The Association between the Hypochloremia and Mortality in Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Patients with Chronic Heart Failure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Source
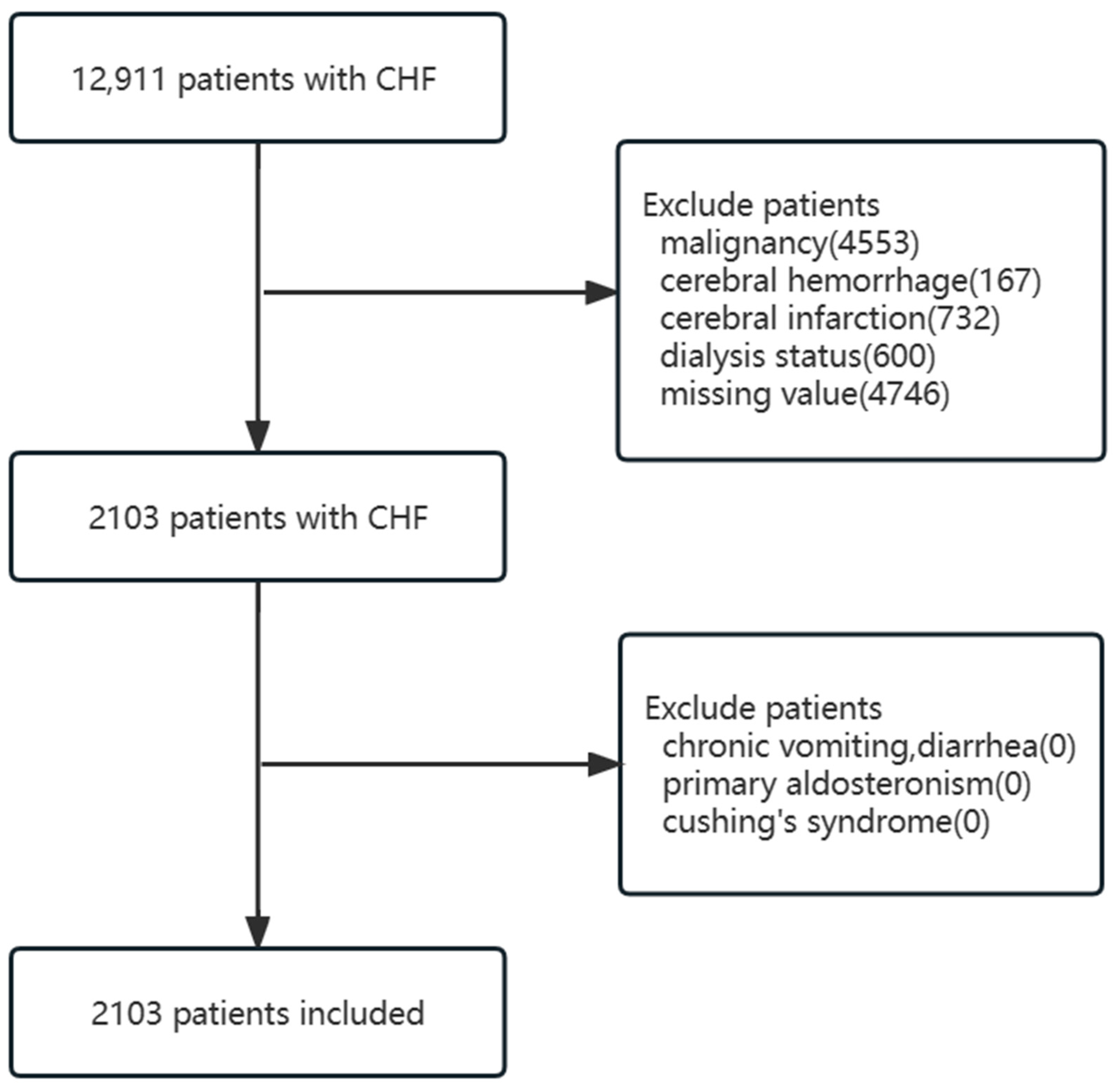
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Primary and Secondary Outcomes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Relationship between Baseline Level of Serum Chloride and Outcomes
3.3. Subgroup Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berend, K.; van Hulsteijn, L.H.; Gans, R.O.B. Chloride: The queen of electrolytes? Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 23, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, T.; Ferrari, M.; Zazzeron, L.; Gattinoni, L.; Caironi, P. Effects of intravenous solutions on acid-base equilibrium: From crystalloids to colloids and blood components. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2014, 46, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunos, N.; Bellomo, R.; Story, D.; Kellum, J. Bench-to-bedside review: Chloride in critical illness. Crit. Care 2010, 14, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, M.; Li, G.; Sarvottam, K.; Wang, S.; Thongprayoon, C.; Dong, Y.; Gajic, O.; Kashani, K. Dyschloremia Is a Risk Factor for the Development of Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, S.; Matsumoto, S.; Muto, N.; Yamanoi, T.; Higashi, T.; Nakamura, K.; Miyazaki, M.; Egi, M. Association of serum chloride concentration with outcomes in postoperative critically ill patients: A retrospective observational study. J. Intensive Care 2014, 2, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tani, M.; Morimatsu, H.; Takatsu, F.; Morita, K. The Incidence and Prognostic Value of Hypochloremia in Critically Ill Patients. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 474185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Regenmortel, N.; Verbrugghe, W.; Van den Wyngaert, T.; Jorens, P.G. Impact of chloride and strong ion difference on ICU and hospital mortality in a mixed intensive care population. Ann. Intensive Care 2016, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuthbert, J.J.; Pellicori, P.; Rigby, A.; Pan, D.; Kazmi, S.; Shah, P.; Clark, A.L. Low serum chloride in patients with chronic heart failure: Clinical associations and prognostic significance. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 10, 1426–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.P.; Girerd, N.; Duarte, K.; Coiro, S.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Dargie, H.J.; Pitt, B.; Dickstein, K.; Testani, J.M.; Zannad, F.; et al. Serum Chloride and Sodium Interplay in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction and Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction: An Analysis From the High-Risk Myocardial Infarction Database Initiative. Circ. Heart Fail. 2017, 10, e003500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grodin, J.L.; Verbrugge, F.H.; Ellis, S.G.; Mullens, W.; Testani, J.M.; Tang, W.H.W. Importance of Abnormal Chloride Homeostasis in Stable Chronic Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2016, 9, e002453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grodin, J.L.; Testani, J.M.; Pandey, A.; Sambandam, K.; Drazner, M.H.; Fang, J.C.; Tang, W.H.W. Perturbations in serum chloride homeostasis in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Insights from TOPCAT: Serum chloride in HFpEF. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 1436–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Testani, J.M.; Hanberg, J.S.; Arroyo, J.P.; Brisco, M.A.; ter Maaten, J.M.; Wilson, F.P.; Bellumkonda, L.; Jacoby, D.; Tang, W.H.W.; Parikh, C.R. Hypochloraemia is strongly and independently associated with mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2016, 18, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moriguchi, T.; Urushiyama, S.; Hisamoto, N.; Iemura, S.; Uchida, S.; Natsume, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Shibuya, H. WNK1 Regulates Phosphorylation of Cation-Chloride-coupled Cotransporters via the STE20-related Kinases, SPAK and OSR1. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 42685–42693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piala, A.T.; Moon, T.M.; Akella, R.; He, H.; Cobb, M.H.; Goldsmith, E.J. Chloride Sensing by WNK1 Involves Inhibition of Autophosphorylation. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, ra41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramanya, A.R.; Yang, C.-L.; McCormick, J.A.; Ellison, D.H. WNK kinases regulate sodium chloride and potassium transport by the aldosterone-sensitive distal nephron. Kidney Int. 2006, 70, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cappola, T.P.; Matkovich, S.J.; Wang, W.; van Booven, D.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Qu, L.; Sweitzer, N.K.; Fang, J.C.; Reilly, M.P.; et al. Loss-of-function DNA sequence variant in the CLCNKA chloride channel implicates the cardio-renal axis in interindividual heart failure risk variation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2011, 108, 2456–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, A.L.; Cherif, M.; McDonagh, T.A.; Squire, I.B. In-hospital worsening heart failure: A clinically relevant endpoint? ESC Heart Fail. 2017, 5, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Peng, R.; Li, X.; Yu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Z. Serum chloride as a novel marker for adding prognostic information of mortality in chronic heart failure. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 483, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro da Silva, F.; Nizet, V. Cell death during sepsis: Integration of disintegration in the inflammatory response to overwhelming infection. Apoptosis 2009, 14, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozierański, K.; Balsam, P.; Tymińska, A.; Peller, M.; Kapłon-Cieślicka, A.; Marchel, M.; Drożdż, J.; Filipiak, K.J.; Opolski, G. Heart failure in elderly patients: Differences in clinical characteristics and predictors of 1-year outcome in the Polish ESC-HF Long-Term Registry. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2016, 126, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wrobel, K.; Stevens, S.R.; Jones, R.H.; Selzman, C.H.; Lamy, A.; Beaver, T.M.; Djokovic, L.T.; Wang, N.; Velazquez, E.J.; Sopko, G.; et al. Influence of Baseline Characteristics, Operative Conduct, and Postoperative Course on 30-Day Outcomes of Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Among Patients with Left Ventricular Dysfunction: Results From the Surgical Treatment for Ischemic Heart Failure (STICH) Trial. Circulation 2015, 132, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bader, F.; Atallah, B.; Brennan, L.F.; Rimawi, R.H.; Khalil, M.E. Heart failure in the elderly: Ten peculiar management considerations. Heart Fail. Rev. 2017, 22, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variable | Total n (n = 2103) | Survivors (n = 1956) | Non-Survivors (n = 147) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 72.6 ± 14.1 | 72.0 ± 14.1 | 79.7 ± 12.1 | <0.001 |
| Male (n (%)) | 1126 (53.5) | 1049 (53.6) | 77 (52.4) | 0.770 |
| Heart rate (bpm) | 83.3 ± 16.4 | 83.1 ± 16.3 | 86.1 ± 17.0 | 0.0347 |
| MAP (mmHg) | 75.7 ± 10.5 | 76.0 ± 10.3 | 71.5 ± 11.4 | <0.001 |
| RR (bpm) | 19.8 ± 3.8 | 19.7 ± 3.7 | 21.3 ± 4.4 | <0.001 |
| SPO2 (%) | 96.5 ± 2.2 | 96.6 ± 2.0 | 95.7 ± 3.4 | <0.001 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 150.6 ± 55.4 | 150.1 ± 54.1 | 157.7 ± 70.1 | 0.1092 |
| Wbc (109/L) | 11.9 ± 9.7 | 11.7 ± 9.7 | 14.0 ± 8.9 | 0.0065 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 11.1 ± 2.3 | 11.1 ± 2.3 | 10.5 ± 2.1 | 0.0012 |
| Platelet (109/L) | 219.1 ± 99.5 | 220.6 ± 98.8 | 199.4 ± 107.0 | 0.0128 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 137.7 ± 5.3 | 137.7 ± 5.2 | 138.1 ± 6.6 | 0.4038 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 4.4 ± 0.8 | 4.3 ± 0.8 | 4.6 ± 1.0 | 0.0004 |
| Bicarbonate (mmol/L) | 24.2 ± 5.2 | 24.3 ± 5.1 | 22.9 ± 6.5 | 0.0019 |
| Aniongap (mmol/L) | 15.5 ± 4.1 | 15.3 ± 3.9 | 17.9 ± 5.5 | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.6 ± 1.2 | 1.5 ± 1.1 | 2.3 ± 1.8 | <0.001 |
| Bun (mg/dL) | 34.1 ± 24.8 | 32.9 ± 23.8 | 50.1 ± 32.1 | <0.001 |
| NT-pro-BNP (pg/mL) | 2819.0 (944.0–7485.0) | 2771.5 (944.5–944.5) | 4798.0 (940.0–13,113.0) | 0.0041 |
| SOFA score | 5.0 ± 3.4 | 4.7 ± 3.2 | 9.2 ± 3.9 | <0.001 |
| ACEI (%) | 1262 (60.0) | 1200 (61.4) | 62 (42.2) | <0.001 |
| ARB (%) | 552 (26.3) | 526 (26.9) | 26 (17.7) | 0.014 |
| β-blocker (%) | 1795 (85.4) | 1683 (86.0) | 112 (76.2) | 0.001 |
| Spirolactone (%) | 604 (28.7) | 575 (29.4) | 29 (19.7) | 0.012 |
| Digoxin (%) | 413 (19.6) | 392 (20.0) | 21 (14.3) | 0.090 |
| Loop diuretic (%) | 1987 (94.5) | 1855 (94.8) | 132 (89.8) | 0.010 |
| Hiazide diuretic (%) | 319 (15.2) | 307 (15.7) | 12 (8.2) | 0.014 |
| CAD (%) | 1389 (66.1) | 1309 (66.9) | 80 (54.4) | 0.002 |
| Hypertension (%) | 1325 (63.0) | 1250 (63.9) | 75 (51.0) | 0.002 |
| Diabetes (%) | 1128 (53.6) | 1059 (54.1) | 69 (46.9) | 0.091 |
| AF (%) | 1255 (59.7) | 1155 (59.1) | 100 (68.0) | 0.032 |
| Sepsis (%) | 680 (32.3) | 602 (30.8) | 78 (53.1) | <0.001 |
| Dopamine (%) | 110 (5.2) | 91 (4.7) | 19 (12.9) | <0.001 |
| Dobutamine (%) | 81 (3.9) | 58 (3.0) | 23 (15.7) | <0.001 |
