Abstract
Considering the complex pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the multitarget ligand strategy is expected to provide superior effects for the treatment of the neurological disease compared to the classic single target approach. Thus, a series of 13 novel (5e-q) pyrrole-based Schiff bases were synthesized by conventional and microwave-assisted condensations, and the compounds were evaluated for MAO-A, MAO-B and AChE inhibitory activities. The chemical structures of the newly formed molecules were elucidated by a combination of spectral methods. The obtained results confirmed the theoretical data. The majority of the title Schiff bases demonstrated good potential towards AChE at 10 μM concentrations, with the most promising compound 5m (58%) exerting a comparative effect to that of the applied standard—Donepezil. 5j and 5o selectively inhibited MAO-B by 26% and 21% (at 1 μM concentration), respectively. The compound condensed with 5-nitro-2-furaldehyde (5j) achieved the best dual MAO-B and AChE inhibitory capacities. In addition to the in vitro analysis, docking simulations targeting the active sites of AChE (PDB ID: 4EY6) and MAO-B (PDB: 2V5Z) were employed to explore the possible interactions of the most prominent dual inhibitor (5j) with the enzymes. Furthermore, in silico ADME and PAMPA-blood–brain barrier (BBB) studies were conducted.
1. Introduction
More than half of the dementia cases established nowadays are related to Alzheimer’s disease (AD). AD is characterized as a neurodegenerative disorder with a chronic and progressive character [1]. These statistics point the attention of scientists towards investing constant efforts into the design and synthesis of novel anti-AD drugs [2]. The newest studies into the design and production of monoclonal antibodies have been of great interest since the amyloid hypothesis suggests targeting them might directly affect the progression of AD [3]. However, several major drawbacks, such as the need for repeated administrations and the associated cost of production, the need for frequent monitoring, and vague efficacy [4] have been reported. In addition, the main symptomatic treatment for AD [5] is based on the classic registered AChE inhibitors, such as Galantamine, Rivastigmine and Donepezil, which to an extent modify the effects of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in support of the cognitive processes [6].
On the other hand, monoamine oxidases (MAOs) are involved in the regulation of amine levels both in the brain and the peripheral tissues which frames them as key metabolic enzymes [7]. The active inhibitors of the former flavoenzymes were also established as potential anti-AD drugs [8]. However, only the highly selective type B inhibitors have been discussed as potential AD compounds. The selectivity towards MAO-B is necessary, since MAO-A inhibitors could cause “cheese syndrome” characterized by elevated blood pressure (hypertensive crises) [9]. Thus, the documented complex pathophysiology of AD and the published research papers affirms the ignited scientific interest in the design and synthesis of novel multitarget compounds prioritizing the symptomatic treatment of AD, where two frequently involved enzyme targets are acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) [2]. Considering the complicated pathophysiology of AD, most recent works have been focused on the search for novel multi target ligands with effects against multiple enzymes. An example is a recent work by Raka et al. which discussed the synthesis and evaluation of novel multitarget drugs which simultaneously interact with acetylcholinesterase, β-secretase and monoamine oxidases. The authors noted the importance of targeting several hypotheses of the pathogenesis of AD [10].
The multi-functionalized pyrrole rings exerting various pharmacological profiles could be successfully implemented in the design of novel multitarget AChE/MAO-B inhibitors, with structures comprising a pyrrole motif often established as novel pharmacologically important drugs [11]. The involvement of a pyrrole core structure in the stabilization of MAO-B/ligand complexes is also discussed by Regina et al. [12]. Recently, prominent pyrrole-based acetylcholinesterase inhibitors were reported by Gümüş et al. [13]. The novel compounds were determined as highly potent AChE inhibitors with nanomolar inhibitory constants and better activity compared to the applied standards. These findings reignited the interest of some research groups to explore the former hetero-compound against receptors involved in the pathogenesis of AD [14,15]. This confirmed pyrrole derivatives as fitting well with the design strategy of identifying new effective compounds targeting AChE and/or MAO as promising agents to support AD therapy.
In addition, molecules comprising a Schiff base moiety are an essential class of organic compounds, formed by the reaction of amine and ketones/aldehydes. The pharmacological profile of compounds comprising the former functional group is broad, which includes antimicrobial, antiseptic, antidepressant, antitubercular, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antiprotozoal effects etc. [16,17,18,19]. Several articles have reported excellent AChE and MAO-B inhibitory capacities of compounds comprising hydrazide or hydrazide–hydrazone motifs [20,21,22]. Moreover, the essential role of the imine group in the synthesis of selective multitarget AChE and MAO-B inhibitors has been discussed [23] and previously reported [24,25]. Recent findings by Tok et al. reported the design and synthesis of pyrrazolone-based Schiff bases as novel dual-acting MAO-B/AChE inhibitors [26]. The novel compounds exerted good AChE and MAO-B blocking capacities in the micromolar range. Additional docking and ADME studies provided information about the pharmacokinetic profile of the lead compounds. Yuldasheva et al. have presented novel Schiff bases of p-vanillin with good in vitro MAO-B and AChE blocking capacities [23]. Literature data describing Schiff bases as MAO and AChE inhibitors has been reported [26]. The aforementioned articles encouraged us to incorporate a Schiff base in a pyrrole-based core motif which could enhance the MAO-B and AChE inhibitory effects of the new compounds. Additionally, the employment of MW irradiation of Schiff bases was reported as superior compared to conventional reflux synthesis [27].
Analyzing the discussed data, it was found that some pyrrole derivatives could obtain good inhibition values against some of the major targets in the pathogenesis of AD. Therefore, this work provides the syntheses of novel pyrrole-based Schiff bases as novel dual MAO-B/AChE inhibitors. Both conventional and microwave-assisted synthesis of 13 novel pyrrole-based Schiff bases are implemented and their MAO and AChE effects explored by in vitro and in silico studies. Visualizations of the major intermolecular interactions in the active sites of MAO-B and AChE are carried out with docking simulations. Finally, the most active dual MAO-B/AChE inhibitor is examined for its ADME properties and PAMPA blood-brain barrier permeability.
2. Results
2.1. Chemistry
The synthetic protocol leading to the final Schiff bases is illustrated in Scheme 1. The synthesis commenced with the reaction of the commercially available 2,4′-dibromoacetophenone and the sodium salt of ethyl acetoacetate to produce the 2,5-dicarbonyl derivative (2), which was utilized for a subsequent Paal–Knorr condensation. An excess amount of the tryptophan amino acid was used (1.2 eq.) to produce the tryptophan-based N-pyrrolyl carboxylic acid (3) through the MW-assisted approach. After a work-up, an esterification of 3 with excess of thionyl chloride and ethanol was carried out [28].
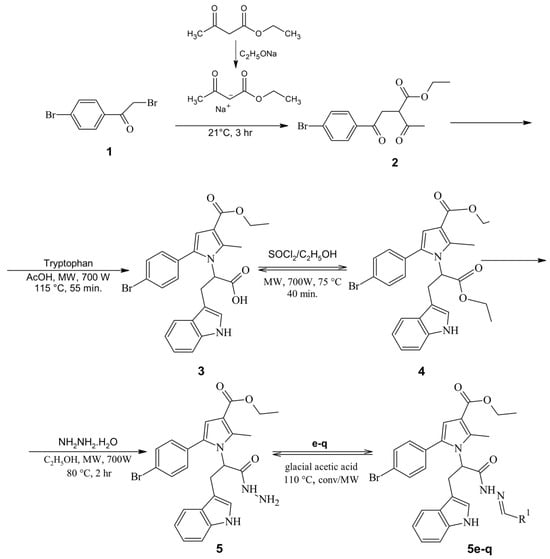
Scheme 1.
Synthetic path for the title compounds 5(e–q).
The hydrazinolysis of the obtained N-pyrrolyl carboxylic ester 4 was conducted in a MW reactor, due to the significant reduction in reaction time. Subsequently, the title Schiff bases were prepared by reacting various carbonyls (Table 1) with the tryptophan-based hydrazide (5). An excess amount of the carbonyl partner was used (1.2 eq.) in a medium of glacial acetic acid. The reactions times achieved by the conventional method were significantly decreased by implementing MW-assisted synthesis (Table 2).

Table 1.
Applied carbonyl compounds (R1 = e–q) in the condensation reactions.

Table 2.
Comparison of the reaction times and yields of compounds 5(e-q) employing conventional and microwave-assisted approaches.
The new compound structures were confirmed by IR (Supplementary, Figures S27–S39), 1H NMR (Supplementary, Figures S1–S13) 13C NMR (Supplementary, Figures S14–S26) and mass spectroscopy (Supplementary, Figures S40–S52). The IR spectra of the Schiff bases demonstrated an intensive band around 1500–1580 cm−1 assigned to the C=N (azomethine) group. The NH group was represented by a broad peak at around 3100–3300 cm−1. The Schiff base condensed with the salicylic aldehyde (5o) comprising an –OH group in the phenol ring and provided a peak at 3434 cm−1. An essential band at around 1700 cm−1 was attributed to a carbonyl group (C=O). The 1H NMR spectra displayed the proton of the amide functional group (CO-NH) in the region δ 11.00–11.20. The proton of the –OH group of the pyrrole-based Schiff base (5o) was observed at δ 11.21. Another signal for all title compounds was detected at δ 10.73–10.70 for the proton of the NH group in the tryptophan moiety. The protons of the methyl group situated at the second position of the pyrrole ring were observed at around δ 2.45. The protons from the ethyl ester CH2 and CH3 groups were observed at δ 4.24–4.29 and δ 1.27–1.30, respectively. The corresponding signals for the evaluated 13C analysis responded fully to the evaluated structures. The masses of the reported compounds were in good agreement with the theoretical data.
