; Westphall, M.S.; Coon, J.J. Development of a GC/Quadrupole-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer, Part II: New Approaches for Discovery Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 10044–10051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockbals, L.; Habicht, M.; Hajdas, I.; Galassi, F.M.; Ruhli, F.J.; Kraemer, T. Untargeted metabolomics-like screening approach for chemical characterization and differentiation of canopic jar and mummy samples from Ancient Egypt using GC-high resolution MS. Analyst 2018, 143, 4503–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, B.B.; Bassey, E.; Bishop, A.C.; Kusel, D.T.; Cox, L.A.; Olivier, M. High-resolution gas chromatography/mass spectrometry metabolomics of non-human primate serum. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 32, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.P.; Moir, R.D.; Willis, I.M.; Seethapathy, S.; Biniakewitz, R.C.; Kurland, I.J. Enhanced Isotopic Ratio Outlier Analysis (IROA) Peak Detection and Identification with Ultra-High Resolution GC-Orbitrap/MS: Potential Application for Investigation of Model Organism Metabolomes. Metabolites 2018, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.S.; Li, L.N.; Song, S.Y.; Bai, Y.; Liu, H.W. Metabolomic study of mouse embryonic fibroblast cells in response to autophagy based on high resolution gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 434, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidt, S.; Haggarty, J.; Kean, R.; Cojocariu, C.I.; Silcock, P.J.; Rajendran, R.; Ramage, G.; Burgess, K.E.V. A novel targeted/untargeted GC-orbitrap metabolomics methodology applied to Candida albicans and staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochat, B. From targeted quantification to untargeted metabolomics: Why LC-high-resolution-MS will become a key instrument in clinical labs. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 84, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alseekh, S.; Fernie, A.R. Metabolomics 20 years on: What have we learned and what hurdles remain? Plant J. 2018, 94, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halket, J.M.; Waterman, D.; Przyborowska, A.M.; Patel, R.K.P.; Fraser, P.D.; Bramley, P.M. Chemical derivatization and mass spectral libraries in metabolic profiling by GC/MS and LC/MS/MS. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oss, M.; Kruve, A.; Herodes, K.; Leito, I. Electrospray Ionization Efficiency Scale of Organic Compounds. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 2865–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demarque, D.P.; Crotti, A.E.M.; Vessecchi, R.; Lopes, J.L.C.; Lopes, N.P. Fragmentation reactions using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry: An important tool for the structural elucidation and characterization of synthetic and natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2016, 33, 432–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, T.; Tsugawa, H.; Miyagawa, H.; Fukusaki, E. Integrated Strategy for Unknown EI–MS Identification Using Quality Control Calibration Curve, Multivariate Analysis, EI–MS Spectral Database, and Retention Index Prediction. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 6766–6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLafferty, F.; Turecek, F. Interpretation of Mass Spectra, 4th ed.; University Science Books: Sausalito, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hufsky, F.; Rempt, M.; Rasche, F.; Pohnert, G.; Bocker, S. De novo analysis of electron impact mass spectra using fragmentation trees. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 739, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiecien, N.W.; Bailey, D.J.; Rushp, M.J.P.; Cole, J.S.; Ulbrich, A.; Hebert, A.S.; Westphall, M.S.; Coon, J.J. High-Resolution Filtering for Improved Small Molecule Identification via GC/MS. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 8328–8335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, S.; Ahn, Y.G.; Kind, T.; Cataldi, T.R.I.; Fiehn, O. Determination of elemental compositions by gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry using chemical and electron ionization. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 24, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessner, U.; Wagner, C.; Kopka, J.; Trethewey, R.N.; Willmitzer, L. Simultaneous analysis of metabolites in potato tuber by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Plant J. 2000, 23, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, F.; Pon, A.; Greiner, R.; Wishart, D. Computational Prediction of Electron Ionization Mass Spectra to Assist in GC/MS Compound Identification. