Association of Antibiotic Use with the Resistance Epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a Hospital Setting: A Four-Year Retrospective Time Series Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Setting
2.2. Antibiotic Consumption
2.3. Microbiological Data
2.4. Data Analysis
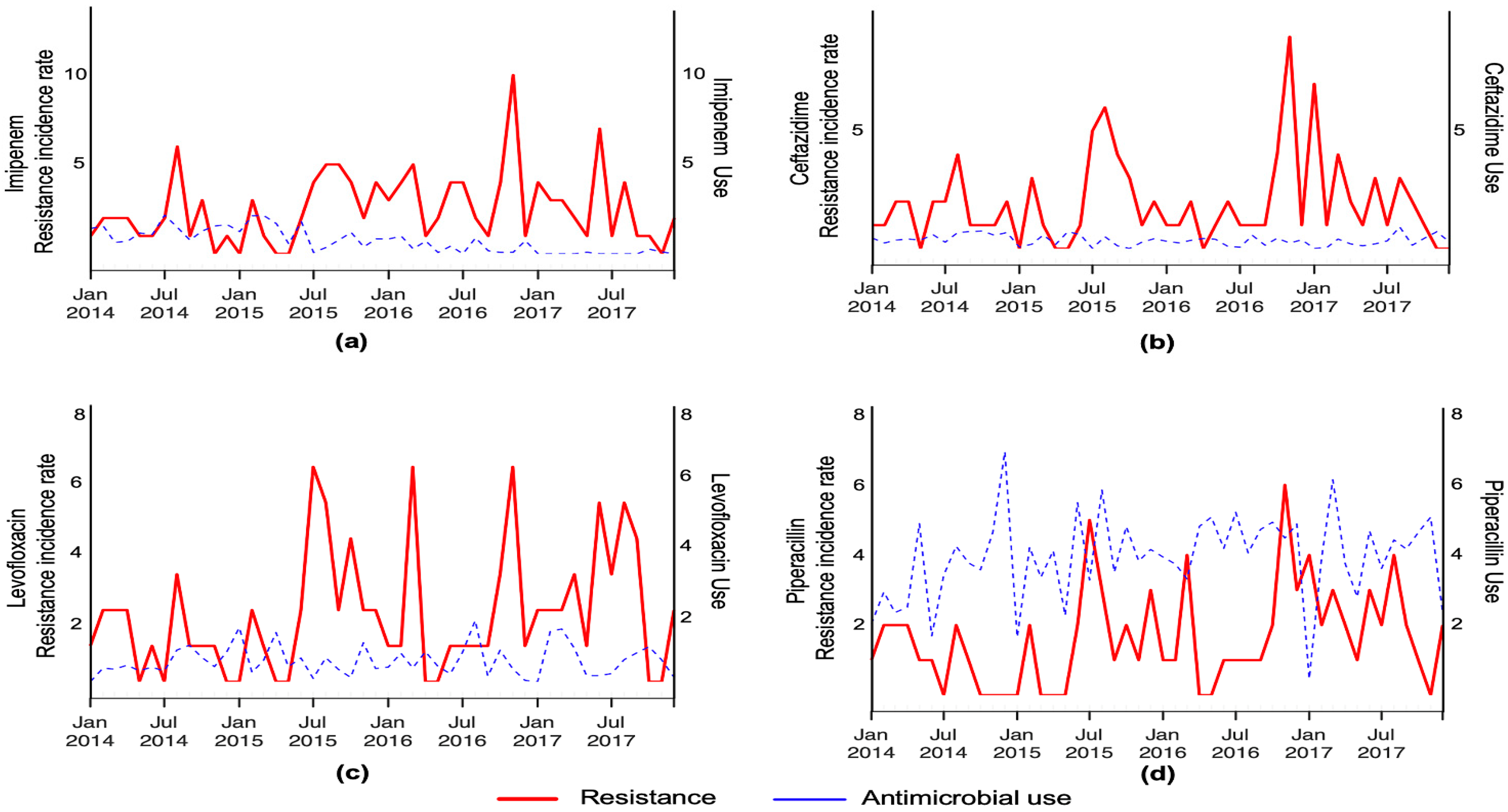
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Carbapenems
4.2. Cephalosporins
4.3. Fluoroquinolones
4.4. Piperacillin/Tazobactam
4.5. Colistin
4.6. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baron, S.; Hadjadj, L.; Rolain, J.M.; Olaitan, A.O. Molecular mechanisms of polymyxin resistance: Knowns and unknowns. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 48, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, D.L. The epidemiological profile of infections with multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter species. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, S43–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.; Kahlmeter, G.; Paterson, D.L.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassetti, M.; Vena, A.; Croxatto, A.; Righi, E.; Guery, B. How to manage Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Drugs Context 2018, 7, 212527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Ouellette, M.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, B.A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Resistance and therapy. Semin. Respir. Infect. 2002, 17, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontefract, B.A.; Ho, H.T.; Crain, A.; Kharel, M.K.; Nybo, S.E. Drugs for Gram-Negative Bugs from 2010–2019: A Decade in Review. Open Forum Inf. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoglund, E.; Abodakpi, H.; Rios, R.; Diaz, L.; De La Cadena, E.; Dinh, A.Q.; Tran, T.T.; Ardila, J.; Miller, W.R.; Munita, J.; et al. In Vivo Resistance to Ceftolozane/Tazobactam in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Arising by AmpC- and Non-AmpC-Mediated Pathways. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2018, 23, 9095203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Ortiz De La Rosa, J.M.; Kieffer, N.; Dubois, V.; Jayol, A.; Nordmann, P. Acquisition of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase GES-6 Leading to Resistance to Ceftolozane-Tazobactam Combination in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01809–e01818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraile-Ribot, P.A.; Cabot, G.; Mulet, X.; Periañez, L.; Martín-Pena, M.L.; Juan, C.; Oliver, A.; Pérez, J.A. Mechanisms leading to in vivo ceftolozane/tazobactam resistance development during the treatment of infections caused by MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepper, P.M.; Grusa, E.; Reichl, H.; Högel, J.; Trautmann, M. Consumption of imipenem correlates with β-lactam resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2920–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, H.; Fésűs, A.; Kungler-Gorácz, O.; Balázs, B.; Majoros, L.; Szarka, K.; Kardos, G. Utilization of Vector Autoregressive and Linear Transfer Models to Follow Up the Antibiotic Resistance Spiral in Gram-negative Bacteria from Cephalosporin Consumption to Colistin Resistance. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 1410–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanasiou, C.I.; Kopsini, A. Systematic review of the use of time series data in the study of antimicrobial consumption and Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistance. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 15, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Lozano, J.M.; Monnet, D.L.; Yagüe, A.; Burgos, A.; Gonzalo, N.; Campillos, P.; Saez, M. Modelling and forecasting antimicrobial resistance and its dynamic relationship to antimicrobial use: A time series analysis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2000, 14, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Lozano, J.M.; Lawes, T.; Nebot, C.; Beyaert, A.; Bertrand, X.; Hocquet, D.; Gould, I.; Aldeyab, M.; Scott, M.; Conlon-Bingham, G.; et al. A nonlinear time-series analysis approach to identify thresholds in associations between population antibiotic use and rates of resistance. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1160–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.P.; Jenkins, G.M. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 21–192. [Google Scholar]
- Mahamat, A.; Lavigne, J.P.; Fabbro-Peray, P.; Kinowski, J.M.; Daures, J.P.; Sotto, A. Evolution of fluoroquinolone resistance among Escherichia coli urinary tract isolates from a French university hospital: Application of the dynamic regression model. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2005, 11, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmann, M.; Marschal, M.; Hölzl, F.; Schröppel, K.; Autenrieth, I.B.; Peter, S. Time series analysis as a tool to predict the impact of antimicrobial restriction in antibiotic stewardship programs using the example of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1797–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bartlett, M.S. Periodogram analysis and continuous spectra. Biometrika 1950, 37, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDowell, A. Transfer functions. Stata J. 2002, 2, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, L.R. Squeezing the antibiotic balloon: The impact of antimicrobial classes on emerging resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2005, 11, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feretzakis, G.; Loupelis, E.; Sakagianni, A.; Skarmoutsou, N.; Michelidou, S.; Velentza, A.; Martsoukou, M.; Valakis, K.; Petropoulou, S.; Koutalas, E. A 2-Year Single-Centre Audit on Antibiotic Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii and Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains from an Intensive Care Unit and Other Wards in a General Public Hospital in Greece. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karampatakis, T.; Antachopoulos, C.; Tsakris, A.; Roilides, E. Molecular epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in an endemic area: Comparison with global data. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, A.; Gato, E.; Pérez-Llarena, J.; Fernández-Cuenca, F.; Gude, M.J.; Oviaño, M.; Pachón, M.E.; Garnacho, J.; González, V.; Pascual, Á.; et al. High incidence of MDR and XDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates obtained from patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia in Greece, Italy and Spain as part of the MagicBullet clinical trial. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Sun, X.; Ma, X. Systematic review and meta-analysis of mortality of patients infected with carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2017, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, D.; Castelo-Corral, L.; Gutiérrez-Urbón, J.M.; Molina, F.; López-Calviño, B.; Bou, G.; Llinares, P. Impact of ertapenem use on Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii imipenem susceptibility rates: Collateral damage or positive effect on hospital ecology? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Carmeli, Y.; Lidji, S.K.; Shabtai, E.; Navon-Venezia, S.; Schwaber, M.J. The effects of group 1 versus group 2 carbapenems on imipenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: An ecological study. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 70, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.M.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.H.; Shi, J.; Fan, T.; Shan, Y.Y.; Yao, H.P.; Dong, Y.L. Trends and correlation of antibacterial usage and bacterial resistance: Time series analysis for antibacterial stewardship in a Chinese teaching hospital (2009–2013). Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdeljić, V.; Francetić, I.; Bošnjak, Z.; Budimir, A.; Kalenić, S.; Bielen, L.; Likić, R.; Makar-Aušperger, K. Distributed lags time series analysis versus linear correlation analysis (Pearson’s r) in identifying the relationship between antipseudomonal antibiotic consumption and the susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates in a single Intensive Care Unit of a tertiary hospital. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2011, 37, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, S.; Shen, P.; Lu, X.; Xiao, Y. Association between the rate of fluoroquinolones-resistant gram-negative bacteria and antibiotic consumption from China based on 145 tertiary hospitals data in 2014. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, P.P.; Gooch, M.; Rizzo, S. Reduction in fluoroquinolone use following introduction of ertapenem into a hospital formulary is associated with improvement in susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to group 2 carbapenems: A 10-year study. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5597–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Huan, J.; Guo, F.; Zhou, Z.; Shi, Y. Pseudomonas aeruginosa prevalence, antibiotic resistance and antimicrobial use in Chinese burn wards from 2007 to 2014. J. Int. Med. Res. 2017, 45, 1124–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallel, H.; Mahjoubi, F.; Dammak, H.; Bahloul, M.; Hammami, A.; Bouaziz, M. Correlation between antibiotic use and changes in susceptibility patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a medical-surgical intensive care unit. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. Peer Rev. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 12, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]


| Antimicrobial Agent | S (%) | I (%) | R (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Imipenem | 63.4 | 2.5 | 34 |
| Meropenem | 66.4 | 5.5 | 28 |
| Ceftazidime | 63.2 | 10.5 | 26.1 |
| Cefepime | 60.9 | 12.5 | 26.5 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 62.3 | 7.4 | 30.1 |
| Levofloxacin | 52.4 | 11.2 | 36.4 |
| Piperacillin/tazobactam | 70.2 | 0 | 29.7 |
| Colistin | 93.1 | 0.8 | 6 |
| Antimicrobial Agent/Class | DDDs/100 PD a | Delay b (In Months) | p-Value c |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbapenems | |||
| Imipenem | 0.71 | 0 | 0.091 |
| Meropenem | 6.74 | 0 | <0.001 |
| Cephalosporins | |||
| Ceftazidime | 0.48 | 0 | 0.201 |
| Cefepime | 1.85 | 0 | 0.005 |
| Fluoroquinolones | |||
| Ciprofloxacin | 4.65 | 2 | <0.001 |
| Levofloxacin | 0.58 | 0 | 0.115 |
| Other | |||
| Piperacillin | 3.94 | 0 | 0.34 |
| Colistin | 3.56 | NA d | NA |
| Estimate | Model Parameter | Standard Error | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. Resistance | |||
| Intercept | 1.25 | 0.244 | <0.001 |
| AIC | 80.82 | / | / |
| R2 | 0.587 | / | / |
| B. Meropenem use (in DDD/100 PD) | |||
| ar1 | −0.831 | 0.122 | <0.001 |
| ar2 | −0.637 | 0.144 | <0.001 |
| ar3 | −0.569 | 0.117 | <0.001 |
| AIC | 242.91 | / | / |