2.2. In Vitro Assays
All novel Schiff bases 5(e–q) were screened for their MAO-A/B, and AChE activities. Among the screening ligands, 5e, 5g, 5j, 5l, 5m and 5o displayed good AChE inhibitory activities, while the pyrrole-based molecule 5j demonstrated the most prominent dual-acting AChE/MAO-B capacities.
2.2.1. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Assay
The activity against eeAChE (electric eel acetylcholinesterase) was measured according to the modified Ellman et al. method as explained in [29]. The reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor Donepezil was applied as a reference compound. The inhibitory capacities of the test compounds, at 10 μM concentrations, are given in Figure 1.
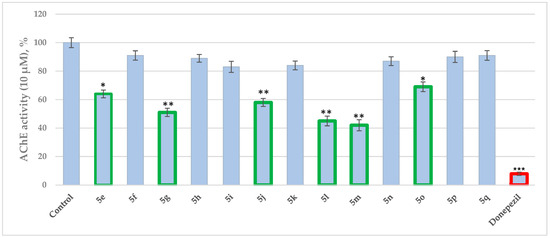
Figure 1.
AChE assay of 5(e–q) applied at 10 μM concentrations. Data are presented as means from three independent experiments ± SD. * p < 0.1, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. control (pure eeAChE).
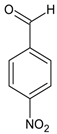
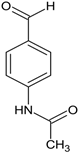
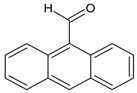
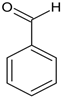
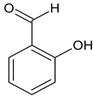
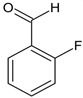
According to Figure 1, the Schiff bases 5e, 5g, 5j, 5l, 5m and 5o effectively inhibit the AChE enzyme in micro molar concentrations. The hydrazide–hydrazone condensed with 9-anthracencarboxaldehyde (5m) was found to be the most prominent AChE inhibitor of the applied series of pyrrole-based compounds. The former compound displayed 58% inhibitory capacity. In addition, the Schiff base condensed with 2-naphthaldehyde—5l, and revealed good effects against AChE (55%). The presence of a hydroxyl moiety (5o) and nitro group (5e) led to moderate increases in the enzyme inhibitory effects, 31% and 36%, respectively. A benzene fragment substituted with a fluorine atom at -o (5p) and -m (5q) positions did not display AChE effects. An increase in the AChE blocking effects were observed when 5g and 5j were tested—49% and 42%, respectively.
2.2.2. Monoamine oxidase Type B (MAO-B) and Monoamine oxidase Type A (MAO-A) Assays
The Schiff bases 5(e–q) were also tested for MAO-A/B effects by in vitro fluorometric methods. Selegiline and Clorgiline were used as standard drugs for MAO-B and MAO-A, respectively. Figure 2 displays the MAO-B activities of the newly synthesized pyrrole-based Schiff bases.
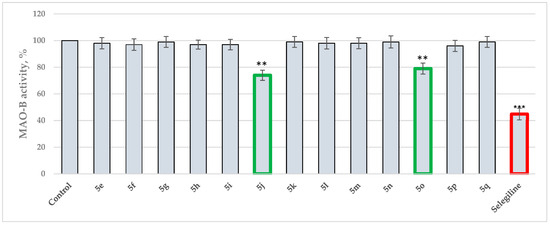
Figure 2.
MAO-B assay of 5(e–q) applied at 1 μM concentrations. Data are presented as means from three independent experiments ± SD., ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. control (pure hMAOB).
Interestingly, only two Schiff bases were identified as moderate MAO-B inhibitors—5o and 5j. The hydrazide–hydrazone condensed with benzaldehyde (5o) acquired 21% inhibitory capacity, while the Schiff base comprising 5-nitrofuran fragment (5j) displayed 26% inhibition of MAO-B. The standard Selegiline demonstrated 55% blocking effect when compared to the control (pure hMAOB). The lack of MAO-B inhibitory activities in the majority of the compounds were further examined through molecular docking studies in Section 2.3.
To observe the MAO-A effects of the tested Schiff bases, additional in vitro evaluations were implemented (Figure 3).
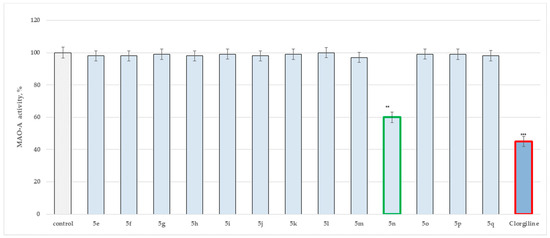
Figure 3.
MAO-A assay of 5(e–q) applied at 1 μM concentrations. Data are presented as means from three independent experiments ± SD., ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. control (pure MAO-A).
Importantly, only one of the title Schiff bases displayed inhibitory activity against MAO-A. The hydrazide–hydrazone condensed with benzaldehyde (5n) demonstrated 40% blocking capacity against the described MAO isoform.
Overall, the in vitro evaluations against MAO-A/B/AChE revealed that the Schiff base 5j is a prominent dual-acting AChE/MAO-B inhibitor with no effects towards the MAO-A isoform. The former compound exerted good MAO-B inhibitory activity (26% at 1 μM concentration) and prominent AChE blocking capacity (42% at 10 μM concentration).
2.3. Molecular Docking
In an attempt to gain further understanding of the in vitro results, and to obtain additional insights into the active binding conformations of the best dual AChE/MAO-B inhibitor 5j, molecular docking simulations in the active sites of AChE (PDB: 4EY6) and MAO-B (PDB: 2V5Z) were carried out. The visualizations of the intermolecular interactions between 5j and the active sites of AChE (Figure 4) and MAO-B (Figure 5) are displayed below.
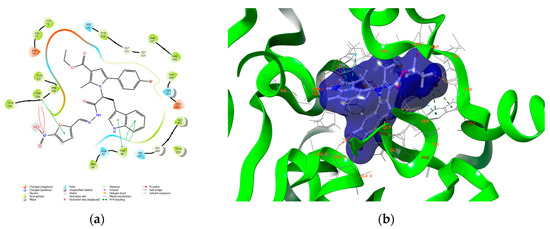
Figure 4.
Major intermolecular interactions between the active site of AChE (PDB: 4EY6) and 5j: (a) 2D visualization; (b) 3D visualization.
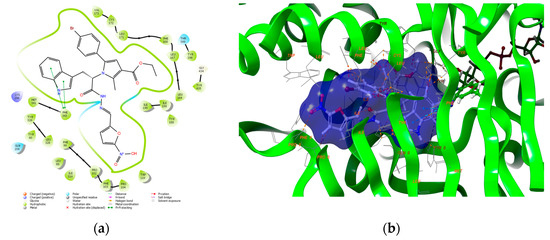
Figure 5.
Visualizations of the intermolecular interactions of 5j with the active site of MAO-B (PDB: 2V5Z): (a) 2D panel; (b) 3D panel.
The obtained docking poses for the interaction of the pyrrole-based hydrazide 5j with AChE revealed that 5j formed a compact complex with the active site of the enzyme. The furan moiety was facing the entrance cavity of the enzyme, while the pyrrole and the tryptophan fragments were situated in the substrate pocket. Several stable π−π bonds were formed between the aromatic moieties and the active amino residues Trp86 and Trp286. Numerous hydrophobic interactions with Tyr72, Val73, Tyr124, Phe295, Phe297, Tyr341, Tyr337, and Ile451 also stabilized the final complex. The binding energy of 5j was −10.57 kcal/mol. The score of the native co-crystallized ligand, Galantamine, was −11.54 kcal/mol. This was close to the results of the most active pyrrole-based compound 5j.
In addition, subsequent 2D and 3D visualizations of the intermolecular interactions between 5j and the active site of MAO-B are provided in Figure 5.
The pyrrole-based Schiff base (5j) formed two π−π interactions with Phe343. The fragments, which participate in the stable bonds of the former, were the pyrrole and tryptophan aromatics. No hydrogen bonds between the examined compound and MAO-B were observed. Importantly, the amino acids constructing the aromatic cage of MAO-B (Tyr398 and Tyr435) stabilized the ligand through hydrophobic interactions. The docking score of 5j in the active site of MAO-B was −8.51 kcal/mol, which was lower than the score of Safinamide—12.94 kcal/mol.
2.4. Pharmacokinetic Study
Finally, several important physicochemical descriptors of 5j were examined through in silico ADME analysis and additionally processed through in vitro PAMPA-BBB permeability assay.
2.4.1. ADME Properties Evaluation
The ADME investigations of the most active dual agent were carried out with the QikProp module in Maestro and the corresponding results are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
In silico ADME investigations of 5j.
As per QikProp ADME analysis, the pyrrole-based compound did not obey Lipinski’s rule of five. Three principles were not matched. Importantly, the in silico calculated BBB partition coefficient of 5j was in the optimal interval. The theoretical oral absorption was 62%. Four primary metabolites produced by hydroxylation, dehydrogenation and epoxidation were hypothesized.
2.4.2. BBB PAMPA Permeability Assay
Since good blood–brain penetration is strongly desirable for CNS active compounds, the PAMPA-BBB assay was used to investigate the passive diffusion of 5j across the blood–brain barrier. Two earlier synthesized hydrazone congeners (5a and 5d) [28] were also tested to probe the effectiveness of the chosen structural modification on the BBB permeability. Values of effective permeability coefficient Pe, presented in terms of –logPe, are given in Table 4 for the evaluated compounds.

Table 4.
pKa, LogP and −logPe for the most active dual inhibitor 5j.
The preliminary PAMPA testing indicated that the blood–brain barrier (BBB) permeability of the active pyrrole-based dual inhibitor (5j) is in the medium range—5.271, compared to the applied references. The experimental result correlated well with the in silico studies.
