Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients Admitted in Cardiac Intensive Care Unit with Cardiogenic Shock: A Single-Center Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Patient Management
2.3. Statistical Analysis
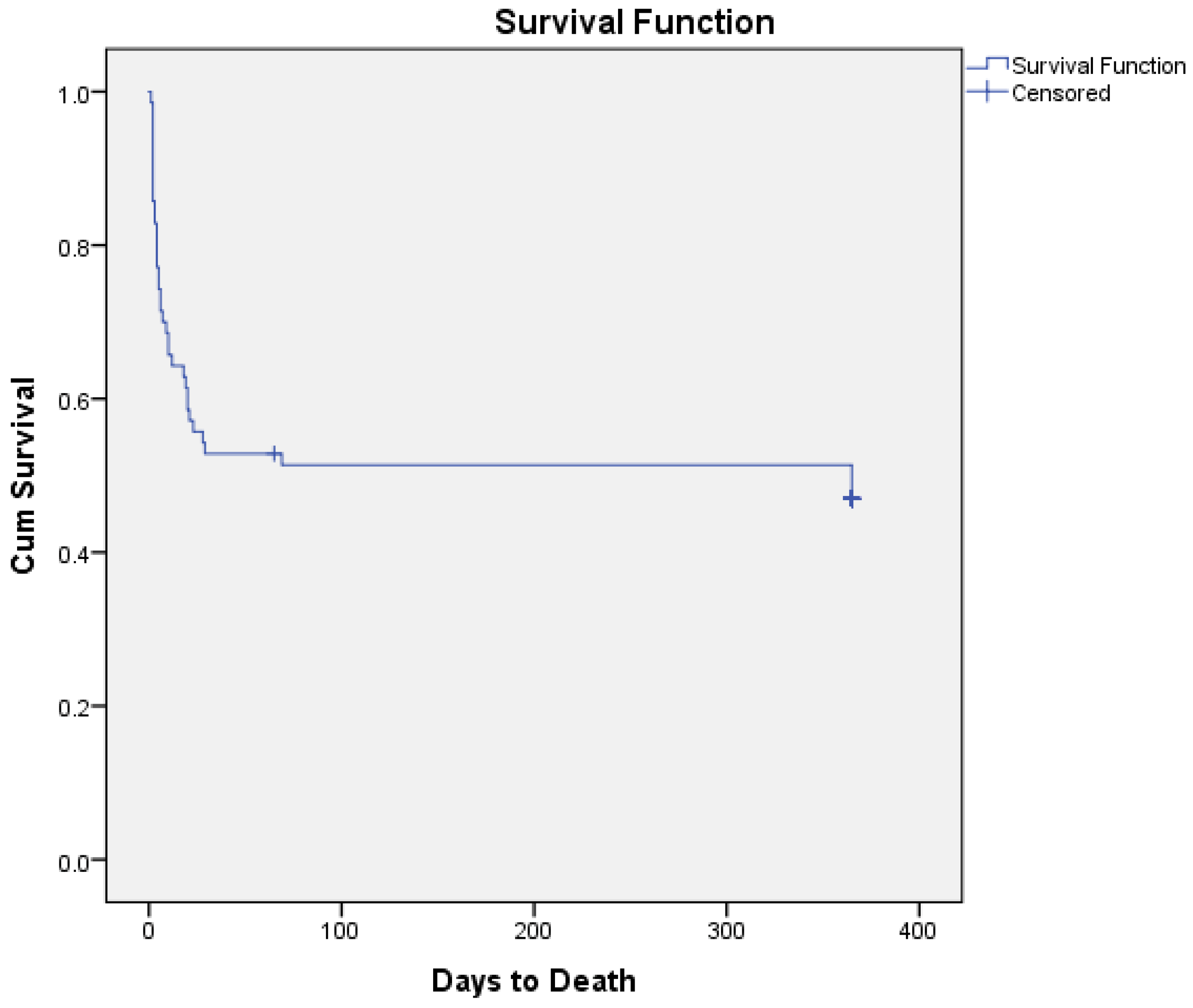
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Subgroup Analysis on Baseline Characteristics
3.3. Subgroup Analysis on Outcomes
3.4. Predictors of In-Hospital Mortality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACSs | Acute coronary syndromes |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| AMI | Acute myocardial infarction |
| AMI-CS | Acute myocardial infarction-related cardiogenic shock |
| APACHE-II | Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II |
| BiV | Biventricular |
| Bpm | Beats per minute |
| CAD | Coronary artery disease |
| Cath-Lab | Catheterization laboratory |
| CICU | Cardiac intensive care unit |
| CI | Cardiac Index |
| CIs | Confidence intervals |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CMP | Cardiomyopathies |
| CO | Cardiac output |
| CRF | Case report form |
| CRRT | Continuous renal replacement therapy |
| CS | Cardiogenic shock |
| CSP | Cardiogenic Shock Prognosis (score) |
| CVP | Central venous pressure |
| CVVHDF | Continuous veno-venous hemodiafiltration |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| ECMO | Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation |
| ESRD | End stage renal disease |
| GRACE | Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events (score) |
| HF | Heart failure |
| HF-CS | Heart failure-related cardiogenic shock |
| HFmrEF | Heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction |
| HFpEF | Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction |
| HFrEF | Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction |
| IABP | Intra-aortic balloon pump |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| ID | Identification |
| IHCA | In-hospital cardiac arrest |
| IVC | Inferior vena cava |
| LVEF | Left ventricular ejection fraction |
| LV | Left ventricular |
| LVOT VTI | Left ventricular outflow tract velocity time integral |
| MBP | Mean blood pressure |
| ML | Machine learning |
| MI | Myocardial infarction |
| MCS | Mechanical circulatory support |
| mPAP | Mean pulmonary artery pressure |
| MV | Mechanical ventilation |
| OHCA | Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| PCAS | Post cardiac arrest syndrome |
| PCI | Percutaneous coronary intervention |
| PE | Pulmonary embolism |
| PH | Pulmonary hypertension |
| RV | Right ventricular |
| SAPS-II | Simplified Acute Physiology Score II |
| SCAI | Society of Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions |
| SOFA | Sequential Organ Failure Assessment |
| SPAP | Systolic pulmonary artery pressure |
| STEMI | ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction |
| TAPSE | Tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion |
| TIMI | Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (score) |
| VHD | Valvular heart disease |
