Abstract
Worldwide, 25% of the population suffers from metabolic syndrome (MetS). The treatment of patients with MetS regularly includes drugs prescribed simultaneously to treat several disorders that manifest at the same time, such as hypercholesterolemia, arterial hypertension, and diabetes. To the authors’ best knowledge, there is no previous published analytical method for the simultaneous quantification of drugs used in the treatment of these diseases. In the present study, a rapid high-performance liquid chromatography with a diode-array detector HPLC-DAD methodology was developed for simultaneous quantification of carvedilol (CVD), telmisartan (TEL), bezafibrate (BZT), gliclazide (GZD), and glimepiride (GMP) in bulk and pharmaceutical form. The chromatographic separation of the five pharmaceuticals was achieved on a Hypersil GOLD C18 Selectivity (5 µm, 150 × 4.60 mm2) using a mobile phase of acetonitrile (50%) and 0.02 M KH2PO4, pH 3 (50%) at a flow rate of 1 mL/min and at 25 °C. The total separation time was 9 min. The analytical method was validated following the International Conference on Harmonization guidelines. A reproducible method was obtained with acceptable limits of detection (LOD) and quantification (LOQ) for CVD (0.012 and 0.035 μg mL−1), TEL (0.103 and 0.313 μg mL−1), BZT (0.025 and 0.076 μg mL−1), GZD (0.039 and 0.117 μg mL−1), and GMP (0.064 and 0.127 μg mL−1). The validated method allowed the determination of these drugs in commercial pharmaceutical products both individually and simultaneously. The present method was found to be suitable for simultaneous quantification of the five drugs that are most commonly used in the simultaneous treatment of the metabolic syndrome.
1. Introduction
Worldwide, at least one in every four people suffer from metabolic syndrome (MetS) [1]. Obesity is a crucial factor in getting MetS, and this condition is reaching epidemic proportions. Only in the U.S., 68% of the population is considered overweight or obese [2]. MetS is defined as a constellation of interrelated risk factors that appear to promote diabetes and cardiovascular diseases [3]. Commonly, a patient with MetS will suffer from hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and diabetes simultaneously [4]. For this reason, the World Health Organization’s Global Hearts has recommended the use of combination therapy (multiple drugs for the treatment of two or three different illnesses at the same time) for improving the treatment of MetS [5]. The development of novel pharmaceutical formulations not only demands the finding of the optimal combination of active ingredients, but it may also require specific analytical methodologies suitable for determination of the multiple drugs that are present in the formulation.
Some of the most used Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API) in the development of formulations for combination therapy for the treatment of metabolic syndrome are: bezafibrate (BZT, pKa = 3.6), a representative fibrate widely used in the treatment of hypercholesterolemia [6,7]; gliclazide (GZD, pKa = 5.8), an oral hypoglycemic agent, belonging to second-generation sulphonylureas, which is used in type II diabetes (non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus) [8,9,10]; glimepiride (GMP, pKa = 6.2), an oral blood-glucose-lowering drug of the third-generation sulfonylureas, used for the treatment of diabetes [11,12,13]; telmisartan (TEL, pKa = 4.5), a synthetic analog of angiotensin II receptor blocker used in the management of hypertension [14,15,16]; and carvedilol (CVD, pKa = 7.5), a non-selective beta-alpha blocker 1, used in the treatment of high blood pressure [17,18,19]. Since all these compounds contain aromatic rings in their structure (see Figure 1), they cannot be simultaneously quantified following a UV−Vis spectrophotometric analytical method since all of them absorb in the same region of the UV-spectrum. Therefore, separation techniques such as high-performance liquid chromatography with a diode-array detector (HPLC-DAD) are required.
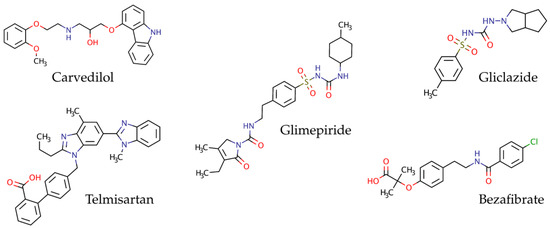
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia (BZT), type II diabetes (GZD and GMP) and hypertension (CVD and TEL).
Different HPLC chromatographic methods have been reported for individual determination of BZT [20,21,22], GZD [8,9,23], GMP [11,12,24], TEL [14,15,25], and CVD [17,18]. However, fast methodologies for the quantification of more than two drugs in a single run are limited. The authors of these studies only focus their analytical methods on drugs prescribed for the treatment of a single type of disease, either hypercholesterolemia [26,27,28,29], hypertension [19,30,31,32] or diabetes [33,34,35,36].