3. Discussion
3.1. Chemistry
The Schiff bases (comprising imines or azomethine groups (-CH=N-)) were synthesized by a nucleophilic addition reaction of aldehydes/ketones and amines [31] by both conventional and MW-assisted approaches. Since the introduction of MW heating in organic chemistry, the number of articles reporting its utilization has been rapidly growing [32]. Fundamentally, the MW irradiation achieves “hot spots” due to the direct heating effect [33]. Ameliorated production of Schiff bases by MW-assisted synthesis has been reported [34]. Therefore, the syntheses of the described 13 novel (5e–q) pyrrole-based Schiff bases were optimized by microwave-assisted condensations. Importantly, the MW irradiation was found to be superior compared to the conventional synthesis in all cases. The synthetic results mirrored recent findings of enhanced yields and faster reaction times when Schiff bases were produced by MW synthesis [27], whereby the yields were enhanced usually by at least 10% (except in the cases of 5n and 5o). Interestingly, most of the MW syntheses led to reaction times of less than 5 min. However, the condensation reactions with 4-nitrobenzaldehyde (5e), 4-acetamidobenzaldehyde (5g), furfural (5i), isatin (5k), 2-naphthaldehyde (5l), and 9-anthracenecarboxaldehyde (5m) required 5 min to complete in the microwave reactor. The conventional heating of the latter required longer reaction times of 1 h and 30 min. The major limitation of the MW heating is the price of the microwave reactor.
3.2. In Vitro Assays
The biological in vitro evaluations showed that the novel compounds are better at AChE inhibition than at blocking MAO-B activities. The obtained in vitro AChE results lead to the observation that most promising AChE inhibitors from this series are the compounds with bulky carbonyl residue (5l and 5m). In addition, the introduction of the electron-withdrawing nitro group in the carbonyl part of the molecules also improves the AChE inhibition performance. Importantly, the introduction of a nitro group in the furan ring (compound 5j) led to significant improvement in the AChE inhibitory activity. Moreover, the Schiff base condensed with p-nitrobenzaldehyde (5e) also showed moderate enhancement of the blocking potential. These results also identify that the replacement of the phenyl moiety in 5e with a furan heterocyclic system in 5j further promotes the inhibitory effect, since the latter has better performance. Thus, an addition of a nitro group increased the potential AChE blocking effects of the novel Schiff bases. A benzene fragment substituted with the halogen fluorine atom at -o (5p) and -m (5q) positions did not display any AChE effects.
After the evaluations of the MAOs activities, it was noted that two Schiff bases are MAO-B inhibitors and only one compound possesses MAO-A blocking capacity. The MAO-B effects of 5o and 5j (at 1 µM concentrations) were found to be similar to recently published pyrrole-based compounds. Moreover, high selectivity of pyrrole-based compounds was recently discussed [35]. Similarly to the AChE findings, good MAO-B inhibitory effects of the compound comprising a nitro moiety was displayed (5j), reaffirming the role of the nitro fragment as recently discussed [26]. Overall, the best MAO-B inhibitor in the evaluated title compounds comprised a furane ring with an attached nitro group which could be used for future designs of selective inhibitors.
In addition, it should also be pointed out the interesting fact that the lack of an o-hydroxylic group in the structure of hydrazone 5n leads to the appearance of an MAO-A inhibitory effect, with this compound being the sole representative with such an effect from this series. In comparison, the corresponding benzaldehyde analogue (5o) lacks any MAO-A inhibitory effect but exerts a relatively good MAO-B inhibitory potential. Nevertheless, by far the most prominent MAO-B inhibitor from the series was compound 5j, thus identifying this structure as the most active dual AChE/MAO-B inhibitor. The presented in vitro results are comparable to recent reports of pyrrole-based AChE and MAO-B inhibitors [10,13]. Therefore, further modifications and evaluations of the title compounds is a subject of interest in future work.
3.3. Molecular Docking Studies
To obtain more insights for conforming the most active dual inhibitor 5j, additional docking simulations towards the crystallographic AChE (PDB: 4EY6) and MAO-B (PDB: 2V5Z) structures were carried out. The optimal docking protocols were achieved through re-docking and ligand enrichments which were reported by [36]. The docking pose of 5j in the active site of AChE indicated that the peripheral active site (PAS) region of the enzyme interacted with the ethyl ester moiety of the structure, while the indole and the p-bromophenyl motifs interacted with the catalytic region.
From the amino acids constructing the PAS (Tyr34, Tyr72, Asp74, Tyr124, and Trp286) [37], Tyr72, Asp74, Tyr124, and Trp286 were involved in the stabilization of the complex. Moreover, Trp286 formed a π−π and a cation–π bond with the 5-nitrofuran fragment of 5j which could potentially block the entrance gorge of the active site [38]. Overall, the majority of the interactions between 5j and AChE were hydrophobic in character which is important for a stable ligand–AChE complex [29,39].
The active cavity of MAO-B is constructed of a substrate cavity and an entrance cavity. Furthermore, the substrate cavity includes an aromatic cage, which is of great importance for the MAO-B activity [40]. The ethyl ester of the Schiff base 5j is located in the aromatic cage where Tyr398 and Tyr435 formed hydrophobic interactions with the latter moiety. Furthermore, essential for the formation of a stable MAO-B/ligand complex, active amino residues Ile199, Tyr326, Tyr398 and Tyr435 [41] interacted with 5j. Importantly, the molecular docking provided the following hypothesis: the removal of the ester functional group (situated at third position of the pyrrole ring) and the elimination of the p-bromophenyl moiety could greatly increase the MAO-B and AChE inhibition of the pyrrole-based compounds, due to the formation of more stable enzyme-ligand complexes. Thus, further experiments in that direction are required.
3.4. Pharmacokinetic Study
All of the compounds evaluated through the PAMPA-BBB permeability tests were classified as medium permeable with –logPe in the range of 5 < –logPe < 6, and only compound 5j showing 1.5 to 3-fold higher penetration ability. The passive diffusion could not be influenced by the ionization of compounds because they are weak acids (pKa values between 9.01 and 11.18) and exist as neutral molecules at physiological pH 7.4. The PAMPA-BBB reliably models the restrictions of intercellular tight junctions in the brain, so not surprisingly, the decrease in molecular weight was associated with an increase in BBB permeability. Although permeability did change monotonically with lipophilicity (logP), clearly future synthesis efforts should be directed toward optimization of molecular weight and lipophilicity of compounds.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry
Available solvents and reactants were acquired from commercial suppliers (Sigma-Aldrich; Fluka, Bulgaria) and applied without purification. The microwave-assisted syntheses were performed by using a FlexiWave Milestone Lab Microwave reactor (equipped with a fiber optic and IR sensors). The completion of the chemical reactions was monitored by thin layer chromatography (TLC) on aluminum sheets of silica gel 60 F254, Merck 1.05554 with mobile phase of chloroform and ethanol (10:0.4). The melting points were determined on Kruss M5000 and are not corrected.
Infrared spectra (4000–400 cm–1 range) were recorded on a Nicolet iS10 FT-IR spectrometer with a Smart iTR adapter (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). 1H spectra were registered on a Bruker Avance Neo 400 (Biospin GmbH, Rheinstetten, Germany) as δ (ppm) relative to TMS (tetramethylsilane) as an internal standard, and the coupling constants (J) were expressed in hertz (Hz). Chemical shifts (δ) were given in parts per million (ppm) relative to deuterated dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSOd) as a solvent. The mass spectra were obtained with a 6410 Agilent LCMS triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (LCMS) with an electrospray ionization (ESI) interface (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA).
4.1.1. General Experimental Information
The necessary 1,4-dicarbonyl compound ethyl 2-acetyl-4-(4-bromophenyl)-4-oxobutanoate (2) was obtained according to a procedure reported by A. Bijev [42].
The initial 2-(5-(4-bromophenyl)-3-(ethoxycarbonyl)-2-methyl-1H-pyrrole-1-yl)-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)propanoic acid (N-pyrrolylcarboxylic acid (3)) was synthesized according to a procedure where 0.1 mol ethyl 2-acetyl-4-(4-bromophenyl)-4-oxobutanoate (2) and 0.12 eq. of tryptophan were dissolved in 10 mL of glacial acetic acid. The mixture was heated by a microwave reactor for 55 min as per synthetic conditions reported by our research group in Mateev et al. [28].
A modified esterification of a recent protocol [28] was carried out for obtaining the intermediate ethyl 5-(4-bromophenyl)-1-(1-ethoxy-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl)-2-methyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxilate (4). SOCl2 (0.1 mol) was added dropwise directly to the N-pyrrolyl carboxylic acid (3) (0.05 mol) diluted in absolute ethanol at 0 °C. After 1 h, the reaction mixture was heated in MW reactor set at 75 °C and 450 W for 30 min. The solvent was removed and the obtained oil was washed with Na2CO3. The final product was incorporated in the next synthetic phase without isolation.
The necessary hydrazide ethyl 5-(4-bromophenyl)-1-(1-hydrazinyl-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl)-2-methyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxilate (5) was synthesized through hydrazinolysis. The hydrazinolysis was conducted as recently reported [28] with 0.04 mol of the ethyl ester (4) and 0.16 mol hydrazine hydrate (64%) dissolved in 25 mL of absolute ethanol and refluxed in the MW reactor. The reaction was completed in 2 h (700 W, 80 °C). The hydrazide was filtered after cooling and washed with ethanol. Recrystallization in ethanol was carried out for purification.
4.1.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of the Target Schiff Bases (5e–q)
The target Schiff bases were produced after reacting equimolar quantities (1 mmol) of the hydrazide (5) and 1 mmol of the corresponding carbonyl partners (e–q) in MW reactor and under conventional heating. A volume of 2 mL of glacial acetic acid was applied as a solvent. When the conventional heating was employed, the condensations were completed in 30–50 min. The microwave heating reduced the reaction times to 30–50 s and the yields were increased by up to 94%. The completed reaction mixture (detected by TLC) was poured into crushed ice and isolated. The hydrazide–hydrazones were purified by washing with hexane and recrystallization was achieved from ethanol/water, where necessary.
