Elevated Gene Expression of Interleukin-32 Isoforms Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta in the Peripheral Blood of Chronic Psoriatic Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patient Recruitment
2.2. Preparation of PBMCs, Reverse Transcription, and Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
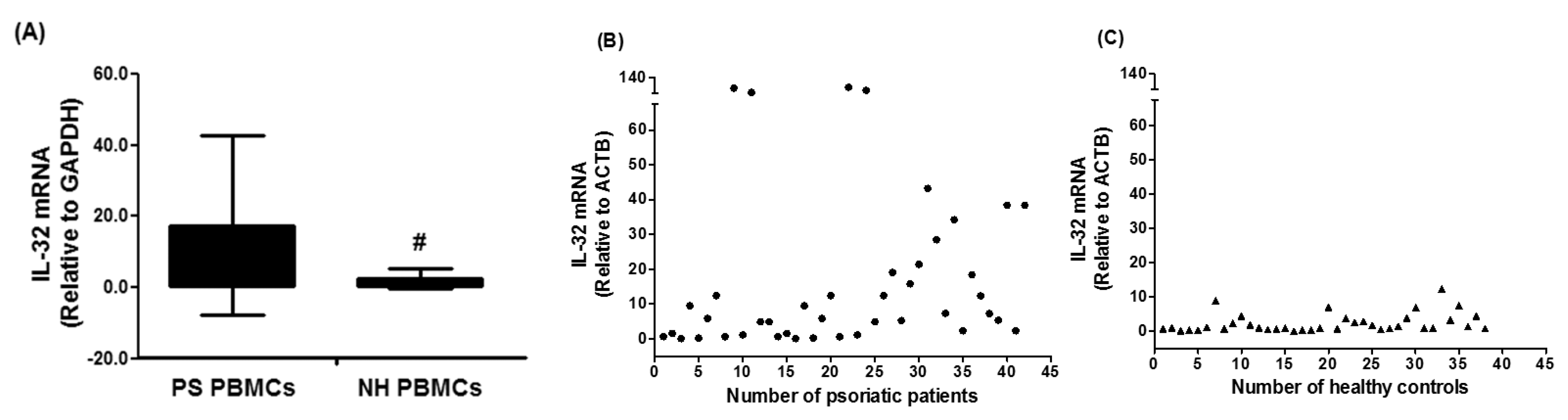
3.1. Gene Expression of IL-32 in PBMCs of Chronic Psoriatic Patients
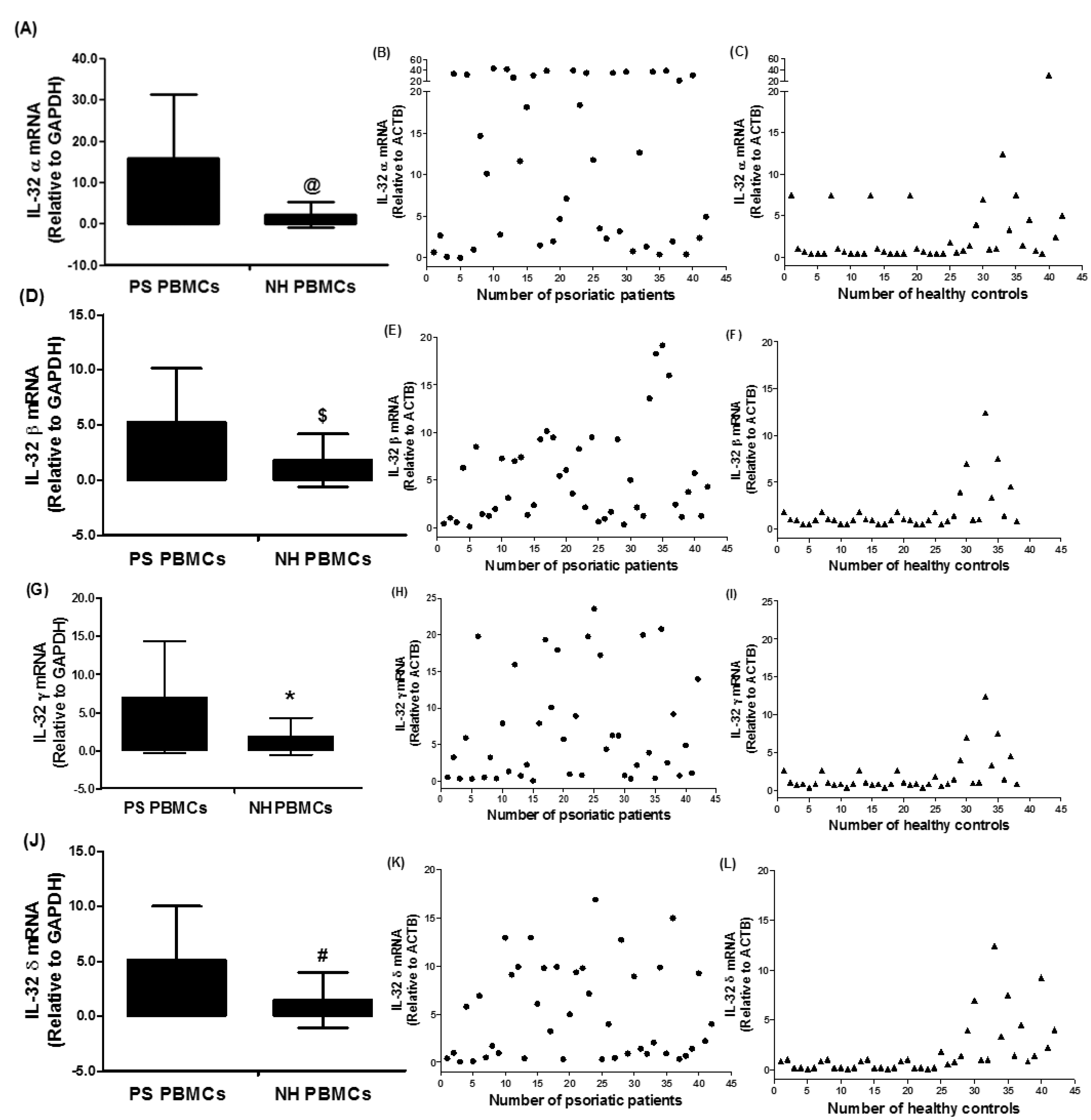
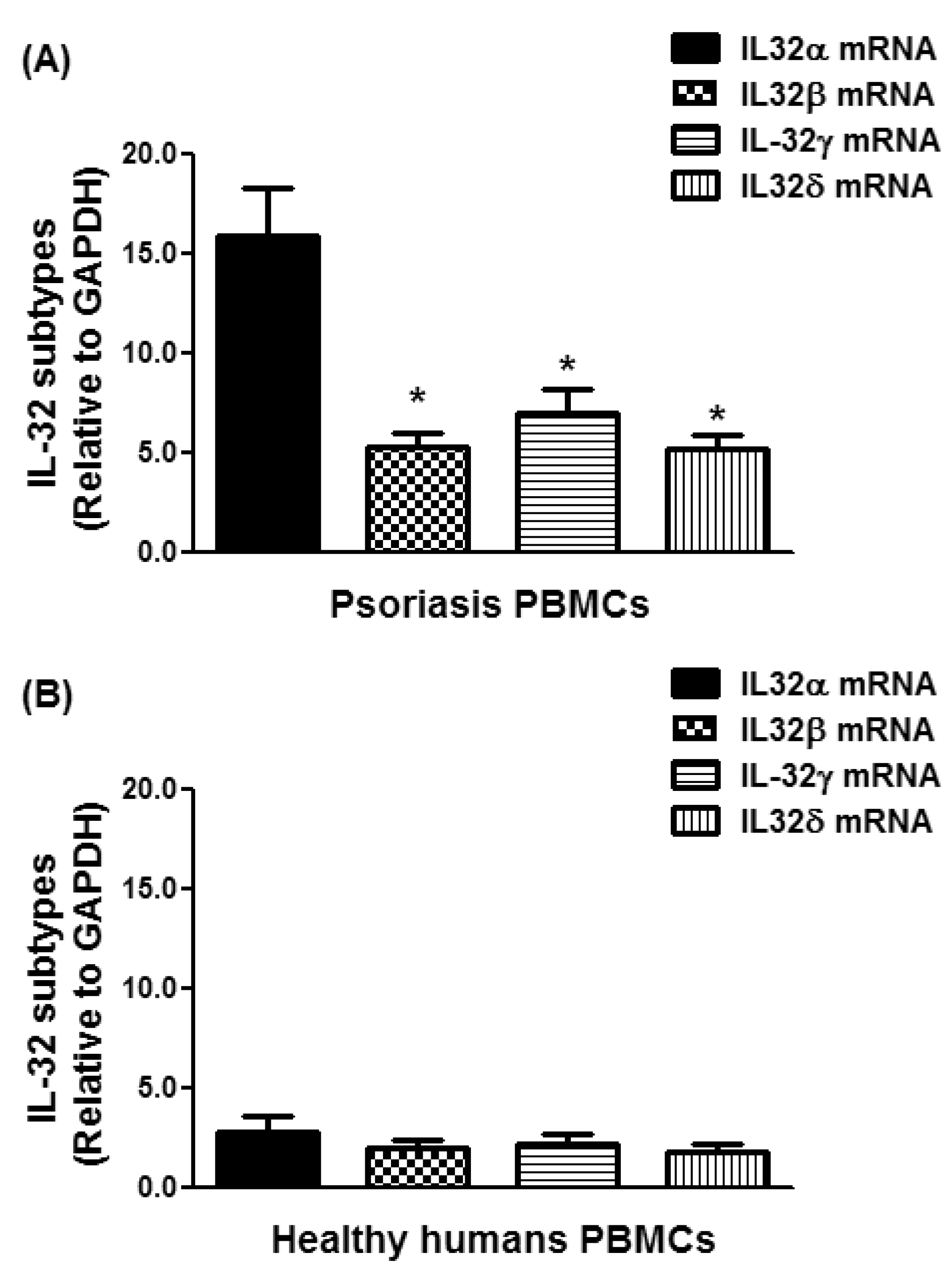
3.2. Expression of IL-32 Isoforms α, β, γ, and δ in PBMCs of Chronic Psoriatic Patients
3.3. Overexpression of IL-32α in Psoriatic Patients
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patel, N.; Nadkarni, A.; Cardwell, L.A.; Vera, N.; Frey, C.; Patel, N.; Feldman, S.R. Psoriasis, Depression, and Inflammatory Overlap: A Review. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2017, 18, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raychaudhuri, S.K.; Maverakis, E.; Raychaudhuri, S.P. Diagnosis and classification of psoriasis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.B.; Jerome, D.; Yeung, J. Diagnosis and management of psoriasis. Can. Fam. Phys. 2017, 63, 278–285. [Google Scholar]
- Wick, M.R. Psoriasiform dermatitides: A brief review. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2017, 34, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobin, A.M.; Kirby, B. TNF alpha inhibitors in the treatment of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Biol. Drugs 2005, 19, 47–57. [Google Scholar]
- Kircik, L.H.; Del Rosso, J.Q. Anti-TNF agents for the treatment of psoriasis. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2009, 8, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Villadsen, L.S.; Schuurman, J.; Beurskens, F.; Dam, T.N.; Dagnaes-Hansen, F.; Skov, L.; Rygaard, J.; Voorhorst-Ogink, M.M.; Gerritsen, A.F.; van Dijk, M.A.; et al. Resolution of psoriasis upon blockade of IL-15 biological activity in a xenograft mouse model. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, A.; Fallen, R.S.; Lima, H.C. Cytokine-based therapy in psoriasis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 44, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliwag, J.; Barnes, D.H.; Johnston, A. Cytokines in psoriasis. Cytokine 2015, 73, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouris, A.; Pistiki, A.; Katoulis, A.; Georgitsi, M.; Giatrakou, S.; Papadavid, E.; Netea, M.G.; Stavrianeas, N.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E. Proinflammatory cytokine responses in patients with psoriasis. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2014, 25, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A.; Kim, S.H. IL-32, a novel cytokine with a possible role in disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65 (Suppl. 