References
- Osman, M.; Syed, M.; Patibandla, S.; Sulaiman, S.; Kheiri, B.; Shah, M.K.; Bianco, C.; Balla, S.; Patel, B. Fifteen-Year Trends in Incidence of Cardiogenic Shock Hospitalization and In-Hospital Mortality in the United States. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e021061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, B.N.; Truesdell, A.G.; Psotka, M.A.; Rosner, C.; Singh, R.; Sinha, S.S.; Damluji, A.A.; Batchelor, W.B. A Standardized and Comprehensive Approach to the Management of Cardiogenic Shock. JACC Heart Fail. 2020, 8, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waksman, R.; Pahuja, M.; van Diepen, S.; Proudfoot, A.G.; Morrow, D.; Spitzer, E.; Nichol, G.; Weisfeldt, M.L.; Moscucci, M.; Lawler, P.R.; et al. Standardized Definitions for Cardiogenic Shock Research and Mechanical Circulatory Support Devices: Scientific Expert Panel from the Shock Academic Research Consortium (SHARC). Circulation 2023, 148, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, D.; Jentzer, J.C. Cardiogenic Shock: Pathogenesis, Classification, and Management. Crit. Care Clin. 2024, 40, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.S. Cardiogenic Shock: Failure of Oxygen Delivery and Oxygen Utilization. Clin. Cardiol. 2016, 39, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jentzer, J.C. Understanding Cardiogenic Shock Severity and Mortality Risk Assessment. Circ. Heart Fail. 2020, 13, e007568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusebrink, E.; Binzenhofer, L.; Adamo, M.; Lorusso, R.; Mebazaa, A.; Morrow, D.A.; Price, S.; Jentzer, J.C.; Brodie, D.; Combes, A.; et al. Cardiogenic shock. Lancet 2024, 404, 2006–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsky, M.D.; Morrow, D.A.; Proudfoot, A.G.; Hochman, J.S.; Thiele, H.; Rao, S.V. Cardiogenic Shock After Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Review. JAMA 2021, 326, 1840–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahdatpour, C.; Collins, D.; Goldberg, S. Cardiogenic Shock. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e011991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, J.; Blumer, V.; Burkhoff, D.; Pahuja, M.; Sinha, S.S.; Rosner, C.; Vorovich, E.; Grafton, G.; Bagnola, A.; Hernandez-Montfort, J.A.; et al. Heart Failure-Related Cardiogenic Shock: Pathophysiology, Evaluation and Management Considerations: Review of Heart Failure-Related Cardiogenic Shock. J. Card. Fail. 2021, 27, 1126–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E.J.; Agarwal, S.; Cullum, C.M.; Sinha, S.S.; Ely, E.W.; Farr, M.A. Survivorship After Cardiogenic Shock. Circulation 2025, 151, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.S.; Morrow, D.A.; Kapur, N.K.; Kataria, R.; Roswell, R.O. 2025 Concise Clinical Guidance: An ACC Expert Consensus Statement on the Evaluation and Management of Cardiogenic Shock: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2025, 85, 