Fatty Acyl Esters of Hydroxy Fatty Acid (FAHFA) Lipid Families
Abstract
1. Introduction
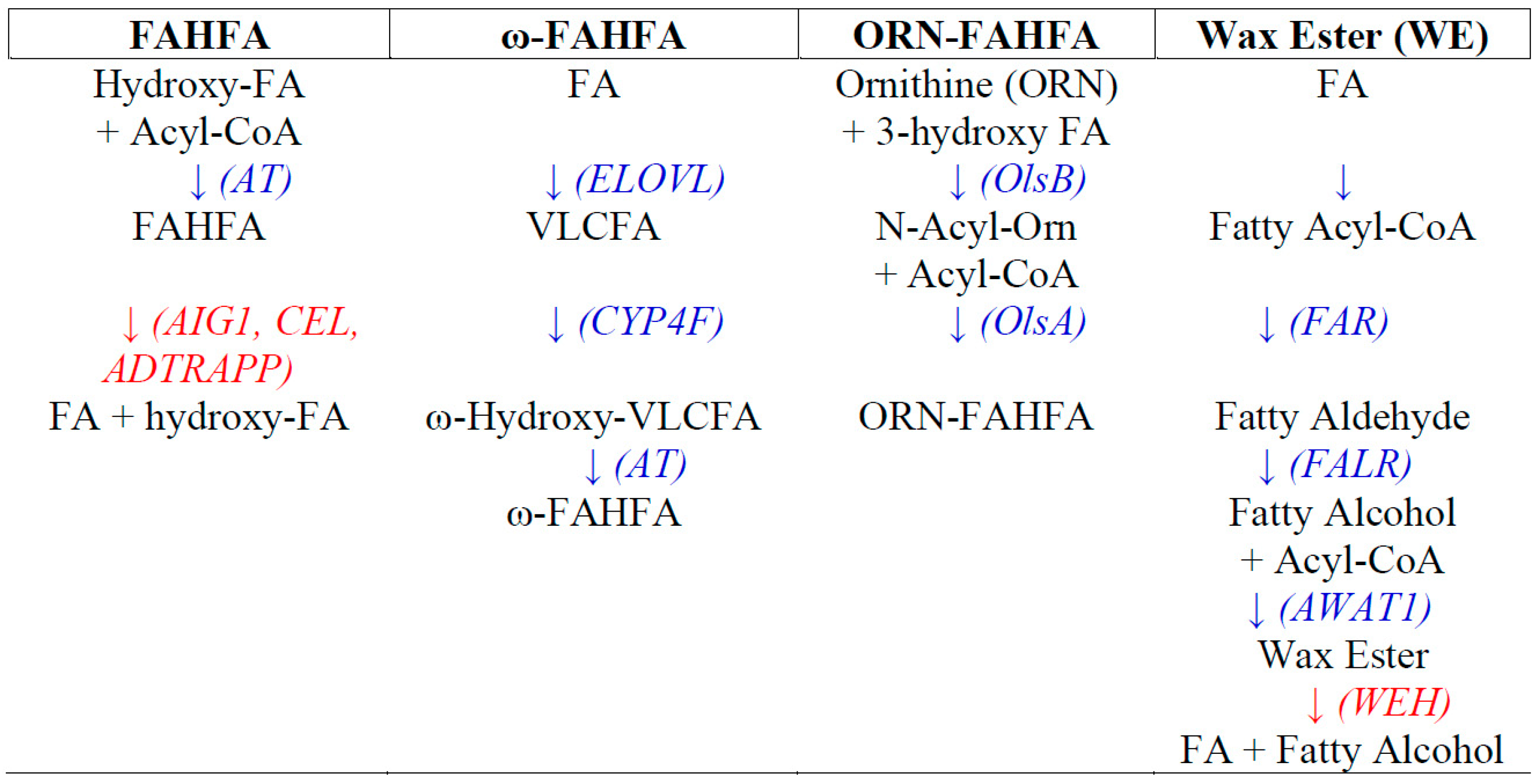
2. FAHFA Lipid Families
2.1. Branched-Chain FAHFA
2.2. ω-FAHFA
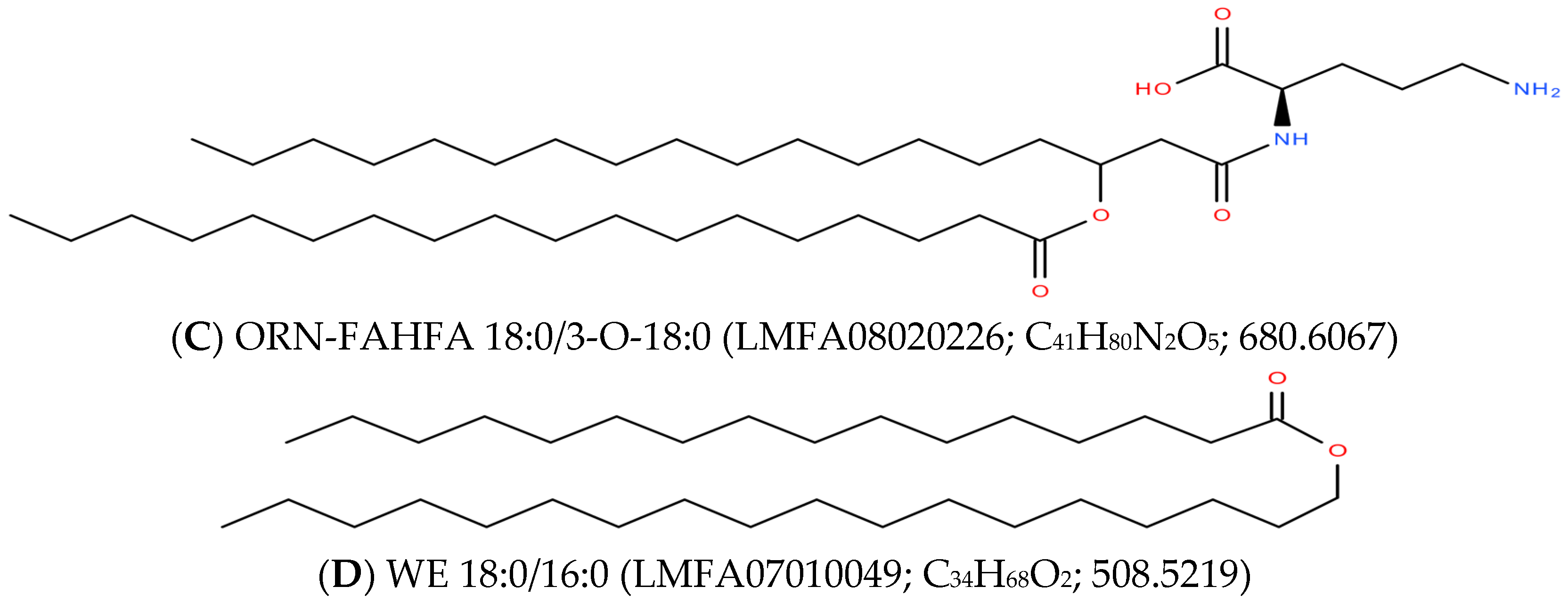
2.3. Ornithine-3-FAHHA (ORN-FAHFA)
2.4. Wax Esters
3. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yore, M.M.; Syed, I.; Moraes-Vieira, P.M.; Zhang, T.; Herman, M.A.; Homan, E.A.; Patel, R.T.; Lee, J.; Chen, S.; Peroni, O.D.; et al. Discovery of a Class of Endogenous Mammalian Lipids with Anti-Diabetic and Anti-inflammatory Effects. Cell 2014, 159, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, I.; Lee, J.; Moraes-Vieira, P.M.; Donaldson, C.J.; Sontheimer, A.; Aryal, P.; Wellenstein, K.; Kolar, M.J.; Nelson, A.T.; Siegel, D.; et al. Palmitic Acid Hydroxystearic Acids Activate GPR40, Which Is Involved in Their Beneficial Effects on Glucose Homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 419–427.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.-F.; Yan, J.-W.; Ni, J.; Feng, Y.-Q. FAHFA footprint in the visceral fat of mice across their lifespan. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2020, 1865, 158639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokotou, M.G. Analytical Methods for the Determination of Fatty Acid Esters of Hydroxy Fatty Acids (FAHFAs) in Biological Samples, Plants and Foods. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolar, M.J.; Nelson, A.T.; Chang, T.; Ertunc, M.E.; Christy, M.P.; Ohlsson, L.; Härröd, M.; Kahn, B.B.; Siegel, D.; Saghatelian, A. Faster Protocol for Endogenous Fatty Acid Esters of Hydroxy Fatty Acid (FAHFA) Measurements. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 5358–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes-Vieira, P.M.; Saghatelian, A.; Kahn, B.B. GLUT4 Expression in Adipocytes Regulates De Novo Lipogenesis and Levels of a Novel Class of Lipids with Antidiabetic and Anti-inflammatory Effects. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1808–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati-Čizmek, A.-M.; Biluš, M.; Brkić, A.L.; Barić, I.C.; Bakula, M.; Hozić, A.; Cindrić, M. Analysis of Fatty Acid Esters of Hydroxyl Fatty Acid in Selected Plant Food. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2019, 74, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolar, M.J.; Konduri, S.; Chang, T.; Wang, H.; McNerlin, C.; Ohlsson, L.; Härröd, M.; Siegel, D.; Saghatelian, A. Linoleic acid esters of hydroxy linoleic acids are anti-inflammatory lipids found in plants and mammals. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 10698–10707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuda, O.; Brezinova, M.; Šilhavý, J.; Landa, V.; Zídek, V.; Dodia, C.; Kreuchwig, F.; Vrbacky, M.; Balas, L.; Durand, T.; et al. Nrf2-Mediated Antioxidant Defense and Peroxiredoxin 6 Are Linked to Biosynthesis of Palmitic Acid Ester of 9-Hydroxystearic Acid. Diabetes 2018, 67, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, M.C.; Siponen, M.I.; Alexson, S.E. The emerging role of acyl-CoA thioesterases and acyltransferases in regulating peroxisomal lipid metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1822, 1397–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planey, S.L.; Zacharias, D.A. Palmitoyl acyltransferases, their substrates, and novel assays to connect them (Review). Mol. Membr. Biol. 2009, 26, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, W.H.; Kolar, M.J.; Kamat, S.S.; Cognetta, A.B., 3rd; Hulce, J.J.; Saez, E.; Kahn, B.B.; Saghatelian, A.; Cravatt, B.F. AIG1 and ADTRP are atypical integral membrane hydrolases that degrade bioactive FAHFAs. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertunc, M.E.; Kok, B.P.; Parsons, W.H.; Wang, J.G.; Tan, D.; Donaldson, C.J.; Pinto, A.F.M.; Vaughan, J.M.; Ngo, N.; Lum, K.M.; et al. AIG1 and ADTRP are endogenous hydrolases of fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 5891–5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolar, M.J.; Kamat, S.S.; Parsons, W.H.; Homan, E.A.; Maher, T.; Peroni, O.D.; Syed, I.; Fjeld, K.; Molven, A.; Kahn, B.B.; et al. Branched Fatty Acid Esters of Hydroxy Fatty Acids Are Preferred Substrates of the MODY8 Protein Carboxyl Ester Lipase. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 4636–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Ertunc, M.E.; Konduri, S.; Zhang, J.; Pinto, A.M.; Chu, Q.; Kahn, B.B.; Siegel, D.; Saghatelian, A. Discovery of FAHFA-Containing Triacylglycerols and Their Metabolic Regulation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 8798–8806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.L.; Edson, K.Z.; Totah, R.A.; Rettie, A.E. Cytochrome P450 ω-Hydroxylases in Inflammation and Cancer. Adv. Pharmacol. 2015, 74, 223–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butovich, I.A. On the presence of (O-acyl)-omega-hydroxy fatty acids and of their esters in human meibomian gland secretions. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 639–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, A.; Lu, H.; Butovich, I.A. A Role for ELOVL4 in the Mouse Meibomian Gland and Sebocyte Cell Biology. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 2832–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, N.; Fukano, Y.; Arita, R.; Shirakawa, R.; Kawazu, K.; Nakamura, M.; Amano, S. Rapid identification of fatty acids and (O-acyl)-ω-hydroxy fatty acids in human meibum by liquid chromatography/high-resolution mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1347, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.M.; Tong, L.; Duan, X.; Petznick, A.; Wenk, M.R.; Shui, G. Extensive characterization of human tear fluid collected using different techniques unravels the presence of novel lipid amphiphiles. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 55, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, P.L.; Donohue, M.N.; Cebak, J.E.; Beckmann, T.G.; Treece, M.; Johnson, J.W.; Miller, L.M.J. Tear Film Amphiphilic and Anti-Inflammatory Lipids in Bovine Pink Eye. Metabolites 2018, 8, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, P.L.; Ball, B.A.; Scoggin, K.; Troedsson, M.H.; Squires, E.L. Lipidomics of equine amniotic fluid: Identification of amphiphilic (O-acyl)-ω-hydroxy-fatty acids. Theriogenology 2018, 105, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, P.L.; Scoggin, K.; Ball, B.A.; Troedsson, M.H.; Squires, E.L. Lipidomics of equine sperm and seminal plasma: Identification of amphiphilic (O-acyl)-ω-hydroxy-fatty acids. Theriogenology 2016, 86, 1212–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirabayashi, T.; Anjo, T.; Kaneko, A.; Senoo, Y.; Shibata, A.; Takama, H.; Yokoyama, K.; Nishito, Y.; Ono, T.; Taya, C.; et al. PNPLA1 has a crucial role in skin barrier function by directing acylceramide biosynthesis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vavrušová, A.; Vrkoslav, V.; Plavka, R.; Bosáková, Z.; Cvačka, J. Analysis of (O-acyl) alpha- and omega-hydroxy fatty acids in vernix caseosa by high-performance liquid chromatography-Orbitrap mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 2291–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalužíková, A.; Vrkoslav, V.; Harazim, E.; Hoskovec, M.; Plavka, R.; Buděšínský, M.; Bosáková, Z.; Cvačka, J. Cholesteryl esters of ω-(O-acyl)-hydroxy fatty acids in vernix caseosa. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1579–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butovich, I.A.; Wilkerson, A.; Bhat, N.; McMahon, A.; Yuksel, S. On the pivotal role of Elovl3/ELOVL3 in meibogenesis and ocular physiology of mice. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 10034–10048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, A.; Westerberg, R.; Jacobsson, A. Fatty acid elongases in mammals: Their regulation and roles in metabolism. Prog. Lipid Res. 2006, 45, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butovich, I.A.; Bhat, N.; Wojtowicz, J.C. Comparative Transcriptomic and Lipidomic Analyses of Human Male and Female Meibomian Glands Reveal Common Signature Genes of Meibogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vences-Guzmán, M.