There are only two analytical methods reported where authors quantify APIs for the three main illnesses of MetS [7,37]. However, these have the disadvantage of long retention times and high limits of detection and quantification. Analytical methods that allow fast simultaneous quantification of five or more drugs may facilitate quality assurance, quality control processes in clinical trials for combined therapy. A short analysis time is a significant parameter to consider since it reduces the number of toxic organic solvents. Economizing in using solvents and supplies and energy consumption would reduce the environmental impact providing the pharmaceutical industry with efficient greener analytical methodologies for developing formulations, quality assurance, quality control, and potential clinical studies [38].
In the present study, a rapid HPLC-DAD methodology was developed for simultaneous quantification of bezafibrate (hypercholesterolemia), gliclazide and glimepiride (diabetes type II), carvedilol and telmisartan (hypertension) in bulk and applied to the quantification of pharmaceutical commercial tablets. The analytical method presented was validated by International Conference on Harmonization guidelines. There is no previous published analytical method in which these five APIs can be determined simultaneously in a single chromatographic run to the authors’ best knowledge.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
All active pharmaceutical ingredients: CVD (PHR1265), TEL (PHR1855), BZT (72516), GZD (G2167), and GMP (PHR1617) with purities higher than 99% were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) and used as received. Methanol (HPLC grade), acetonitrile (ACN, HPLC grade), orthophosphoric acid (analytical reagent grade) and potassium dihydrogen phosphate anhydrous (analytical reagent grade) were purchased from J.T. Baker Inc. (Columbus, OH, USA). Milli Q (Millipore, Milford, MA, USA) grade water was used for the preparation of buffer for the HPLC mobile phase and all aqueous solutions.
2.2. Equipments
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis was performed with an Agilent 1200 Series HPLC system (Agilent Technologies, Waldbronn, Germany) consisting of a quaternary pump (G1311A quat pump), degasser (G1322A Degasser), DAD SL diode-array detector (G1315D DAD), thermostatted column compartment (G1316A COLCOM), and autosampler thermostat (G1330B FC/ALS Therm). A Hypersil GOLD C18 Selectivity, 5 µm (150 × 4.60 mm2) column, with a precolumn guard cartridge, was used (Thermo scientific, Bellefonte, PA, USA). Analysis of chromatographic peaks and calculation of the areas were performed using the ChemStation for LC 3D systems software (Agilent Technologies, Waldbronn, Germany). A C18 column was selected because it is an appropriate stationary phase to achieve the separation of acidic and neutral drugs, providing an excellent choice for the separation of these drugs at short retention times
2.3. Chromatographic Conditions
The simultaneous analysis of the five drugs was carried out with a mobile phase of acetonitrile: phosphate buffer in the ratio of 50:50 v/v with a pH 3 (adjusted with orthophosphoric acid). ACN was selected because of its low UV cutoff and lower viscosity in mixtures with water (compared to methanol). Multiple water/acetonitrile ratios were tested to find that coelution was avoided in the 50/50 ratio. Finally, a pH = 3 for the mobile phase was selected because it fell below the analytes’ pKa values, ensuring that these existed in the unionized form.
The mobile phase was filtered through a 0.2 µm pore size nylon membrane of 47 mm diameter (Thermo scientific, Dreieich, Germany). The isocratic flow rate of the mobile phase was 1 mL/min, column temperature was set to 25 °C, and the injection volume was 20 µL. The selected absorption wavelengths for detection were 242 nm for CVD, 298 nm for TEL, and 230 nm for BZT, GZD and GMP.
2.4. Preparation of Standard Solutions
Individual standard solutions were prepared for the construction of calibration curves for each drug. A 10 mg dose of API was added to 50 mL of methanol and stirred until complete dissolution. The solution was then transferred into a 100 mL volumetric flask, and water was added to complete the volume (stock solutions of 100 μg mL−1). A series of standard solutions was prepared using the appropriate dilution of stock solution in water−methanol (50/50) to reach eight concentrations: 0.5, 2.5, 5, 7, 10, 15, 20, and 25 μg mL−1. These standard solutions were used for the determination of linearity and the construction of calibration curves.
2.5. Working Standard Solution
A mixture of CVD, TEL, BZT, GZD, and GMP was prepared using 10 mL from each stock solution into a 100 mL volumetric flask. Water−methanol (50/50) was added to complete the volume, obtaining a working standard solution with 10 μg mL−1 of each API. Working standard solutions were analyzed to evaluate the feasibility of chromatographic separation of all drugs for their simultaneous determination. The area of every peak observed, corresponding to each API, was compared with the area of standard solution, and methodology was accepted if relative error RE% was <15%.