1618–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammos, A.; Bechlioulis, A.; Chatzipanteliadou, S.; Sioros, S.A.; Floros, C.D.; Stamou, I.; Lakkas, L.; Kalogeras, P.; Bouratzis, V.; Katsouras, C.S.; et al. The Role of Prognostic Scores in Assessing the Prognosis of Patients Admitted in the Cardiac Intensive Care Unit: Emphasis on Heart Failure Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweck, E.; Li, S.; Burkhoff, D.; Kapur, N.K. Profiling of Cardiogenic Shock: Incorporating Machine Learning Into Bedside Management. J. Soc. Cardiovasc. Angiogr. Interv. 2025, 4 Pt B, 102047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumer, V.; Kanwar, M.K.; Barnett, C.F.; Cowger, J.A.; Damluji, A.A.; Farr, M.; Goodlin, S.J.; Katz, J.N.; Mcilvennan, C.K.; American Heart Association Cardiovascular Disease in Older Populations Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology and Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing; et al. Cardiogenic Shock in Older Adults: A Focus on Age-Associated Risks and Approach to Management: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2024, 149, e1051–e1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos, L.M.; Baro Vila, R.C.; Botto, F.; Diez, M. SCAI Cardiogenic Shock Classification for Predicting In-Hospital and Long-Term Mortality in Acute Heart Failure. J. Soc. Cardiovasc. Angiogr. Interv. 2022, 1, 100496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tsao, C.W.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Arora, P.; Avery, C.L.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Beaton, A.Z.; Boehme, A.K.; American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2023 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023, 147, e93–e621, Erratum in Circulation 2023, 147, e622 and Circulation 2023, 148, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, P.R.; Berg, D.D.; Park, J.G.; Katz, J.N.; Baird-Zars, V.M.; Barsness, G.W.; Bohula, E.A.; Carnicelli, A.P.; Chaudhry, S.-P.; Jentzer, J.C.; et al. The Range of Cardiogenic Shock Survival by Clinical Stage: Data from the Critical Care Cardiology Trials Network Registry. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, K.L.; Rustin, M.A.; Asche, M.A.; Bennett, C.E.; Patel, P.C.; Jentzer, J.C. Cardiogenic Shock Classification and Associated Mortality Risk. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2023, 98, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldetti, L.; Gallone, G.; Filiberti, G.; Pescarmona, L.; Cesari, A.; Rizza, V.; Roagna, E.; Gurrieri, D.; Peveri, B.; Nocera, L.; et al. Mixed Shock Complicating Cardiogenic Shock: Frequency, Predictors, and Clinical Outcomes. Circ. Heart Fail. 2024, 17, e011404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldetti, L.; Pagnesi, M.; Gramegna, M.; Belletti, A.; Beneduce, A.; Pazzanese, V.; Calvo, F.; Sacchi, S.; Van Mieghem, N.M.; den Uil, C.A.; et al. Intra-Aortic Balloon Pumping in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure with Hypoperfusion: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Practice. Circ. Heart Fail. 2021, 14, e008527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Montfort, J.; Kanwar, M.; Sinha, S.S.; Garan, A.R.; Blumer, V.; Kataria, R.; Whitehead, E.H.; Yin, M.