Á.; Geiger, O.; Sohlenkamp, C. Ornithine lipids and their structural modifications: From A to E and beyond. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 335, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, O.; González-Silva, N.; López-Lara, I.M.; Sohlenkamp, C. Amino acid-containing membrane lipids in bacteria. Prog. Lipid Res. 2010, 49, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ferguson-Miller, S.M.; Reid, G.E. Characterization of ornithine and glutamine lipids extracted from cell membranes of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 20, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, E.K.; Hopmans, E.C.; Rijpstra, W.I.C.; Villanueva, L.; Dedysh, S.N.; Kulichevskaya, I.S.; Wienk, H.; Schoutsen, F.; Damsté, J.S.S. Novel Mono-, Di-, and Trimethylornithine Membrane Lipids in Northern Wetland Planctomycetes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 6874–6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishige, T.; Tani, A.; Sakai, Y.; Kato, N. Wax ester production by bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wältermann, M.; Stöveken, T.; Steinbüchel, A. Key enzymes for biosynthesis of neutral lipid storage compounds in prokaryotes: Properties, function and occurrence of wax ester synthases/acyl-CoA:diacylglycerol acyltransferases. Biochimie 2007, 89, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, A.L.; Kunst, L.; Jetter, R. Sealing Plant Surfaces: Cuticular Wax Formation by Epidermal Cells. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 683–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchman, D.; Ramasubramanian, A.; Foulks, G.N. Human Meibum Cholesteryl and Wax Ester Variability with Age, Sex, and Meibomian Gland Dysfunction. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 2286–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camera, E.; Ludovici, M.; Galante, M.; Sinagra, J.-L.; Picardo, M. Comprehensive analysis of the major lipid classes in sebum by rapid resolution high-performance liquid chromatography and electrospray mass spectrometry. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 3377–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.E. Sebaceous Gland Lipids. Semin. Dermatol. 1992, 11, 100–105. [Google Scholar]