2.6. Analytical Method Validation
The validation of the method was carried out evaluating solution stability, linearity range, limit of detection (LOD), limit of quantification (LOQ), accuracy, and precision, according to International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) validation guidelines [39].
2.6.1. Solution Stability
A common practice in industry is the use of an autosampler for continuous automatized analysis; thus, it is important to evaluate the API’s standard solution stability over several hours since some drugs may undergo degradation [30]. Therefore, to determine the stability of CVD, TEL, BZT, GZD and GMP dilutions from stock standard solutions (10 μg mL−1) were assayed after 72 h of storage at −20, 4, and 25 °C. For accelerated studies, dilutions from the five APIs’ stock solutions were also stored for 8 h at 80 °C. The area corresponding to the peak of API was compared against the area obtained for fresh standard solutions. Three replicates were performed, and stability of API was accepted if percentage coefficient of variation (CV%) was < 3% and percentage relative error (%RE) was <15% for the areas.
2.6.2. Linearity
The linear range analysis for each API was carried out analyzing standard solution at five concentrations: 0.5, 2.5, 5, 7, 10, 15, 20, and 25 μg mL−1, prepared from a stock solution. Every solution was evaluated in five replicates. The corresponding area of the peak was recorded and plotted as a function of concentrations. The range was considered linear if the correlation coefficient (R2) was larger than 0.999 [29,39].
2.6.3. Limit of Detection and Quantification
LOD and LOQ were determined based on the standard deviation of the response and the slope, according to ICH. LOD was calculated according to equation 1 and, LOQ was calculated according to Equation (2) [39].
where σ corresponds to standard deviation of the y-intercepts of regression line and S is the slope of calibration curve. Both LOD and LOQ were validated by independent analysis of three different concentrations, at LOD and LOQ, under and above.
LOD = 3.3 σ/S
LOQ = 10 σ/S
2.6.4. Precision and Accuracy
To determine the method’s precision and accuracy, three independent concentrations (2.5, 10 and 25 μg mL−1) were measured for each API. Each concentration was evaluated as five replicates under two different conditions: (1) all solutions were evaluated the same day (repeatability intraday), and (2) samples were evaluated on three different days (repeatability interday). Precision was determined by repeatability intraday and interday, and this parameter was expressed as CV%. A precision (CV%) less than or equal to 15% is acceptable. In the case of accuracy, this parameter is expressed by relative error (RE%), and a value less than or equal to 15% is acceptable [40,41].
2.7. Sample Solutions of Commercially Available Drug Products
In order to apply the methodology to commercially available products, tablets of carvedilol (25 mg), telmisartan (40 mg), bezafibrate (200 mg), gliclazide (60 mg), and glimepiride (2 mg) were quantified following two different procedures: (1) five tablets of each commercial product were weighed and ground with mortar and pestle for 5 min. After the tablets were ground, an amount equivalent to 10 mg of API was used to prepare sample solutions in 100 mL water−methanol 50/50 (100 μg mL−1). The final concentration of solutions was 10 μg mL−1; this concentration was the commercial API’s nominal concentration. (2) The content of a single tablet was quantified; the tablet was weighed and ground with a mortar and pestle for 5 min and then dissolved in 50/50 water−methanol.
Samples solutions of commercially available drug products were analyzed individually, and the concentration obtained was compared with the nominal concentration of 10 μg mL−1. The API’s quantified mass in a single tablet was also compared to the labeled product’s expected content. Recovery percentages and relative errors were reported. Sample solutions were prepared and analyzed in triplicate.
2.8. Working Sample Solutions of Commercially Available Drug Products
The simultaneous quantification of the five commercially available drug products was evaluated. Working sample solutions were prepared by addition of 10 mL from each sample solution (100 μg mL−1) into 100 mL volumetric flask and water−methanol (50/50) to complete volume, obtaining a working sample solution with 10 μg mL−1 of each commercial API.
3. Results
3.1. Standard Working Solution
Figure 2 shows the chromatogram of the standard working solutions of five APIs. As can be seen, each API had a defined and unique retention time; therefore, the present methodology allowed the simultaneous determination of CVD, TEL, BZT, GZD and GMP under the same chromatographic conditions, as inferred from the symmetry of the peaks and their separation.