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Clinical Presentation and In-Hospital Trajectory of Heart Failure and Cardiogenic Shock. JACC Heart Fail. 2023, 11, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Sunkara, A.; Varnado, S. Management of Cardiogenic Shock in a Cardiac Intensive Care Unit. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc. J. 2020, 16, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Diepen, S.; Katz, J.N.; Albert, N.M.; Henry, T.D.; Jacobs, A.K.; Kapur, N.K.; Kilic, A.; Menon, V.; Ohman, E.M.; Sweitzer, N.K.; et al. Contemporary Management of Cardiogenic Shock: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 136, e232–e268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.S.; Gonzalez-Costello, J.; Belohlavek, J.; Zweck, E.; Blumer, V.; Schrage, B.; Hanff, T.C. Hemodynamic management of cardiogenic shock in the intensive care unit. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2024, 43, 1059–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basir, M.B.; Schreiber, T.L.; Grines, C.L.; Dixon, S.R.; Moses, J.W.; Maini, B.S.; Khandelwal, A.K.; Ohman, E.M.; O’Neill, W.W. Effect of Early Initiation of Mechanical Circulatory Support on Survival in Cardiogenic Shock. Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 119, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyzogopoulou, E.; Arfaras-Melainis, A.; Bistola, V.; Parissis, J. Inotropic agents in cardiogenic shock. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2020, 26, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, Z.; Agostoni, P.; Alvarez, J.; Bettex, D.; Bouchez, S.; Brito, D.; Černý, V.; Comin-Colet, J.; Crespo-Leiro, M.G.; Delgado, J.F.; et al. Levosimendan Efficacy and Safety: 20 years of SIMDAX in Clinical Use. Card. Fail. Rev. 2020, 6, e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.; Bruno, R.R.; Jumean, M.; Price, S.; Krychtiuk, K.A.; Ramanathan, K.; Dankiewicz, J.; French, J.; Delmas, C.; Mendoza, A.-A.; et al. Management of cardiogenic shock: State-of-the-art. Intensive Care Med. 2024, 50, 1814–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, B.; Clere-Jehl, R.; Legras, A.; Morichau-Beauchant, T.; Leone, M.; Frederique, G.; Quenot, J.-P.; Kimmoun, A.; Cariou, A.; Lassus, J.; et al. Epinephrine Versus Norepinephrine for Cardiogenic Shock After Acute Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, R.; Santos, G.M.; Visintini, S.M.; Daniel, F.; Ramirez, F.D.; DiSanto, P.; Simard, T.; Labinaz, M.; Hibbert, B.M. Efficacy of milrinone and dobutamine in low cardiac output states: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Investig. Med. 2019, 42, E26–E32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jentzer, J.C.; Berg, D.D.; Chonde, M.D.; Dahiya, G.; Elliott, A.; Rampersad, P.; Sinha, S.S.; Truesdell, A.G.; Yohannes, S.; Vallabhajosyula, S. Mixed Cardiogenic-Vasodilatory Shock: Current Insights and Future