3), iii61–iii614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netea, M.G.; Lewis, E.C.; Azam, T.; Joosten, L.A.; Jaekal, J.; Bae, S.Y.; Dinarello, C.A.; Kim, S.H. Interleukin-32 induces the differentiation of monocytes into macrophage-like cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3515–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Han, S.Y.; Azam, T.; Yoon, D.Y.; Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-32: A cytokine and inducer of TNFalpha. Immunity 2005, 22, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, J.C.; Heinhuis, B.; Gomes, R.S.; Damen, M.S.; Real, F.; Mortara, R.A.; Keating, S.T.; Dinarello, C.A.; Joosten, L.A.; Ribeiro-Dias, F. Cytokines and microbicidal molecules regulated by IL-32 in THP-1-derived human macrophages infected with New World Leishmania species. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, S.; Pan, X.; Cao, H.; Huang, X.; Xu, Q.; Zhong, H.; Peng, X. TIMP-1 expression induced by IL-32 is mediated through activation of AP-1 signal pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 38, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.T.; Son, D.J.; Lee, C.K.; Yoon, D.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Park, M.H. Interleukin 32, inflammation and cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 174, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.S.; Kim, J.A.; Park, J.H.; Park, I.H.; Han, I.H.; Lee, H.M. Toll-like receptor 4-mediated expression of interleukin-32 via the c-Jun N-terminal kinase/protein kinase B/cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein pathway in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016, 6, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Far, M.; Kouassi, P.; Sylla, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fouda, A.; Fabre, T.; Goulet, J.P.; van Grevenynghe, J.; Lee, T.; Singer, J.; et al. Investigators of the Canadian HIV+ Slow Progressor Cohort. Proinflammatory isoforms of IL-32 as novel and robust biomarkers for control failure in HIV-infected slow progressors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Sun, Z.; Li, X.; Leng, C.; Zhang, L.; Fu, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Chang, Y.U.; Nan, F.; et al. Expression and clinical significance of cyclooxygenase-2 and interleukin-32 in primary gastric B-cell lymphoma. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netea, M.G.; Azam, T.; Ferwerda, G.; Girardin, S.E.; Walsh, M.; Park, J.S.; Abraham, E.; Kim, J.M.; Yoon, D.Y.; Dinarello, C.A.; et al. IL-32 synergizes with nucleotide oligomerization domain (NOD) 1 and NOD2 ligands for IL-1beta and IL-6 production through a caspase 1-dependent mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 16309–16314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joosten, L.A.; Netea, M.G.