- Picardo, M.; Ottaviani, M.; Camera, E.; Mastrofrancesco, A. Sebaceous gland lipids. Derm. Endocrinol. 2009, 1, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, A. Epidermal surface lipids. Derm. Endocrinol. 2009, 1, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, M.; Murphy, R.C. Electrospray mass spectrometry of human hair wax esters. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 1231–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasser, A.J.; Barwacz, C.A.; Dawson, D.V.; Brogden, K.A.; Drake, D.R.; Wertz, P.W. Presence of wax esters and squalene in human saliva. Arch. Oral Biol. 2011, 56, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, W.B. Fatty aldehyde and fatty alcohol metabolism: Review and importance for epidermal structure and function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, H.M. Triacylglycerol and wax ester-accumulating machinery in prokaryotes. Biochimie 2016, 120, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| ω-FAHFA | Fatty Acid | ω-Hydroxy Fatty Acid |
|---|---|---|
| 46:1 | 14:0 | 32:1 |
| 16:0 | 30:1 | |
| 46:2 | 16:1 | 30:1 |
| 14:1 | 32:1 | |
| 48:1 | 16:0 | 32:1 |
| 18:1 | 30:0 | |
| 48:2 | 16:1 | 32:1 |
| 18:1 | 30:1 | |
| 50:1 | 16:0 | 34:1 |
| 18:0 | 32:1 | |
| 50:2 | 18:1 | 32:1 |
| 16:1 | 34:1 | |
| 50:3 | 18:2 | 32:1 |
| 51:2 | 18:1 | 33:1 |
| 52:2 | 18:1 | 34:1 |
| 52:3 | 18:2 | 34:1 |
| 18:0 | 34:3 |
| Lipid Class | Occurrence | Functions | MS2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Branched-Chain FAHFA [3,4,5,6,7,8,9] |
|
| [M − H]− ↓ [FA]− > [Hydroxy-FA]− |
| Branched-Chain FAHFA—DAG [15] |
|
| [M + NH4]+ ↓ [DAG—H2O]+ [M-FA-H2O]+ [M-Hydroxy-FA-H2O]+ |
| ω-FAHFA [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25] |
|
| [M − H]− ↓ [FA]− > [Hydroxy-FA]− |
| ω-FAHFA—CE [26] |
|
| [M + H]+ ↓ [M-(cholesterol-H2O)]+ |
| ORN-FAHFA [30,31,32] |
|
| [M + H]+ → [M-(FA-H2O)]+ [M − H]− → [M-FA]− |
| Methyl-ORN-FAHFA [33] |
|
| [M + H]+ → [M-FA]+ > [M-FA-CH5N]+ |
| Tri-Methyl-ORN-FAHFA [33] |
|
| [M + H]+ → [M-FA]+ > [M-FA-C2H7N]+ |
| Tri-Methyl-ORN-FAHFA [33] |
|
| [M + H]+ → [M-FA]+ > [M-FA-C3H9N]+ |
| Wax Ester [34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43] |
|
| [M + NH4]+ ↓ [FA + H]+ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wood, P.L. Fatty Acyl Esters of Hydroxy Fatty Acid (FAHFA) Lipid Families. Metabolites 2020, 10, 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10120512
Wood PL. Fatty Acyl Esters of Hydroxy Fatty Acid (FAHFA) Lipid Families. Metabolites. 2020; 10(12):512. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10120512
Chicago/Turabian StyleWood, Paul L. 2020. "Fatty Acyl Esters of Hydroxy Fatty Acid (FAHFA) Lipid Families" Metabolites 10, no. 12: 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10120512
APA StyleWood, P. L. (2020). Fatty Acyl Esters of Hydroxy Fatty Acid (FAHFA) Lipid Families. Metabolites, 10(12), 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10120512