Directions. JACC Adv. 2024, 4, 101432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlig, K.; Efremov, L.; Tongers, J.; Frantz, S.; Mikolajczyk, R.; Sedding, D.; Schumann, J.; Cochrane Heart Group. Inotropic agents and vasodilator strategies for the treatment of cardiogenic shock or low cardiac output syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 11, CD009669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, J.; Henrich, E.C.; Strobl, H.; Prondzinsky, R.; Weiche, S.; Thiele, H.; Werdan, K.; Frantz, S.; Unverzagt, S.; Cochrane Heart Group. Inotropic agents and vasodilator strategies for the treatment of cardiogenic shock or low cardiac output syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 1, CD009669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, N.; Du, D.; Mahesh, B. Temporary Mechanical Support in Cardiogenic Shock Secondary to Heart Failure: An Evolving Paradigm. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, J.E.; Engstrom, T.; Jensen, L.O.; Eiskjaer, H.; Mangner, N.; Polzin, A.; Schulze, P.C.; Skurk, C.; Nordbeck, P.; Clemmensen, P.; et al. Microaxial Flow Pump or Standard Care in Infarct-Related Cardiogenic Shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 1382–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attachaipanich, T.; Attachaipanich, S.; Kaewboot, K. Timing of mechanical circulatory support in acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. Heart J. Plus. 2025, 50, 100506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadosh, B.S.; Berg, D.D.; Bohula, E.A.; Park, J.G.; Baird-Zars, V.M.; Alviar, C.; Alzate, J.; Barnett, C.F.; Barsness, G.W.; Burke, J.; et al. Pulmonary Artery Catheter Use and Mortality in the Cardiac Intensive Care Unit. JACC Heart Fail. 2023, 11 Pt 1, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Cao, J.; Ge, J. Prognostic value of baseline glucose levels for mortality in patients with cardiogenic shock: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2025, 20, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dina Liastuti, L.; Bahirah, S.A.; Lestari, H.M.; Nursakina, Y. The efficacy of artificial intelligence in predicting mortality rate and cardiogenic shock in acute coronary syndrome patients. Int. J. Cardiol. Cardiovasc. Risk Prev. 2025, 26, 200407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mughayyar, D.; Marshall, T.; D’Souza, K.; MacLeod, J.B.; McCoy, A.; Morris, S.; Smith, M.; White, C.W.; Sarkar, S.; Brunt, K.R.; et al. Implementation of a Multidisciplinary Cardiogenic Shock Team in a Nonacademic Canadian Heart Centre: An Implementation Study. CJC Open 2025, 7, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimmoun, A.; O’Brien, C.; Blumer, V.; Wenzl, F.A.; Poss, J.; Zeymer, U.; E Møller, J.; Aissaoui, N.; Sinha, S.S.; Combes, A.; et al. Optimising trial design for cardiogenic shock: Insights from the sixth Critical Care Clinical Trialists Workshop. Lancet Respir. Med. 2025, 13, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total * (n = 70) | AMI-CS * (n = 24) | HF-CS * (n = 20) | p-Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender: Male n (%): | 54 (77) | 22 (92) | 13 (65) | 0.02 |
