Preliminary Study: Purple Sweet Potato Extract Seems to Be Superior to Increase the Migration of Impaired Endothelial Progenitor Cells Compared to l-Ascorbic Acid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PSP and l-Ascorbic Acid Preparation
2.2. Subject Recruitment and Sample Collection
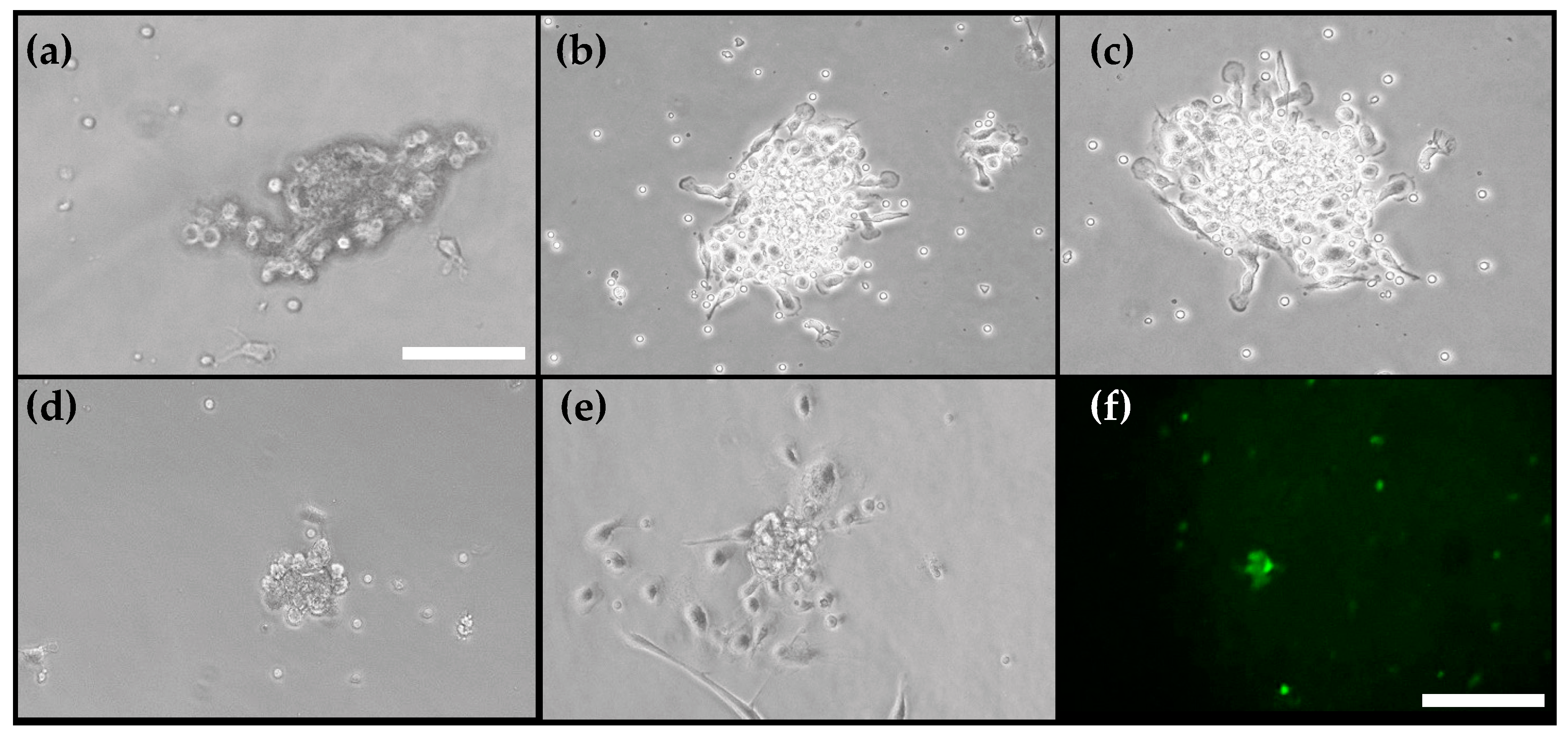
2.3. EPCs Isolation and Culture
2.4. EPCs Proliferation Assay
2.5. EPCs Migration Assay