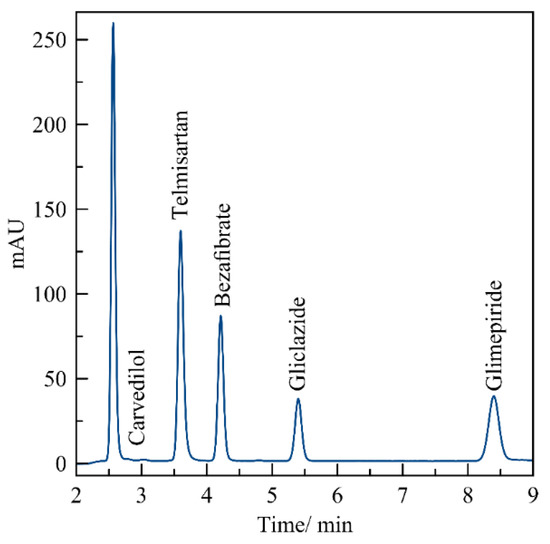
Figure 2.
Chromatogram for the simultaneous determination of CVD, TEL, BZT, GZD and GMP at 10 μg mL−1. Conditions: stationary phase, C18 column, mobile phase acetonitrile: buffer phosphate pH 3 (50/50 v/v), isocratic flow rate 1 mL/min and 25 °C.
The proposed chromatographic methodology: stationary phase-reverse, C18 column, mobile phase acetonitrile: buffer phosphate, pH 3, (50/50 v/v), isocratic flow rate 1 mL/min and 25 °C, allowed the simultaneous determination of CVD, TEL, BZT, GZD and GMP. Retention times were a function of polarity and pKa value of each active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). The first drug to elute was CVD (2.57 min) because of its high polarity, and because it is a weak base (pKa = 7.5) [19]. Then followed TEL (3.60 min), BZT (4.21 min), and GZD (5.40 min), which are weak acids with pKa value of 4.45 [16], 3.6 [7] and 5.8 [10], respectively. The combination of polarity and pKa values made the correct separation of these three drugs in under 6 min possible. Finally, although glimepiride is a weak acid (pKa = 6.2) [13], its non-polar nature caused it to elude at 8.4 min.
The recovery evaluation results from working solutions showed that the recovery of each API was greater than 95%, and the value of CV% for all APIs was under 3%, therefore, the developed methodology was found reproducible in the quantification of each API in the presence of the others.
3.2. Analytical Method Validation
3.2.1. Solution Stability
Stability of APIs after storage (Table 1) shows that after 72 h of storage at −20, 4 and 25 °C, CVD, TEL, BZT, GZD, and GMP remained stable since both CV%, and RE% were less than 3% and 15%, respectively. The analysis of the samples immediately after preparation and after 72 h showed a recovery average above 95%; therefore, there was no effect of storage at −20, 4, and 25 °C on the quantifying of APIs.

Table 1.
Results of stability solutions of active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) after storage.
After 8 h of storage at 80 °C, the standard solutions of CVD, TEL, BZT, and GMP did not show any sign of thermal degradation in their chromatogram, retaining the peak integrity of each drug. This result can be confirmed by the percentages of recovery shown in Table 1 for these APIs, which were higher than 90% for the three drugs. In the case of GZD, as can be seen in Table 1, at 80 °C, the recovery percentage was only 22.30%. As seen in the chromatogram in Figure 3, in addition to the gliclazide signal, the chromatogram also showed four other signals, marked I-IV, whose relative retention times coincided with those found by Gulshan Bansal et al., [42]., for the possible hydrolysis of gliclazide into urea, p-toluensulfonylurea, octahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrol-2-amine and p-toluensulfonamide.
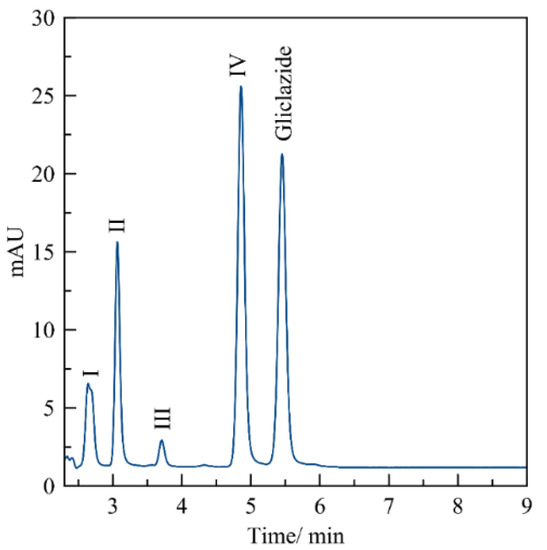
Figure 3.
Chromatogram of gliclazide at 10 μg mL−1 after 3 h at 80 °C. Conditions: stationary phase, C18 column, mobile phase acetonitrile: buffer phosphate, pH 3 (50/50 v/v), isocratic flow rate 1 mL/min and 25 °C. The notations I−IV correspond to products of the thermally induced hydrolysis of gliclazide.