| Age (years): | 67 (±24) | 64 (±26) | 72 (±26) | 0.05 |
| Hypertension n (%): | 41 (58) | 15 (63) | 10 (50) | 0.40 |
| Dyslipidemia n (%): | 46 (65) | 14 (58) | 11 (55) | 0.82 |
| Diabetes mellitus n (%): | 29 (42) | 10 (42) | 10 (50) | 0.58 |
| Current smoking n (%): | 26 (37) | 11 (46) | 8 (40) | 0.69 |
| Chronic kidney disease n (%): | 25 (35) | 6 (25) | 11 (55) | 0.04 |
| End stage renal disease n (%): | 4 (5) | 1 (4) | 2 (10) | 0.44 |
| Previous history of CAD n (%): | 27 (38) | 5 (21) | 10 (50) | 0.04 |
| Previous history of stroke n (%): | 2 (3) | 2 (8) | 0 (0) | 0.18 |
| Previous history of pulmonary hypertension n (%): | 7 (10) | 0 (0) | 4 (20) | 0.02 |
| SCAI class n (%): B: C: D: E:0 | 20 (28) 48 (68) 1 (2) 1 (2) | 6 (25) 17 (71) 1 (4) 0 (0) | 10 (50) 10 (50) 0 (0) 0 (0) | 0.17 |
| Etiology of cardiogenic shock n (%): AMI-CS: HF-CS: Valvular: Arrhythmia: Post cardiac arrest syndrome: Tamponade: Myocarditis: Pulmonary embolism: | 24 (35) 20 (29) 11 (16) 6 (8) 5 (7) 2 (3) 1 (1) 1 (1) | 24 (100) | 20 (100) | |
| Phenotype n (%): Left ventricular: Biventricular: Right ventricular: | 47 (67) 22 (31) 1 (2) | 21 (88) 3 (12) 0 (0) | 15 (75) 5 (25) 0 (0) | 0.28 |
| Total * (n = 70) ±SD | AMI-CS * (n = 24) ±SD | HF-CS * (n = 20) ±SD | p-Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart rate (BPM): | 96 (±38) | 97 (±36) | 88 (±30) | 0.10 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg): | 108 (±36) | 110 (±40) | 112 (±42) | 0.74 |
| Mean blood pressure (mmHg): | 79 (±24) | 82 (±28) | 78 (±22) | 0.32 |
| Pulse pressure (mmHg): | 34 (±17) | 42 (±14) | 44 (±22) | 0.41 |
| Glucose (mg/dL): | 213 (±116) | 229 (±196) | 209 (±186) | 0.61 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL): | 1.9 (±1.4) | 1.74 (±1.55) | 2.04 (±1.21) | 0.49 |
| Estimated GFR (ml/min/1.73m2): | 49 (±46) | 53 (±52) | 44 (±40) | 0.07 |
| Potassium (mEq/L): | 4.3 (±1.48) | 4.43 (±1.2) | 4.35 (±1.4) | 0.71 |
| Sodium (mEq/L): | 135 (±10) | 134 (±10) | 136 (±10) | 0.30 |
| ALT (IU/L): | 149 (±80) | 142 (±131) | 238 (±206) | 0.44 |
| AST (IU/L): | 196 (±93) | 279 (±134) | 116 (±94) | 0.12 |
| High sensitivity troponin (pg/mL): | 18,000 (±12,000) | 48,728 (±47,134) | 1632 (±1601) | 0.01 |
| Lactate levels (mmol/L): | 3.6 (±3) | 3.9 (±3.6) | 3.6 (±3.3) | 0.55 |
| LVEF (%): | 30 (±24) | 24 (±20) | 35 (±26) | 0.04 |
| TAPSE (mm): | 16 (±6) | 18 (±6) | 16 (±5) | 0.15 |
| IVC (mm): | 21 (±10) | 18 (±10) | 21 (±8) | 0.01 |
| LVOT VTI (cm): | 15 (±8) | 24 (±8) | 16 (±8) | 0.17 |
| CVP (cmH2O): | 15 (±12) | 12 (±10) | 16 (±14) | 0.03 |
| CO (L/min): | 3.8 (±2.6) | 3.4 (±1.6) | 3.9 (±1.9) | 0.19 |
| CI (L/min/m2): | 2 (±1.4) | 1.7 (±0.8) | 2.1 (±0.8) | 0.01 |
| CPO (Watts): | 0.72 (±0.56) | 0.6 (±0.3) | 0.6 (±0.4) | 0.68 |
| PAPi: | 1.74 (±1.5) | 1.7 (±0.8) | 2.1 (±1.3) | 0.56 |
| Total * (n = 70) | AMI-CS * (n = 24) | HF-CS * (n = 20) | p-Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IABP: | 15 (21) | 11 (45) | 4 (20) | 0.02 |