| R2 | 0.638 | / | / |
| C. Impact of meropenem use on resistance | |||
| mer0 | 0.175 | 0.029 | <0.001 |
| AIC | 77.09 | / | / |
| R2 | 0.183 | / | / |
| Estimate | Model Parameter | Standard Error | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. Resistance | |||
| ar1 | −0.453 | 0.18368 | 0.013 |
| AIC | 87.58 | / | / |
| R2 | 0.175 | / | / |
| B. Cefepime use (in DDD/100 PD) | |||
| ar1 | −0.463 | 0.137 | <0.001 |
| ar2 | −0.466 | 0.133 | <0.001 |
| AIC | 139.03 | / | / |
| R2 | 0.619 | / | / |
| C. Impact of cefepime use on resistance | |||
| ar1 | −0.506 | 0.176 | 0.004 |
| cef0 | 0.482 | 0.175 | 0.005 |
| AIC | 73.3 | / | / |
| R2 | 0.422 | / | / |
| Estimate | Model Parameter | Standard Error | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. Resistance | |||
| ar1 | 0.502 | 0.167 | 0.002 |
| intercept | 2.556 | 0.727 | <0.001 |
| AIC | 106.74 | / | / |
| R2 | 0.267 | / | / |
| B. Ciprofloxacin use (in DDD/100 PD) | |||
| ar1 | −0.527 | 0.147 | 0.000 |
| ar3 | −0.299 | 0.152 | 0.004 |
| AIC | 77.76 | / | / |
| R2 | 0.550 | / | / |
| C. Impact of ciprofloxacin use on resistance | |||
| ar1 | 0.560 | 0.17137 | 0.001 |
| cip2 | 0.464 | 0.12727 | <0.001 |
| AIC | 93.62 | / | / |
| R2 | 0.404 | / | / |
| Estimate | Model Parameter | Standard Error | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. Imipenem | |||
| Model | ARIMA (0,0,0) | / | / |
| Intercept | 3.166 | 0.435 | <0.001 |
| Imipenem use | −0.792 | 0.450 | 0.091 |
| AIC | 191.880 | / | / |
| R2 | 0.066 | / | / |
| B. Ceftazidime | |||
| Model | ARIMA (0,1,1) | / | / |
| Intercept | −1.000 | 0.083 | <0.001 |
| Ceftazidime use | −1.550 | 1.213 | 0.201 |
| AIC | 184.690 | / | / |
| R2 | 0.043 | / | / |
| C. Levofloxacin | |||
| Model | ARIMA (0,0,0) | / | / |
| Intercept | 2.510 | 0.463 | <0.001 |
| Levofloxacin use | −0.972 | 0.618 | 0.115 |
| AIC | 179.270 | / | / |
| R2 | 0.053 | / | / |
| D. Piperacillin | |||
| Model | ARIMA (1,0,0) | / | / |
| Intercept | 0.305 | 0.152 | 0.0448 |
| Piperacillin use | 0.368 | 0.072 | 0.34 |
| AIC | 155.290 | / | / |
| R2 | 0.079 | / | / |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kousovista, R.; Athanasiou, C.; Liaskonis, K.; Ivopoulou, O.; Karalis, V. Association of Antibiotic Use with the Resistance Epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a Hospital Setting: A Four-Year Retrospective Time Series Analysis. Sci. Pharm. 2021, 89, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm89010013
Kousovista R, Athanasiou C, Liaskonis K, Ivopoulou O, Karalis V. Association of Antibiotic Use with the Resistance Epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a Hospital Setting: A Four-Year Retrospective Time Series Analysis. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2021; 89(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm89010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleKousovista, Rania, Christos Athanasiou, Konstantinos Liaskonis, Olga Ivopoulou, and Vangelis Karalis. 2021. "Association of Antibiotic Use with the Resistance Epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a Hospital Setting: A Four-Year Retrospective Time Series Analysis" Scientia Pharmaceutica 89, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm89010013
APA StyleKousovista, R., Athanasiou, C., Liaskonis, K., Ivopoulou, O., & Karalis, V. (2021). Association of Antibiotic Use with the Resistance Epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a Hospital Setting: A Four-Year Retrospective Time Series Analysis. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 89(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm89010013