2.6. CFU Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demography of Subjects
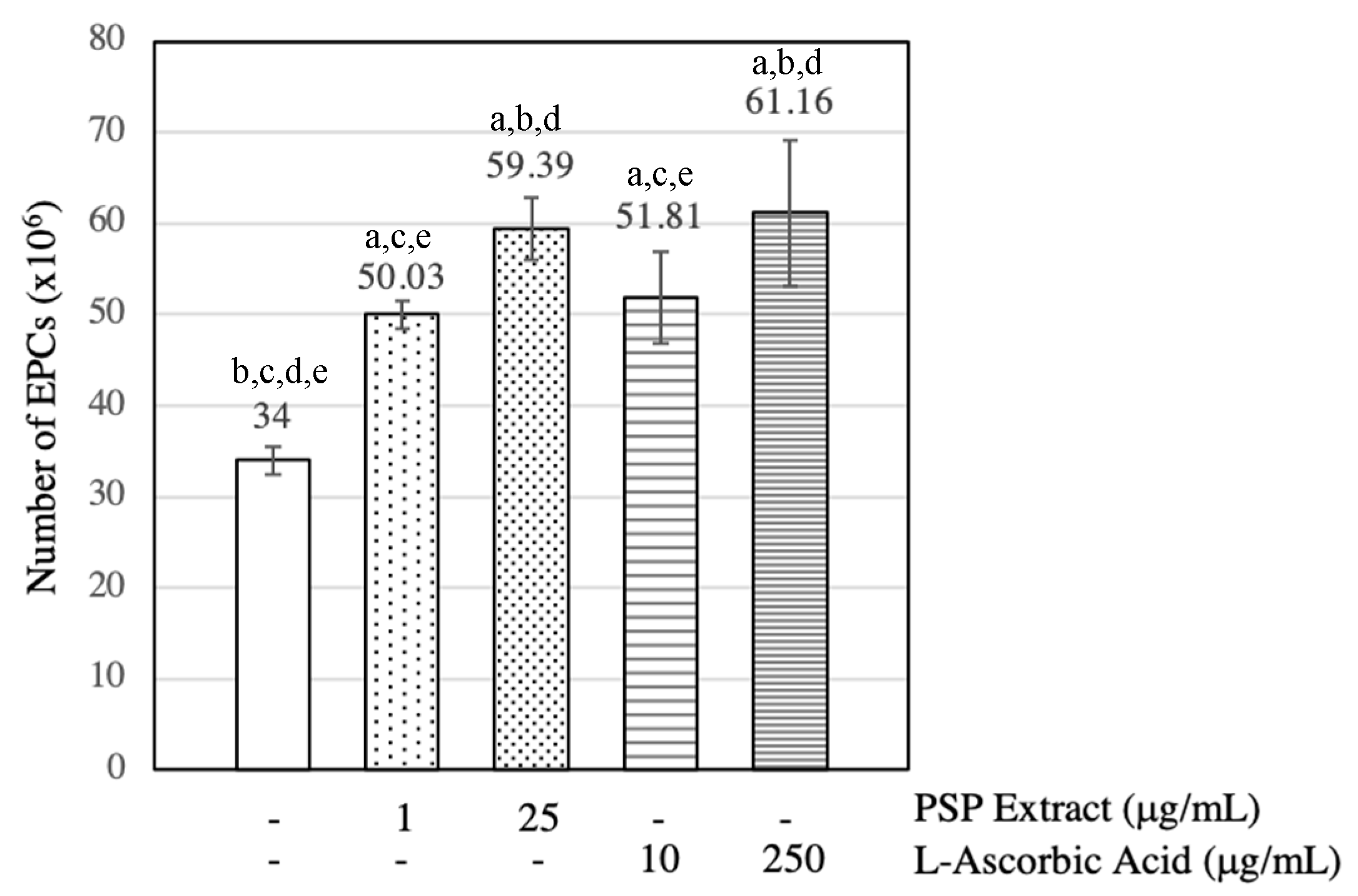
3.2. PSP Extract and l-Ascorbic Acid Increased EPCs Numbers
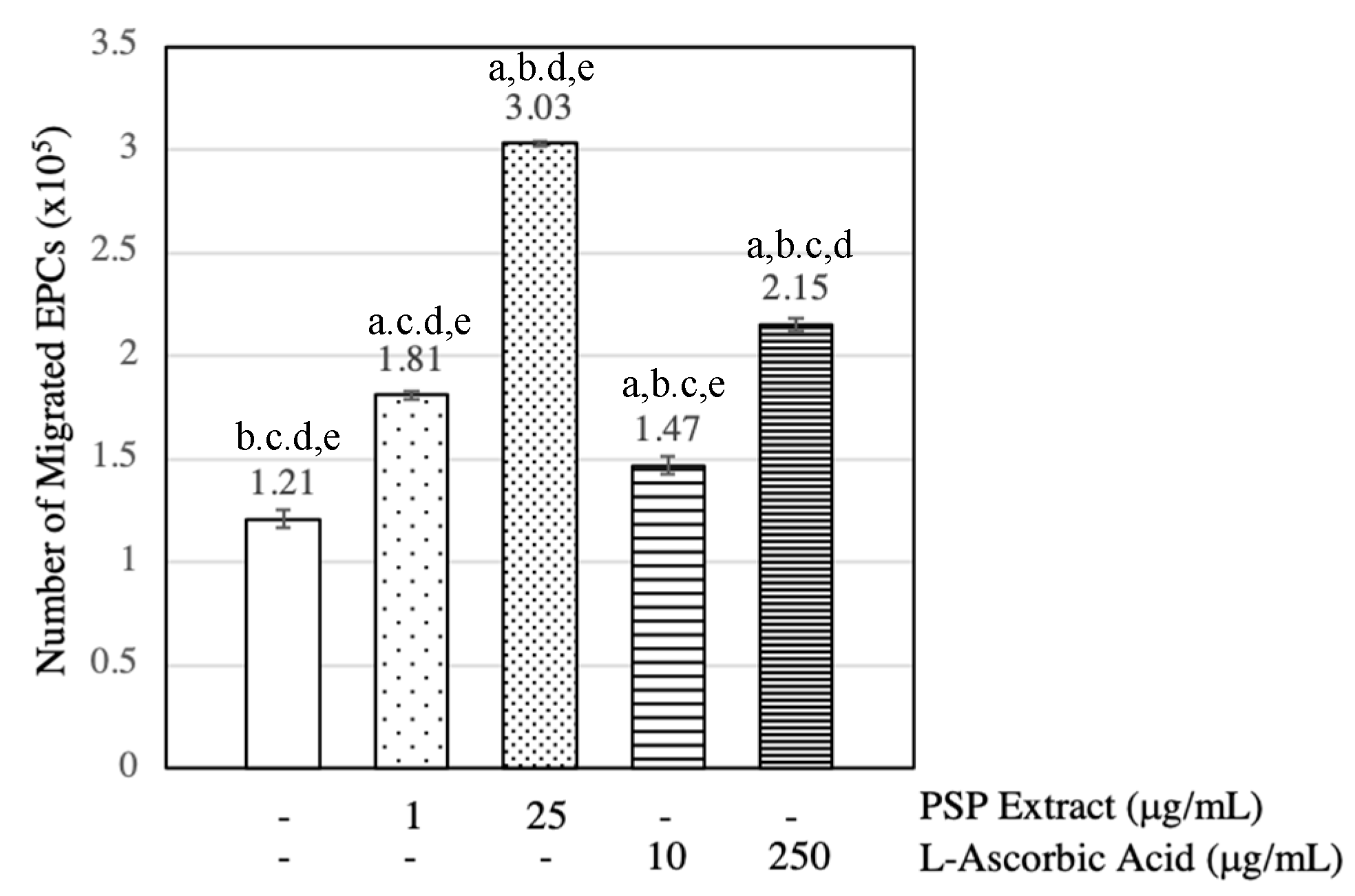
3.3. PSP Extract and l-Ascorbic Acid Induced EPCs Migration
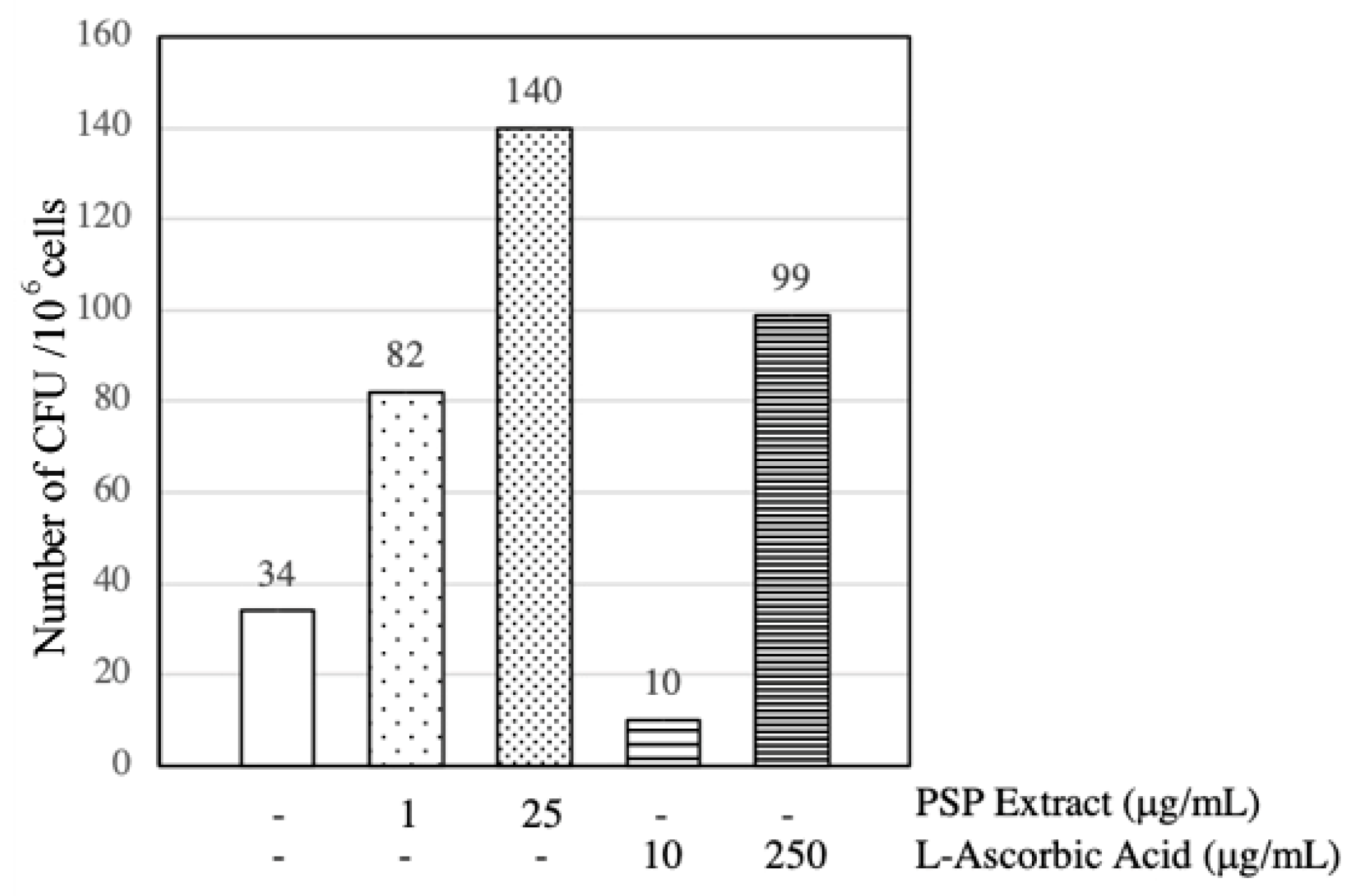
3.4. PSP Extract and l-Ascorbic Acid Induced EPCs CFU Formation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosamond, W.; Flegal, K.; Furie, K.; Go, A.; Greenlund, K.; Haase, N.; Hailpern, S.M.; Ho, M.; Howard, V.; Kissela, B.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2008 update: A report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation 2008, 117, e25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nichols, M.; Townsend, N.; Scarborough, P.; Rayner, M. Cardiovascular disease in Europe 2014: Epidemiological update. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Heart Association. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2018 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2018, 137, e67. [Google Scholar]
- The George Institute for Global Health. Reducing the burden of Cardiovascular Disease in Indonesia: Evidence Review. Available online: https://www.georgeinstitute.org/sites/default/files/reducing-the-burden-of-cvd-in-indonesia-evidence-review.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2019).
