Serum Cystatin C as a Biomarker in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients: Clinical Data and Treatment
2.2. Determination of Serum Cystatin C Levels
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
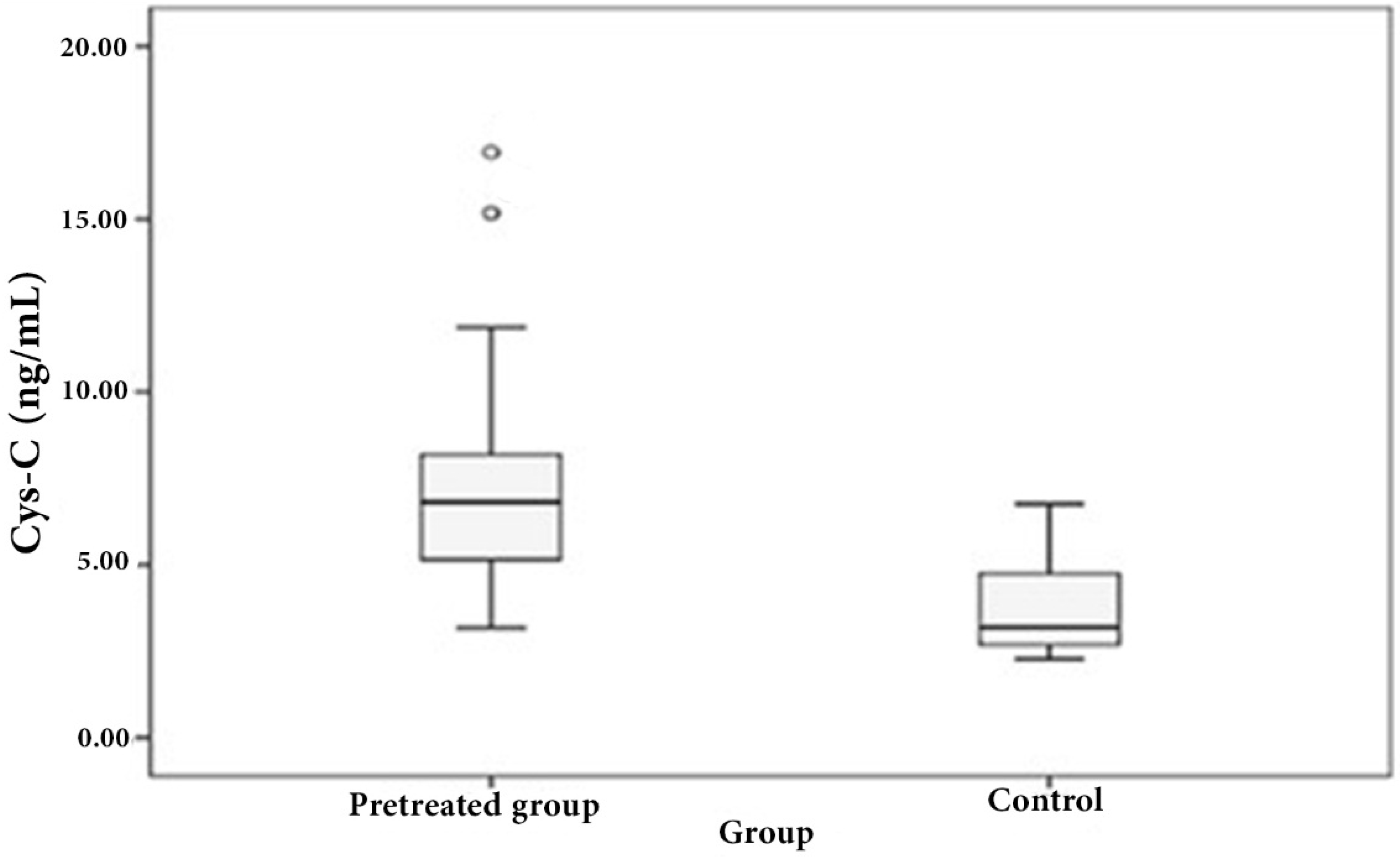
3.1. Distribution of Serum Cystatin C in Patient and Control Sera
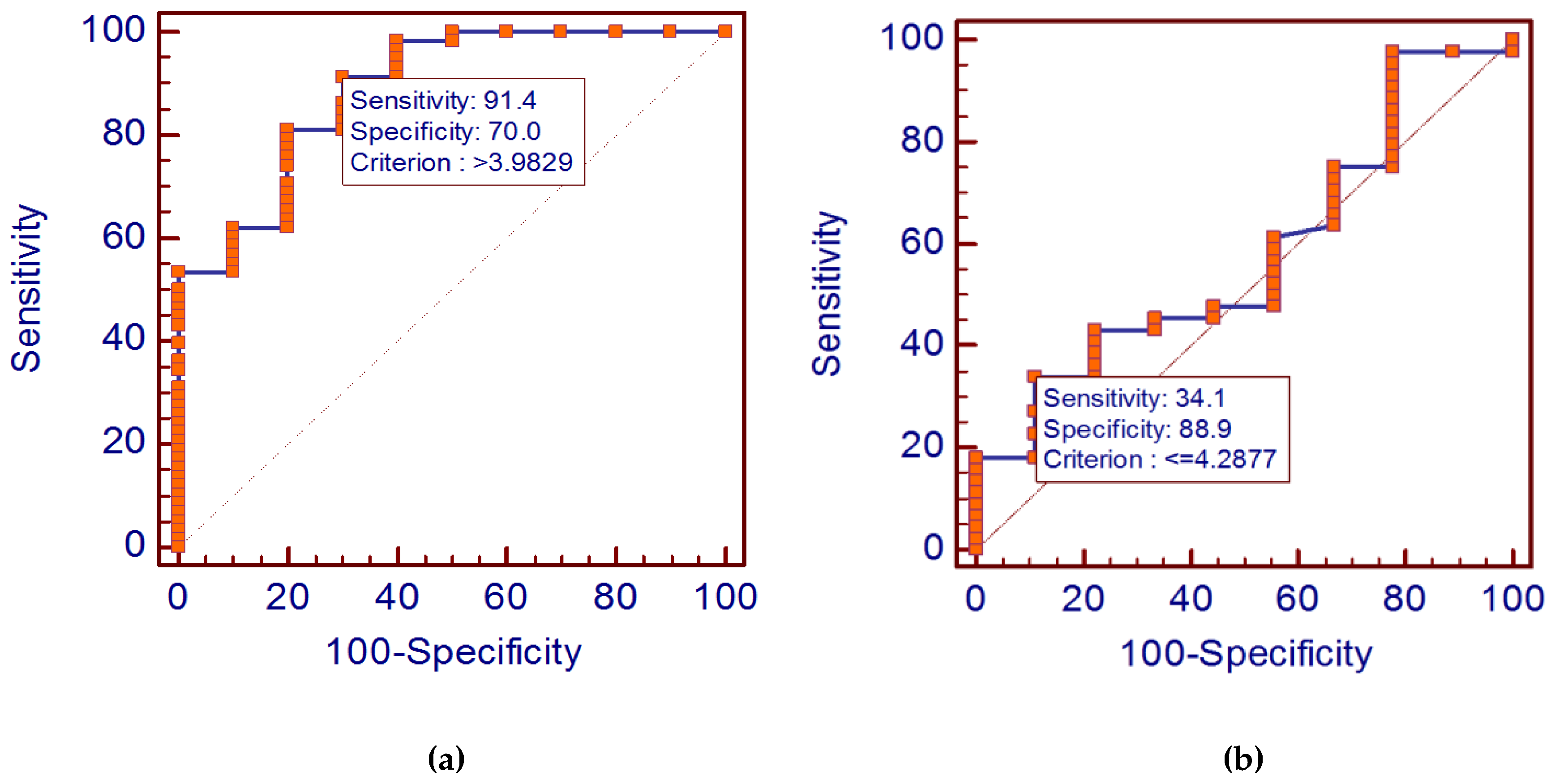
3.2. Diagnostic Value of Cystatin C Levels in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
3.2.1. Relations between Serum Cystatin C Levels and Other Biological and Clinical Parameters
- Those aged over 60 years showed significantly more elevated levels of cystatin C than the others (p = 0.049; Spearman rank correlation coefficients, r = 0.260).
- Those who had advanced disease with extra-nodal involvement also had higher levels of cystatin C compared to those without extra-nodal disease (r = 0.573, p = 0.005).
- Moreover, high cystatin C levels were correlated significantly with high serum LDH level, with a rank correlation coefficient r = 0.325 (p < 0.013).
- We did not observe any difference in cystatin C levels among patients according to performance status (r = 0.056, p = 0.763), or disease stage (r = 0.107, p = 0.491). Lastly, we found that cystatin C levels could not correlate with IPI score (r = 0.0874, p = 0.604).