| Mechanical Ventilation: | 16 (23) | 6 (25) | 3 (15) | 0.41 |
| CRRT: | 7 (10) | 1 (4) | 2 (10) | 0.44 |
| Hospitalization survival: | 36 (51) | 14 (58) | 10 (50) | 0.58 |
| In-hospital mortality: | 34 (49) | 10 (42) | 10 (50) | 0.58 |
| Cause of death: Pump failure: Septic shock: | 18 (25.7) 16 (23) | 6 (25) 4 (16) | 7 (35) 3 (15) | 0.78 |
| Hospitalization duration: | 11 (±9) | 11 (±10) | 8 (±7) | 0.11 |
| AMI-CS n = 24 (%) | HF-CS n = 20 (%) | Odds Ratio | CIs | p-Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In-hospital: | 10 (41,7) | 10 (50) | 0.71 | 0.21–2.35 | 0.58 |
| 1-month mortality: | 10 (41.7) | 10 (50) | 0.71 | 0.21–2.35 | 0.58 |
| 1-year mortality: | 10 (41.7) | 11 (55) | 0.58 | 0.17–1.93 | 0.37 |
| LV n = 47 (%) | BiV n = 22 (%) | Odds Ratio | CIs | p-Values | |
| In-hospital: | 20 (43) | 14 (63.6) | 0.42 | 0.14–1.20 | 0.10 |
| 1-month mortality: | 20 (43) | 14 (63.6) | 0.42 | 0.14–1.20 | 0.10 |
| 1-year mortality: | 20 (43) | 15 (68.2) | 0.79 | 0.64–0.89 | <0.01 |
| SCAI C n = 48 (%) | SCAI B n = 20 (%) | Odds Ratio | CIs | p-Values | |
| In-hospital: | 28 (58) | 4 (20) | 1.17 | 1.05–1.61 | <0.01 |
| 1-month mortality: | 28 (58) | 4 (20) | 1.17 | 1.05–1.61 | <0.01 |
| 1-year mortality: | 29 (60) | 4 (20) | 1.13 | 1.03–1.47 | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siaravas, K.C.; Rammos, A.; Bechlioulis, A.; Floros, C.D.; Papaioannou, E.; Samara, I.; Stamou, I.; Kalogeras, P.; Sioros, S.A.; Bouratzis, V.; et al. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients Admitted in Cardiac Intensive Care Unit with Cardiogenic Shock: A Single-Center Study. Diseases 2025, 13, 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13090302
Siaravas KC, Rammos A, Bechlioulis A, Floros CD, Papaioannou E, Samara I, Stamou I, Kalogeras P, Sioros SA, Bouratzis V, et al. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients Admitted in Cardiac Intensive Care Unit with Cardiogenic Shock: A Single-Center Study. Diseases. 2025; 13(9):302. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13090302
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiaravas, Konstantinos C., Aidonis Rammos, Aris Bechlioulis, Christos D. Floros, Eftychia Papaioannou, Ioanna Samara, Ilektra Stamou, Petros Kalogeras, Spyridon Athanasios Sioros, Vasilis Bouratzis, and et al. 2025. "Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients Admitted in Cardiac Intensive Care Unit with Cardiogenic Shock: A Single-Center Study" Diseases 13, no. 9: 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13090302
APA StyleSiaravas, K. C., Rammos, A., Bechlioulis, A., Floros, C. D., Papaioannou, E., Samara, I., Stamou, I., Kalogeras, P., Sioros, S. A., Bouratzis, V., Lakkas, L., Katsouras, C. S., Naka, K. K., & Michalis, L. K. (2025). Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients Admitted in Cardiac Intensive Care Unit with Cardiogenic Shock: A Single-Center Study. Diseases, 13(9), 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13090302