- Vasa, M.; Ficht, L.; Scherer, S.; Aicher, A.; Adler, K.; Urbich, C.; Martin, H.; Zeiher, A.M.; Dimmeler, S. Number and migratory activity of circulating endothelial progenitor cells inversely correlate with risk factors for coronary artery disease. Circ. Res. 2001, 89, E1–E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oktaviono, Y.H.; Sargowo, D.; Widodo, M.A.; Dirgantara, Y.; Chouw, A.; Sandra, F. Proliferation of Peripheral Blood-derived Endothelial Progenitor Cells from Stable Angina Subjects. Indones Biomed. J. 2014, 6, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, N.; Wassmann, S.; Ahlers, P.; Schiegl, T.; Kosiol, S.; Link, A.; Walenta, K.; Nickenig, G. Endothelial progenitor cells correlate with endothelial function in patients with coronary artery disease. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2007, 102, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomans, C.J.; De Koning, E.J.; Staal, F.J.; Rabelink, T.J.; Zonneveld, A.J. Endothelial progenitor cell dysfunction in type 1 diabetes: Another consequence of oxidative stress? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2005, 7, 1468–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, J.; Li, J.; Orschell, C.M.; March, K.L. Peripheral blood endothelial progenitor cells are derived from monocyte/macrophages and secrete angiogenic growth factors. Circulation. 2003, 107, 1164–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widowati, W.; Sardjono, C.T.; Wijaya, L.; Laksmitawati, D.R.; Sandra, F. Extract of Curcuma longa L. and (-)-Epigallo Catechin-3-Gallate Enhanced Proliferation of Adipose Tissue–derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (AD-MSCs) and Differentiation of AD-MSCs into Endothelial Progenitor Cells. J. USA-China Med. Sci. 2012, 9, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Widowati, W.; Wijaya, L.; Laksmitawati, D.R.; Widyanto, R.M.; Erawijantari, P.P.; Fauziah, N.; Bachtiar, I.; Sandra, F. Tea Flavonoids Induced Differentiation of Peripheral Blood-derived Mononuclear Cells into Peripheral Blood-derived Endothelial Progenitor Cells and Suppressed Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species Level of Peripheral Blood-derived Endothelial Progenitor Cells. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2016, 22, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Lucchesi, D.; Russo, R.; Gabriele, M.; Longo, V.; Del Prato, S.; Penno, G.; Pucci, L. Grain and bean lysates improve function of endothelial progenitor cells from human peripheral blood: Involvement of the endogenous antioxidant defenses. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, B.J.; Han, S.S.; Ha, J.H.; Park, S.N. Antioxidant Activities of Ipomoea batatas L. Lam. (Purple Sweet Potato) Extracts Cultured in Korea. J. Soc. Cosmet. Sci. Korea 2014, 40, 423–430. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorito, C.; Rienzo, M.; Crimi, E.; Rossiello, R.; Balestrieri, M.L.; Casamassimi, A.; Muto, F.; Grimaldi, V.; Giovane, A.; Farzati, B.; et al. Antioxidants increase number of progenitor endothelial cells through multiple gene expression pathways. Free Radic Res. 2008, 42, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parzonko, A.; Oświt, A.; Bazylko, A.; Naruszewicz, M. Anthocyans-rich Aronia melanocarpa extract possesses ability to protect endothelial progenitor cells against angiotensin II induced dysfunction. Phytomedicine. 2015, 22, 1238–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iordache, F.; Iordache, C.; Pop, A.; Lupu, M.; Andrei, E.; Buzila, C.; Maniu, H. Effects of plant lectin and extracts on adhesion molecules of endothelial progenitors. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2011, 6, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, M.; Takayanagi, T.; Harada, K.; Makino, K.; Ishikawa, F. Antioxidative activity of anthocyanins from purple sweet potato, Ipomoea batatas cultivar Ayamurasaki. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 979–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teow, C.C.; Truong, V.D.; McFeetersa, R.F.; Thompsona, R.L.; Pecotab, K.V.; Yenchob, G.C. Antioxidant activities, phenolic and β-carotene contents of sweet potato genotypes with varying flesh colours. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Fan, S.; Wang, X.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, D.; Shan, Q.; Zheng, Y. Purple sweet potato color inhibits endothelial premature senescence by blocking the NLRP3 inflammasome. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawi, I.; Indrayani, W.; Arijana, I.; Subawa, A.; Suprapta, D. Aqueous extratc of purple sweet potato increased SOD-2 and SOD-3 expression on human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro. J. Biol. Agric. Health 2016, 6, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Tu, Y.K.; Tang, Y.B.; Cheng, N.C. Stemness and transdifferentiation of adipose-derived stem cells using l-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate-induced cell sheet formation. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3516–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandra, F.; Oktaviono, Y.H.; Widodo, M.A.; Dirgantara, Y.; Chouw, A.; Sargowo, D. Endothelial Progenitor Cells Proliferated via MEK-dependent p42 MAPK Signaling Pathway. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2015, 400, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, N.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, T.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Y.; Qin, L.; Kang, J.; Wei, B.; et al. Ascorbic acid enhances the cardiac differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells through promoting the proliferation of cardiac progenitor cells. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.S.; Chen, Y.; Yao, C.L. A serum-free medium developed for in vitro expansion of murine intestinal stem cells. Biotechnol. J. 2014, 9, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balestrieri, M.L.; Schiano, C.; Felice, F.; Casamassimi, A.; Balestrieri, A.; Milone, L.; Servillo, L.; Napoli, C. Effect of low doses of red wine and pure resveratrol on circulating endothelial progenitor cells. J. Biochem. 2008, 143, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleissner, F.; Thum, T. Critical Role of the Nitric Oxide/Reactive Oxygen Species Balance in Endothelial Progenitor Dysfunction. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 933–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhai, W.; Yang, Z. Studies on antioxidant capacity of anthocyanin extract from purple sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 7046–7054. [Google Scholar]
| Variable | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Age (year) | 54.5 ± 4.31 |
| Height (cm) | 168.0 ± 1.3 |
| Weight (kg) | 70.25 ± 6.34 |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | 25.39 ± 2.13 |
| Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | 137.5 ± 24.35 |
| Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | 80.0 ± 7.56 |
| Heart Rate (beats/min) | 86 ± 8.68 |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 200.5 ± 74.75 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 97 ± 11.64 |
| Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) (mg/dL) | 145 ± 61.11 |
| High-density lipoprotein (HDL) (mg/dL) | 35 ± 7.64 |
| Left Ventricle Ejection Fraction (%) | 53.5 ± 4.11 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oktaviono, Y.H.; Al-Farabi, M.J.; Suastika, L.O.S.; Hartono, F.; Dirgantara, Y.; Sandra, F. Preliminary Study: Purple Sweet Potato Extract Seems to Be Superior to Increase the Migration of Impaired Endothelial Progenitor Cells Compared to l-Ascorbic Acid. Sci. Pharm. 2019, 87, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm87030016
Oktaviono YH, Al-Farabi MJ, Suastika LOS, Hartono F, Dirgantara Y, Sandra F. Preliminary Study: Purple Sweet Potato Extract Seems to Be Superior to Increase the Migration of Impaired Endothelial Progenitor Cells Compared to l-Ascorbic Acid. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2019; 87(3):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm87030016
Chicago/Turabian StyleOktaviono, Yudi Her, Makhyan Jibril Al-Farabi, Luh Oliva Saraswati Suastika, Febriyanti Hartono, Yanni Dirgantara, and Ferry Sandra. 2019. "Preliminary Study: Purple Sweet Potato Extract Seems to Be Superior to Increase the Migration of Impaired Endothelial Progenitor Cells Compared to l-Ascorbic Acid" Scientia Pharmaceutica 87, no. 3: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm87030016
APA StyleOktaviono, Y. H., Al-Farabi, M. J., Suastika, L. O. S., Hartono, F., Dirgantara, Y., & Sandra, F. (2019). Preliminary Study: Purple Sweet Potato Extract Seems to Be Superior to Increase the Migration of Impaired Endothelial Progenitor Cells Compared to l-Ascorbic Acid. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 87(3), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm87030016






