A Perspective and Framework for Developing Sample Type Specific Databases for LC/MS-Based Clinical Metabolomics
Abstract
1. Introduction
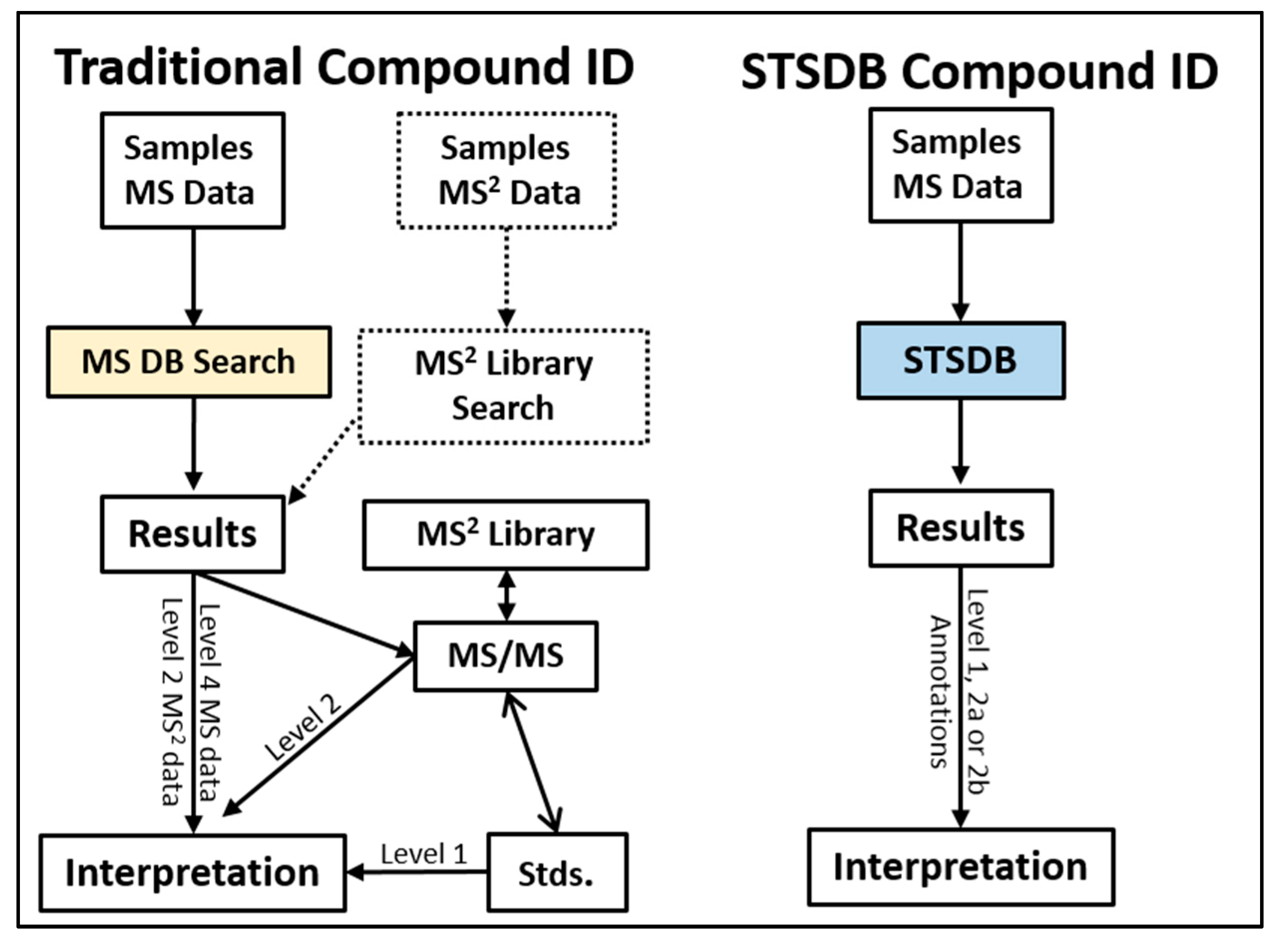
2. Traditional Strategies in LC/MS-Based Metabolomics Compound ID
3. Basic STSDB Strategy
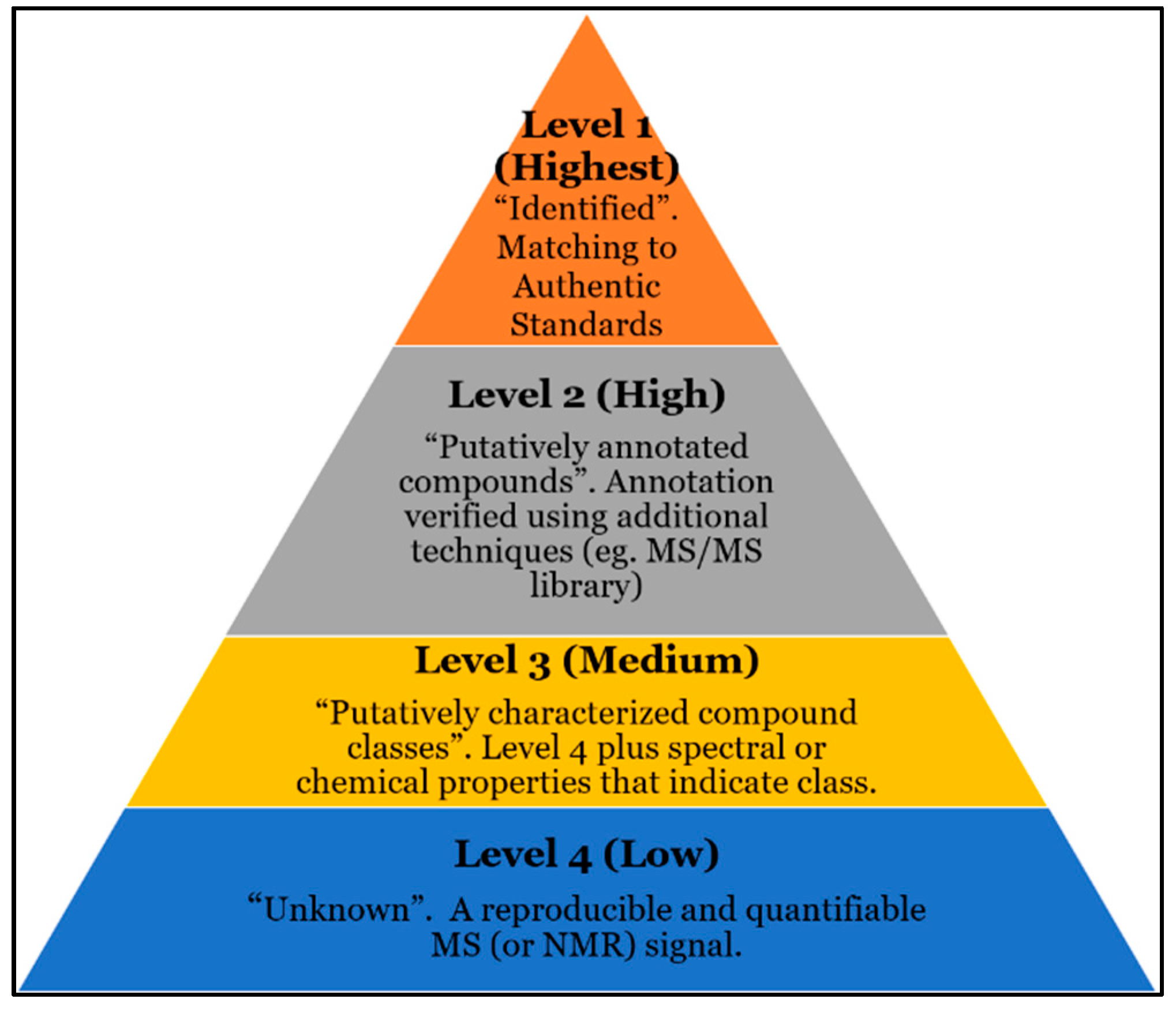
4. Current Challenges with Compound ID
5. Challenges with Current Databases
6. Challenges with Current Focused DB Approaches
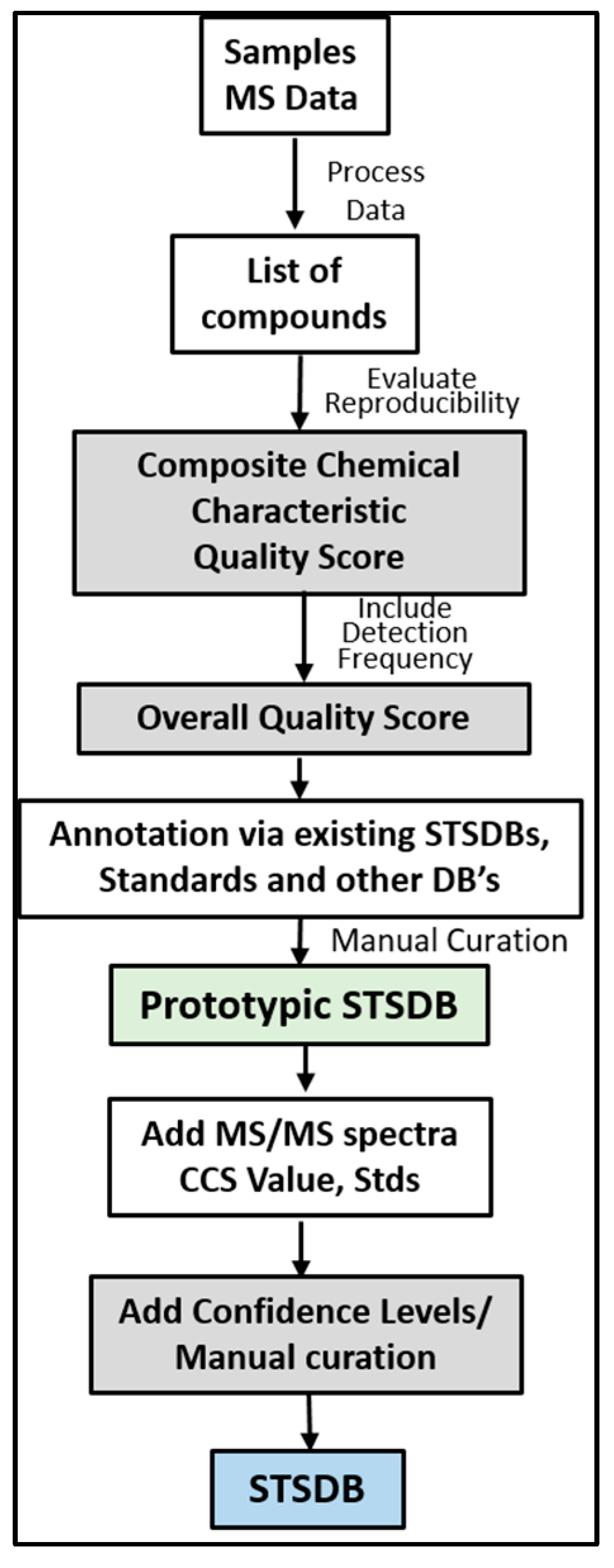
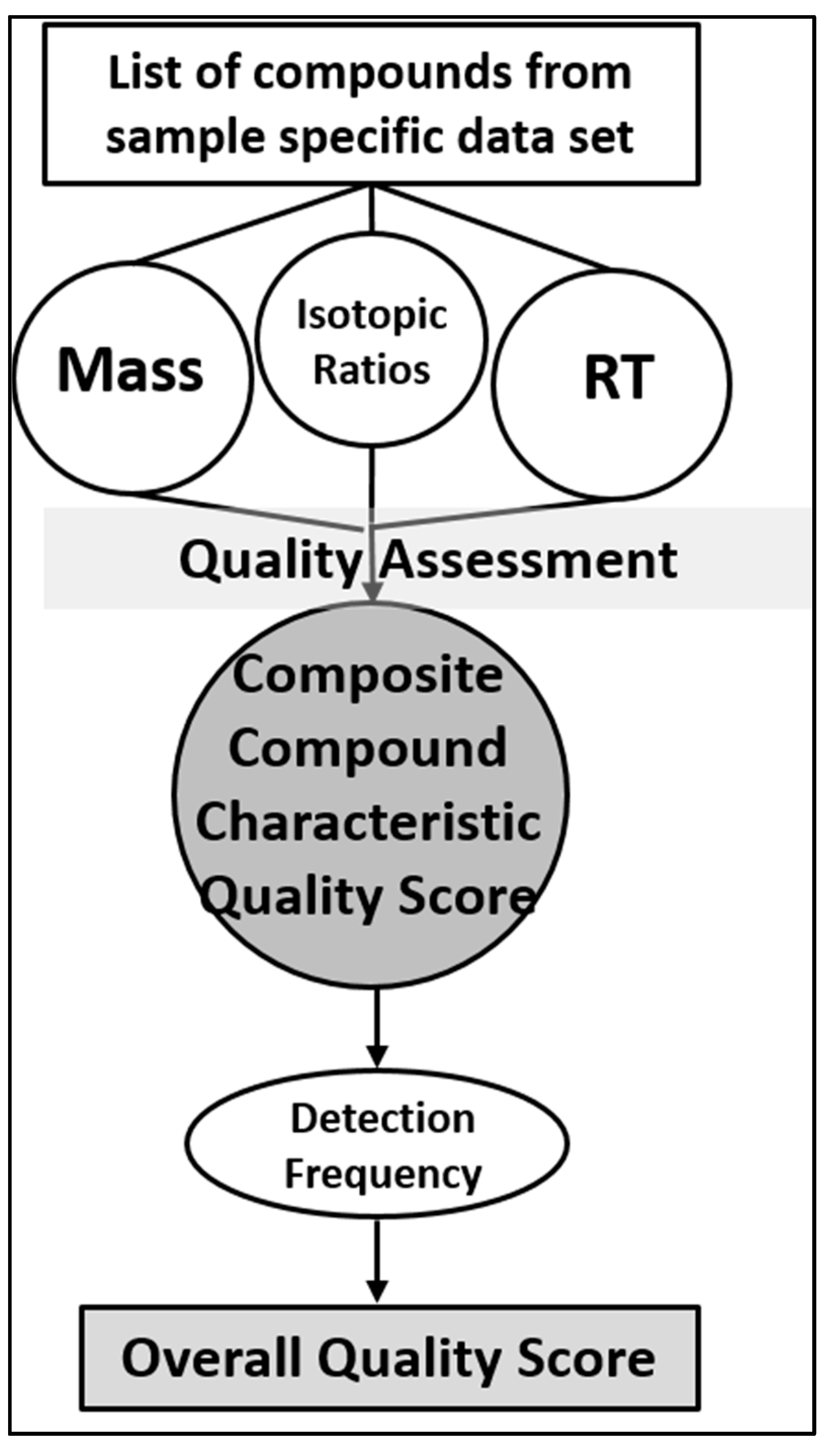
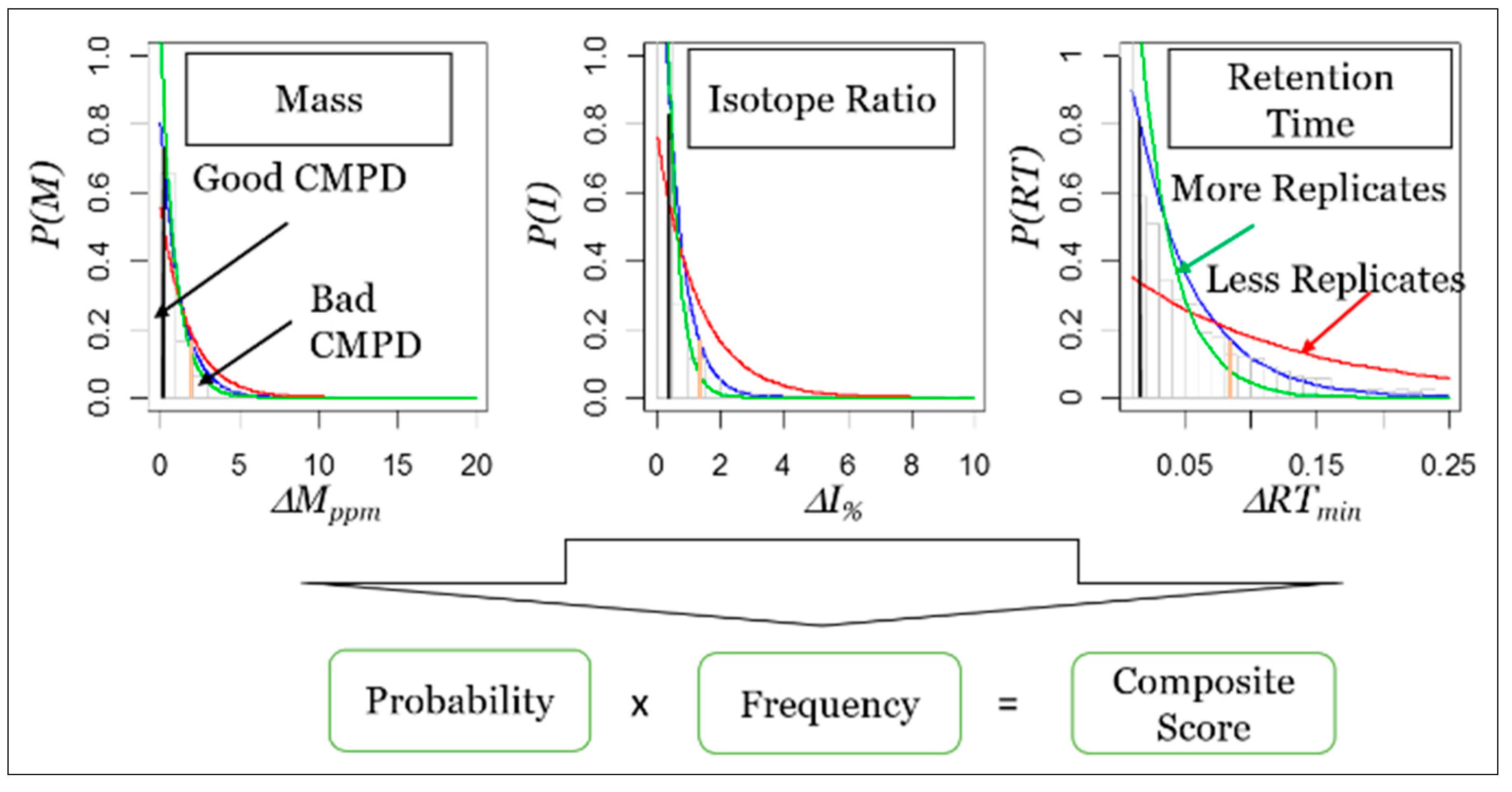
7. Framework for Developing STSDBs
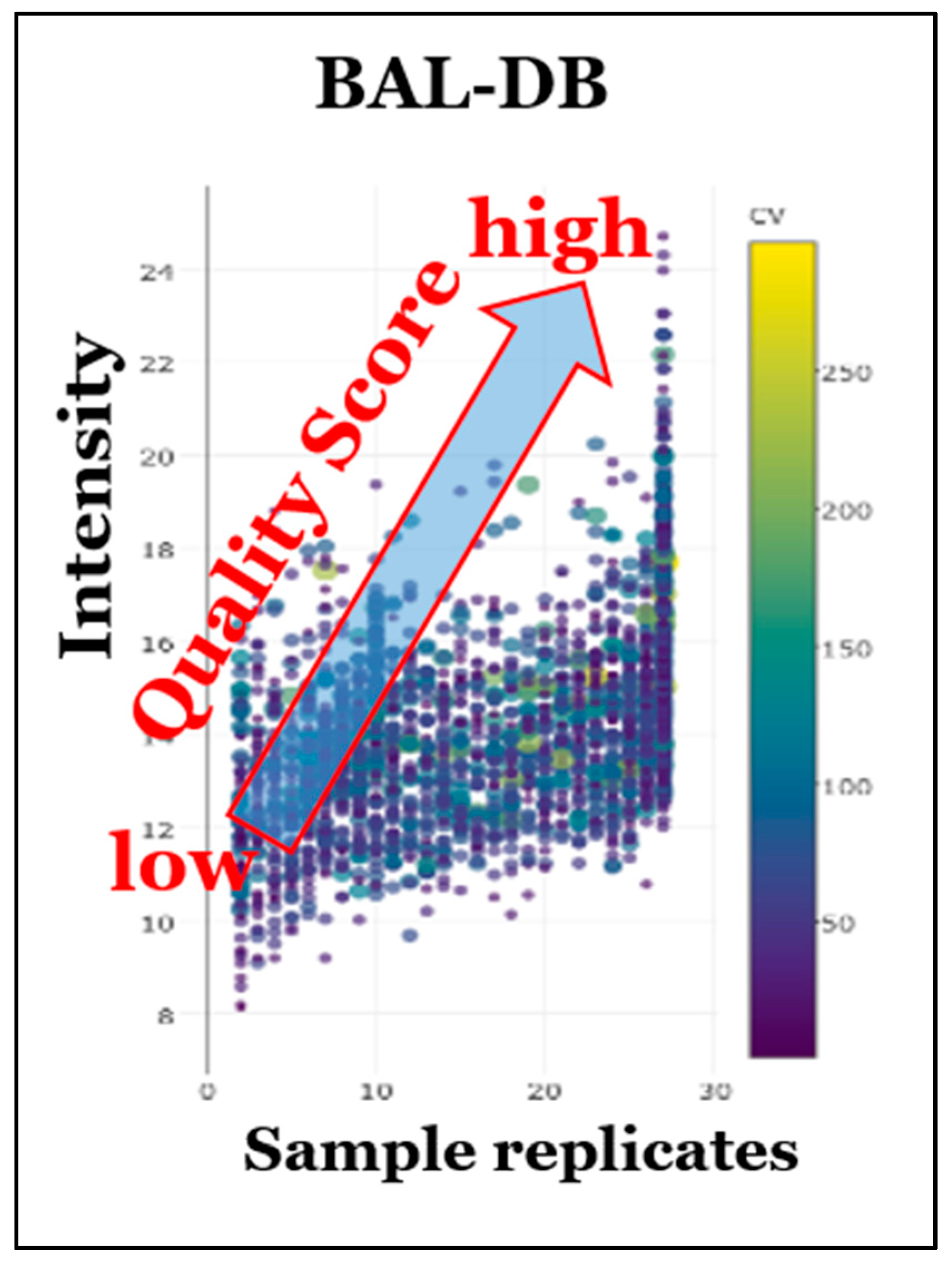
8. Prototypic STSDBs for Bronchoalveolar Lavage (BAL) and HEK293 Cells
9. STSDB Computational Strategies
10. Limitations of STSDBs
11. Advantages of STSDBs
12. The Way Forward
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Psychogios, N.; Hau, D.D.; Peng, J.; Guo, A.C.; Mandal, R.; Bouatra, S.; Sinelnikov, I.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Eisner, R.; Gautam, B.; et al. The human serum metabolome. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Cruickshank, C.; Armstrong, M.; Mahaffey, S.; Reisdorph, R.; Reisdorph, N. New sample preparation approach for mass spectrometry-based profiling of plasma results in improved coverage of metabolome. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1300, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.P. Sequencing the exposome: A call to action. Toxicol. Rep. 2016, 3, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, F. Rethinking Mass Spectrometry-Based Small Molecule Identification Strategies in Metabolomics. Mass Spectr. 2014, 3, S0038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, F.; Shinbo, Y.; Oikawa, A.; Hirai, M.Y.; Fiehn, O.; Kanaya, S.; Saito, K. Assessment of metabolome annotation quality: A method for evaluating the false discovery rate of elemental composition searches. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry: Combined Targeted and Untargeted Profiling. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2016, 114, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingol, K. Recent Advances in Targeted and Untargeted Metabolomics by NMR and MS/NMR Methods. High Throughput 2018, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, B.B.; Mohapatra, S. Tools and resources for metabolomics research community: A 2017–2018 update. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazenovic, I.; Kind, T.; Ji, J.; Fiehn, O. Software Tools and Approaches for Compound Identification of LC-MS/MS Data in Metabolomics. Metabolites 2018, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazenovic, I.; Kind, T.; Sa, M.R.; Ji, J.; Vaniya, A.; Wancewicz, B.; Roberts, B.S.; Torbasinovic, H.; Lee, T.; Mehta, S.S.; et al. Structure Annotation of All Mass Spectra in Untargeted Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 2155–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walmsley, S.; Cruickshank-Quinn, C.; Quinn, K.; Zhang, X.; Petrache, I.; Bowler, R.P.; Reisdorph, R.; Reisdorph, N. A prototypic small molecule database for bronchoalveolar lavage-based metabolomics. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.M.; Heyman, H.M. Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1775, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis Chemical Analysis Working Group (CAWG) Metabolomics Standards Initiative (MSI). Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, V.J.; Bandrowski, A.E.; Pepin, A.S.; Gonzalez, B.J.; Desfeux, A. OMICtools: An informative directory for multi-omic data analysis. Database 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warth, B.; Spangler, S.; Fang, M.; Johnson, C.H.; Forsberg, E.M.; Granados, A.; Martin, R.L.; Domingo-Almenara, X.; Huan, T.; Rinehart, D.; et al. Exposome-Scale Investigations Guided by Global Metabolomics, Pathway Analysis, and Cognitive Computing. Anal. Chem. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruttkies, C.; Schymanski, E.L.; Wolf, S.; Hollender, J.; Neumann, S. MetFrag relaunched: Incorporating strategies beyond in silico fragmentation. J. Cheminformatics 2016, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, F.; Pon, A.; Wilson, M.; Greiner, R.; Wishart, D. CFM-ID: A web server for annotation, spectrum prediction and metabolite identification from tandem mass spectra. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W94–W99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kind, T.; Liu, K.H.; Lee, D.Y.; DeFelice, B.; Meissen, J.K.; Fiehn, O. LipidBlast in silico tandem mass spectrometry database for lipid identification. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhrkop, K.; Fleischauer, M.; Ludwig, M.; Aksenov, A.A.; Melnik, A.V.; Meusel, M.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Rousu, J.; Bocker, S. SIRIUS 4: A rapid tool for turning tandem mass spectra into metabolite structure information. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhrkop, K.; Shen, H.; Meusel, M.; Rousu, J.; Bocker, S. Searching molecular structure databases with tandem mass spectra using CSI:FingerID. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12580–12585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barupal, D.K.; Fan, S.; Fiehn, O. Integrating bioinformatics approaches for a comprehensive interpretation of metabolomics datasets. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 54, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hufsky, F.; Bocker, S. Mining molecular structure databases: Identification of small molecules based on fragmentation mass spectrometry data. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2017, 36, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Neta, P.; Stein, S.E. Extending a Tandem Mass Spectral Library to Include MS(2) Spectra of Fragment Ions Produced In-Source and MS(n) Spectra. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 28, 2280–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, T.N.; Weber, R.J.; Jones, M.R.; Chetwynd, A.J.; Rodri Guez-Blanco, G.; Di Guida, R.; Viant, M.R.; Dunn, W.B. msPurity: Automated Evaluation of Precursor Ion Purity for Mass Spectrometry-Based Fragmentation in Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 2432–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffin, M.D.; Cao, L.; Deik, A.A.; Clish, C.B.; Hu, F.B.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Razquin, C.; Bullo, M.; Corella, D.; Gomez-Gracia, E.; et al. MetProc: Separating measurement artifacts from true metabolites in an untargeted metabolomics experiment. J. Proteome Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.M.; Flight, R.M.; Wang, Q.J.; Higashi, R.M.; Fan, T.W.; Lane, A.N.; Moseley, H.N.B. New methods to identify high peak density artifacts in Fourier transform mass spectra and to mitigate their effects on high-throughput metabolomic data analysis. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahieu, N.G.; Patti, G.J. Systems-Level Annotation of a Metabolomics Data Set Reduces 25,000 Features to Fewer than 1000 Unique Metabolites. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 10397–10406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymanski, E.L.; Ruttkies, C.; Krauss, M.; Brouard, C.; Kind, T.; Duhrkop, K.; Allen, F.; Vaniya, A.; Verdegem, D.; Bocker, S.; et al. Critical Assessment of Small Molecule Identification 2016: Automated methods. J. Cheminformatics 2017, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Kind, T.; Fiehn, O. Using Accurate Mass Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry with the MINE Database for Epimetabolite Annotation. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajka, T.; Fiehn, O. LC-MS-Based Lipidomics and Automated Identification of Lipids Using the LipidBlast In-Silico MS/MS Library. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1609, 149–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Cajka, T.; Kind, T.; Ma, Y.; Higgins, B.; Ikeda, K.; Kanazawa, M.; VanderGheynst, J.; Fiehn, O.; Arita, M. MS-DIAL: Data-independent MS/MS deconvolution for comprehensive metabolome analysis. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Jewison, T.; Guo, A.C.; Wilson, M.; Knox, C.; Liu, Y.; Djoumbou, Y.; Mandal, R.; Aziat, F.; Dong, E.; et al. HMDB 3.0—The Human Metabolome Database in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kind, T.; Tsugawa, H.; Cajka, T.; Ma, Y.; Lai, Z.; Mehta, S.S.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Barupal, D.K.; Showalter, M.R.; Arita, M.; et al. Identification of small molecules using accurate mass MS/MS search. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2018, 37, 513–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kind, T.; Fiehn, O. Seven Golden Rules for heuristic filtering of molecular formulas obtained by accurate mass spectrometry. BMC Bioinformatics 2007, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athersuch, T.J. The role of metabolomics in characterizing the human exposome. Bioanalysis 2012, 4, 2207–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andra, S.S.; Austin, C.; Patel, D.; Dolios, G.; Awawda, M.; Arora, M. Trends in the application of high-resolution mass spectrometry for human biomonitoring: An analytical primer to studying the environmental chemical space of the human exposome. Environ. Int. 2017, 100, 32–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppal, K.; Walker, D.I.; Liu, K.; Li, S.; Go, Y.M.; Jones, D.P. Computational Metabolomics: A Framework for the Million Metabolome. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2016, 29, 1956–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putignani, L.; Dallapiccola, B. Foodomics as part of the host-microbiota-exposome interplay. J. Proteomics 2016, 147, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viant, M.R.; Kurland, I.J.; Jones, M.R.; Dunn, W.B. How close are we to complete annotation of metabolomes? Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2017, 36, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauling, J.; Klipp, E. Computational Lipidomics and Lipid Bioinformatics: Filling In the Blanks. J. Integr. Bioinform. 2016, 13, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, S.E.; Poad, B.L.; Batarseh, A.; Abbott, S.K.; Mitchell, T.W. Advances and unresolved challenges in the structural characterization of isomeric lipids. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 524, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chintapalli, V.R.; Al Bratty, M.; Korzekwa, D.; Watson, D.G.; Dow, J.A. Mapping an atlas of tissue-specific Drosophila melanogaster metabolomes by high resolution mass spectrometry. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.J.; Zhang, C.; Zou, Q.; Ji, Z.L. TiSGeD: A database for tissue-specific genes. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1273–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yu, X.; Zack, D.J.; Zhu, H.; Qian, J. TiGER: A database for tissue-specific gene expression and regulation. BMC Bioinformatics 2008, 9, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omenn, G.S.; Lane, L.; Lundberg, E.K.; Overall, C.M.; Deutsch, E.W. Progress on the HUPO Draft Human Proteome: 2017 Metrics of the Human Proteome Project. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 4281–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouatra, S.; Aziat, F.; Mandal, R.; Guo, A.C.; Wilson, M.R.; Knox, C.; Bjorndahl, T.C.