Ethyl 1-(3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-(2-(4-nitrobenzylidene)hydrazineyl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl)-5-(4-bromophenyl)-2-methyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate (5e): 5e was obtained according to the aforementioned general procedure. Yield 68%; melting point 198.7–198.9 °C; Rf 0.40/(10:0.4); IR vmax: 2976 (NH), 1689 (C=O), 1586 (C=N); 1H NMR (DMSO, 400 MHz) δ 11.97 (1H, s, CO-NH), 10.76 (1H, d, J = 12.45 Hz, NH (tryp.)), 8.12 (1H, d, H-7 (tryp.)), 8.09 (2H, t, J = 7.50, H-2′, H-6′ (4-nitrobenzene)), 7.17 (1H, s, H-2 (tryp.)), 7.26 (2H, t, J = 7.80, H-2, H-6 (bromobenzene)), 7.02 (2H, t, J = 6.70 Hz, H-3′, H-5′ (4-nitrobenzene)), 6.86 (1H, t, J = 7.70 Hz, H-5 (tryp.)), 6.78 (1H, s, H-4), 6.65 (2H, t, J = 8.00 Hz, H-3′, H-5′), 6.30 (1H, d, H-4 (tryp.)), 6.06 (1H, t, J = 7.40 Hz, H-6 (tryp.)), 5.98 (1H, t, J = 7.40 Hz, CH2-CH-(N)CO), 4.17 (2H, q, CH2-CH3), 3.34 (3H, s, CH3), 2.59 (2H, d, CH2-CH), 1.25 (3H, t, J = 7.90 Hz, CH2-CH3); 13C-NMR (101 MHz) δ ppm: 11.8 (CH3), 14.1 (CH3, ester), 30.7 (CH2), 60.9 (CH2, ester), 72.8 (CH-N, pyrrole), 104.7, 108.2 (CHCO), 111.1, 118.8, 119.4, 119.8, 121.7, 123.1 (C-Br), 123.4 (C-NH), 124.1, 124.4, 127.4, 128.3, 131.1, 131.2, 131.3, 132.1, 132.7, 136.5, 139.8, 142.1, 144.1 (N-CH), 150.2 (C-NO2), 165.9 (CO, ester), 175.5 (C=O, hydrazide). m/z (FTMS+pESI) 644.13 [M+2H+].
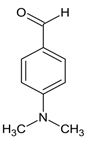
Ethyl 5-(4-bromophenyl)-1-(1-(2-(4-(dimethylamino)benzylidene)hydrazineyl)-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl)-2-methyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate (5f): 5f was obtained according to the aforementioned general procedure. Yield 77%; melting point 169.7–170.4 °C; Rf 0.47/(10:0.4); IR vmax: 2928 (NH), 1670 (C=O), 1596 (C=N); 1H NMR (DMSO, 400 MHz) δ 11.41 (1H, s, CO-NH), 10.72 (1H, d, J = 10.45 Hz, NH (tryp.)), 8.25 (1H, s, HN-CH), 7.53 (1H, d, H-4 (tryp.)), 7.32 (2H, t, J = 8.00 Hz, H-3′, H-5′), 7.21 (2H, t, J = 6.45, H-2, H-6 (4-N(CH3)2Benzene)), 7.27 (2H, t, J = 7.80, H-2′, H-6′), 7.18 (1H, s, H-2 (tryp.)), 7.04 (1H, t, J = 7.10 Hz, H-6 (tryp.)), 6.69 (2H, t, J = 7.20, H-3, H-5 (4-N(CH3)2Benzene)), 6.75 (1H, t, J = 7.70 Hz, H-5 (tryp.)), 6.54 (1H, s, H-4), 6.21 (1H, d, H-7 (tryp.)), 5.01 (1H, t, J = 7.40 Hz, CH2-CH-(N)CO), 4.16 (2H, q, CH2-CH3), 3.04 (3H, s, CH3), 2.97 (2H, d, CH2-CH), 2.61 (3H, s, CH3), 1.25 (3H, t, J = 7.90 Hz, CH2-CH3); 13C-NMR (101 MHz) δ ppm: 11.8 (CH3), 14.1 (CH3, ester), 30.7 (CH2), 41.3 (N-CH3), 60.9 (CH2, ester), 72.8 (CH-N, pyrrole), 104.7, 108.2 (CHCO), 111.1, 118.8, 119.4, 119.8, 121.7, 123.1 (C-Br), 123.4 (C-NH), 124.1, 124.4, 127.4, 128.3, 131.1, 131.2, 131.3, 132.1, 132.7, 136.5, 142.1, 144.1 (N-CH), 165.9 (CO, ester), 175.5 (C=O, hydrazide). m/z (FTMS+pESI) 642.18 [M+2H+].
Ethyl 1-(1-(2-(4-acetamidobenzylidene)hydrazineyl)-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl)-5-(4-bromophenyl)-2-methyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate (5g): 5g was obtained according to the aforementioned general procedure. Yield 61%; melting point 152.7–153.5 °C; Rf 0.40/(10:0.4); IR vmax: 3307 (NH), 1668 (C=O), 1589 (C=N); 1H NMR (DMSO, 400 MHz) δ 11.61 (1H, s, CO-NH), 10.74 (1H, d, J = 10.25 Hz, NH (tryp.)), 8.35 (1H, s, NH-CO-CH3), 7.96 (1H, s, HN-CH), 7.61 (1H, d, J = 6.40 Hz, H-4 (tryp.)), 7.24 (2H, t, J = 7.50, H-2, H-6 (bromobenzene)), 7.06 (2H, t, J = 7.10, H-2′, H-6′), 7.01 (2H, t, J = 8.15, H-3′, H-5′), 6.78 (2H, t, J = 8.00 Hz, H-3, H-5), 6.74 (1H, s, H-4), 6.67 (1H, t, J = 7.30 Hz, H-6 (tryp.)), 6.54 (1H, s, H-2 (tryp.)), 6.20 (1H, d, H-7 (tryp.)), 5.97 (1H, t, J = 7.70 Hz, H-5 (tryp.)), 5.12 (1H, t, J = 7.40 Hz, CH2-CH-(N)CO), 4.16 (2H, q, CH2-CH3), 2.81 (3H, s, CH3), 2.50 (3H, s, CO-CH3), 2.07 (2H, d, CH2-CH), 1.25 (3H, t, J = 7.85 Hz, CH2-CH3); 13C-NMR (101 MHz) δ ppm: 11.8 (CH3), 14.0 (CH3, ester), 24.0 (CH3, acetamide), 30.6 (CH2), 41.3 (N-CH3), 60.9 (CH2, ester), 72.8 (CH-N, pyrrole), 104.7, 108.2 (CHCO), 111.1, 118.8, 119.4, 119.8, 121.7, 123.1 (C-Br), 123.4 (C-NH), 124.1, 124.4, 127.4, 128.3, 131.1, 131.2, 131.3, 132.1, 132.7, 136.5, 139.8, 142.1, 144.1 (N-CH), 165.9 (CO, ester), 168.9 (C=O, amide), 175.5 (C=O, hydrazide). m/z (FTMS+pESI) 656.16 [M+2H+].
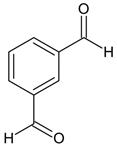
Ethyl 5-(4-bromophenyl)-1-(1-(2-(3-formylbenzylidene)hydrazineyl)-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl)-2-methyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate (5h): 5h was obtained according to the aforementioned general procedure. Yield 59%; melting point 154.2–155.1 °C; Rf 0.43/(10:0.4); IR vmax: 3337 (NH), 2977 (NH), 1682 (C=O), 1557 (C=N); 1H NMR (DMSO, 400 MHz) δ 11.79 (1H, s, CO-NH), 10.73 (1H, d, J = 11.10 Hz, NH (tryp.)), 9.88 (1H, s, COH), 8.51 (1H, s, HN-CH), 8.34 (1H, s, H-2′), 8.23 (2H, d, J = 7.80 Hz, H-4′, H-6′), 8.05 (2H, t, J = 7.80 Hz, H-2, H-6 (bromobenzene)), 7.86 (1H, t, J = 6.70 Hz, H-5′), 7.57 (1H, d, J = 6.40 Hz, H-4 (tryp.)), 7.16 (2H, t, J = 7.10 Hz, H-3, H-5), 7.02 (1H, t, J = 7.50 Hz, H-5 (tryp.)), 6.75 (1H, d, H-7 (tryp.)), 6.24 (1H, t, J = 7.20 Hz, H-6 (tryp.)), 6.21 (1H, s, H-2 (tryp.), 5.16 (1H, t, J = 8.50 Hz, CH2-CH-(N)CO), 4.16 (2H, q, CH2-CH3), 3.62 (2H, d, CH2-CH), 2.50 (3H, s, CH3), 1.24 (3H, t, J = 7.20 Hz, CH2-CH3); 13C-NMR (101 MHz) δ ppm: 11.8 (CH3), 14.1 (CH3, ester), 30.7 (CH2), 60.9 (CH2, ester), 72.8 (CH-N, pyrrole), 104.7, 108.2 (CHCO), 111.1, 118.8, 119.8, 121.7, 123.1 (C-Br), 123.4 (C-NH), 124.1, 124.4, 127.5, 128.3, 131.1, 131.2, 131.3, 132.1, 132.7, 136.5, 139.8, 142.1, 144.1 (N-CH), 146.8, 165.9 (CO, ester), 175.5 (C=O, amide), 191.0. m/z (FTMS+pESI) 628.50 [M+2H+].