| Norepinephrine (%) | 430 (20.5) | 344 (17.6) | 86 (58.5) | <0.001 |
| Variable | All Patients | Serum Chloride (mmol/L) Median (P25, P75) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <96 92 (89, 94) | ≥96, <108 102 (99, 104) | ≥108 110 (109, 112) | |||
| n | 2103 | 328 | 1437 | 338 | |
| In-hospital mortality | 147 (7.0%) | 36 (11.0%) | 86 (6.0%) | 25 (7.4%) | 0.006 |
| 30-day mortality | 140 (6.7%) | 35 (10.7%) | 83 (5.8%) | 22 (6.5%) | 0.006 |
| Time in hospital (days) | 7.7 (4.7, 12.7) | 7.9 (4.9, 12.9) | 7.2 (4.5, 12.3) | 8.7 (5.0, 13.6) | 0.013 |
| Time in ICU (days) | 2.1 (1.2, 4.0) | 2.2 (1.2, 4.2) | 2.0 (1.1, 3.8) | 2.3 (1.3, 4.5) | 0.002 |
| 30-Day Mortality | Model-1 | Model-2 | Model-3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum Chlorion (mmol/L) | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
| <96 | 2.07 | (1.36, 3.16) | 0.001 | 1.98 | (1.18, 3.31) | 0.009 | 2.23 | (1.27, 3.92) | 0.005 |
| ≥96, <108 | 1.0 | reference | 1.0 | reference | 1.0 | reference | |||
| <108 | 1.11 | (0.68, 1.82) | 0.665 | 1.01 | (0.57, 1.79) | 0.967 | 0.73 | (0.39, 1.37) | 0.331 |
| n | Hypochloremia Group | Normal Serum Chlorion Group Reference | Hyperchloremia Group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | ||||
| Age (years) | <65 | 582 | 2.51 | (0.30, 21.27) | 0.400 | 1.0 | 0.06 | (0.00, 2.18) | 0.123 |
| ≥65 | 1521 | 2.29 | (1.25, 4.20) | 0.007 | 1.0 | 0.81 | (0.42, 1.55) | 0.523 | |
| Gender | Male | 1126 | 2.16 | (0.98, 4.72) | 0.055 | 1.0 | 0.55 | (0.21, 1.42) | 0.217 |
| Female | 977 | 2.31 | (0.99, 5.37) | 0.052 | 1.0 | 0.94 | (0.40, 2.24) | 0.893 | |
| CHF | HFrEF | 1127 | 2.02 | (0.84, 4.90) | 0.118 | 1.0 | 0.76 | (0.28, 2.06) | 0.596 |
| HFpEF | 976 | 2.07 | (0.96, 4.48) | 0.064 | 1.0 | 0.69 | (0.30, 1.57) | 0.376 | |
| Sepsis | Without sepsis | 1423 | 1.95 | (0.91, 4.19) | 0.087 | 1.0 | 1.19 | (0.58, 2.41) | 0.635 |
| With sepsis | 680 | 2.47 | (1.21, 5.05) | 0.013 | 1.0 | 0.51 | (0.21, 1.25) | 0.141 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, B.; Ma, J. The Association between the Hypochloremia and Mortality in Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. J. Vasc. Dis. 2023, 2, 188-196. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd2020013
Zhang J, Yu Z, Zhu B, Ma J. The Association between the Hypochloremia and Mortality in Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. Journal of Vascular Diseases. 2023; 2(2):188-196. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd2020013
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jinping, Zhenze Yu, Binghua Zhu, and Jianxin Ma. 2023. "The Association between the Hypochloremia and Mortality in Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Patients with Chronic Heart Failure" Journal of Vascular Diseases 2, no. 2: 188-196. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd2020013
APA StyleZhang, J., Yu, Z., Zhu, B., & Ma, J. (2023). The Association between the Hypochloremia and Mortality in Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. Journal of Vascular Diseases, 2(2), 188-196. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd2020013