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, D.Y.; Oppers-Walgreen, B.; Radstake, T.R.; Barrera, P.; van de Loo, F.A.; Dinarello, C.A.; van den Berg, W.B. IL-32, a proinflammatory cytokine in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3298–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousif, N.G.; Al-Amran, F.G.; Hadi, N.; Lee, J.; Adrienne, J. Expression of IL-32 modulates NF-κB and p38 MAP kinase pathways in human esophageal cancer. Cytokine 2013, 61, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, K.E.; Cheon, S.; Song, J.H.; Houh, Y.; Kim, T.S.; Gil, M.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.; et al. Interleukin-32α induces migration of human melanoma cells through downregulation of E-cadherin. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 65825–65836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Su, J.; Chu, G.; You, H.; Chen, Z.; Sun, H.; Chen, B.; Zhou, M. Interleukin-32α inactivates JAK2/STAT3 signaling and reverses interleukin-6-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion, and metastasis in pancreatic cancer cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 4225–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joosten, L.A.; Heinhuis, B.; Netea, M.G.; Dinarello, C.A. Novel insights into the biology of interleukin-32. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 3883–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro-Dias, F.; SaarGomes, R.; de LimaSilva, L.L.; DosSantos, J.C.; Joosten, L.A. Interleukin 32: A novel player in the control of infectious diseases. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 101, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasiuniene, E.; Lavinskiene, S.; Sakalauskas, R.; Sitkauskiene, B. Levels of IL-32 in Serum, Induced Sputum Supernatant, and Bronchial Lavage Fluid of Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. COPD 2016, 13, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitayama, N.; Otsuka, A.; Nonomura, Y.; Nakashima, C.; Honda, T.; Kabashima, K. Decrease of serum IL-32 level in patients with atopic dermatitis after cyclosporine treatment. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, e449–e450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomi, R.; Yerly, D.; Yawalkar, N.; Simon, D.; Schlapbach, C.; Hunger, R.E. Interleukin-32 is highly expressed in lesions of hidradenitis suppurativa. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L. Association of Plasma IL-32 Levels and Gene Polymorphisms with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Chinese Han Population. Dis. Markers 2016, 2016, 2460206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempuraj, D.; Conti, P.; Vasiadi, M.; Alysandratos, K.D.; Tagen, M.; Kalogeromitros, D.; Kourelis, T.; Gregoriou, S.; Makris, M.; Stavrianeas, N.G.; et al. IL-32 is increased along with tryptase in lesional psoriatic skin and is up-regulated by substance P in human mast cells. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2010, 20, 865–867. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Shobaili, H.A.; Ahmed, A.A.; Rasheed, Z. Recognition of oxidized albumin and thyroid antigens by psoriasis autoantibodies. A possible role of reactive-oxygen-species induced epitopes in chronic plaque psoriasis. Saudi Med. J. 2015, 36, 1408–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzolibani, A.A.; Rasheed, Z.; Bin Saif, G.; Al-Dhubaibi, M.S.; Al Robaee, A.A. Altered expression of intracellular Toll-like receptors in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with alopecia areata. BBA Clin. 2016, 5, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasheed, Z.; Al-Shobaili, H.A.; Rasheed, N.; Mahmood, A.; Khan, M.I. MicroRNA-26a-5p regulates the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase via activation of NF-κB pathway in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 594, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasheed, Z.; Rasheed, N.; Al-Shobaili, H.A. Epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate up-regulates microRNA-199a-3p expression by down-regulating the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in stimulated human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 2241–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasheed, Z.; Haqqi, T.M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress induces the expression of COX-2 through activation of eIF2α, p38-MAPK and NF-κB in advanced glycation end products stimulated human chondrocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 2179–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piskin, G.; Tursen, U.; Sylva-Steenland, R.M.; Bos, J.D.; Teunissen, M.B. Clinical improvement in chronic plaque-type psoriasis lesions after narrow-band UVB therapy is accompanied by a decrease in the expression of IFN-gamma inducers–IL-12, IL-18 and IL-23. Exp. Dermatol. 2004, 13, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadullah, K.; Sterry, W.; Stephanek, K.; Jasulaitis, D.; Leupold, M.; Audring, H.; Volk, H.D.; Docke, W.D. IL-10 is a key cytokine in psoriasis. Proof of principle by IL-10 therapy: A new therapeutic approach. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sa, S.M.; Valdez, P.A.; Wu, J.; Jung, K.; Zhong, F.; Hall, L.; Kasman, I.; Winer, J.; Modrusan, Z.; Danilenko, D.M.; et al. The effects of IL-20 subfamily cytokines on reconstituted human epidermis suggest potential roles in cutaneous innate defense and pathogenic adaptive immunity in psoriasis. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 2229–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutz, S.; Wang, X.; Ouyang, W. The IL-20 subfamily of cytokines–from host defence to tissue homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.C.; Liang, W.G.; Chen, F.W.; Hsu, J.H.; Yang, J.J.; Chang, M.S. IL-19 induces production of IL-6 and TNF-alpha and results in cell apoptosis through TNF-alpha. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 4288–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenderup, K.; Rosada, C.; Worsaae, A.; Clausen, J.T.; NormanDam, T. Interleukin-20 as a target in psoriasis treatment. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1110, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.L.; Liang, S.; Li, J.; Napierata, L.; Brown, T.; Benoit, S.; Senices, M.; Gill, D.; Dunussi-Joannopoulos, K.; Collins, M.; et al. IL-22 is required for Th17 cell-mediated pathology in a mouse model of psoriasis-like skin inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.D.; Bae, S.Y.; Hong, J.W.; Azam, T.; Dinarello, C.A.; Her, E.; Choi, W.S.; Kim, B.K.; Lee, C.K.; Yoon, D.Y.; et al. Identification of the most active interleukin-32 isoform. Immunology 2009, 126, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene Name | Accession Number | Sense | Anti-Sense |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-32 | NM_004221 | 5′TCGCGGAGGTGGGTTTC3′ | 5′AAAACGGACTAATACGGCAACAG-3′ |
| IL-32 α | NM_001012633.1 | 5′GCTGGAGGACGACTTCAAAGA3′ | 5′GGGCTCCGTAGGACTTGTCA3′ |
| IL-32 β | NM_001012631.1 | 5′CAGTGGAGCTGGGTCATCTCA3′ | 5′GGGCCTTCAGCTTCTTCATGTCATCA3′ |
| IL-32 γ | NM_001012635.1 | 5′AGGCCCGAATGGTAATGCT3′ | 5′CCACAGTGTCCTCAGTGTCACA3′ |
| IL-32 δ | NM_001012636.1 | 5′TCTGTCTCTCTCGGGTCCTCTCT3′ | 5′TGTCTCCAGGTAGCCCTCTTTG3′ |
| GAPDH | NM_002046 | 5′TCGACAGTCAGCCGCATCTTCTTT3′ | 5′ACCAAATCCGTTGACTCCGACCTT3′ |
| ACTB | NM_001101 | 5′-AGAGCTACGAGCTGCCTGAC-3′ | 5′-AGCACTGTGTTGGCGTACAG-3′ |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Shobaili, H.A.; Rasheed, Z. Elevated Gene Expression of Interleukin-32 Isoforms Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta in the Peripheral Blood of Chronic Psoriatic Patients. Diseases 2018, 6, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases6010021
Al-Shobaili HA, Rasheed Z. Elevated Gene Expression of Interleukin-32 Isoforms Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta in the Peripheral Blood of Chronic Psoriatic Patients. Diseases. 2018; 6(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases6010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Shobaili, Hani A., and Zafar Rasheed. 2018. "Elevated Gene Expression of Interleukin-32 Isoforms Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta in the Peripheral Blood of Chronic Psoriatic Patients" Diseases 6, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases6010021
APA StyleAl-Shobaili, H. A., & Rasheed, Z. (2018). Elevated Gene Expression of Interleukin-32 Isoforms Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta in the Peripheral Blood of Chronic Psoriatic Patients. Diseases, 6(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases6010021