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Saleem, F.; Liu, P.; et al. The human urine metabolome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dame, Z.T.; Aziat, F.; Mandal, R.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Bouatra, S.; Borzouie, S.; Guo, A.C.; Sajed, T.; Deng, L.; Lin, H.; et al. The human saliva metabolome. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 1864–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, R.; Guo, A.C.; Chaudhary, K.K.; Liu, P.; Yallou, F.S.; Dong, E.; Aziat, F.; Wishart, D.S. Multi-platform characterization of the human cerebrospinal fluid metabolome: A comprehensive and quantitative update. Genome Med. 2012, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Lewis, M.J.; Morrissey, J.A.; Flegel, M.D.; Jeroncic, K.; Xiong, Y.; Cheng, D.; Eisner, R.; Gautam, B.; Tzur, D.; et al. The human cerebrospinal fluid metabolome. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 871, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Walmsley, S.; Cheung, G.C.M.; Chen, L.; Cheng, C.Y.; Beuerman, R.W.; Wong, T.Y.; Zhou, L.; Choi, H. Customized Consensus Spectral Library Building for Untargeted Quantitative Metabolomics Analysis with Data Independent Acquisition Mass Spectrometry and MetaboDIA Workflow. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 4897–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermin, D.; Walmsley, S.J.; Gingras, A.C.; Choi, H.; Nesvizhskii, A.I. LuciPHOr: Algorithm for phosphorylation site localization with false localization rate estimation using modified target-decoy approach. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2013, 12, 3409–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.J.; Liu, S.J.; Zhu, Q.F.; Guo, N.; Wang, Y.L.; Yuan, B.F.; Feng, Y.Q. Establishment of Liquid Chromatography Retention Index Based on Chemical Labeling for