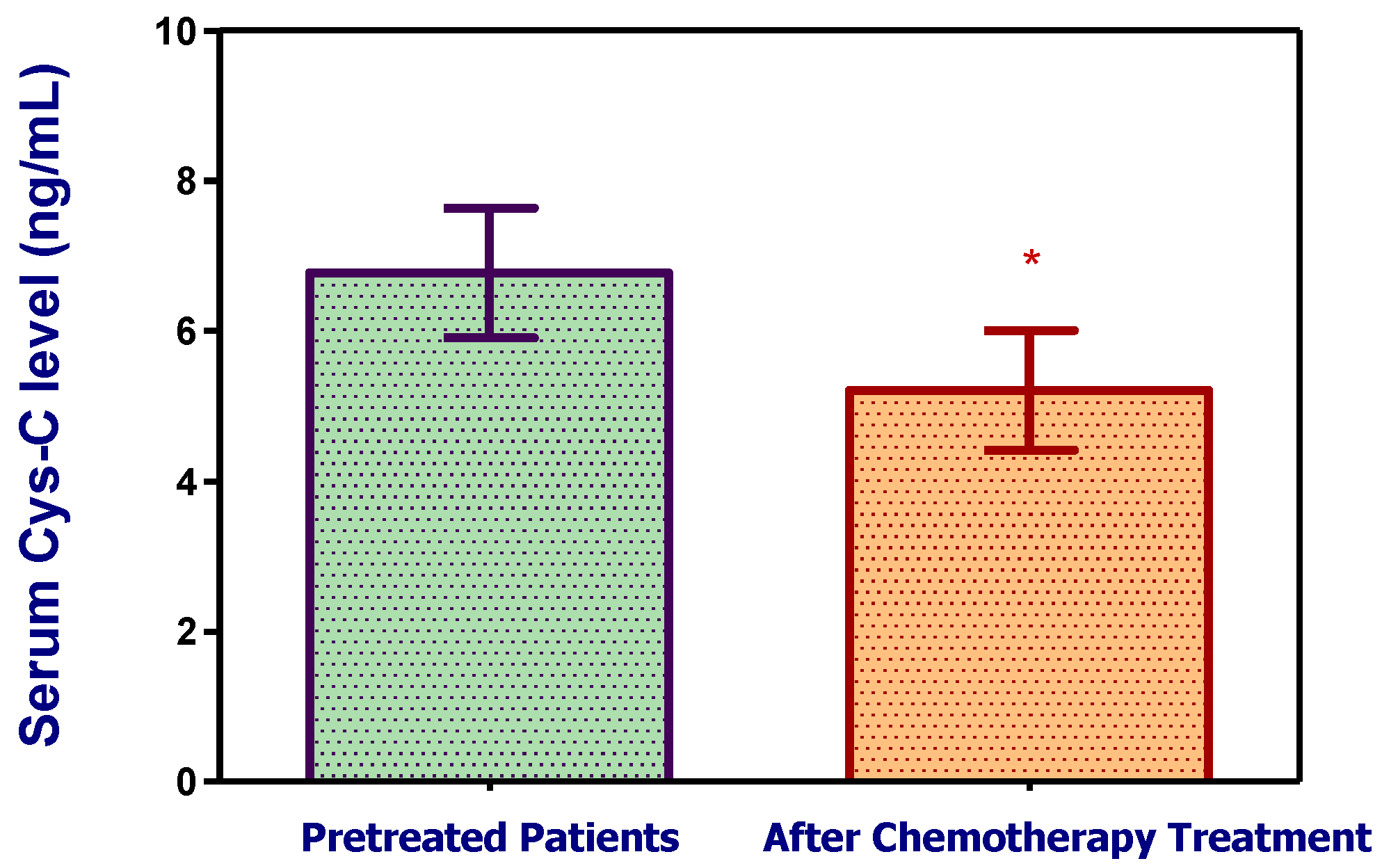
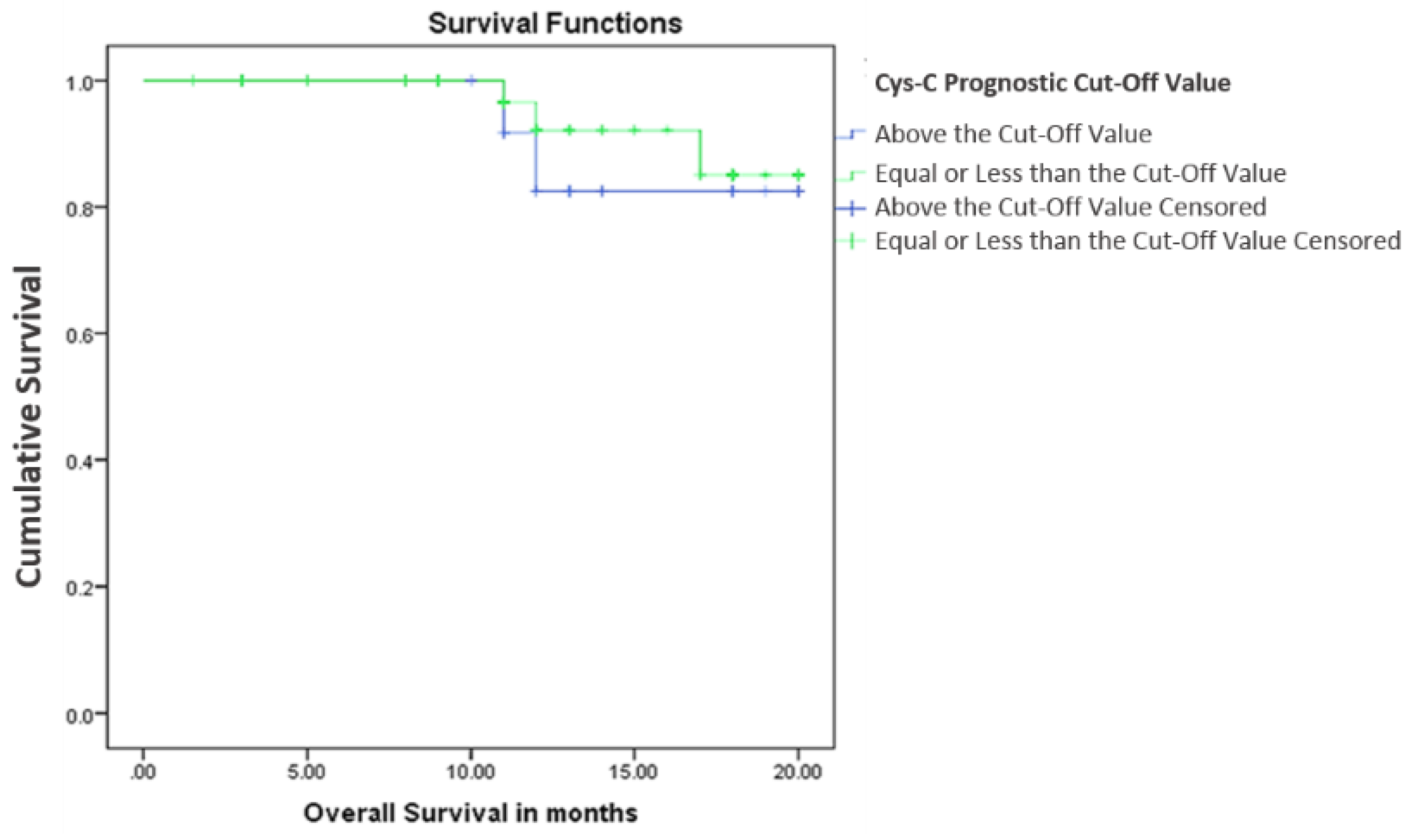
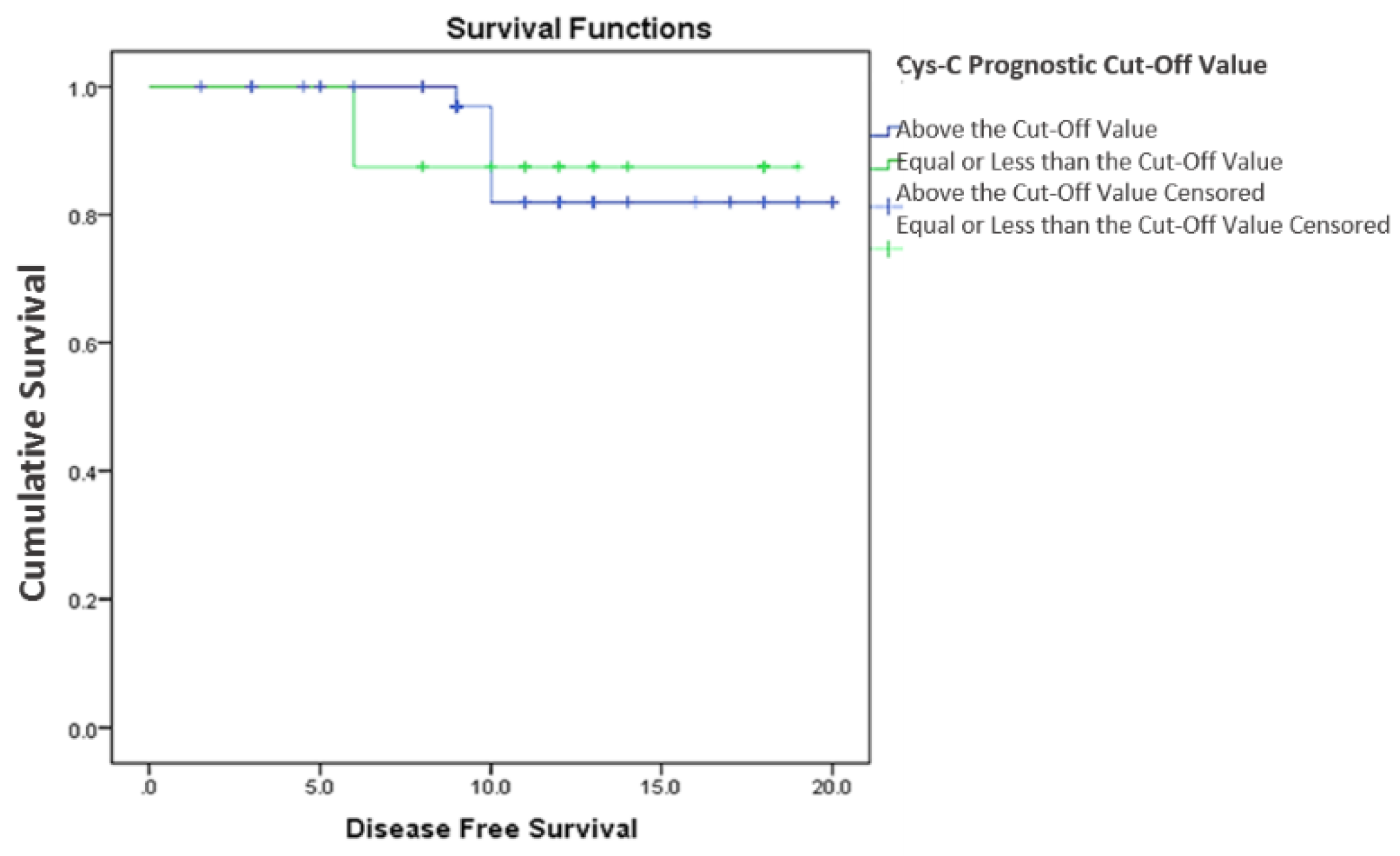
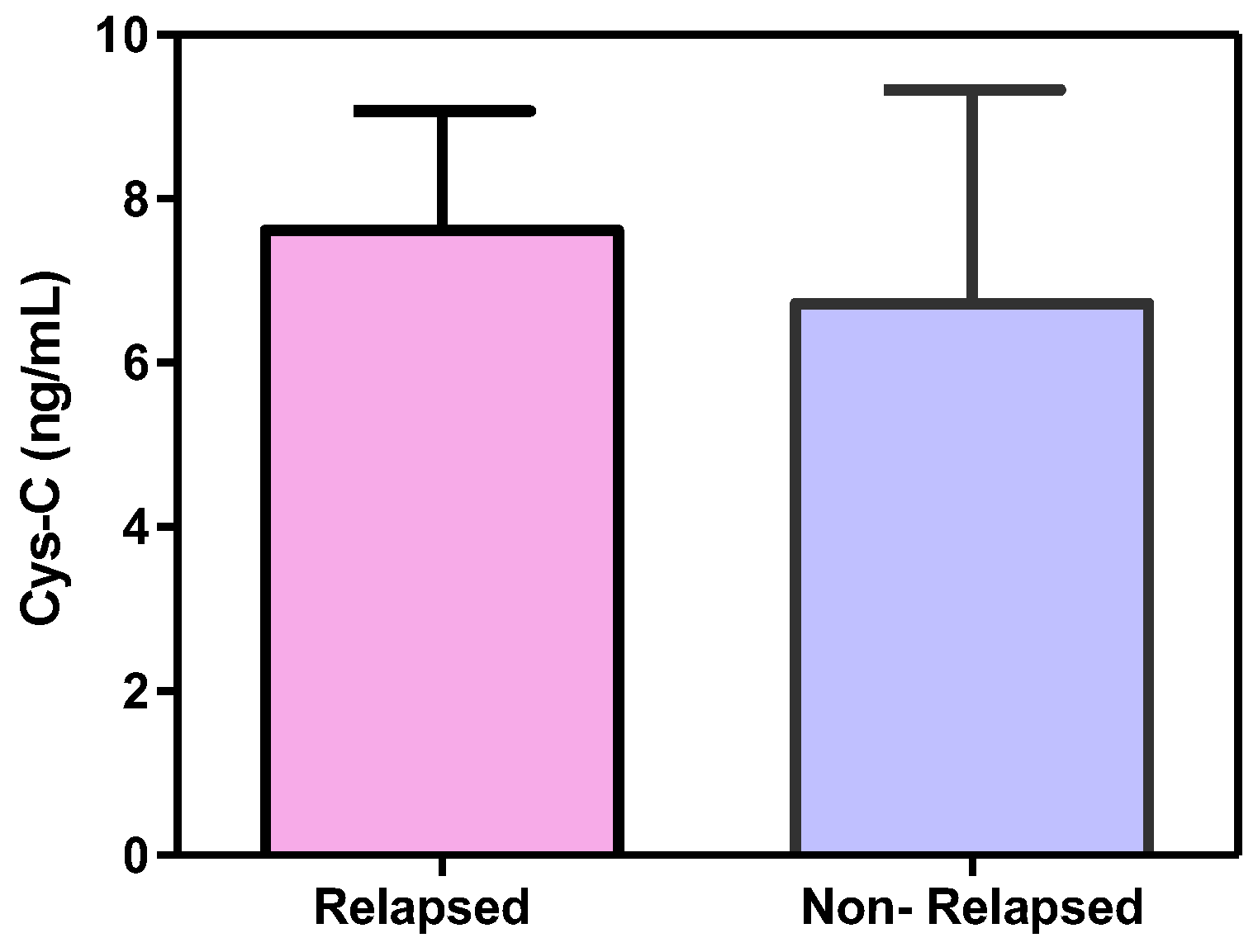
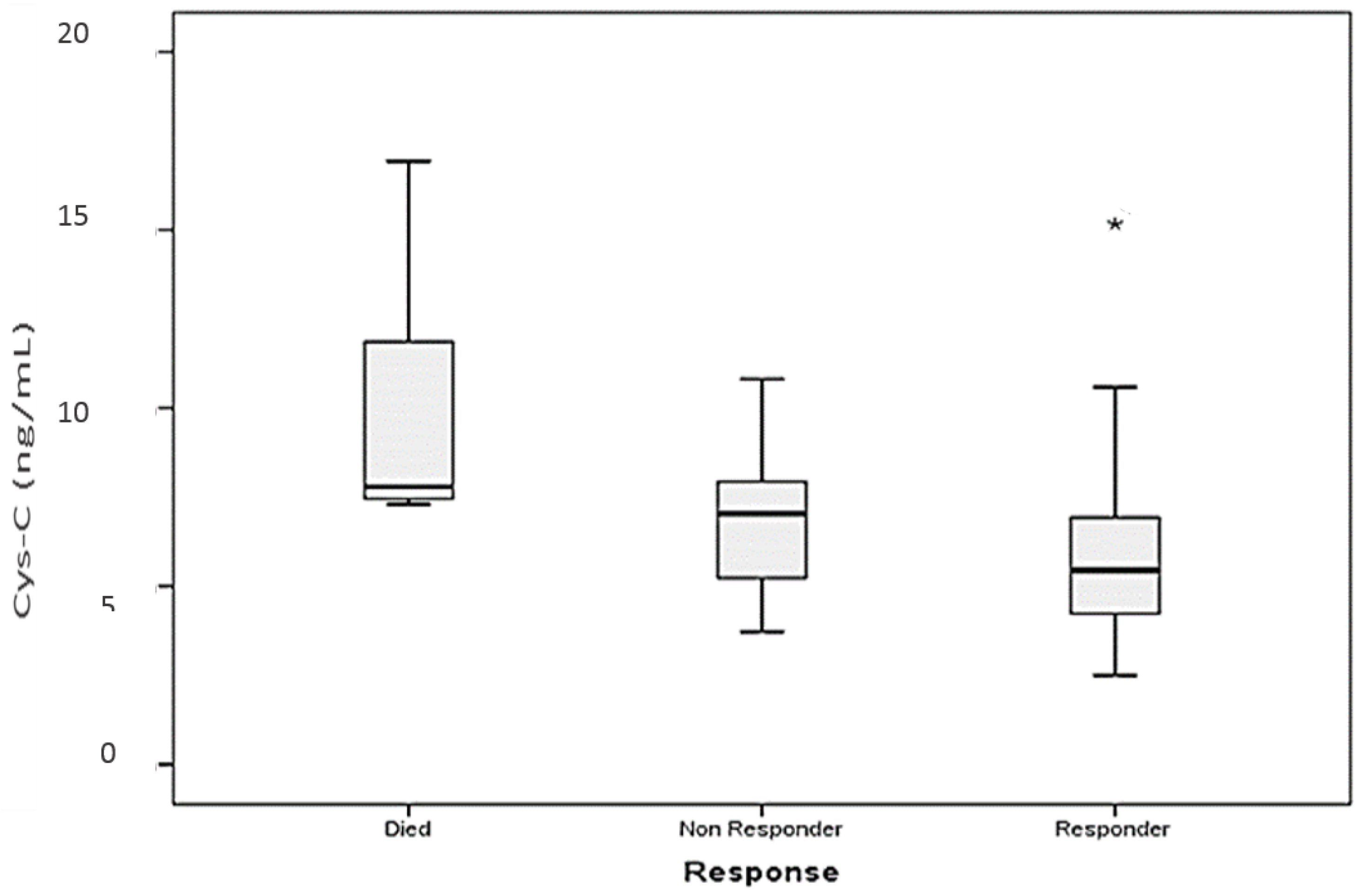
3.2.2. Cystatin C, Response to Treatment and Outcome
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, K.C.; Huang, G.C.; Jones, D.; Tsao, C.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Su, I.J. Distribution and prognosis of WHO lymphoma subtypes in Taiwan reveals a low incidence of germinal-center derived tumors. Leuk. Lymphoma 2004, 45, 1375–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J.; Vardiman, J.W. WHO Classification of Tumours. of Haematopoietic. and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Coiffier, B. Immunochemotherapy: the new standard in aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in the elderly. Semin. Oncol. 2003, 30, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, R.J.; Seibert, K.; Passe, S.; Little, C.; Gee, T.; Lee, B.J., 3rd; Miké, V.; Young, C.W. Prognostic significance of serum lactate dehydrogenase in malignant lymphoma. Cancer 1980, 46, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAdam, B.; Smith, T.; Love, W.C.; Murphy, M.; Daly, P.A. Lactate dehydrogenase levels during MACOP-B chemotherapy for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Med. Oncol. Tumor Pharmacother. 1993, 10, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Terol, M.J.; Tormo, M.; Martinez-Climent, J.A.; Marugan, I.; Benet, I.; Ferrandez, A.; Teruel, A.; Ferrer, R.; García-Conde, J. Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (s-ICAM-1/s-CD54) in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: association with clinical characteristics and outcome. Ann. Oncol. 2003, 14, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niitsu, N.; Sasaki, K.; Umeda, M. A high serum soluble Fas/APO-1 level is associated with a poor outcome of aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Leukemia 1999, 13, 1434–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, N.; Tsurumi, H.; Takemura, M.; Hara, T.; Sawada, M.; Kasahara, S.; Kanemura, N.; Yamada, T.; Shimizu, M.; Takahashi, T.; et al. Serum-soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 (sTNF-R2) level determines clinical outcome in patients with aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Eur. J. Haematol. 2006, 77, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, H.; Tsurumi, H.; Takemura, M.; Ino-Shimomura, Y.; Kasahara, S.; Sawada, M.; Yamada, T.; Hara, T.; Fukuno, K.; Goto, N.; et al. Serum-soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R) level determines clinical outcome in patients with aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: in combination with the International Prognostic Index. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 131, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niitsu, N.; Okabe-Kado, J.; Okamoto, M.; Takagi, T.; Yoshida, T.; Aoki, S.; Hirano, M.; Honma, Y. Serum nm23-H1 protein as a prognostic factor in aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2001, 97, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niitsu, N.; Iijima, K. High serum soluble CD44 is correlated with a poor outcome of aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Leuk. Res. 2002, 26, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimerman, N.; Brguljan, P.M.; Krasovec, M.; Suskovic, S.; Kos, J. Serum cystatin C, a potent inhibitor of cysteine proteinases, is elevated in asthmatic patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2000, 300, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, R.; Takano, T.; Sato, S.; Yajima, A. Serum Soluble Fas Level as a Prognostic Factor in Patients with Gynecological Malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 3576–3580. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rentzos, M.; Michalopoulou, M.; Nikolaou, C.; Cambouri, C.; Rombos, A.; Dimitrakopoulos, A.; Vassilopoulos, D. The role of soluble intercellular adhesion molecules in neurodegenerative disorders. J. Neurol. Sci 2005, 228, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahamson, M.; Barrett, A.J.; Salvesen, G.; Grubb, A. Isolation of six cysteine proteinase inhibitors from human urine. Their physicochemical and enzyme kinetic properties and concentrations in biological fluids. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 11282–11289. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henskens, Y.; Veerman, M.E.; Amerongen, A.V. Cystatins in health and disease. Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler 1996, 377, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pierre, P.; Mellman, I. Developmental Regulation of Invariant Chain Proteolysis Controls MHC Class II Trafficking in Mouse Dendritic Cells. Cell 1998, 93, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kos, J.; Krašovec, K.; Cimerman, N.; Nielsen, H.J.; Christensen, I.J.; Brünner, N. Cysteine Proteinase Inhibitors Stefin A, Stefin B, and Cystatin C in Sera from Patients with Colorectal Cancer: Relation to Prognosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zore, I.; Krašovec, M.; Cimerman, N.; Kuhelj, R.; Werle, B.; Nielsen, H.J.; Brünner, N.; Kos, J. Cathepsin B/Cystatin C Complex Levels in Sera from Patients with Lung and Colorectal Cancer. Biol. Chem. 2001, 382, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kos, J.; Štabuc, B.; Schweiger, A.; Krašovec, M.; Cimerman, N.; Kopitar-Jerala, N.; Vrhovec, I. Cathepsins B, H, L, and their inhibitors stefin A and cystatin C in sera of melanoma patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 1997, 3, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- The international non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma prognostic factors project. A Predictive Model for Aggressive Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulaomerović, A.; Halilbašić, A.; Čičkušić, E.; Zavašnik-Bergant, T.; Begić, L.; and Kos, J. Cystatin C as a potential marker for relapse in patients with non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Lett. 2007, 248, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, P.P.; Kaplan, H.S.; Musshoff, K.; Smithers, D.W.; Tubiana, M. Report of the Committee on Hodgkin’s Disease Staging Classification. Cancer Res. 1971, 31, 1860–1861. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheson, B.D.; Horning, S.J.; Coiffier, B.; Shipp, M.; Fisher, R.I.; Connors, J.M.; Lister, T.A.; Vose, J.; Grillo-López, A.; Hagenbeek, A.; et al. Report of an International Workshop to standardize response criteria for non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Softić, A.; Begić, L.; Halilbašić, A.; Vižin, T.; Kos, J. The Predictive Value of Cystatin C in Monitoring of B Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas: Relation to Biochemical and Clinical Parameters. ISRN Oncol. 2013, 2013, 752792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galteau, M.M.; Guyon, M.; Gueguen, R.; Siest, G. Determination of Serum Cystatin C: Biological Variation and Reference Values. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2001, 39, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloane, B.F. Suicidal tumor proteases. Nat. Biotechnol. 1996, 14, 826–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, G.; Miyazaki, K.; Kurishima, K.; Kagohashi, K.; Ishikawa, H.; Satoh, H.; Hizawa, N. Serum levels of cystatin C in elderly lung cancer patients. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 3, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodnar, L.; Wcislo, G.B.; Smoter, M.; Gasowska-Bodnar, A.; Stec, R.; Synowiec, A.; Szczylik, C. Cystatin C as a Parameter of Glomerular Filtration Rate in Patients with Ovarian Cancer. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2010, 33, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | No. of Patients (%) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | |
| <60 | 38(65.5) |
| ≥60 | 20 (34.5) |
| Male sex | 25 (43.1) |
| Performance status a | |
| <2 | 39 (67.2) |
| ≥2 | 19 (32.8) |
| Ann Arbor stage | |
| I/II | 8 (13.8) |
| III/IV | 50 (86.2) |
| B symptoms | 28 (48.3) |
| Extra-nodal involvement | 20 (34.5) |
| High serum lactate dehydrogenase (>ULN) | 48 (82.8) |
| International prognostic index group | |
| Low (0–1) | 2 (3.4) |
| Low–intermediate (2) | 8 (13.8) |
| High–intermediate (3) | 22 (37.9) |
| High (4–5) | 26 (44.8) |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hammouda, N.E.; Salah El-Din, M.A.; El-Shishtawy, M.M.; El-Gayar, A.M. Serum Cystatin C as a Biomarker in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Sci. Pharm. 2017, 85, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm85010009
Hammouda NE, Salah El-Din MA, El-Shishtawy MM, El-Gayar AM. Serum Cystatin C as a Biomarker in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2017; 85(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm85010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleHammouda, Nada E., Manal A. Salah El-Din, Mamdouh M. El-Shishtawy, and Amal M. El-Gayar. 2017. "Serum Cystatin C as a Biomarker in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma" Scientia Pharmaceutica 85, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm85010009
APA StyleHammouda, N. E., Salah El-Din, M. A., El-Shishtawy, M. M., & El-Gayar, A. M. (2017). Serum Cystatin C as a Biomarker in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 85(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm85010009






