Cytotoxic Desulfated Saponin from Holothuria atra Predicted to Have High Binding Affinity to the Oncogenic Kinase PAK1: A Combined In Vitro and In Silico Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
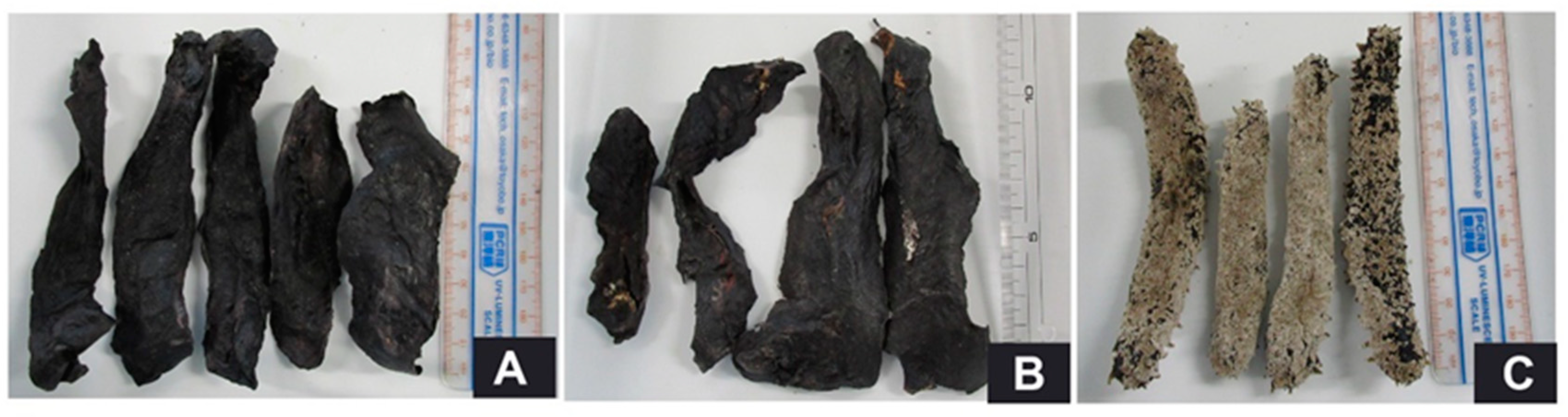
2.2. Collection of Sea Cucumber Species and Their Extraction
2.3. Extraction of Crude Saponin and Its Fractionation
2.4. Phytochemical Characterization of Crude Saponin
2.5. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.6. In Vivo Cytotoxicity Assay
2.7. Molecular Docking Simulation
2.8. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulation
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cytotoxic Effects of Sea Cucumber Components
3.2. Phytochemical Profile of H. atra Saponin
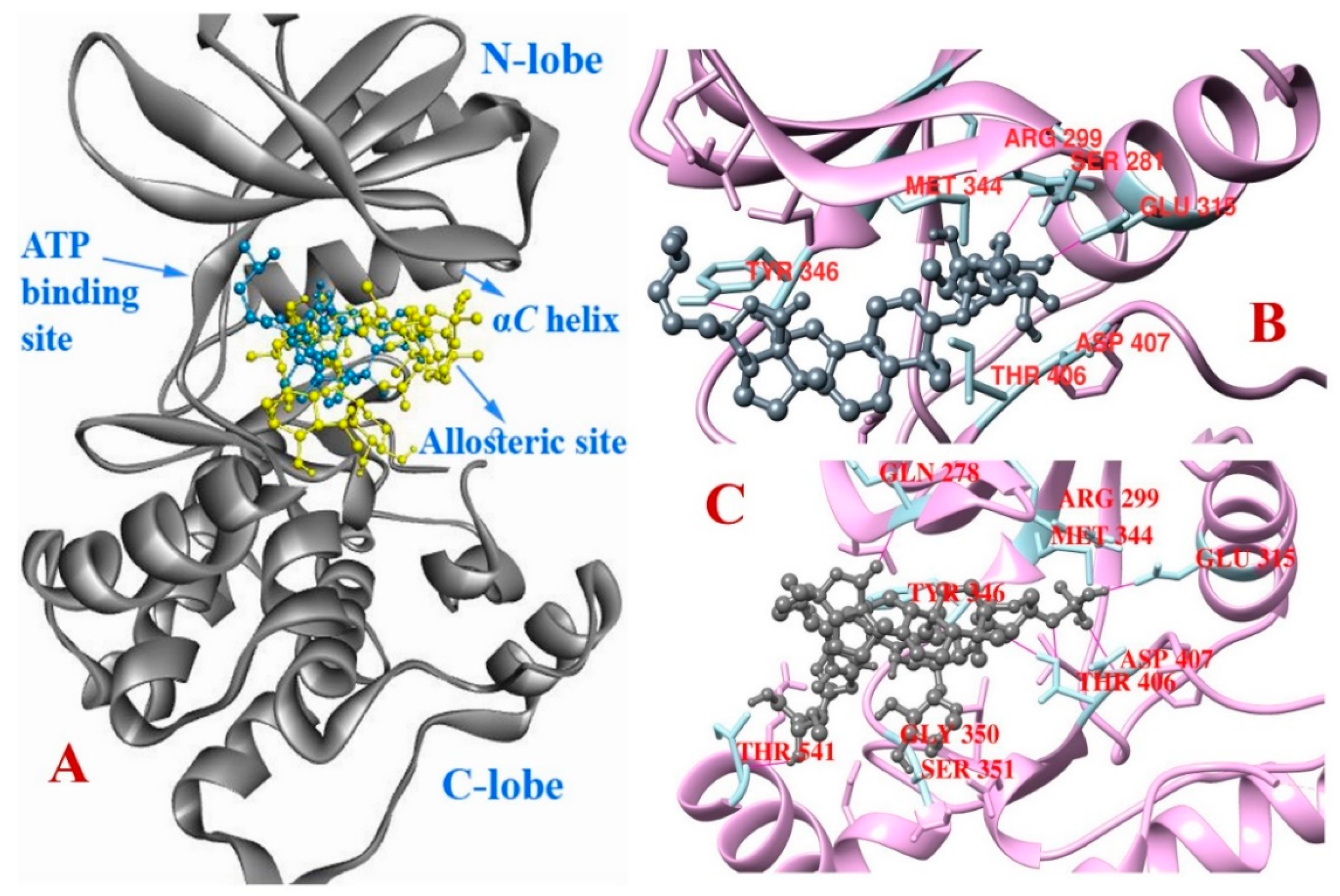
3.3. Molecular Docking Studies
3.4. Molecular Dynamics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blunden, G. Biologically active compounds from marine organisms. Phytother. Res. 2001, 15, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerard, F.; Decourcelle, N.; Sabourin, C.; Floch-laizet, C.; Le Grel, L.; Le Floch, P.; Gourlay, F.; Le Delezir, R.; Jaouen, P.; Bourseau, P. Recent developments of marine ingredients for food and nutraceutical applications: A review. J. Sci. Hal. Aquat. 2011, 2, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Sarfaraj, H.M.; Sheeba, F.; Saba, A.; Mohd, S. Marine natural products: A lead for Anti-cancer. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 2012, 41, 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Kiew, P.L.; Don, M.M. Jewel of the seabed: Sea cucumbers as nutritional and drug candidates. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 63, 616–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, T.; Zaima, N.; Yamamoto, A.; Sakai, S.; Noguchi, R.; Hirata, T. Isolation of sphingoid bases of sea cucumber cerberosides and their cytotoxicity against human colon cancer cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 2906–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridzwan, B.H. Sea Cucumbers, A Malaysian Heritage, 1st ed.; Research Centre of International Islamic University Malaysia (IIUM): Kuala Lumpur Wilayah Persekutuan, Malaysia, 2007; ISBN 9789833855117. [Google Scholar]