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 7689–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.J.; Kind, T.; Fiehn, O. Using Accurate Mass Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry with the MINE Database for Epimetabolite Annotation. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 10171–10180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Z.J.; Tsugawa, H.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Mehta, S.; Mueller, M.; Zheng, Y.X.; Ogiwara, A.; Meissen, J.; Showalter, M.; Takeuchi, K.; et al. Identifying metabolites by integrating metabolome databases with mass spectrometry cheminformatics. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.-C.; Maillot, M.; Mazerolles, G.; Verdu, A.; Lyan, B.; Migné, C.; Defoort, C.; Canlet, C.; Junot, C.; Guillou, C.; et al. Can we trust untargeted metabolomics? Results of the metabo-ring initiative, a large-scale, multi-instrument inter-laboratory study. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 807–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benton, H.P.; Want, E.; Keun, H.C.; Amberg, A.; Plumb, R.S.; Goldfain-Blanc, F.; Walther, B.; Reily, M.D.; Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E.; et al. Intra- and Interlaboratory Reproducibility of Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography-Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry for Urinary Metabolic Profiling. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 2424–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito-Shida, S.; Hamasaka, T.; Nemoto, S.; Akiyama, H. Multiresidue determination of pesticides in tea by liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry: Comparison between Orbitrap and time-of-flight mass analyzers. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, A.; Dvorak, V.; Cruzer, C.; Butcher, P.; Maden, K.; Walker, S.; Widmer, M.; Schurmann, A. Study of High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry Technology as a Replacement for Tandem Mass Spectrometry in the Field of Quantitative Pesticide Residue Analysis. J. AOAC Int. 2012, 95, 528–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, A.; Butcher, P.; Maden, K.; Walker, S.; Widmer, M. Development of an improved high resolution mass spectrometry based multi-residue method for veterinary drugs in various food matrices. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 700, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajski, L.; Gomez-Ramos, M.D.; Fernandez-Alba, A.R. Large pesticide multiresidue screening method by liquid chromatography-Orbitrap mass spectrometry in full scan mode applied to fruit and vegetables. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1360, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.A.; Ammar, N.M.; Serag, A.; Shaker, O.G.; El Gendy, A.N.; Abdel-Hamid, A.-H.Z. Metabolomics driven analysis of obesity-linked colorectal cancer patients via gc-ms and chemometrics: A pilot study. Microchem. J. 2020, 155, 104742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fegel, T.; Boot, C.M.; Broeckling, C.D.; Baron, J.S.; Hall, E.K. Assessing the chemistry and bioavailability of dissolved organic matter from glaciers and rock glaciers. J. Geophys. Res.-Biogeosci. 2019, 124, 1988–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidis, M.; Karagiannis, E.; Tanou, G.; Sarrou, E.; Stavridou, E.; Ganopoulos, I.; Karamanoli, K.; Madesis, P.; Martens, S.; Molassiotis, A. An integrated metabolomic and gene expression analysis identifies heat and calcium metabolic networks underlying postharvest sweet cherry fruit senescence. Planta 2019, 250, 2009–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.A.; Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS: Processing Mass Spectrometry Data for Metabolite Profiling Using Nonlinear Peak Alignment, Matching, and Identification. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, A.M.; Bridgewater, B.R.; Liu, Q.; Mitchell, M.W.; Robinson, R.J.; Dai, H.; Stewart, S.J.; DeHaven, C.D.; Miller, L.A.D. High resolution mass spectrometry improves data quantity and quality as compared to unit mass resolution mass spectrometry in high-throughput profiling metabolomics. Metabolomics: Open Access 2014, 4, 132. [Google Scholar]