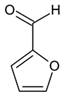
Ethyl 5-(4-bromophenyl)-1-(1-(2-(furan-2-ylmethylene)hydrazineyl)-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl)-2-methyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate (5i): 5i was obtained according to the aforementioned general procedure. Yield 73%; melting point 149.5–150.3 °C; Rf 0.61/(10:0.4); IR vmax: 2930 (NH), 1667 (C=O), 1558 (C=N); 1H NMR (DMSO, 400 MHz) δ 11.54 (1H, s, CO-NH), 10.73 (1H, d, J = 10.75 Hz, NH (tryp.)), 8.35 (1H, s, HN-CH), 7.66 (1H, d, J = 6.90 Hz, H-3 (furan)), 7.29 (2H, t, J = 7.55 Hz, H-2, H-6 (bromobenzene)), 7.16 (1H, d, J = 6.50 Hz, H-4 (tryp.)), 7.06 (2H, t, J = 7.00 Hz, H-3, H-5), 6.91 (1H, d, H-7 (tryp.)), 6.84 (1H, t, J = 7.20 Hz, H-6 (tryp.)), 6.74 (1H, s, H-2 (tryp.), 6.69 (1H, t, J = 7.50 Hz, H-5 (tryp.)), 6.21 (1H, d, J = 6.70 Hz, H-1 (furan)), 5.99 (1H, t, J = 7.20 Hz, H-2 (furan)), 5.12 (1H, t, J = 8.20 Hz, CH2-CH-(N)CO), 4.17 (2H, q, CH2-CH3), 3.80 (2H, d, CH2-CH), 2.50 (3H, s, CH3), 1.25 (3H, t, J = 7.20 Hz, CH2-CH3); 13C-NMR (101 MHz) δ ppm: 11.8 (CH3), 14.0 (CH3, ester), 30.6 (CH2), 60.9 (CH2, ester), 72.8 (CH-N, pyrrole), 104.7, 108.2 (CHCO), 111.1, 118.8, 119.4, 119.8, 121.7, 123.1 (C-Br), 123.4 (C-NH), 124.1, 124.4, 127.4, 128.3, 131.1, 131.2, 131.3, 132.1, 132.7, 136.5, 139.8, 142.1, 144.1 (N-CH), 149.1, 165.9 (CO, ester), 175.5 (C=O, hydrazide). m/z (FTMS+pESI) 590.13 [M+2H+].
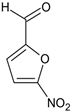
Ethyl 1-(3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-(2-((5-nitrofuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazineyl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl)-5-(4-bromophenyl)-2-methyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate (5j): 5j was obtained according to the aforementioned general procedure. Yield 65%; melting point 242.7–243.6 °C; Rf 0,18/(10:0.4); IR vmax: 3216 (NH), 1683 (C=O), 1471 (C=N); 1H NMR (DMSO, 400 MHz) δ 12.05 (1H, s, CO-NH), 10.74 (1H, d, J = 10.75 Hz, NH (tryp.)), 8.41 (1H, s, HN-CH), 7.81 (1H, d, H-7 (tryp.)), 7.74 (1H, d, J = 6.50 Hz, H-4 (tryp.)), 7.34 (1H, d, J = 6.70 Hz, H-1 (furan)), 7.04 (2H, t, J = 7.50 Hz, H-2, H-6 (bromobenzene)), 6.88 (1H, t, J = 7.10 Hz, H-2 (furan)), 6.77 (2H, t, J = 7.00 Hz, H-3, H-5), 6.68 (1H, t, J = 7.20 Hz, H-6 (tryp.)), 6.21 (1H, s, H-2 (tryp.), 5.85 (1H, t, J = 7.50 Hz, H-5 (tryp.)), 5.17 (1H, t, J = 8.20 Hz, CH2-CH-(N)CO), 4.14 (2H, q, CH2-CH3), 2.72 (3H, s, CH3), 2.54 (2H, d, CH2-CH), 1.24 (3H, t, J = 7.20 Hz, CH2-CH3); 13C-NMR (101 MHz) δ ppm: 11.8 (CH3), 14.1 (CH3, ester), 30.7 (CH2), 60.9 (CH2, ester), 72.8 (CH-N, pyrrole), 104.7, 108.2 (CHCO), 111.1, 112.6, 118.8, 118.9, 119.4, 119.8, 121.7, 123.1 (C-Br), 123.4 (C-NH), 124.1, 124.4, 127.5, 128.3, 131.1, 131.3, 132.1, 132.7, 136.5, 139.8, 142.1, 151.8, 152.0, 165.8 (CO, ester), 175.6 (C=O, amide). m/z (FTMS+pESI) 634.11 [M+2H+].
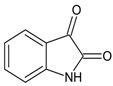
Ethyl 1-(3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-oxo-1-(2-(2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)hydrazineyl)propan-2-yl)-5-(4-bromophenyl)-2-methyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate (5k): 5k was obtained according to the aforementioned general procedure. Yield 56%; melting point 170.4–171.8 °C; Rf 0.45/(10:0.4); IR vmax: 3369 (NH), 1698 (C=O), 1668 (C=O), 1593 (C=N); 1H NMR (DMSO, 400 MHz) δ 13.29 (1H, s, CO-NH), 11.22 (1H, d, J = 10.25 Hz, NH (tryp.)), 10.78 (1H, s, NH (isatin)), 7.61 (1H, d, H-4 (isatin), 7.38 (2H, t, J = 8.10 Hz, H-2, H-6 (bromobenzene)), 7.31 (1H, d, H-7 (isatin)), 7.21 (1H, t, J = 6.85 Hz, H-6 (isatin)), 7.05 (2H, t, J = 7.60 Hz, H-3, H-5), 6.93 (1H, d, J = 6.50 Hz, H-4 (tryp.)), 7.34 (1H, t, J = 7.50 Hz, H-5 (isatin)), 7.22 (1H, s, H-2 (tryp.), 7.06 (1H, t, J = 7.40 Hz, H-6 (tryp.)), 6.98 (1H, t, J = 7.80 Hz, H-5 (tryp.)), 6.81 (1H, d, H-7 (tryp.)), 6.26 (1H, s, H-4), 5.21 (1H, t, J = 7.40 Hz, CH2-CH-(N)CO), 4.16 (2H, q, CH2-CH3), 3.36 (3H, s, CH3), 2.54 (2H, d, CH2-CH), 1.26 (3H, t, J = 8.15 Hz, CH2-CH3); 13C-NMR (101 MHz) δ ppm: 11.8 (CH3), 14.1 (CH3, ester), 30.7 (CH2), 47.3, 60.9 (CH2, ester), 72.8 (CH-N, pyrrole), 104.7, 108.2 (CHCO), 111.1, 112.4, 118.8, 119.4, 119.8, 121.7, 123.1 (C-Br), 123.4 (C-NH), 124.1, 124.4, 127.4, 128.3, 131.1, 131.2, 131.3, 132.7, 136.5, 139.8, 142.1, 144.1 (N-CH), 154.7, 165.8 (CO, ester), 168,2, 175.5 (C=O, hydrazide), 187.4 (C=O, isatin). m/z (FTMS+pESI) 640.13 [M+2H+].
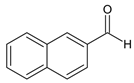
Ethyl 1-(3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-(2-(naphthalen-2-ylmethylene)hydrazineyl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl)-5-(4-bromophenyl)-2-methyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate (5l): 5l was obtained according to the aforementioned general procedure. Yield 68%; melting point 233–233.7 °C; Rf 0.64/(10:0.4); IR vmax: 3115 (NH), 1655 (C=O), 1500 (C=N); 1H NMR (DMSO, 400 MHz) δ 11.78 (1H, s, CO-NH), 10.74 (1H, d, J = 12.15 Hz, NH (tryp.)), 8.58 (1H, s, H-1 (naphthalene)), 8.17 (1H, d, J = 6.50 Hz, 3-H (naphthalene)), 7.95 (2H, t, J = 7.40 Hz, H-2′, H-6′), 7.92 (2H, t, J = 6.90 Hz, H-6, H-7 (naphthalene)), 7.87 (1H, d, J = 6.90 Hz, H-4 (naphthalene)), 7.79 (2H, t, J = 7.10 Hz, H-5, H-8 (naphthalene)), 7.59 (2H, t, J = 6.90, H-6, H-7 (naphth.)), 7.51 (1H, d, J = 6.50 Hz, H-4 (tryp.)), 7.47 (2H, t, J = 7.30 Hz, H-3′, H-5′), 7.41 (1H, d, H-7 (tryp.)), 7.28 (1H, t, J = 7.80 Hz, H-5 (tryp.)), 7.02 (1H, t, J = 7.40 Hz, H-6 (tryp.)), 6.24 (1H, s, H-2 (tryp.), 6.21 (1H, s, H-4), 5.18 (1H, t, J = 7.50 Hz, CH2-CH-(N)CO), 4.16 (2H, q, CH2-CH3), 2.81 (2H, d, CH2-CH), 2.51 (3H, s, CH3), 1.25 (3H, t, J = 7.40 Hz, CH2-CH3); 13C-NMR (101 MHz) δ ppm: 11.8 (CH3), 14.1 (CH3, ester), 30.7 (CH2), 60.9 (CH2, ester), 72.8 (CH-N, pyrrole), 104.7, 108.2 (CHCO), 111.1, 118.8, 119.4, 119.8, 121.7, 123.1 (C-Br), 123.4 (C-NH), 124.1, 124.4, 126.2, 126.5, 126.9 127.2, 127.4, 128.1, 128.2, 128.5, 128.9, 131.1, 131.2, 131.3, 132.1, 133.9, 134.2, 136.5, 139.8, 142.1, 146.8 (N-CH), 165.8 (CO, ester), 175.5 (C=O, hydrazide). m/z (FTMS+pESI) 649.16 [M+2H+].