- Janakiram, N.B.; Mohammed, A.; Rao, C.V. Sea cucumbers metabolites as potent anti-cancer agents. Mar. Drugs. 2015, 13, 2909–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.R.; Yi, Y.H.; Wu, H.M.; Wu, J.H.; Liaw, C.C.; Lee, K.H. Intercedensides A–C, three new cytotoxic triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Mensamaria intercedens Lampert. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Zhang, X.W.; Tong, Y.G.; Yi, Y.H.; Zhang, S.L.; Li, L.; Sun, P.; Lin, L.; Ding, J. PE, a new sulfated saponin from sea cucumber, exhibits anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor activities in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2005, 4, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, B.C.Q.; Yoshimura, K.; Kumazawa, S.; Tawata, S.; Maruta, H. Frondoside A from sea cucumber and nymphaeols from Okinawa propolis: Natural anti-cancer agents that selectively inhibit PAK1 in vitro. Drug Discov. Ther. 2017, 11, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, B.C.; Kim, S.A.; Won, S.M.; Park, S.K.; Uto, Y.; Maruta, H. 1, 2, 3-Triazolyl ester of ketorolac (15K): Boosting both heat-endurance and lifespan of C. elegans by down-regulating PAK1 at nM levels. Drug Discov. Ther. 2018, 12, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruta, H. Herbal therapeutics that block the oncogenic kinase PAK1: A practical approach towards PAK1-dependent diseases and longevity. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 656–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruta, H.; Ahn, M.R. From bench (laboratory) to bed (hospital/home): How to explore effective natural and synthetic PAK1-blockers/longevity-promoters for cancer therapy. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 142, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzaghi-Asl, N.; Mirzayi, S.; Mahnam, K.; Sepehri, S. Identification of COX-2 inhibitors via structure-based virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulation. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2018, 83, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazi, S.; Purohit, M.; Sonawani, A.; Niazi, J.H. Revealing the molecular interactions of aptamers that specifically bind to the extracellular domain of HER2 cancer biomarker protein: An in silico assessment. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2018, 83, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiaterra, G.; Laudadio, E.; Cometti, M.; Mobbili, G.; Minnelli, C.; Massaccesi, L.; Citterio, B.; Biavasco, F.; Galeazzi, R. Inhibitors of multidrug efflux pumps of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from natural sources: An in silico high-throughput virtual screening and in vitro