3.2.2. Linearity Range
The linearity of the calibration curves for the APIs can be seen in Figure 4. The values of R2 are higher than 0.999 for all APIs. Therefore, the range (0.5–25 μg mL−1) used in the analytical method is linear and suitable for quantification.
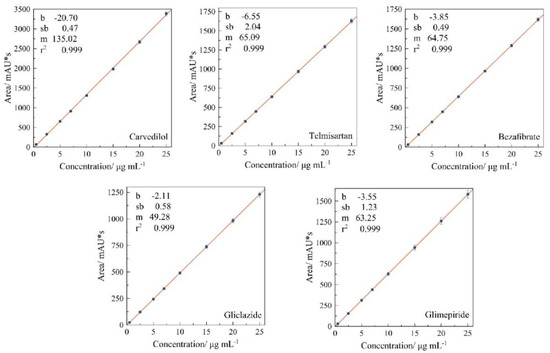
Figure 4.
Calibration curves for the active pharmaceutical ingredients showing the linearity of the method. Error bars represent standard deviation from n = 5. Value of intercept (b), standard deviation of intercept (σb), slope (m), and correlation coefficient (R2) were obtained from linear regression (y = mx + b).
3.2.3. Limit of Detection and Quantification
Figure 4 also shows the parameters of linear regression: intercept (b), standard deviation of intercept (σb), and slope (m); these parameters were used to calculate the limit of detection and limit of quantification. The resulting values for the LOD and LOQ for each drug were: carvedilol (0.012 and 0.035), telmisartan (0.103 and 0.313), bezafibrate (0.025 and 0.076), gliclazide (0.039 and 0.117), and glimepiride (0.064 and 0.127), in units of μg mL−1, respectively. These results show that this methodology allows quantification of the APIs in concentrations under 0.313 μg mL−1, and detection in the range of 0.012–0.103 μg mL−1. Likewise, the methodology developed in this work reports LOD and LOQ lower than those reported in different simultaneous methodologies for determination of telmisartan [26,29], bezafibrate [7], gliclazide [33,36], and glimepiride [36], therefore this methodology is more sensible than methodologies previously reported.
As recommended by the ICH, quantification limits, which are calculated from the calibration curve, must be validated by analyzing solutions with concentrations at the limit of quantification, as well as solutions with concentrations below and above the LOQ. Table 2 shows that the percentage of relative error between the calculated and experimental LOQ for each API %RE was lower than 15%, which validates the methodology’s limit of quantification. In Table 2, two additional concentrations are shown, one below and one above the limit of quantification. For the concentrations below LOQ, only gliclazide showed %RE values lower than 15%. In the case of carvedilol, it could not be detected, and the other APIs (BZT, TEL, and GMP) showed %RE values above 15%, which was coherent with the method because these concentrations were below LOQ. In the case of solutions above LOQ, the five APIs showed RE% and CV% lower than 15%, in agreement with what was expected from the methodology because these concentrations were above LOQ.

Table 2.
Validation of limit of quantification (LOQ) of active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) with concentration at, below and above LOQ.
3.2.4. Precision and Accuracy
Table 3 shows the results for precision and accuracy in terms of the coefficients of variation and relative error, respectively. Both values of CV% and RE% for evaluation in intraday and interday in the three concentrations were under 15%; therefore, the present method was precise and accurate [40,41].

Table 3.
Results of precision (CV%) and accuracy (RE%) of active pharmaceutical ingredients (API).
Comparing the retention times obtained from the methodology reported in this work with those previously reported in which the APIs of interest were in the presence of other drugs showed that: the retention times for TEL telmisartan [26,29] and glimepiride [36] were similar to those previously reported; in the cases of CVD [19,31], BZT [7], and GZD [33,36] retentions times were shorter; therefore the methodology developed was faster than methodologies previously reported, at least for these three APIs.
The presence of a single, symmetrical peak for each API proved that these chromatographic conditions avoided any interaction between APIs, so quantifying one API in the presence of another could be performed correctly. Besides, the methodology developed in this study was a rapid (lower than 9 min to quantify five APIs), accessible (did not use sophisticated chromatography equipment), sensible (allowed the quantification of API in low levels of concentration), and green analytical method (determination of multiple drugs at the same time reduced the use of toxic organic solvents, energy, economic cost and impact on the environment).
3.3. Evaluation of the Method by Working Sample Solutions
The validated method was applied to quantifying commercial pharmaceutical products to determine its feasibility as a method for quantifying commercial drug formulations both individually and simultaneously.