Ethyl 1-(1-(2-(anthracen-9-ylmethylene)hydrazineyl)-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl)-5-(4-bromophenyl)-2-methyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate (5m): 5m was obtained according to the aforementioned general procedure. Yield 59%; melting point 235–235.4 °C; Rf 0.76/(10:0.4); IR vmax: 3314 6 (NH), 1689 (C=O), 1490 (C=N); 1H NMR (DMSO, 400 MHz); δ 10.83 (1H, s, CO-NH), 10.58 (1H, d, J = 11.35 Hz, NH (tryp.)), 8.91 (1H, s, H-5 (anthracene)), 8.65 (1H, s, N=CH), 8.16 (2H, t, J = 7.10 Hz, H-4, H-6 (anthr.)), 7.85 (2H, d, J = 6.85, H-1, H-8, (anthr.)), 7.42 (2H, t, J = 6.20 Hz, H-2, H-6 (bromobenzene)), 7.34 (1H, d, J = 6.50 Hz, H-4 (tryp.)), 7.20 (1H, d, H-7 (tryp.)), 7.11 (1H, t, J = 7.60 Hz, H-6 (tryp.)), 6.94 (2H, t, J = 7.20 Hz, H-3, H-5), 6.89 (m, H-2, H-3, H-7, H-8 (anthr.), 6.03 (1H, s, H-2 (tryp.)), 5.74 (1H, t, J = 8.00 Hz, H-5 (tryp.)), 4.65 (1H, t, J = 7.10 Hz, CH2-CH-(N)CO), 4.27 (2H, q, CH2-CH3), 3.45 (2H, d, CH2-CH), 2.72 (3H, s, CH3), 1.31 (3H, t, J = 8.30 Hz, CH2-CH3); m/z (FTMS+pESI) 13C-NMR (101 MHz) δ ppm: 11.8 (CH3), 14.1 (CH3, ester), 30.7 (CH2), 60.9 (CH2, ester), 72.8 (CH-N, pyrrole), 104.7, 108.2 (CHCO), 111.1, 118.8, 119.4, 119.8, 121.7, 123.1 (C-Br), 123.4 (C-NH), 124.1, 124.4, 125.6, 126.2, 126.5, 126.9 127.2, 127.4, 127.4, 128.1, 128.5, 131.1, 131.2, 131.3, 132.1, 133.9, 134.2, 136.5, 139.8, 142.1, 143.3 (N-CH), 165.8 (CO, ester), 175.5 (C=O, hydrazide). m/z 699.17 [M+2H+].
Ethyl 1-(1-(2-benzylidenehydrazineyl)-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl)-5-(4-bromophenyl)-2-methyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate (5n): 5n was obtained according to the aforementioned general procedure. Yield 89%; melting point 139.4–141.1 °C; Rf 0.52/(10:0.4); IR vmax: 3296 (NH), 1678 (C=O), 1539 (C=N); 1H NMR (DMSO, 400 MHz) δ 11.75 (1H, s, CO-NH), 10.73 (1H, d, J = 10.20 Hz, NH (tryp.)), 8.47 (1H, s, HN-CH), 7.78 (2H, t, J = 7.30 Hz, H-2′, H-6′), 7.71 (2H, t, J = 7.90 Hz, H-2, H-6 (bromobenzene)), 7.64 (m, H-3′, H-4′, H-5′), 7.55 (2H, d, J = 6.60 Hz, H-3, H-5), 7.48 (1H, d, J = 6.80 Hz, H-4 (tryp.)), 7.32 (1H, d, J = 6.90 Hz, H-7 (tryp.)), 7.18 (1H, s, H-2 (tryp.)), 7.06 (1H, t, J = 7.60 Hz, H-6 (tryp.)), 7.05 (1H, t, J = 8.10 Hz, H-5 (tryp.)), 6.26 (1H, s, H-4 (pyrrole)), 6.02 (1H, t, J = 7.40 Hz, CH2-CH-(N)CO), 4.16 (2H, q, CH2-CH3), 2.80 (2H, d, CH2-CH), 1.91 (3H, s, CH3), 1.25 (3H, t, J = 8.30 Hz, CH2-CH3); 13C-NMR (101 MHz) δ ppm: 11.8 (CH3), 14.1 (CH3, ester), 30.7 (CH2), 60.9 (CH2, ester), 72.8 (CH-N, pyrrole), 104.7, 108.2 (CHCO), 111.1, 118.8, 119.4, 119.8, 121.7, 123.1 (C-Br), 123.4 (C-NH), 124.1, 124.4, 127.4, 128.3, 131.1, 131.2, 131.3, 132.7, 136.5, 142.1, 144.1 (N-CH), 165.9 (CO, ester), 175.5 (C=O, hydrazide). m/z (FTMS+pESI) 599.14 [M+2H+].
Ethyl 5-(4-bromophenyl)-1-(1-(2-(2-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazineyl)-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl)-2-methyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate (5o): 5o was obtained according to the aforementioned general procedure. Yield 83%; melting point 177.1–177.2 °C; Rf 0.71/(10:0.4); IR vmax: 3337 (OH), 2977 (NH), 1674 (C=O), 1558 (C=N); 1H NMR (DMSO, 400 MHz) δ 11.76 (1H, s, OH), 11.13 (1H, s, CO-NH), 10.73 (1H, d, J = 10.15 Hz, NH (tryp.)), 8.64 (1H, s, HN-CH), 7.54 (1H, d, J = 7.15 Hz H-6′), 7.26 (2H, t, J = 7.90 Hz, H-2, H-6 (bromobenzene)), 7.16 (2H, d, J = 6.60 Hz, H-3, H-5), 7.44 (1H, d, J = 6.80 Hz, H-4 (tryp.)), 7.33 (1H, d, J = 6.87 Hz, H-7 (tryp.)), 7.18 (1H, s, H-2 (tryp.)), 7.02 (1H, t, J = 7.60 Hz, H-6 (tryp.)), 6.97 (1H, t, J = 7.00 Hz, H-4′), 6.94 (1H, t, J = 8.10 Hz, H-5 (tryp.)), 6.89 (1H, d, J = 7.20 Hz, H-6′), 6.86 (1H, t, J = 7.40 Hz, H-3′, 5′), 6.74 (1H, s, H-4 (pyrrole)), 5.15 (1H, t, J = 7.40 Hz, CH2-CH-(N)CO), 4.16 (2H, q, CH2-CH3), 3.43 (2H, d, CH2-CH), 2.50 (3H, s, CH3), 1.25 (3H, t, J = 8.30 Hz, CH2-CH3); 13C-NMR (101 MHz) δ ppm: 11.7 (CH3), 14.2 (CH3, ester), 30.7 (CH2), 60.7 (CH2, ester), 72.8 (CH-N, pyrrole), 104.7, 108.2 (CHCO), 111.1, 118.5, 119.4, 119.8, 121.4, 123.2 (C-Br), 123.4 (C-NH), 124.1, 124.4, 127.4, 128.3, 131.1, 131.2, 131.3, 132.4, 133.5, 136.5, 142.1, 144.1 (N-CH), 157.2 (C-OH), 165.9 (CO, ester), 175.5 (C=O, hydrazide). m/z (FTMS+pESI) 615.14 [M+2H+].
Ethyl 5-(4-bromophenyl)-1-(1-(2-(2-fluorobenzylidene)hydrazineyl)-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl)-2-methyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate (5p): 5p was obtained according to the aforementioned general procedure. Yield 73%; melting point 146.3–147.1 °C; Rf 0.39/(10:0.4); IR vmax: 3114 (NH), 1686 (C=O), 1459 (C=N); 1H NMR (DMSO, 400 MHz) δ 11.77 (1H, s, CO-NH), 10.73 (1H, d, J = 10.75 Hz, NH (tryp.)), 8.01 (1H, s, HN-CH), 7.54 (2H, t, J = 7.55 Hz, H-2, H-6 (bromobenzene)), 7.40 (1H, d, J = 7.10 Hz H-6′), 7.27 (2H, d, J = 6.60 Hz, H-3, H-5), 7.19 (1H, d, J = 6.80 Hz, H-4 (tryp.)), 7.10 (1H, t, J = 6.7 Hz, H-4′), 7.04 (1H, d, J = 6.9 Hz, H-3′), 6.85 (1H, d, J = 6.90 Hz, H-7 (tryp.)), 6.74 (1H, t, J = 7.5 Hz, H-5′), 6.67 (1H, s, H-2 (tryp.)), 6.56 (1H, t, J = 7.60 Hz, H-6 (tryp.)), 6.34 (1H, t, J = 8.10 Hz, H-5 (tryp.)), 6.20 (1H, s, H-4 (pyrrole)), 5.15 (1H, t, J = 7.40 Hz, CH2-CH-(N)CO), 4.16 (2H, q, CH2-CH3), 2.80 (2H, d, CH2-CH), 2.45 (3H, s, CH3), 1.30 (3H, t, J = 8.30 Hz, CH2-CH3); 13C-NMR (101 MHz) δ ppm: 11.7 (CH3), 14.2 (CH3, ester), 30.7 (CH2), 60.7 (CH2, ester), 72.8 (CH-N, pyrrole), 104.7, 108.2 (CHCO), 111.1, 118.2, 119.4, 119.8, 121.4, 123.2 (C-Br), 123.4 (C-NH), 124.1, 124.4, 127.4, 128.3, 131.1, 131.2, 131.3, 132.4, 133.5, 136.5, 139.8, 142.1, 144.1 (N-CH), 159.6 (C-F), 165.9 (CO, ester), 175.5 (C=O, hydrazide). m/z (FTMS+pESI) 617.13 [M+2H+].