validation. Med. Chem. Res. 2017, 26, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.Q.; Wang, Y.M.; Wang, J.F.; Xue, Y.; Li, Z.J.; Nagao, K.; Yanagita, T.; Xue, C.H. Dietary saponins of sea cucumber alleviate orotic acid-induced fatty liver in rats via PPARα and SREBP-1c signaling. Lipids Health Dis. 2010, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baharara, J.; Amini, E.; Nikdel, N.; Salek-Abdollahi, F. The cytotoxicity of dacarbazine potentiated by sea cucumber saponin in resistant B16F10 melanoma cells through apoptosis induction. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2016, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moghadam, F.D.; Baharara, J.; Balanezhad, S.Z.; Jalali, M.; Amini, E. Effect of Holothuria leucospilota extracted saponin on maturation of mice oocyte and granulosa cells. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 11, 130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, I.; Kobayashi, M.; Inamoto, T.; Fuchida, M.; Kyogoku, Y. Structures of echinosides A and B, antifungal lanostane-oligosides from the sea cucumber Actinopyga echinites (JAEGER). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1985, 33, 5214–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjaneyulu, A.S.R.; Raju, K.V.S. A new triterpene glycoside from the sea cucumber Holothuria atra off Mandapam Coast. Indian J. Chem. 1996, 35B, 810–814. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, Y.M.; Chung, S.W.; Song, S.; Lee, H.; Suh, H.; Chung, H.Y. 4-(6-Hydroxy-2-naphthyl)-1,3-bezendiol: A potent, new tyrosinase inhibitor. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 1711–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solis, P.N.; Wright, C.W.; Anderson, M.M.; Gupta, M.P.; Phillipson, J.D. A microwell cytotoxicity assay using Artemia salina (brine shrimp). Planta Med. 1993, 59, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. ff14SB: Improving the accuracy of protein side chain and backbone parameters from ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, F.; Fierz, B.; Bieri, O.; Drewello, M.; Kiefhaber, T. Dynamics of unfolded polypeptide chains as model for the earliest steps in protein folding. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 332, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, E.; Darden, T.; Nabuurs, S.B.; Finkelstein, A.; Vriend, G. Making optimal use of empirical energy functions: Force-field parameterization in crystal space. Proteins 2004, 57, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N·log (N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Himaya, S.W. Triterpene glycosides from sea cucumbers and their biological activities. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2012, 65, 297–319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.H.; Park, E.S.; Shin, S.W.; Na, Y.W.; Han, J.Y.; Jeong, J.S.; Shastina, V.V.; Stonik, V.A.; Park, J.I.; Kwak, J.Y. Stichoposide C induces apoptosis through the generation of ceramide in leukemia and colorectal cancer cells and shows in vivo antitumor activity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5934–5948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Tang, H.; Lin, H.; Cheng, G.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X. Saponins: The potential chemotherapeutic agents in pursuing new anti-glioblastoma drugs. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1709–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhinakaran, D.I.; Lipton, A.P. Bioactive compounds from Holothuria atra of Indian ocean. SpringerPlus 2014, 3, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parveen, M.; Ahmad, F.; Malla, A.M.; Azaz, S.; Alam, M.; Basudan, O.A.; Silva, M.R.; Silva, P.S.P. Acetylcholinesterase and cytotoxic activity of chemical constituents of Clutia lanceolata leaves and its molecular docking study. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2016, 6, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dyck, S.; Gerbaux, P.; Flammang, P. Qualitative and quantitative saponin contents in five sea cucumbers from the Indian Ocean. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo, G.V. Comparative Analysis of the Natural Products of Three Sea Cucumber Species: Holothuria grisea, Synaptula reciprocans and Holothuria manningí. Master’s Thesis, University of Aberdeen, Aberdeen, Scotland, September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Van Thanh, N.; Dang, N.H.; van Kiem, P.; Cuong, N.X.; Huong, H.T.; van Minh, C. A new triterpene glycoside from the sea cucumber Holothuria scabra collected in Vietnam. ASEAN J. Sci. Technol. Dev. 2017, 23, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpov, A.S.; Amiri, P.; Bellamacina, C.; Bellance, M.H.; Breitenstein, W.; Daniel, D.; Denay, R.; Fabbro, D.; Fernandez, C.; Galuba, I.; et al. Optimization of a dibenzodiazepine hit to a potent and selective allosteric PAK1 inhibitor. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wu, J.W.; Wang, Z.X. Structural insights into the autoactivation mechanism of p21-activated protein kinase. Structure 2011, 19, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licciulli, S.; Maksimoska, J.; Zhou, C.; Troutman, S.; Kota, S.; Liu, Q.; Duron, S.; Campbell, D.; Chernoff, J.; Field, J.; et al. FRAX597, a small molecule inhibitor of the p21-activated kinases, inhibits tumorigenesis of neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2)-associated Schwannomas. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 29105–29114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balupuri, A.; Balasubramanian, P.K.; Cho, S.J. Molecular Docking Studies of p21-Activated Kinase-1 (PAK1) Inhibitors. J. Chosun Nat. Sci. 2016, 9, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

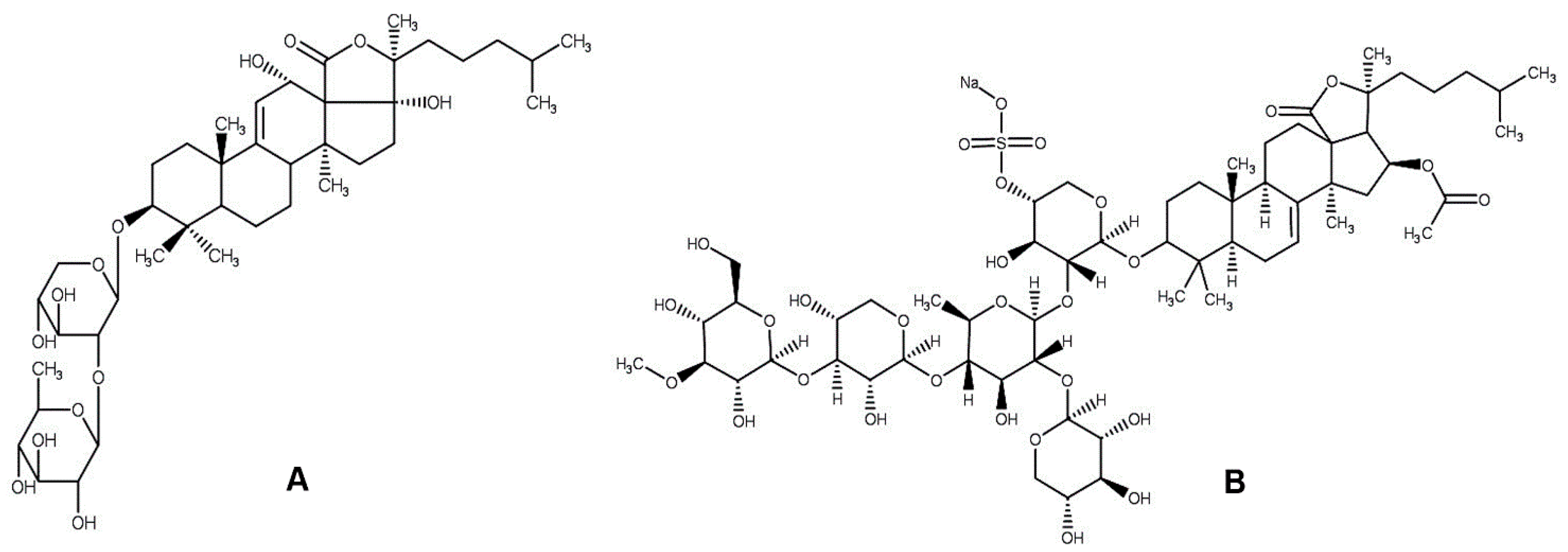
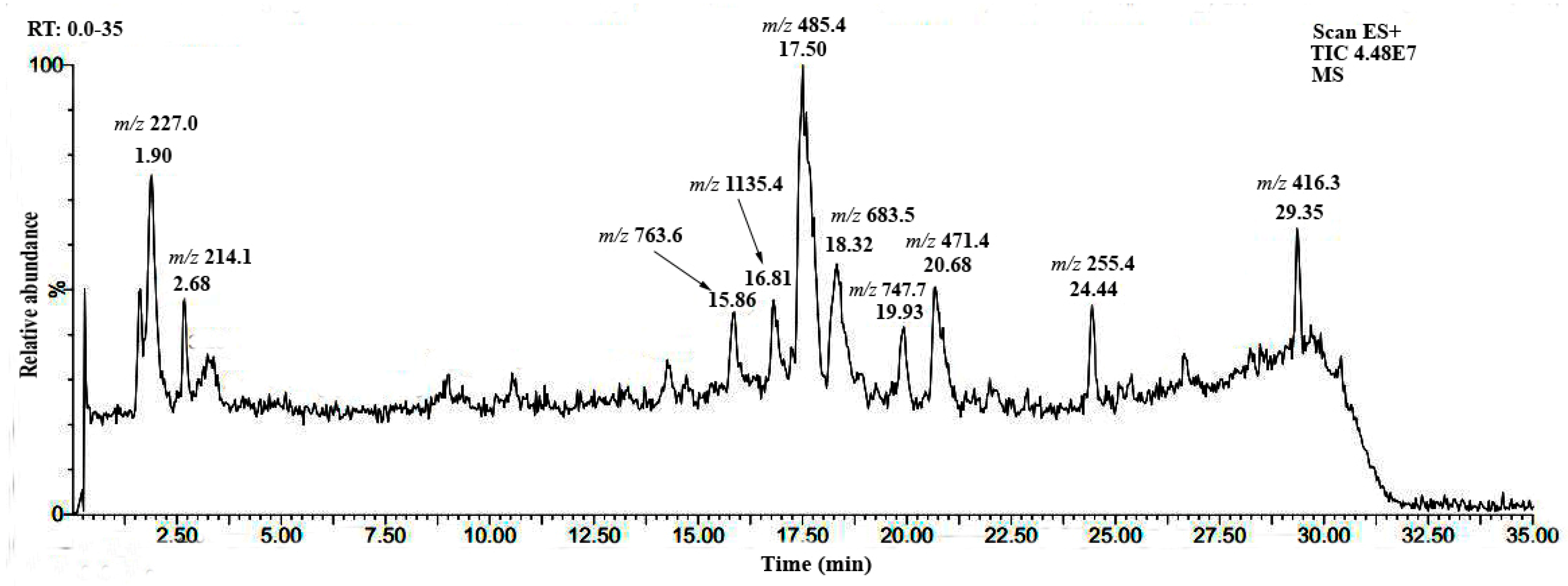


| Sea Cucumber Species | Extracts/Crude Saponin | Cytotoxic Effects (IC50 Value, µg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A549 | B16F10 | ||
| H. atra | 70% EtOH Extract | 10.5 | 7.9 |
| Hot Water Extract | 20.9 | 85.0 | |
| Crude Saponin | 1.8 | 0.5 | |
| H. leucospilota | 70% EtOH Extract | 15.9 | 9.5 |
| Hot Water Extract | 28.5 | 125.3 | |
| Crude Saponin | 3.7 | 1.4 | |
| P. nigripunctatus | 70% EtOH Extract | 36.9 | 8.0 |
| Hot Water Extract | 26.5 | - | |
| Crude Saponin | 11.5 | 3.3 | |
| Fractions | Cytotoxic Effects (IC50 Value, µg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|
| A549 | B16F10 | |
| Fr 1 | 1.35 | 0.60 |
| Fr 2 | 0.72 | 0.24 |
| Fr 3 | 3.40 | 0.90 |
| Fr 4 | 1.34 | 0.50 |
| Fr 5 | 2.38 | 2.42 |
| Compound | Cytotoxic Effects (IC50 Value, µM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A549 | B16F10 | HuH-7 | HepG2 | Brine Shrimp | |
| Desulfated echinoside B | 1.5 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 2.1 | 9.2 |
| Frondoside A | 1.6 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 11.5 |
| Compound | Binding Affinity (kcal/mol) | Hydrogen Bond Interaction | Hydrophobic Interaction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino Acid Residue | Distance (Å) | Amino Acid Residue (Bond) | Distance (Å) | ||
| DEB | −8.2 | Glu315 | 2.17 | Tyr346 (Alkyl-Pi) | 5.34 |
| Tyr346 | 2.50 | Leu396 (Alkyl) | 5.37 | ||
| Arg299 | 2.52 | Leu396 (Alkyl) | 4.01 | ||
| Arg299 | 2.17 | Ile276 (Alkyl) | 5.31 | ||
| Thr406 | 2.76 | Tyr346 (Alkyl) | 5.10 | ||
| FRA | −7.7 | Lys538 | 2.93 | Tyr346 (Alkyl-Pi) | 5.04 |
| Thr541 | 2.08 | Ile276 (Alkyl) | 5.39 | ||