- Gika, H.G.; Theodoridis, G.A.; Earll, M.; Snyder, R.W.; Sumner, S.J.; Wilson, I.D. Does the Mass Spectrometer Define the Marker? A Comparison of Global Metabolite Profiling Data Generated Simultaneously via UPLC-MS on Two Different Mass Spectrometers. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 8226–8234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Glauser, G.; Veyrat, N.; Rochat, B.; Wolfender, J.L.; Turlings, T.C.J. Ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for plant metabolomics: A systematic comparison of high-resolution quadrupole-time-of-flight and single stage Orbitrap mass spectrometers. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1292, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cajka, T.; Smilowitz, J.T.; Fiehn, O. Validating Quantitative Untargeted Lipidomics Across Nine Liquid Chromatography-High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry Platforms. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 12360–12368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Berg, R.A.; Hoefsloot, H.C.; Westerhuis, J.A.; Smilde, A.K.; van der Werf, M.J. Centering, scaling, and transformations: Improving the biological information content of metabolomics data. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazenovic, I.; Kind, T.; Ji, J.; Fiehn, O. Software Tools and Approaches for Compound Identification of LC-MS/MS Data in Metabolomics. Metabolites 2018, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, I.; Calenberg, M. Effect of extracellular Ca2+ antagonists on the movement and chemoorientation of male gametes of Ectocarpus siliculosus (Phaeophyceae). Bot. Acta 1994, 107, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidoudez, C.; Pohnert, G. Comparative metabolomics of the diatom Skeletonema marinoi in different growth phases. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 654–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Begley, P.; Zelena, E.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Anderson, N.; Brown, M.; Knowles, J.D.; Halsall, A.; Haselden, J.N.; et al. Procedures for large-scale metabolic profiling of serum and plasma using gas chromatography and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhl, C.; Tautenhahn, R.; Böttcher, C.; Larson, T.R.; Neumann, S. CAMERA: An Integrated Strategy for Compound Spectra Extraction and Annotation of Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry Data Sets. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehrens, R.; Weingart, G.; Mattivi, F. metaMS: An open-source pipeline for GC-MS-based untargeted metabolomics. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 966, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, H.M.; Ji, F.F.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Z.W. statTarget: A streamlined tool for signal drift correction and interpretations of quantitative mass spectrometry-based omics data. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1036, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, J.; Yamamoto, M.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalystR 2.0: From Raw Spectra to Biological Insights. Metabolites 2019, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Soufan, O.; Li, C.; Caraus, I.; Li, S.; Bourque, G.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 4.0: Towards more transparent and integrative metabolomics analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W486–W494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopka, J.; Schauer, N.; Krueger, S.; Birkemeyer, C.; Usadel, B.; Bergmüller, E.; Dörmann, P.; Weckwerth, W.; Gibon, Y.; Stitt, M.; et al. GMD@CSB.DB: The Golm Metabolome Database. Bioinformatics 2004, 21, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kind, T.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Lee, D.Y.; Lu, Y.; Palazoglu, M.; Shahbaz, S.; Fiehn, O. FiehnLib: Mass Spectral and Retention Index Libraries for Metabolomics Based on Quadrupole and Time-of-Flight Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 10038–10048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stettin, D.; Poulin, R.X.; Pohnert, G. Metabolomics Benefits from Orbitrap GC–MS—Comparison of Low- and High-Resolution GC–MS. Metabolites 2020, 10, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10040143
Stettin D, Poulin RX, Pohnert G. Metabolomics Benefits from Orbitrap GC–MS—Comparison of Low- and High-Resolution GC–MS. Metabolites. 2020; 10(4):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10040143
Chicago/Turabian StyleStettin, Daniel, Remington X. Poulin, and Georg Pohnert. 2020. "Metabolomics Benefits from Orbitrap GC–MS—Comparison of Low- and High-Resolution GC–MS" Metabolites 10, no. 4: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10040143
APA StyleStettin, D., Poulin, R. X., & Pohnert, G. (2020). Metabolomics Benefits from Orbitrap GC–MS—Comparison of Low- and High-Resolution GC–MS. Metabolites, 10(4), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10040143