Metabolomic Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8412–8420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crouch, M.J.; Kosaraju, R.; Guesdon, W.; Armstrong, M.; Reisdorph, N.; Jain, R.; Fenton, J.; Shaikh, S.R. Frontline Science: A reduction in DHA-derived mediators in male obesity contributes toward defects in select B cell subsets and circulating antibody. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, C.R.; Denman, B.A.; Mazzo, M.R.; Armstrong, M.L.; Reisdorph, N.; McQueen, M.B.; Chonchol, M.; Seals, D.R. Chronic nicotinamide riboside supplementation is well-tolerated and elevates NAD(+) in healthy middle-aged and older adults. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheubert, K.; Hufsky, F.; Petras, D.; Wang, M.; Nothias, L.F.; Duhrkop, K.; Bandeira, N.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Bocker, S. Significance estimation for large scale metabolomics annotations by spectral matching. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reisdorph, N.A.; Walmsley, S.; Reisdorph, R. A Perspective and Framework for Developing Sample Type Specific Databases for LC/MS-Based Clinical Metabolomics. Metabolites 2020, 10, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10010008
Reisdorph NA, Walmsley S, Reisdorph R. A Perspective and Framework for Developing Sample Type Specific Databases for LC/MS-Based Clinical Metabolomics. Metabolites. 2020; 10(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleReisdorph, Nichole A., Scott Walmsley, and Rick Reisdorph. 2020. "A Perspective and Framework for Developing Sample Type Specific Databases for LC/MS-Based Clinical Metabolomics" Metabolites 10, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10010008
APA StyleReisdorph, N. A., Walmsley, S., & Reisdorph, R. (2020). A Perspective and Framework for Developing Sample Type Specific Databases for LC/MS-Based Clinical Metabolomics. Metabolites, 10(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10010008