| Leu347 | 2.79 | Ala297 (Alkyl) | 4.23 | ||
| Glu315 | 1.97 | ||||
| Gln278 | 2.07 | ||||
| Thr406 | 2.28 | ||||
| Asp407 | 2.00 | ||||
| Asp354 | 2.21 | ||||
| Lys538 | 2.76 | ||||
| Asp354 | 2.66 | ||||
| Asp354 | 2.75 | ||||
| Arg299 | 2.57 | ||||
| Gly350 | 2.88 | ||||
| Compound | Binding Affinity (kcal/mol) | Hydrogen Bond Interaction | Hydrophobic Interaction | Electrostatic Interaction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino Acid Residue | Distance (Å) | Amino Acid Residue (Bond) | Distance (Å) | Amino Acid Residue | Distance (Å) | ||
| DEB | −9.3 | Asp407 | 1.63 | Tyr346 (Pi-alkyl) | 5.32 | ||
| Glu315 | 1.78 | Leu396 (Alkyl) | 5.24 | ||||
| Asp407 | 2.72 | Met344 (Alkyl) | 4.65 | ||||
| Asp407 | 2.40 | Ile276 (Alkyl) | 4.33 | ||||
| Gly277 | 2.81 | ||||||
| Asp407 | 2.35 | ||||||
| FRA | −7.6 | Asp354 | 1.82 | Tyr346 (Pi-alkyl) | 4.80 | Arg299 | 5.48 |
| Thr406 | 1.89 | Ile276 (Alkyl) | 4.93 | ||||
| Tyr346 | 2.65 | Val284 (Alkyl) | 4.27 | ||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shahinozzaman, M.; Ishii, T.; Takano, R.; Halim, M.A.; Hossain, M.A.; Tawata, S. Cytotoxic Desulfated Saponin from Holothuria atra Predicted to Have High Binding Affinity to the Oncogenic Kinase PAK1: A Combined In Vitro and In Silico Study. Sci. Pharm. 2018, 86, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm86030032
Shahinozzaman M, Ishii T, Takano R, Halim MA, Hossain MA, Tawata S. Cytotoxic Desulfated Saponin from Holothuria atra Predicted to Have High Binding Affinity to the Oncogenic Kinase PAK1: A Combined In Vitro and In Silico Study. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2018; 86(3):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm86030032
Chicago/Turabian StyleShahinozzaman, Md, Takahiro Ishii, Ryo Takano, Mohammad A. Halim, Md Amzad Hossain, and Shinkichi Tawata. 2018. "Cytotoxic Desulfated Saponin from Holothuria atra Predicted to Have High Binding Affinity to the Oncogenic Kinase PAK1: A Combined In Vitro and In Silico Study" Scientia Pharmaceutica 86, no. 3: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm86030032
APA StyleShahinozzaman, M., Ishii, T., Takano, R., Halim, M. A., Hossain, M. A., & Tawata, S. (2018). Cytotoxic Desulfated Saponin from Holothuria atra Predicted to Have High Binding Affinity to the Oncogenic Kinase PAK1: A Combined In Vitro and In Silico Study. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 86(3), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm86030032