As previously described, commercially available drug products were quantified in two different ways. Table 4 shows the determination of experimental concentration, prepared from five different tablets; it was found that recovery for TEL, BZT, and GMP agreed with the nominal concentration. The relative error was lower than 7% for these commercial products. However, for CVD and GZD, the recovery was lower than 78%, suggesting a limited homogeneity for tablets of these drugs, preventing a correct quantification. The quantification of a single tablet of each drug (see Table 4) showed that, except for the GZD, the tablets of CVD, TEL, BZT, and GMP conducted a recovery greater than 95%.

Table 4.
Evaluation of experimental concentration and mass of active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) from sample solutions prepared with commercially available drug products.
All five drugs were quantified from a single solution. Figure 5 shows the simultaneous determination of these commercial pharmaceutical products. Each drug’s retention peaks were symmetric and well defined; therefore, the present method is suitable for simultaneously quantifying the five APIs in their commercial pharmaceutical form. This method could be used for quality control purposes by the pharmaceutical industry. It facilitates the simultaneous and rapid quantification of five APIs that are typically prescribed together to treat metabolic syndrome. This method would then allow the determination of these drugs in patients with multiple drug intake.

Figure 5.
Chromatogram for the simultaneous determination of CVD, TEL, BZT, GZD, and GMP at 10 μg mL−1 from the five commercial pharmaceutical products. Conditions: stationary phase, C18 column, mobile phase acetonitrile: buffer phosphate, pH 3, (50/50 v/v), isocratic flow rate 1 mL/min and 25 °C.
4. Conclusions
A novel isocratic reverse-phase HPLC-DAD methodology was developed for the simultaneous quantification of bezafibrate, gliclazide, glimepiride, telmisartan, and carvedilol. The method developed was rapid, linear, reproducible, and a greener analytical method. The results showed that the limit of detection and limit of quantification for the simultaneous determination of bezafibrate, gliclazide, glimepiride, and telmisartan were improved compared to previously reported methodologies. These results contribute to a methodology that could be applied in quality control in the pharmaceutical industry or the development of pharmaceutical formulations or clinical studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.C.-A. and L.M.M.; data curation, J.C.-A.; formal analysis, J.C.-A.; funding acquisition, L.M.M. and M.V.; investigation, J.C.-A., L.M.M., M.V. and C.M.-J.; methodology, J.C.-A., L.M.M., J.R.-R. and C.M.-J.; project administration, L.M.M.; resources, L.M.M.; supervision, L.M.M. and M.V.; validation, J.C.-A.; visualization, J.C.-A. and M.V.; writing—original draft, J.C.-A.; writing—review and editing, L.M.M., M.V. and J.R.-R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We thank the financial support provided by Secretaría de Educación Pública y Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (SEP-CONACyT) through the Basic Scientific Research Program (No. 255135), and the School of Engineering and Sciences at Tecnologico de Monterrey and the Research Chair of Emerging Technologies.
Acknowledgments
We also thank the Center of Biotechnology and Centro del Agua para América Latina y el Caribe, CAALCA, for access to the HPLC facilities. J.C.-A. and C.M.-J. thank the scholarships provided by CONACyT (285482, 25585).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
| MetS | Metabolic Syndrome |
| HPLC-DAD | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Diode-Array Detection |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| API | Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient |
| CVD | Carvedilol |
| TEL | Telmisartan |
| BZT | Bezafibrate |
| GZD | Gliclazide |
| GMP | Glimepiride |
| CV% | Coefficient of variation |
| RE% | Relative error |
References
- Nolan, P.B.; Carrick-Ranson, G.; Stinear, J.W.; Reading, S.A.; Dalleck, L.C. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and metabolic syndrome components in young adults: A pooled analysis. Prev. Med. Rep. 2017, 7, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, S.; O’Driscoll, L. Metabolic syndrome: A closer look at the growing epidemic and its associated pathologies. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, S.M.; Cleeman, J.I.; Daniels, S.R.; Donato, K.A.; Eckel, R.H.; Franklin, B.A.; Gordon, D.J.; Krauss, R.M.; Savage, P.J.; Smith, S.C.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of the Metabolic Syndrome: An American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation 2005, 112, 2735–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z. The metabolic syndrome. Lancet 2005, 365, 1415–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahiru, E.; de Cates, A.N.; Farr, M.R.; Jarvis, M.C.; Palla, M.; Rees, K.; Ebrahim, S.; Huffman, M.D. Fixed-dose combination therapy for the prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 3, CD009868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T.; Kazumi, T.; Yoshino, G. Long-Term Efficacy of Bezafibrate in Reduction of Small, Dense Low-Density Lipoprotein by Hypotriglyceridemic Action. Curr. Ther. Res. 2000, 61, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kommos, M.E.; Mohamed, N.A.; Ali, H.R.H.; Abdel Hakiem, A.F. Simultaneous Estimation of Metformin Hydrochloride and Certain Cardiovascular Drugs with a Pharmacokinetic Study. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2015, 38, 1759–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouini, M.-R.; Mohajer, A.; Tahami, M.-H. A simple and sensitive HPLC method for determination of gliclazide in human serum. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 785, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan, S.M.; Zarghi, A.; Shafaati, A.; Khoddam, A. Application of monolithic column in quantification of gliclazide in human plasma by liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 42, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jondhale, S.; Bhise, S.; Pore, Y. Physicochemical Investigations and Stability Studies of Amorphous Gliclazide. AAPS PharmSciTech 2012, 13, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhya, S.M.; Kumar, P.S. Simple and Rapid Simultaneous RP-HPLC Method for Determination of Glimepiride and Metformin in Tablet Dosage Form. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2014, 7, 906–909. [Google Scholar]
- Vaingankar, P.N.; Amin, P.D. Development and Validation of Stability-Indicating RP-HPLC Method for Simultaneous Determination of Metformin HCI and Glimepiride in Fixed-Dose Combination. Anal. Chem. Insights 2016, 11, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Singh, O.P.B.; Biswal, S.; Sahoo, J.; Murthy, P.N. Physicochemical Properties of Glimepiride in Solid Dispersions with Polyethylene Glycol 20,000. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Nanotechnol. 2009, 2, 537–543. [Google Scholar]
- Babu, K.R.; Sarma, E.S.R.S.; Kumari, N.A.; Raju, G.M.J.; Sarma, G.V.S. Simple and stability indicating RP-HPLC assay method development and validation lisinopril dihydrate by RP-HPLC in bulk and dosage form. Der. Pharm. Lett. 2015, 7, 274–280. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, J.M.; Dhingani, A.P.; Garala, K.C.; Raval, M.K.; Sheth, N.R. Development and Validation of Bioanalytical HPLC Method For Estimation of Telmisartan In Rat Plasma: Application To Pharmacokinetic Studies. Dhaka Univ. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 11, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, A.; Rao, M.R.P.; Pardeshi, A.; Sali, D. Nanocrystallization by Evaporative Antisolvent Technique for Solubility and Bioavailability Enhancement of Telmisartan. AAPS PharmSciTech 2012, 13, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, K.B.; Reddy, M.R.M.; Naidu, N.V. Development and validation of RP-HPLC method for determination of carvedilol in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage forms. Der. Pharm. Lett. 2014, 6, 198–206. [Google Scholar]
- Swetha, E.; Vijitha, C.; Veeresham, C. HPLC Method Development and Validation of S (-)-Carvedilol from API and Formulations. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 6, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyban, A.; Sorouraddin, M.H.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Somi, M.H.; Fazeli-Bakhtiyari, R. Determination of five antiarrhythmic drugs in human plasma by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and high-performance liquid chromatography. Talanta 2015, 134, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo, J.; Hurtado, F.K.; Poitevin, F.S.; Flores, F.C.; Sonego, E.; Dalmora, S.L.; Madalena, C.; Rolim, B. HPLC Determination of Bezafibrate in Human Plasma and its Application to Pharmacokinetics Studies. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2010, 48, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xiang, B.-R.; Zhan, Y.; Yu, L.-Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, C.-Y. HPLC Method for the Determination of Bezafibrate in Human Plasma and Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study of Bezafibrate Dispersible Tablet. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2008, 46, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Jiang, J.-Q. Simultaneous Detection of Sulfamethoxazole, Diclofenac, Carbamazepine, and Bezafibrate by Solid Phase Extraction and High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Diode Array Detection. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2014, 81, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichal, C.R.; Rao, M.G. Development and validation of PR-HPLC method for simultaneous estimation of gliclazide and sitagliptin phosphate monohydrate in bulk and tablet dosage form. Int. J. Pharma Sci. 2015, 6, 361–369. [Google Scholar]
- Chakradhar, L.; Kallem, R.; Karthik, A.; Sundari, B.T.; Ramesh, S.; Mullangi, R.; Srinivas, N.R. A rapid and highly sensitive method for the determination of glimepiride in human plasma by liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry: Application to a pre-clinical pharmacokinetic study. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2008, 22, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surekha, M.L.; Kumara Swamy, G.; Ashwini, G.L. Development and Validation of RP—HPLC method for the estimation of Telmisartan in bulk and tablet dosage Form. Int. J. Drug Dev. Res. 2012, 4, 200–205. [Google Scholar]