Ethyl 5-(4-bromophenyl)-1-(1-(2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)hydrazineyl)-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl)-2-methyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate (5q): 5q was obtained according to the aforementioned general procedure. Yield 78%; melting point 129.3–130.1 °C; Rf 0.43/(10:0.4); IR vmax: 3328 (NH), 1709 (C=O), 1581 (C=N); 1H NMR (DMSO, 400 MHz) δ 9.42 (1H, s, CO-NH), 8.13 (1H, s, HN-CH), 7.96 (1H, d, J = 10.05 Hz, NH (tryp.)), 7.70 (1H, s, H-2′), 7.50 (2H, d, J = 6.60 Hz, H-3, H-5), 7.46 (1H, d, J = 6.80 Hz, H-4 (tryp.)), 7.39 (2H, t, J = 7.55 Hz, H-2, H-6 (bromobenzene)), 7.35 (1H, t, J = 7.5 Hz, H-5′), 7.29 (1H, s, H-2 (tryp.)), 7.23 (1H, d, J = 7.10 Hz H-6′), 7.19 (1H, d, J = 6.6 Hz, H-4′), 7.15 (1H, d, J = 6.90 Hz, H-7 (tryp.)), 7.13 (1H, t, J = 7.60 Hz, H-6 (tryp.)), 6.98 (1H, t, J = 8.10 Hz, H-5 (tryp.)), 6.68 (1H, s, H-4 (pyrrole)), 5.20 (1H, t, J = 7.40 Hz, CH2-CH-(N)CO), 4.30 (2H, q, CH2-CH3), 2.83 (2H, d, CH2-CH), 2.13 (3H, s, CH3), 1.39 (3H, t, J = 8.30 Hz, CH2-CH3); 13C-NMR (101 MHz) δ ppm: 11.8 (CH3), 14.3 (CH3, ester), 30.7 (CH2), 60.7 (CH2, ester), 72.8 (CH-N, pyrrole), 104.7, 108.2 (CHCO), 111.1, 114.0, 117.8, 119.4, 119.8, 121.4, 123.2 (C-Br), 123.4 (C-NH), 124.4, 124.8, 127.4, 128.3, 130.4, 131.2, 131.3, 132.4, 133.5, 136.5, 139.8, 142.1, 144.1 (N-CH), 163.0 (C-F), 165.9 (CO, ester), 175.6 (C=O, hydrazide). m/z (FTMS+pESI) 617.13 [M+2H+].
4.2. In Vitro Assays
4.2.1. In Vitro MAO-B Activity
The MAO-B effect was tested on a recombinant human MAO-B by the fluorometric Amplex® UltraRed reagent with several modifications [43]. Selegiline was used as a positive control and tyramine hydrochloride as a substrate. The results are expressed as a mean ± SD (n = 3). Values of p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
4.2.2. In Vitro AChE Activity
The inhibitory AChE potentials of the title compounds were measured according to a modified Ellman’s method [43]. Stock solutions (1 mg/mL) of the test compounds were diluted in DMSO. Working solutions (10 μM) were prepared by serial dilutions. The test compounds (10 μM) were incubated with sodium phosphate buffer (0.1 M; pH 8.0; 200 μL), and AChE solution (0.1 U/mL; 40 μL) for 10 min at 37 °C. The reaction was initiated by addition of 5,5-dithio-bis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB) (10 mM; 20 μL) and acetylthiocholine iodide (min. 99%, ATChI) (14 mM; 20 μL). The absorbance was measured using a microplate reader at 412 nm wavelength against the blank reading containing 300 μL DMSO. The % inhibition was calculated against the blank probe. Donepezil (10 μM) was used as the positive control. The results are expressed as a mean ± SD (n = 3). Values of p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
4.3. Molecular Docking
The crystallographic structures of AChE (PDB: 4EY6) and MAO-B (PDB: 2V5Z) were retrieved from the Protein Data Bank (PDB). The retrieved protein structures of the target enzymes were refined with the protein preparation module. Applying the former, hydrogen bonds were added, het states were generated and the crystallographic structures were minimized with the OPLS4 force field. The docking simulations were carried out with the docking module of Schrödinger Maestro Suite–Glide. The grid boxes were set around each co-crystallized ligand—Galanthamine for AChE and Safinamide for MAO-B. The chemical structure of 5j was drawn with the 2D sketcher module in Maestro, and converted to the corresponding three-dimensional (3D) structure with the Ligprep module (Schrödinger Release 2021-3: LigPrep, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, USA, 2021). Moreover, the OPLS4 force field was applied to identify hydrogen bonds and for energy minimization.
4.4. Pharmacokinetic Study
4.4.1. In Silico ADME Simulations
To calculate the significant physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties of the most prominent dual-acting MAO-B/AChE inhibitor, ADME predictions were performed with the QikProp module in Schrodinger (Schrödinger Release 2022-2: QikProp, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, USA, 2022). The simulations provide ranges based on the properties of 95% of the known drugs and also evaluates outliers based on the Lipinski’s rule of five [44].
4.4.2. PAMPA-BBB Assay
In vitro Parallel Artificial Permeability blood-brain barrier (PAMPA-BBB) Assay test was applied by using PAMPA Permeability Analyzer (pIONInc, Billerica, MA, USA). The effective permeabilities (Pe) of compounds were measured following the manufacturer BBB Protocol. Briefly, 10 mM stock solutions of 5j and reference compounds in DMSO were diluted with Prisma HT buffer pH 7.4 (Pion Inc.) to achieve a final concentration of 50 μM and the donor plate of PAMPA “sandwich” was loaded with 200 µL samples. The membranes of the acceptor plate were impregnated with BBB-1 lipid (Pion Inc.) and the wells were filled with 200 µL BSB (Brain Skin Buffer, Pion Inc.). The plates were assembled with the acceptor compartment above the donor one. Incubation was set up for 4 h at 25 °C with no stirring in the Gut-Box. To assess the permeability of compounds, their concentrations in both the donor and acceptor phases were spectrophotometrically determined (250–500 nm) after the end of incubation. Blank and reference samples were also UV scanned at the same wavelength range. Effective permeability coefficients Pe (10−6 cm/s) were calculated by PAMPA Explorer Command Software (Ver 3.8) as an average of three replicates and presented as −logPe. A compound was predicted as highly permeable if −logPe < 5 and having low permeability if −logPe > 6. When 6 < −logPe < 5, the compound was classified as having medium permeability [45]. Theophylline, corticosterone, and propranolol HCl were used as reference standards for low, medium and high permeability, respectively [46].
5. Conclusions
The microwave-assisted and classical synthetic approaches for obtaining a series of N-pyrrole based Schiff-bases is presented. The reactions identified the application of the MW-assisted methodology as more useful due to the increased yields and shortened reaction times of up to 5 min for the synthesis of the Schiff-bases 5(e-q) and up to 2 h for the initial molecules 2, 3, 4 and 5. The decreased reaction times led expectedly to increased yields of more than 10% for some of the target hydrazones for purified products.
In addition, the corresponding AChE, MAO-B and MAO-A inhibitory effects were evaluated, in the search for novel multi target drugs. Compound 5j was identified as the most promising structure.
Additional docking simulations targeting the active sites of AChE (PDB ID: 4EY6) and MAO-B (PDB: 2V5Z) were employed to explore the possible interactions of the most prominent dual inhibitor (5j) with the enzymes, identifying interaction between the Trp286 from the active site of AChE forming a π−π and a cation–π bonds with the 5-nitrofuran fragment of 5j. The performed in silico pharmacokinetic studies clarified that future synthesis efforts should be directed toward optimization of molecular weight and lipophilicity of compounds. Importantly, the molecular docking provided the following hypothesis: the removal of the ester functional group (situated at third position of the pyrrole ring), and the elimination of the p-bromophenyl moiety could greatly increase the MAO-B and AChE inhibition of the pyrrole-based compounds, due to the formation of more stable enzyme–ligand complexes. Thus, further experiments in that direction are required.
Overall, this research provides valuable insights into the synthesis and identification of novel Schiff bases acting as dual MAO-B/AChE inhibitors. In our future work, we will include the in vivo experimental evaluation of the most active compounds, as well as an assessment of their toxicological profile.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/scipharm92020018/s1, 1H NMR (Figures S1–S13), 13 C NMR (Figures S14–S26), IR (Figures S27–S39) and MAS Spectra (Figures S40–S52) of Compounds 5e–5q.