- Sree Janardhanan, V.; Manavalan, R.; Valliappan, K. Chemometric technique for the optimization of chromatographic system: Simultaneous HPLC determination of Rosuvastatin, Telmisartan, Ezetimibe and Atorvastatin used in combined cardiovascular therapy. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, S1378–S1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, N.; Arayne, M.S.; Shafi, N.; Siddiqui, F.A.; Hussain, A. Development of a RP-HPLC method for the simultaneous analysis of diltiazem and statin: Application in pharmaceuticals and human serum. Anal. Methods 2010, 2, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, M.K.; Muzeeb, S.; Basha, S.J.S.; Shashikumar, D.; Mullangi, R.; Srinivas, N.R. Analysis of five HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors—Atorvastatin, lovastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin and simvastatin: Pharmacological, pharmacokinetic and analytical overview and development of a new method for use in pharmaceutical formulations analysis an. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2006, 20, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhazmi, H.; Alnami, A.; Arishi, M.; Alameer, R.; Al Bratty, M.; Rehman, Z.; Javed, S.; Arbab, I. A Fast and Validated Reversed-Phase HPLC Method for Simultaneous Determination of Simvastatin, Atorvastatin, Telmisartan and Irbesartan in Bulk Drugs and Tablet Formulations. Sci. Pharm. 2018, 86, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnuvardhan, C.; Radhakrishnanand, P.; Navalgund, S.G.; Atcha, K.R.; Satheeshkumar, N. RP-HPLC Method for the Simultaneous Estimation of Eight Cardiovascular Drugs. Chromatographia 2014, 77, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, S.; Jouyban, A. Optimization and validation of an isocratic HPLC-UV method for the simultaneous determination of five drugs used in combined cardiovascular therapy in human plasma. Asian J. Chem. 2011, 23, 1728–1734. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, O.; Iriarte, G.; Ferreirós, N.; Maguregui, M.I.; Alonso, R.M.; Jiménez, R.M. Optimization and validation of a SPE-HPLC-PDA-fluorescence method for the simultaneous determination of drugs used in combined cardiovascular therapy in human plasma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 50, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, P.; Harisudhan, T.; Choudhury, H.; Mullangi, R.; Srinivas, N.R. Simultaneous estimation of six anti-diabetic drugs—glibenclamide, gliclazide, glipizide, pioglitazone, repaglinide and rosiglitazone: Development of a novel HPLC method for use in the analysis of pharmaceutical formulations and its application to human pl. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2006, 20, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.K.; Hassan, A.A. Development of a RP-HPLC Method for Simultaneous Determination of Some Antidiabetic Sulfonylurea Drugs in Bulk and Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2014, 25, 207–210. [Google Scholar]
- Pednekar, S.; Lokhande, R.; Sutar, R.; Kolhal, S.; Surve, S.; Gudekar, S. Simultaneous Determination of Metformin, Sitagliptin, Saxagliptin, Linagliptin and Vildagliptin in Multicomponent Pharmaceutical Preparations by RP-HPLC. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2014, 28, 128–133. [Google Scholar]
- AbuRuz, S.; Millership, J.; McElnay, J. The development and validation of liquid chromatography method for the simultaneous determination of metformin and glipizide, gliclazide, glibenclamide or glimperide in plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 817, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, N.; Arayne, M.S.; Iftikhar, B. Simultaneous Determination of Atenolol, Rosuvastatin, Spironolactone, Glibenclamide and Naproxen Sodium in Pharmaceutical Formulations and Human Plasma by RP-HPLC. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2008, 55, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldin, A.B.; Ismaiel, O.A.; Hassan, W.E.; Shalaby, A.A. Green analytical chemistry: Opportunities for pharmaceutical quality control. J. Anal. Chem. 2016, 71, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Conference on Harmonization (ICH). Topic Q2 (R1): Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology; ICH: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, V.P.; Midha, K.K.; Dighe, S.; McGilveray, I.J.; Skelly, J.P.; Yacobi, A.; Layloff, T.; Viswanathan, C.T.; Edgar Cook, C.; Mcdowall, R.D.; et al. Analytical Methods Validation: Bioavailability, Bioequivalence, and Pharmacokinetic Studies. J. Pharm. Sci. 1992, 81, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnes, H.T.; Shiu, G.; Shah, V.P. Validation of Bioanalytical Methods. Pharm. Res. 1991, 08, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, G.; Singh, M.; Jindal, K.C. Forced Degradation Study on Gliclazide and Application of Validated Stability-Indicating HPLC-UV Method in Stability Testing of Gliclazide Tablets. Chromatographia 2007, 66, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).