Author Contributions
E.M. contributed to the microwave-assisted synthesis of the target hydrazones and the molecular docking simulations and analysis; M.K.-B. contributed to the MAO-B inhibitory activity determination; M.G. contributed to the conventional synthesis of the target compounds; A.M. contributed to the acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity evaluation; I.V. contributed to the in silico ADME assessment and PAMPA-BBB assay; V.T. contributed to the MAO-A inhibitory activity determination; A.Z. contributed to the initiation of the scientific idea, the composing of the manuscript and the overall data evaluation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study is financed by the European Union-NextGenerationEU, through the National Recovery and Resilience Plan of the Republic of Bulgaria, project № BG-RRP-2.004-0004-C01.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Con sent Statement: Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Paraskev Nedjalkov, for the support in the conductance of the LC–MS evaluations for structure elucidation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Huang, L.K.; Chao, S.P.; Hu, C.J. Clinical trials of new drugs for Alzheimer disease. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, B.; Parambi, D.G.T.; Mathew, G.E.; Uddin, M.S.; Inasu, S.T.; Kim, H.; Marathakam, A.; Unnikrishnan, M.K.; Carradori, S. Emerging therapeutic potentials of dual-acting MAO and AChE inhibitors in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Arch. Pharm. 2019, 352, e1900177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanzi, R.E. FDA Approval of Aduhelm paves a new path for Alzheimer’s disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 2714–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlawish, J.; Grill, J.D. The approval of Aduhelm risks eroding public trust in Alzheimer research and the FDA. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 523–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raina, P.; Santaguida, P.; Ismaila, A.; Patterson, C.; Cowan, D.; Levine, M.; Booker, L.; Oremus, M. Effectiveness of cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine for treating dementia: Evidence review for a clinical practice guideline. Ann. Intern. Med. 2008, 148, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitaram, N.; Weingartner, H.; Caine, E.D.; Gillin, J.C. Choline: Selective enhancement of serial learning and encoding of low imagery words in man. Life Sci. 1978, 22, 1555–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rullo, M.; La Spada, G.; Miniero, D.V.; Gottinger, A.; Catto, M.; Delre, P.; Mastromarino, M.; Latronico, T.; Marchese, S.; Mangiatordi, G.F.; et al. Bioisosteric replacement based on 1,2,4-oxadiazoles in the discovery of 1H-indazole-bearing neuroprotective MAO B inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 255, 115352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Lv, Y.; Bai, R.; Xie, Y. Structural exploration of multifunctional monoamine oxidase B inhibitors as potential drug candidates against Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 114, 105070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Prada, M.; Zürcher, G.; Wüthrich, I.; Haefely, W.E. On tyramine, food, beverages and the reversible MAO inhibitor moclobemide. J. Neural. Transm. Suppl. 1988, 26, 31–56. [Google Scholar]
- Raka, S.C.; Ahamed, R.; Rahman, A.; Momen, A.R. In silico discovery of noteworthy multi-targeted acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Adv. Tradit. Med. 2020, 20, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateev, E.; Georgieva, M.; Zlatkov, A. Pyrrole as an Important Scaffold of Anticancer Drugs: Recent Advances. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 25, 24–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Regina, G.; Silvestri, R.; Artico, M.; Lavecchia, A.; Novellino, E.; Befani, O.; Turini, P.; Agostinelli, E. New pyrrole inhibitors of monoamine oxidase: Synthesis, biological evaluation, and structural determinants of MAO-A and MAO-B selectivity. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gümüş, M.; Babacan, Ş.N.; Demir, Y.; Sert, Y.; Koca, İ.; Gülçin, İ. Discovery of sulfadrug-pyrrole conjugates as carbonic anhydrase and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Arch. Pharm. 2022, 355, e2100242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourtaher, H.; Hasaninejad, A.; Iraji, A. Design, synthesis, In silico and biological evaluations of novel polysubstituted pyrroles as selective acetylcholinesterase inhibitors against Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peitzika, S.C.; Pontiki, E. A Review on recent approaches on molecular docking studies of novel compounds targeting acetylcholinesterase in Alzheimer disease. Molecules 2023, 28, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zianna, A.; Geromichalos, G.D.; Pekou, A.; Hatzidimitriou, A.G.; Coutouli-Argyropoulou, E.; Lalia-Kantouri, M.; Pantazaki, A.A.; Psomas, G. A palladium (II) complex with the Schiff base 4-chloro-2-(N-ethyliminomethyl)-phenol: Synthesis, structural characterization, and in vitro and In silico biological activity studies. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 199, 110792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raczuk, E.; Dmochowska, B.; Samaszko-Fiertek, J.; Madaj, J. Different Schiff Bases-structure, importance and classification. Molecules 2022, 27, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Asiri, A.M. Synthesis and spectroscopic studies of Ru(II) complexes of steroidal thiosemicarbazones by multi step reaction: As anti-bacterial agents. Steroids 2017, 124, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, W.; Sumrra, S.H.; Chohan, Z.H. A review: Pharmacological aspects of metal based 1,2,4-triazole derived Schiff bases. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 222, 113602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, U.; Koçyiğit-Kaymakçıoğlu, B.; Oruç-Emre, E.; Kaplancıklı, Z.; Rollas, S. Studies on hydrazide-hydrazones derivatives as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. MÜSBED 2015, 1, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popiołek, Ł. The bioactivity of benzenesulfonyl hydrazones: A short review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateeva, A.; Peikova, L.; Kondeva-Burdina, M.; Georgieva, M. Development of new HPLC method for identification of metabolic degradation of N-pyrrolylhydrazide hydrazones with determined MAO- B activity in cellular cultures. Pharmacia 2022, 69, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuldasheva, N.; Acikyildiz, N.; Akyuz, M.; Yabo-Dambagi, L.; Aydin, T.; Cakir, A.; Kazaz, C. The Synthesis of Schiff bases and new secondary amine derivatives of p-vanillin and evaluation of their neuroprotective, antidiabetic, antidepressant and antioxidant potentials. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1270, 133883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumrra, S.H.; Zafar, W.; Asghar, M.L.; Mushtaq, F.; Raza, M.A.; Nazar, M.F.; Nadeem, M.A.; Imran, M.; Mumtaz, S. Computational investigation of molecular structures, spectroscopic properties, cholinesterase inhibition and antibacterial activities of triazole Schiff bases endowed metal chelates. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1238, 130382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateev, E.; Georgieva, M.; Mateeva, A.; Zlatkov, A.; Ahmad, S.; Raza, K.; Azevedo, V.; Barh, D. Structure-based design of novel MAO-B inhibitors: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tok, F.; Koçyiğit-Kaymakçıoğlu, B.; Sağlık, B.N.; Levent, S.; Özkay, Y.; Kaplancıklı, Z.A. Synthesis and biological evaluation of new pyrazolone Schiff bases as monoamine oxidase and cholinesterase inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 84, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Sun, P. Compare of three ways of synthesis of simple Schiff base. Molbank 2006, 2006, M514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateev, E.; Georgieva, M.; Zlatkov, A. Design, microwave-assisted synthesis, biological evaluation, molecular docking, and ADME studies of pyrrole-based hydrazide-hydrazones as potential antioxidant agents. Maced. J. Chem. Chem. 2022, 41, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigurupati, S.; Selvaraj, M.; Mani, V.; Selvarajan, K.K.; Mohammad, J.I.; Kaveti, B.; Bera, H.; Palanimuthu, V.R.; The, L.K.; Salleh, M.Z. Identification of novel acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: Indolopyrazoline derivatives and molecular docking studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2016, 67, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, S.; Ozkok, F.; Ozel, A.E.; Cakir, E.; Akyuz, S. Synthesis, FT-IR and NMR characterization, antibacterial and antioxidant activities, and DNA docking analysis of a new vanillin-derived imine compound. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1236, 130288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henary, M.; Kananda, C.; Rotolo, L.; Savino, B.; Owens, E.A.; Cravotto, G. Benefits and applications of microwave-assisted synthesis of nitrogen containing heterocycles in medicinal chemistry. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 14170–14197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappe, C.O. Controlled microwave heating in modern organic synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2004, 43, 6250–6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; De, S.; Barman, P. Microwave-assisted synthesis and notable applications of Schiff-base and metal complexes: A comparative study. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2022, 48, 2199–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minders, C.; Petzer, J.P.; Petzer, A.; Lourens, A.C. Monoamine oxidase inhibitory activities of heterocyclic chalcones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 5270–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateev, E.; Kondeva-Burdina, M.; Georgieva, M.; Zlatkov, A. Repurposing of FDA-approved drugs as dual-acting MAO-B and AChE inhibitors against Alzheimer’s disease: An In silico and in vitro study. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2023, 122, 108471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunakaran, K.B.; Thiyagaraj, A.; Santhakumar, K. Novel insights on acetylcholinesterase inhibition by Convolvulus pluricaulis, scopolamine and their combination in zebrafish. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2022, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkrishna, A.; Pokhrel, S.; Tomer, M.; Verma, S.; Kumar, A.; Nain, P.; Gupta, A.; Varshney, A. Anti-acetylcholinesterase activities of mono-herbal extracts and exhibited synergistic effects of the phytoconstituents: A biochemical and computational study. Molecules 2019, 24, 4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Song, P.; Li, J.; Zhao, D. Effect of Salvia miltiorrhiza on acetylcholinesterase: Enzyme kinetics and interaction mechanism merging with molecular docking analysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Sekar, K.; Mukhopadhyay, B.P. The conformational dynamics of wing gates Ile199 and Phe103 on the binding of dopamine and benzylamine substrates in human monoamine Oxidase B. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzvetkov, N.T.; Hinz, S.; Küppers, P.; Gastreich, M.; Müller, C.E. Indazole- and indole-5-carboxamides: Selective and reversible monoamine oxidase B inhibitors with subnanomolar potency. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 6679–6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijev, A. New heterocyclic hydrazones in the search for antitubercular agents: Synthesis and in vitro evaluations. Lett. Drug Des. Dis. 2006, 3, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondeva-Burdina, M.; Mateev, E.; Angelov, B.; Tzankova, V.; Georgieva, M. In silico evaluation and in vitro determination of neuroprotective and MAO-B inhibitory effects of pyrrole-based hydrazones: A therapeutic approach to Parkinson’s disease. Molecules 2022, 27, 8485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poovaiah, N.; Davoudi, Z.; Peng, H.; Schlichtmann, B.; Mallapragada, S.; Narasimhan, B.; Wang, Q. Treatment of neurodegenerative disorders through the blood-brain barrier using nanocarriers. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 16962–16983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doytchinova, I.; Atanasova, M.; Valkova, I.; Stavrakov, G.; Philipova, I.; Zhivkova, Z.; Zheleva-Dimitrova, D.; Konstantinov, S.; Dimitrov, I. Novel hits for acetylcholinesterase inhibition derived by docking-based screening on ZINC database. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2018, 33, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, L.; Kerns, E.H.; Fan, K.; McConnell, O.J.; Carter, G.T. High throughput artificial membrane permeability assay for blood-brain barrier. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 38, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).